.NET Framework 依赖版本冲突解决方案:从现象到本质
问题背景
在工业自动化软件开发中,我遇到了一个典型但令人困惑的问题。当PostgreSQL数据库连接组件初始化时,系统抛出了以下异常:
未能加载文件或程序集"System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe, Version=4.0.4.1,
Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a"或它的某一个依赖项。
找到的程序集清单定义与程序集引用不匹配。 (异常来自 HRESULT:0x80131040)更令人疑惑的是,通过依赖检查工具发现,不同的DLL需要不同版本的 System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe:
- Npgsql.dll 要求:
System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.5.0 - System.Memory.dll 要求:
System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.4.1 - System.Text.Json.dll 要求:
System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.5.0 - System.Threading.Tasks.Extensions.dll 要求:
System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.4.1
依赖检查工具实现
为了诊断这类问题,我做了一套完整的诊断工具,包括控制台辅助类和依赖检查器。
控制台辅助工具
对于 Windows 窗体应用程序(WinForms/WPF),默认没有控制台窗口。这个工具可以在运行时动态创建控制台进行调试:
csharp
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace DH.Util.DebugUtil
{
/// <summary>
/// 控制台辅助工具类,用于在 Windows 窗体应用程序中动态创建和管理调试控制台
/// </summary>
public static class ConsoleHelper
{
#region Win32 API 声明
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
private static extern bool AllocConsole();
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
private static extern bool FreeConsole();
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
private static extern IntPtr GetConsoleWindow();
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
private static extern bool ShowWindow(IntPtr hWnd, int nCmdShow);
private const int SW_HIDE = 0;
private const int SW_SHOW = 5;
#endregion Win32 API 声明
#region 私有字段
private static bool _consoleAllocated = false;
private static readonly object _lock = new object();
#endregion 私有字段
#region 公共方法 - 控制台生命周期管理
/// <summary>
/// 显示控制台窗口
/// </summary>
/// <returns>成功返回 true,失败返回 false</returns>
public static bool ShowConsole()
{
lock (_lock)
{
if (_consoleAllocated)
{
Console.WriteLine("控制台已经启动!");
return true;
}
// 分配控制台
if (!AllocConsole())
{
int errorCode = Marshal.GetLastWin32Error();
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"AllocConsole 失败,错误代码: {errorCode}");
return false;
}
// 重新初始化控制台流
InitializeConsoleStreams();
// 设置编码
Console.OutputEncoding = Encoding.UTF8;
Console.InputEncoding = Encoding.UTF8;
// 设置标题和欢迎信息
SetConsoleTitle();
PrintWelcomeMessage();
_consoleAllocated = true;
return true;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 隐藏控制台窗口(不释放,可以重新显示)
/// </summary>
/// <returns>成功返回 true</returns>
public static bool HideConsoleWindow()
{
IntPtr consoleWindow = GetConsoleWindow();
if (consoleWindow != IntPtr.Zero)
{
return ShowWindow(consoleWindow, SW_HIDE);
}
return false;
}
/// <summary>
/// 显示已隐藏的控制台窗口
/// </summary>
/// <returns>成功返回 true</returns>
public static bool ShowConsoleWindow()
{
IntPtr consoleWindow = GetConsoleWindow();
if (consoleWindow != IntPtr.Zero)
{
return ShowWindow(consoleWindow, SW_SHOW);
}
return false;
}
/// <summary>
/// 隐藏并释放控制台窗口
/// </summary>
public static void HideConsole()
{
lock (_lock)
{
if (_consoleAllocated)
{
FreeConsole();
_consoleAllocated = false;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查控制台是否已创建
/// </summary>
/// <returns>已创建返回 true</returns>
public static bool IsConsoleVisible()
{
return GetConsoleWindow() != IntPtr.Zero;
}
#endregion 公共方法 - 控制台生命周期管理
#region 公共方法 - 便捷输出
/// <summary>
/// 清空控制台屏幕
/// </summary>
public static void Clear()
{
if (IsConsoleVisible())
{
Console.Clear();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 输出带颜色的文本
/// </summary>
/// <param name="message">消息内容</param>
/// <param name="color">文字颜色</param>
public static void WriteLineColored(string message, ConsoleColor color)
{
if (!IsConsoleVisible()) return;
var originalColor = Console.ForegroundColor;
Console.ForegroundColor = color;
Console.WriteLine(message);
Console.ForegroundColor = originalColor;
}
/// <summary>
/// 输出成功信息(绿色)
/// </summary>
public static void WriteSuccess(string message)
{
WriteLineColored($"✓ {message}", ConsoleColor.Green);
}
/// <summary>
/// 输出警告信息(黄色)
/// </summary>
public static void WriteWarning(string message)
{
WriteLineColored($"⚠ {message}", ConsoleColor.Yellow);
}
/// <summary>
/// 输出错误信息(红色)
/// </summary>
public static void WriteError(string message)
{
WriteLineColored($"✗ {message}", ConsoleColor.Red);
}
/// <summary>
/// 输出信息(青色)
/// </summary>
public static void WriteInfo(string message)
{
WriteLineColored($"ℹ {message}", ConsoleColor.Cyan);
}
/// <summary>
/// 输出分隔线
/// </summary>
/// <param name="length">分隔线长度,默认 60</param>
/// <param name="character">分隔符字符,默认 '='</param>
public static void WriteSeparator(int length = 60, char character = '=')
{
if (!IsConsoleVisible()) return;
Console.WriteLine(new string(character, length));
}
/// <summary>
/// 等待用户按任意键继续
/// </summary>
/// <param name="message">提示消息</param>
public static void WaitForKey(string message = "按任意键继续...")
