智能行为通常不仅仅涉及对即时输入做出反应。它需要远见、将复杂任务分解为更小的可管理步骤,以及制 定实现期望结果的策略。这就是规划模式发挥作用的地方。规划的核心是 Agent 或 Agent 系统制定一系列行 动以从初始状态向目标状态移动的能力。
规划模式概述
在 AI 背景下,可将规划 Agent 视为处理复杂目标的专家。当您要求"组织团队外出活动"时,您只需定义"
目标"(内容及约束),而无需指定"方法"。Agent 的核心任务是自主规划实现目标的路径:先理解初始状态 (如预算、参与人数、期望日期)和目标状态(成功预订活动),再设计连接两者的最优行动序列。计划并非预先设定,而是根据请求动态生成。
此过程的核心在于适应性。初始计划仅是起点而非固定脚本,Agent 的真正价值在于整合新信息、规避障碍的能力。例如,当首选场地不可用或餐饮服务商满员时,高效 Agent 不会失败,而是记录新约束、重新评估 选项,并制定新计划(如推荐替代场地或日期)。
然而,认识到灵活性和可预测性之间的权衡至关重要。动态规划是一个特定的工具,而不是通用解决方案。 当问题的解决方案已经被充分理解且可重复时,将 Agent 限制为预定的固定工作流更有效。这种方法限制 Agent 的自主性以减少不确定性和不可预测行为的风险,保证可靠和一致的结果。因此,使用规划 Agent 与 简单任务执行 Agent 的决定取决于一个问题:是否需要发现"如何",还是已经知道?
实际应用与用例
规划模式是自主系统中的核心计算过程,使 Agent 能够综合一系列行动以实现指定目标,特别是在动态或复 杂环境中。这个过程将高级目标转换为由离散可执行步骤组成的结构化计划。
在过程任务自动化等领域,规划用于编排复杂的工作流。例如,像新员工入职这样的业务流程可以分解为定 向的子任务序列,例如创建系统帐户、分配培训模块和与不同部门协调。Agent 生成一个计划以逻辑顺序执 行这些步骤,调用必要的工具或与各种系统交互以管理依赖关系。
在机器人和自主导航中,规划对于状态空间遍历是基础性的。一个系统,无论是物理机器人还是虚拟实体, 都必须生成路径或行动序列以从初始状态转换到目标状态。这涉及优化时间或能源消耗等指标,同时遵守环 境约束,如避开障碍物或遵守交通规则。
此模式对于结构化信息综合也至关重要。当被要求生成像研究报告这样的复杂输出时,Agent 可以制定一个 包括信息收集、数据总结、内容结构化和迭代完善的不同阶段的计划。同样,在涉及多步问题解决的客户支持场景中,Agent 可以创建并遵循诊断、解决方案实施和升级的系统计划。
从本质上讲,规划模式允许 Agent 从简单的反应性行动转向目标导向的行为。它提供了解决需要一系列相互 依赖操作的问题所必需的逻辑框架。
概览
是什么:
复杂问题通常无法单步解决,需前瞻性规划实现目标。缺乏结构化方法时,Agent 系统难以处理多步骤、多依赖的复杂请求,导致高级目标无法分解为可执行子任务,进而产生策略缺陷及错误结果。
为什么:
规划模式通过让 Agent 系统首先创建一个连贯的计划来解决目标提供了标准化解决方案。它涉及将 高级目标分解为一系列更小的可操作步骤或子目标。这允许系统管理复杂的工作流、编排各种工具并以逻辑 顺序处理依赖关系。LLM 特别适合这一点,因为它们可以基于其庞大的训练数据生成合理且有效的计划。这 种结构化方法将简单的反应性 Agent 转变为战略执行者,可以主动朝着复杂目标工作,甚至在必要时调整其 计划。
经验法则:
当用户的请求太复杂而无法通过单个操作或工具处理时使用此模式。它非常适合自动化多步流 程,例如生成详细的研究报告、新员工入职或执行竞争分析。每当任务需要一系列相互依赖的操作以达到最 终的综合结果时,应用规划模式。
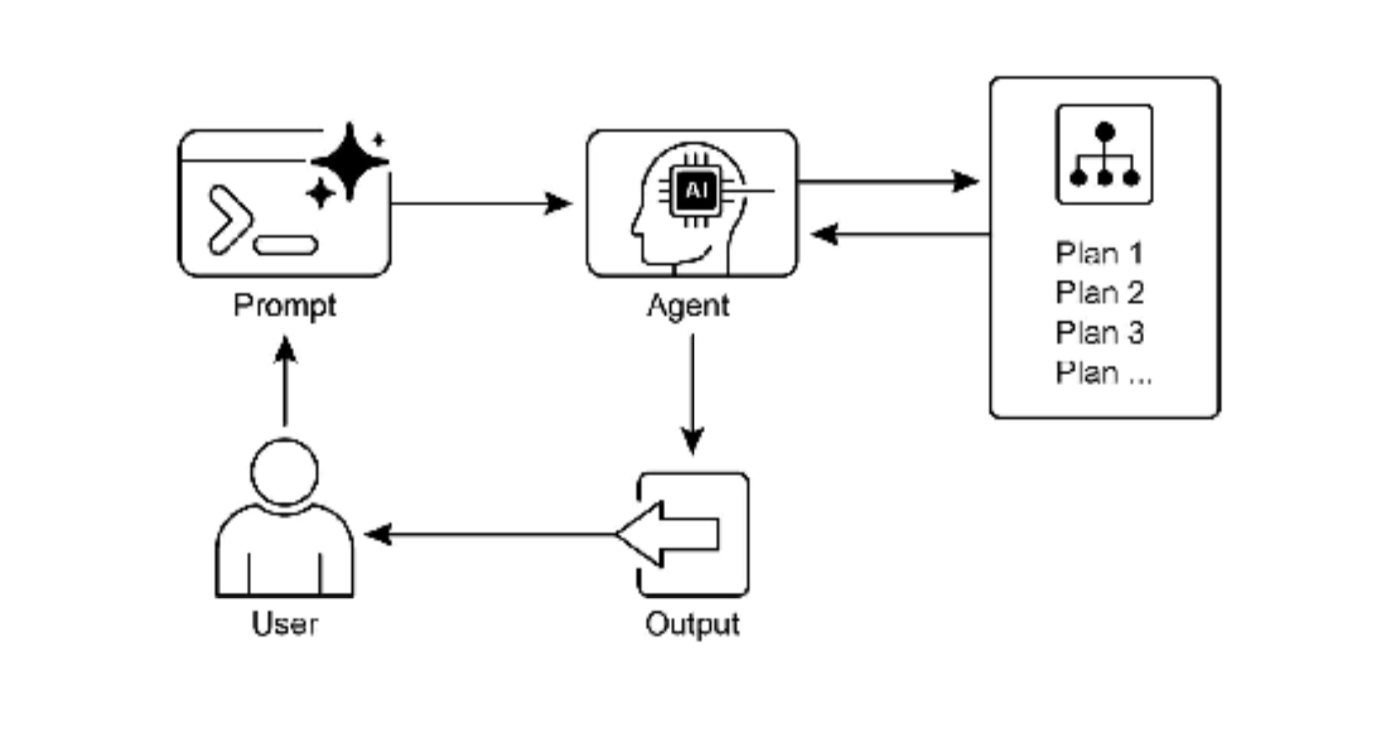
图 1:规划设计模式
关键要点
-
・ 规划使Agent能够将复杂目标分解为可操作的顺序步骤。
-
・ 它对于处理多步任务、工作流自动化和导航复杂环境至关重要。
-
・ LLM可以通过基于任务描述生成逐步方法来执行规划。
-
・ 明确提示或设计任务以要求规划步骤会在Agent框架中鼓励这种行为。
规划Agent代码实现示例
1. 基础规划Agent类
python
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Optional, Callable
from dataclasses import dataclass
from enum import Enum
import json
from datetime import datetime
import asyncio
class PlanStatus(Enum):
"""计划状态枚举"""
PENDING = "pending"
EXECUTING = "executing"
SUCCESS = "success"
FAILED = "failed"
