引言:那个让我重构的千行数据处理代码
还记得刚开始用Kotlin时,我接手了一个数据处理模块。代码是典型的Java风格,充满了for循环和临时变量:
java
// Java风格 - 冗长的数据处理
List<User> activeAdultUsers = new ArrayList<>();
for (User user : users) {
if (user.isActive() && user.getAge() >= 18) {
activeAdultUsers.add(user);
}
}
List<String> userNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (User user : activeAdultUsers) {
userNames.add(user.getName());
}
Collections.sort(userNames);
// 取前10个
List<String> top10 = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(10, userNames.size()); i++) {
top10.add(userNames.get(i));
}30多行代码,创建了4个临时变量,逻辑分散在多个循环中,维护起来令人头疼。
同事用Kotlin重写后,我惊呆了:
kotlin
// Kotlin风格 - 函数式链式调用
val top10 = users
.filter { it.isActive && it.age >= 18 }
.map { it.name }
.sorted()
.take(10)仅仅5行代码,没有临时变量,逻辑清晰流畅,可读性极强!这就是Kotlin集合框架的魔法。
今天,我们就来深入探索这个强大而优雅的集合系统。
Kotlin集合体系概览
Kotlin的集合分为两大类:不可变集合 (只读)和可变集合。
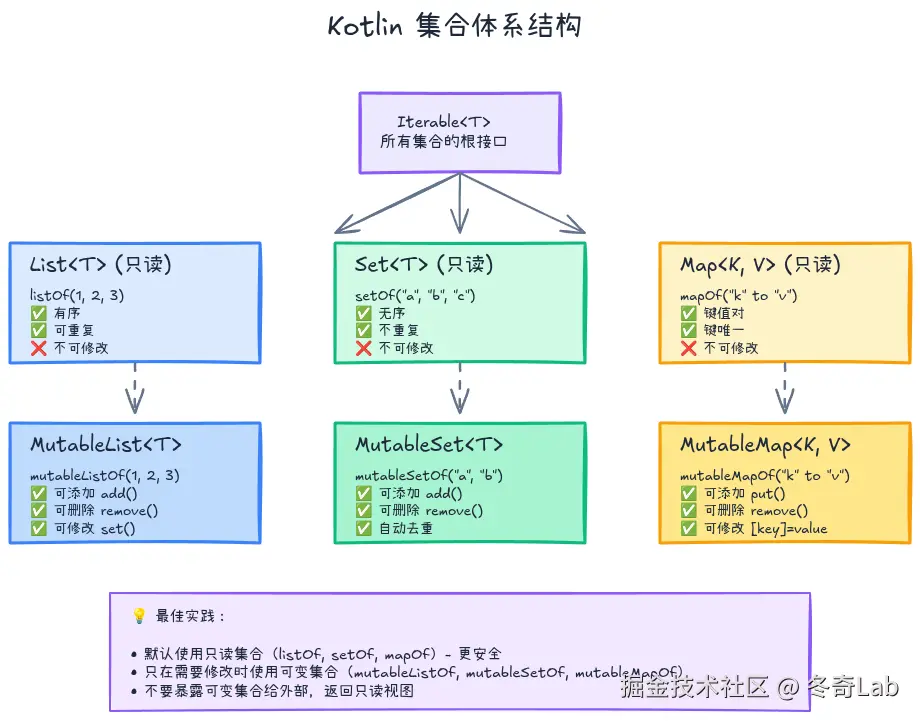
不可变集合 vs 可变集合
kotlin
// 不可变集合(只读)
val readOnlyList = listOf(1, 2, 3)
val readOnlySet = setOf("a", "b", "c")
val readOnlyMap = mapOf("key1" to "value1", "key2" to "value2")
// readOnlyList.add(4) // ❌ 编译错误:没有add方法
// 可变集合
val mutableList = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3)
val mutableSet = mutableSetOf("a", "b", "c")
val mutableMap = mutableMapOf("key1" to "value1")
mutableList.add(4) // ✅ OK
mutableSet.remove("a") // ✅ OK
mutableMap["key3"] = "value3" // ✅ OK**最佳实践**:默认使用不可变集合(`listOf`、`setOf`、`mapOf`),只有在需要修改时才使用可变集合。这能避免意外修改,提高代码安全性。
集合的类型层级
| 接口 | 不可变实现 | 可变实现 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
List |
listOf() |
mutableListOf() |
有序、可重复 |
Set |
setOf() |
mutableSetOf() |
无序、不重复 |
Map |
mapOf() |
mutableMapOf() |
键值对、键唯一 |
List:有序集合
创建List
kotlin
// 不可变List
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
val names = listOf("Alice", "Bob", "Charlie")
// 可变List
val mutableNumbers = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3)
val arrayList = ArrayList<Int>() // Java的ArrayList
// 空List
val emptyList = emptyList<Int>()
val emptyList2 = listOf<Int>()
// 指定大小的List
val zeros = List(5) { 0 } // [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
val squares = List(5) { it * it } // [0, 1, 4, 9, 16]List常用操作
kotlin
val list = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// 访问元素
