引言:那个让我重写整个if-else的when表达式
2023年,我在重构一个支付系统的状态处理代码。原本有一个30行的if-else链条:
java
// Java:臃肿的if-else
if (status.equals("PENDING")) {
return "等待支付";
} else if (status.equals("PROCESSING")) {
return "处理中";
} else if (status.equals("SUCCESS")) {
return "支付成功";
} else if (status.equals("FAILED")) {
return "支付失败";
} else if (status.equals("CANCELLED")) {
return "已取消";
} else if (status.equals("REFUNDED")) {
return "已退款";
} else {
return "未知状态";
}代码审查时,同事说:"你知道Kotlin的when表达式吗?"
5分钟后,代码变成了这样:
kotlin
// Kotlin:优雅的when表达式
val statusText = when (status) {
"PENDING" -> "等待支付"
"PROCESSING" -> "处理中"
"SUCCESS" -> "支付成功"
"FAILED" -> "支付失败"
"CANCELLED" -> "已取消"
"REFUNDED" -> "已退款"
else -> "未知状态"
}那一刻我意识到:Kotlin不只是Java的简化版,它是对编程范式的重新思考。
今天这篇文章,我们将学习Kotlin的控制流和函数,看看它如何让代码更简洁、更表达性。
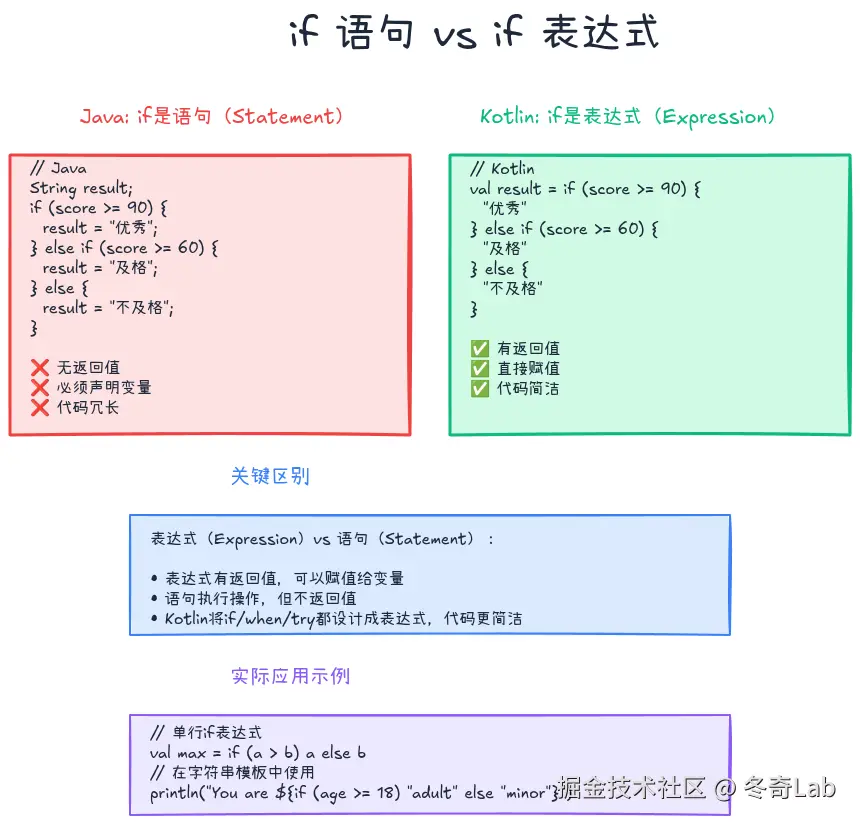
if:不是语句,是表达式
Java的if是语句
在Java中,if是语句(statement),不返回值:
java
// Java
String result;
if (score >= 90) {
result = "优秀";
} else if (score >= 60) {
result = "及格";
} else {
result = "不及格";
}Kotlin的if是表达式
在Kotlin中,if是表达式(expression),有返回值:
kotlin
// Kotlin:if作为表达式
val result = if (score >= 90) {
"优秀"
} else if (score >= 60) {
"及格"
} else {
"不及格"
}更简洁的单行写法:
kotlin
val result = if (score >= 90) "优秀" else if (score >= 60) "及格" else "不及格"
// 或者使用when(后面会讲)
val result = when {
score >= 90 -> "优秀"
score >= 60 -> "及格"
else -> "不及格"
}if表达式的强大之处
1. 直接赋值给变量
kotlin
val max = if (a > b) a else b
val message = if (user != null) {
"Hello, ${user.name}"
} else {
"Hello, Guest"
}2. 作为函数返回值
kotlin
fun getDiscount(vipLevel: Int): Double {
return if (vipLevel >= 3) 0.8
