一.二分查找
1.解法1
为什么是 i<=j 意味着区间内有未比较的元素, 而不是 i<j ? i==j 意味着 i,j 它们指向的元素也会参与比较 i<j 只意味着 m 指向的元素参与比较
java
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int target) {
int i = 0;
int j = a.length - 1;
while (i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) >>> 1;
if (target < a[m]) {
j = m - 1;
} else if (a[m] < target) {
i = m + 1;
} else {
return m;
}
}
return -1;
}2.解法2
1.i, m 指针可能是查找目标
2.j 指针不可能是查找目标(这种方法j只是代表一个边界)
3.因为 1. 2. i >= j 时表示区域内没有要找的了
4.改变 i 边界时, m 已经比较过不是目标, 因此需要 i=m+1
5.改变 j 边界时, m 已经比较过不是目标, 同时因为 2. 所以 j=m,怕错过目标值
java
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int target) {
int i = 0;
int j = a.length;
while (i < j) {
int m = (i + j) >>> 1;
if (target < a[m]) {
j = m;
} else if (a[m] < target) {
i = m + 1;
} else {
return m;
}
}
return -1;
}3.有重复元素时的处理及应用
1.leftmost
能找到就是返回最左侧的值;找不到就返回比目标大的第一个索引位置。
所以就说返回的i就是大于等于目标最靠左的索引位置。
java
public static int leftMost(int[] a, int target) {
int i = 0;
int j = a.length - 1;
while (i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) >>> 1;
if (target <= a[m]) {
j = m - 1;
} else if (a[m] < target) {
i = m + 1;
}
}
return i;
}搜索插入位置
2.rightmost
i-1返回的是:找的到就是最右边的值;找不到就是比目标小的最右边的值。
java
public static int rightMost(int[] a, int target) {
int i = 0;
int j = a.length - 1;
while (i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) >>> 1;
if (target < a[m]) {
j = m - 1;
} else if (a[m] <= target) {
i = m + 1;
}
}
return i - 1;
}重复元素的开是位置和结束位置
3.应用
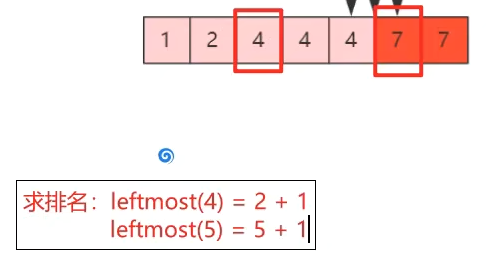
1.求排名(leftmost)
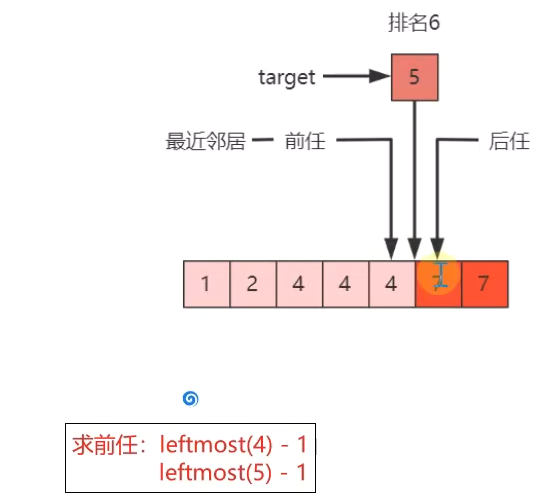
2.求前任(leftmost)
3.范围查询

二.排序
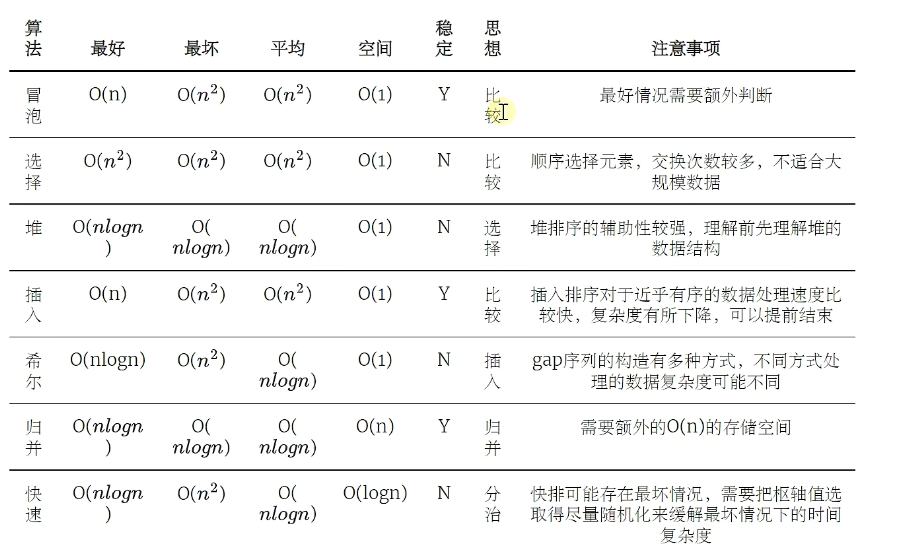

插入排序
从第二个开始不断地向前比较,找到合适的插入位置。排好序的顺序是从前到后逐渐排好的。
这里的i可以理解为已排序好的右边界,low是未排序区的左边界,所以我们可以理解a[low]就是我们想要插入的元素,先把它弄一个临时变量存起来,然后它与前面的所有元素依次对比来找到合适的位置插入,插入的位置就是索引i+1的位置,因为i是已排序好的右边界。
java
public static void sort(int[] a) {
for (int low = 1; low < a.length; low++) {
int t = a[low];
int i = low - 1;
// 自右向左找插入位置,如果比待插入元素大,则不断右移,空出插入位置
while (i >= 0 && t < a[i]) {
a[i + 1] = a[i];
i--;
}
// 找到插入位置
//如果i= low - 1的话,i+1就是low,相当于重复赋值了,没意义。
//也就是只比前一个元素小,移动了一个位置
if (i != low - 1) {
a[i + 1] = t;
}
}
}希尔排序(插入排序的优化)
可以将插入排序理解为希尔排序的一种特殊情况,也是最终情况,当gap=1时的情况。
只需将上面的代码的1的位置改成gap即可。
java
public static void sort(int[] a) {
for (int gap = a.length >> 1; gap >= 1; gap = gap >> 1) {
// gap=4
for (int low = gap; low < a.length; low++) {
int t = a[low]; // t=5
int i = low - gap;
// 自右向左找插入位置,如果比待插入元素大,则不断右移,空出插入位置
while (i >= 0 && t < a[i]) {
a[i + gap] = a[i];
i -= gap;
}
// 找到插入位置
if (i != low - gap) {
a[i + gap] = t;
}
}
}
}简单选择排序
核心思想是从序列中选择一个最大/最小值,然后确定它的最终位置。
java
public static void sort(int[] a) {
