模型架构
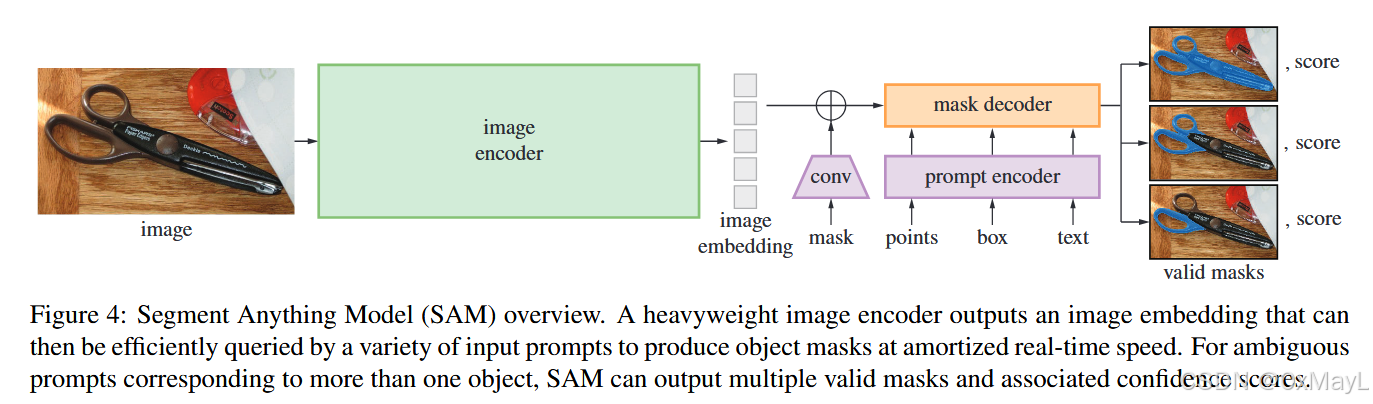
前向过程
输入参数的含义
- 视觉编码器:输入分辨率为1024x1024,下采样16倍,得到64x64分辨率的图像,然后通道维度是256
- 点提示:被编码为特定位置(x,y)的位置编码+一个可以学习的表示前景/背景的嵌入(类似CLS token),维度为256
- 锚框提示:被编码为左上角的位置编码+一个可以学习的表示左上角的嵌入 ,右下角的位置编码+一个可以学习的表示表示右下角的嵌入,维度均为256
- 掩码提示:输入可能分辨率不一致,下采样至64x64即可
- 文本嵌入:训练时,被裁剪区域的output token(CLS)会被当作点/框提示拼接到一起 ,推理时,CLIP文本编码器的输出[EOS]会被拼接到一起。
- 掩膜与输入图像叠加(分辨率都为64x64)
解码过程
- 点,框都是prompt tokens
- output tokens包括5个:1个用于预测掩膜iou,3个用于预测掩膜,1个用于预测多个prompts下的掩膜
- output tokens与prompt tokens拼接在一起,分别与image嵌入进行交叉注意力(相互进行),然后输出更新后的image嵌入和output tokens
- 注意:image嵌入已经叠加了掩膜嵌入!!!
产生掩膜和预测分数
- 第一个output进行mlp负责预测后面3个掩膜的IoU值,用于置信度计算
- 每一个output token进行mlp后,与上采样后的image嵌入进行相似度计算,得到最终的掩膜
- 最后一个output token仅在提供多个prompt时才会输出
总体架构如下:
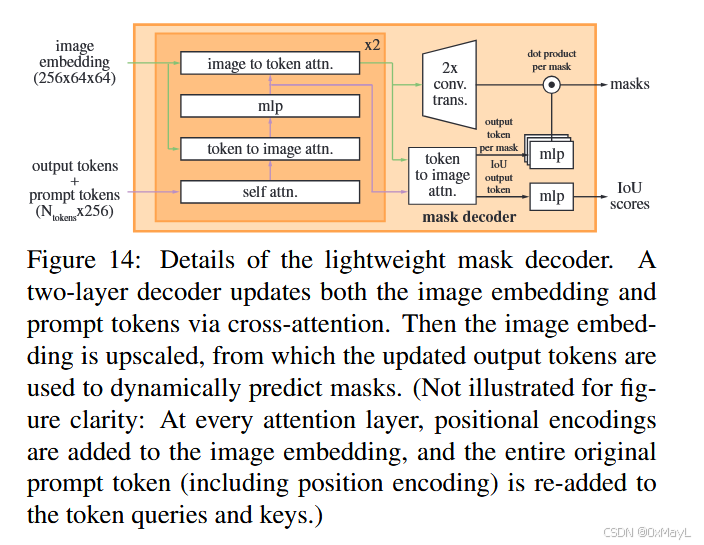
输出的是一个二值的掩膜(类无关)!!!