ADAPTING = "adapting"
@dataclass
class PlanStep:
"""计划步骤定义"""
id: str
action: str
parameters: Dict[str, Any]
preconditions: List[str] # 前置条件
postconditions: List[str] # 后置条件
status: PlanStatus = PlanStatus.PENDING
result: Optional[Any] = None
error: Optional[str] = None
@dataclass
class PlanningContext:
"""规划上下文"""
goal: str
constraints: Dict[str, Any]
current_state: Dict[str, Any]
history: List[Dict[str, Any]] = None
class BasePlanningAgent:
"""基础规划Agent"""
def __init__(self, name: str, domain_knowledge: Dict[str, Any]):
self.name = name
self.domain_knowledge = domain_knowledge
self.current_plan: List[PlanStep] = []
self.context: Optional[PlanningContext] = None
self.execution_history = []
def analyze_goal(self, goal: str) -> PlanningContext:
"""分析目标并创建规划上下文"""
# 这里可以集成NLP分析目标,提取约束条件
constraints = self._extract_constraints(goal)
current_state = self._assess_current_state()
self.context = PlanningContext(
goal=goal,
constraints=constraints,
current_state=current_state,
history=[]
)
return self.context
def generate_plan(self) -> List[PlanStep]:
"""生成初始计划 - 模板方法,由子类实现"""
raise NotImplementedError
async def execute_plan(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""执行计划"""
self.execution_history.append({
"timestamp": datetime.now(),
"action": "plan_execution_started"
})
for step in self.current_plan:
try:
# 检查前置条件
if not self._check_preconditions(step):
await self._adapt_plan(step)
continue
# 执行步骤
step.status = PlanStatus.EXECUTING
result = await self._execute_step(step)
# 更新状态
step.result = result
step.status = PlanStatus.SUCCESS
self._update_current_state(step)
self.execution_history.append({
"timestamp": datetime.now(),
"step_id": step.id,
"action": step.action,
"result": result
})
except Exception as e:
step.status = PlanStatus.FAILED
step.error = str(e)
await self._handle_failure(step, e)
return {
"status": "completed",
"steps_executed": len(self.current_plan),
"success_rate": self._calculate_success_rate()
}
async def _adapt_plan(self, failed_step: PlanStep) -> bool:
"""动态调整计划"""
print(f"Adapting plan due to failure in step: {failed_step.id}")
# 重新规划策略
alternatives = self._generate_alternatives(failed_step)