println(list[0]) // 1(使用下标)
println(list.first()) // 1
println(list.last()) // 5
println(list.get(2)) // 3
// 安全访问
println(list.getOrNull(10)) // null(越界返回null)
println(list.getOrElse(10) { 0 }) // 0(越界返回默认值)
// 查询
println(list.contains(3)) // true
println(3 in list) // true(更简洁)
println(list.indexOf(3)) // 2
println(list.isEmpty()) // false
println(list.size) // 5
// 子列表
println(list.subList(1, 4)) // [2, 3, 4](包含start,不包含end)
println(list.slice(1..3)) // [2, 3, 4]
println(list.take(3)) // [1, 2, 3](前3个)
println(list.takeLast(2)) // [4, 5](后2个)
println(list.drop(2)) // [3, 4, 5](跳过前2个)可变List操作
kotlin
val list = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3)
// 添加
list.add(4) // [1, 2, 3, 4]
list.add(0, 0) // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4](在索引0处插入)
list.addAll(listOf(5, 6)) // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
// 删除
list.remove(0) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6](删除值为0的元素)
list.removeAt(0) // [2, 3, 4, 5, 6](删除索引0的元素)
list.removeAll { it % 2 == 0 } // [3, 5](删除偶数)
// 修改
list[0] = 10 // [10, 5]
list.set(1, 20) // [10, 20]
// 排序
list.sort() // 原地排序
list.reverse() // 原地翻转Set:无重复集合
kotlin
// 创建Set
val set = setOf(1, 2, 3, 2, 1) // 自动去重:{1, 2, 3}
val mutableSet = mutableSetOf("a", "b", "c")
// Set操作
println(set.contains(2)) // true
println(2 in set) // true
// 可变Set操作
mutableSet.add("d") // {a, b, c, d}
mutableSet.remove("a") // {b, c, d}
mutableSet.addAll(listOf("e", "f")) // {b, c, d, e, f}
// 集合运算
val set1 = setOf(1, 2, 3)
val set2 = setOf(3, 4, 5)
println(set1 union set2) // {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}(并集)
println(set1 intersect set2) // {3}(交集)
println(set1 subtract set2) // {1, 2}(差集)**使用场景**:当你需要确保元素唯一性时,使用Set。例如:去重、成员检查、集合运算。
Map:键值对集合
创建Map
kotlin
// 不可变Map
val map = mapOf(
"name" to "Alice",
"age" to 25,
"city" to "Beijing"
)
// 可变Map
val mutableMap = mutableMapOf(
1 to "one",
2 to "two"
)
// 空Map
val emptyMap = emptyMap<String, Int>()**to的秘密**:`to`是Kotlin的中缀函数,`"key" to "value"`实际上创建了一个`Pair("key", "value")`对象。
Map常用操作
kotlin
val map = mapOf(
"name" to "Alice",
"age" to 25,
"city" to "Beijing"
)
// 访问元素
println(map["name"]) // "Alice"
println(map.get("name")) // "Alice"
println(map["country"]) // null(键不存在)
