NiFi Rule Engine Processor 是一个功能强大的处理器,核心作用是基于用户定义的一系列规则,对数据流(FlowFile)进行动态的、可配置的逻辑判断和处理。
简单来说,它将业务逻辑"规则化",允许你在一个处理器内实现复杂的路由、修改、过滤等操作,而无需串联多个条件判断处理器。
核心作用与特点
1、规则驱动的处理逻辑:你可以编写一系列"如果...那么..."式的规则。每条规则包含:
- 条件: 一个或多个针对 FlowFile 属性或内容的表达式(使用 NiFi 表达式语言)。
- 动作: 当条件满足时执行的操作(例如,路由到某个关系、修改属性、丢弃数据等)。
2、集中化的逻辑控制: 替代了传统上需要多个 RouteOnAttribute、UpdateAttribute、RouteOnContent 等处理器串联才能实现的复杂逻辑。将所有规则集中在一个处理器内,使数据流图更简洁、更易于管理和维护。
3、灵活的数据路由与属性操作: 这是它最主要的功能之一。
- 路由: 可以根据规则将 FlowFile 发送到不同的下游关系(如 matched, unmatched, 或自定义关系)。
- 属性操作: 可以在规则动作中添加、修改或删除 FlowFile 的属性。
工作原理流程
- 处理器接收 FlowFile。
- 按顺序评估 用户预先定义好的规则列表。
- 条件匹配: 对每条规则,检查其"条件"是否被满足。
- 执行动作:如果某条规则的条件被满足,则立即执行该规则配置的"动作"(如路由、修改属性),并且通常停止评估后续规则(除非配置为继续); 如果没有任何规则匹配,FlowFile 将被路由到默认的 unmatched 关系。
- 流出: 处理后的 FlowFile 根据匹配的规则动作,从对应的关系传送给下游处理器。
2.1、安装
https://blog.csdn.net/xiunai78/article/details/96152611 Apache NiFi With Rule Engine
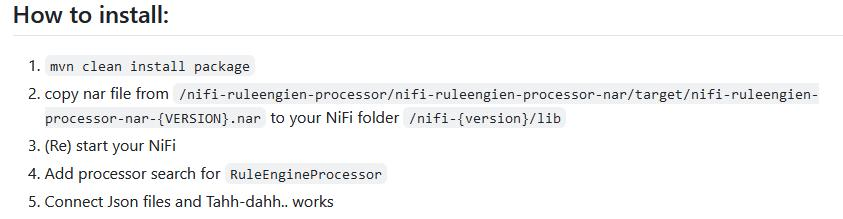
1、git clone https://github.com/budney/NiFi-Rule-engine-processor
2、# 编译成nar包 需要修改源码以适配Nifi2.2.0
cd NiFi-Rule-engine-processor
mvn clean install package -U # apt install maven
3、# 复制到nifi安装目录下的lib/目录下
cp nifi-ruleengien-processor-nar/target/nifi-ruleengien-processor-1.0.nar /path-to-nifi/lib/
4、重启nifi服务最终编译结果:
2.2、示例
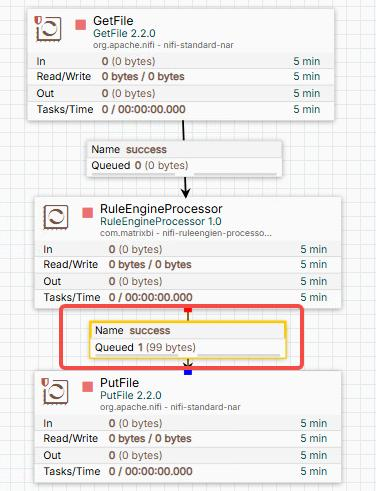
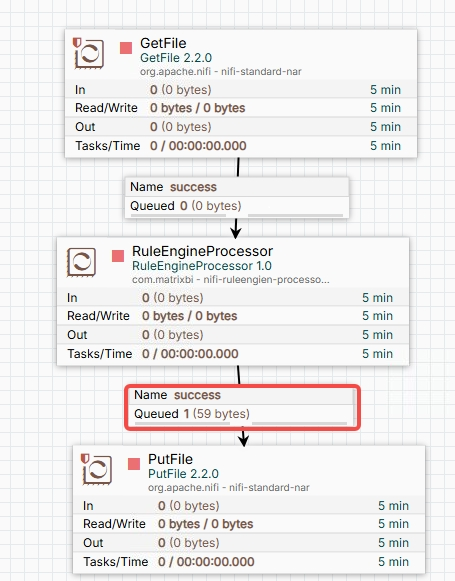
2.2.1、Create a NiFi Flow
- GetFile处理器 Set property
source folder: /data/nifi-project/IN - RuleEngineProcessor Set the property DRL file path to /data/nifi-project/DRL/business_object_json_test1.drl
- PutFile处理器 Set the property
dest folderto /data/nifi-project/OUT
2.2.2、Create Files and Relevant Folders
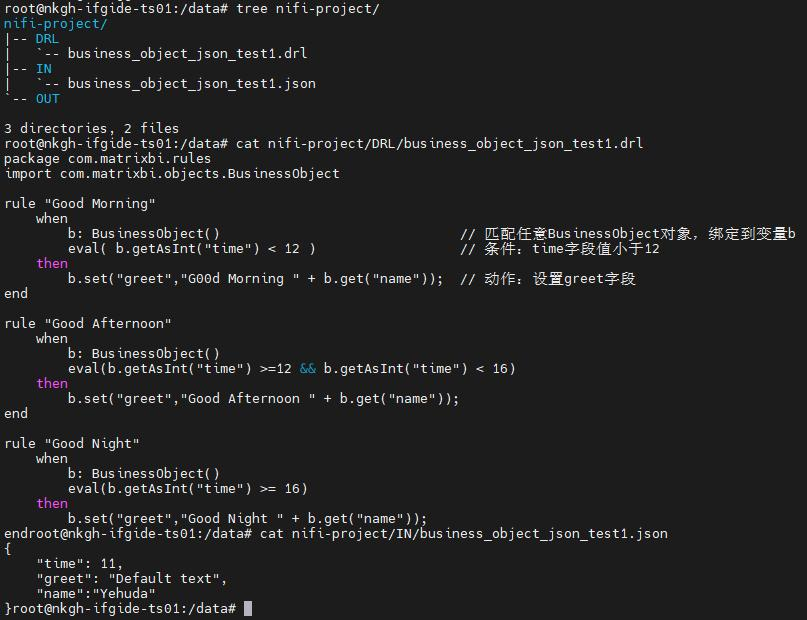
创建DRL文件 /data/nifi-project/DRL/business_object_json_test1.drl
bash
package com.matrixbi.rules
import com.matrixbi.objects.BusinessObject
rule "Good Morning"
when
b: BusinessObject() // 匹配任意BusinessObject对象,绑定到变量b
eval(b.getAsInt("time") < 12) // 条件:time字段值小于12
then
b.set("greet","G00d Morning " + b.get("name")); // 动作:设置greet字段
end
rule "Good Afternoon"
when
b: BusinessObject()
eval(b.getAsInt("time") >=12 && b.getAsInt("time") < 16)
then
b.set("greet","Good Afternoon " + b.get("name"));
end
rule "Good Night"
when
