前言
最近做项目,嗯,一些外购项目,实际上是解决历史遗留问题,这么多年😅都没解决。分析全链路和埋点,发现在一张表执行saveall超级慢,需要半小时之久,幸好是异步,可能正因为是异步没人管。这张表其实也不大,200w多点,执行的saveall才100多条啊。而且也配置了jpa的批量任务,这就要分析原因了。
准备demo
简单创建一个表来试试,当然实际项目字段多得多,数据量大得多,这个索引埋坑了,后面会说明原因
sql
create table user
(
id varchar(50) not null,
name varchar(50) not null,
age int null,
addr varchar(255) null,
iid bigint auto_increment
primary key,
constraint user_pk
unique (iid, id)
)
collate = utf8mb4_bin;加上日常配置,随便写个entity代码逻辑,这里外购代码比较奇怪,没有使用自增ID字段作为ID
java
@Entity
@Table(name = "user")
public class UserEntity {
@Id
@Column(name = "id")
// @GeneratedValue(generator = "sys-uuid")
// @GenericGenerator(name= "sys-uuid", strategy = "uuid")
private String id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "age")
private int age;
@Column(name = "addr")
private String addr;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<UserEntity, String> {
}
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/users/200")
public String add200User() {
List<UserEntity> list = new ArrayList<>(200);
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
