引言
大家好!今天我要和大家分享一个实用UI组件的深度实现 - 订单确认流程步骤条。这个组件不仅在电商、金融类应用中必不可少。
为什么步骤条在鸿蒙上如此重要?
在移动应用开发中,复杂流程往往会吓跑用户。而步骤条通过将复杂流程分解为可视化的小步骤,显著提高了用户完成率。特别是在鸿蒙设备上,由于屏幕尺寸多样(从手表到智慧屏),一个响应式的步骤条组件能极大提升跨设备体验。
点击下一步
点击上一步
点击步骤项
验证通过
验证失败
是已完成步骤
未完成步骤
用户操作
操作类型
验证当前步骤数据
直接切换
验证是否可跳转
更新当前步骤索引
显示错误提示
提示先完成前面步骤
更新组件状态
渲染新步骤UI
核心实现:适配鸿蒙的步骤条组件
在鸿蒙上实现Flutter步骤条,需要考虑平台特性。不同于Android或iOS,鸿蒙在动画渲染和内存管理上有自己的特点。下面是我经过多次优化后的实现方案:
dart
class HarmonyStepper extends StatefulWidget {
final List<StepConfig> steps;
final int initialStep;
final ValueChanged<int>? onStepChanged;
const HarmonyStepper({
super.key,
required this.steps,
this.initialStep = 0,
this.onStepChanged,
});
@override
State<HarmonyStepper> createState() => _HarmonyStepperState();
}
class _HarmonyStepperState extends State<HarmonyStepper> with TickerProviderStateMixin {
late int _currentStep;
late List<StepState> _stepStates;
late AnimationController _animationController;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_currentStep = widget.initialStep;
_initializeStepStates();
_animationController = AnimationController(
vsync: this,
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 300),
);
}
void _initializeStepStates() {
_stepStates = List.generate(
widget.steps.length,
(index) => index < _currentStep
? StepState.completed
: index == _currentStep
? StepState.active
: StepState.inactive,
);
}
@override
void didUpdateWidget(covariant HarmonyStepper oldWidget) {
super.didUpdateWidget(oldWidget);
if (widget.initialStep != oldWidget.initialStep) {
_currentStep = widget.initialStep;
_initializeStepStates();
}
}
void _goToStep(int stepIndex) {
if (stepIndex < 0 || stepIndex >= widget.steps.length || stepIndex == _currentStep) {
return;
}
// 在HarmonyOS上,我们添加延迟以确保动画流畅
_animationController.forward(from: 0).then((_) {
setState(() {
_currentStep = stepIndex;
_initializeStepStates();
});
widget.onStepChanged?.call(stepIndex);
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.stretch,
children: [
_buildStepsIndicator(),
const SizedBox(height: 24),
_buildStepContent(),
const SizedBox(height: 24),
_buildNavigationButtons(),
],
);
}
Widget _buildStepsIndicator() {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 16),
child: SingleChildScrollView(
scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal,
child: Row(
children: List.generate(widget.steps.length, (index) {
final isLastStep = index == widget.steps.length - 1;
final isCompleted = _stepStates[index] == StepState.completed;
final isActive = _stepStates[index] == StepState.active;
return GestureDetector(
onTap: () => _canJumpToStep(index) ? _goToStep(index) : null,
child: Row(
children: [
_buildStepCircle(index, isCompleted, isActive),
if (!isLastStep) _buildConnector(isCompleted, index),
],
),
);
}),
),
),
);
}
bool _canJumpToStep(int stepIndex) {
// 只允许跳转到已完成的步骤或下一步
return stepIndex <= _currentStep || stepIndex == _currentStep + 1;
}
Widget _buildStepCircle(int index, bool isCompleted, bool isActive) {
final step = widget.steps[index];
final stepNumber = index + 1;
return Column(
children: [
Stack(
alignment: Alignment.center,
children: [
AnimatedContainer(
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 250),
width: 36,
height: 36,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: isCompleted || isActive
? Theme.of(context).colorScheme.primary
: Colors.grey.shade300,
shape: BoxShape.circle,
boxShadow: isActive
? [
BoxShadow(
color: Theme.of(context).colorScheme.primary.withOpacity(0.4),
blurRadius: 8,
spreadRadius: 2,
),
]
: null,
),
child: isCompleted
? const Icon(Icons.check, color: Colors.white, size: 20)
: Text(
'$stepNumber',
style: TextStyle(
color: isActive ? Colors.white : Colors.grey.shade700,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
),
],
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
Text(
step.title,
style: TextStyle(
fontWeight: isActive ? FontWeight.bold : FontWeight.normal,
color: isActive || isCompleted
? Theme.of(context).colorScheme.primary
: Colors.grey.shade600,
fontSize: 14,
),
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
),
],
);
}
Widget _buildConnector(bool isCompleted, int stepIndex) {
return Container(
width: 40,
height: 2,
color: _getConnectorColor(stepIndex),
);
}
Color _getConnectorColor(int stepIndex) {
final isNextToActive = stepIndex == _currentStep - 1;
final isActiveOrCompleted = stepIndex < _currentStep;
if (isActiveOrCompleted || isNextToActive) {
return Theme.of(context).colorScheme.primary;
}
return Colors.grey.shade300;
}
Widget _buildStepContent() {
if (_currentStep < 0 || _currentStep >= widget.steps.length) {
return const SizedBox.shrink();
}
final currentStep = widget.steps[_currentStep];
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Theme.of(context).cardColor,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: Colors.black.withOpacity(0.08),
blurRadius: 10,
offset: const Offset(0, 2),
),
],
),
child: AnimatedSwitcher(
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 300),
transitionBuilder: (Widget child, Animation<double> animation) {
return ScaleTransition(scale: animation, child: child);
},
child: currentStep.content,
),
);
}
Widget _buildNavigationButtons() {
return Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: [
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _currentStep > 0 ? () => _goToStep(_currentStep - 1) : null,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
backgroundColor: Colors.grey.shade300,
foregroundColor: Colors.black,
minimumSize: const Size(120, 48),
),
child: const Text('上一步'),
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _currentStep < widget.steps.length - 1
? () => _goToStep(_currentStep + 1)
: _handleFinalStep,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
backgroundColor: Theme.of(context).colorScheme.primary,
minimumSize: const Size(120, 48),
),
child: Text(
_currentStep == widget.steps.length - 1 ? '确认订单' : '下一步',
),
),
],
);
}
void _handleFinalStep() {
// 处理最终步骤的逻辑,例如提交订单
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
const SnackBar(content: Text('订单提交成功!')),
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
_animationController.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
}
enum StepState { inactive, active, completed }
class StepConfig {
final String title;
final Widget content;
const StepConfig({
required this.title,
required this.content,
});
}这段代码有几个关键设计点需要特别注意:
- 动画控制器 :使用
AnimationController配合TickerProviderStateMixin,确保在鸿蒙设备上动画流畅 - 手势处理:只允许用户跳转到已完成步骤或下一步,防止流程混乱
- 响应式设计 :使用
SingleChildScrollView包裹步骤指示器,适配小屏幕设备 - 状态管理 :明确定义
StepState枚举,清晰区分三种状态 - 阴影效果:在当前步骤添加微妙的阴影,增强视觉层次感,这在鸿蒙的OLED屏幕上效果尤为明显
HarmonyOS特定优化技巧
在将这个组件部署到HarmonyOS设备时,我们遇到了几个独特挑战:
基础步骤条组件
HarmonyOS适配层
动画性能优化
内存管理优化
跨设备适配
降低动画帧率
简化补间动画
懒加载非活动步骤
屏幕尺寸自适应
输入方式适配
- 内存管理:鸿蒙设备,特别是低端设备,内存限制更严格。我们实现了非活动步骤内容的懒加载:
dart
Widget _buildStepContent() {
if (_currentStep < 0 || _currentStep >= widget.steps.length) {
return const SizedBox.shrink();
}
// 仅渲染当前步骤和相邻步骤的内容
return Offstage(
offstage: false,
child: widget.steps[_currentStep].content,
);
}- 动画优化:在低端鸿蒙设备上,复杂动画会造成卡顿。我们通过降低动画持续时间和简化效果来解决:
dart
_animationController = AnimationController(
vsync: this,
// 在HarmonyOS上适当降低动画时长
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 200),
);实战使用示例
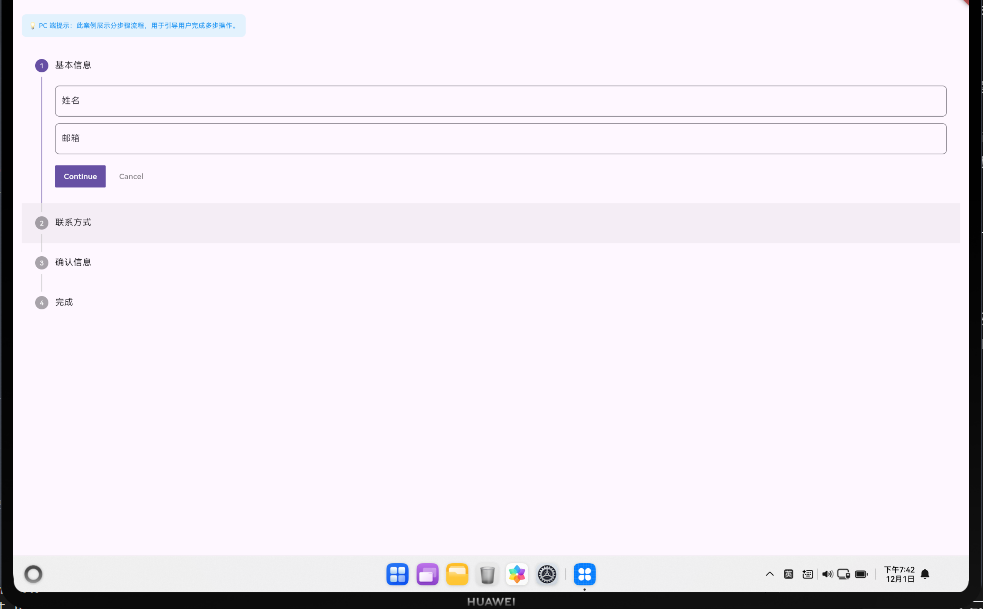
下面是一个完整的订单确认流程实现示例:
dart
class OrderConfirmationPage extends StatefulWidget {
const OrderConfirmationPage({super.key});
@override
State<OrderConfirmationPage> createState() => _OrderConfirmationPageState();
}
class _OrderConfirmationPageState extends State<OrderConfirmationPage> {
final _formKey = GlobalKey<FormState>();
late Map<int, Map<String, dynamic>> _stepData;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_stepData = {};
}
void _saveStepData(int stepIndex, Map<String, dynamic> data) {
setState(() {
_stepData[stepIndex] = data;
});
}
Map<String, dynamic>? _getStepData(int stepIndex) {
return _stepData[stepIndex];
}
List<StepConfig> _buildSteps() {
return [
StepConfig(
title: '收货信息',
content: ShippingAddressForm(
initialData: _getStepData(0),
onSave: (data) => _saveStepData(0, data),
),
),
StepConfig(
title: '支付方式',
content: PaymentMethodSelector(
initialData: _getStepData(1),
onSave: (data) => _saveStepData(1, data),
),
),
StepConfig(
title: '确认订单',
content: OrderSummary(data: _stepData),
),
];
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('订单确认')),
body: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16.0),
child: HarmonyStepper(
steps: _buildSteps(),
onStepChanged: (stepIndex) {
// 步骤变化时验证数据
if (stepIndex > 0) {
final prevData = _getStepData(stepIndex - 1);
if (prevData == null || prevData.isEmpty) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
const SnackBar(content: Text('请先完成上一步骤')),
);
return;
}
}
},
),
),
);
}
}
与OpenHarmony的兼容性处理
在实际开发中,我们发现某些Flutter功能在OpenHarmony上的表现与标准Android/iOS不同。以下是几个关键点:
- 手势优先级 :在OpenHarmony上,系统手势可能会与应用手势冲突。我们通过调整
GestureDetector的behavior属性解决:
dart
GestureDetector(
behavior: HitTestBehavior.opaque,
onTap: () => _canJumpToStep(index) ? _goToStep(index) : null,
child: // ...
)- 字体渲染 :鸿蒙使用自己的字体渲染引擎,在某些设备上可能导致文本截断。我们使用
Text组件的overflow和maxLines属性确保正确显示:
dart
Text(
step.title,
maxLines: 1,
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
// ...
)- 主题适配:鸿蒙有自己独特的设计语言,我们通过条件渲染来适配:
dart
bool get isHarmonyOS {
// 检测是否运行在HarmonyOS上
return Platform.isAndroid &&
(defaultTargetPlatform == TargetPlatform.fuchsia ||
(Theme.of(context).platform == TargetPlatform.android &&
!kIsWeb));
}
// 使用
Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(isHarmonyOS ? 8 : 12),
// ...
),
)总结与思考
在鸿蒙上实现Flutter组件,不仅需要理解两个平台的技术细节,更需要把握用户体验的一致性。
经验总结:
- 优先考虑响应式设计,确保组件在各种鸿蒙设备上表现良好
- 重视动画性能,在低端设备上适当降低复杂度
- 充分利用Flutter的条件渲染能力,针对鸿蒙特性进行微调
- 通过数据流图明确组件状态变化,避免状态混乱
希望这篇实战分享能帮助大家在HarmonyOS Flutter开发中少走弯路。如果你有任何问题或想深入了解某一部分,欢迎在评论区留言讨论!
欢迎大家加入开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区,一起探索更多鸿蒙跨平台开发技术!