day06-SpringDI 依赖注入
前言:2026新年第一篇文章,首先祝福大家,马年大吉,马年吉祥。开始继续编写源码...
1、依赖注入的流程

2、寻找注入点
创建bean的过程中,Spring会利用
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#buildAutowiringMetadata() 找出注入点,并缓存
- 遍历所有类的属性filed【字段扫描】
- 查看Field上面是否存在@Autowired、@Value、@Inject中注解任何一个
- 如果 Field是static,则不自动注入
- 获取@Autowired注入点的request的数值
- 为true 构建AutowiredFieldElement 对象,并添加到currElements里面
- 遍历 当前类所有的方法 Method 【方法扫描】
- 判断是否是桥接方法
- 不是桥接方法
- 直接返回
- 不是桥接方法
- 是桥接方法
- 检查是否缓存
- 没有缓存进行查找
- 收集声明类中所有方法名和参数数量与桥接方法相同的方法(通过isBridgedCandidateFor方法过滤)
- 如果只有一个候选方法,那么就是它;如果有多个,则通过searchCandidates方法进一步筛选
- 如果没有找到桥接方法,返回桥接方法本身
- 没有缓存进行查找
- 检查是否缓存
- 判断当前方法Method是否存在@Autowired、@Value、@Inject中注解任何一个
- 如果方法不是statis,则注入
- 获取@Autowired 中的required属性的值
- 构建AutowiredMethodElement属性,并添加到 currElements集合中
c
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
// 如果一个Bean的类型是String...,那么则根本不需要进行依赖注入
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历targetClass中的所有Field
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
// field上是否存在@Autowired、@Value、@Inject中的其中一个
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
// static filed不是注入点,不会进行自动注入
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
// 构造注入点
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
// 遍历targetClass中的所有Method
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
// method上是否存在@Autowired、@Value、@Inject中的其中一个
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
// static method不是注入点,不会进行自动注入
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
// set方法最好有入参
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
// 父类的注入点会先处理(插入表头)
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
// 保证注入顺序:父类字段|方法 -> 子类字段|方法
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}关键特性:
1、继承层次扫描
c
// 父类的注入点会先处理(插入表头)
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
// 保证注入顺序:父类字段|方法 -> 子类字段|方法
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();2、桥接方法处理
c
// 为什么需要处理桥接方法:
// 1. 泛型方法在编译时会生成桥接方法
// 2. 注解可能只存在于原始方法上
// 3. 使用BridgeMethodResolver确保找到正确的注解方法
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);3、性能优化
c
// 1. 预先过滤候选类(避免不必要的扫描)
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
// 2. 只扫描本地字段/方法,父类在后续循环中处理
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, ...)
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, ...)桥接
c
interface Converter<S, T> {
T convert(S source);
}
c
public class StringToInteger implements Converter<String, Integer> {
@Override
public Integer convert(String source) {
return Integer.valueOf(source);
}
}字节码
c
// class version 52.0 (52)
// access flags 0x21
// signature Ljava/lang/Object;Lcom/xx/service/Converter<Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/Integer;>;
// declaration: com/xxx/service/StringToInteger implements com.xxx.service.Converter<java.lang.String, java.lang.Integer>
