1 ArrayList原理
ArrayList 是基于动态数组实现的,适合随机访问和顺序添加,扩容机制保证了动态增长,但插入和删除效率较低,且不是线程安全的。理解其实现原理有助于在实际开发中合理选择和使用。
1.1 数据结构
ArrayList 是基于动态数组实现的 List。其核心字段如下:
java
transient Object[] elementData; // 存储元素的数组
private int size; // 实际元素个数-
elementData 是一个 Object 数组,存储所有元素。
-
size 表示当前 ArrayList 中的有效元素数量。
1.2 构造方法
-
ArrayList():默认初始容量为 0。
-
ArrayList(int initialCapacity):指定初始容量。
-
ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c):用集合初始化。
java
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}1.3 扩容机制
当我们使用ArrayList的无参构造的时候:
java
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>();从构造方法中可以看出,无参构造方法构造ArrayList的时候,初始化的ArrayList的大小为0。那什么时候初始化ArrayList大小的呢?看一下add方法:
java
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e; // 将元素存储到数组
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
// 判断当前数组的大小,如果为0,那么将取2这最大的值作为当前数组的大小
// DEFAULT_CAPACITY为10
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
// 执行扩容
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// Increments modCount!!
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code 扩容操作
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
// 先获取当前数组的大小
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 先初步计算新的数组大小为现有数组大小的1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 新的数组大小比当前要设置的数组大小小的时候,使用要设置的数组大小
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 如果新的数组大小大于数组最大值,那么采用适配方案
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
// 将旧数组的大小复制到新数组中,并且返回
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
// 最大值适配方案
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}在每次调用add方法向ArrayList内添加元素时候,容器都会调用ensureCapacityInternal方法取确保此时容量可以容纳这个元素,如果不能容下,则去扩容。如果此时容量为0,则扩容到10。如果此时容量不是0,扩容为当前容量的1.5倍,同时我们知道了它的极限容量是2147483647。确定好扩容的容量以后具体是如何实现扩容呢?
java
public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) {
return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass());
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
@FastNative
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);由此可知扩容时,容器重新创建了一个数组,容量为当前计算出来的容量,然后调用JDK底层的C++代码完成批量数组复制操作。
1.4 性能特性
-
随机访问快:底层是数组,get/set 时间复杂度 O(1)。
-
插入/删除慢:插入/删除时需要移动元素,时间复杂度 O(n)。
-
扩容有开销:扩容时需要分配新数组并复制数据,性能有波动。
-
ArrayList 不是线程安全的。多线程环境下需外部加锁或使用线程安全的集合(如 CopyOnWriteArrayList)。
针对ArrayList删除/插入慢的特性,就有了LinkedList的出现,接下来我们看一下LinkedList的实现。
LinkedList
LinkedList 基于双向链表实现,适合插入/删除频繁的场景,支持队列和栈操作,但随机访问性能较差,空间开销大。理解其实现原理有助于在实际开发中合理选择和使用。
-
LinkedList 是一个继承于AbstractSequentialList的双向链表。它也可以被当作堆栈、队列或双端队列进行操作。
-
LinkedList 实现 List 接口,能对它进行队列操作。
-
LinkedList 实现 Deque 接口,即能将LinkedList当作双端队列使用。
-
LinkedList 实现了Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),能克隆。
-
LinkedList 实现java.io.Serializable接口,这意味着LinkedList支持序列化,能通过序列化去传输。