for alternative in alternatives:
if await self._evaluate_alternative(alternative):
# 替换失败的步骤并继续执行
idx = self.current_plan.index(failed_step)
self.current_plan = (
self.current_plan[:idx] +
alternative +
self.current_plan[idx+1:]
)
return True
return False
def _extract_constraints(self, goal: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""从目标描述中提取约束(简化示例)"""
constraints = {}
# 示例:简单关键词提取
if "budget" in goal.lower():
constraints["budget_limit"] = self._extract_budget(goal)
if "date" in goal.lower() or "day" in goal.lower():
constraints["date_constraint"] = self._extract_dates(goal)
return constraints
# 以下方法为示例,实际实现需要具体化
def _assess_current_state(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {}
def _check_preconditions(self, step: PlanStep) -> bool:
return True
async def _execute_step(self, step: PlanStep) -> Any:
return None
def _update_current_state(self, step: PlanStep):
pass
async def _handle_failure(self, step: PlanStep, error: Exception):
pass
def _generate_alternatives(self, step: PlanStep) -> List[List[PlanStep]]:
return []
async def _evaluate_alternative(self, alternative: List[PlanStep]) -> bool:
return True
def _calculate_success_rate(self) -> float:
success_count = sum(1 for s in self.current_plan
if s.status == PlanStatus.SUCCESS)
return success_count / len(self.current_plan) if self.current_plan else 0.02. 团队活动规划Agent实现
python
class TeamEventPlanner(BasePlanningAgent):
"""团队活动规划Agent"""
def __init__(self):
domain_knowledge = {
"venue_types": ["restaurant", "park", "museum", "bowling", "escape_room"],
"budget_ranges": {
"low": {"min": 0, "max": 1000},
"medium": {"min": 1000, "max": 5000},
"high": {"min": 5000, "max": 20000}
},
"cuisine_types": ["chinese", "western", "japanese", "vegetarian"],
"activity_types": ["indoor", "outdoor", "adventure", "cultural"]
}
super().__init__("TeamEventPlanner", domain_knowledge)
self.venue_api = VenueAPI() # 假设的场地API
self.weather_api = WeatherAPI() # 天气API
def generate_plan(self) -> List[PlanStep]:
"""生成团队活动规划"""
if not self.context:
raise ValueError("Context not initialized. Call analyze_goal first.")
plan = [
PlanStep(
id="step1",
action="collect_requirements",
parameters={"context": self.context},
preconditions=[],
postconditions=["requirements_collected"]
),
PlanStep(
id="step2",
action="search_venues",
parameters={
"participants": self.context.constraints.get("participants", 10),
"budget": self.context.constraints.get("budget", 5000),
"preferred_date": self.context.constraints.get("date"),
"activity_type": self.context.constraints.get("activity_type")
},
preconditions=["requirements_collected"],
postconditions=["venues_shortlisted"]
),
PlanStep(
id="step3",
action="check_availability",
parameters={},
preconditions=["venues_shortlisted"],
postconditions=["availability_confirmed"]
),
PlanStep(
id="step4",
action="book_venue",
parameters={},
preconditions=["availability_confirmed"],
postconditions=["venue_booked"]
),
PlanStep(
id="step5",
action="arrange_transportation",
parameters={
"participants": self.context.constraints.get("participants", 10),
"venue_location": None # 将从步骤4的结果中获取
},
preconditions=["venue_booked"],
postconditions=["transportation_arranged"]
),
PlanStep(
id="step6",
action="send_invitations",
parameters={
"event_details": None # 将从之前步骤的结果中组合
},
preconditions=["venue_booked"],
postconditions=["invitations_sent"]
)
]
self.current_plan = plan
return plan
async def _execute_step(self, step: PlanStep) -> Any:
"""执行具体步骤"""
if step.action == "collect_requirements":
return await self._collect_requirements(step.parameters)
elif step.action == "search_venues":
return await self._search_venues(step.parameters)
elif step.action == "check_availability":
return await self._check_availability(step.parameters)
elif step.action == "book_venue":
return await self._book_venue(step.parameters)
elif step.action == "arrange_transportation":
return await self._arrange_transportation(step.parameters)
elif step.action == "send_invitations":
return await self._send_invitations(step.parameters)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown action: {step.action}")
async def _collect_requirements(self, params: Dict) -> Dict:
"""收集详细需求"""
print("Collecting detailed requirements...")
# 这里可以与用户交互获取更多信息
requirements = {
"participants": params["context"].constraints.get("participants", 10),
"budget": params["context"].constraints.get("budget", 5000),
"preferred_dates": params["context"].constraints.get("date"),
"dietary_restrictions": ["vegetarian", "gluten_free"], # 示例
"accessibility_needs": False
}
# 更新上下文
self.context.constraints.update(requirements)
return {
"status": "success",
"requirements": requirements
}
async def _search_venues(self, params: Dict) -> Dict:
"""搜索合适的场地"""
print(f"Searching venues for {params['participants']} participants...")