{
if (!IsConsoleVisible()) return;
Console.WriteLine(message);
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
#endregion 公共方法 - 便捷输出
#region 私有方法
/// <summary>
/// 初始化控制台输入输出流
/// </summary>
private static void InitializeConsoleStreams()
{
try
{
// 重定向标准输出
var stdOut = Console.OpenStandardOutput();
var stdOutWriter = new StreamWriter(stdOut, Encoding.UTF8)
{
AutoFlush = true
};
Console.SetOut(stdOutWriter);
// 重定向标准错误
var stdErr = Console.OpenStandardError();
var stdErrWriter = new StreamWriter(stdErr, Encoding.UTF8)
{
AutoFlush = true
};
Console.SetError(stdErrWriter);
// 重定向标准输入
var stdIn = Console.OpenStandardInput();
var stdInReader = new StreamReader(stdIn, Encoding.UTF8);
Console.SetIn(stdInReader);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"初始化控制台流失败: {ex.Message}");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 设置控制台标题
/// </summary>
private static void SetConsoleTitle()
{
try
{
string exePath = Path.Combine(
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory,
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.FriendlyName
);
Console.Title = $"调试控制台 - {Path.GetFileName(exePath)}";
}
catch
{
Console.Title = "调试控制台";
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 输出欢迎信息
/// </summary>
private static void PrintWelcomeMessage()
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("╔═════════════════════════════╗");
Console.WriteLine(" 控制台调试模式已启动 ");
Console.WriteLine("╚═════════════════════════════╝");
Console.WriteLine($"时间: {DateTime.Now:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}");
Console.WriteLine($"目录: {AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory}");
string exePath = Path.Combine(
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory,
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.FriendlyName
);
Console.WriteLine($"程序: {exePath}");
Console.WriteLine();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"输出欢迎信息失败: {ex.Message}");
}
}
#endregion 私有方法
}
}依赖检查器
csharp
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace DH.Util.DebugUtil
{
/// <summary>
/// 依赖项检查工具类
/// </summary>
public class DependencyChecker
{
/// <summary>
/// 检查当前执行程序集的所有依赖项
/// </summary>
public static void CheckCurrentAssemblyDependencies()
{
Console.WriteLine("=== 当前程序集的依赖项 ===\n");
var currentAssembly = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly();
var references = currentAssembly.GetReferencedAssemblies();
foreach (var reference in references)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{reference.Name}");
Console.WriteLine($" 版本: {reference.Version}");
Console.WriteLine($" PublicKeyToken: {BitConverter.ToString(reference.GetPublicKeyToken())}");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查指定程序集的所有依赖项
/// </summary>
/// <param name="assemblyPath">程序集文件路径(相对或绝对路径)</param>
/// <param name="filterKeyword">可选的过滤关键字,只显示包含此关键字的依赖项</param>
public static void CheckAssemblyDependencies(string assemblyPath, string filterKeyword = null)
{
try
{
// 加载程序集
var assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(assemblyPath);
Console.WriteLine($"=== 程序集依赖项分析 ===");
Console.WriteLine($"程序集: {assembly.GetName().Name}");
Console.WriteLine($"版本: {assembly.GetName().Version}");
Console.WriteLine($"路径: {assemblyPath}");
Console.WriteLine();
var references = assembly.GetReferencedAssemblies();
// 应用过滤
bool hasFilter = !string.IsNullOrEmpty(filterKeyword);
int matchCount = 0;
foreach (var reference in references)
{
// 如果有过滤关键字,检查是否匹配
if (hasFilter && !reference.Name.Contains(filterKeyword))
{
continue;
}
matchCount++;
Console.WriteLine($"{reference.Name}");
Console.WriteLine($" 版本: {reference.Version}");
Console.WriteLine($" 完整名称: {reference.FullName}");
Console.WriteLine($" PublicKeyToken: {BitConverter.ToString(reference.GetPublicKeyToken())}");