println(map.getOrDefault("country", "Unknown")) // "Unknown"
println(map.getValue("name")) // "Alice"(键不存在会抛异常)
// 查询
println(map.containsKey("name")) // true
println("name" in map) // true
println(map.containsValue("Alice")) // true
println(map.isEmpty()) // false
println(map.size) // 3
// 遍历
for ((key, value) in map) {
println("$key: $value")
}
map.forEach { (key, value) ->
println("$key: $value")
}
// 获取键和值
println(map.keys) // [name, age, city]
println(map.values) // [Alice, 25, Beijing]
println(map.entries) // [name=Alice, age=25, city=Beijing]可变Map操作
kotlin
val map = mutableMapOf(
"name" to "Alice",
"age" to 25
)
// 添加/修改
map["city"] = "Beijing" // 添加新键值对
map["age"] = 26 // 修改已有键的值
map.put("email", "alice@example.com")
map.putAll(mapOf("country" to "China", "job" to "Engineer"))
// 删除
map.remove("email") // 删除键为email的条目
map.remove("name", "Bob") // 仅当键为name且值为Bob时删除(返回false)
// 条件操作
map.putIfAbsent("name", "Bob") // name已存在,不会修改集合操作符:函数式编程的精华
这是Kotlin集合最强大的部分!通过链式调用操作符,可以用极其简洁的代码完成复杂的数据处理。
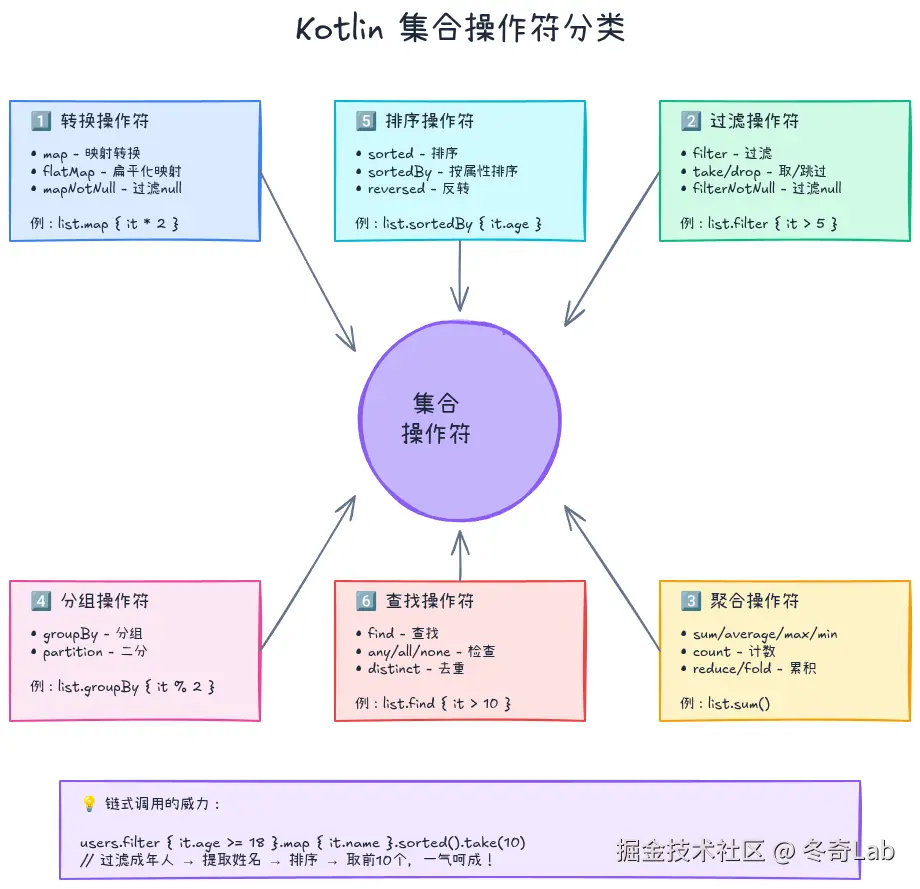
转换操作符
map - 映射转换
将集合中的每个元素转换为另一种形式。
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// 转换为平方
val squares = numbers.map { it * it }
println(squares) // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
// 转换为字符串
val strings = numbers.map { "Number $it" }
println(strings) // [Number 1, Number 2, Number 3, Number 4, Number 5]
// 实际应用:提取对象属性
data class User(val name: String, val age: Int)
val users = listOf(
User("Alice", 25),
User("Bob", 30),
User("Charlie", 35)
)
val names = users.map { it.name }
println(names) // [Alice, Bob, Charlie]mapNotNull - 映射并过滤null
kotlin
val list = listOf("1", "2", "abc", "3")
val numbers = list.mapNotNull { it.toIntOrNull() }
println(numbers) // [1, 2, 3]("abc"被过滤掉)flatMap - 扁平化映射
将每个元素映射为一个集合,然后合并所有集合。
kotlin
val list = listOf(
listOf(1, 2, 3),
listOf(4, 5),
listOf(6, 7, 8)
)
// map vs flatMap
val mapped = list.map { it.map { num -> num * 2 } }
println(mapped) // [[2, 4, 6], [8, 10], [12, 14, 16]](嵌套列表)
val flatMapped = list.flatMap { it.map { num -> num * 2 } }
println(flatMapped) // [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16](扁平列表)
// 实际应用:一对多关系
data class Department(val name: String, val employees: List<String>)
val departments = listOf(
Department("IT", listOf("Alice", "Bob")),
