专栏:JavaEE 进阶跃迁营
个人主页:手握风云
目录
[1.1. 获取 URL 路径参数(@PathVariable)](#1.1. 获取 URL 路径参数(@PathVariable))
[1.2. 上传文件(@RequestPart)](#1.2. 上传文件(@RequestPart))
[1.3. 获取 Cookie 和 Session](#1.3. 获取 Cookie 和 Session)
[1. Cookie 和 Session](#1. Cookie 和 Session)
[2. 获取 Cookie](#2. 获取 Cookie)
[3. 获取 Session](#3. 获取 Session)
[1.4. 获取 Header](#1.4. 获取 Header)
一、请求
1.1. 获取 URL 路径参数(@PathVariable)
适用于参数直接嵌入 URL 路径中。核心注解:@PathVariable,通过 value 绑定 URL 中的占位符。
java
package com.yang.test1_7_1;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequestMapping("/request")
@RestController
public class RequestController {
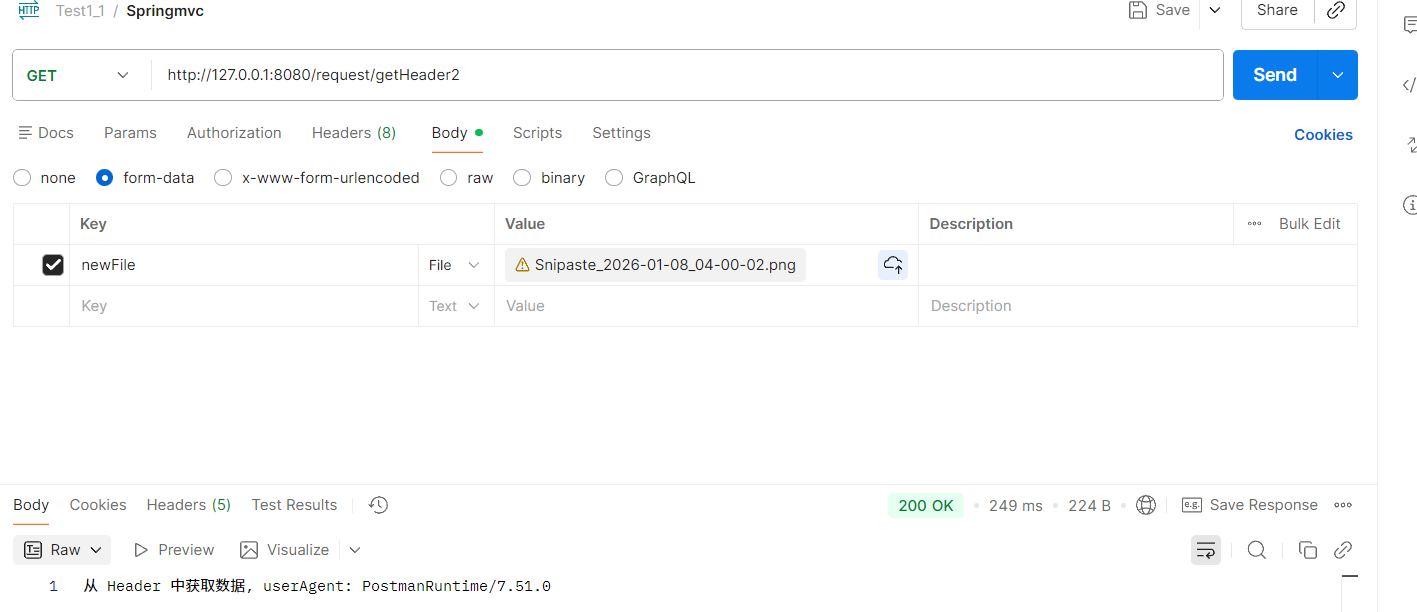
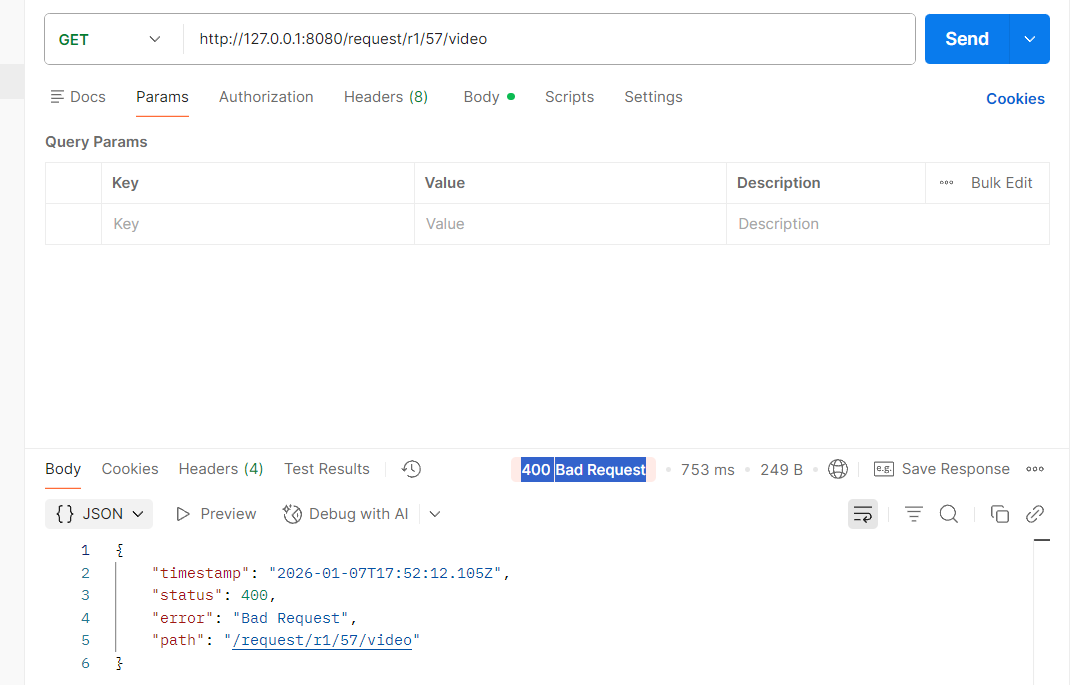
@RequestMapping("/r1/{type}/{articleID}")
public String r1(@PathVariable String type, @PathVariable Integer articleID) {
return "接收到的参数 type: " + type + " articleID: " + articleID;
}
}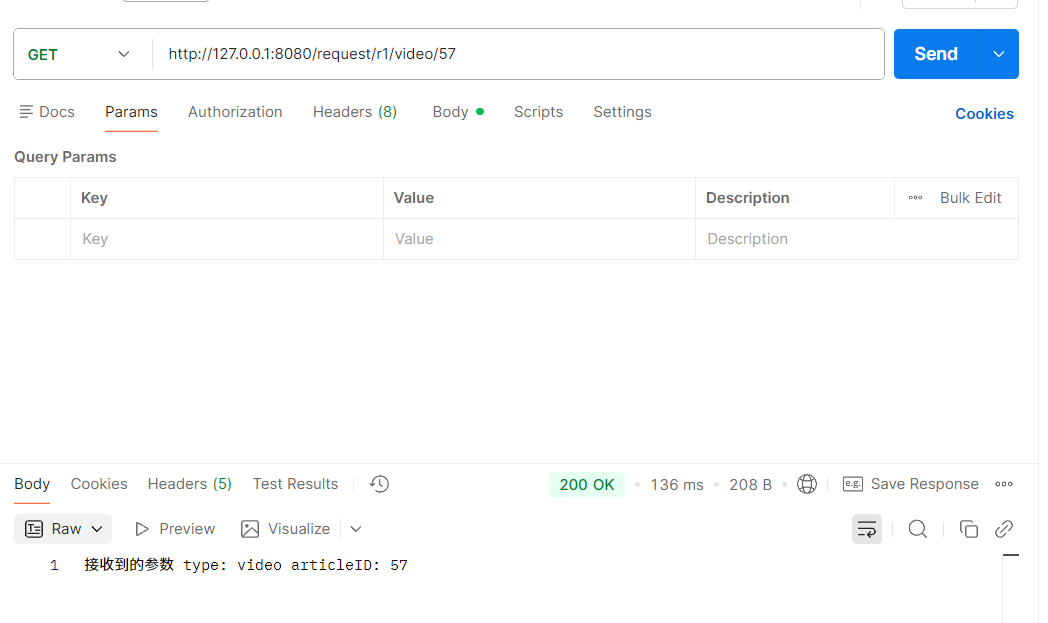