-
LinkedList 是非同步的。
为什么要继承自AbstractSequentialList ?
AbstractSequentialList 实现了get(int index)、set(int index, E element)、add(int index, E element) 和 remove(int index)这些骨干性函数。降低了List接口的复杂度。这些接口都是随机访问List的,LinkedList是双向链表;既然它继承于AbstractSequentialList,就相当于已经实现了"get(int index)这些接口"。
此外,我们若需要通过AbstractSequentialList自己实现一个列表,只需要扩展此类,并提供 listIterator() 和 size() 方法的实现即可。若要实现不可修改的列表,则需要实现列表迭代器的 hasNext、next、hasPrevious、previous 和 index 方法即可。
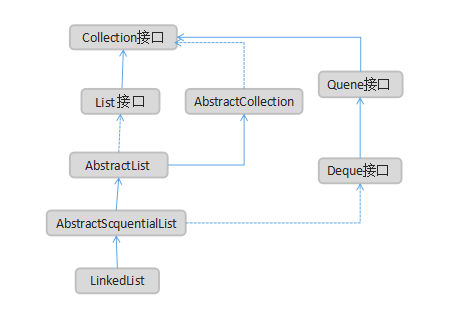
LinkedList的类图关系:
2.1 数据结构
LinkedList 是基于双向链表实现的,是双向链表但不是双向循环链表。其核心数据结构如下:
java
transient int size = 0;
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}-
每个 Node 节点包含数据(item)、前驱(prev)、后继(next)指针。
-
first 指向链表头节点,last 指向链表尾节点。
-
size 记录链表元素个数。
LinkedList底层的数据结构是基于双向 链表 的,如下:
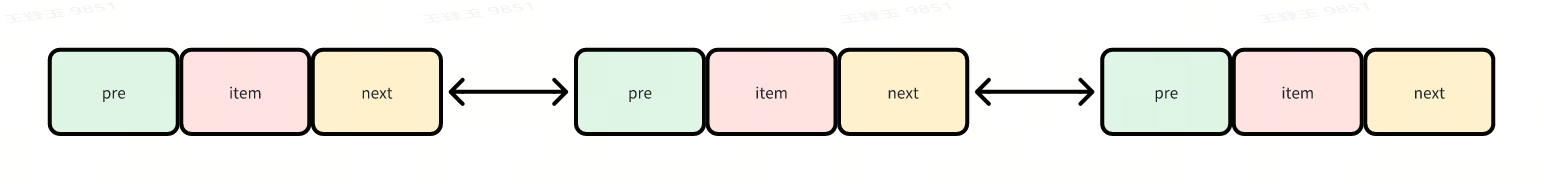
既然是双向链表,那么必定存在一种数据结构------我们可以称之为节点,节点实例保存业务数据,前一个节点的位置信息和后一个节点位置信息,如下图所示:

2.2 构造方法
-
LinkedList():创建一个空链表。
-
LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c):用集合初始化链表,依次添加元素
java
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}2.3 核心操作
2.3.1 添加操作
-
add(E e):默认在链表尾部添加元素,调用 linkLast(e)。
-
addFirst(E e) / addLast(E e):分别在头部/尾部插入。
-
add(int index, E element):在指定位置插入,内部会定位到 index 处节点,然后插入。
java
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
// 先临时存储当前最后一个节点
final Node<E> l = last;
// 将当前最后一个节点作为新添加节点的前置节点,后置节点为空,当前节点存储当前数据
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
// 将新添加的节点存储为最后一个节点
last = newNode;
// 之前的最后一个节点是否为null,
// 如果为空那就证明当前链表中没有节点,新添加的节点既是第一个节点也是最后一个节点
// 如果不为空那就将之前最后一个节点的后一个节点指向当前新添加的节点,这样就形成了双向
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
java
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* Links e as first element.
*/
private void linkFirst(E e) {
// 临时存储当前第一个节点
final Node<E> f = first;
// 新添加一个节点,存储当前新添加的数据,并且将新添加节点的后置指向当前第一个节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
// 更新当前第一个节点为新添加的节点
first = newNode;
// 如果更新前第一个节点为null,那新添加的节点既是第一个节点也是最后一个节点,所以更新last为新添加节点
// 如果不为null,那么将之前的第一个节点的前置指向新添加的节点
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
java
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #add}.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}2.3.2 删除元素
-
remove() / removeFirst() / removeLast():删除头/尾节点。
-
remove(Object o):遍历查找并删除第一个匹配元素。
-
remove(int index):定位到 index 处节点并删除。
java
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* Removes and returns the first element from this list.
*
* @return the first element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeFirst() {
// 先存储当前第一个节点
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null first node f.
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// 取出当前第一个节点数据