UserEntity userEntity = new UserEntity();
userEntity.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
userEntity.setName("Tom" + i);
userEntity.setAge(12 + 1);
userEntity.setAddr("us tom ` home " + i);
list.add(userEntity);
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
userRepository.saveAll(list);
System.out.println("use time " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
return "success";
}配置文件
XML
#数据库配置
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456i
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC
# JPA配置
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true
# formatSQL得这样写
properties:
hibernate:
format_sql: true
jdbc:
batch_versioned_data: true
batch_size: 200加上pom
XML
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--Web必要的-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.7.18</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring data jpa-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
<version>2.7.18</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL的java driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<version>8.3.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>数据库随便造点数据
然后启动程序,执行任务
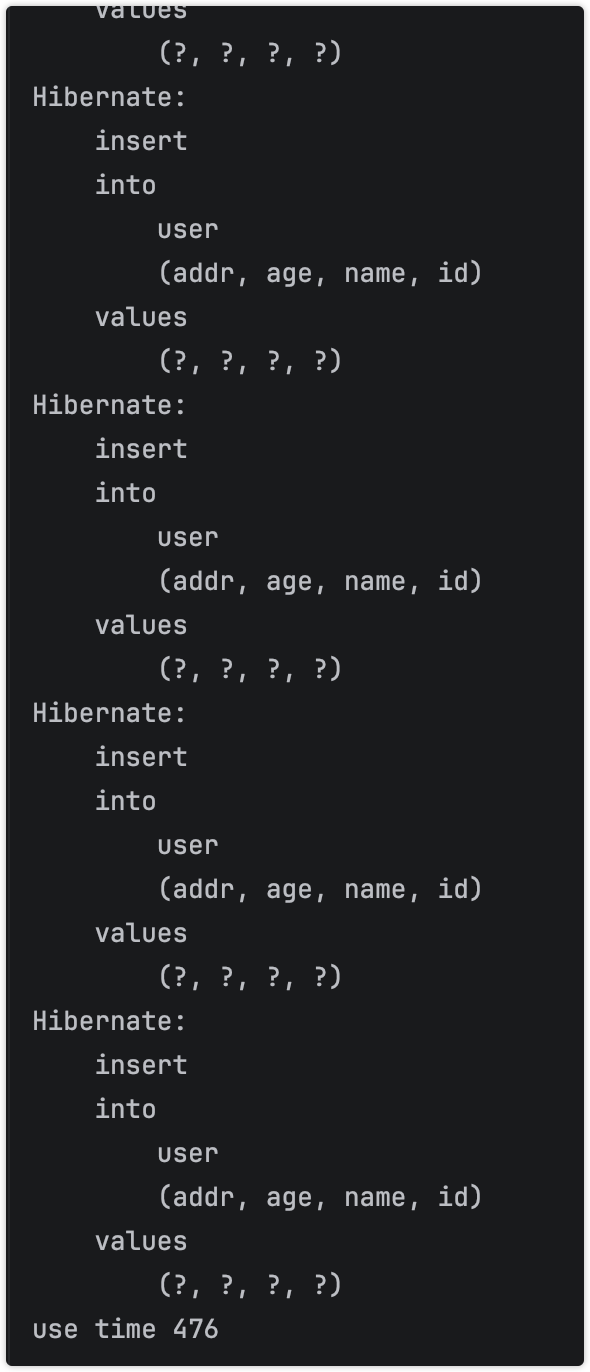
看到这一系列SQL,就知道不好的事发生了
测试一般耗时在500毫秒左右,而且耗时波动极大,示例波动大概150毫秒左右,随着MySQL表的数据量的增加,耗时会增加,估计在10w的时候会大幅度增加。
且批量未生效(按照理解,但是源码分析是生效的),伴随着查询语句
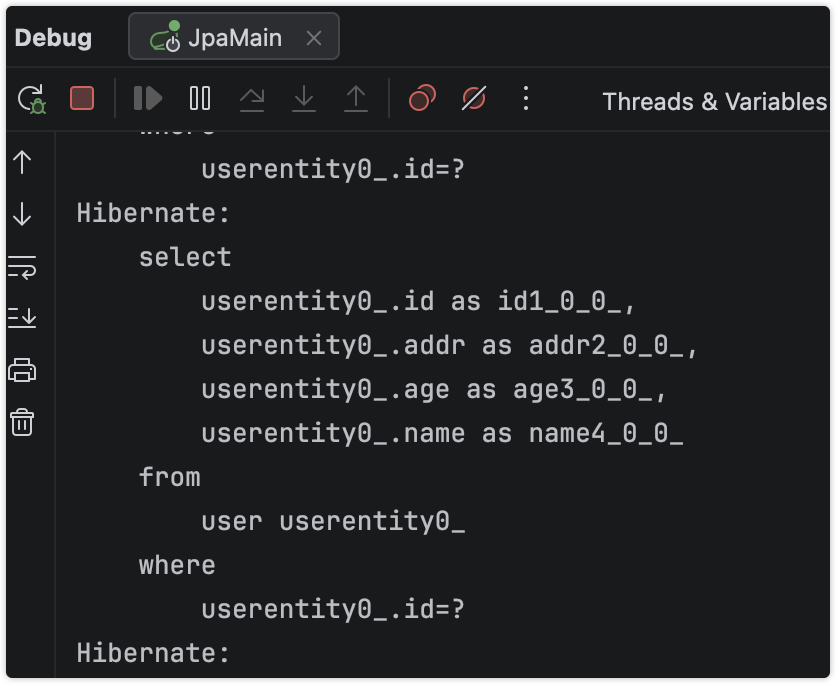
使用@Id字段来查询???这个分析源码非常有意思。
对比jdbctemplate
那么如果使用jdbctemplate呢,写个代码试试
java
@RequestMapping("/users/batch200")
public String add200UserBatch() {
List<UserEntity> list = new ArrayList<>(200);
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
UserEntity userEntity = new UserEntity();
userEntity.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
userEntity.setName("Tom" + i);
userEntity.setAge(12 + 1);
userEntity.setAddr("us tom ` home " + i);
list.add(userEntity);
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("insert into user (id, name, age, addr) values (?,?,?,?)", new BatchPreparedStatementSetter() {
@Override
public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps, int i) throws SQLException {
ps.setString(1, list.get(i).getId());