需要注意,在或者 URL 路径参数时,参数顺序不能改变,否则就会出现"400 Bad Request"。
1.2. 上传文件(@RequestPart)
核心注解:@RequestPart,绑定上传的文件,形参类型为 MultipartFile。
java
package com.yang.test1_8_1;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestPart;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
@RequestMapping("/request")
@RestController
public class RequestController {
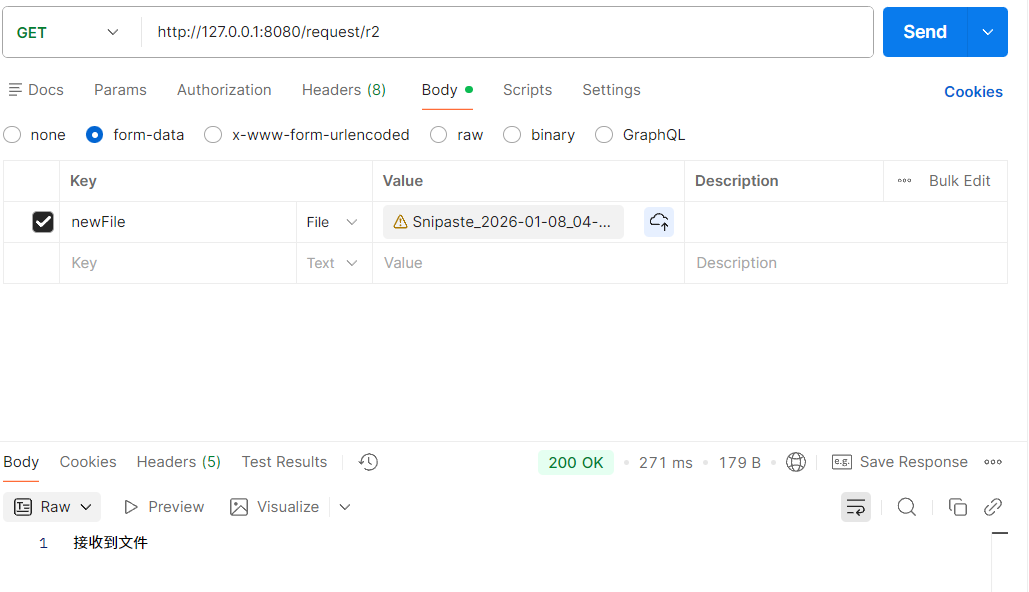
@RequestMapping("/r2")
public String r2(@RequestPart("newFile") MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println(file.getOriginalFilename());
System.out.println(file.getContentType());
File file1 = new File("D:/tmp/" + file.getOriginalFilename());
file.transferTo(file1);
return "接收到文件";
}
}
1.3. 获取 Cookie 和 Session
1. Cookie 和 Session
在 HTTP 协议中,"无状态" 是其核心特性之一,这意味着客户端与服务器的每次通信都是独立的,服务器无法天然识别连续请求是否来自同一用户。为解决这一问题,Cookie 和 Session 两种会话机制应运而生,它们分别从客户端和服务器端入手,实现了请求间的关联,支撑起登录状态保持、用户身份识别等核心功能,且二者通过 "SessionID" 紧密关联,共同构成了 Web 应用的会话管理体系。
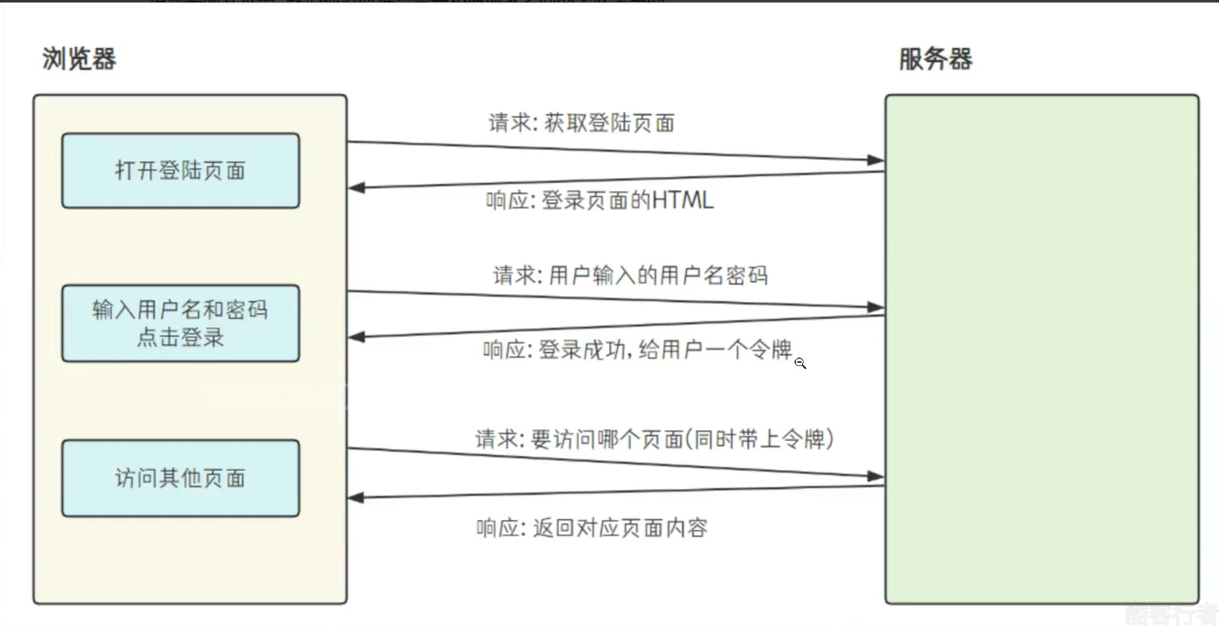
Cookie 是客户端(通常是浏览器)端保存用户信息的一种机制,本质是服务器下发给客户端的一段小型文本数据(通常不超过 4KB)。当客户端首次向服务器发送请求时,服务器可通过 HTTP 响应头中的 "Set-Cookie" 字段,将包含特定标识(如 SessionID)或临时数据的 Cookie 下发给客户端;客户端收到后,会将其存储在本地(如浏览器的缓存目录),后续向该服务器发送请求时,会自动在请求头的 "Cookie" 字段中携带这些数据,供服务器识别。Cookie 适合保存非敏感、短期的临时数据,比如用户登录时勾选 "记住我" 后,服务器会下发包含登录标识的 Cookie,下次用户访问该网站时,浏览器自动携带此 Cookie,服务器验证后无需用户重新输入账号密码;再比如电商网站的购物车功能,未登录状态下,用户添加的商品 ID 会被保存在 Cookie 中,切换页面或短暂关闭浏览器后,再次打开仍能看到之前添加的商品;还有医院挂号场景,患者首次挂号时,医院会发放一张 "就诊卡",这张就诊卡就类似 Cookie,后续患者去各科室检查、开药时,无需重复出示身份证,只需携带就诊卡(对应客户端携带 Cookie),医院就能识别患者身份并调取挂号信息。
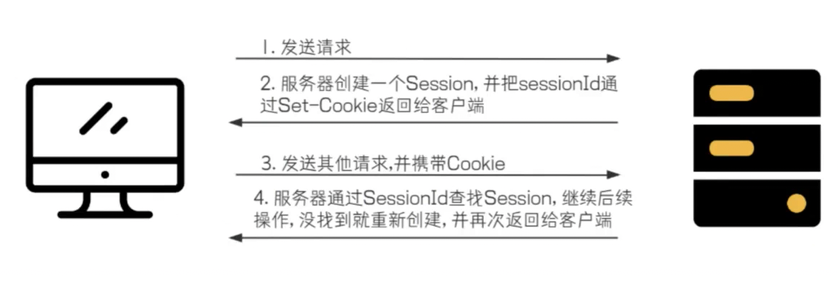
Session 则是服务器端为保存用户信息创建的特殊对象,本质是一个存储在服务器内存(或数据库、缓存)中的 "哈希表",其中 Key 是唯一的 "SessionID",Value 是用户的敏感信息(如账号、权限、登录时间等)。当客户端首次登录时,服务器会创建一个 Session 对象,生成对应的 SessionID,并通过 "Set-Cookie" 将 SessionID 下发给客户端;客户端后续请求时,会携带包含 SessionID 的 Cookie,服务器通过 SessionID 在内存中找到对应的 Session 对象,从而获取用户信息,实现 "连续服务"。Session 适合保存敏感、与用户身份强关联的数据,比如用户拨打客服电话时,接通瞬间客服系统会为该用户创建一个 "会话"(类似 Session),记录用户的手机号、咨询需求等信息,整个通话过程中,客服无需反复询问用户基本信息,就能基于这个会话持续提供服务,直到用户挂断电话(会话超时或主动结束),该会话信息才会被清理;再比如使用在线办公软件(如企业微信网页版)时,登录成功后服务器会为该用户创建 Session,存储用户的部门、角色、权限等信息,用户在软件内切换邮件、文档、会议等功能时,服务器通过请求中的 SessionID 找到对应的 Session,确认用户身份并开放对应权限,若服务器重启,默认存储在内存中的 Session 数据会丢失,用户需要重新登录才能恢复服务。
Cookie 和 Session 并非相互独立,而是通过 "SessionID" 紧密关联:Cookie 是 SessionID 的 "传输载体",负责将服务器生成的 SessionID 安全地保存在客户端并在后续请求中携带;Session 则依赖 SessionID 实现 "用户身份与信息的绑定",避免了敏感信息直接在客户端存储的安全风险。二者的核心区别在于存储位置和安全性:Cookie 存储在客户端,安全性较低(可能被篡改或伪造),因此不适合保存密码、权限等敏感数据;Session 存储在服务器端,仅通过 SessionID 与客户端交互,敏感信息不暴露在外部,安全性更高,但 Session 默认存储在服务器内存中,若服务器重启或集群部署,需结合数据库、Redis 等工具实现持久化,否则数据易丢失。
2. 获取 Cookie
Spring MVC 是基于 Servlet API 构建的原始 Web 框架,也是在 Servlet 的基础上实现的。HttpServletRequest 和 HttpServletResponse 是 Java Servlet API 核心类,也是 Spring MVC 内置对象,在控制器方法中声明即可调用。