// assert f == first && f != null
final E element = f.item;
// 定义一个节点存储第一个节点的后置指向的节点(也就是第二个节点)
final Node<E> next = f.next;
// 将当前第一个节点的数据清空,后置指向清空
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
// 重新将第二个节点更新到第一个节点
first = next;
// 如果第二个为null,那说明当前当前节点中已经没有节点数据了,将最后节点指引设置为null
// 如果不为null,那需要将前置执行置为null(因为前置节点已经删除了,第二个节点已经成第一个节点)
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}2.4 性能特征
-
插入/删除效率高:O(1)(已知节点时),在任意位置插入/删除只需修改指针。
-
随机访问慢:O(n),需遍历链表定位节点。
-
空间开销大:每个元素需额外存储前后指针。
-
LinkedList是线程不安全的,多线程环境需外部加锁或使用并发集合。
到这里我们是不是就思考有没有删除/添加快、查找也快的数据结构呢?那就要看HashMap的了。
3 HashMap
3.1 数据结构
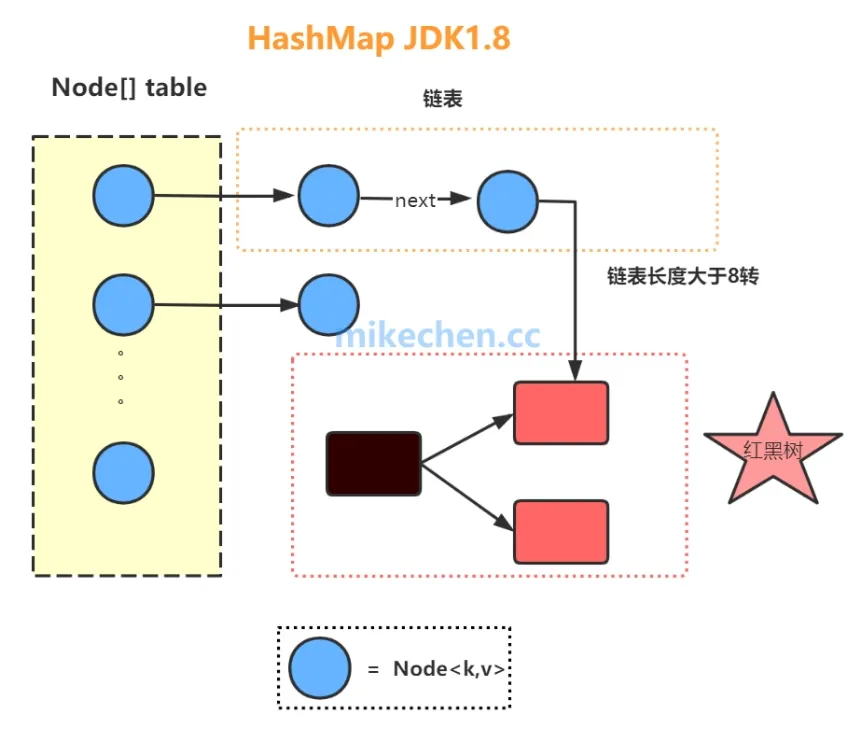
从数据结构的角度来看:HashMap是:数组+链表+红黑树(JDK1.8增加了红黑树部分)的数据结构,如下所示:
3.1.1.1 核心成员
java
// 默认初始容量(数组默认大小):16,2的整数次方
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
// 最大容量
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认负载因子,装载因子用来衡量HashMap满的程度,
// 表示当map集合中存储的数据达到当前数组大小的75%则需要进行扩容
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 链表转红黑树边界
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// 红黑树转离链表边界
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
// 哈希桶数组
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
// 实际存储的元素个数
transient int size;
// 当map里面的数据大于这个threshold就会进行扩容
int threshold 阈值 = table.length * loadFactor3.1.1.2 Node数组
java
/**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash; //用来定位数组索引位置
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next; //链表的下一个Node节点
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}Node是HashMap的一个内部类,实现了Map.Entry接口,本质是就是一个映射(键值对)。
3.2 数据存储
3.2.1 哈希表来存储
HashMap采用哈希表来存储数据。
哈希表(Hash table,也叫散列表),是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构,只要输入待查找的值即key,即可查找到其对应的值。
哈希表其实就是数组的一种扩展,由数组演化而来。可以说,如果没有数组,就没有散列表。
3.2.2 哈希函数
-
put/get/remove 等操作,首先对 key 计算 hash 值。
-
通过 hash & (table.length - 1) 定位到桶数组的下标。
-
在该桶链表/树中查找目标 key。
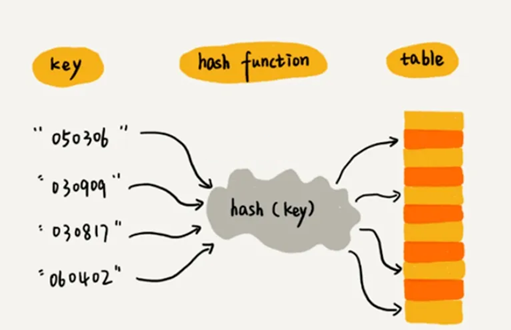
哈希表中哈希函数的设计是相当重要的,这也是建哈希表过程中的关键问题之一。
java
// 添加操作
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
// 计算hash值
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
// h = key.hashCode() 为第一步 取hashCode值
// h ^ (h >>> 16) 为第二步 高位参与运算
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}对key进行了hashCode运算,得到一个32位的int值h,然后用h 异或 h>>>16位。在JDK1.8的实现中,优化了高位运算的算法,通过hashCode()的高16位异或低16位实现的:(h = k.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16)。
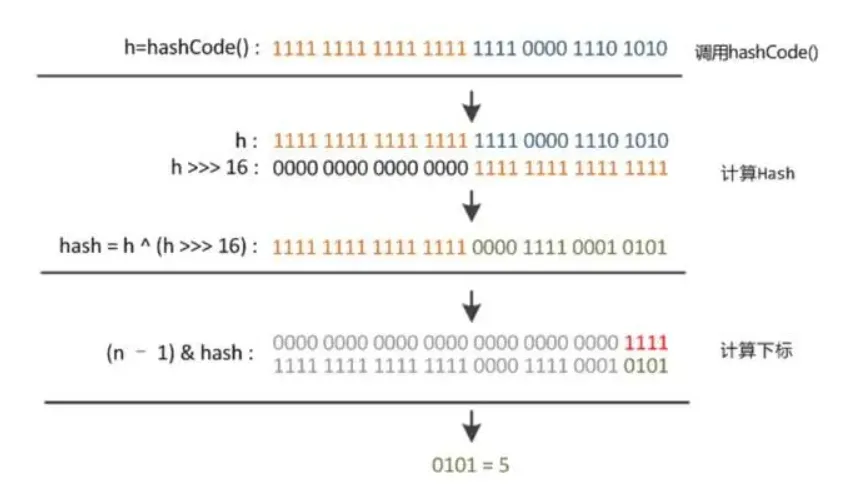
这样做的好处是,可以将hashcode高位和低位的值进行混合做异或运算,而且混合后,低位的信息中加入了高位的信息,这样高位的信息被变相的保留了下来。
等于说计算下标时把hash的高16位也参与进来了,掺杂的元素多了,那么生成的hash值的随机性会增大,减少了hash碰撞。
备注:
-
^异或:不同为1,相同为0
-
>>>:无符号右移:右边补0
-
&运算:两位同时为"1",结果才为"1,否则为0
h & (table.length -1)来得到该对象的保存位,而HashMap底层数组的长度总是2的n次方。
为什么槽位数必须使用2^n?