Department("HR", listOf("Charlie", "David"))
)
val allEmployees = departments.flatMap { it.employees }
println(allEmployees) // [Alice, Bob, Charlie, David]过滤操作符
filter - 过滤
保留符合条件的元素。
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
// 过滤偶数
val evens = numbers.filter { it % 2 == 0 }
println(evens) // [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
// 过滤奇数
val odds = numbers.filter { it % 2 != 0 }
println(odds) // [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
// 实际应用:过滤用户
val users = listOf(
User("Alice", 25),
User("Bob", 17),
User("Charlie", 30)
)
val adults = users.filter { it.age >= 18 }
println(adults) // [User(Alice, 25), User(Charlie, 30)]filterNot - 反向过滤
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
val notEvens = numbers.filterNot { it % 2 == 0 }
println(notEvens) // [1, 3, 5]filterNotNull - 过滤null
kotlin
val list = listOf(1, null, 2, null, 3)
val nonNulls = list.filterNotNull()
println(nonNulls) // [1, 2, 3]take / drop - 取/跳过元素
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
println(numbers.take(3)) // [1, 2, 3](前3个)
println(numbers.takeLast(3)) // [8, 9, 10](后3个)
println(numbers.drop(3)) // [4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10](跳过前3个)
println(numbers.dropLast(3)) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7](跳过后3个)
// 条件take/drop
println(numbers.takeWhile { it < 5 }) // [1, 2, 3, 4]
println(numbers.dropWhile { it < 5 }) // [5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]聚合操作符
sum / average / max / min
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
println(numbers.sum()) // 15
println(numbers.average()) // 3.0
println(numbers.max()) // 5(Kotlin 1.4+已弃用,使用maxOrNull())
println(numbers.maxOrNull()) // 5
println(numbers.minOrNull()) // 1count - 计数
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
println(numbers.count()) // 10(总数)
println(numbers.count { it % 2 == 0 }) // 5(偶数个数)reduce / fold - 累积计算
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// reduce: 从第一个元素开始累积
val sum = numbers.reduce { acc, num -> acc + num }
println(sum) // 15
// fold: 指定初始值
val sumWithInitial = numbers.fold(100) { acc, num -> acc + num }
println(sumWithInitial) // 115(100 + 15)
// 实际应用:计算总价
data class Product(val name: String, val price: Double)