HttpServletRequest 封装客户端 HTTP 请求信息,如 URL、方法、Cookie 等。通过 getCookies()、getHeader(String name) 等方法,可获取请求细节,用于处理用户登录等场景。
HttpServletResponse 对应服务器响应,封装响应数据、状态码等。借助 setStatus(int sc)、setHeader(String name, String value) 等方法,能构建响应并发送给客户端。在 Session 机制中,它还负责传递 SessionId 建立会话。
java
package com.yang.test1_14_1;
import jakarta.servlet.http.Cookie;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequestMapping("/request")
@RestController
public class RequestController {
@RequestMapping("/getCookie1")
public String getCookie(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
if (cookies != null) {
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
System.out.println(cookie.getName() + ":" + cookie.getValue());
}
}
return "获取 cookie 成功";
}
}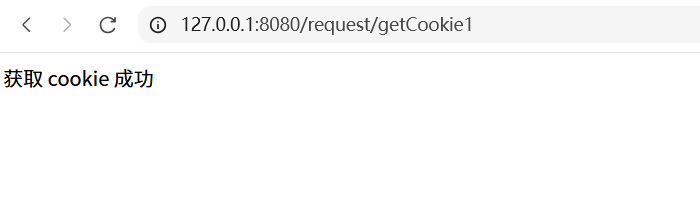
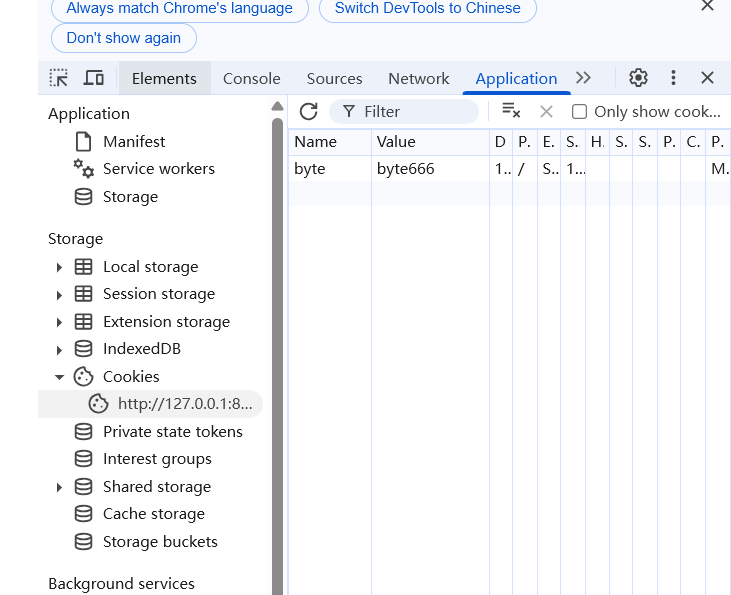
此时没有设置 Cookie,我们按下 F12 即可自动添加。从这个例⼦中,也可以看出 Cookie 是可以伪造的,也就是不安全的。所以使⽤Cookie时,后端需要进行 Cookie 校验。