Console.WriteLine();
}
// 显示统计信息
if (hasFilter)
{
Console.WriteLine($"匹配 '{filterKeyword}' 的依赖项: {matchCount}/{references.Length}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"总依赖项数: {references.Length}");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"错误: 无法加载程序集 '{assemblyPath}'");
Console.WriteLine($"异常信息: {ex.Message}");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 批量检查多个程序集的依赖项
/// </summary>
/// <param name="assemblyPaths">程序集路径数组</param>
/// <param name="filterKeyword">可选的过滤关键字</param>
public static void CheckMultipleAssemblies(string[] assemblyPaths, string filterKeyword = null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < assemblyPaths.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\n{'=',60}");
Console.WriteLine($"[{i + 1}/{assemblyPaths.Length}]");
Console.WriteLine($"{'=',60}\n");
CheckAssemblyDependencies(assemblyPaths[i], filterKeyword);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查指定目录下所有 DLL 的依赖项
/// </summary>
/// <param name="directoryPath">目录路径</param>
/// <param name="filterKeyword">可选的过滤关键字</param>
public static void CheckDirectoryAssemblies(string directoryPath, string filterKeyword = null)
{
try
{
var dllFiles = System.IO.Directory.GetFiles(directoryPath, "*.dll");
Console.WriteLine($"在目录 '{directoryPath}' 中找到 {dllFiles.Length} 个 DLL 文件\n");
CheckMultipleAssemblies(dllFiles, filterKeyword);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"错误: 无法读取目录 '{directoryPath}'");
Console.WriteLine($"异常信息: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
}实际使用示例:扫描 System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe 依赖
在程序启动时,使用以下代码扫描所有DLL对 Unsafe 的依赖情况:
csharp
// 在程序入口处(如 Main 方法或窗体构造函数)
ConsoleHelper.ShowConsole();
string binDir = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory;
Console.WriteLine($"扫描目录: {binDir}\n");
// 获取所有 DLL 文件
string[] allDlls = Directory.GetFiles(binDir, "*.dll");
Console.WriteLine($"找到 {allDlls.Length} 个 DLL 文件\n");
List<string> dllsWithUnsafe = new List<string>();
foreach (string dllPath in allDlls)
{
try
{
var assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(dllPath);
var references = assembly.GetReferencedAssemblies();
foreach (var reference in references)
{
if (reference.Name.Contains("Unsafe"))
{
string dllName = Path.GetFileName(dllPath);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine($"📦 {dllName}");
Console.ResetColor();
Console.WriteLine($" └─ 要求: {reference.Name} v{reference.Version}");
dllsWithUnsafe.Add($"{dllName} -> {reference.Version}");
break;
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 跳过无法加载的 DLL(可能是 native 库)
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
Console.WriteLine($"⚠️ 无法加载 DLL: {Path.GetFileName(dllPath)} | 异常: {ex.Message}");
Console.ResetColor();
}
}
// 输出汇总信息
Console.WriteLine($"\n{'=',60}");
Console.WriteLine($"汇总: 共 {dllsWithUnsafe.Count} 个 DLL 依赖 System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe");
Console.WriteLine($"{'=',60}\n");
foreach (var item in dllsWithUnsafe)
{
Console.WriteLine($" • {item}");
}实际运行效果:
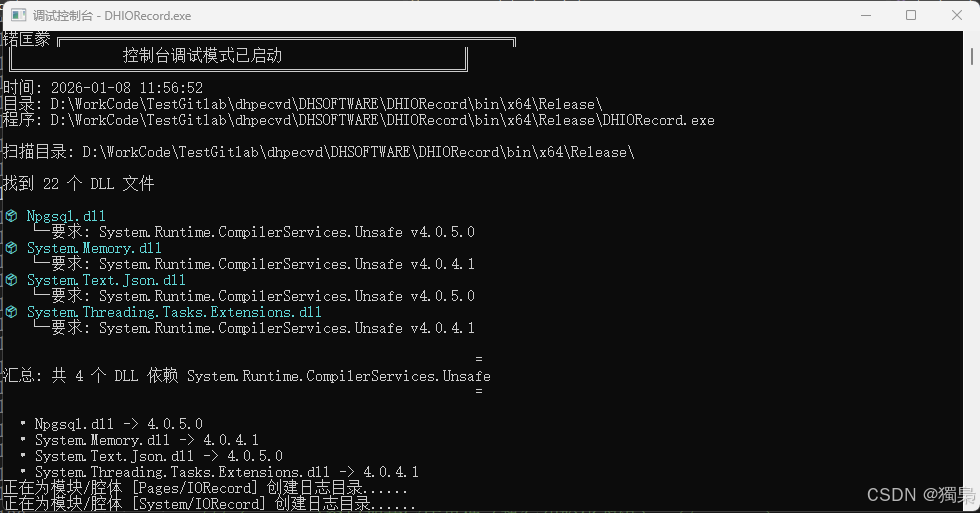
扫描目录: D:\WorkCode\TestGitlab\dhpecvd\DHSOFTWARE\DHIORecord\bin\x64\Release\
找到 22 个 DLL 文件
📦 Npgsql.dll
└─ 要求: System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.5.0
📦 System.Memory.dll
└─ 要求: System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.4.1
📦 System.Text.Json.dll
└─ 要求: System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.5.0
📦 System.Threading.Tasks.Extensions.dll
└─ 要求: System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.4.1
通过这个扫描结果,我们可以清晰地看到:
- 有2个DLL要求 v4.0.5.0
- 有2个DLL要求 v4.0.4.1
- 这正是导致版本冲突的根源
使用 DependencyChecker 类的简化版本
如果你已经有了封装好的 DependencyChecker 工具类,可以更简洁地实现同样的功能:
csharp
// ============================================================
// 方式一:使用 CheckDirectoryAssemblies 扫描整个目录
// ============================================================
ConsoleHelper.ShowConsole();
string binDir = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory;
Console.WriteLine("方式一:使用 CheckDirectoryAssemblies 扫描\n");
// 扫描目录下所有DLL,只显示包含"Unsafe"的依赖
DependencyChecker.CheckDirectoryAssemblies(binDir, "Unsafe");
Console.WriteLine("\n" + new string('=', 60) + "\n");
// ============================================================
// 方式二:使用 CheckAssemblyDependencies 检查单个程序集
// ============================================================
Console.WriteLine("方式二:检查特定 DLL 的所有依赖\n");
string npgsqlPath = Path.Combine(binDir, "Npgsql.dll");
if (File.Exists(npgsqlPath))
{
Console.WriteLine("检查 Npgsql.dll 的依赖项:\n");
DependencyChecker.CheckAssemblyDependencies(npgsqlPath, "Unsafe");
}
Console.WriteLine("\n" + new string('=', 60) + "\n");
// ============================================================
// 方式三:批量检查多个关键程序集
// ============================================================
Console.WriteLine("方式三:批量检查关键程序集\n");
string[] keyAssemblies = new string[]
{
Path.Combine(binDir, "Npgsql.dll"),
Path.Combine(binDir, "System.Memory.dll"),
Path.Combine(binDir, "System.Text.Json.dll"),
Path.Combine(binDir, "System.Threading.Tasks.Extensions.dll")
};
DependencyChecker.CheckMultipleAssemblies(keyAssemblies, "Unsafe");使用 DependencyChecker 的优势:
- 代码更简洁 - 一行调用即可完成扫描
- 功能更强大 - 支持过滤关键字、批量检查、递归扫描
- 输出更规范 - 统一的格式化输出
- 错误处理完善 - 内置异常处理和提示信息
- 可复用性强 - 可以在多个项目中使用同一个工具类
输出效果对比:
使用 CheckDirectoryAssemblies 的输出:
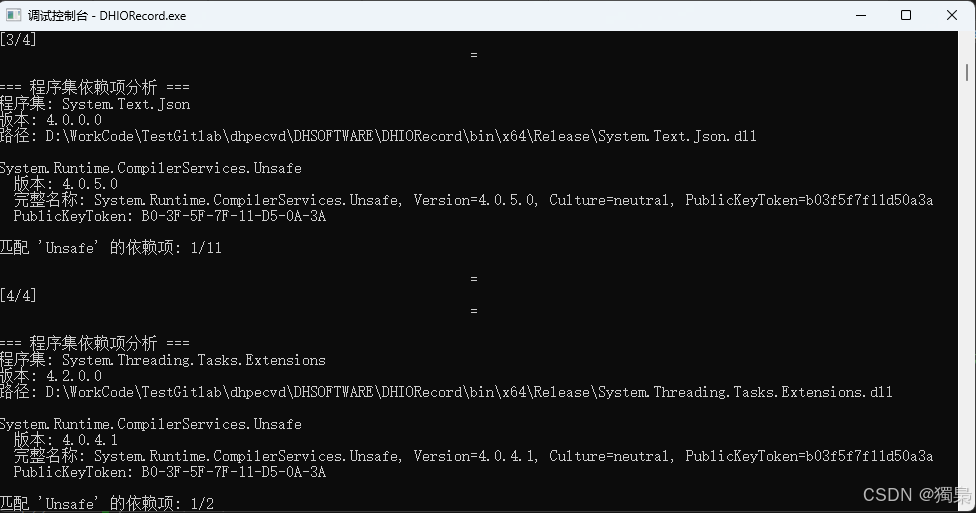
推荐使用场景:
| 场景 | 推荐方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 快速诊断 | CheckDirectoryAssemblies | 扫描整个目录,快速定位问题 |
| 详细分析 | CheckAssemblyDependencies | 检查单个程序集的完整依赖树 |
| 自动化测试 | 自定义代码 + 汇总统计 | 更灵活的控制和数据收集 |
| 生产环境监控 | 封装后的工具类方法 | 标准化输出,便于日志分析 |
.NET Framework 配置文件系统详解
app.config 的作用
app.config 是开发时配置文件,存在于项目根目录中。
主要功能:
- 应用程序配置设置(连接字符串、自定义配置等)
- 程序集绑定重定向(assemblyBinding)
- 运行时版本指定
- 启动设置
关键点:
- 这是一个XML文件,在开发阶段编辑
- 编译时会被复制到输出目录,重命名为
<程序集名称>.exe.config或<程序集名称>.dll.config - 只对编译生成的主程序集有效
典型结构:
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<runtime>
<assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1">
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe" publicKeyToken="b03f5f7f11d50a3a" culture="neutral" />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-4.0.5.0" newVersion="4.0.5.0" />
</dependentAssembly>
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Buffers" publicKeyToken="cc7b13ffcd2ddd51" culture="neutral" />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-4.0.3.0" newVersion="4.0.3.0" />
</dependentAssembly>
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Memory" publicKeyToken="cc7b13ffcd2ddd51" culture="neutral" />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-4.0.1.1" newVersion="4.0.1.1" />
</dependentAssembly>
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Numerics.Vectors" publicKeyToken="b03f5f7f11d50a3a" culture="neutral" />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-4.1.4.0" newVersion="4.1.4.0" />
</dependentAssembly>
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.ValueTuple" publicKeyToken="cc7b13ffcd2ddd51" culture="neutral" />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-4.0.3.0" newVersion="4.0.3.0" />
</dependentAssembly>
</assemblyBinding>
</runtime>
</configuration>packages.config 的作用
packages.config 是NuGet包管理文件(PackageReference之前的包管理方式)。
主要功能:
- 记录项目依赖的NuGet包及其版本
- NuGet还原时的依据
- 包版本锁定
关键点:
- 这是项目的依赖清单,不是运行时配置
- 不会被复制到输出目录
- 由NuGet工具读取和管理
典型内容:
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<packages>
<package id="BouncyCastle" version="1.8.3.1" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="Google.Protobuf" version="3.6.1" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="K4os.Compression.LZ4" version="1.1.11" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="K4os.Compression.LZ4.Streams" version="1.1.11" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="K4os.Hash.xxHash" version="1.0.6" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="Microsoft.Bcl.AsyncInterfaces" version="1.0.0" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="MySql.Data" version="8.0.21" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="Npgsql" version="5.0.18" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="SSH.NET" version="2016.1.0" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="System.Buffers" version="4.5.0" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="System.Memory" version="4.5.3" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="System.Numerics.Vectors" version="4.5.0" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe" version="4.6.0" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="System.Text.Encodings.Web" version="4.6.0" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="System.Text.Json" version="4.6.0" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="System.Threading.Channels" version="4.7.0" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="System.Threading.Tasks.Extensions" version="4.5.2" targetFramework="net48" />
<package id="System.ValueTuple" version="4.5.0" targetFramework="net48" />
</packages>两者的根本区别
| 特性 | app.config | packages.config |
|---|---|---|
| 作用时机 | 运行时 | 编译/还原时 |
| 主要用途 | 应用程序配置 | 依赖管理 |
| 是否复制到bin | 是(改名为.exe.config) | 否 |
| 谁来读取 | CLR运行时 | NuGet工具 |
| 能否解决版本冲突 | 能(binding redirect) | 不能 |
问题的根本原因:程序集绑定失败
CLR如何加载程序集
当.NET程序运行时,CLR按以下顺序加载程序集:
- 检查GAC(全局程序集缓存)
- 检查应用程序目录
- 读取配置文件的绑定重定向规则
为什么会出现版本冲突
在我们的场景中:
依赖关系树:
DHIORecord.exe
├── Npgsql.dll → 需要 Unsafe v4.0.5.0
├── System.Memory.dll → 需要 Unsafe v4.0.4.1
└── System.Text.Json.dll → 需要 Unsafe v4.0.5.0问题在于:
- bin目录中只有一个
System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe.dll文件(比如v4.0.5.0) - 但
System.Memory.dll明确要求v4.0.4.1版本 - CLR在没有配置文件指导下,严格匹配版本号
- 找不到精确匹配的版本,抛出异常
异常解析
未能加载文件或程序集"System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe, Version=4.0.4.1"
找到的程序集清单定义与程序集引用不匹配这段话的意思是:
- 程序需要加载版本4.0.4.1
- 实际找到的程序集是版本4.0.5.0
- 清单定义 (实际DLL的版本)与程序集引用(代码要求的版本)不匹配
解决方案:Binding Redirect(绑定重定向)
什么是Binding Redirect
绑定重定向是告诉CLR:"当程序要求版本A时,实际加载版本B"。
app.config中的配置
xml
<configuration>
<runtime>
<assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1">
<dependentAssembly>
<!-- 程序集标识 -->
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe" publicKeyToken="b03f5f7f11d50a3a" culture="neutral" />
<!-- 绑定重定向:将0.0.0.0-4.0.5.0范围内的所有版本请求重定向到4.0.5.0 -->
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-4.0.5.0" newVersion="4.0.5.0" />
</dependentAssembly>
</assemblyBinding>
</runtime>
</configuration>为什么复制.exe.config文件能解决问题
当你把生成的 .exe.config 文件复制到运行目录时:
场景分析:
假设你有两个程序:
- 开发程序A(DHIORecord.exe):有完整的app.config,编译后生成DHIORecord.exe.config
- 运行程序B(可能是另一个测试程序):在B的目录运行,但缺少配置文件
问题流程:
1. 程序B启动
2. 加载Npgsql.dll
3. Npgsql要求System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.4.1
4. CLR在程序B目录查找配置文件(B.exe.config)
5. 找不到配置文件 → 没有绑定重定向规则
6. CLR尝试精确匹配v4.0.4.1 → 失败
7. 抛出异常复制配置文件后:
1. 程序B启动
2. 加载Npgsql.dll
3. Npgsql要求System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.4.1
4. CLR在程序B目录查找配置文件
5. 找到B.exe.config(从DHIORecord.exe.config复制来的)
6. 读取绑定重定向规则:4.0.4.1 → 4.0.5.0
7. 成功加载v4.0.5.0版本
8. 程序正常运行配置文件的查找规则
CLR查找配置文件的规则:
- 查找
<可执行文件名>.exe.config - 必须与可执行文件在同一目录
- 文件名必须精确匹配
示例:
正确的配置:
D:\MyApp\
├── MyApp.exe
└── MyApp.exe.config ✓ CLR会读取
错误的配置:
D:\MyApp\
├── MyApp.exe
└── app.config ✗ CLR不会读取(这是源文件名)
└── DHIORecord.exe.config ✗ CLR不会读取(名称不匹配)实际操作指南
方法1:让Visual Studio自动处理
在项目的app.config中添加绑定重定向,Visual Studio编译时会自动:
- 生成对应的
.exe.config文件 - 复制到输出目录
- 随程序一起部署
方法2:手动管理配置文件
如果需要手动部署:
powershell
# 部署时确保配置文件正确命名
Copy-Item "源项目\bin\Debug\DHIORecord.exe.config" "目标目录\实际程序名.exe.config"方法3:使用NuGet自动生成
在项目文件中启用自动绑定重定向:
xml
<Project>
<PropertyGroup>
<AutoGenerateBindingRedirects>true</AutoGenerateBindingRedirects>
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>NuGet会在包还原时自动在app.config中添加必要的绑定重定向。
方法4:使用 Fusion Log Viewer 诊断绑定问题
工具:FUSLOGVW.exe(程序集绑定日志查看器)
powershell
# 启用程序集绑定日志(需要管理员权限)
# 1. 以管理员身份运行 Developer Command Prompt
# 2. 启动 Fusion Log Viewer
fuslogvw.exe
# 在界面中:
# - 启用日志记录
# - 选择"记录绑定失败到磁盘"
# - 关闭 Fusion Log Viewer
# - 手动创建设置的路径
# - 运行你的程序
# - 重新打开 Fusion Log Viewer
# - 查看详细的失败日志
优势:
- 精确定位哪个程序集加载失败
- 显示 CLR 查找程序集的完整路径
- 查看实际加载的版本 vs 请求的版本
- 判断是否是 GAC、配置文件或其他原因导致的问题
方法5:统一依赖版本(根本解决)
在 NuGet 包管理器中统一所有依赖的版本:
xml
<!-- 方式1:在项目文件中指定统一版本 -->
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe" Version="4.5.3" />
<PackageReference Include="Npgsql" Version="4.1.9" />
<PackageReference Include="System.Memory" Version="4.5.4" />
</ItemGroup>
<!-- 方式2:使用 Directory.Packages.props 集中管理 -->
<!-- 在解决方案根目录创建 Directory.Packages.props -->
<Project>
<PropertyGroup>
<ManagePackageVersionsCentrally>true</ManagePackageVersionsCentrally>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageVersion Include="System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe" Version="4.5.3" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>步骤:
- 右键解决方案 → "管理 NuGet 程序包"
- 选择"合并"选项卡
- 查看所有版本冲突
- 统一到最高兼容版本
优势:
- 从源头避免版本冲突
- 不需要配置绑定重定向
- 维护更简单
方法6:使用 AppDomain.AssemblyResolve 事件(代码级解决)
在程序启动时注册程序集解析事件:
csharp
// 在 Program.Main 或 Application 启动处
static Program()
{
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.AssemblyResolve += OnAssemblyResolve;
}
private static Assembly OnAssemblyResolve(object sender, ResolveEventArgs args)
{
// 解析程序集名称
AssemblyName assemblyName = new AssemblyName(args.Name);
// 特定处理 Unsafe 的版本冲突
if (assemblyName.Name == "System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe")
{
// 强制加载特定版本
string targetPath = Path.Combine(
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory,
"System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe.dll"
);
if (File.Exists(targetPath))
{
return Assembly.LoadFrom(targetPath);
}
}
return null;
}优势:
- 不依赖配置文件
- 可以实现复杂的加载逻辑
- 适合插件架构或无法修改配置文件的场景
劣势:
- 需要额外的代码维护
- 性能稍有影响
方法7:使用 IL 合并工具(ILMerge / Costura.Fody)
将所有依赖打包进单一程序集:
xml
<!-- 使用 Costura.Fody -->
<PackageReference Include="Costura.Fody" Version="5.7.0" />
<!-- 编译后,所有依赖 DLL 会被嵌入到主 EXE 中 -->
<!-- 不再需要单独部署 DLL -->
<!-- 自然也就没有版本冲突问题 -->优势:
- 单文件部署
- 彻底避免依赖冲突
- 简化部署流程
劣势:
- 主程序体积变大
- 不适合需要动态更新 DLL 的场景
方法8:降级依赖到兼容版本
查找所有依赖都能接受的版本:
System.Memory.dll → 要求 Unsafe v4.0.4.1
Npgsql.dll → 要求 Unsafe v4.0.5.0
分析:
- v4.0.4.1 太低,Npgsql 不接受
- v4.0.5.0 应该向下兼容 v4.0.4.1
决策:使用 v4.0.5.0 + 绑定重定向如果高版本不兼容:
xml
<!-- 降级 Npgsql 到旧版本 -->
<PackageReference Include="Npgsql" Version="4.0.x" />
<!-- 这个旧版本可能只要求 Unsafe v4.0.4.1 -->方法9:使用私有路径(privatePath)
为不同版本创建隔离目录:
xml
<configuration>
<runtime>
<assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1">
<!-- 指定额外的探测路径 -->
<probing privatePath="libs;plugins;bin\x64" />
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe" ... />
<codeBase version="4.0.5.0"
href="libs\System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe.dll" />
</dependentAssembly>
</assemblyBinding>
</runtime>
</configuration>目录结构:
MyApp\
├── MyApp.exe
├── MyApp.exe.config
└── libs\
└── System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe.dll ← v4.0.5.0方法10:使用 MSBuild 自动化脚本
在项目编译后自动处理配置文件:
xml
<Project>
<!-- 编译后自动添加/更新绑定重定向 -->
<Target Name="UpdateBindingRedirects" AfterTargets="Build">
<Exec Command="powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "$(ProjectDir)UpdateConfig.ps1"" />
</Target>
</Project>
powershell
# UpdateConfig.ps1
$configPath = "$PSScriptRoot\bin\Debug\MyApp.exe.config"
[xml]$config = Get-Content $configPath
# 自动扫描 bin 目录并生成绑定重定向
# ... PowerShell 脚本逻辑 ...
$config.Save($configPath)推荐方案矩阵
| 场景 | 推荐方法 | 优先级 |
|---|---|---|
| 开发阶段快速解决 | 方法1(VS自动)+ 方法5(统一版本) | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 生产环境标准部署 | 方法1(VS自动)+ 方法3(NuGet) | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 诊断疑难问题 | 方法4(Fusion Log) | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 无法修改配置文件 | 方法6(AssemblyResolve) | ⭐⭐ |
| 简化部署 | 方法7(ILMerge/Costura) | ⭐⭐ |
| 插件架构 | 方法6 + 方法9(privatePath) | ⭐⭐ |
| 持续集成自动化 | 方法10(MSBuild脚本) | ⭐ |
最佳实践组合:方法5(统一版本)+ 方法1(自动配置)+ 方法4(诊断工具)
最佳实践建议
开发阶段
xml
<!-- app.config中添加宽泛的绑定重定向 -->
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe" publicKeyToken="b03f5f7f11d50a3a" culture="neutral" />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-4.0.5.0" newVersion="4.0.5.0" />
</dependentAssembly>优点:
- 覆盖所有可能的版本请求
- 避免后续添加新包时出现版本冲突
依赖诊断
使用依赖检查工具定期扫描:
csharp
// 启动时诊断
#if DEBUG
ConsoleHelper.ShowConsole();
string binDir = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory;
DependencyChecker.ScanForDependency(binDir, "Unsafe");
#endif部署检查清单
- 确认
.exe.config文件存在 - 确认配置文件名与可执行文件名匹配
- 验证关键程序集的绑定重定向配置
- 测试所有依赖PostgreSQL的功能
版本选择策略
当bin目录需要放置具体版本的DLL时:
选择策略:
1. 查看所有依赖项要求的版本
2. 选择最高版本号(通常向后兼容)
3. 在绑定重定向中将所有旧版本指向这个最高版本示例:
发现的依赖:
- Npgsql → Unsafe v4.0.5.0
- System.Memory → Unsafe v4.0.4.1
- System.Text.Json → Unsafe v4.0.5.0
决策:使用 v4.0.5.0
理由:这是最高版本,且有多个组件要求它
配置:
bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-4.0.5.0" newVersion="4.0.5.0" />深入理解:为什么需要这种机制
.NET Framework的设计理念
.NET Framework采用强命名程序集(Strong-Named Assembly)机制:
程序集标识 = 名称 + 版本 + 文化 + 公钥令牌这种设计的初衷是:
- 版本隔离:不同版本可以并存
- 安全性:公钥确保程序集未被篡改
- 明确性:程序明确知道自己依赖哪个版本
但问题在于:
- 过于严格:即使是微小版本差异也会导致加载失败
- 依赖地狱:不同包要求不同版本,难以协调
Binding Redirect的妥协
绑定重定向是一种运行时妥协机制:
编译时:严格的版本依赖(保证类型安全)
运行时:灵活的版本解析(允许管理员调整)这允许:
- 开发人员在编译时获得类型安全保证
- 系统管理员在部署时解决版本冲突
- 在不重新编译的情况下升级依赖项
常见陷阱与解决
陷阱1:配置文件名称错误
❌ 错误:保留源文件名
MyApp\
├── MyApp.exe
└── app.config
✓ 正确:匹配可执行文件名
MyApp\
├── MyApp.exe
└── MyApp.exe.config陷阱2:绑定重定向版本不对
xml
❌ 错误:newVersion指向不存在的版本
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-6.0.0.0" newVersion="4.0.4.1" />
<!-- 但bin目录中实际是v4.0.5.0 -->
✓ 正确:newVersion必须是实际存在的DLL版本
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-4.0.5.0" newVersion="4.0.5.0" />陷阱3:忘记复制配置文件到测试环境
开发环境正常,测试环境失败的原因:
开发环境:
ProjectA\bin\Debug\
├── ProjectA.exe
└── ProjectA.exe.config ✓ Visual Studio自动生成
测试环境:
TestDirectory\
├── ProjectA.exe
└── [缺少配置文件] ✗ 手动复制时遗漏陷阱4:DLL 自己的 config 永远不会被读取
这是最容易被忽视的陷阱!
❌ 无效:DLL 的配置文件
MyProject\
├── MyApp.exe
├── MyApp.exe.config ✓ 这个会被读取
├── Util.dll
└── Util.dll.config ✗ 这个永远不会被读取关键规则:
- CLR 只读取启动可执行文件的配置文件
- 所有 DLL 的绑定重定向必须写在启动 exe 的 config 里
- 即使 DLL 有自己的 config 文件,运行时也会被忽略
正确做法:
xml
<!-- 在 MyApp.exe.config 中统一配置所有依赖 -->
<configuration>
<runtime>
<assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1">
<!-- Util.dll 需要的重定向也写在这里 -->
<dependentAssembly>
...
</dependentAssembly>
</assemblyBinding>
</runtime>
</configuration>陷阱5:assemblyBinding 少了命名空间导致完全不生效(不报错)
这是一个极其隐蔽的陷阱,会让你的重定向完全失效且没有任何提示!
xml
❌ 错误:缺少 xmlns 命名空间声明
<configuration>
<runtime>
<assemblyBinding> <!-- 缺少 xmlns 属性 -->
<dependentAssembly>
...
</dependentAssembly>
</assemblyBinding>
</runtime>
</configuration>
✓ 正确:必须包含 xmlns 属性
<configuration>
<runtime>
<assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1">
<dependentAssembly>
...
</dependentAssembly>
</assemblyBinding>
</runtime>
</configuration>症状:
- 程序仍然抛出版本不匹配异常
- 配置文件格式看起来正确
- 没有任何错误提示或警告
- 让人怀疑配置文件根本没被读取
排查方法:
- 仔细检查
<assemblyBinding>标签是否包含xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" - 使用 Fusion Log Viewer 查看绑定日志
陷阱6:publicKeyToken 或 culture 写错/缺失
绑定重定向的匹配是精确匹配 assemblyIdentity 的所有属性:
xml
❌ 错误:publicKeyToken 写错
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe" publicKeyToken="b03f5f7f11d50a3b" culture="neutral" />
✓ 正确:必须与实际 DLL 的标识完全一致
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe" publicKeyToken="b03f5f7f11d50a3a" culture="neutral" />关键点:
publicKeyToken必须完全正确(大小写不敏感,但每个字符必须匹配)culture属性也需要匹配(大多数是neutral,但有些库可能是特定文化)- 缺少或写错任何一个属性都会导致匹配失败
如何获取正确的标识信息:
- 从异常信息中复制(异常通常会显示完整的程序集标识)
- 使用 ILSpy、dnSpy 等工具查看 DLL 属性
- 使用依赖检查工具输出的完整名称
示例:从异常信息获取
异常信息:
"Could not load file or assembly 'System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe,
Version=4.0.4.1, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a'"
配置文件:
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe" publicKeyToken="b03f5f7f11d50a3a" culture="neutral" />陷阱7:配置被"更上层"的 config 覆盖(插件/服务宿主场景)
典型场景:
- Windows Service
- IIS 应用程序(Web.config)
- 插件式架构中的宿主进程
- 工控平台的壳程序
问题描述:
场景:工控软件插件架构
HostPlatform\
├── Host.exe ← 实际启动的程序
├── Host.exe.config ← CLR 读取这个配置
└── Plugins\
├── MyPlugin.dll ← 你的插件
└── MyPlugin.dll.config ✗ 不会被读取如果真正启动的是 Host.exe,那么应该修改的是 Host.exe.config,而不是你的插件配置文件。
解决方案:
-
找到真正的启动程序
- 在工控软件中,通常是平台的主程序(如
DHIORecord.exe) - 在 Windows Service 中,是服务的可执行文件
- 在 IIS 中,需要修改应用程序的
Web.config
- 在工控软件中,通常是平台的主程序(如
-
在启动程序的配置文件中添加重定向
xml
<!-- Host.exe.config -->
<configuration>
<runtime>
<assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1">
<!-- 为插件 DLL 添加必要的重定向 -->
<dependentAssembly>
...
</dependentAssembly>
</assemblyBinding>
</runtime>
</configuration>- 如果无法修改宿主配置
- 考虑在插件中使用
AppDomain.AssemblyResolve事件手动解析 - 或者协调宿主程序统一管理依赖版本
- 考虑在插件中使用
这条在"插件式架构 / 工控平台壳程序"中非常常见!
陷阱8:GAC 中的旧版本抢占加载优先级
当程序集在 GAC(全局程序集缓存) 中存在时,绑定行为可能与预期不同。
问题场景:
系统环境:
GAC: System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.4.1 ← 旧版本
应用目录: System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe v4.0.5.0 ← 新版本
结果:CLR 可能优先加载 GAC 中的旧版本
配置文件的重定向可能不生效CLR 程序集加载顺序:
- 已加载的程序集缓存
- GAC(优先级很高)
- 探测路径(应用程序目录、私有路径等)
- 代码库提示(codeBase)
排查方法:
powershell
# 检查 GAC 中是否存在该程序集
gacutil /l System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe
# 输出示例:
# System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe, Version=4.0.4.1, Culture=neutral,
# PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a, processorArchitecture=MSIL解决方案:
- 卸载 GAC 中的旧版本(需要管理员权限)
powershell
gacutil /u System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe- 安装新版本到 GAC
powershell
gacutil /i "path\to\System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe.dll"- 使用 codeBase 强制指定加载路径
xml
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe" ... />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-6.0.0.0" newVersion="4.0.5.0" />
<codeBase version="4.0.5.0" href="file:///C:/MyApp/System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe.dll" />
</dependentAssembly>注意事项:
- 在生产环境修改 GAC 需要谨慎(可能影响其他应用程序)
- 如果是客户机器,通常无法要求修改 GAC
- 最好的方案是选择不会安装到 GAC 的程序集版本
陷阱9:运行时不是 .NET Framework 还在写 bindingRedirect
这是版本迁移时的常见误区:
关键区别:
| 运行时 | 绑定重定向机制 | 配置文件 |
|---|---|---|
| .NET Framework | 需要 bindingRedirect |
app.config → .exe.config |
| .NET Core / .NET 5+ | 自动统一版本 | runtimeconfig.json |
xml
❌ 错误:.NET 5/6/7/8 项目中写 bindingRedirect
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>net8.0</TargetFramework> <!-- 注意:net8.0 -->
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>
<!-- app.config 中写了 bindingRedirect -->
<runtime>
<assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1">
<dependentAssembly>
... ← 这些在 .NET 5+ 中通常是无效的
</dependentAssembly>
</assemblyBinding>
</runtime>
✓ 正确:.NET Framework 才需要 bindingRedirect
<Project>
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>net48</TargetFramework> <!-- 注意:net48 -->
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>.NET Core / .NET 5+ 的版本策略:
- 采用"最高兼容版本"策略(Highest Compatible Version)
- NuGet 包会自动解决版本冲突
- 通常不需要手动配置绑定重定向
- 依赖版本统一在
.deps.json和runtimeconfig.json中管理
判断方法:
csharp
// 在代码中检查运行时类型
string framework = System.Runtime.InteropServices.RuntimeInformation.FrameworkDescription;
Console.WriteLine(framework);
// 输出示例:
// .NET Framework 4.8.4084.0
// .NET 8.0.0何时需要关注:
- 如果你的工控软件基于 .NET Framework 4.x :必须使用 bindingRedirect
- 如果迁移到 .NET 6/7/8 :通常不需要 bindingRedirect,依赖问题由运行时自动处理
总结
问题本质
.NET Framework的版本冲突问题源于强命名程序集的严格版本匹配机制。当不同的依赖项要求同一个程序集的不同版本时,CLR无法自动决定加载哪个版本。
解决方案核心
通过 app.config中的绑定重定向 告诉CLR:当程序要求某个版本范围时,实际加载另一个版本。这个配置在编译时会生成为 .exe.config 文件,并必须与可执行文件一起部署。
为什么复制配置文件有效
因为:
- 配置文件包含了绑定重定向规则
- CLR运行时读取这些规则
- 按规则将版本请求重定向到实际存在的版本
- 成功加载程序集,避免版本不匹配异常
关键要点
- app.config = 运行时配置(包括绑定重定向)
- packages.config = 编译时依赖清单
- 绑定重定向 = 版本冲突的官方解决方案
- 配置文件名 = 必须与可执行文件名精确匹配
- 版本选择 = 通常选择最高版本并重定向所有旧版本
工具化建议
建议在所有工业自动化项目中集成依赖检查工具:
- 启动时自动检查关键依赖
- 输出清晰的版本信息
- 在出现问题时快速定位
- 形成标准化的部署检查流程
参考资料: