Spring AOP详解:从原理到实战
前言
AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming,面向切面编程)是Spring框架的另一大核心特性。它通过将横切关注点(Cross-Cutting Concerns)从业务逻辑中分离出来,实现了代码的解耦和复用。本文将深入讲解Spring AOP的核心概念、实现原理和实战应用。
一、什么是AOP
1.1 AOP的概念
AOP是一种编程范式,它将程序中的横切关注点(如日志、事务、安全等)从业务逻辑中分离出来,形成独立的切面。
1.2 核心概念

1.3 为什么需要AOP
java
/**
* 没有AOP的代码 - 存在的问题
*/
public class UserServiceWithoutAOP {
public void createUser(User user) {
// 1. 日志记录
System.out.println("开始创建用户: " + user.getUsername());
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 2. 权限检查
if (!SecurityContext.hasPermission("user:create")) {
throw new SecurityException("没有权限");
}
// 3. 参数校验
if (user.getUsername() == null || user.getUsername().isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("用户名不能为空");
}
// 4. 事务开启
Transaction tx = TransactionManager.begin();
try {
// 5. 核心业务逻辑
saveUser(user);
// 6. 事务提交
tx.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 7. 事务回滚
tx.rollback();
throw e;
}
// 8. 日志记录
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("创建用户完成,耗时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
private void saveUser(User user) {
// 实际的业务逻辑
System.out.println("保存用户到数据库");
}
}
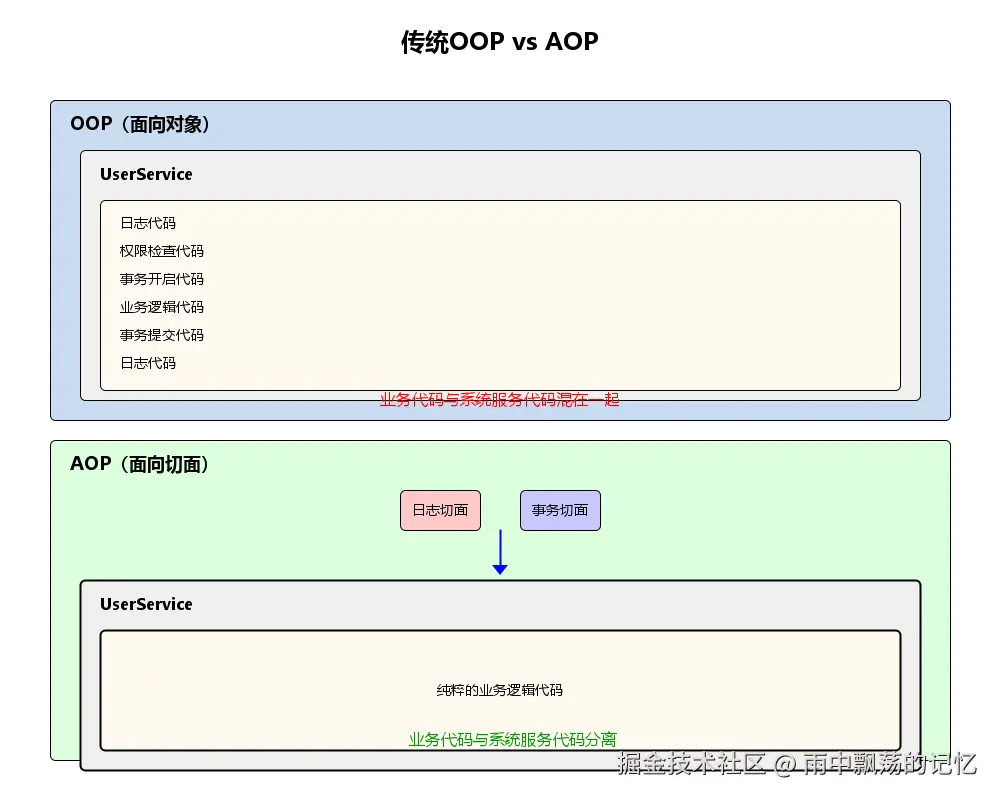
// 问题:
// 1. 代码重复:日志、权限、事务等代码在每个方法中重复
// 2. 代码混乱:业务逻辑与系统服务代码混在一起
// 3. 难以维护:修改日志逻辑需要改动所有方法
// 4. 违反单一职责:一个方法承担了太多责任
java
/**
* 使用AOP的代码 - 简洁清晰
*/
@Service
public class UserServiceWithAOP {
@Transactional
@RequiresPermission("user:create")
@Validated
public void createUser(User user) {
// 纯粹的业务逻辑
saveUser(user);
}
private void saveUser(User user) {
System.out.println("保存用户到数据库");
}
}
// 优势:
// 1. 代码简洁:只包含核心业务逻辑
// 2. 易于维护:系统服务代码集中管理
// 3. 可复用:切面可以应用于多个方法
// 4. 符合单一职责:业务方法只关注业务逻辑二、Spring AOP基础
2.1 通知类型
java
/**
* 五种通知类型演示
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class AdviceTypeDemo {
/**
* 前置通知:在目标方法执行之前执行
*/
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void beforeAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("前置通知:准备执行方法 " + methodName);
}
/**
* 后置通知:在目标方法执行之后执行(无论是否抛出异常)
*/
@After("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void afterAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("后置通知:方法 " + methodName + " 执行完成");
}
/**
* 返回通知:在目标方法正常返回之后执行
*/
@AfterReturning(
pointcut = "execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))",
returning = "result"
)
public void afterReturningAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("返回通知:方法 " + methodName + " 返回值 " + result);
}
/**
* 异常通知:在目标方法抛出异常后执行
*/
@AfterThrowing(
pointcut = "execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))",
throwing = "ex"
)