1.为了让哈希后的结果更加均匀
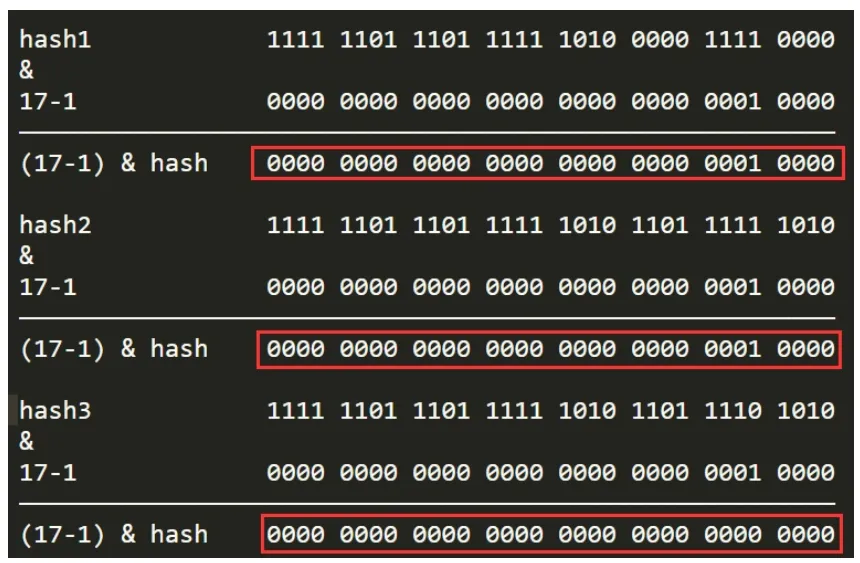
假如槽位数不是16,而是17,则槽位计算公式变成:(17 -- 1) & hash
从上文可以看出,计算结果将会大大趋同,hashcode参加&运算后被更多位的0屏蔽,计算结果只剩下两种0和16,这对于hashmap来说是一种灾难。2.等价于length取模
当length总是2的n次方时,h& (length-1)运算等价于对length取模,也就是h%length,但是&比%具有更高的效率。
位运算的运算效率高于算术运算,原因是算术运算还是会被转化为位运算。
最终目的还是为了让哈希后的结果更均匀的分布,减少哈希碰撞,提升hashmap的运行效率
分析HashMap的put方法
java
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
// 添加函数
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 当前对象的数组是null 或者数组长度时0时,则需要初始化数组
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 使用hash与数组长度减一的值进行异或得到分散的数组下标,预示着按照计算现在的
// key会存放到这个位置上,如果这个位置上没有值,那么直接新建k-v节点存放
// 其中长度n是一个2的幂次数
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {// 如果走到else这一步,说明key索引到的数组位置上已经存在内容,即出现了碰撞,这个时候需要更为复杂处理碰撞的方式来处理,如链表和树
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//节点key存在,直接覆盖value
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 判断该链为红黑树
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
// 其中this表示当前HashMap, tab为map中的数组
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 判断该链为链表
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
// 如果当前碰撞到的节点没有后续节点,则直接新建节点并追加
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8
// 从0开始的,如果到了7则说明满8了,这个时候就需要转
// 重新确定是否是扩容还是转用红黑树了
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 找到了碰撞节点中,key完全相等的节点,则用新节点替换老节点
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 此时的e是保存的被碰撞的那个节点,即老节点
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
// onlyIfAbsent是方法的调用参数,表示是否替换已存在的值,
// 在默认的put方法中这个值是false,所以这里会用新值替换旧值
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
// Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actions
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
// map变更性操作计数器
// 比如map结构化的变更像内容增减或者rehash,这将直接导致外部map的并发
// 迭代引起fail-fast问题,该值就是比较的基础
// 在 HashMap 的实现中,modCount 字段用于记录结构性修改(structural modification)的次数。结构性修改指的是影响 HashMap 元素数量的操作,比如 put(插入新键)、remove(删除键)、clear(清空)等。
// 如果只是更新已存在节点的 value(即 key 已存在,只是 value 发生变化),modCount 的值不会发生变化
++modCount;
// size即map中包括k-v数量的多少
// 超过最大容量 就扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
// Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actions
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}HashMap的put方法执行过程整体如下:
-
判断键值对数组table[i]是否为空或为null,否则执行resize()进行扩容;
-
根据键值key计算hash值得到插入的数组索引i,如果table[i]==null,直接新建节点添加
-
判断table[i]的首个元素是否和key一样,如果相同直接覆盖value
-
判断table[i] 是否为treeNode,即table[i] 是否是红黑树,如果是红黑树,则直接在树中插入键值对
-
遍历table[i],判断链表长度是否大于8,大于8的话把链表转换为红黑树,在红黑树中执行插入操作,否则进行链表的插入操作;遍历过程中若发现key已经存在直接覆盖value即可;
-
插入成功后,判断实际存在的键值对数量size是否超多了最大容量threshold,如果超过,进行扩容。
3.3 HashMap总结
HashMap底层结构?
基于Map接口的实现,数组+链表的结构,JDK 1.8后加入了红黑树,链表长度>8变红黑树,<6变链表。
两个对象的hashcode相同会发生什么?
Hash冲突,HashMap通过链表来解决hash冲突。
HashMap 中 equals() 和 hashCode() 有什么作用?