b: BusinessObject()
eval(b.getAsInt("time") >= 16)
then
b.set("greet","Good Night " + b.get("name"));
end创建一个JSON测试文件 /data/nifi-project/IN/business_object_json_test1.json
bash
{
"time": 11,
"greet": "Default text",
"name":"Yehuda"
}激活所有并运行它。
2.2.3、结果
过了一会儿,你可以在 /data/nifi-project/OUT目录下看到business_object_json_test1.json
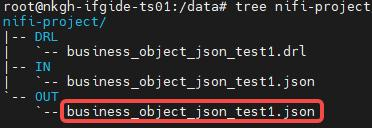
输入:
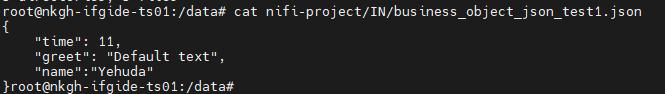
输出:

2.3、不支持json嵌套
修改源码: 加粗部分是修改的
NiFi-Rule-engine-processor\nifi-ruleengien-processor-processors\src\main\java\com\matrixbi\objects\BusinessObjectJson.java
java
package com.matrixbi.objects;
import java.util.Arrays;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.JsonElement;
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import com.google.gson.JsonArray;
import com.google.gson.JsonParser;
import com.google.gson.JsonSyntaxException;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* Business object
*
* @author Yehuda Korotkin
*
*/
public class BusinessObjectJson extends BusinessObject {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -856082492778433564L;
private JsonObject jObj;
private Boolean change = false;
private Gson gson;
private JsonBusinessObjects parent;
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BusinessObjectJson.class);
public BusinessObjectJson(JsonBusinessObjects jsonBusinessObjects, JsonElement je) {
this.gson = new Gson();
this.jObj = (JsonObject) je;
this.parent = jsonBusinessObjects;
}
private void trigger_change() {
this.parent.trigger_change();
this.change = true;
}
public String get(String path) {
return getPath(path).getAsString();
}
public float getAsFloat(String path) {
return getPath(path).getAsFloat();
}
public int getAsInt(String path) {
return getPath(path).getAsInt();
}
public boolean getAsBoolean(String path) {
return getPath(path).getAsBoolean();
}
public void set(String path, String value) {
String[] s = getParentPath(path);
JsonObject o = (JsonObject) getPath(s[0]);
o.addProperty( s[1], value);
trigger_change();
}
public void set(String path, Boolean value) {
String[] s = getParentPath(path);
JsonObject o = (JsonObject) getPath(s[0]);
o.addProperty(s[1], value);
trigger_change();