public void afterThrowingAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("异常通知:方法 " + methodName + " 抛出异常 " + ex.getMessage());
}
/**
* 环绕通知:包围目标方法执行,最强大的通知类型
*/
@Around("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public Object aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("环绕通知:方法 " + methodName + " 开始执行");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 执行目标方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("环绕通知:方法 " + methodName + " 执行成功,耗时 " +
(endTime - startTime) + "ms");
return result;
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("环绕通知:方法 " + methodName + " 执行失败");
throw e;
}
}
}通知执行顺序:


2.2 切点表达式
java
/**
* 切点表达式示例
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class PointcutExpressionDemo {
/**
* execution表达式:最常用
* 语法:execution(修饰符? 返回类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数) 异常?)
*/
// 匹配UserService的所有public方法
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.service.UserService.*(..))")
public void userServiceMethods() {}
// 匹配所有Service的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void allServiceMethods() {}
// 匹配所有返回User的方法
@Pointcut("execution(com.example.entity.User *.*(..))")
public void returnUser() {}
// 匹配第一个参数是Long类型的方法
@Pointcut("execution(* *(Long, ..))")
public void firstParamIsLong() {}
/**
* within表达式:匹配特定类型
*/
// 匹配service包下的所有类
@Pointcut("within(com.example.service.*)")
public void withinService() {}
// 匹配service包及子包下的所有类
@Pointcut("within(com.example.service..*)")
public void withinServicePackage() {}
/**
* @annotation表达式:匹配带有特定注解的方法
*/
// 匹配带有@Transactional注解的方法
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)")
public void transactionalMethods() {}
// 匹配带有@RequiresPermission注解的方法
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.annotation.RequiresPermission)")
public void requiresPermissionMethods() {}
/**
* @within表达式:匹配带有特定注解的类的所有方法
*/
// 匹配带有@Service注解的类的所有方法
@Pointcut("@within(org.springframework.stereotype.Service)")
public void serviceBeans() {}
/**
* args表达式:匹配参数类型
*/
// 匹配参数是User类型的方法
@Pointcut("args(com.example.entity.User)")
public void argsUser() {}
/**
* 组合切点表达式
*/
// 与运算:同时满足两个条件
@Pointcut("userServiceMethods() && args(Long)")
public void userServiceWithLongParam() {}
// 或运算:满足任一条件
@Pointcut("withinService() || withinServicePackage()")
public void serviceOrPackage() {}
// 非运算:不满足条件
@Pointcut("allServiceMethods() && !userServiceMethods()")
public void excludeUserService() {}
}2.3 完整的切面示例
java
/**
* 日志切面
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LoggingAspect {
/**
* 定义切点:service层所有方法
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service..*.*(..))")
