前言
其实去年就想写这篇文章,但因为拖延症就拖到了26年。本文主要介绍 LangChain v0.3 版本中 create_react_agent 所创建的 ReAct Agent 的工作原理。在准备这篇文章之前,LangChain 就已经发布 v1.0 版本了,但继续继续研究 v0.3 版本仍然具有意义:
- 不管是什么版本,我们都可以学习其 Agent 的设计思路,为日后工作提供参考。
- v1.0版本使用
create_agent作为新一代 Agent 构建方案,取代原有的create_react_agent,并且将 LangGraph 作为 v1.0 版本 Agent 的底层引擎,这加大了 1.0 版本 ReAct Agent 研究难度。我们可以从易到难,逐步研究。 - 我们可以与 v1.0 版本进行对比,研究其改进方向。
本文的目标是通过了解 LangChain v0.3 ReAct Agent 的工作原理,能够回答以下两个问题:
- Agent 接收任务之后,是如何规划和执行的?
- Agent 是如何判断任务达到完成状态的?
用法
正文开启前,我们先简单回顾一下 v0.3 版本创建一个 ReAct Agent 的基本流程:
- 准备工具:使用
langchain_core.tools导出的tool装饰器将函数转变为工具,或者导入现成的工具。 - 创建 prompt:创建一个 prompt,并在 prompt 中为工具预留插槽。
- 组装 Agent:
- 声明工具数组,包含所有的工具。
- 创建一个聊天模型。
- 使用
langchain.agents导出的create_react_agent将 模型、工具数组、prompt 组装成一个 Agent。
- 使用
langchain.agents导出的AgentExecutor执行 Agent。AgentExecutor本质是一个循环,会一直执行到大模型认为已经找到了答案。
一个简单的例子如下:
python
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_react_agent
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
import os
from src.config import OPENAI_API_KEY, OPENAI_BASE_URL, LANGSMITH_API_KEY
# 可以按需使用 LangSmith
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true"
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_API_KEY"] = LANGSMITH_API_KEY
# tool装饰器将函数转变为工具
@tool
def calculate(what: str) -> float:
"""Runs a calculation and returns the number - uses Python so be sure to use floating point syntax if necessary"""
return eval(what)
@tool(
"ask_fruit_unit_price",
description = "Asks the user for the price of a fruit",
)
def ask_fruit_unit_price(fruit: str):
# casefold() 方法用于对字符串进行大小写不敏感的比较
if fruit.casefold() == "apple":
return "Apple unit price is 10/kg"
elif fruit.casefold() == "banana":
return "Banana unit price is 6/kg"
else:
return f"{fruit} unit price is 20/kg"
# 参考 https://smith.langchain.com/hub/hwchase17/react
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template("""Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:
{tools}
Use the following format:
Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [{tool_names}]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can repeat N times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input question
Begin!
Question: {input}
Thought:{agent_scratchpad}""")
# agent_scratchpad 是在 Agent 的执行过程中,存放中间过程的,类似于聊天记录
# 组装 Agent
tools = [calculate, ask_fruit_unit_price]
model = ChatOpenAI(
model = "gpt-4o-mini",
api_key = OPENAI_API_KEY,
base_url = OPENAI_BASE_URL
)
agent = create_react_agent(model, tools, prompt)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent = agent, tools = tools, verbose = True)
result = agent_executor.invoke({
"input": "What is the total price of 3kg of apple and 2kg of banana?"
})
print(result)上面的代码执行打印日志如下:
plainText
calculate.name: calculate
calculate.description: Runs a calculation and returns the number - uses Python so be sure to use floating point syntax if necessary
calculate.args: {'what': {'title': 'What', 'type': 'string'}}
> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...
I need to find out the unit prices of apples and bananas in order to calculate the total price. I'll start by asking for the unit price of apples.
Action: ask_fruit_unit_price
Action Input: "apple" Apple unit price is 10/kgNow that I have the unit price of apples, I'll ask for the unit price of bananas to proceed with the total price calculation.
Action: ask_fruit_unit_price
Action Input: "banana" Banana unit price is 6/kgI now have both unit prices: apples cost 10 per kg and bananas cost 6 per kg. Now, I can calculate the total price for 3 kg of apples and 2 kg of bananas.
I will calculate the total price using the formula:
Total Price = (Unit Price of Apple * Quantity of Apple) + (Unit Price of Banana * Quantity of Banana).
Action: calculate
Action Input: "(10 * 3) + (6 * 2)" 42I now know the final answer.
Final Answer: The total price of 3kg of apple and 2kg of banana is 42.
> Finished chain.