ps.setString(2, list.get(i).getName());
ps.setInt(3, list.get(i).getAge());
ps.setString(4, list.get(i).getAddr());
}
@Override
public int getBatchSize() {
return list.size();
}
});
System.out.println("use time batch " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
return "success";
}纯粹的batch经典代码,质量有保证,耗时稳定150毫秒左右
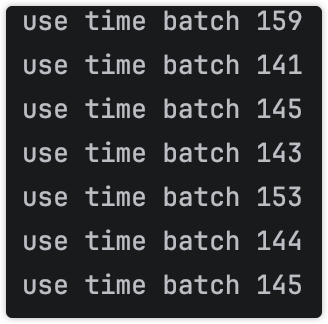
jpa开启批量任务原理
先说索引的坑,创建唯一索引把iid放在第一位,且id字段为字符串,这个就是坑,按照联合索引的按坐匹配原则,实际是索引失效。
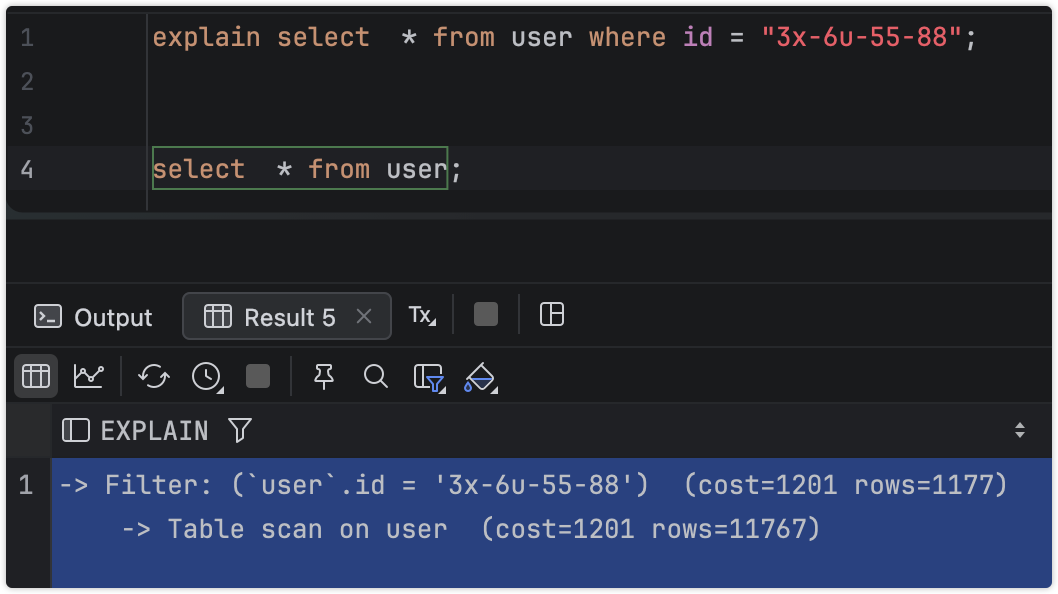
执行一次查询的代价非常大。当我们调整id字符串字段作为第一位索引列时
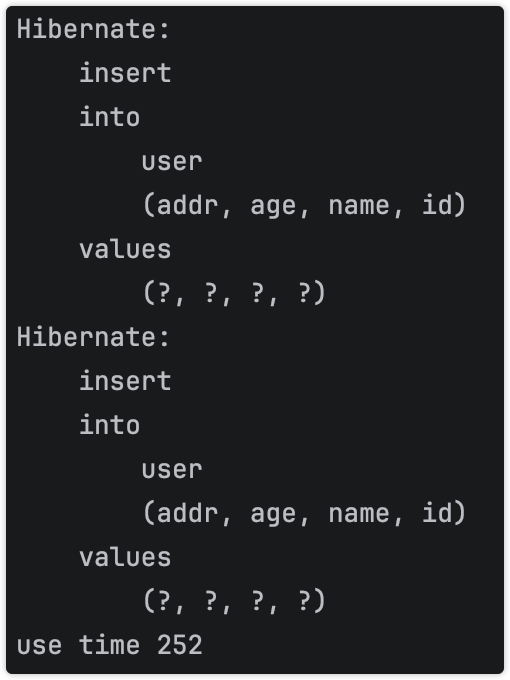
耗时骤降到250多毫秒,但是波动很大,有时候会到300多毫秒,且还是不执行批量事务(实际上是批量事务,源码分析得出),但是对比批量还是慢,且波动不稳定。
jpa saveall源码分析
要了解为什么jpa的批量未生效(猜测),先了解saveall的源码,看看是怎么实现的
java
@Transactional
@Override
public <S extends T> List<S> saveAll(Iterable<S> entities) {
Assert.notNull(entities, "Entities must not be null!");
List<S> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (S entity : entities) {
result.add(save(entity));
}
return result;
}for循环,然后单条save方法,但是这里明显是一个事务统领,根据方法内部调用方法,save的方法事务失效(动态代理的原理)
java
@Transactional
@Override