HashMap 的添加、获取时需要通过 key 的 hashCode() 进行 hash(),然后计算下标 ( n-1 & hash),从而获得要找的同的位置。当发生冲突(碰撞)时,利用 key.equals() 方法去链表或树中去查找对应的节点
HashMap 何时扩容?
put的元素达到容量乘负载因子的时候,默认16*0.75
hash 的实现?
h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16), hashCode 进行无符号右移 16 位,然后进行按位异或,得到这个键的哈希值,由于哈希表的容量都是 2 的 N 次方,在当前,元素的 hashCode() 在很多时候下低位是相同的,这将导致冲突(碰撞),因此 1.8 以后做了个移位操作:将元素的 hashCode() 和自己右移 16 位后的结果求异或。
HashMap线程安全吗?
HashMap读写效率较高,但是因为其是非同步的,即读写等操作都是没有锁保护的,所以在多线程场景下是不安全的,容易出现数据不一致的问题,在单线程场景下非常推荐使用。
HashMap采用的是空间换时间的方式,这样就会有大量的空间浪费,那么有没有增删改查都快,但是又不浪费空间的数据结构呢?那么SparseArray就应运而生。
4 SparseArray
SparseArray采用时间换取空间的方式来提高手机App的运行效率,这也是其与HashMap的区别;HashMap通过空间换取时间,查找迅速;HashMap中当table数组中内容达到总容量0.75时,则扩展为当前容量的两倍。
-
SparseArray的key为int,value为Object。
-
在Android中,数据长度小于千时,用于替换HashMap
-
相比于HashMap,其采用 时间换空间 的方式,使用更少的内存来提高手机APP的运行效率。
4.1 数据结构
-
用两个数组存储数据:mKeys(int[])保存所有 key,mValues(Object[])保存所有 value。
-
mSize 记录当前有效元素数量。
java
private int[] mKeys;
private Object[] mValues;
private int mSize;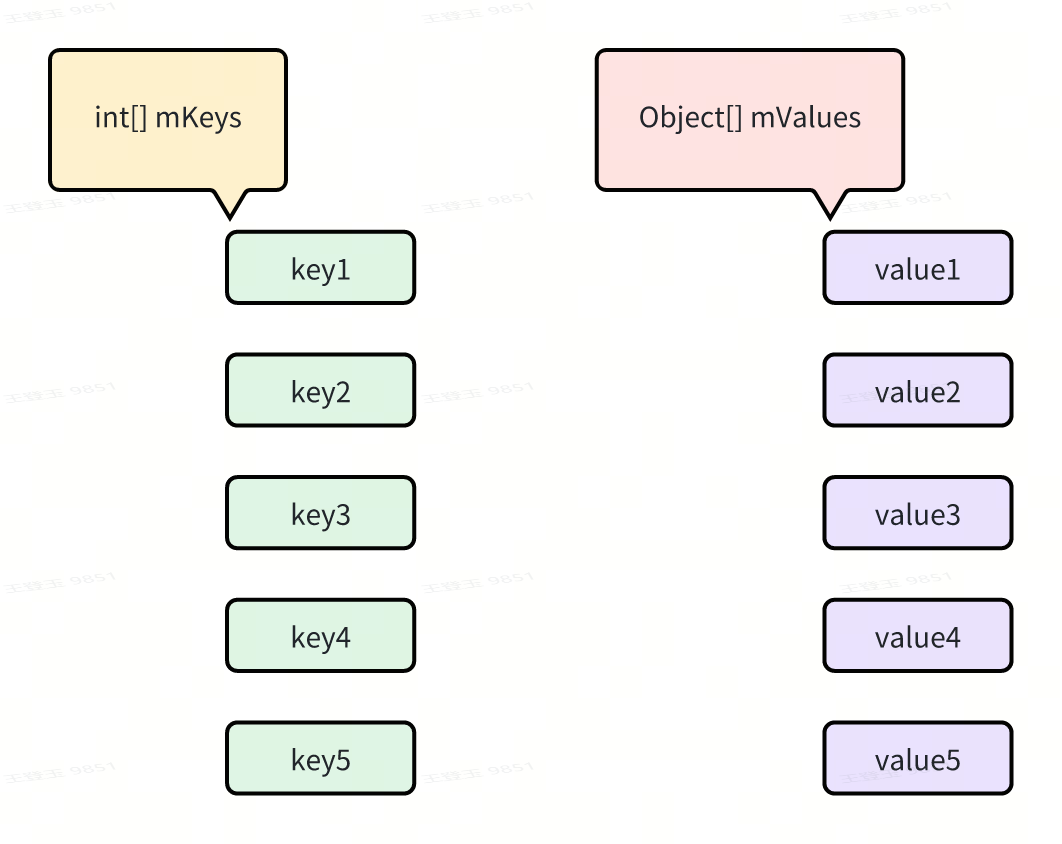
4.2 构造方法
java
/**
* Creates a new SparseArray containing no mappings.
*/
public SparseArray() {
// 默认初始化大小为10
this(10);
}
/**
* Creates a new SparseArray containing no mappings that will not
* require any additional memory allocation to store the specified
* number of mappings. If you supply an initial capacity of 0, the
* sparse array will be initialized with a light-weight representation
* not requiring any additional array allocations.