for (int right = a.length - 1; right > 0; right--) {
int max = right;
for (int i = 0; i < right; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[max]){
max = i;
}
}
if (max != right) {
int t = a[right];
a[right] = a[max];
a[max] = t;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}代码并不复杂,只是找出最大/最小值,然后把它放在最后/最前的位置即可,但是寻找最大小值的效率很低。下面会推荐一种非常快速的找最大/小值的办法------堆排序
堆排序
1.堆的介绍
堆是一种基于树的数据机构,用完全二叉树实现(除了最后一层都必须填满)

由于它的特性可以用数组来存储元素。
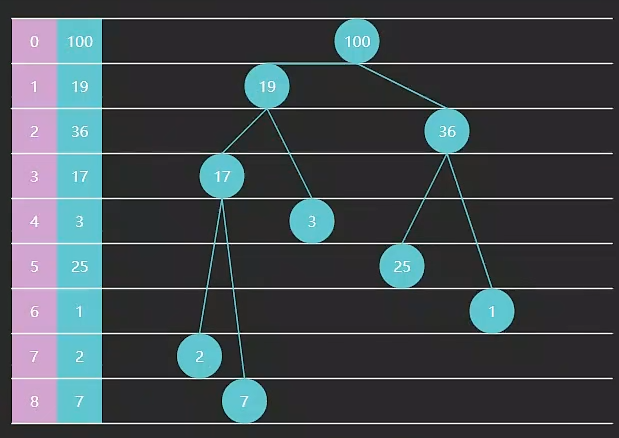
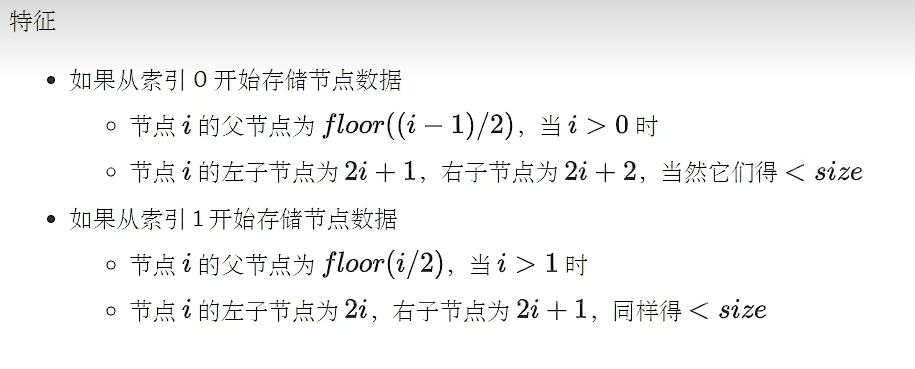
2.建堆(建立大顶堆/小顶堆)以及堆的相关方法

与更大的一个孩子进行交换,直至停止。
java
public class MaxHeap {
int[] array;
int size;
public MaxHeap(int capacity) {
this.array = new int[capacity];
}
public MaxHeap(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
this.size = array.length;
heapify();
}
//建堆
private void heapify() {
//找到最后一个非叶子节点,从后往前将所有的非叶子节点依次下潜
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
down(i);
}
}
//添加元素
//先添加在尾部,然后逐渐上浮。
public boolean offer(int offered) {
if (size == array.length) {
return false;
}
array[size] = offered;
up(offered, size);
size++;
return true;
}
//删除堆顶元素
//替换堆顶和末尾的元素,然后让堆顶元素不断下潜
public int poll() {
int top = array[0];
swap(0, size - 1);
size--;
down(0);
return top;
}
//删除指定索引位置的元素
//替换index处的元素和末尾的元素,然后让index元素不断下潜
public int poll(int index) {
if (index > size - 1) {
return -1;
}
int deleted = array[index];
swap(index, size - 1);
size--;
down(index);
return deleted;
}
//取出堆顶元素
public int peek() {
int top = array[0];
return top;
}
//替换堆顶元素
public void replace(int top) {
array[0] = top;
down(0);
}
//交换
private void swap(int i, int j) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
//下潜
private void down(int parent) {
while (true) {
int max = parent;
//左孩子
int left = parent * 2 + 1;
//右孩子
int right = left + 1;
if (left < size && array[max] < array[left]) {
max = left;
}
if (right < size && array[max] < array[right]) {
max = right;
}
//找到了更大了
if (max == parent) {
break;
}
swap(max, parent);
parent = max;
}
}
//上浮方法
private void up(int offered, int index) {
int child = index;
while (child > 0) {
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
if (offered > array[parent]) {
array[child] = array[parent];
child = parent;
} else {
break;
}
}
array[child] = offered;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {2, 3, 1, 7, 6, 4, 5};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
MaxHeap maxHeap = new MaxHeap(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(maxHeap.array));
int peek = maxHeap.peek();
System.out.println(peek);
int poll = maxHeap.poll(2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(maxHeap.array));
}