else if (vipLevel >= 2) 0.9
else 1.0
}
// 更简洁(单表达式函数)
fun getDiscount(vipLevel: Int) = if (vipLevel >= 3) 0.8 else if (vipLevel >= 2) 0.9 else 1.03. 在表达式中使用
kotlin
println("You are ${if (age >= 18) "adult" else "minor"}")
val price = basePrice * if (isMember) 0.9 else 1.0**表达式 vs 语句**: - **表达式(Expression)**:有返回值,如`if`、`when`、`try` - **语句(Statement)**:无返回值,如Java的`if`、`for`
Kotlin将很多传统的"语句"设计成"表达式",让代码更简洁、更函数式。
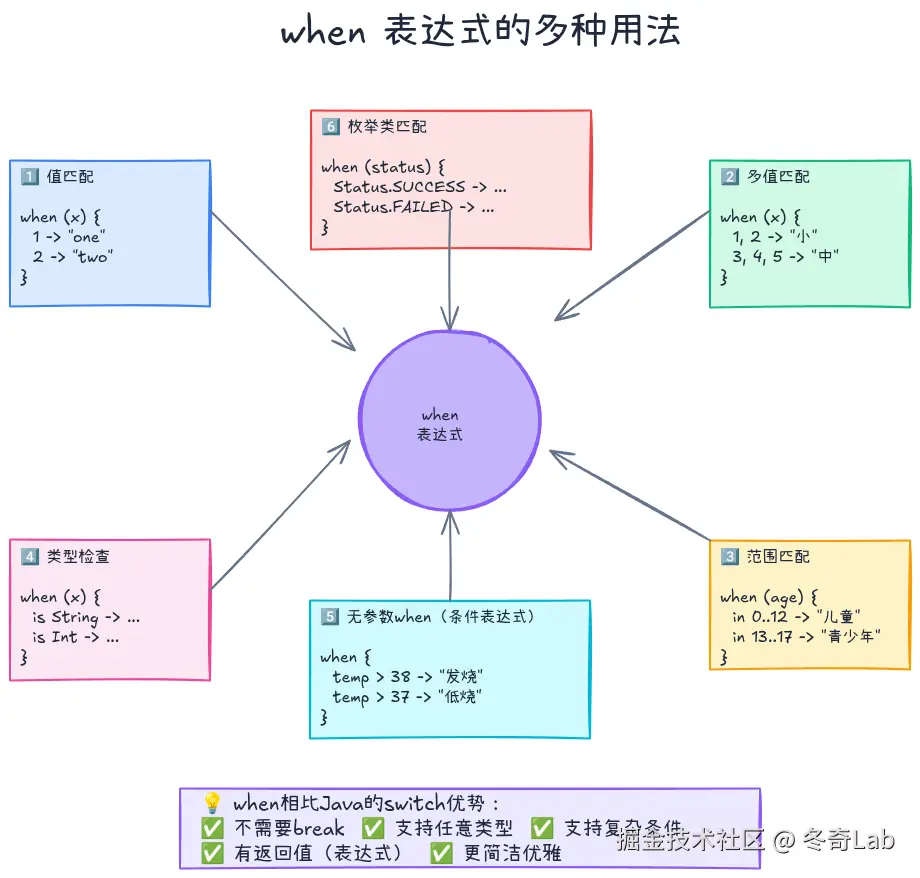
when:强大的模式匹配
when是Kotlin最强大的控制流特性之一,相当于Java的switch,但功能强大得多。
基本用法
kotlin
val dayName = when (dayOfWeek) {
1 -> "星期一"
2 -> "星期二"
3 -> "星期三"
4 -> "星期四"
5 -> "星期五"
6 -> "星期六"
7 -> "星期日"
else -> "无效的星期"
}相比Java的switch优势:
- ✅ 不需要
break(自动break) - ✅ 可以返回值(是表达式)
- ✅ 支持任意类型(不限于int、String、enum)
- ✅ 支持复杂条件
多值匹配
kotlin
val isWeekend = when (dayOfWeek) {
6, 7 -> true // 周六或周日
else -> false
}
val season = when (month) {
3, 4, 5 -> "春季"
6, 7, 8 -> "夏季"
9, 10, 11 -> "秋季"
12, 1, 2 -> "冬季"
else -> "无效月份"
}范围匹配
kotlin
val ageGroup = when (age) {
in 0..12 -> "儿童"
in 13..17 -> "青少年"
in 18..59 -> "成年人"
in 60..Int.MAX_VALUE -> "老年人"
else -> "无效年龄"
}
val grade = when (score) {
in 90..100 -> "A"
in 80..89 -> "B"
in 70..79 -> "C"
in 60..69 -> "D"
else -> "F"
}类型检查
kotlin
fun describe(obj: Any): String = when (obj) {
is String -> "String of length ${obj.length}"
is Int -> "Integer: $obj"
is List<*> -> "List of size ${obj.size}"
is Boolean -> "Boolean: $obj"
else -> "Unknown type"
}
// 智能类型转换
val result = when (value) {
is String -> value.uppercase() // value自动转为String
is Int -> value * 2 // value自动转为Int