*/
public SparseArray(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity == 0) {
mKeys = EmptyArray.INT;
mValues = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else {
// key value各自为一个数组,默认长度为10
mValues = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedObjectArray(initialCapacity);
mKeys = new int[mValues.length];
}
mSize = 0;
}SparseArray构造方法中,创建了两个数组mKeys、mValues分别存放int与Object,其默认长度为10。
4.3 操作核心
4.3.1 put(int key, E value)
java
public void put(int key, E value) {
// 二分查找,key在mKeys列表中对应的index
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {// 如果找到,则直接赋值
mValues[i] = value;
} else {// 找不到
i = ~i;// binarySearch方法中,找不到时,i取了其非,这里再次取非,则非非则正
// 如果该位置的数据正好被删除,则赋值
if (i < mSize && mValues[i] == DELETED) {
mKeys[i] = key;
mValues[i] = value;
return;
}
// 如果有数据被删除了,则gc
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {
gc();
// Search again because indices may have changed.
i = ~ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
}
// 插入数据,增长mKeys与mValues列表
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mKeys, mSize, i, key);
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mValues, mSize, i, value);
mSize++;
}
}-
因为key为int,不存在hash冲突
-
mKeys为有序列表,通过二分查找,找到要插入的key对应mKeys数组中的index (这里相对于查找hash表应该算是费时间吧,但节省了内存,所以是 时间换取了空间)
-
通过key对应mKeys数组中的index,将Value插入到mValues数组的index对应位置
插入数据过程中:
-
如果mValues数组index位置的数据已经删除,则直接插入;
-
如果mValues数组index位置存在有效数据,或者数组长度不足了,则需要查看
GrowingArrayUtils.insert代码了
java
package com.android.internal.util;
/**
* A helper class that aims to provide comparable growth performance to ArrayList, but on primitive
* arrays. Common array operations are implemented for efficient use in dynamic containers.
*
* All methods in this class assume that the length of an array is equivalent to its capacity and
* NOT the number of elements in the array. The current size of the array is always passed in as a
* parameter.
*
* @hide
*/
public final class GrowingArrayUtils {
// ......省略代码
/**
* Primitive int version of {@link #insert(Object[], int, int, Object)}.
*/
public static int[] insert(int[] array, int currentSize, int index, int element) {
assert currentSize <= array.length;
// 如果mValues数组index位置存在有效数据,而且数组长度够。
// 则将mValues数组index位置后的元素都向后移动一位
// index位置存入对应的element
if (currentSize + 1 <= array.length) {
System.arraycopy(array, index, array, index + 1, currentSize - index);
array[index] = element;
return array;
}
// 如果长度不够,则扩容到原长度的两倍,并将其他数据复制到新数组中
int[] newArray = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedIntArray(growSize(currentSize));
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, index);
newArray[index] = element;
System.arraycopy(array, index, newArray, index + 1, array.length - index);
return newArray;
}
// ......省略代码
}-
如果mValues数组index位置存在有效数据,而且数组长度够。则将mValues数组index位置后的元素都向后移动一位,index位置存入对应的element
-
如果长度不够,则扩容到原长度的两倍,并将其他数据复制到新数组中
4.3.2 get(int key)
java
/**
* Gets the Object mapped from the specified key, or <code>null</code>
* if no such mapping has been made.
*/
public E get(int key) {
// 通过key查找对应的value
return get(key, null);
}
/**
* Gets the Object mapped from the specified key, or the specified Object
* if no such mapping has been made.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 通过key查找对应的value
public E get(int key, E valueIfKeyNotFound) {
// mKeys数组中采用二分查找,找到key对应的index
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i < 0 || mValues[i] == DELETED) {// 没有找到,则返回空
return valueIfKeyNotFound;
} else {// 找到则返回对应的value
return (E) mValues[i];
}
}每次调用get,则需经过一次mKeys数组的二分查找,因此mKeys数组越大则二分查找的时间就越长,因此SparseArray在大量数据,千以上时,会效率较低。
4.3.3 ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key)二分查找
java
package android.util;
class ContainerHelpers {
// array为有序数组
// size数组中内容长度
// value要查找的值
// This is Arrays.binarySearch(), but doesn't do any argument validation.
