缓存穿透
缓存穿透是指客户端请求的数据在缓存中和数据库中都不存在,这样缓存永远不会生效,这些请求都会打到数据库。
解决方法之一:缓存空值
思路:当用户查询一个不存在的内容时,在redis不命中,在数据库也不命中,这个时候就在redis里存放一个有有效期的空值;当下一次访问且命中redis时,如果命中的是空值,则直接结束访问并返回错误
java
public Result queryById(Long id) {
String key= RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id;
// 1.从redis查询商铺数据
String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
// 2.判断是否存在
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(shopJson)) {
// 3.存在,直接返回
Shop shop = JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, Shop.class);
return Result.ok(shop);
}
// 判断命中的是否是空值
// 此时的shopJson要么是null,要么是空串,所以用 !=null 来判断是空串是没问题的
if (shopJson != null) {
// 返回错误
return Result.fail("店铺不存在");
}
// 4.不存在,根据id查询数据库
Shop shop = getById(id);
// 5.不存在,返回错误
if (shop == null){
// 将空值写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", RedisConstants.CACHE_NULL_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
// 返回错误信息
return Result.fail("店铺不存在");
}
// 6.存在,写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(shop), RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
// 7.返回数据
return Result.ok(shop);
}缓存雪崩
缓存雪崩是指在同一时段大量的缓存key同时失效或者Redis服务岩机,导致大量请求到达数据库,带来巨大压力。
解决方案:
- 给不同的Key的TTL添加随机值
- 利用Redis集群提高服务的可用性(后续redis高级会讲)
- 给缓存业务添加降级限流策略(SpringCloud里讲到)
- 给业务添加多级缓存(后续redis高级会讲)
缓存击穿
缓存击穿问题 也叫热点Key问题,就是一个被高并发访问 并且缓存重建业务较复杂的key突然失效了,无数的请求访问会在瞬间给数据库带来巨大的冲击。
常见的解决方案有两种:
- 互斥锁
- 逻辑过期
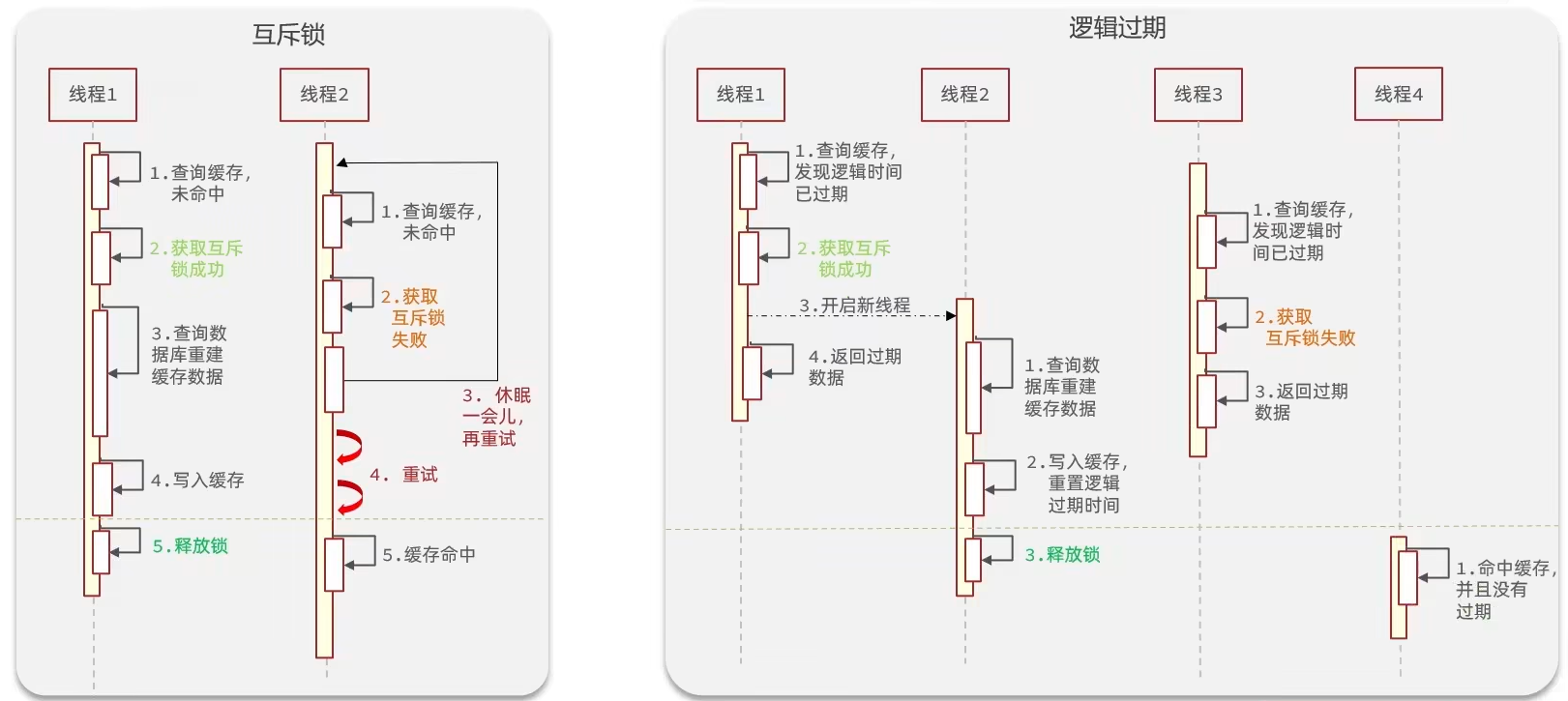
互斥锁
使用 setnx 来模拟互斥锁
java
public Result queryById(Long id) {
// 互斥锁解决缓存击穿
Shop shop = queryWithMutex(id);
if (shop == null) {
return Result.fail("店铺不存在");
}
// 返回数据
return Result.ok(shop);
}
// 互斥锁逻辑
public Shop queryWithMutex(Long id) {
String key= RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id;
// 1.从redis查询商铺数据
String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
// 2.判断是否存在
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(shopJson)) {
// 3.存在,直接返回
return JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, Shop.class);
}
// 判断命中的是否是空值
if (shopJson != null) {
// 返回空值
return null;
}
String lockKey = null;
Shop shop = null;
try {
// 4.实现缓存重建
// 4.1 获取互斥锁
lockKey = RedisConstants.LOCK_SHOP_KEY + id;
boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey);
// 4.2 判断是否获取成功
if(!isLock){
// 4.3 失败,则休眠并重试
Thread.sleep(50);
return queryWithMutex(id);
}
// 4.4 成功,根据id查询数据库
shop = getById(id);
// 5.不存在,返回错误
if (shop == null){
// 将空值写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", RedisConstants.CACHE_NULL_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
// 返回空值
return null;
}
// 6.存在,写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(shop), RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
// 7.释放锁
unLock(lockKey);
}
// 8.返回数据
return shop;
}
// 获取锁
private boolean tryLock(String key) {
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag);
}
// 释放锁
private void unLock(String key) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}逻辑过期
创建一个RedisData类来存放过期时间和想要存进redis的万能数据data
java
@Data
public class RedisData {
private LocalDateTime expireTime;
private Object data;
}创建一个方法来将RedisData类数据存入Redis中,此时data存放Shop类型数据
java
public void saveShop2Redis(Long id, Long expireSeconds) {
// 1.查询店铺数据
Shop shop = getById(id);
// 2.封装逻辑过期时间
RedisData redisData = new RedisData();
redisData.setData(shop);