val cart = listOf(
Product("Book", 29.9),
Product("Pen", 5.5),
Product("Notebook", 15.0)
)
val totalPrice = cart.fold(0.0) { total, product -> total + product.price }
println("Total: $$totalPrice") // Total: $50.4分组操作符
groupBy - 分组
按条件将集合分组。
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
// 按奇偶分组
val grouped = numbers.groupBy { it % 2 == 0 }
println(grouped) // {false=[1, 3, 5, 7, 9], true=[2, 4, 6, 8, 10]}
// 实际应用:按年龄段分组
data class Person(val name: String, val age: Int)
val people = listOf(
Person("Alice", 25),
Person("Bob", 17),
Person("Charlie", 30),
Person("David", 16),
Person("Eve", 28)
)
val ageGroups = people.groupBy {
when {
it.age < 18 -> "未成年"
it.age < 30 -> "青年"
else -> "成年"
}
}
println(ageGroups)
// {未成年=[Person(Bob, 17), Person(David, 16)],
// 青年=[Person(Alice, 25), Person(Eve, 28)],
// 成年=[Person(Charlie, 30)]}partition - 二分
将集合分为符合和不符合条件的两部分。
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
val (evens, odds) = numbers.partition { it % 2 == 0 }
println("偶数: $evens") // 偶数: [2, 4, 6]
println("奇数: $odds") // 奇数: [1, 3, 5]排序操作符
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6)
// 升序排序
println(numbers.sorted()) // [1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9]
// 降序排序
println(numbers.sortedDescending()) // [9, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 1]
// 自定义排序
data class User(val name: String, val age: Int)
val users = listOf(
User("Alice", 25),
User("Bob", 30),
User("Charlie", 20)
)
val sortedByAge = users.sortedBy { it.age }
println(sortedByAge) // [Charlie(20), Alice(25), Bob(30)]
val sortedByName = users.sortedByDescending { it.name }
println(sortedByName) // [Charlie, Bob, Alice]查找操作符
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// 查找第一个符合条件的
println(numbers.find { it > 3 }) // 4
println(numbers.firstOrNull { it > 3 }) // 4(同find)
// 查找最后一个符合条件的
println(numbers.lastOrNull { it < 3 }) // 2
// 检查是否存在
println(numbers.any { it > 10 }) // false(是否有任意元素满足)
println(numbers.all { it > 0 }) // true(是否所有元素都满足)
println(numbers.none { it < 0 }) // true(是否没有元素满足)去重操作符
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4)
// 去重
println(numbers.distinct()) // [1, 2, 3, 4]
// 按条件去重
data class User(val id: Int, val name: String)
val users = listOf(
User(1, "Alice"),
User(2, "Bob"),