else -> "Unknown"
}无参数when(条件表达式)
最灵活的形式,类似if-else链:
kotlin
val healthStatus = when {
temperature > 38.5 -> "发烧"
temperature > 37.5 -> "低烧"
temperature >= 36.0 -> "正常"
else -> "体温过低"
}
val recommendation = when {
age < 18 -> "建议家长陪同"
age >= 65 -> "建议体检"
hasChronicDisease -> "请咨询医生"
else -> "可以独立出行"
}when的高级用法
1. 作为语句(执行多条指令)
kotlin
when (command) {
"start" -> {
println("Starting service...")
serviceManager.start()
println("Service started")
}
"stop" -> {
println("Stopping service...")
serviceManager.stop()
println("Service stopped")
}
else -> println("Unknown command")
}2. 替代多个if-else
kotlin
// ❌ 不好:多个if-else
if (user.isVip) {
showVipContent()
} else if (user.isPremium) {
showPremiumContent()
} else if (user.isRegistered) {
showRegisteredContent()
} else {
showGuestContent()
}
// ✅ 好:使用when
when {
user.isVip -> showVipContent()
user.isPremium -> showPremiumContent()
user.isRegistered -> showRegisteredContent()
else -> showGuestContent()
}3. 枚举类匹配
kotlin
enum class PaymentStatus { PENDING, SUCCESS, FAILED, CANCELLED }
fun handlePayment(status: PaymentStatus) = when (status) {
PaymentStatus.PENDING -> "等待支付"
PaymentStatus.SUCCESS -> "支付成功"
PaymentStatus.FAILED -> "支付失败"
PaymentStatus.CANCELLED -> "已取消"
// 注意:枚举类完全覆盖后,不需要else分支
}
循环:for和while
for循环
Kotlin的for循环比Java更灵活,支持多种迭代方式。
1. 遍历范围
kotlin
// 1到10(包含10)
for (i in 1..10) {
println(i)
}
// 1到9(不包含10)
for (i in 1 until 10) {
println(i)
}
// 10到1(倒序)
for (i in 10 downTo 1) {
println(i)
}
// 步长为2
for (i in 1..10 step 2) {
println(i) // 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