static int binarySearch(int[] array, int size, int value) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = size - 1;
// 循环查找
while (lo <= hi) {
// 取中间位置元素
final int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
final int midVal = array[mid];
if (midVal < value) {// 如果中间元素小于要查找元素,则midIndex赋值给 lo
lo = mid + 1;
} else if (midVal > value) {// 如果中间元素大于要查找元素,则midIndex赋值给 hi
hi = mid - 1;
} else {// 找到则返回
return mid; // value found
}
}
// 找不到,则lo 取非
return ~lo; // value not present
}
}通过二分查找(ContainerHelpers.binarySearch)在 mKeys 中定位 key 的索引,查找速度为 O(logN)。
4.4 性能特征
-
插入与删除
插入时,先查找 key 是否存在。存在则直接更新 value,不存在则插入新 key/value。
删除时,不立即移除元素,而是将对应的 value 标记为 DELETED,并设置 mGarbage = true。
-
延迟垃圾回收 删除后不会立刻移动数组,而是等到数组扩容或访问 size/keyAt/valueAt 时,才通过 gc() 方法一次性清理所有被标记为 DELETED 的项,提升性能。
-
空间效率
由于 key 是 int 类型,避免了 HashMap 的装箱(auto-boxing)和额外的 Entry 对象,节省内存。
适合 key 分布稀疏、元素数量不大的场景。
-
有序性
mKeys 始终保持升序,遍历时 key/value 顺序一致。
SparseArray 通过有序数组和延迟垃圾回收机制,在小规模稀疏映射场景下比 HashMap 更节省内存,但插入/删除/查找的性能略低于 HashMap(O(logN) vs O(1))。
SparseArray整体来说对于千内的数据量是比较高效的,但是SparseArray有个问题就是key必须是int,这就有了局限性。那么为了解决这个问题ArrayMap就应运而生。
5 ArrayMap
ArrayMap 是 Android 平台为内存优化而设计的轻量级 Map 实现,主要用于 key/value 数量较少的场景。ArrayMap和SparseArray有点类似;其中含有两个数组,一个是mHashes(key的hash值数组,为一个有序数组),另一个数组存储的是key和value,其中key和value是成对出现的,key存储在数组的偶数位上,value存储在数组的奇数位上。
5.1 数据结构
ArrayMap 通过两个数组实现存储:
-
mHashes:int[],存储每个 key 的 hashCode,始终有序。
-
mArray:Object[],交替存储 key 和 value(即 [key0, value0, key1, value1, ...])。
-
mSize:当前实际存储的键值对数量。
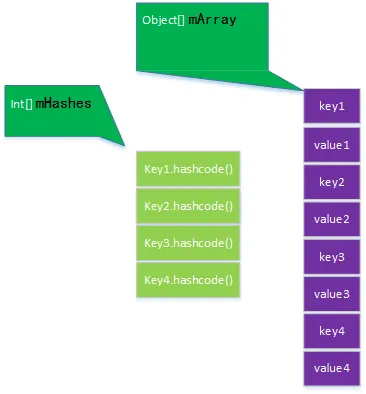
这样做的好处就是它避免了为每个加入到map的实体构造额外的对象。在ArrayMap大小增长的时候,我们也只需要复制两个数组的实体,而不需要重新构建一个hash map。
我们需要注意的是这种数据结构不适合包含大量数据项的数据结构,因为它内部使用的是数组,对数组进行插入和删除操作效率比较低。
5.2 构造方法
java
/**
* Create a new empty ArrayMap. The default capacity of an array map is 0, and
* will grow once items are added to it.
*/
public ArrayMap() {
// 初始化数组大小为0
this(0, false);
}
/**
* Create a new ArrayMap with a given initial capacity.
*/
public ArrayMap(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}
/** {@hide} */
public ArrayMap(int capacity, boolean identityHashCode) {
mIdentityHashCode = identityHashCode;
// If this is immutable, use the sentinal EMPTY_IMMUTABLE_INTS
// instance instead of the usual EmptyArray.INT. The reference
// is checked later to see if the array is allowed to grow.
if (capacity < 0) { // 初始化数组大小小于0时给出默认值
mHashes = EMPTY_IMMUTABLE_INTS;
mArray = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else if (capacity == 0) {
// 这里为数组的初始化设置了一个大小,如果capacity为0,那么就跟上面第一个构造函数一样
mHashes = EmptyArray.INT;
mArray = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else {
// 如果不为0,那么需要为数组分配大小,
// 具体看看allocArrays函数。
allocArrays(capacity);
}
mSize = 0; // 最开始的数组数据大小为0
}
java
package android.util;
public final class EmptyArray {
public static final int[] INT = new int[0];
public static final Object[] OBJECT = new Object[0];
// 其他类型...
}可以看到,这里就是对这两个数组以及这个size进行初始化,它定义了两个空数组,并且把大小置为0。从上面可以看到,它并没有为数组分配空间,在要使用的时候才会分配空间,这也是ArrayMap比HashMap内存占用率低的一个原因。
5.3 核心操作
5.3.1 put(K key, V value)
java
/**
* Add a new value to the array map.
* @param key The key under which to store the value. If
* this key already exists in the array, its value will be replaced.
* @param value The value to store for the given key.
* @return Returns the old value that was stored for the given key, or null if there
* was no such key.