}
public void set(String path, Character value) {
String[] s = getParentPath(path);
JsonObject o = (JsonObject) getPath(s[0]);
o.addProperty(s[1], value);
trigger_change();
}
public void set(String path, Number value) {
String[] s = getParentPath(path);
JsonObject o = (JsonObject) getPath(s[0]);
o.addProperty(s[1], value);
trigger_change();
}
public String getJson() {
return gson.toJson(this.jObj);
}
@Override
public Boolean isChanged() {
return this.change;
}
private String[] getParentPath(String path) {
String[] seg = path.split("\\.");
if(seg.length <= 1) {
return new String[]{"", path};
}
String[] seg2 = Arrays.copyOfRange(seg, 0, seg.length - 1);
String x1 = String.join(".", seg2);
String[] seg3 = Arrays.copyOfRange(seg, seg.length - 1, seg.length);
String x2 = String.join(".", seg3);
return new String[]{x1, x2};
}
private JsonElement getPath(String path) throws JsonSyntaxException {
if(path == null || path.isEmpty()) {
return this.jObj;
}
JsonElement current = this.jObj;
String[] seg = path.split("\\.");
log.info("********************seg: {}", seg);
for (String element : seg) {
log.info("********************element: {}", element);
if (current == null || current.isJsonNull()) {
return null;
}
// 处理数组
if (current.isJsonArray()) {
try {
int index = Integer.parseInt(element);
JsonArray arr = current.getAsJsonArray();
if (index < 0 || index >= arr.size()) {
return null;
}
current = arr.get(index);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
return null;
}
}
// 处理对象
else if (current.isJsonObject()) {
JsonObject obj = current.getAsJsonObject();
if (!obj.has(element)) {
return null;
}
current = obj.get(element);
}
// 既不是对象也不是数组,路径却还没结束
else {
return null;
}
}
log.info("********************current: {}",current);
return current;
}
}测试 1--json嵌套:
输入:
java
{
"person": {
"time": 11,
"name": "Yehuda"
},
"greet": "Default text"
}drl文件:
bash
package com.matrixbi.rules
import com.matrixbi.objects.BusinessObject
rule "Good Morning"
when
b: BusinessObject() // 匹配任意BusinessObject对象,绑定到变量b
eval(b.getAsInt("person.time") < 12) // 条件:time字段值小于12
then
b.set("greet","G00d Morning " + b.get("person.name")); // 动作:设置greet字段
end
rule "Good Afternoon"
when
b: BusinessObject()
eval(b.getAsInt("person.time") >=12 && b.getAsInt("person.time") < 16)
then
b.set("greet","Good Afternoon " + b.get("person.name"));
end
rule "Good Night"
when
b: BusinessObject()
eval(b.getAsInt("person.time") >= 16)
then
b.set("greet","Good Night " + b.get("person.name"));
end输出:
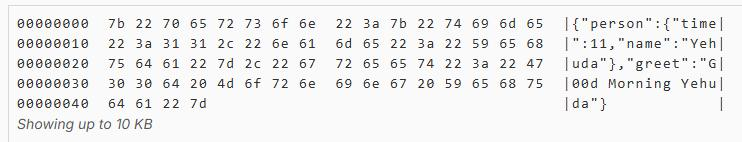
测试 2--json数组:
输入:
bash
{
"user": {
"roles": [
{ "name": "admin", "age": 10 },
{ "name": "test", "age": 11 }
]
}
}drl:
bash
package com.matrixbi.rules
import com.matrixbi.objects.BusinessObject
rule "minor"
when
b: BusinessObject()
eval(b.getAsInt("user.roles.0.age") < 18)
then
b.set("user.roles.0.desc","minor");
end
rule "middle-aged person"
when
b: BusinessObject()
eval(b.getAsInt("user.roles.0.age") >=18 && b.getAsInt("user.roles.0.age") < 60)
then
b.set("user.roles.0.desc", "middle-aged person");
end
rule "elderly people"
when
b: BusinessObject()
eval(b.getAsInt("user.roles.0.age") >= 60)
then
b.set("user.roles.0.desc","elderly people");
end输出:

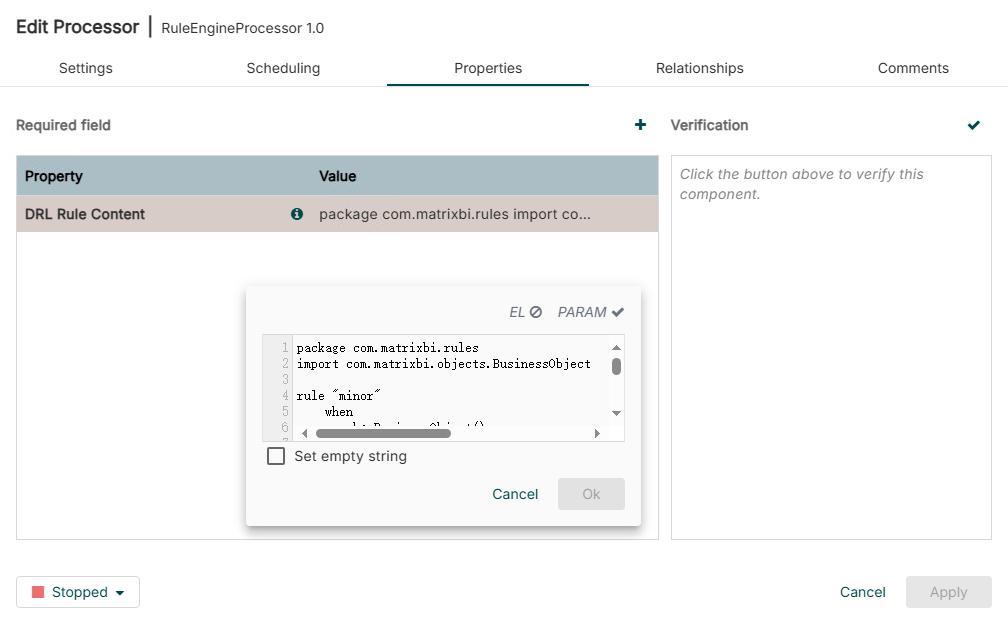
2.4、算子参数里面直接读取drl内容
之前是路径,现在修改为有用户在算子输入框里直接输入DRL规则内容,不再是DRL文件路径
修改源码:NiFi-Rule-engine-processor\nifi-ruleengien-processor-processors\src\main\java\com\matrixbi\nifi\processor\RuleEngineProcessor.java
java
...
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
@SideEffectFree
@Tags({"Rule Engine","Processor","Drools","drl","MatrixBI"})
@CapabilityDescription("Rule engine for nifi")
@Description("This is rule engien")
public class RuleEngineProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
// public static final PropertyDescriptor DRL_PATH = new PropertyDescriptor
// .Builder().name("DRL file path")
// .displayName("DRL file path")
// .description("File ends with .drl or .xls that contines drools rules")
// .required(true)
// .addValidator(StandardValidators.NON_EMPTY_VALIDATOR)
// .addValidator(StandardValidators.FILE_EXISTS_VALIDATOR)
// .build();
public static final PropertyDescriptor DRL_CONTENT = new PropertyDescriptor
.Builder().name("DRL Content")
.displayName("DRL Rule Content")
.description("Drools DRL rule content")
.required(true)
.addValidator(StandardValidators.NON_EMPTY_VALIDATOR)
.build();
....
// 废弃
private static RuleEngine getRuleEngineService_old(String filepath) {
if(!ruleEngineServices.containsKey(filepath))
ruleEngineServices.put(filepath, RuleEngine.createSession(filepath));
return ruleEngineServices.get(filepath);
}
// 生成内容哈希(MD5/SHA-256)
private static String generateHash(String content) {
try {
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
byte[] hash = md.digest(content.getBytes("UTF-8"));
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(hash);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 如果哈希失败,使用内容本身作为键(注意内容太长的情况)
return content.length() > 100 ? content.substring(0, 100) : content;
}
}
// 从字符串内容创建RuleEngine(需要RuleEngine支持)
private static RuleEngine createEngineFromContent(String drlContent) {
// 方法二:创建临时文件
try {
Path tempFile = Files.createTempFile("rules_", ".drl");
Files.write(tempFile, drlContent.getBytes());
RuleEngine engine = RuleEngine.createSession(tempFile.toString());
// 可以选择删除临时文件,或让RuleEngine读取后删除
return engine;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create temp DRL file", e);
}
}
private static RuleEngine getRuleEngineService(String drlContent) {
// 1. 生成DRL内容的哈希作为唯一标识
String contentHash = generateHash(drlContent);
// 2. 检查缓存
if(!ruleEngineServices.containsKey(contentHash)) {
// 3. 使用内容创建RuleEngine(假设RuleEngine支持从字符串创建)
RuleEngine engine = createEngineFromContent(drlContent);
ruleEngineServices.put(contentHash, engine);
}
return ruleEngineServices.get(contentHash);
}
@Override
protected void init(final ProcessorInitializationContext context) {
log = getLogger();
log.debug("Init MatrixBI's RuleEngineProcesor");
final List<PropertyDescriptor> descriptors = new ArrayList<PropertyDescriptor>();
// descriptors.add(DRL_PATH);
descriptors.add(DRL_CONTENT);
this.descriptors = Collections.unmodifiableList(descriptors);
final Set<Relationship> relationships = new HashSet<Relationship>();
relationships.add(SUCCESS);
relationships.add(FAILD);
this.relationships = Collections.unmodifiableSet(relationships);
}
...
@Override
public void onTrigger(final ProcessContext context, final ProcessSession session) throws ProcessException {
FlowFile flowFile = session.get();
if ( flowFile == null ) {
return;
}
final AtomicReference<JsonBusinessObjects> value = new AtomicReference<>();
session.read(flowFile, new InputStreamCallback() {
@Override
public void process(InputStream flowfileInputStream) throws IOException {
try{
InputStreamReader flowfileInputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(flowfileInputStream);
JsonBusinessObjects jsonBusinessObjects = new JsonBusinessObjects(flowfileInputStreamReader);
// String drl_path = context.getProperty(DRL_PATH).getValue();
String drl_content = context.getProperty(DRL_CONTENT).getValue();
while(jsonBusinessObjects.hasNext()) {
// getRuleEngineService(drl_path).execute(jsonBusinessObjects.next());
// 使用DRL内容获取RuleEngine
getRuleEngineService(drl_content).execute(jsonBusinessObjects.next());
}
value.set(jsonBusinessObjects);
}catch(Exception ex){
log.error("Failed to read json string", ex);
}
}
});
// Write the results to an attribute
JsonBusinessObjects results = value.get();
if(results==null)
{
log.error("Failed to get results");
session.transfer(flowFile, FAILD);
return;
}
// if changed
if(results.hasChanged()) {
flowFile = session.write(flowFile, new OutputStreamCallback() {
@Override
public void process(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
out.write(value.get().getJson().getBytes());
}
});
}
session.transfer(flowFile, SUCCESS);
}
@OnStopped
public void onStopped() {
bufferQueue.clear();
}
}测试结果: