第一章:为什么需要微前端?
1.1 单体应用的瓶颈
| 问题 | 表现 |
|---|---|
| 构建慢 | 修改一行代码需 5 分钟全量构建 |
| 发布风险高 | 支付模块 bug 导致整个站点回滚 |
| 技术栈锁定 | 无法在新模块中使用 React 或 Svelte |
| 团队协作冲突 | 多人修改同一 Git 仓库,合并频繁冲突 |
1.2 微前端的核心价值
- 技术无关:每个微应用可使用不同框架(Vue/React/Angular)
- 独立交付 :团队 A 部署
user-app不影响团队 B 的order-app - 渐进演进:新功能用微前端,旧功能逐步重构
- 故障隔离:一个微应用崩溃,不影响主壳和其他模块
注意 :微前端不是银弹!适用于大型产品、多团队、长期维护场景。
第二章:架构选型 ------ 为什么选 Module Federation?
2.1 主流方案对比
| 方案 | 原理 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| iframe | 页面嵌套 | 隔离性强 | SEO 差、通信复杂、URL 同步难 |
| Web Components | 自定义元素 | 原生支持 | 生态弱、状态管理难 |
| Single-SPA | 路由劫持 + 生命周期 | 成熟生态 | 需手动管理加载/卸载 |
| Module Federation (MF) | 运行时远程模块加载 | 原生 Webpack 支持、按需加载、共享依赖 | 需 Webpack 5+,配置复杂 |
结论 :MF 是当前最贴近"模块化"理念的方案,尤其适合已有 Webpack 项目的演进。
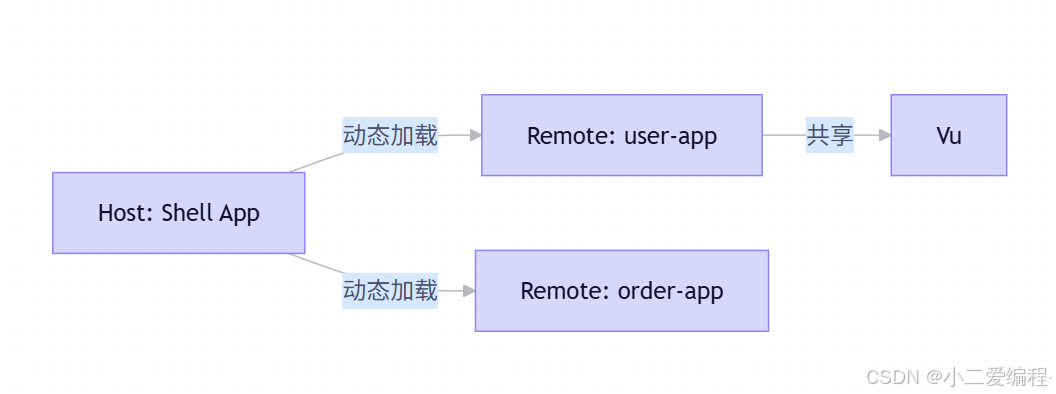
2.2 Module Federation 核心概念
- Host(主应用):消费远程模块的应用(Shell)
- Remote(微应用) :暴露可复用模块的应用(如
user-app) - Shared Dependencies:共享公共库(如 Vue、Pinia),避免重复加载
第三章:工程结构设计
3.1 目录布局(Monorepo)
micro-frontend-project/
├── apps/
│ ├── shell/ # 主壳应用(Host)
│ ├── user-app/ # 用户中心(Remote)
│ ├── order-app/ # 订单系统(Remote)
│ └── payment-app/ # 支付模块(Remote)
├── packages/
│ └── shared/ # 共享工具、类型、组件
├── package.json
└── lerna.json # 使用 Lerna 管理 Monorepo工具链:Lerna + Yarn Workspaces(或 Nx / Turborepo)
3.2 独立开发与部署
-
每个
app/xxx是一个完整 Vue 应用 -
可单独运行:
cd apps/user-app && npm run dev -
构建产物独立部署到 CDN 或静态服务器:
https://cdn.example.com/user-app/remoteEntry.js https://cdn.example.com/order-app/remoteEntry.js
第四章:主壳应用(Shell)搭建
4.1 初始化 Shell
cd apps/shell
npm init vue@3
# 选择 Webpack(非 Vite!),因 MF 依赖 Webpack 5安装依赖:
npm install --save-dev webpack webpack-cli webpack-dev-server html-webpack-plugin
npm install vue-router pinia4.2 Webpack 配置(关键:ModuleFederationPlugin)
// apps/shell/webpack.config.js
const { ModuleFederationPlugin } = require('webpack').container;
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/main.js',
plugins: [
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: 'shell',
remotes: {
// 映射远程应用名称 -> 地址
userApp: 'userApp@http://localhost:3001/remoteEntry.js',
orderApp: 'orderApp@http://localhost:3002/remoteEntry.js'
},
shared: {
vue: { singleton: true, requiredVersion: '^3.0.0' },
pinia: { singleton: true, requiredVersion: '^2.0.0' }
}
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: './public/index.html' })
],
devServer: { port: 3000 }
};关键参数:
singleton: true:确保全局只有一个 Vue 实例requiredVersion:版本兼容性检查
4.3 路由集成
Shell 负责全局路由:
// apps/shell/src/router/index.ts
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
// 动态导入微应用组件
const UserDashboard = () => import('userApp/UserDashboard.vue')
const OrderList = () => import('orderApp/OrderList.vue')
const routes = [
{ path: '/user', component: UserDashboard },
{ path: '/orders', component: OrderList }
]
export default createRouter({ history: createWebHistory(), routes })注意 :
userApp/UserDashboard.vue是远程模块的暴露路径(见第五章)。
第五章:微应用(Remote)开发
5.1 初始化 user-app
cd apps/user-app
npm init vue@3 # 同样选择 Webpack5.2 暴露组件(ModuleFederationPlugin)
// apps/user-app/webpack.config.js
const { ModuleFederationPlugin } = require('webpack').container;
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: 'userApp', // 必须与 Shell 中 remotes 名称一致
filename: 'remoteEntry.js',
exposes: {
// 暴露具体组件
'./UserDashboard': './src/components/UserDashboard.vue',
'./UserProfile': './src/components/UserProfile.vue'
},
shared: {
vue: { singleton: true, requiredVersion: '^3.0.0' },
pinia: { singleton: true }
}
})
],
devServer: { port: 3001 }
};5.3 微应用内部结构
UserDashboard.vue 可正常使用 Pinia、Vue Router(仅用于内部跳转):
<!-- apps/user-app/src/components/UserDashboard.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<h1>User Dashboard</h1>
<UserProfile />
<!-- 内部路由 -->
<router-link to="/settings">Settings</router-link>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import UserProfile from './UserProfile.vue'
</script>原则 :微应用不控制全局 URL,仅渲染自身内容。
第六章:跨应用状态共享
6.1 共享 Pinia Store
在 packages/shared 中定义通用 Store:
// packages/shared/stores/auth.ts
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useAuthStore = defineStore('auth', {
state: () => ({
token: localStorage.getItem('token') || '',
user: null
}),
actions: {
login(token: string) {
this.token = token
localStorage.setItem('token', token)
}
}
})6.2 在 Shell 中初始化 Store
// apps/shell/src/main.ts
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
const pinia = createPinia()
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(pinia).use(router).mount('#app')6.3 微应用直接使用共享 Store
<!-- apps/user-app/src/components/UserDashboard.vue -->
<script setup>
import { useAuthStore } from 'shared/stores/auth' // 来自 shared 包
const auth = useAuthStore()
console.log(auth.user?.name)
</script>关键 :通过
shared配置,Pinia 实例在 Shell 和微应用间完全共享。
第七章:渐进式迁移策略
7.1 混合路由:新旧页面共存
Shell 路由同时支持微应用和旧页面:
const routes = [
// 新:微应用
{ path: '/user', component: () => import('userApp/UserDashboard.vue') },
// 旧:本地组件(逐步淘汰)
{ path: '/legacy-profile', component: () => import('@/views/LegacyProfile.vue') }
]7.2 构建时 fallback
若远程模块加载失败,降级到本地备用组件:
// utils/async-component.ts
export const loadRemoteComponent = (loader, fallback) => {
return defineAsyncComponent({
loader,
loadingComponent: LoadingSpinner,
errorComponent: fallback,
delay: 200,
timeout: 5000
})
}
// 在路由中使用
const UserDashboard = loadRemoteComponent(
() => import('userApp/UserDashboard.vue'),
() => import('@/components/FallbackUser.vue')
)第八章:独立构建与部署
8.1 构建脚本
每个微应用独立构建:
// apps/user-app/package.json
{
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack --mode production"
}
}产物结构:
dist/
├── remoteEntry.js ← MF 入口文件
├── js/
│ ├── userApp.[hash].js
│ └── ...
└── index.html ← 可选:用于独立访问调试8.2 部署到 CDN
-
将
dist上传至对象存储(如 AWS S3 + CloudFront) -
确保
remoteEntry.js可公开访问:https://cdn.example.com/user-app/remoteEntry.js
8.3 版本管理与缓存
-
问题 :Shell 加载旧版
remoteEntry.js,导致兼容性错误 -
解决方案 :
-
禁用
remoteEntry.js缓存(Cache-Control: no-cache) -
版本化目录 :
https://cdn.example.com/user-app/v1.2.3/remoteEntry.js -
Shell 配置中心化:从 API 动态获取 Remote 地址
// apps/shell/src/mf-config.ts
export const getRemotes = async () => {
const res = await fetch('/api/mf-config')
return res.json() // { userApp: 'userApp@https://.../v1.2.3/remoteEntry.js' }
} -
第九章:开发体验优化
9.1 本地联调
使用 concurrently 同时启动所有应用:
// root package.json
{
"scripts": {
"dev": "concurrently \"npm:dev:*\"",
"dev:shell": "cd apps/shell && npm run dev",
"dev:user": "cd apps/user-app && npm run dev",
"dev:order": "cd apps/order-app && npm run dev"
}
}9.2 类型安全(TypeScript)
在 packages/shared 中导出类型:
// packages/shared/types/user.ts
export interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
email: string;
}微应用和 Shell 均可引用,确保跨应用类型一致。
第十章:生产监控与错误处理
10.1 微应用加载失败监控
// apps/shell/src/plugins/mf-monitor.ts
window.addEventListener('module-federation-error', (e) => {
const { moduleName, error } = e.detail
// 上报 Sentry
Sentry.captureException(error, { tags: { mf_module: moduleName } })
})在异步组件中触发事件:
defineAsyncComponent({
errorComponent: (error) => {
window.dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent('module-federation-error', {
detail: { moduleName: 'userApp', error }
}))
return FallbackComponent
}
})10.2 性能指标
- 首屏加载时间:记录从路由切换到微应用渲染完成的时间
- Bundle 大小 :监控
remoteEntry.js及其依赖体积