public <S extends T> S save(S entity) {
Assert.notNull(entity, "Entity must not be null.");
if (entityInformation.isNew(entity)) {
em.persist(entity);
return entity;
} else {
return em.merge(entity);
}
}这里的isNew不会去查询数据库,因为本次示例id不是主键,且设置有值,使用@Id值判空org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.support.JpaMetamodelEntityInformation
org.springframework.data.repository.core.support.AbstractEntityInformation
所以走merge逻辑,去查数据库,否则是会直接入库的,一会演示直接入库的情况。
通过反射org.springframework.orm.jpa.SharedEntityManagerCreator,来merge
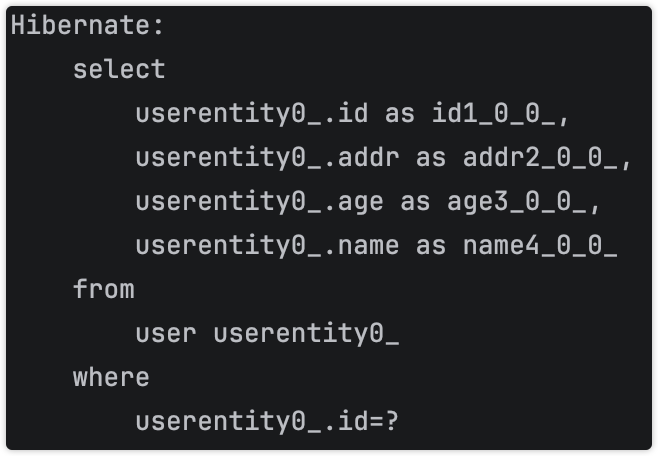
先查询,再新增或更新
// Determine current EntityManager: either the transactional one
// managed by the factory or a temporary one for the given invocation.
EntityManager target = EntityManagerFactoryUtils.doGetTransactionalEntityManager(
this.targetFactory, this.properties, this.synchronizedWithTransaction);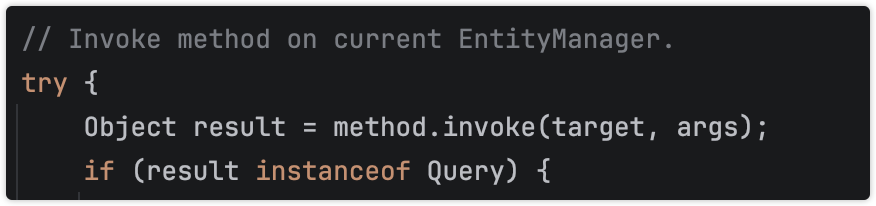
看看是否独立提交事务
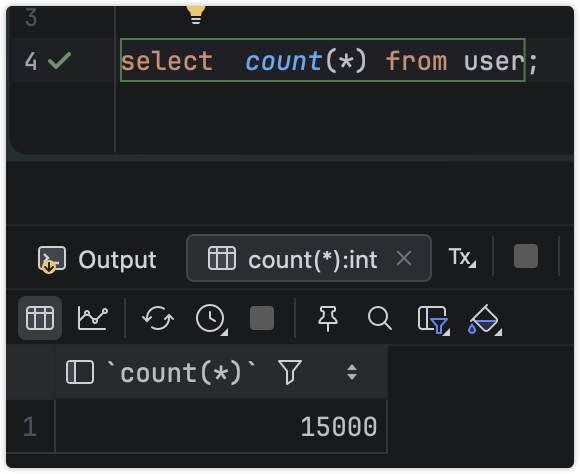
执行完后
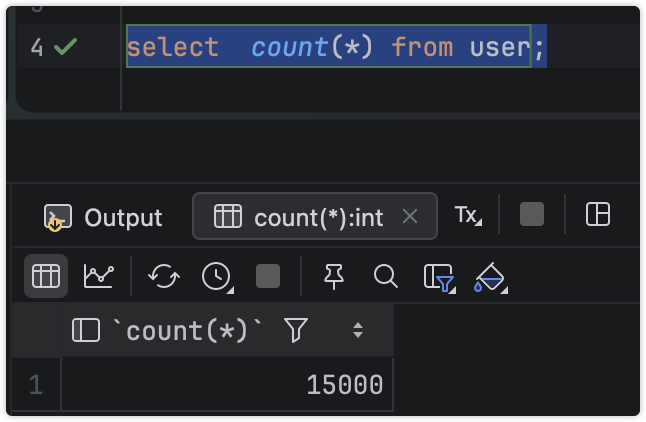
事务并未提交,说明确实批量生效,事务是一次性事务,那么效率低下应该是执行200次查询(本次示例),且索引设计不合理。
当修改entity,加速@Id的生成注解,同时停止设置id属性的值