}3.堆的力扣题
1.数据流取最大的第K个数
java
public class StreamKBigNum {
private MinHeap minHeap;
public StreamKBigNum(int k, int[] nums) {
minHeap = new MinHeap(k);
}
public int add(int val) {
if (!minHeap.isFull()){
minHeap.offer(val);
}else if (minHeap.peek() < val){
minHeap.replace(val);
}
return minHeap.peek();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StreamKBigNum test = new StreamKBigNum(3, new int[]{});
System.out.println(test.add(3)); // [3] 3
System.out.println(test.add(5)); // [3 5] 3
System.out.println(test.add(10));
System.out.println(test.add(9));
System.out.println(test.add(4));
}
}2.数据流取数据的中位数

java
public class MediumNum {
//大顶堆
private PriorityQueue<Integer> left = new PriorityQueue<>(
(a, b) -> Integer.compare(b, a)
);
//小顶堆
private PriorityQueue<Integer> right = new PriorityQueue<>();
public void addNum(int num) {
if (left.size() == right.size()){
right.offer(num);
Integer poll = right.poll();
left.offer(poll);
}else {
left.offer(num);
right.offer(left.poll());
}
}
public double findMedian() {
if (left.size() == right.size()){
return (left.peek() + right.peek()) / 2.0;
}else {
return left.peek();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MediumNum test = new MediumNum();
test.addNum(1);
test.addNum(2);
test.addNum(3);
test.addNum(7);
test.addNum(8);
test.addNum(9);
System.out.println(test.findMedian());
test.addNum(10);
System.out.println(test.findMedian());
test.addNum(4);
System.out.println(test.findMedian());
}
}3.收集hashmap缓存中出现频率最高的n个字符串
java
public void QueryTopN(List<String> input, List<String> result, int n) {
// 统计每个字符串出现的次数
Map<String, Integer> frequencyMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : input) {
frequencyMap.put(str, frequencyMap.getOrDefault(str, 0) + 1);
}
// 小顶堆,用于存储出现次数最多的n个字符串
PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(
(e1, e2) -> e1.getValue().compareTo(e2.getValue())
);
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : frequencyMap.entrySet()) {
if (minHeap.size() < n) {
minHeap.offer(entry);
} else if (entry.getValue() > minHeap.peek().getValue()) {
minHeap.poll();
minHeap.offer(entry);
}
}
// 将堆中的元素取出并反转,得到出现次数从多到少的结果
List<String> temp = new ArrayList<>();
while (!minHeap.isEmpty()) {
temp.add(minHeap.poll().getKey());
}
Collections.reverse(temp);
result.addAll(temp);
}4.用大顶堆实现优先级队列
java
public class PriorityQueue4<E extends Priority> implements Queue<E> {
Priority[] array;
int size;
public PriorityQueue4(int capacity) {
array = new Priority[capacity];
}
/*
1. 入堆新元素, 加入到数组末尾 (索引位置 child)
2. 不断比较新加元素与它父节点(parent)优先级 (上浮)
- 如果父节点优先级低, 则向下移动, 并找到下一个 parent
- 直至父节点优先级更高或 child==0 为止