redisData.setExpireTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(expireSeconds));
// 3.写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(redisData));
}实现
java
public Result queryById(Long id) {
// 逻辑过期解决缓存击穿
Shop shop = queryWithLogicalExpire(id);
// 返回数据
return Result.ok(shop);
}
// 线程池
private static final ExecutorService CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
// 逻辑过期实现
public Shop queryWithLogicalExpire(Long id) {
String key= RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id;
// 1.从redis查询商铺数据
String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
// 2.判断是否存在
if (StrUtil.isBlank(shopJson)) {
// 3.不存在,直接返回空值
return null;
}
// 4.命中,需要先把json反序列化为对象
RedisData redisData = JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, RedisData.class);
JSONObject data = (JSONObject) redisData.getData();
Shop shop = JSONUtil.toBean(data, Shop.class);
LocalDateTime expireTime = redisData.getExpireTime();
// 5.判断是否过期
if (expireTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())){
// 5.1 未过期,直接返回数据
return shop;
}
// 5.2 已过期,获取锁进行缓存重建
// 6.重建缓存
// 6.1 获取互斥锁
String lockKey = RedisConstants.LOCK_SHOP_KEY + id;
boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey);
// 6.2 判断是否获取成功
if (isLock){
// 6.3 成功,再次判断是否过期
shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (StrUtil.isBlank(shopJson)) {
return null;
}
redisData = JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, RedisData.class);
data = (JSONObject) redisData.getData();
shop = JSONUtil.toBean(data, Shop.class);
expireTime = redisData.getExpireTime();
if (expireTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())){
// 未过期,释放锁,直接返回数据
unLock(lockKey);
return shop;
}
// 6.4 依旧过期,开启独立线程,实现缓存重建
CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR.submit(() -> {
try {
// 缓存重建
this.saveShop2Redis(id, 20L);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
unLock(lockKey);
}
});
}
// 6.4 返回过期的数据
return shop;
}
private boolean tryLock(String key) {
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag);
}
private void unLock(String key) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
public void saveShop2Redis(Long id, Long expireSeconds) {
// 1.查询店铺数据
Shop shop = getById(id);
// 2.封装逻辑过期时间
RedisData redisData = new RedisData();
redisData.setData(shop);
redisData.setExpireTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(expireSeconds));
// 3.写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(redisData));
}封装Redis工具类
使用泛型,代码如下(可复用)
java
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheClient {
//构造器注入
private final StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public CacheClient(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate) {
this.stringRedisTemplate = stringRedisTemplate;
}
public void set(String key, Object value, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(value), time, unit);
}
public void setWithLogicalExpire(String key, Object value, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {
// 设置逻辑过期
RedisData redisData = new RedisData();
redisData.setData(value);
redisData.setExpireTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(unit.toSeconds(time)));
// 写入Redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(redisData));
}
//缓存空值解决缓存穿透的实现