User(1, "Alice2") // id重复
)
val distinctUsers = users.distinctBy { it.id }
println(distinctUsers) // [User(1, Alice), User(2, Bob)]链式操作:组合的威力
Kotlin集合操作符的真正威力在于链式组合:
kotlin
data class Student(val name: String, val age: Int, val scores: List<Int>)
val students = listOf(
Student("Alice", 20, listOf(85, 90, 92)),
Student("Bob", 19, listOf(78, 82, 80)),
Student("Charlie", 21, listOf(92, 95, 98)),
Student("David", 20, listOf(88, 85, 90))
)
// 需求:找出20岁以上、平均分大于90的学生名字,按平均分降序排列
val result = students
.filter { it.age >= 20 } // 过滤年龄
.map { it to it.scores.average() } // 计算平均分
.filter { (_, avg) -> avg > 90 } // 过滤平均分
.sortedByDescending { (_, avg) -> avg } // 降序排序
.map { (student, avg) -> "${student.name}: $avg" } // 格式化输出
println(result) // [Charlie: 95.0, Alice: 89.0]**可读性提示**:链式调用很强大,但也要注意可读性。如果链条过长(超过5-6个操作),考虑: 1. 分解为多个步骤,使用中间变量 2. 添加注释说明每个步骤的目的 3. 提取复杂的Lambda为命名函数
Sequence:惰性求值的秘密武器
当处理大量数据时,普通集合操作会创建多个中间集合,影响性能。Sequence提供惰性求值,只在需要时才计算。
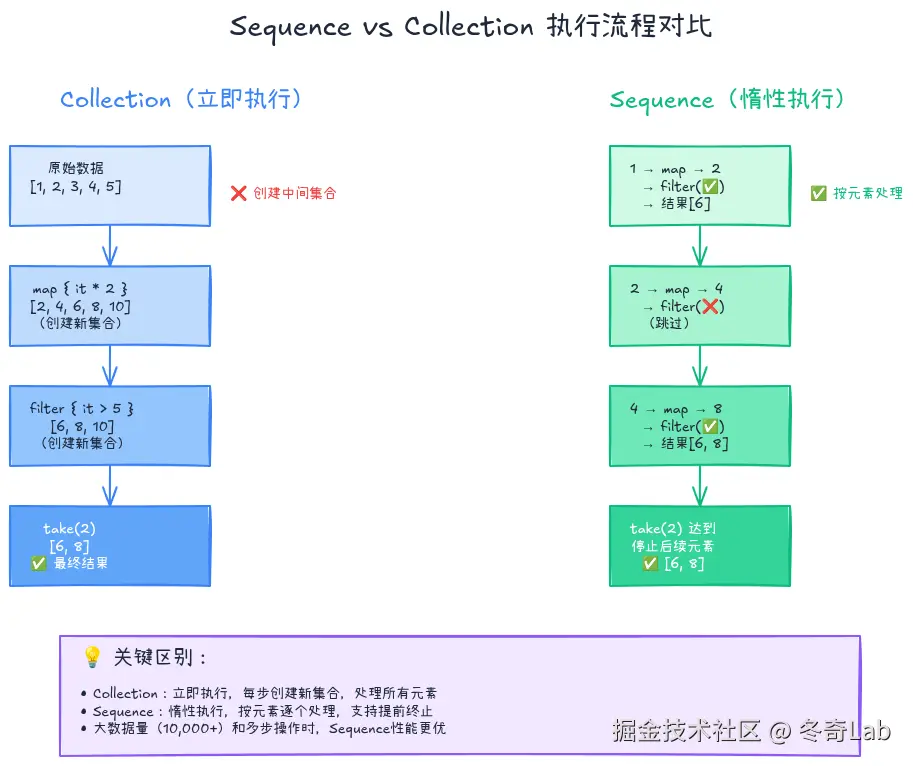
Collection vs Sequence
kotlin
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
// Collection:立即执行,创建中间集合
val result1 = numbers
.map {
println("map: $it")
it * 2
}
.filter {
println("filter: $it")
it > 10
}
.take(2)
// 输出:map 1, map 2, ... map 10, filter 2, filter 4, ... filter 20
// Sequence:惰性执行,不创建中间集合
val result2 = numbers.asSequence()
.map {
println("map: $it")
it * 2
}
.filter {
println("filter: $it")
it > 10
}
.take(2)
.toList() // 终端操作,触发计算
// 输出:map 1, filter 2, map 2, filter 4, ... map 6, filter 12
// 找到2个后就停止何时使用Sequence
kotlin
// ❌ 小集合不需要Sequence
val small = listOf(1, 2, 3).asSequence() // 过度优化
// ✅ 大集合使用Sequence
val large = (1..1_000_000).asSequence()
.map { it * 2 }
.filter { it % 3 == 0 }
.take(100)
.toList()
// ✅ 多步操作使用Sequence
val result = someList.asSequence()
.map { /* 步骤1 */ }
.filter { /* 步骤2 */ }
.flatMap { /* 步骤3 */ }
.distinct()
.sorted()
.toList()
// ✅ 可能提前终止的操作
val firstMatch = largeList.asSequence()
.map { expensiveOperation(it) }
.find { it > 100 } // 找到第一个就停止**注意**:Sequence的惰性求值意味着: 1. 必须有终端操作(`toList()`、`toSet()`、`find()`等)才会执行 2. 不要在Sequence上执行有副作用的操作(如打印日志),因为执行顺序可能不符合预期 3. Sequence不是线程安全的
创建Sequence
kotlin
// 从集合转换
val seq1 = listOf(1, 2, 3).asSequence()
// 从生成器
val seq2 = generateSequence(1) { it + 1 } // 无限序列:1, 2, 3, ...
val first10 = seq2.take(10).toList()
// 斐波那契数列
val fibonacci = generateSequence(Pair(0, 1)) { (a, b) -> Pair(b, a + b) }
.map { it.first }
val first10Fib = fibonacci.take(10).toList()
println(first10Fib) // [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34]
// 从文件读取行(自动惰性处理)
fun readLargeFile(path: String) {
File(path).useLines { lines ->
lines
.filter { it.isNotEmpty() }
.map { it.trim() }
.take(100)
.forEach { println(it) }
}
}实战:电商订单数据分析
让我们用一个完整的实战案例,综合运用所学的集合操作:
kotlin
// 数据模型
data class Product(val id: Int, val name: String, val category: String, val price: Double)
data class Order(val orderId: String, val userId: Int, val products: List<Product>, val date: String)
data class User(val userId: Int, val name: String, val city: String)
// 订单数据
val orders = listOf(
Order("O001", 1, listOf(
Product(101, "Laptop", "Electronics", 5999.0),
Product(102, "Mouse", "Electronics", 99.0)
), "2024-01-15"),
Order("O002", 2, listOf(
Product(201, "Book", "Books", 49.9),
Product(202, "Pen", "Stationery", 5.0)
), "2024-01-16"),
Order("O003", 1, listOf(
Product(103, "Keyboard", "Electronics", 299.0)
), "2024-01-17"),
Order("O004", 3, listOf(
Product(301, "Shirt", "Clothing", 199.0),
Product(302, "Pants", "Clothing", 299.0)
), "2024-01-18")
)
val users = listOf(
User(1, "Alice", "Beijing"),
User(2, "Bob", "Shanghai"),
User(3, "Charlie", "Beijing")
)
// 分析1:计算每个用户的总消费
fun analyzeUserSpending(): Map<String, Double> {
return orders
.groupBy { it.userId }
.mapValues { (_, userOrders) ->
userOrders.sumOf { order ->
order.products.sumOf { it.price }
}
}
.mapKeys { (userId, _) ->
users.find { it.userId == userId }?.name ?: "Unknown"
}
}
println("用户总消费:")
analyzeUserSpending().forEach { (name, total) ->
println(" $name: ¥$total")
}
// 输出:
// Alice: ¥6397.0
// Bob: ¥54.9
// Charlie: ¥498.0
// 分析2:找出最受欢迎的商品类别
fun findPopularCategories(): List<Pair<String, Int>> {
return orders
.flatMap { it.products }
.groupBy { it.category }
.mapValues { (_, products) -> products.size }
.toList()
.sortedByDescending { (_, count) -> count }
}
println("\n商品类别销量排行:")
findPopularCategories().forEach { (category, count) ->
println(" $category: $count 件")
}
// 输出:
// Electronics: 3 件
// Clothing: 2 件
// Books: 1 件
// Stationery: 1 件
// 分析3:计算每个城市的订单总额
fun analyzeCityRevenue(): Map<String, Double> {
return orders
.map { order ->
val user = users.find { it.userId == order.userId }
val total = order.products.sumOf { it.price }
user?.city to total
}
.filterNotNull()
.groupBy({ it.first!! }, { it.second })
.mapValues { (_, totals) -> totals.sum() }
}
println("\n城市订单总额:")
analyzeCityRevenue().forEach { (city, total) ->
println(" $city: ¥$total")
}
// 输出:
// Beijing: ¥6895.0
// Shanghai: ¥54.9
// 分析4:找出高价值订单(总额>500)的用户
fun findHighValueCustomers(): List<String> {
return orders
.filter { order ->
order.products.sumOf { it.price } > 500
}
.map { it.userId }
.distinct()
.mapNotNull { userId ->
users.find { it.userId == userId }?.name
}
}
println("\n高价值客户:")
findHighValueCustomers().forEach { name ->
println(" $name")
}
// 输出:
// Alice常见问题
Q1: 什么时候用List、Set、Map?
选择指南:
| 需求 | 选择 | 原因 |
|---|---|---|
| 需要保持元素顺序 | List | 有序集合 |
| 需要通过索引访问 | List | 支持下标访问 |
| 需要去重 | Set | 自动去重 |
| 需要快速检查元素存在性 | Set | O(1)查找 |
| 需要键值对映射 | Map | 键值对存储 |
| 需要按键快速查找值 | Map | O(1)查找 |
kotlin
// 示例:记录用户访问历史
val visitHistory = mutableListOf<String>() // ✅ 需要顺序
// 示例:记录访问过的页面(不重复)
val visitedPages = mutableSetOf<String>() // ✅ 需要去重
// 示例:记录页面访问次数
val pageViews = mutableMapOf<String, Int>() // ✅ 需要统计Q2: filter和map的顺序有什么影响?
kotlin
val numbers = (1..1000).toList()
// 方案1:先过滤再映射(推荐)
val result1 = numbers
.filter { it % 2 == 0 } // 处理1000个元素,保留500个
.map { it * it } // 处理500个元素
// 方案2:先映射再过滤
val result2 = numbers
.map { it * it } // 处理1000个元素
.filter { it % 2 == 0 } // 处理1000个元素
// 方案1更高效:尽早减少数据量原则 :先过滤再映射,尽早减少数据量。
Q3: 何时使用Sequence?
kotlin
// ❌ 不需要Sequence
listOf(1, 2, 3).asSequence().map { it * 2 }.toList() // 小集合,overhead更大
// ✅ 需要Sequence
(1..1_000_000)
.asSequence() // 大集合
.map { it * 2 }
.filter { it > 100 }
.take(10) // 提前终止
.toList()使用Sequence的场景:
- 处理大集合(10,000+元素)
- 多步操作(3+个操作符)
- 可能提前终止(find、take等)
- 处理无限序列
Q4: 如何选择可变/不可变集合?
kotlin
// ✅ 默认使用不可变
val config = mapOf("host" to "localhost", "port" to 8080)
// ✅ 需要修改时使用可变
val cache = mutableMapOf<String, Any>()
cache["user"] = loadUser()
// ❌ 不要暴露可变集合
class UserManager {
private val _users = mutableListOf<User>()
val users: List<User> = _users // ✅ 只读视图
}最佳实践:
- 默认使用不可变集合(
listOf、setOf、mapOf) - 只在必要时使用可变集合
- 不要暴露可变集合,返回只读视图
总结
本文深入探索了Kotlin强大的集合框架:
1. 集合体系
- List(有序可重复)、Set(无序不重复)、Map(键值对)
- 不可变集合 vs 可变集合
- 默认使用不可变,提高安全性
2. 集合操作符
- 转换:map、flatMap、mapNotNull
- 过滤:filter、filterNot、take、drop
- 聚合:sum、average、reduce、fold
- 分组:groupBy、partition
- 排序:sorted、sortedBy、sortedDescending
- 查找:find、any、all、none
- 去重:distinct、distinctBy
3. 函数式编程
- 链式调用,代码简洁优雅
- 无副作用,易于理解和测试
- 声明式而非命令式
4. Sequence惰性求值
- 不创建中间集合,节省内存
- 支持提前终止,提高效率
- 适合大数据和多步操作
5. 最佳实践
- 优先使用不可变集合
- 先过滤再映射
- 大数据使用Sequence
- 注意链式操作的可读性
下一篇文章我们将学习面向对象进阶:接口、抽象类与多态,深入探索Kotlin的OOP特性。
练习题
练习1:学生成绩管理系统
kotlin
data class Student(val id: Int, val name: String, val grades: Map<String, Int>)
val students = listOf(
Student(1, "Alice", mapOf("Math" to 95, "English" to 88, "Physics" to 92)),
Student(2, "Bob", mapOf("Math" to 78, "English" to 85, "Physics" to 80)),
Student(3, "Charlie", mapOf("Math" to 92, "English" to 95, "Physics" to 98))
)
// TODO 1: 找出数学成绩大于90的学生名字
// TODO 2: 计算每个学生的平均分,返回Map<String, Double>
// TODO 3: 找出平均分最高的学生
// TODO 4: 统计每门课的平均分
// TODO 5: 找出所有科目都及格(>=60)的学生练习2:日志分析系统
kotlin
data class LogEntry(val timestamp: String, val level: String, val message: String)
val logs = """
2024-01-15 10:23:45 INFO User login: alice
2024-01-15 10:24:12 ERROR Failed to connect to database
2024-01-15 10:25:30 WARN Memory usage: 85%
2024-01-15 10:26:15 INFO User logout: alice
2024-01-15 10:27:22 ERROR Null pointer exception
""".trimIndent().lines().filter { it.isNotEmpty() }
// TODO 1: 解析日志(提示:使用split)
// TODO 2: 统计各级别日志数量
// TODO 3: 找出所有ERROR级别的消息
// TODO 4: 按小时分组统计日志数量(提示:提取timestamp的小时部分)练习3:使用Sequence优化性能
kotlin
// TODO: 重写以下代码,使用Sequence提高性能
fun findPrimeNumbers(max: Int): List<Int> {
return (2..max)
.filter { isPrime(it) }
.take(100)
}
fun isPrime(n: Int): Boolean {
if (n < 2) return false
return (2..Math.sqrt(n.toDouble()).toInt()).none { n % it == 0 }
}
// TODO: 对比性能差异系列文章导航:
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,欢迎点赞、收藏、分享!有任何问题或建议,欢迎在评论区留言讨论。让我们一起学习,一起成长!
也欢迎访问我的个人主页发现更多宝藏资源