public void serviceLayer() {}
/**
* 环绕通知:记录方法执行时间和参数
*/
@Around("serviceLayer()")
public Object logAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
// 获取方法信息
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName();
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
// 记录开始
log.info("开始执行: {}.{}(), 参数: {}", className, methodName, Arrays.toString(args));
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 执行目标方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
// 记录成功
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("执行成功: {}.{}(), 耗时: {}ms, 返回值: {}",
className, methodName, (endTime - startTime), result);
return result;
} catch (Throwable e) {
// 记录异常
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.error("执行失败: {}.{}(), 耗时: {}ms, 异常: {}",
className, methodName, (endTime - startTime), e.getMessage());
throw e;
}
}
}三、AOP实现原理
3.1 JDK动态代理
java
/**
* JDK动态代理示例
* 要求:目标对象必须实现接口
*/
public interface UserService {
User findById(Long id);
void save(User user);
}
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public User findById(Long id) {
System.out.println("查询用户: " + id);
return new User(id, "User" + id);
}
@Override
public void save(User user) {
System.out.println("保存用户: " + user.getUsername());
}
}
/**
* 自定义InvocationHandler
*/
public class LogInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object target;
public LogInvocationHandler(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 前置增强
System.out.println("JDK代理 - 方法开始: " + method.getName());
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 调用目标方法
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
// 后置增强
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("JDK代理 - 方法结束: " + method.getName() +
", 耗时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
return result;
}
/**
* 创建代理对象
*/
public static <T> T createProxy(T target) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new LogInvocationHandler(target)
);
}
}
/**
* 使用JDK代理
*/
public class JdkProxyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建目标对象
UserService target = new UserServiceImpl();
// 创建代理对象
UserService proxy = LogInvocationHandler.createProxy(target);
// 调用代理对象的方法
proxy.findById(1L);
proxy.save(new User(null, "张三"));
}
}3.2 CGLIB代理
java
/**
* CGLIB代理示例
* 优势:不需要实现接口,通过继承实现
*/
public class OrderService {
public Order findById(Long id) {
System.out.println("查询订单: " + id);
return new Order(id, "ORDER" + id);
}
public void save(Order order) {
System.out.println("保存订单: " + order.getOrderNo());
}
}
/**
* 自定义MethodInterceptor
*/
public class LogMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args,
MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
// 前置增强
System.out.println("CGLIB代理 - 方法开始: " + method.getName());
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 调用父类方法(目标方法)
Object result = proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
// 后置增强
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("CGLIB代理 - 方法结束: " + method.getName() +
", 耗时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
return result;
}
/**
* 创建代理对象
*/
public static <T> T createProxy(Class<T> clazz) {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(clazz);
enhancer.setCallback(new LogMethodInterceptor());
return (T) enhancer.create();
}
}
/**
* 使用CGLIB代理
*/
public class CglibProxyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建代理对象(无需目标对象)
OrderService proxy = LogMethodInterceptor.createProxy(OrderService.class);
// 调用代理对象的方法
proxy.findById(1L);
proxy.save(new Order(null, "ORD20240101"));
}
}3.3 Spring AOP代理选择
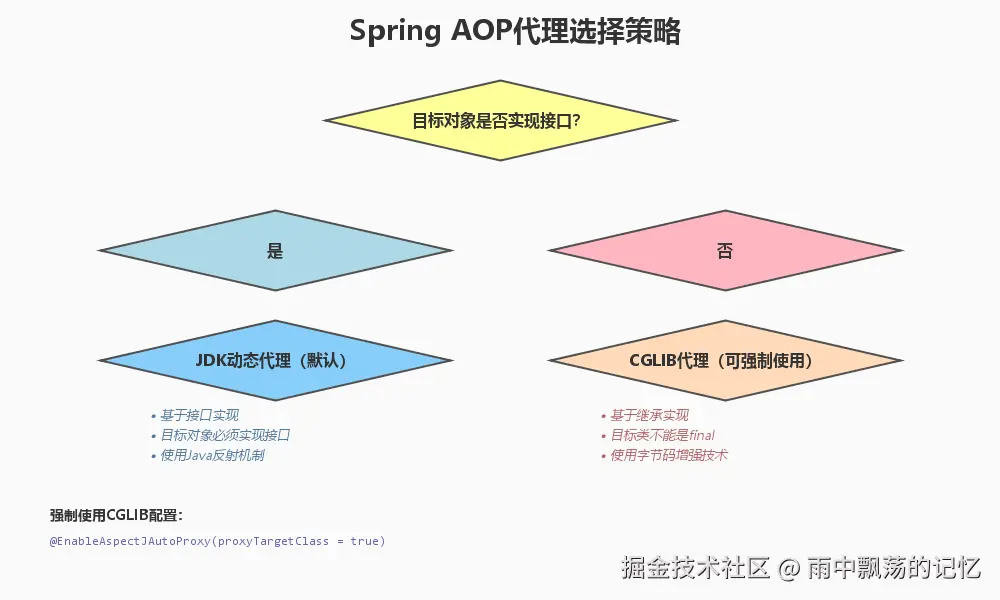
java
/**
* Spring AOP配置
*/