public class com/xxx/service/StringToInteger implements com/xxx/service/Converter {
// compiled from: StringToInteger.java
// access flags 0x1
public <init>()V
L0
LINENUMBER 3 L0
ALOAD 0
INVOKESPECIAL java/lang/Object.<init> ()V
RETURN
L1
LOCALVARIABLE this Lcom/xxxx/service/StringToInteger; L0 L1 0
MAXSTACK = 1
MAXLOCALS = 1
// access flags 0x1
public convert(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Integer;
L0
LINENUMBER 6 L0
ALOAD 1
INVOKESTATIC java/lang/Integer.valueOf (Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Integer;
ARETURN
L1
LOCALVARIABLE this Lcom/xxx/service/StringToInteger; L0 L1 0
LOCALVARIABLE source Ljava/lang/String; L0 L1 1
MAXSTACK = 1
MAXLOCALS = 2
// access flags 0x1041
public synthetic bridge convert(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
L0
LINENUMBER 3 L0
ALOAD 0
ALOAD 1
CHECKCAST java/lang/String
INVOKEVIRTUAL com/xx/service/StringToInteger.convert (Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Integer;
ARETURN
L1
LOCALVARIABLE this Lcom/xx/service/StringToInteger; L0 L1 0
MAXSTACK = 2
MAXLOCALS = 2
}字节码有2个convert
public convert(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Integer;
public synthetic bridge convert(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
spring当遍历桥接时候会找到原方法。
3、Spring在AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessProperties() 字段注入

第一步:遍历注入点进行注入
属性填充阶段有入口org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties
方法,找到所有的注入点
注入点找逻辑同上。
第二步:封装 DependencyDescriptor
入口:
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata#inject
核心代码如下:
c
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());这里将Java反射的 Field 对象、以及 @Autowired 的 required 属性等信息封装成一个
DependencyDescriptor 对象。
第三步: beanFactory.resolveDependency() 解析依赖
入口:
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory#resolveDependency(org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DependencyDescriptor, java.lang.String, java.util.Set<java.lang.String>, org.springframework.beans.TypeConverter)
核心方法
c
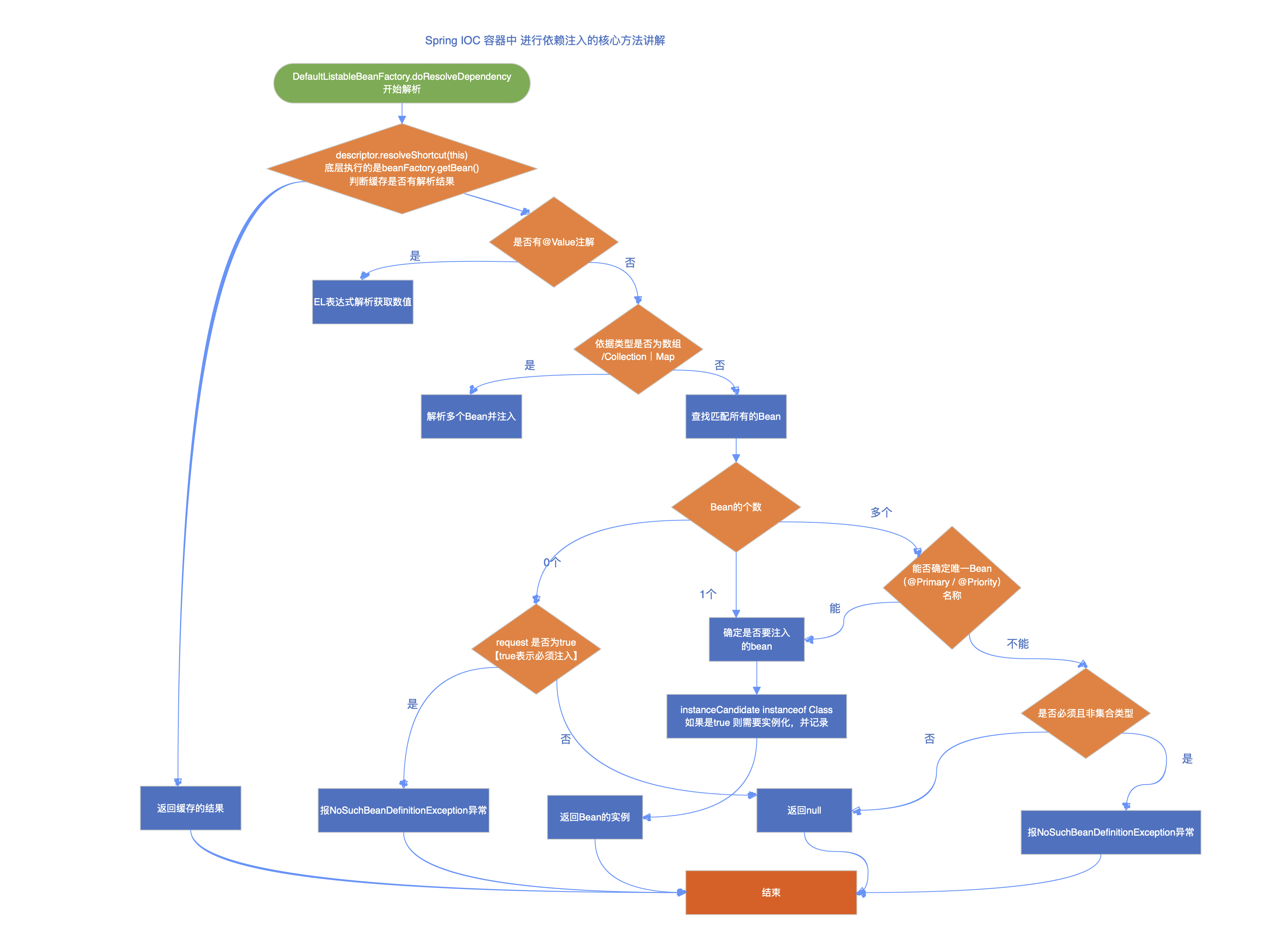
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);解析流程:
- resolveDependency() 方法会处理一些特殊类型比如(Optional、ObjectFactroy或者ObjectProvider,并且检查@Lazy注解 如果没有特殊处理走 doResolveDependency() 方法 )主要负责功能如下:
- 检查缓存:通过descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
- 处理@Value注解,如果有使用则这里进行解析
- 按照类型进行获取Beans,调用findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor) 获取所有匹配的数据
- 确定唯一Bean:如果找到多个,则通过@Primary、@Priority 属性匹配规则确定唯一值
c
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);第四步:创建缓存 ShortcutDependencyDescriptor
解析完成后,为了后续提高原型Bean的场景,会进行缓存
位置:org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.ShortcutDependencyDescriptor
c
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
Object cachedFieldValue = null;
if (value != null || this.required) {
cachedFieldValue = desc;
// ... 注册依赖关系 ...