}2. 遍历集合
kotlin
val fruits = listOf("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry")
// 遍历元素
for (fruit in fruits) {
println(fruit)
}
// 遍历索引
for (i in fruits.indices) {
println("$i: ${fruits[i]}")
}
// 同时遍历索引和元素
for ((index, fruit) in fruits.withIndex()) {
println("$index: $fruit")
}3. 遍历Map
kotlin
val map = mapOf("a" to 1, "b" to 2, "c" to 3)
for ((key, value) in map) {
println("$key -> $value")
}4. 遍历字符串
kotlin
val text = "Kotlin"
for (char in text) {
println(char)
}while和do-while
kotlin
// while循环
var count = 0
while (count < 5) {
println("Count: $count")
count++
}
// do-while循环(至少执行一次)
var input: String
do {
print("Enter 'yes' to continue: ")
input = readLine() ?: ""
} while (input != "yes")循环控制
kotlin
// break:跳出循环
for (i in 1..10) {
if (i == 5) break
println(i) // 1, 2, 3, 4
}
// continue:跳过当前迭代
for (i in 1..10) {
if (i % 2 == 0) continue // 跳过偶数
println(i) // 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
}
// 标签(Label):跳出嵌套循环
loop@ for (i in 1..3) {
for (j in 1..3) {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) break@loop
println("$i, $j")
}
}**性能提示**:对于大量数据的处理,考虑使用`forEach`、`map`、`filter`等集合操作符(第5篇会详细讲解),它们更简洁且性能更好。
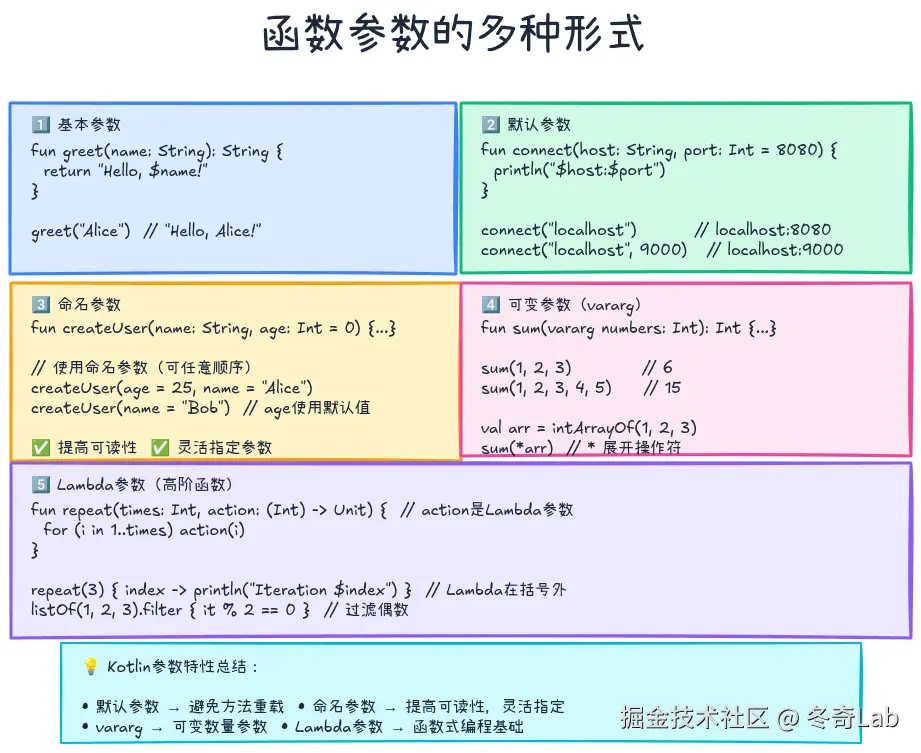
函数基础
函数定义
kotlin
// 基本函数
fun greet(name: String): String {
return "Hello, $name!"
}
// 单表达式函数(自动推断返回类型)
fun greet(name: String) = "Hello, $name!"
// 无返回值函数(返回Unit,类似Java的void)
fun printGreeting(name: String) {
println("Hello, $name!")
}
// Unit可以省略
fun printGreeting(name: String): Unit {
println("Hello, $name!")
}参数与返回值
1. 默认参数
kotlin
// Java需要方法重载
public void connect(String host) {
connect(host, 8080, 3000);
}
public void connect(String host, int port) {
connect(host, port, 3000);
}
public void connect(String host, int port, int timeout) {
// 实际逻辑
}
// Kotlin只需一个函数
fun connect(host: String, port: Int = 8080, timeout: Int = 3000) {
println("Connecting to $host:$port with timeout $timeout ms")
}
// 调用
connect("localhost") // 使用默认port和timeout
connect("localhost", 9000) // 使用默认timeout
connect("localhost", 9000, 5000) // 全部指定2. 命名参数
kotlin
fun createUser(
name: String,
email: String,
age: Int = 0,
isActive: Boolean = true
) {
println("User: $name, $email, $age, $isActive")
}
// 使用命名参数(可以任意顺序)
createUser(
name = "Alice",
email = "alice@example.com"
)
createUser(
email = "bob@example.com",
name = "Bob",
age = 25
)
createUser(
name = "Charlie",
email = "charlie@example.com",
isActive = false
)**最佳实践**: - 当函数有多个相同类型的参数时,使用命名参数提高可读性 - 当只想指定部分默认参数时,使用命名参数跳过前面的参数
3. 可变参数(vararg)
kotlin
fun sum(vararg numbers: Int): Int {
var result = 0
for (num in numbers) {
result += num
}
return result
}
// 调用
println(sum(1, 2, 3)) // 6
println(sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)) // 15
// 展开数组
val array = intArrayOf(1, 2, 3)
println(sum(*array)) // * 是展开操作符函数返回值
1. 返回多个值(使用Pair/Triple)
kotlin
fun getMinMax(numbers: List<Int>): Pair<Int, Int> {
return Pair(numbers.minOrNull() ?: 0, numbers.maxOrNull() ?: 0)
}
// 解构赋值
val (min, max) = getMinMax(listOf(1, 5, 3, 9, 2))
println("Min: $min, Max: $max")
// 三个值用Triple
fun getUserInfo(): Triple<String, Int, String> {
return Triple("Alice", 25, "alice@example.com")
}
val (name, age, email) = getUserInfo()2. 返回null(可空返回类型)
kotlin
fun findUser(id: Int): User? {
return if (id > 0) User(id, "User$id") else null
}
// 使用
val user = findUser(123)
user?.let {
println("Found user: ${it.name}")
}3. Nothing类型(永不返回)
kotlin
fun fail(message: String): Nothing {
throw IllegalArgumentException(message)
}
fun validateAge(age: Int) {
if (age < 0) {
fail("Age cannot be negative")
}
// 编译器知道这里age >= 0
}
Lambda表达式:函数式编程的基石
什么是Lambda
Lambda表达式是匿名函数的简洁写法:
kotlin
// 普通函数
fun double(x: Int): Int {
return x * 2
}
// Lambda表达式
val double: (Int) -> Int = { x -> x * 2 }
// 使用
println(double(5)) // 10Lambda语法
kotlin
// 完整语法
val sum: (Int, Int) -> Int = { a, b -> a + b }
// 单参数时可以用it
val double: (Int) -> Int = { it * 2 }
// 多行Lambda
val complexCalc: (Int) -> Int = { x ->
val temp = x * 2
temp + 10
}
// 无参数Lambda
val greet: () -> String = { "Hello!" }Lambda作为参数
kotlin
// 高阶函数:接受函数作为参数
fun repeat(times: Int, action: (Int) -> Unit) {
for (i in 1..times) {
action(i)
}
}
// 调用
repeat(3) { index ->
println("Iteration $index")
}
// 实际应用
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// filter:过滤元素
val evenNumbers = numbers.filter { it % 2 == 0 }
println(evenNumbers) // [2, 4]
// map:转换元素
val doubled = numbers.map { it * 2 }
println(doubled) // [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
// forEach:遍历
numbers.forEach { println(it) }Lambda的简化规则
Kotlin有一套Lambda简化规则,让代码更简洁:
kotlin
// 1. 如果Lambda是函数的最后一个参数,可以移到括号外
repeat(3, { index -> println(index) })
repeat(3) { index -> println(index) } // ✅ 更简洁
// 2. 如果Lambda是唯一参数,括号可以省略
listOf(1, 2, 3).forEach({ println(it) })
listOf(1, 2, 3).forEach { println(it) } // ✅ 更简洁
// 3. 单参数Lambda可以用it
listOf(1, 2, 3).filter { number -> number % 2 == 0 }
listOf(1, 2, 3).filter { it % 2 == 0 } // ✅ 更简洁
// 4. 不使用的参数可以用下划线
val map = mapOf("a" to 1, "b" to 2)
map.forEach { (key, _) -> println(key) } // 只用key,忽略value函数引用
有时候已经有一个函数,不想重复写Lambda:
kotlin
fun isEven(number: Int): Boolean {
return number % 2 == 0
}
// 使用Lambda
val evenNumbers1 = numbers.filter { isEven(it) }
// 使用函数引用(::)
val evenNumbers2 = numbers.filter(::isEven) // ✅ 更简洁
// 成员函数引用
val lengths = listOf("a", "bb", "ccc").map(String::length)
println(lengths) // [1, 2, 3]实战:构建一个灵活的计算器
让我们综合运用本文所学知识,构建一个支持多种运算的计算器:
kotlin
// 定义运算类型
enum class Operation {
ADD, SUBTRACT, MULTIPLY, DIVIDE, POWER, MODULO
}
class Calculator {
// 使用when表达式选择运算
fun calculate(a: Double, b: Double, operation: Operation): Double {
return when (operation) {
Operation.ADD -> a + b
Operation.SUBTRACT -> a - b
Operation.MULTIPLY -> a * b
Operation.DIVIDE -> {
if (b == 0.0) throw IllegalArgumentException("除数不能为0")
a / b
}
Operation.POWER -> Math.pow(a, b)
Operation.MODULO -> a % b
}
}
// 使用Lambda实现自定义运算
fun calculateCustom(a: Double, b: Double, operation: (Double, Double) -> Double): Double {
return operation(a, b)
}
// 批量计算(vararg + Lambda)
fun batchCalculate(
vararg values: Double,
operation: (Double, Double) -> Double
): Double {
if (values.isEmpty()) return 0.0
var result = values[0]
for (i in 1 until values.size) {
result = operation(result, values[i])
}
return result
}
// 条件计算(if表达式)
fun calculateWithTax(
amount: Double,
includesTax: Boolean = false,
taxRate: Double = 0.1
): Double {
return if (includesTax) {
amount
} else {
amount * (1 + taxRate)
}
}
}
// 使用示例
fun main() {
val calc = Calculator()
// 1. 基本运算(when表达式)
println("10 + 5 = ${calc.calculate(10.0, 5.0, Operation.ADD)}")
println("10 - 5 = ${calc.calculate(10.0, 5.0, Operation.SUBTRACT)}")
println("10 * 5 = ${calc.calculate(10.0, 5.0, Operation.MULTIPLY)}")
println("10 / 5 = ${calc.calculate(10.0, 5.0, Operation.DIVIDE)}")
// 2. 自定义运算(Lambda)
val avg = calc.calculateCustom(10.0, 20.0) { a, b -> (a + b) / 2 }
println("Average: $avg") // 15.0
val max = calc.calculateCustom(10.0, 20.0) { a, b ->
if (a > b) a else b
}
println("Max: $max") // 20.0
// 3. 批量计算
val sum = calc.batchCalculate(1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0) { a, b -> a + b }
println("Sum: $sum") // 15.0
val product = calc.batchCalculate(2.0, 3.0, 4.0) { a, b -> a * b }
println("Product: $product") // 24.0
// 4. 条件计算(默认参数 + 命名参数)
println("不含税: ${calc.calculateWithTax(100.0)}") // 110.0
println("含税: ${calc.calculateWithTax(100.0, includesTax = true)}") // 100.0
println("自定义税率: ${calc.calculateWithTax(100.0, taxRate = 0.15)}") // 115.0
// 5. 链式计算(函数引用)
val numbers = listOf(1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0)
val sumUsingFilter = numbers
.filter { it > 2.0 } // [3.0, 4.0, 5.0]
.map { it * 2 } // [6.0, 8.0, 10.0]
.reduce { acc, value -> acc + value } // 24.0
println("Filtered sum: $sumUsingFilter")
}代码亮点分析:
- when表达式:简洁的运算类型选择
- Lambda参数:支持自定义运算逻辑
- 默认参数 + 命名参数:灵活的函数调用
- vararg:支持任意数量的参数
- 高阶函数:函数作为参数传递
- 链式调用 :
filter→map→reduce
常见问题
Q1: if表达式必须有else吗?
kotlin
// 作为表达式时,必须有else
val result = if (condition) "yes" else "no" // ✅
// 编译错误:缺少else
// val result = if (condition) "yes" // ❌
// 作为语句时,可以没有else
if (condition) {
println("yes")
} // ✅Q2: when什么时候需要else?
kotlin
// 1. 作为表达式时,如果未穷尽所有可能,需要else
val result = when (value) {
1 -> "one"
2 -> "two"
else -> "other" // 必须有else
}
// 2. 枚举类型穷尽所有情况时,不需要else
enum class Color { RED, GREEN, BLUE }
val colorName = when (color) {
Color.RED -> "红色"
Color.GREEN -> "绿色"
Color.BLUE -> "蓝色"
// 不需要else,已穷尽
}
// 3. 作为语句时,可以没有else
when (command) {
"start" -> start()
"stop" -> stop()
// 不需要else
}Q3: Lambda里的return会返回什么?
kotlin
fun example() {
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// 错误:return会退出example函数,不是退出Lambda
numbers.forEach {
if (it == 3) return // 退出example函数!
println(it)
}
println("This won't print if 3 is in list")
}
// 正确:使用return@forEach标签返回Lambda
fun example2() {
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
numbers.forEach {
if (it == 3) return@forEach // 只退出当前Lambda
println(it)
}
println("This will always print") // 输出:1 2 4 5 This will always print
}Q4: 什么时候用for,什么时候用forEach?
| 场景 | 推荐 | 原因 |
|---|---|---|
| 简单遍历 | forEach |
更简洁,函数式风格 |
| 需要break/continue | for |
forEach不支持break |
| 需要索引 | forEachIndexed 或 for |
都可以,看个人喜好 |
| 性能关键 | for |
避免Lambda开销 |
| 链式操作 | 集合操作符 | 如map、filter |
kotlin
// forEach:简洁
numbers.forEach { println(it) }
// for:需要break
for (num in numbers) {
if (num > 5) break
println(num)
}
// forEachIndexed:需要索引
numbers.forEachIndexed { index, value ->
println("$index: $value")
}总结
今天我们学习了Kotlin控制流和函数的核心知识:
- if表达式:不仅是语句,更是表达式,有返回值
- when表达式:强大的模式匹配,支持多值、范围、类型检查
- for循环:灵活的迭代方式,支持范围、集合、步长
- 函数:默认参数、命名参数、可变参数,让函数调用更灵活
- Lambda表达式:匿名函数的简洁写法,函数式编程的基石
- 高阶函数:函数作为参数,实现更灵活的代码
最重要的收获 :Kotlin的控制流不是简单的语法糖,而是将表达式思维融入语言设计。这让代码更简洁、更表达性、更函数式。
下一篇文章,我们将学习类与对象基础,包括类定义、构造函数、属性、数据类等。这将让你开始面向对象编程的Kotlin之旅。
练习题
巩固今天的知识,尝试完成以下练习:
- when表达式练习:
kotlin
// 实现一个函数,根据HTTP状态码返回描述
fun getHttpStatusDescription(code: Int): String {
// 使用when表达式实现
// 200 -> "OK"
// 201 -> "Created"
// 400 -> "Bad Request"
// 401 -> "Unauthorized"
// 404 -> "Not Found"
// 500 -> "Internal Server Error"
// 其他 -> "Unknown Status"
}- Lambda练习:
kotlin
// 实现一个高阶函数,对列表进行条件过滤和转换
fun transformList(
numbers: List<Int>,
filter: (Int) -> Boolean,
transform: (Int) -> Int
): List<Int> {
// 使用filter和map实现
}
// 使用示例
val result = transformList(
listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6),
filter = { it % 2 == 0 }, // 只保留偶数
transform = { it * it } // 平方
)
// 结果应该是 [4, 16, 36]- 综合练习:
kotlin
// 实现一个成绩管理系统
data class Student(val name: String, val score: Int)
fun analyzeScores(students: List<Student>) {
// 1. 统计各等级人数(A: 90+, B: 80-89, C: 70-79, D: 60-69, F: <60)
// 2. 找出最高分和最低分的学生
// 3. 计算平均分
// 4. 输出所有不及格学生的姓名
}答案在文章评论区,或者你可以在Kotlin Playground中自己尝试!
系列文章导航:
- 👉 上一篇: 变量与数据类型:从val/var到空安全的第一课
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,欢迎点赞、收藏、分享!有任何问题或建议,欢迎在评论区留言讨论。让我们一起学习,一起成长!
也欢迎访问我的个人主页发现更多宝藏资源