output token经过mlp后维度为1xC,与上采样后的image嵌入(HW*C)进行相似度计算,最终的掩膜是(H,W),也就是二值的。
方法
图像编码器
Image encoder. Motivated by scalability and powerful pretraining methods, we use an MAE [47] pre-trained Vision Transformer (ViT) [33] minimally adapted to process high resolution inputs [62]. The image encoder runs once per image and can be applied prior to prompting the model.
使用MAE预训练的ViT-H作为图像编码器
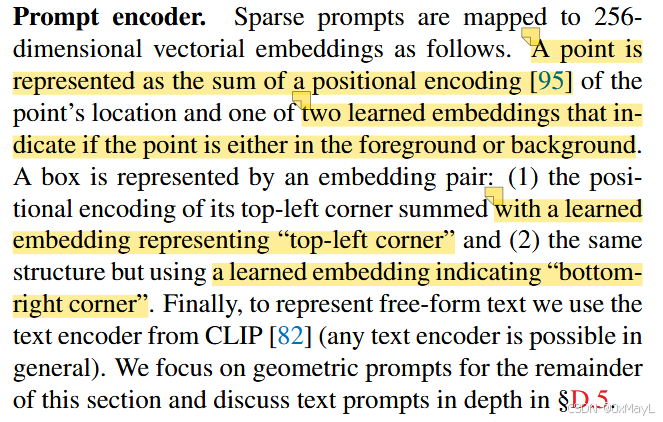
提示编码器
- 文本由CLIP处理
- 点和框(x,y)坐标使用位置编码+学习到的嵌入确定
- 掩膜比较复杂:和原始image嵌入逐元素求和得到
Prompt encoder. We consider two sets of prompts: sparse (points, boxes, text) and dense (masks). We represent points and boxes by positional encodings [95] summed with learned embeddings for each prompt type and free-form text with an off-the-shelf text encoder from CLIP [82]. Dense prompts (i.e., masks) are embedded using convolutions and summed element-wise with the image embedding.
掩膜解码器
简单来说,掩膜解码器的主要思想是DETR (端到端目标检测,使用查询向量,匈牙利匹配等算法直接生成锚框)和MaskFormer(DETR思想在语义分割领域的直接应用,简单来说就是将特征图放大后进行匹配得到掩膜)
Mask decoder. The mask decoder efficiently maps the image embedding, prompt embeddings, and an output token to a mask. This design, inspired by [14, 20], employs a modification of a Transformer decoder block [103] followed by a dynamic mask prediction head. Our modified decoder block uses prompt self-attention and cross-attention in two directions (prompt-to-image embedding and vice-versa) to update all embeddings. After running two blocks, we upsample the image embedding and an MLP maps the output token to a dynamic linear classifier, which then computes the mask foreground probability at each image location.
提示二义性的方法
- 根据一个提示会输出3个掩膜 ,模型除了输出掩膜,还会输出其置信分数。
- 训练过程中,只反向传播最小的损失。
- 多个prompt的条件下,仅输出一个掩膜
Resolving ambiguity. With one output, the model will average multiple valid masks if given an ambiguous prompt. To address this, we modify the model to predict multiple output masks for a single prompt (see Fig. 3). We found 3 mask outputs is sufficient to address most common cases (nested masks are often at most three deep: whole, part, and subpart). During training, we backprop only the minimum loss [15, 45, 64] over masks. To rank masks, the model predicts a confidence score (i.e., estimated IoU) for each mask.
损失和训练
Losses and training. We supervise mask prediction with the linear combination of focal loss [65] and dice loss [73] used in [14]. We train for the promptable segmentation task using a mixture of geometric prompts (for text prompts see §7.5). Following [92, 37], we simulate an interactive setup by randomly sampling prompts in 11 rounds per mask, allowing SAM to integrate seamlessly into our data engine.
损失和培训。我们使用[14]中使用的焦点损失[65]和骰子损失[73]的线性组合来监督掩模预测。我们使用几何提示的混合来训练可提示的分割任务(有关文本提示,请参见第 7.5 节)。遵循 [92, 37],我们通过在每个掩码 11 轮中随机采样提示来模拟交互式设置,从而使 SAM 能够无缝集成到我们的数据引擎中。
实现
Implementation. Unless otherwise specified: (1) SAM uses an MAE [47] pre-trained ViT-H [33] image encoder and (2) SAM was trained on SA-1B, noting that this dataset includes only automatically generated masks from the final stage of our data engine. For all other model and training details, such as hyperparameters, refer to §A.
SAM的实验(展示SAM的用法)
示例分割
使用目标检测器生成的锚框作为SAM的提示
Approach. Moving to higher-level vision, we use SAM as the segmentation module of an instance segmenter. The implementation is simple: we run a object detector (the ViTDet used before) and prompt SAM with its output boxes. This illustrates composing SAM in a larger system.
文本到图像分割
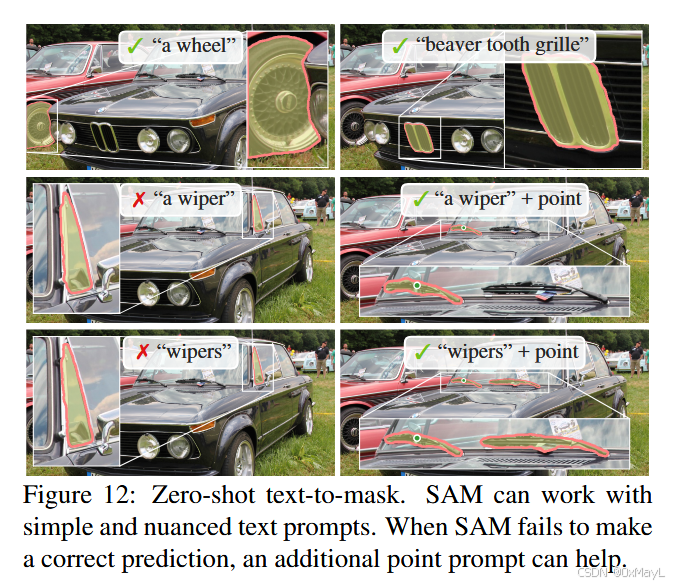
7.5. Zero-Shot Text-to-Mask Approach. Finally, we consider an even higher-level task: segmenting objects from free-form text. This experiment is a proof-of-concept of SAM's ability to process text prompts. While we used the exact same SAM in all prior experiments, for this one SAM's training procedure is modified to make it text-aware, but in a way that does not require new text annotations. Specifically, for each manually collected mask with area larger than 1002 we extract the CLIP image embedding. Then, during training, we prompt SAM with the extracted CLIP image embeddings as its first interaction. The key observation here is that because CLIP's image embeddings are trained to align with its text embeddings, we can train with image embeddings, but use text embeddings for inference. That is, at inference time we run text through CLIP's text encoder and then give the resulting text embedding as a prompt to SAM (see §D.5 for details)
假设:CLIP的视觉和文本特征是在同一个语义空间
训练过程不需要文本特征(也没有那么多文本特征可以用),只需要将CLIP对某一区域的视觉编码作为提示(类似密集提示那样)直接给SAM就好 、
推理过程中,基于上述假设,我们将CLIP本来对某一区域的视觉特征,替换为文本嵌入,也能使SAM准确地分割。
实现
直接裁剪特定大小的区域,提取CLIP的视觉特征,送到SAM中作为提示进行训练。
原文:During inference we use the CLIP text encoder without any modifications to create a prompt for SAM. We rely on the fact that text and image embeddings are aligned by CLIP, which allows us to train without any explicit text supervision while using text-based prompts for inference.
翻译:推理时,我们直接使用未经任何修改的 CLIP 文本编码器来为 SAM 生成 prompt 。我们依赖 CLIP 将文本与图像嵌入对齐这一事实:因此训练时不需要任何显式文本监督,但推理时却可以使用文本 prompt。
事实
直接使用文本编码效果比较一般,但是文本编码+对应的点效果就比较好了。
这可能暗示作者的设计可能不明显,在SAM的提示中,点的作用更大!