*/
@Override
public boolean offer(E offered) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
int child = size++;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0 && offered.priority() > array[parent].priority()) {
array[child] = array[parent];
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
array[child] = offered;
return true;
}
/*
1. 交换堆顶和尾部元素, 让尾部元素出队
2. (下潜)
- 从堆顶开始, 将父元素与两个孩子较大者交换
- 直到父元素大于两个孩子, 或没有孩子为止
*/
@Override
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
swap(0, size - 1);
size--;
Priority e = array[size];
array[size] = null; // help GC
// 下潜
down(0);
return (E) e;
}
private void down(int parent) {
int left = 2 * parent + 1;
int right = left + 1;
int max = parent; // 假设父元素优先级最高
if (left < size && array[left].priority() > array[max].priority()) {
max = left;
}
if (right < size && array[right].priority() > array[max].priority()) {
max = right;
}
if (max != parent) { // 有孩子比父亲大
swap(max, parent);
down(max);
}
}
private void swap(int i, int j) {
Priority t = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = t;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return (E) array[0];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == array.length;
}
}5.堆排序

java
//堆排序
public void sort(int[] a) {
//这里一般还要加一个建堆的函数,因为我们已经在构造函数里加了,这里就没加
for (int right = size - 1; right > 0; right--) {
swap(0, right);
size--;
down(0);
}
}6.合并多个有序链表

小顶堆的大小就是链表的个数。
1.先将每个链表的头结点放到小顶堆中
2.移除堆顶元素,并将堆顶元素加入到链表中
3.将加入到新链表中元素所在的链表的next节点再加入到小顶堆中,依次循环。
java
public ListNode mergeKLists2(ListNode[] lists) {
//小顶堆
PriorityQueue<ListNode> min = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (ListNode head : lists) {
if (head != null) {
min.offer(head);
}
}
//新链表
ListNode s = new ListNode(-1, null);
//指针
ListNode p = s;
while (!min.isEmpty()) {
ListNode poll = min.poll();
p.next = poll;
p = poll;
if (poll.next != null) {
min.offer(poll.next);
}
}
return s.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode[] lists = {
ListNode.of(1, 4, 5),
ListNode.of(1, 3, 4),
ListNode.of(2, 6),
null,
};
ListNode m = new E01Leetcode23().mergeKLists2(lists);
System.out.println(m);
}冒泡排序
从头开始相邻的两两比对,然后交换,每次都会将最大的元素确定到数组的末尾处,然后不断缩小未排序的边界,逐渐减小。
java
public static void sort(int[] a) {
int j = a.length - 1;
while (true) {
int x = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[i + 1]) {
swap(a, i, i + 1);
x = i;
}
}
j = x;
if (j == 0){
break;
}
}
}
private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}快排
java
public class QuickSelectSort {
public static void sort(int[] a) {
quick(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