public <R,ID> R queryWithPassThrough(String keyPrefix, ID id,Class<R> type, Function<ID,R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {
String key= keyPrefix + id;
// 1.从redis查询数据
String json = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
// 2.判断是否存在
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(json)) {
// 3.存在,直接返回
return JSONUtil.toBean(json, type);
}
// 判断命中的是否是空值
if (json != null) {
// 返回错误
return null;
}
// 4.不存在,根据id查询数据库
R r = dbFallback.apply(id);
// 5.不存在,返回错误
if (r == null){
// 将空值写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", RedisConstants.CACHE_NULL_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
// 返回错误信息
return null;
}
// 6.存在,写入redis
this.set(key, r, time, unit);
// 7.返回数据
return r;
}
//线程池
private static final ExecutorService CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//逻辑过期解决缓存击穿的实现
public <R,ID> R queryWithLogicalExpire(String keyPrefix, ID id,Class<R> type, Function<ID,R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit, String lockKeyPrefix) {
String key= keyPrefix + id;
// 1.从redis查询数据
String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
// 2.判断是否存在
if (StrUtil.isBlank(shopJson)) {
// 3.不存在,直接返回空值
return null;
}
// 4.命中,需要先把json反序列化为对象
RedisData redisData = JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, RedisData.class);
JSONObject data = (JSONObject) redisData.getData();
R r = JSONUtil.toBean(data, type);
LocalDateTime expireTime = redisData.getExpireTime();
// 5.判断是否过期
if (expireTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())){
// 5.1 未过期,直接返回数据
return r;
}
// 5.2 已过期,获取锁进行缓存重建
// 6.重建缓存
// 6.1 获取互斥锁
String lockKey = lockKeyPrefix + id;
boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey);
// 6.2 判断是否获取成功
if (isLock){
// 6.3 成功,再次判断是否过期
shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (StrUtil.isBlank(shopJson)) {
return null;
}
redisData = JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, RedisData.class);
data = (JSONObject) redisData.getData();
r = JSONUtil.toBean(data, type);
expireTime = redisData.getExpireTime();
if (expireTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())){
// 未过期,释放锁,直接返回数据
unLock(lockKey);
return r;
}
// 6.4 依旧过期,开启独立线程,实现缓存重建
CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR.submit(() -> {
try {
// 查询数据库
R r1= dbFallback.apply(id);
// 写入redis
this.setWithLogicalExpire(key, r1, time, unit);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
unLock(lockKey);
}
});
}
// 6.4 返回过期的数据
return r;
}
//获取锁
private boolean tryLock(String key) {
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag);
}
//释放锁
private void unLock(String key) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}其中的Function<T,R>类型的参数是指一个有参数且有返回值的方法
注:这里还是存储RedisData这种类型的数据到redis
使用方法
先注入CacheClient
java
@Autowired
private CacheClient cacheClient;然后根据参数逐一填写即可,例:
java
// 缓存穿透
Shop shop = cacheClient.queryWithPassThrough(RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_KEY, id, Shop.class, this::getById, RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
// 逻辑过期解决缓存击穿
Shop shop = cacheClient.queryWithLogicalExpire(RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_KEY, id, Shop.class, this::getById, RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES, RedisConstants.LOCK_SHOP_KEY);