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true) // 强制使用CGLIB
public class AopConfig {
}四、实战案例
4.1 案例1:性能监控切面
java
/**
* 性能监控注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface PerformanceMonitor {
String value() default "";
long threshold() default 1000; // 默认阈值1秒
}
/**
* 性能监控切面
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class PerformanceMonitorAspect {
@Around("@annotation(monitor)")
public Object monitor(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, PerformanceMonitor monitor)
throws Throwable {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().toShortString();
String operationName = monitor.value().isEmpty() ? methodName : monitor.value();
long threshold = monitor.threshold();
// 开始计时
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
// 计算耗时
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
// 记录性能数据
if (duration > threshold) {
log.warn("性能警告: {} 执行耗时 {}ms,超过阈值 {}ms",
operationName, duration, threshold);
} else {
log.info("性能监控: {} 执行耗时 {}ms", operationName, duration);
}
// 可以将性能数据发送到监控系统
sendToMonitoringSystem(operationName, duration);
return result;
} catch (Throwable e) {
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
log.error("性能监控: {} 执行失败,耗时 {}ms", operationName, duration);
throw e;
}
}
private void sendToMonitoringSystem(String operation, long duration) {
// 发送到Prometheus、Grafana等监控系统
// MetricsRegistry.timer(operation).record(duration, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
/**
* 使用性能监控
*/
@Service
public class ProductService {
@PerformanceMonitor(value = "查询商品列表", threshold = 500)
public List<Product> findProducts(String category) {
// 模拟数据库查询
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return Arrays.asList(
new Product(1L, "商品1"),
new Product(2L, "商品2")
);
}
@PerformanceMonitor(value = "生成报表", threshold = 2000)
public void generateReport() {
// 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}4.2 案例2:操作日志切面
java
/**
* 操作日志注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface OperationLog {
String module(); // 模块名
String operation(); // 操作类型
String description(); // 操作描述
}
/**
* 操作日志实体
*/
@Data
public class SysOperationLog {
private Long id;
private String module;
private String operation;
private String description;
private String method;
private String params;
private String result;
private String username;
private String ip;
private Long duration;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private String errorMsg;
}
/**
* 操作日志切面
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class OperationLogAspect {
@Autowired
private OperationLogService operationLogService;
@Around("@annotation(operationLog)")
public Object logOperation(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, OperationLog operationLog)
throws Throwable {
// 创建日志对象
SysOperationLog sysLog = new SysOperationLog();
sysLog.setModule(operationLog.module());
sysLog.setOperation(operationLog.operation());
sysLog.setDescription(operationLog.description());
sysLog.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
// 获取方法信息
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
sysLog.setMethod(className + "." + methodName);
// 获取方法参数
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
sysLog.setParams(JSON.toJSONString(args));
// 获取用户信息
sysLog.setUsername(getCurrentUsername());
sysLog.setIp(getClientIp());
// 开始计时
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 执行目标方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
// 记录返回值
sysLog.setResult(JSON.toJSONString(result));
// 计算耗时
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
sysLog.setDuration(endTime - startTime);
// 异步保存日志
operationLogService.saveAsync(sysLog);
return result;
} catch (Throwable e) {
// 记录异常
sysLog.setErrorMsg(e.getMessage());
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
sysLog.setDuration(endTime - startTime);
// 异步保存日志
operationLogService.saveAsync(sysLog);
throw e;
}
}
private String getCurrentUsername() {
// 从SecurityContext获取当前用户
return "admin"; // 简化示例
}
private String getClientIp() {
// 从HttpServletRequest获取客户端IP
return "127.0.0.1"; // 简化示例
}
}
/**
* 使用操作日志
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@PostMapping
@OperationLog(
module = "用户管理",
operation = "创建",
description = "创建新用户"
)
public Result<User> createUser(@RequestBody User user) {
userService.createUser(user);
return Result.success(user);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
@OperationLog(
module = "用户管理",
operation = "删除",
description = "删除用户"
)
public Result<Void> deleteUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
userService.deleteUser(id);
return Result.success();
}
}4.3 案例3:权限校验切面
java
/**
* 权限校验注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RequiresPermission {
String[] value(); // 需要的权限
Logical logical() default Logical.AND; // 多个权限的逻辑关系
}
public enum Logical {
AND, OR
}
/**
* 权限校验切面
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class PermissionAspect {
@Autowired
private PermissionService permissionService;
@Before("@annotation(requiresPermission)")
public void checkPermission(JoinPoint joinPoint, RequiresPermission requiresPermission) {
String[] permissions = requiresPermission.value();
Logical logical = requiresPermission.logical();
// 获取当前用户
String username = getCurrentUsername();
// 检查权限
boolean hasPermission = false;
if (logical == Logical.AND) {
// AND:需要拥有所有权限
hasPermission = permissionService.hasAllPermissions(username, permissions);
} else {
// OR:拥有任一权限即可
hasPermission = permissionService.hasAnyPermission(username, permissions);
}
if (!hasPermission) {
String method = joinPoint.getSignature().toShortString();
log.warn("权限不足: 用户[{}]访问方法[{}]需要权限{}", username, method, permissions);
throw new PermissionDeniedException("权限不足");
}
log.info("权限校验通过: 用户[{}]访问方法[{}]", username, joinPoint.getSignature().toShortString());
}
private String getCurrentUsername() {
// 从SecurityContext获取当前用户
return "admin"; // 简化示例
}
}
/**
* 权限服务
*/
@Service
public class PermissionService {
// 用户权限缓存(实际应从数据库或Redis获取)
private Map<String, Set<String>> userPermissions = new HashMap<>();
public PermissionService() {
// 初始化测试数据
userPermissions.put("admin", new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(
"user:create", "user:update", "user:delete", "user:view"
)));
userPermissions.put("user", new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(
"user:view"
)));
}
public boolean hasAllPermissions(String username, String[] permissions) {
Set<String> userPerms = userPermissions.getOrDefault(username, new HashSet<>());
return userPerms.containsAll(Arrays.asList(permissions));
}
public boolean hasAnyPermission(String username, String[] permissions) {
Set<String> userPerms = userPermissions.getOrDefault(username, new HashSet<>());
for (String permission : permissions) {
if (userPerms.contains(permission)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* 使用权限校验
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping
@RequiresPermission("user:create")
public Result<User> createUser(@RequestBody User user) {
// 只有拥有user:create权限的用户才能访问
return Result.success(user);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
@RequiresPermission({"user:delete", "admin:all"}, logical = Logical.OR)
public Result<Void> deleteUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
// 拥有user:delete或admin:all权限之一即可访问
return Result.success();
}
}4.4 案例4:缓存切面
java
/**
* 缓存注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Cacheable {
String key(); // 缓存key
int expire() default 3600; // 过期时间(秒)
}
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface CacheEvict {
String key(); // 要删除的缓存key
}
/**
* 缓存切面
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheAspect {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 缓存查询
*/
@Around("@annotation(cacheable)")
public Object cache(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, Cacheable cacheable) throws Throwable {
// 构建缓存key
String cacheKey = buildCacheKey(cacheable.key(), joinPoint);
// 尝试从缓存获取
Object cachedValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(cacheKey);
if (cachedValue != null) {
log.info("缓存命中: {}", cacheKey);
return cachedValue;
}
// 缓存未命中,执行方法
log.info("缓存未命中: {}", cacheKey);
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
// 存入缓存
if (result != null) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(cacheKey, result,
cacheable.expire(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
log.info("缓存写入: {}, 过期时间: {}秒", cacheKey, cacheable.expire());
}
return result;
}
/**
* 缓存清除
*/
@AfterReturning("@annotation(cacheEvict)")
public void evictCache(JoinPoint joinPoint, CacheEvict cacheEvict) {
String cacheKey = buildCacheKey(cacheEvict.key(), joinPoint);
redisTemplate.delete(cacheKey);
log.info("缓存清除: {}", cacheKey);
}
/**
* 构建缓存key
*/
private String buildCacheKey(String keyPattern, JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
// 支持SpEL表达式(简化版)
String key = keyPattern;
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
key = key.replace("#p" + i, String.valueOf(args[i]));
}
return key;
}
}
/**
* 使用缓存
*/
@Service
public class ProductService {
@Cacheable(key = "product:#p0", expire = 1800)
public Product findById(Long id) {
log.info("从数据库查询商品: {}", id);
// 模拟数据库查询
return new Product(id, "商品" + id);
}
@CacheEvict(key = "product:#p0.id")
public void updateProduct(Product product) {
log.info("更新商品: {}", product.getId());
// 更新数据库
}
}4.5 案例5:防重复提交切面
java
/**
* 防重复提交注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface PreventDuplicateSubmit {
int timeout() default 5; // 锁定时间(秒)
}
/**
* 防重复提交切面
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class PreventDuplicateSubmitAspect {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
@Around("@annotation(preventDuplicate)")
public Object preventDuplicate(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint,
PreventDuplicateSubmit preventDuplicate) throws Throwable {
// 构建唯一key(用户 + 方法 + 参数)
String key = buildSubmitKey(joinPoint);
int timeout = preventDuplicate.timeout();
// 尝试获取锁
Boolean success = redisTemplate.opsForValue()
.setIfAbsent(key, "1", timeout, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (success == null || !success) {
log.warn("重复提交: {}", key);
throw new DuplicateSubmitException("请勿重复提交");
}
try {
// 执行方法
return joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
// 发生异常时释放锁
redisTemplate.delete(key);
throw e;
}
}
private String buildSubmitKey(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String username = getCurrentUsername();
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName();
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
return String.format("submit:%s:%s:%s:%s",
username, className, methodName, Arrays.hashCode(args));
}
private String getCurrentUsername() {
return "user123"; // 简化示例
}
}
/**
* 使用防重复提交
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/orders")
public class OrderController {
@PostMapping
@PreventDuplicateSubmit(timeout = 10)
public Result<Order> createOrder(@RequestBody Order order) {
// 创建订单(防止用户重复点击)
return Result.success(order);
}
}五、事务管理与AOP
5.1 声明式事务原理
java
/**
* Spring事务是基于AOP实现的
* @Transactional注解的处理流程
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class TransactionAspectSimulation {
@Around("@annotation(transactional)")
public Object handleTransaction(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint,
Transactional transactional) throws Throwable {
// 1. 获取事务管理器
TransactionManager txManager = getTransactionManager();
// 2. 开启事务
TransactionStatus status = txManager.begin();
try {
// 3. 执行业务方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
// 4. 提交事务
txManager.commit(status);
return result;
} catch (Throwable e) {
// 5. 回滚事务
txManager.rollback(status);
throw e;
}
}
private TransactionManager getTransactionManager() {
return new TransactionManager();
}
}
/**
* 事务传播行为示例
*/
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderDao orderDao;
@Autowired
private OrderItemService orderItemService;
/**
* REQUIRED:如果当前有事务,加入该事务;否则创建新事务
*/
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void createOrder(Order order) {
orderDao.save(order);
// 加入当前事务
orderItemService.saveItems(order.getItems());
}
/**
* REQUIRES_NEW:总是创建新事务,挂起当前事务
*/
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void createOrderWithNewTransaction(Order order) {
orderDao.save(order);
// 在新事务中执行
orderItemService.saveItemsInNewTransaction(order.getItems());
}
/**
* NESTED:嵌套事务
*/
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NESTED)
public void createOrderWithNested(Order order) {
orderDao.save(order);
try {
// 嵌套事务,可以独立回滚
orderItemService.saveItemsNested(order.getItems());
} catch (Exception e) {
// 子事务回滚不影响主事务
log.error("保存订单项失败", e);
}
}
}5.2 事务失效场景
java
/**
* 事务失效的常见场景
*/
@Service
public class TransactionFailureDemo {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
/**
* 场景1:方法不是public(事务失效)
*/
@Transactional
private void privateMethod() { //事务不生效
userDao.save(new User());
}
/**
* 场景2:同类内部调用(事务失效)
*/
public void outerMethod() {
//直接调用,绕过代理,事务不生效
this.innerMethod();
}
@Transactional
public void innerMethod() {
userDao.save(new User());
}
/**
* 场景3:异常被捕获(事务失效)
*/
@Transactional
public void catchException() {
try {
userDao.save(new User());
throw new RuntimeException();
} catch (Exception e) {
//异常被捕获,事务不会回滚
}
}
/**
* 场景4:抛出检查异常(默认不回滚)
*/
@Transactional //默认只回滚RuntimeException
public void checkedExceptionMethod() throws Exception {
userDao.save(new User());
throw new Exception(); // 不会回滚
}
/**
* 正确做法:指定回滚异常
*/
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void correctMethod() throws Exception {
userDao.save(new User());
throw new Exception(); // ✓ 会回滚
}
}
/**
* 解决同类调用问题
*/
@Service
public class TransactionSolution {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext context;
/**
* 方案1:注入自己
*/
@Autowired
private TransactionSolution self;
public void outerMethod1() {
self.innerMethod(); // ✓ 通过代理调用
}
/**
* 方案2:从容器获取
*/
public void outerMethod2() {
TransactionSolution proxy = context.getBean(TransactionSolution.class);
proxy.innerMethod(); // ✓ 通过代理调用
}
/**
* 方案3:使用AopContext
*/
public void outerMethod3() {
((TransactionSolution) AopContext.currentProxy()).innerMethod(); // ✓
}
@Transactional
public void innerMethod() {
userDao.save(new User());
}
}六、最佳实践
6.1 切面设计原则
java
/**
* 1. 切面职责单一
*/
//不好:一个切面做太多事
@Aspect
public class BadAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.example..*(..))")
public Object doEverything(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
// 日志
// 权限检查
// 缓存
// 事务
// ...
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
// ✓ 好:每个切面专注一个职责
@Aspect
public class LoggingAspect { /* 只负责日志 */ }
@Aspect
public class SecurityAspect { /* 只负责权限 */ }
@Aspect
public class CachingAspect { /* 只负责缓存 */ }
/**
* 2. 精确的切点表达式
*/
// 不好:范围太大
@Pointcut("execution(* *.*(..))") // 匹配所有方法
// ✓ 好:精确匹配
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))") // 只匹配service层6.2 性能优化
java
/**
* 1. 使用@Pointcut复用切点表达式
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class OptimizedAspect {
// 定义可复用的切点
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service..*.*(..))")
public void serviceLayer() {}
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.annotation.Log)")
public void logAnnotation() {}
// 复用切点
@Before("serviceLayer() && logAnnotation()")
public void beforeLog() {
// ...
}
@After("serviceLayer() && logAnnotation()")
public void afterLog() {
// ...
}
}
/**
* 2. 避免在切面中进行耗时操作
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class AsyncLoggingAspect {
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor;
@Around("@annotation(com.example.annotation.Log)")
public Object log(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
// ✓ 异步保存日志,不阻塞业务
executor.execute(() -> saveLog(joinPoint, result));
return result;
}
private void saveLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
// 耗时的日志保存操作
}
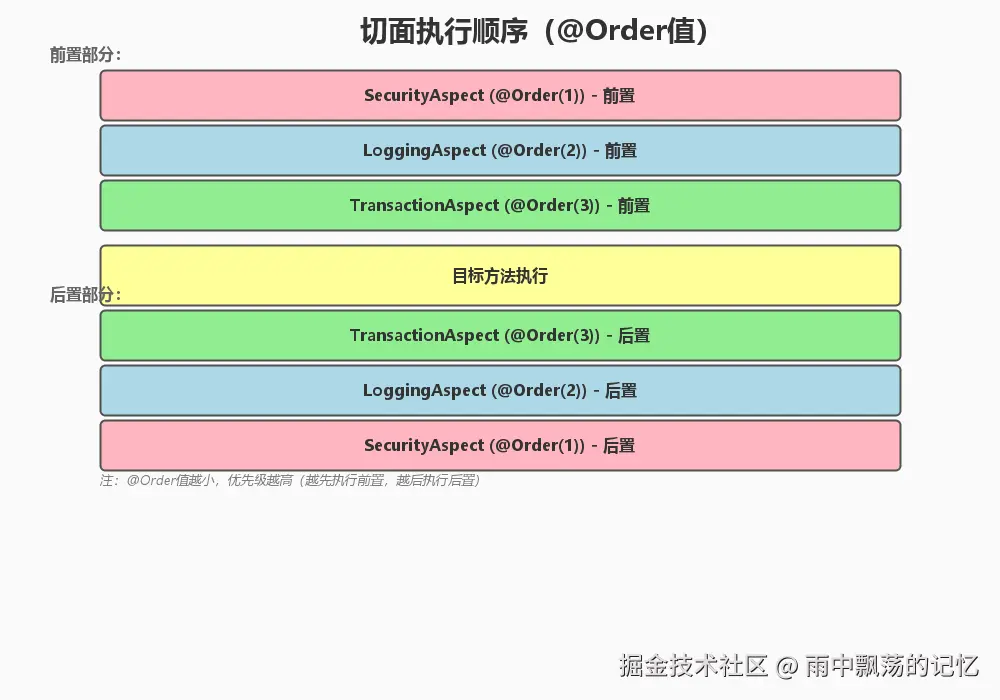
}6.3 切面执行顺序
java
/**
* 使用@Order控制切面执行顺序
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(1) // 数字越小,优先级越高
public class SecurityAspect {
// 最先执行
}
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(2)
public class LoggingAspect {
// 第二执行
}
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(3)
public class TransactionAspect {
// 最后执行
}
七、总结
Spring AOP是Spring框架的重要组成部分,它将横切关注点从业务逻辑中分离出来,使代码更加简洁、易于维护。在实际开发中,合理运用AOP可以大大提高开发效率和代码质量。