private static void quick(int[] a, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
int p = partition(a, left, right);
quick(a, left, p - 1);
quick(a, p + 1, right);
}
private static int partition(int[] a, int left, int right) {
int idx = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(right - left + 1) + left;
// [0~9] right-left+1=3 [0,2]+4=[4,6]
swap(a, idx, left);
int pv = a[left];
int i = left;
int j = right;
while (i < j) {
// 1. j 从右向左找小(等)的
while (i < j && a[j] > pv) {
j--;
}
// 2. i 从左向右找大的
while (i < j && a[i] <= pv) {
i++;
}
// 3. 交换位置
swap(a, i, j);
}
swap(a, left, i);
return i;
}
private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {9, 3, 7, 2, 8, 5, 1, 4};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}相关算法题
1.快速选择算法
基于快排每一次分区就可以确定基准点元素的最终位置,然后再基准点左边的就是比基准点元素小的,右边的就是比基准点元素大的。所以我们想找到数组中第i个元素的位置(从小到大排列),就可以基于快排来做。
java
static int quick(int[] array, int left, int right, int i) {
/*
6 5 1 2 [4]
2
1 2 4 6 5
1 2 4 6 [5]
3
1 2 4 5 6
*/
int p = partition(array, left, right); // 基准点元素索引值
if (p == i) {
return array[p];
}
if(i < p) { // 到左边找
return quick(array, left, p - 1, i);
} else { // 到右边找
return quick(array, p + 1, right, i);
}
}2.数组中第k大的元素
这个算法题也是基于上面的思想来的,只不过上面的i指的是索引,而这道算法题找的是第k大,比如说第二大找的就是排在倒数第二索引位置的元素,所以只用改一下i的参数即可,改为a.length - k。
java
public int findKthLargest(int[] a, int k) {
return QuickSelect.quick(
a, 0, a.length - 1, a.length - k
);
}3.数组中中位数
java
public static double findMedian(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length % 2 == 1) { // 奇数
return QuickSelect.quick(nums, 0, nums.length - 1, nums.length / 2);
} else { // 偶数
int x = QuickSelect.quick(nums, 0, nums.length - 1, nums.length / 2);
int y = QuickSelect.quick(nums, 0, nums.length - 1, nums.length / 2 - 1);
return (x + y) / 2.0;
}
}归并排序
要点
分:每次从中间切一刀,处理的数据也就少了一半
治:当切到还只剩下一个数据时,就可以认为是有序的了,因为一个数据本身就有序
合:合并两个有序结果(算法题:合并有序数组)
java
private static void split(int[] a1, int left, int right) {
// 治:只有一个元素时,已经有序
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
// 分:找到中点
int mid = (left + right) >>> 1; // 等价于 (left + right) / 2,防溢出
// 递归拆分左半部分 [left, mid]
split(a1, left, mid);
// 递归拆分右半部分 [mid+1, right]
split(a1, mid + 1, right);
// 合:合并两个有序子数组
combine(a1, left, mid, right);
}
// 合并两个有序区间:[left, mid] 和 [mid+1, right]
public static void combine(int[] a, int left, int mid, int right) {
// 临时数组存放合并结果
int[] temp = new int[right - left + 1];
int i = left; // 左子数组起点
int j = mid + 1; // 右子数组起点
int k = 0; // temp 数组索引
// 合并两个有序子数组
while (i <= mid && j <= right) {
if (a[i] <= a[j]) {
temp[k++] = a[i++];
} else {
temp[k++] = a[j++];
}
}
// 复制剩余元素
while (i <= mid) {
temp[k++] = a[i++];