*/
@Override
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 当前的数组数据大小
final int osize = mSize;
// key 对应的hash值
final int hash;
// hash对应的mHashes列表的index
int index;
// key为空,hash为0
if (key == null) {
hash = 0;
index = indexOfNull();
} else {
// 获取hash值,mIdentityHashCode 用于存储对象的唯一身份标识,
// 确保以对象实例为 key 时的唯一性,避免因重写 equals/hashCode 导致的冲突。
hash = mIdentityHashCode ? System.identityHashCode(key) : key.hashCode();
// 查找key对应mHashes中的index,大于0则找到了,否则为未找到
// 这里涉及到hash冲突,如果hash冲突,则在index的相邻位置插入数据
index = indexOf(key, hash);
}
// 找到key对应mHashes中的index
if (index >= 0) {
// 取出基数位置原有的Value
index = (index<<1) + 1;
final V old = (V)mArray[index];
// 将新数据放到基数index位置
mArray[index] = value;
return old;
}
// indexOf中取了反,这里反反则正
index = ~index;
// 如果满了就扩容
// 当容量不足时,ArrayMap 会扩容为当前容量的1.5倍(growSize)。
// 删除大量元素后,若剩余元素很少,会自动收缩数组以节省内存。
if (osize >= mHashes.length) {
final int n = osize >= (BASE_SIZE*2) ? (osize+(osize>>1))
: (osize >= BASE_SIZE ? (BASE_SIZE*2) : BASE_SIZE);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: grow from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
// 扩容
allocArrays(n);
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS && osize != mSize) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
// 把原来的数据拷贝到扩容后的数组中
if (mHashes.length > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: copy 0-" + osize + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, ohashes.length);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, oarray.length);
}
// 释放原数组
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, osize);
}
// 根据上面的二分法查找,如果index小于mSize,
// 说明新的数据是插入到数组之间index位置,插入之前需要把后面的移位
if (index < osize) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: move " + index + "-" + (osize-index)
+ " to " + (index+1));
System.arraycopy(mHashes, index, mHashes, index + 1, osize - index);
System.arraycopy(mArray, index << 1, mArray, (index + 1) << 1, (mSize - index) << 1);
}
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS) {
if (osize != mSize || index >= mHashes.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// 保存数据
mHashes[index] = hash;
mArray[index<<1] = key;
mArray[(index<<1)+1] = value;
mSize++;
return null;
}从上面的代码分析,插入操作最重要的是获取到了index,index决定了后续的操作,所以index的获取就比较重要,分析一下index的获取实现
java
// 根据key 与key的hash,查找key对应的index
int indexOf(Object key, int hash) {
final int N = mSize;
// Important fast case: if nothing is in here, nothing to look for.
if (N == 0) {
return ~0;
}
// 二分查找mHashes有序数组,查找hash对应的index
int index = binarySearchHashes(mHashes, N, hash);
// 没有找到
// If the hash code wasn't found, then we have no entry for this key.
if (index < 0) {
return index;
}
// 偶数位为对应的key,则找到了
// If the key at the returned index matches, that's what we want.
if (key.equals(mArray[index<<1])) {
return index;
}
// index之后查找
// 这里涉及到hash冲突,如果hash冲突,则在index的相邻位置插入数据
// mHashes 中的 hash 值可能会有连续重复的值
// Search for a matching key after the index.
int end;
for (end = index + 1; end < N && mHashes[end] == hash; end++) {
if (key.equals(mArray[end << 1])) return end;
}
// index之前查找
// Search for a matching key before the index.
for (int i = index - 1; i >= 0 && mHashes[i] == hash; i--) {
if (key.equals(mArray[i << 1])) return i;
}
// 没有找到就返回末尾最后一个相同hashcode的值的index的下一个位置的索引,也就是hash冲突顺延位置
// Key not found -- return negative value indicating where a
// new entry for this key should go. We use the end of the
// hash chain to reduce the number of array entries that will
// need to be copied when inserting.
return ~end;
}查找 key 时,先用二分查找在 mHashes 中定位 hashCode。如果有 hash 冲突(即 hashCode 相同),则在 mArray 中顺序比对 key 的 equals。查找复杂度为 O(logN)(二分查找)+ O(k)(冲突时的线性查找,k为冲突数)。
插入时,先查找 key 是否存在。
-
存在则直接覆盖 value。
-
不存在则插入新 key/value,并保持 mHashes 有序(需要移动数组元素)。
特别强调的一点是mHashes 是一个 int 数组,用于存储每个 key 的 hashCode,并且始终保持升序排列。mHashes 中的 hash 值可能会有连续重复的值,原因如下:
-
如果插入的多个 key 对象的 hashCode 相同(比如不同对象但 hashCode 计算结果一样,或者同一个对象多次插入),那么 mHashes 中就会出现连续的相同 hash 值。
-
ArrayMap 的查找逻辑是先用二分查找定位 hashCode,再在冲突区间内用 equals 线性查找 key。
5.3.2 get(Object key)
java
/**
* Retrieve a value from the array.
* @param key The key of the value to retrieve.
* @return Returns the value associated with the given key,
* or null if there is no such key.
*/
@Override
public V get(Object key) {
// 先获取key所在的索引值
final int index = indexOfKey(key);
// 根据索引值获取mArray中位置的数据
return index >= 0 ? (V)mArray[(index<<1)+1] : null;
}
/**
* Returns the index of a key in the set.
*
* @param key The key to search for.
* @return Returns the index of the key if it exists, else a negative integer.
*/
public int indexOfKey(Object key) { // 还是老方法indexof,查看前面的分析
return key == null ? indexOfNull()
: indexOf(key, mIdentityHashCode ? System.identityHashCode(key) : key.hashCode());
}5.4 特性特征
- 内存优化:
-
ArrayMap 通过静态缓存池(如 BASE_SIZE、CACHED_HASHES、CACHED_ARRAYS)复用小数组,减少频繁分配和回收内存的开销。
-
由于采用数组存储,避免了 HashMap 的 Entry 对象和装箱操作,极大节省内存。
- 扩容与收缩
-
当容量不足时,ArrayMap 会扩容为当前容量的1.5倍(growSize)。
-
删除大量元素后,若剩余元素很少,会自动收缩数组以节省内存。
- 有序性
mHashes 始终有序,遍历时 key/value 顺序与插入顺序无关,而是按 hashCode 升序。
- 适用场景
-
适合 key/value 数量较少(几十以内)、对内存敏感的场景。
-
大量数据时,插入/删除/查找性能不如 HashMap。