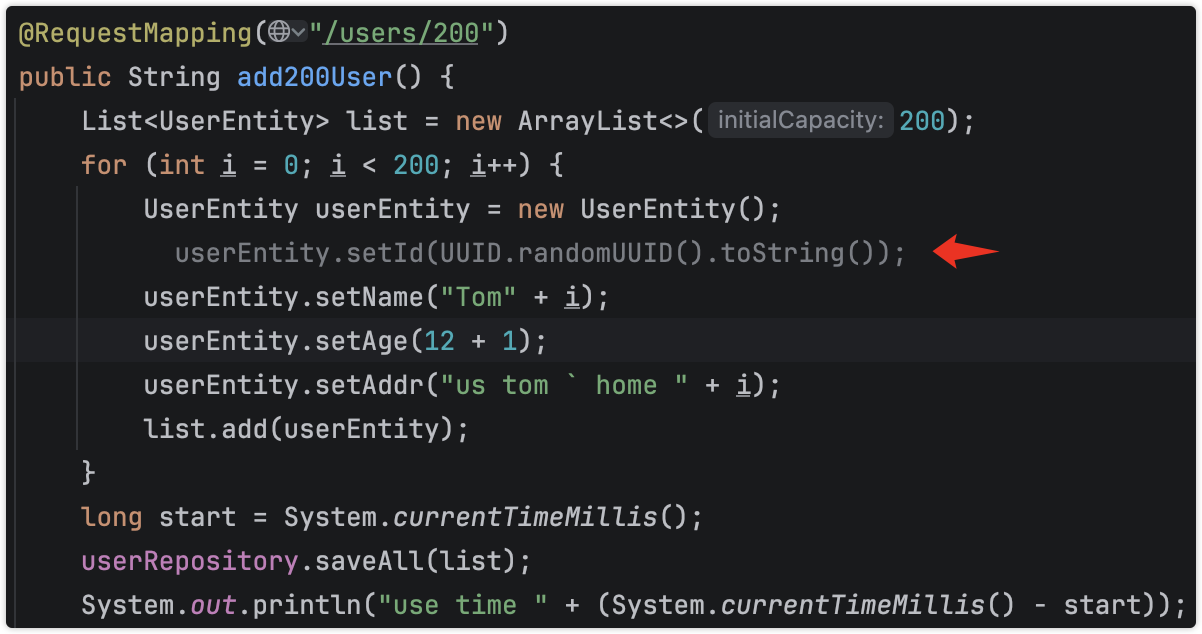
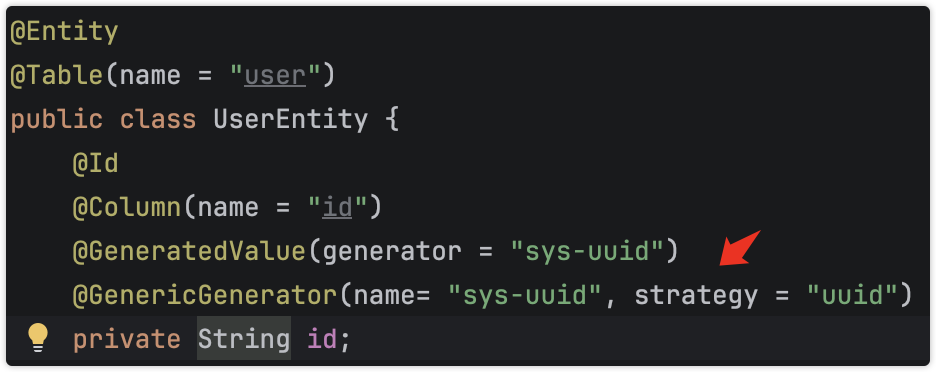
当然索引,把id字段设置为第一位。
实际上效果比jdbctemplate的batchupdate还好一些
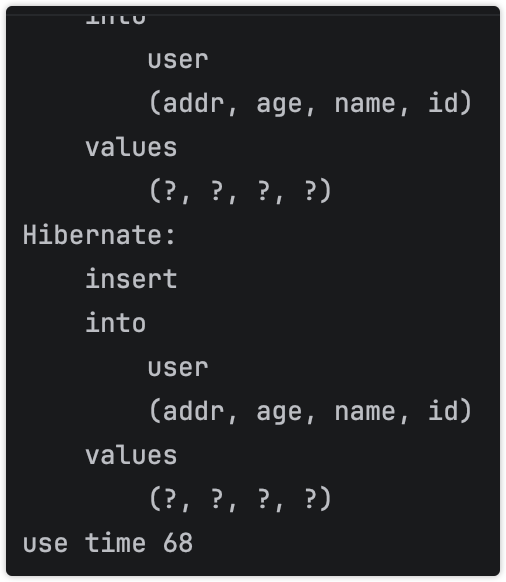
最终发现jpa saveall慢的根源在于2点:
-
@Id字段的索引是否合理
-
@Id字段不能由代码赋值,需要jpa自动生成,或者编写生成@Id赋值的注解的实现方式
分析jdbctemplate
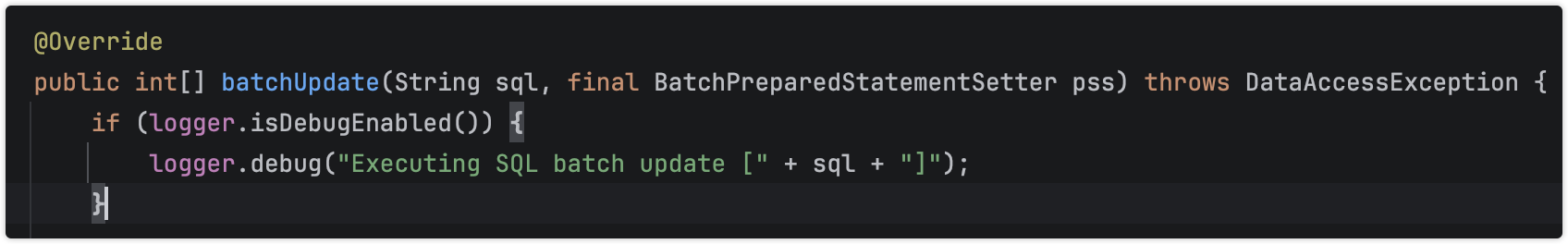
看sql的日志是debug
配置
logging:
level:
org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate: DEBUG
bash
2026-01-12 19:04:54.303 DEBUG 3213 --- [nio-8887-exec-2] o.s.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate : Executing SQL batch update [insert into user (id, name, age, addr) values (?,?,?,?)]
2026-01-12 19:04:54.303 DEBUG 3213 --- [nio-8887-exec-2] o.s.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate : Executing prepared SQL statement [insert into user (id, name, age, addr) values (?,?,?,?)]
use time batch 131
2026-01-12 19:04:57.680 DEBUG 3213 --- [nio-8887-exec-3] o.s.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate : Executing SQL batch update [insert into user (id, name, age, addr) values (?,?,?,?)]
2026-01-12 19:04:57.680 DEBUG 3213 --- [nio-8887-exec-3] o.s.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate : Executing prepared SQL statement [insert into user (id, name, age, addr) values (?,?,?,?)]
use time batch 137源码分析,事务管理机制
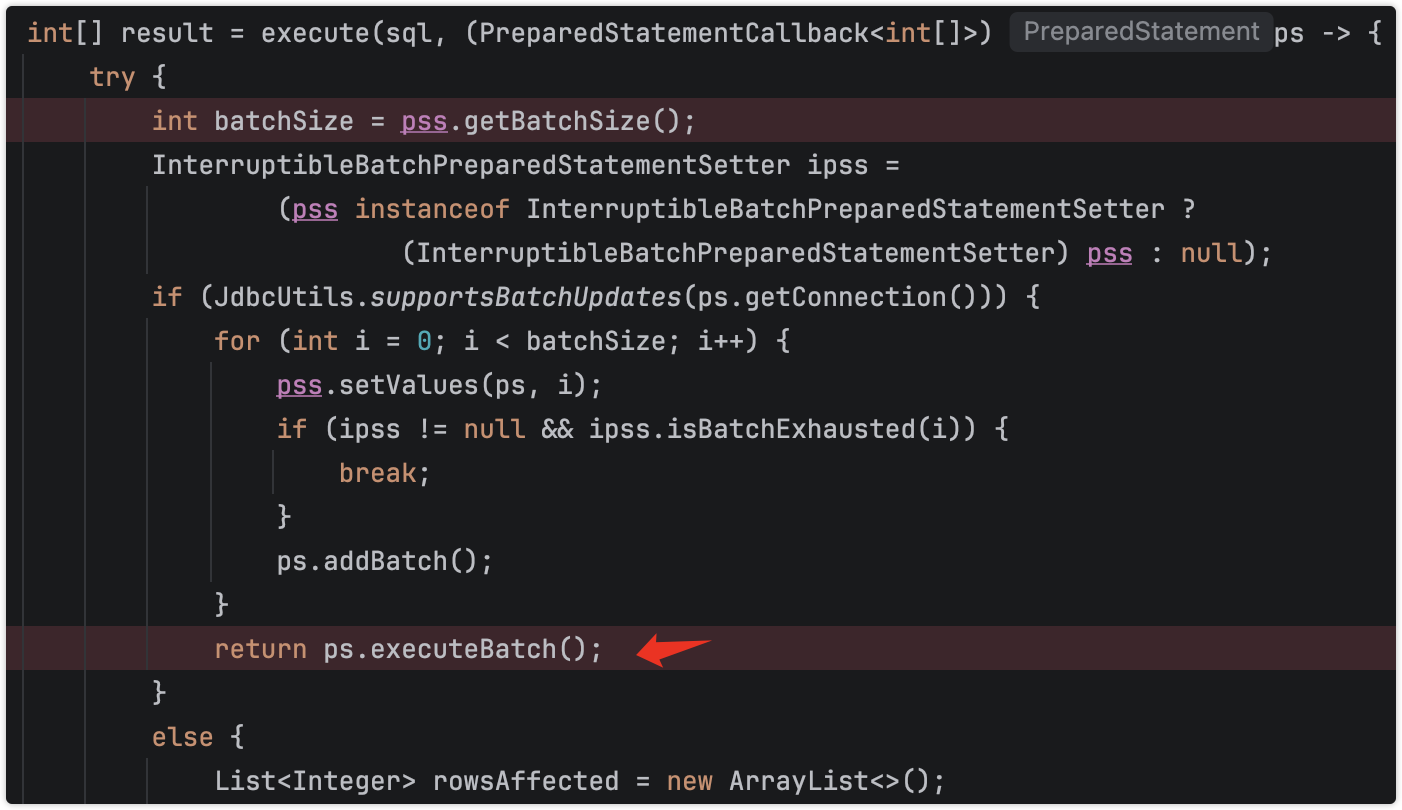
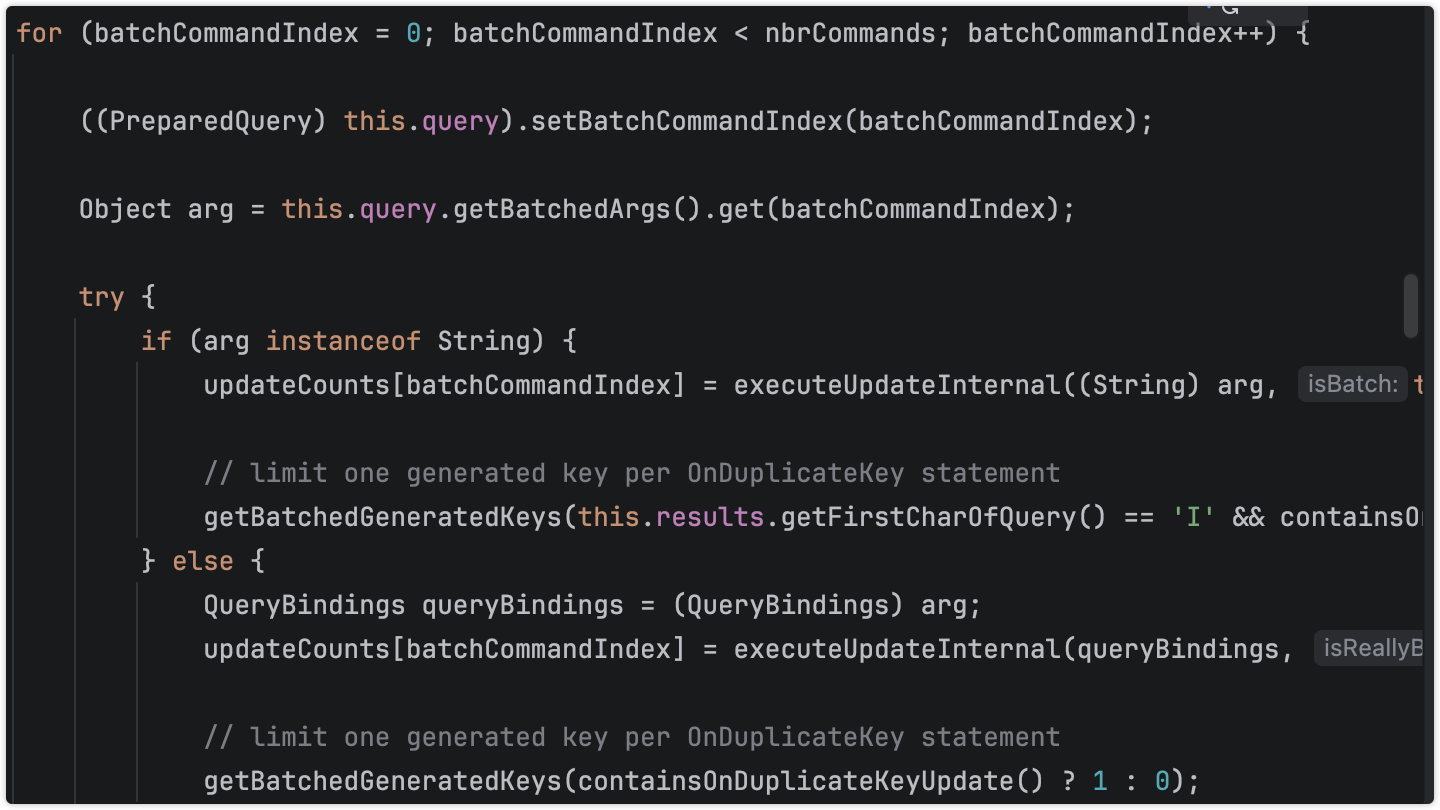
确实是一次事务提交,但是中间会多次for循环进行1. jdbc参数绑定;2. MySQL驱动进行for循环提交SQL(事务未提交),最后事务提交。
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ClientPreparedStatement
总结
其实spring data jpa的saveall并不慢,效率非常高,只不过因为各种原因未生效,其中包括如下原因:
-
索引创建是否合理,@Id的字段一般需要为主键,或者唯一键的第一个字段
-
@Id字段需要jpa自动生成,或者写算法定义,jpa通过@Id的字段是否为空判断是否merge
通过上面的方式,jpa的saveall可以性能超越jdbctemplate的batchupdate,但是jdbctemplate的batchupdate性能稳定,适合所有场景,依赖MySQL驱动的batch能力。