}
while (j <= right) {
temp[k++] = a[j++];
}
// 将合并结果拷贝回原数组
for (int p = 0; p < temp.length; p++) {
a[left + p] = temp[p];
}
}基数排序
1.代码
java
public class RadixSort {
/*
110 088 009
0 088 009
1 110
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
088 009 110 第一轮 重新放回原数组
0 009
1 110
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 088
9
009 110 088 第二轮 重新放回原数组
0 110
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 088
9 009
110 088 009 第三轮 重新放回原数组
*/
public static void radixSort(String[] a, int length) {
// 1. 准备桶
ArrayList<String>[] buckets = new ArrayList[128];
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 2. 进行多轮按位桶排序
for (int i = length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 将字符串放入合适的桶
for (String s : a) {
buckets[s.charAt(i)].add(s);
}
// 重新取出排好序的字符串,放回原始数组
int k = 0;
for (ArrayList<String> bucket : buckets) {
for (String s : bucket) {
a[k++] = s;
}
bucket.clear();
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] phoneNumbers = new String[10]; // 0~127
phoneNumbers[0] = "13812345678"; // int long
phoneNumbers[1] = "13912345678";
phoneNumbers[2] = "13612345678";
phoneNumbers[3] = "13712345678";
phoneNumbers[4] = "13512345678";
phoneNumbers[5] = "13412345678";
phoneNumbers[6] = "15012345678";
phoneNumbers[7] = "15112345678";
phoneNumbers[8] = "15212345678";
phoneNumbers[9] = "15712345678";
/*String[] phoneNumbers = new String[6];
phoneNumbers[0] = "158";
phoneNumbers[1] = "151";
phoneNumbers[2] = "235";
phoneNumbers[3] = "138";
phoneNumbers[4] = "139";
phoneNumbers[5] = "159";*/
/*
0
1 151
2
3
4
5 135
6
7
8 158 138
9 139 159
151 135 158 138 139 159 按个位排
0
1
2
3 135 138 139
4
5 151 158 159
6
7
8
9
135 138 139 151 158 159 按十位排
*/
RadixSort.radixSort(phoneNumbers, 11);
for (String phoneNumber : phoneNumbers) {
System.out.println(phoneNumber);
}
}
}处理不同长度的字符串
java
public static void radixSort(String[] a) {
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return;
// 1. 找到最长字符串的长度
int maxLength = 0;
for (String s : a) {
if (s.length() > maxLength) {
maxLength = s.length();
}
}
// 2. 准备桶(ASCII 范围 0-127)
ArrayList<String>[] buckets = new ArrayList[128];
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 3. 从最低位到最高位进行桶排序
for (int pos = maxLength - 1; pos >= 0; pos--) {
// 将字符串放入合适的桶
for (String s : a) {
// 关键修改:处理不同长度的字符串
//含义是:如果小于就说明字符串在当前位置是有元素的
if (pos < s.length()) {
// 字符串在当前位置有字符
buckets[s.charAt(pos)].add(s);
} else {
// 字符串较短,视为空字符(ASCII 0)
buckets[0].add(s);
}
}
// 重新取出排好序的字符串
int k = 0;
for (ArrayList<String> bucket : buckets) {
for (String s : bucket) {
a[k++] = s;
}
bucket.clear(); // 清空桶,准备下一轮
}
}
}2.应用场景