文章目录
一、数据读取与预处理
首先,读取原始文本数据。本实验使用两个文本文件分别存储差评和好评数据:
python
import pandas as pd
import jieba
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
# 1. 读取数据
cp_content = pd.read_table(r".\差评1.txt", encoding='utf-8')
yzpj_content = pd.read_table(r".\好评1.txt", encoding='utf-8')参数说明:
pd.read_table():Pandas库中的函数,用于读取以制表符分隔的文本文件encoding='utf-8':指定文件编码格式为UTF-8,确保中文字符正确读取
二、中文分词处理
中文文本分析首先需要进行分词处理,将连续的字符序列切分成有意义的词语单元:
python
# 2. 定义分词函数
def segment_content(content_data):
"""对内容进行分词处理"""
segments = []
contents = content_data.iloc[:, 0].values.tolist()
for content in contents:
results = jieba.lcut(content)
if len(results) > 1: # 过滤掉只有一个词的评论
segments.append(results)
return segments方法分析:
jieba.lcut():结巴分词库的精确模式分词函数,返回分词后的列表iloc[:, 0]:提取DataFrame的第一列数据(假设文本内容在第一列)- 过滤单词语句:通过
len(results) > 1条件去除过于简单的评论,提高数据质量
三、数据清洗与转换
分词完成后,将结果转换为结构化数据格式以便后续处理:
python
# 3. 分词处理
cp_segments = segment_content(cp_content)
yzpj_segments = segment_content(yzpj_content)
# 4. 转换为DataFrame
cp_fc_results = pd.DataFrame({'content': cp_segments})
yzpj_fc_results = pd.DataFrame({'content': yzpj_segments})
# 5. 保存分词结果
cp_fc_results.to_excel('cp_fc_results.xlsx', index=False)
yzpj_fc_results.to_excel('yzpj_fc_results.xlsx', index=False)四、停用词处理
停用词是指在文本分析中没有实际意义的词语,需要去除以减少噪声:
python
# 6. 读取停用词
stopwords_df = pd.read_csv(r"./红楼梦/StopwordsCN.txt", encoding='utf8', engine='python', index_col=False)
stopwords_list = stopwords_df.stopword.values.tolist()
# 7. 定义去除停用词函数
def drop_stopwords(contents, stopwords):
"""去除内容中的停用词"""
segments_clean = []
for content in contents:
line_clean = []
for word in content:
if word in stopwords:
continue
line_clean.append(word)
segments_clean.append(line_clean)
return segments_clean
# 8. 去除停用词
cp_fc_contents_clean = drop_stopwords(cp_fc_results.content.values.tolist(), stopwords_list)
yzpj_fc_contents_clean = drop_stopwords(yzpj_fc_results.content.values.tolist(), stopwords_list)五、数据集构建与标签化
将处理后的数据整合为统一的训练数据集,并添加情感标签:
python
# 9. 构建训练数据集并打标签
cp_train = pd.DataFrame({'segments_clean': cp_fc_contents_clean, 'label': 1}) # 差评标签为1
yzpj_train = pd.DataFrame({'segments_clean': yzpj_fc_contents_clean, 'label': 0}) # 优质评价标签为0
pj_train = pd.concat([cp_train, yzpj_train])
# 10. 保存训练数据
pj_train.to_excel('pj_train.xlsx', index=False)标签设定:
- 差评:标签为1
- 好评:标签为0
六、数据集划分与特征提取
将数据集划分为训练集和测试集,并提取文本特征:
python
# 11. 划分训练集和测试集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(pj_train['segments_clean'].values, pj_train['label'].values,
random_state=0)
# 12. 为CountVectorizer准备数据格式
words_train = []
for line in x_train:
words_train.append(' '.join(line))
words_test = []
for line in x_test:
words_test.append(' '.join(line))
print(words_train)
print("训练集样本数:", len(words_train))
print("测试集样本数:", len(words_test))
print("前5个训练样本:", words_train[:5])
vec = CountVectorizer(max_features=4000, lowercase=False, ngram_range=(1, 3))
vec.fit(words_train)
x_train_vec = vec.transform(words_train)
x_test_vec = vec.transform(words_test)CountVectorizer关键参数:
max_features=4000:限制特征维度为4000,只保留最重要的4000个特征词lowercase=False:对于中文,保持原样(英文通常设为True进行小写转换)ngram_range=(1, 3):提取1-gram到3-gram特征,即单个词、双词组合和三词组合
七、模型训练与评估
使用多项式朴素贝叶斯算法进行模型训练和评估:
python
classifier = MultinomialNB(alpha=0.1)
classifier.fit(x_train_vec, y_train)
train_pr = classifier.predict(x_train_vec)
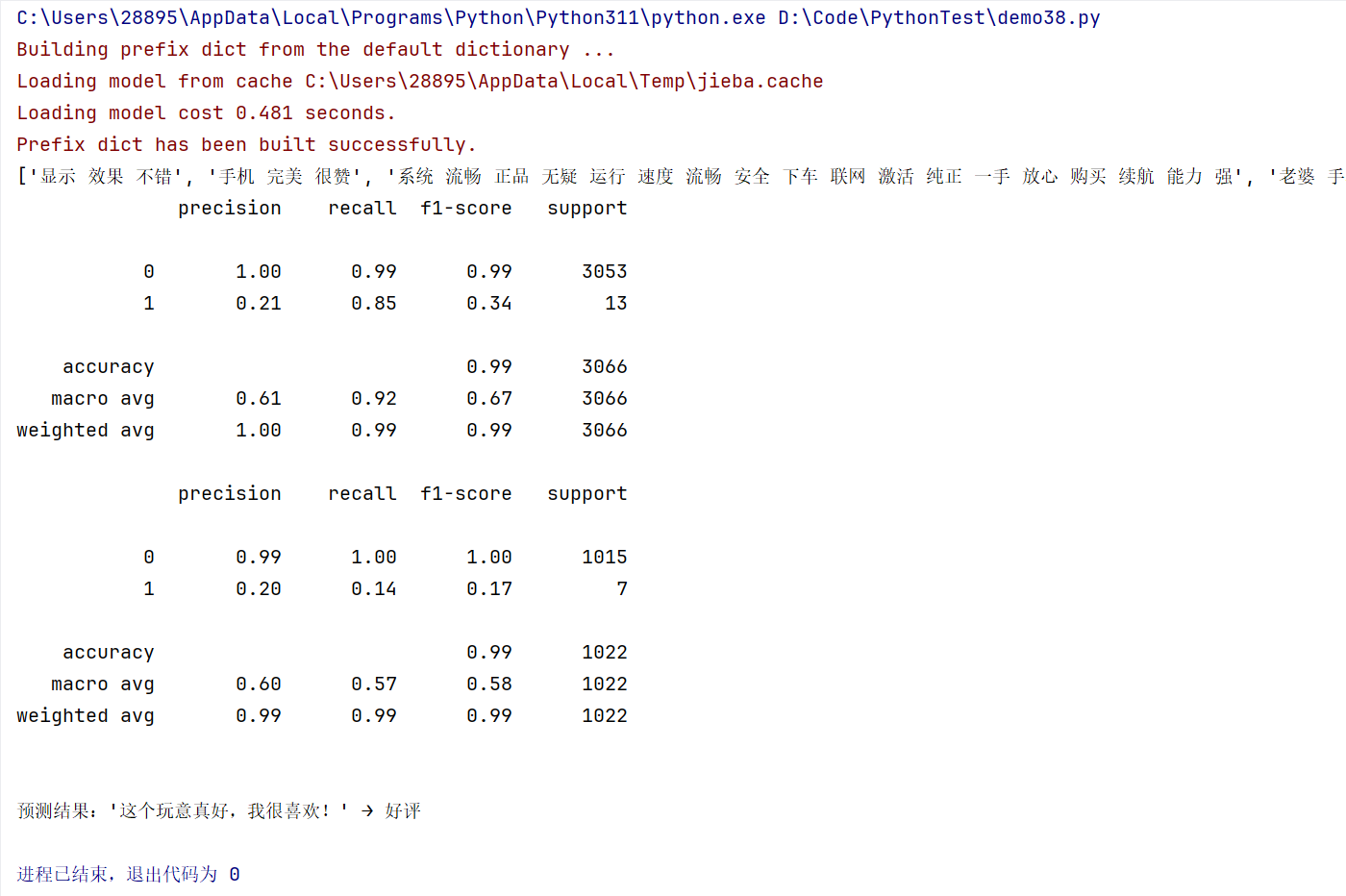
print(metrics.classification_report(y_train, train_pr))
test_pr = classifier.predict(x_test_vec)
print(metrics.classification_report(y_test, test_pr))模型参数:
MultinomialNB(alpha=0.1):多项式朴素贝叶斯分类器alpha=0.1:拉普拉斯平滑参数,防止概率为零的情况
八、新样本预测
训练完成后,可以对新的文本样本进行预测:
python
s = "这个玩意真好,我很喜欢!"
# 1. 分词
words = jieba.lcut(s)
# 2. 去除停用词
words_clean = [word for word in words if word not in stopwords_list]
# 3. 构建成词向量转换的标准格式
s_processed = ' '.join(words_clean)
# 4. 进行词向量转换(使用训练好的vec)
s_vec = vec.transform([s_processed])
# 5. 预测
prediction = classifier.predict(s_vec)
# 输出结果
if prediction[0] == 0:
print(f"\n预测结果:'{s}' → 好评")
else:
print(f"\n预测结果:'{s}' → 差评")