try:
# 调用场地API
venues = await self.venue_api.search(
capacity=params["participants"],
budget=params["budget"],
date=params.get("preferred_date"),
activity_type=params.get("activity_type")
)
# 根据天气调整户外场地推荐
if params.get("activity_type") == "outdoor":
weather = await self.weather_api.get_forecast(
params.get("preferred_date")
)
if weather.get("condition") == "rainy":
print("Weather warning: rain predicted. Filtering outdoor venues...")
venues = [v for v in venues if v.get("has_indoor_option")]
# 排序和筛选
sorted_venues = sorted(
venues,
key=lambda x: (
x.get("rating", 0),
-x.get("price_per_person", float('inf'))
),
reverse=True
)[:5] # 取前5个
return {
"status": "success",
"venues": sorted_venues,
"count": len(sorted_venues)
}
except Exception as e:
print(f"Venue search failed: {e}")
return {
"status": "partial",
"venues": [],
"fallback_options": self._get_fallback_venues(params)
}
async def _check_availability(self, params: Dict) -> Dict:
"""检查场地可用性"""
# 获取上一步的结果
previous_result = next(
(s.result for s in self.current_plan
if s.action == "search_venues" and s.status == PlanStatus.SUCCESS),
None
)
if not previous_result or "venues" not in previous_result:
raise ValueError("No venues to check availability for")
available_venues = []
for venue in previous_result["venues"]:
try:
is_available = await self.venue_api.check_availability(
venue_id=venue["id"],
date=self.context.constraints.get("preferred_date")
)
if is_available:
available_venues.append(venue)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to check availability for venue {venue['id']}: {e}")
if not available_venues:
# 触发重新规划
raise Exception("No venues available for the selected date")
return {
"status": "success",
"available_venues": available_venues,
"recommended": available_venues[0] # 推荐第一个
}
async def _book_venue(self, params: Dict) -> Dict:
"""预订场地"""
# 获取推荐场地
availability_result = next(
(s.result for s in self.current_plan
if s.action == "check_availability" and s.status == PlanStatus.SUCCESS),
None
)
if not availability_result:
raise ValueError("No venue selected for booking")
venue = availability_result["recommended"]
try:
booking_result = await self.venue_api.book(
venue_id=venue["id"],
date=self.context.constraints.get("preferred_date"),
participants=self.context.constraints.get("participants")
)
# 记录预订信息到上下文
self.context.current_state["booking"] = booking_result
return {
"status": "success",
"booking_id": booking_result["booking_id"],
"venue": venue["name"],
"confirmation": booking_result["confirmation_code"]
}
except Exception as e:
print(f"Booking failed: {e}")
raise
async def _arrange_transportation(self, params: Dict) -> Dict:
"""安排交通"""
print("Arranging transportation...")
# 获取预订信息
booking_info = self.context.current_state.get("booking", {})
# 模拟交通安排逻辑
participants = params["participants"]
if participants <= 10:
# 小团队,建议拼车
return {
"status": "success",
"transportation": "carpool",
"instructions": "Please coordinate carpooling among participants"
}
elif participants <= 30:
# 中型团队,预订小巴
return {
"status": "success",
"transportation": "minibus",
"provider": "Local Transport Co.",
"cost": participants * 25
}
else:
# 大型团队,需要大巴
return {
"status": "success",
"transportation": "coach",
"provider": "City Bus Services",
"cost": participants * 20
}
async def _send_invitations(self, params: Dict) -> Dict:
"""发送邀请"""
print("Sending invitations...")
# 收集活动详情
booking_result = next(
(s.result for s in self.current_plan
if s.action == "book_venue" and s.status == PlanStatus.SUCCESS),
None
)
transportation_result = next(
(s.result for s in self.current_plan
if s.action == "arrange_transportation" and s.status == PlanStatus.SUCCESS),
None
)
event_details = {
"title": "Team Building Event",
"venue": booking_result["venue"] if booking_result else "TBD",
"date": self.context.constraints.get("preferred_date"),
"transportation": transportation_result["transportation"] if transportation_result else "TBD",
"meeting_point": "Office lobby at 9:00 AM"
}
# 模拟发送邀请(实际应集成邮件/消息API)
print(f"Sending invitations with details: {event_details}")
return {
"status": "success",
"invitations_sent": True,
"recipients_count": self.context.constraints.get("participants", 10),
"event_details": event_details
}
def _generate_alternatives(self, failed_step: PlanStep) -> List[List[PlanStep]]:
"""生成替代方案"""
alternatives = []
if failed_step.action == "check_availability" or failed_step.action == "book_venue":
# 如果场地不可用,尝试替代方案
alternatives.append([
PlanStep(
id=f"alt_{failed_step.id}_1",
action="search_alternative_venues",
parameters={
"retry_count": 1,
"flexible_date": True
},
preconditions=failed_step.preconditions,
postconditions=["alternative_venues_found"]
),
PlanStep(
id=f"alt_{failed_step.id}_2",
action="check_availability",
parameters={},
preconditions=["alternative_venues_found"],
postconditions=["availability_confirmed"]
),
failed_step # 重新尝试预订
])
return alternatives3. 模拟API类(用于演示)
python
class VenueAPI:
"""模拟场地API"""
async def search(self, capacity: int, budget: float, date=None, activity_type=None):
# 模拟API调用延迟
await asyncio.sleep(0.5)
# 模拟数据
venues = [
{
"id": "v001",
"name": "Green Park Restaurant",
"type": "restaurant",
"capacity": 50,
"price_per_person": 120,
"rating": 4.5,
"has_indoor_option": True
},
{
"id": "v002",
"name": "Adventure Zone",
"type": "outdoor",
"capacity": 30,
"price_per_person": 200,
"rating": 4.8,
"has_indoor_option": False
},
# 更多模拟数据...
]
# 过滤
filtered = [
v for v in venues
if v["capacity"] >= capacity and
v["price_per_person"] * capacity <= budget
]
if activity_type:
filtered = [v for v in filtered if v["type"] == activity_type]
return filtered
async def check_availability(self, venue_id: str, date):
await asyncio.sleep(0.3)
# 模拟随机可用性(80%概率可用)
import random
return random.random() > 0.2
async def book(self, venue_id: str, date, participants: int):
await asyncio.sleep(0.5)
return {
"booking_id": f"BKG_{venue_id}_{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')}",
"confirmation_code": "ABC123XYZ",
"status": "confirmed"
}
class WeatherAPI:
"""模拟天气API"""
async def get_forecast(self, date):
await asyncio.sleep(0.2)
# 模拟数据
conditions = ["sunny", "cloudy", "rainy", "windy"]
import random
return {
"date": date,
"condition": random.choice(conditions),
"temperature": random.randint(15, 30)
}4. 使用示例
python
async def main():
"""主函数示例"""
# 创建规划Agent
planner = TeamEventPlanner()
# 定义目标
goal = "组织团队建设活动,预算5000元,20人参加,下周五,偏好户外活动"
try:
# 1. 分析目标
print("步骤1: 分析目标...")
context = planner.analyze_goal(goal)
print(f"分析完成: {context.goal}")
print(f"约束条件: {context.constraints}")
# 2. 生成计划
print("\n步骤2: 生成计划...")
plan = planner.generate_plan()
print(f"生成 {len(plan)} 个步骤:")
for step in plan:
print(f" - {step.id}: {step.action}")
# 3. 执行计划
print("\n步骤3: 执行计划...")