java
package com.yang.test1_14_1;
import jakarta.servlet.http.Cookie;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CookieValue;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequestMapping("/request")
@RestController
public class RequestController {
@RequestMapping("/getCookie2")
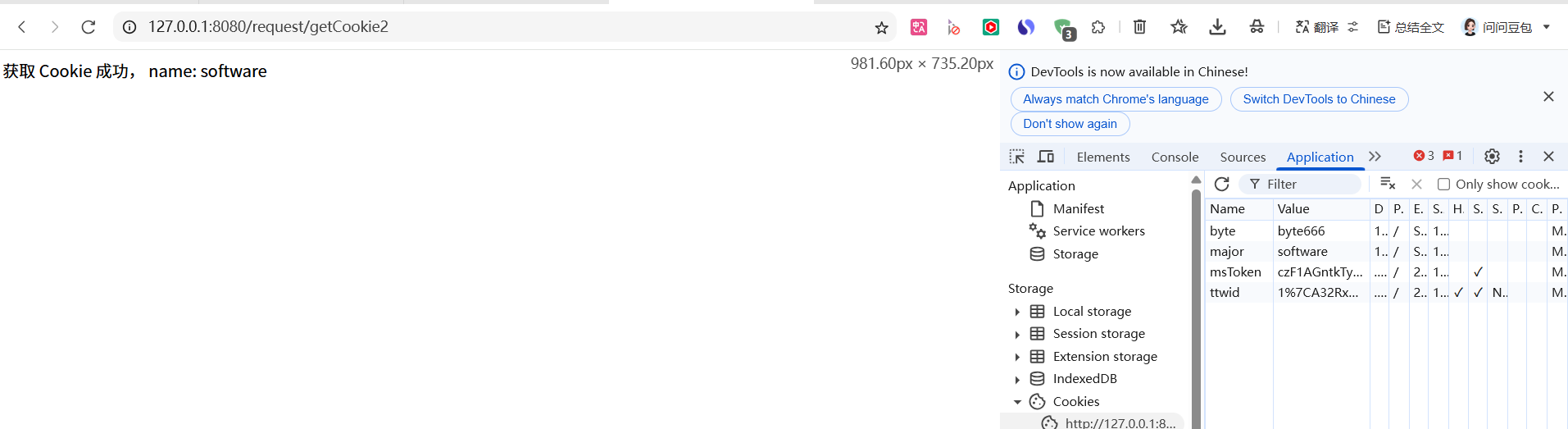
public String getCookie2(@CookieValue("major") String name) {
return "获取 Cookie 成功, name: " + name;
}
}
3. 获取 Session
Session 是服务器端的机制,我们需要先存储,才能再获取。Session 也是基于HttpServletRequest 来存储和获取的。
java
package com.yang.test1_14_2;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequestMapping("/request")
@RestController
public class RequestController {
@RequestMapping("/setSession")
public String setSession(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
// 设置用户信息
session.setAttribute("name", "Paul");
session.setAttribute("age", 22);
return "设置 Session 成功";
}
@RequestMapping("/getSession")
public String getSession(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
// 获取用户信息
String name = (String) session.getAttribute("name");
Integer age = (Integer) session.getAttribute("age");
return "从 Session 中获取数据: name: " + name + ", age: " + age;
}
}在 setSession() 方法里看不到 SessionID,是因为框架帮我们封装了细节。当客户端发请求时,getSession() 方法会自动从请求的 Cookie 里提取 SessionID,再到这个映射表里找对应的记录,最终拿到对应的 HttpSession 对象,这样就能用会话数据了。
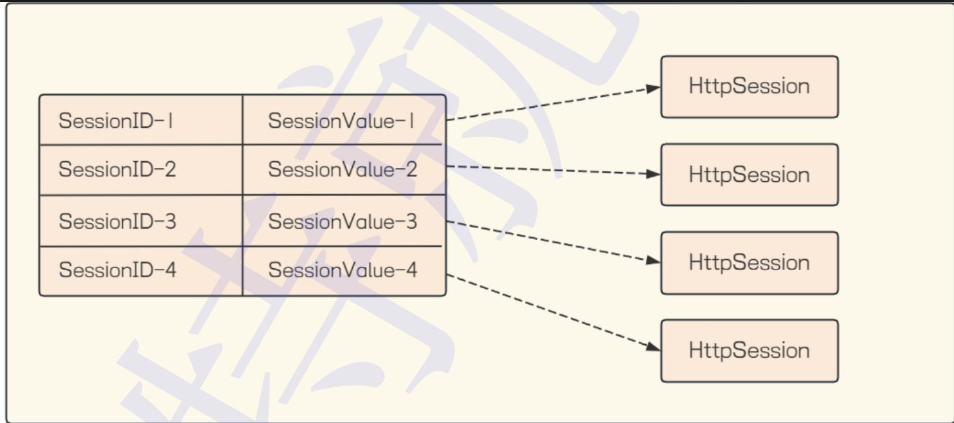
获取 Session 有两种方式:
java
HttpSession getSession(boolean var1);
HttpSession getSession();HttpSession getSession(boolean var1) : 参数如果为 true,则当不存在会话时新建会话;参数如果为 false,则当不存在会话时返回 null。
读取 Session 可以使用 HttpServletRequest。Object getAttribute(String name): 返回在该 session 会话中具有指定名称的对象,如果没有指定名 称的对象,则返回 null。
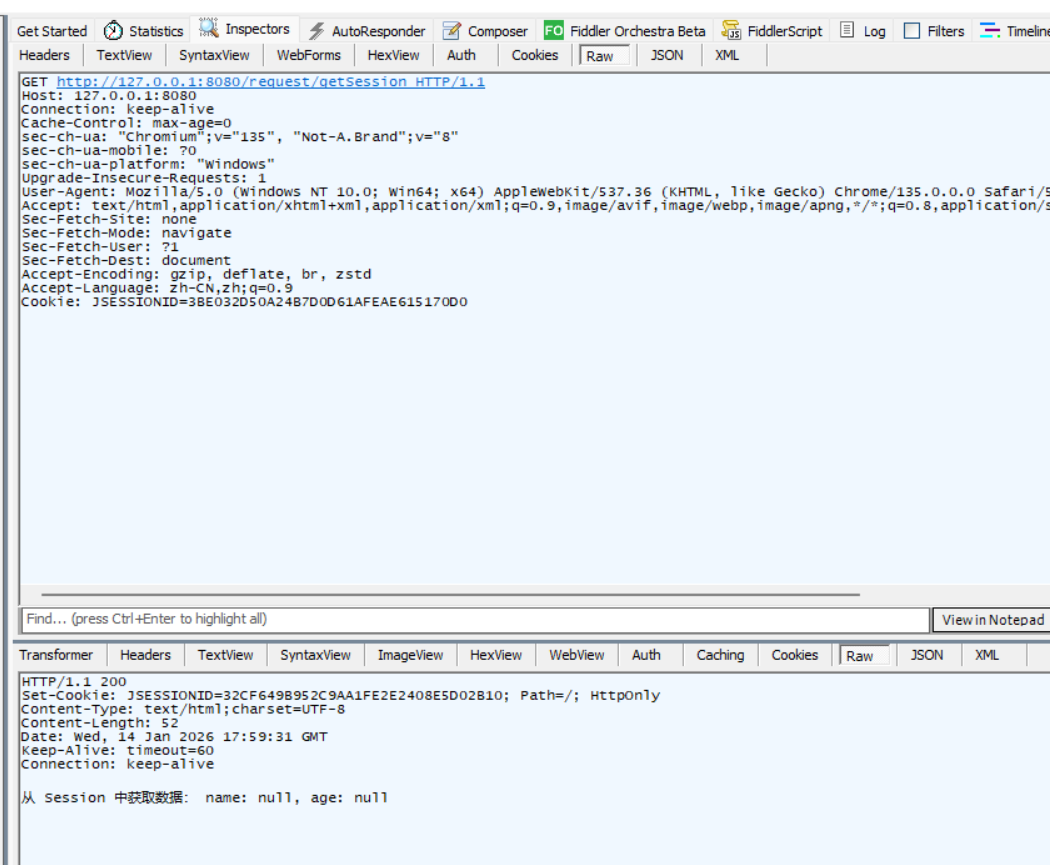
通过Fiddler观察Http请求和响应情况:可以看到,Http响应中,通过Set-Cookie告知客户端, 把 SessionID 存储在 Cookie 中。
1.4. 获取 Header
获取请求头也是通过 HttpServletRequest 类实现。
java
package com.yang.test1_15_1;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequestMapping("/request")
@RestController
public class RequestController {
@RequestMapping("/getHeader1")
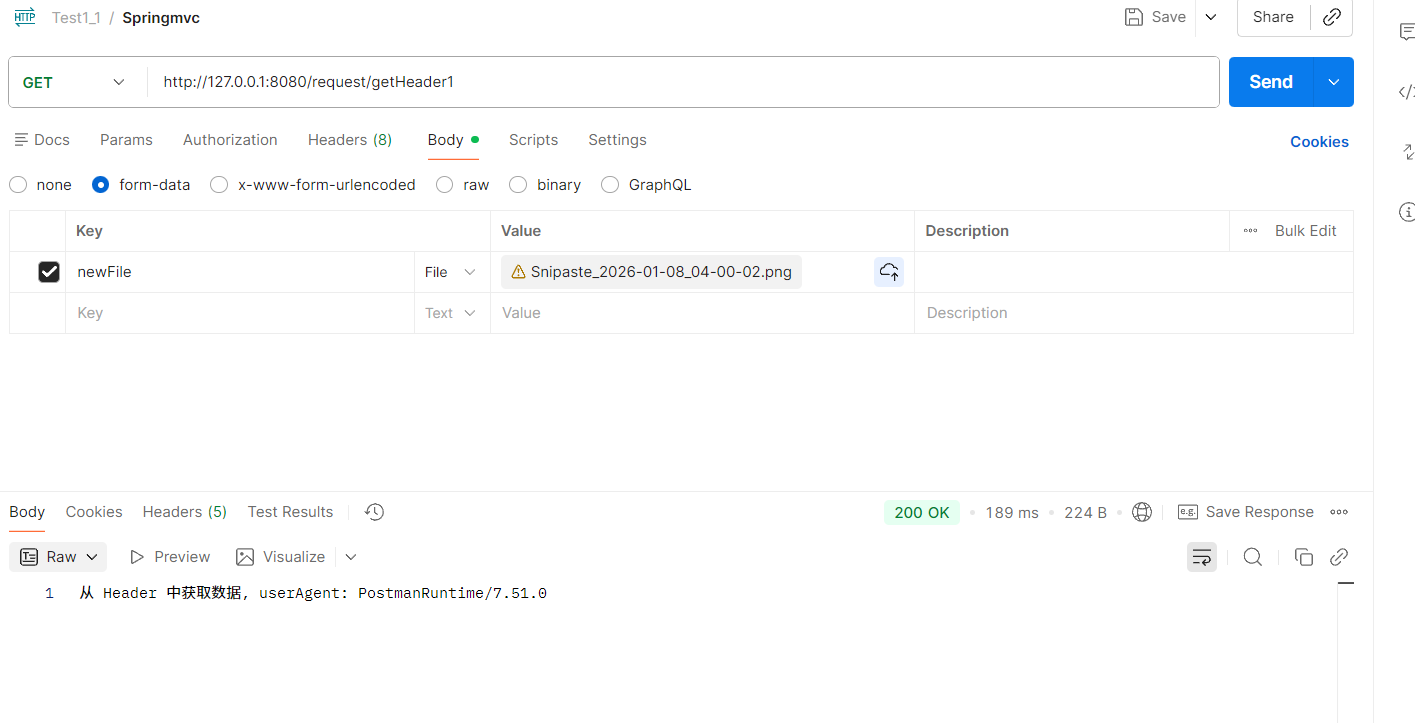
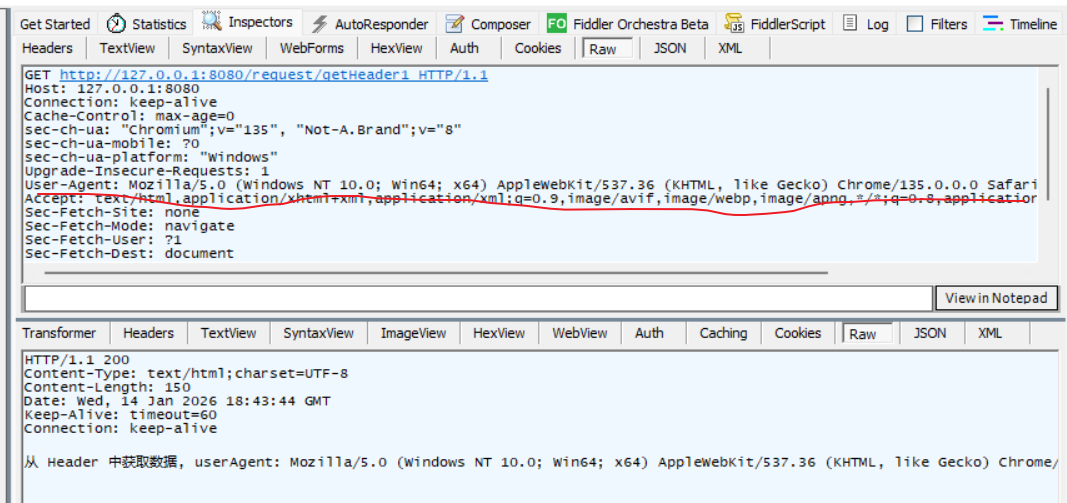
public String getHeader(HttpServletRequest request) {
String userAgent = request.getHeader("User-Agent");
return "从 Header 中获取数据, userAgent: " + userAgent;
}
}

java
package com.yang.test1_15_1;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestHeader;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequestMapping("/request")
@RestController
public class RequestController {
@RequestMapping("/getHeader2")
public String getHeader2(@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent) {
return "从 Header 中获取数据, userAgent: " + userAgent;
}
}