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
// 构建缓存
cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
this.cachedFieldValue = cachedFieldValue;
this.cached = true;
}
}逻辑判断:如果(!this.cached) ,并且成功找到唯一 Bean 则会封装一个 ShortcutDependencyDescriptor 对象细节如下resolveShortcut 方法重写,能够直接返回之前解析好的Bean的名称。
c
private static class ShortcutDependencyDescriptor extends DependencyDescriptor {
private final String shortcut;
private final Class<?> requiredType;
public ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(DependencyDescriptor original, String shortcut, Class<?> requiredType) {
super(original);
this.shortcut = shortcut;
this.requiredType = requiredType;
}
// 会对 resolveShortcut 方法重写
@Override
public Object resolveShortcut(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
return beanFactory.getBean(this.shortcut, this.requiredType);
}
}第五步:反射赋值
查到到的 Bean实例反射设置到目标字段中。
入口:org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils#makeAccessible(java.lang.reflect.Field)
c
if (value != null) {
// 反射赋值
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}字段和方法的区别:
统一入口地方:org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement#inject
| 注入类型 | 核心处理类 | 依赖描述符封装来源 |
|---|---|---|
| 字段注入 | AutowiredFieldElement | 直接由 Field 对象创建 DependencyDescriptor。 |
| 方法注入 | AutowiredMethodElement | 遍历方法的每个参数,为每个 MethodParameter 对象创建 DependencyDescriptor。 |
| SpringIOC容器的核心方法 | ||
| DefaultListableBeanFactory.doResolveDependency | ||
| 流程图。 |
4、@Resource 注解
1、@Autowired和@Resource的区别
| @Autowired | @Resource | |
|---|---|---|
| 字段加static | 不会报错 | 会报错IllegalStateException 异常 |
| 包位置 | org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation | javax.annotation (Java EE)jakarta.annotation (Jakarta EE) |
| 默认的注入类型 | 按类型(byType) | 按名称 (byName) |
| 是否必须 | required=true (默认) | 总是必须 |
| 名称指定 | 需要结合 @Qualifier | 使用 name 属性 |
| 参数注入 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 数据来源 | Spring 框架原生注解 | JSR-250 (Java 标准) |
2、@Resource 执行流程如下:
c
-- 属性填充后
org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties
↓
↓
-- 寻找注入点
org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#buildResourceMetadata
↓
↓
-- 组装bean的名称,bean的类型,如果指定类型,校验bean的类型