result = await planner.execute_plan()
print(f"\n执行结果: {result['status']}")
print(f"成功率: {result['success_rate']:.1%}")
# 4. 显示执行历史
print("\n执行历史:")
for record in planner.execution_history[:5]: # 显示前5条
print(f" {record['timestamp'].strftime('%H:%M:%S')} - {record.get('action', 'unknown')}")
# 5. 显示最终状态
print("\n最终状态:")
successful_steps = [s for s in planner.current_plan if s.status == PlanStatus.SUCCESS]
for step in successful_steps:
print(f" {step.id}: {step.action} - 成功")
if step.result:
print(f" 结果: {step.result.get('status', 'N/A')}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"规划过程出错: {e}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
# 运行示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())5. 高级功能扩展
python
class HierarchicalPlanningAgent(BasePlanningAgent):
"""分层规划Agent"""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__("HierarchicalPlanner", {})
self.high_level_planner = HighLevelPlanner()
self.low_level_planners = {
"logistics": LogisticsPlanner(),
"content": ContentPlanner(),
"budget": BudgetPlanner()
}
async def generate_hierarchical_plan(self, goal: str):
"""生成分层计划"""
# 高层规划:分解目标
high_level_steps = await self.high_level_planner.decompose_goal(goal)
master_plan = []
for hl_step in high_level_steps:
# 为每个高层步骤选择低层规划器
planner_type = self._select_low_level_planner(hl_step)
low_level_planner = self.low_level_planners[planner_type]
# 生成详细步骤
detailed_steps = await low_level_planner.generate_detailed_plan(hl_step)
master_plan.extend(detailed_steps)
return master_plan
class MultiAgentPlanningSystem:
"""多Agent规划系统"""
def __init__(self):
self.agents = []
self.coordinator = CoordinationModule()
async def coordinate_planning(self, goal: str):
"""协调多个Agent进行规划"""
# 任务分配
tasks = self._decompose_task(goal)
# 并行规划
agent_tasks = []
for i, task in enumerate(tasks):
agent = self._select_agent_for_task(task)
agent_tasks.append(agent.generate_plan(task))
# 等待所有Agent完成规划
plans = await asyncio.gather(*agent_tasks)
# 协调和整合计划
integrated_plan = await self.coordinator.integrate_plans(plans)
# 解决冲突
resolved_plan = await self.coordinator.resolve_conflicts(integrated_plan)
return resolved_plan6. 测试用例
python
import pytest
class TestPlanningAgent:
"""规划Agent测试"""
@pytest.fixture
def planner(self):
return TeamEventPlanner()
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_goal_analysis(self, planner):
"""测试目标分析"""
goal = "组织团队活动,预算3000元,15人"
context = planner.analyze_goal(goal)
assert context.goal == goal
assert "budget" in context.constraints
assert context.constraints.get("participants") == 15
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_plan_generation(self, planner):
"""测试计划生成"""
goal = "团队建设活动"
planner.analyze_goal(goal)
plan = planner.generate_plan()
assert len(plan) > 0
assert all(isinstance(step, PlanStep) for step in plan)
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_plan_execution(self, planner):
"""测试计划执行"""
goal = "测试活动"
planner.analyze_goal(goal)
planner.generate_plan()
result = await planner.execute_plan()
assert "status" in result
assert 0 <= result.get("success_rate", 0) <= 1总结
这个代码示例展示了:
-
基础架构:定义了规划Agent的核心类和数据结构
-
具体实现:实现了团队活动规划的具体逻辑
-
动态适应性:展示了如何在执行过程中调整计划
-
模拟环境:提供了API模拟类进行测试
-
高级功能:展示了分层规划和多Agent系统的扩展
实际应用中,需要根据具体业务场景:
-
集成真实的外部API(如预订系统、天气服务)
-
添加更复杂的约束处理和优化逻辑
-
实现更智能的重新规划策略
-
集成机器学习模型进行预测和优化
-
添加用户交互和反馈机制
-
这个框架可以作为构建实际规划系统的基础,根据具体需求进行扩展和优化。
总之,规划模式是将 Agent 系统从简单的反应性响应者提升为战略性、目标导向的执行者的基础组件。现代大型语言模型为此提供了核心能力,自主地将高级目标分解为连贯的可操作步骤。此模式从简单的顺序任务执行扩展到更复杂和动态的系统。最终,规划为复杂问题 的人类意图和自动化执行之间提供了必要的桥梁。通过构建问题解决方法,此模式使 Agent 能够管理复杂的 工作流并提供全面的综合结果。