org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.ResourceElement#ResourceElement
↓
↓
-- 遍历每一个注入点
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement#inject
↓
↓
org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.ResourceElement#getResourceToInject
↓
↓
org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#autowireResource3、@Resource流程图详解
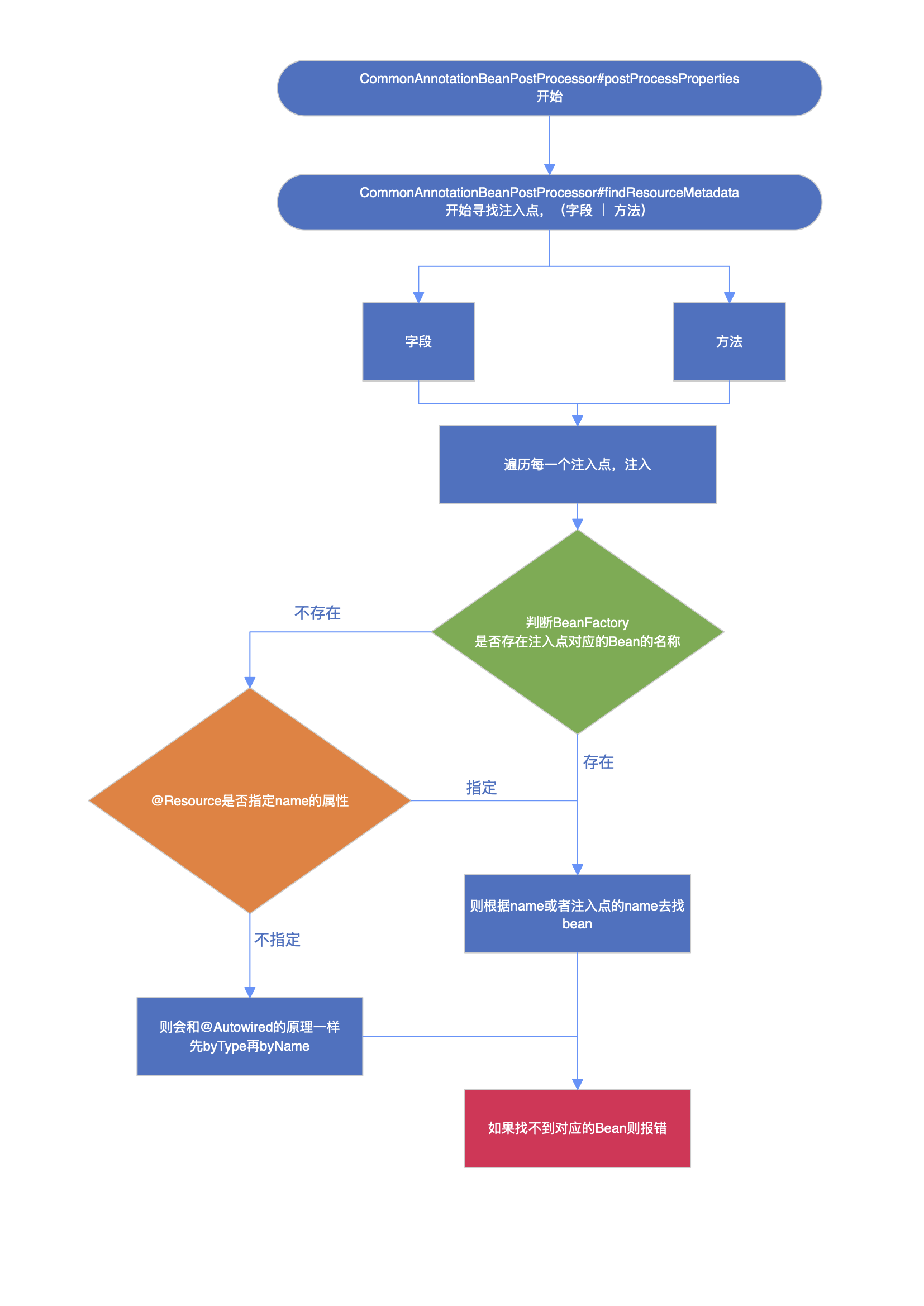
4、核心源码讲解:
c
/**
*factory:Spring 容器,负责查找和提供 Bean。
*element: 封装了被 @Resource 注解的字段或方法的所有信息,
*requestingBeanName:当前正在被注入的、发出依赖请求的那个 Bean 的名字。
*/
protected Object autowireResource(BeanFactory factory, LookupElement element, @Nullable String requestingBeanName)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
Object resource;
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames;
String name = element.name;
if (factory instanceof AutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory = (AutowireCapableBeanFactory) factory;
DependencyDescriptor descriptor = element.getDependencyDescriptor();
// 主要判断是否会退到"按照类型查找"
if (this.fallbackToDefaultTypeMatch && element.isDefaultName && !factory.containsBean(name)) {
autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 路径A:根据类型查找
resource = beanFactory.resolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, null);
if (resource == null) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(element.getLookupType(), "No resolvable resource object");
}
}
else {
// 路径B:按照名称查找,如果有名称,根据名称查找bean
resource = beanFactory.resolveBeanByName(name, descriptor);
autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);
}
}
else {
resource = factory.getBean(name, element.lookupType);
autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);
}
if (factory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {
ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = (ConfigurableBeanFactory) factory;
for (String autowiredBeanName : autowiredBeanNames) {
if (requestingBeanName != null && beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName)) {
beanFactory.registerDependentBean(autowiredBeanName, requestingBeanName);
}
}
}
return resource;
}喜欢我的文章记得点个在看,或者点赞,持续更新中ing...