{'input': 'What is the total price of 3kg of apple and 2kg of banana?', 'output': 'The total price of 3kg of apple and 2kg of banana is 42.'}基本流程
v0.3 ReAct Agent 的基本运行流程如下:
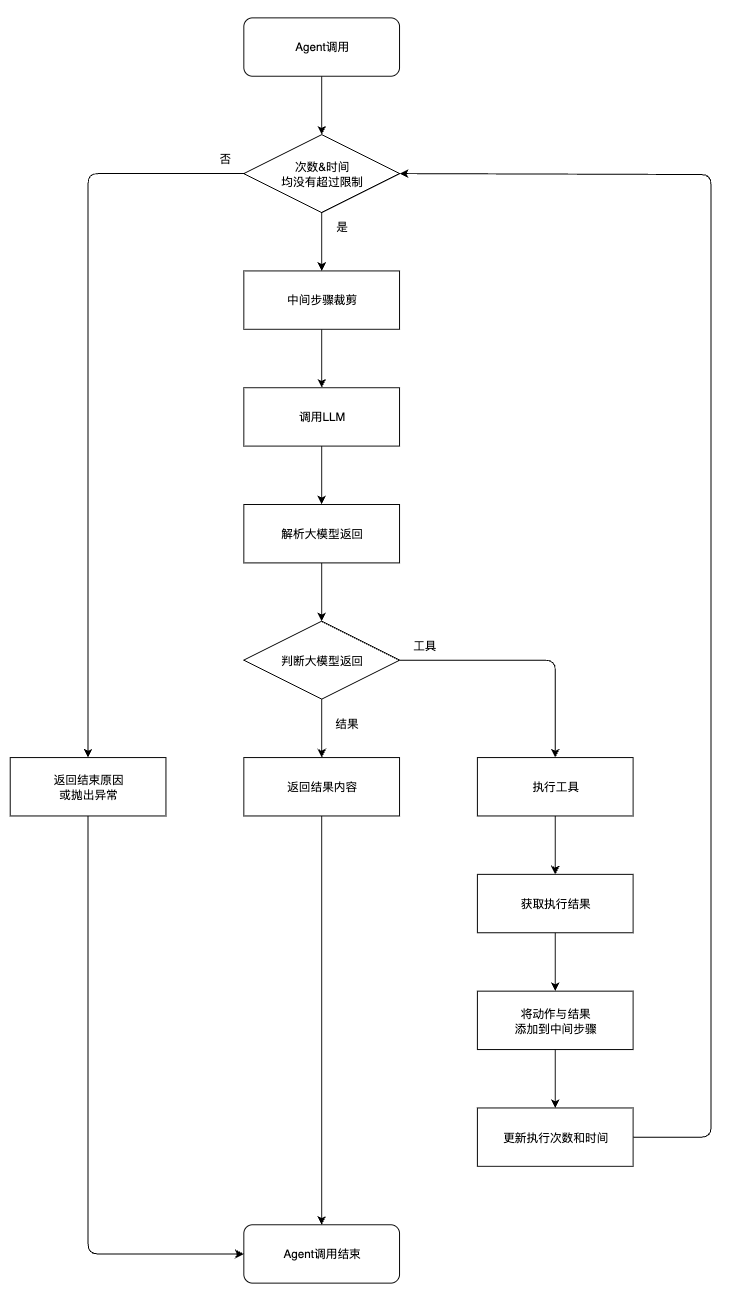
create_react_agent
create_react_agent 将模型、工具、prompt 组装成一个 Agent,这个 Agent 的主要功能就是调用大模型获取下一步的行动,本身没有记忆能力。
源码
create_react_agent 方法的源码并不复杂,除开注释只有如下几行:
python
def create_react_agent(
llm: BaseLanguageModel,
tools: Sequence[BaseTool],
prompt: BasePromptTemplate,
output_parser: Optional[AgentOutputParser] = None,
tools_renderer: ToolsRenderer = render_text_description,
*,
stop_sequence: Union[bool, List[str]] = True,
) -> Runnable:
missing_vars = {"tools", "tool_names", "agent_scratchpad"}.difference(
prompt.input_variables + list(prompt.partial_variables)
)
if missing_vars:
raise ValueError(f"Prompt missing required variables: {missing_vars}")
prompt = prompt.partial(
tools=tools_renderer(list(tools)),
tool_names=", ".join([t.name for t in tools]),
)
if stop_sequence:
stop = ["\nObservation"] if stop_sequence is True else stop_sequence
llm_with_stop = llm.bind(stop=stop)
else:
llm_with_stop = llm
output_parser = output_parser or ReActSingleInputOutputParser()
agent = (
RunnablePassthrough.assign(
agent_scratchpad=lambda x: format_log_to_str(x["intermediate_steps"]),
)
| prompt
| llm_with_stop
| output_parser
)
return agentPrompt要求
create_react_agent 方法要求 Prompt 中必须包含如下占位符:
tools: 包含每个工具的描述和参数。tool_names:包含所有工具名称。agent_scratchpad:以字符串形式在 Agent 的执行过程中,存放中间过程。
在源码的注释中有如下示例:
plainText
Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:
{tools}
Use the following format:
Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [{tool_names}]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can repeat N times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input question
Begin!
Question: {input}
Thought:{agent_scratchpad}这也是之前"用法"已接种所使用的 Prompt。其实还有一些隐藏的要求------大模型的输出最好按照以下格式:
plainText
Thought: ...
Action: ...
Action Input: ...
Observation: ...
...(循环 N 次)
Final Answer: ...否则后续解析时可能出现异常。
主要流程
create_react_agent 方法主要流程如下:
- 检查提示模板是否包含必需变量;
- 渲染工具描述并绑定到提示;
- 设置停止序列防止模型幻觉;
- 组装代理执行链。
检查入参
如下代码负责检查方法入参:
python
missing_vars = {"tools", "tool_names", "agent_scratchpad"}.difference(
prompt.input_variables + list(prompt.partial_variables)
)
if missing_vars:
raise ValueError(f"Prompt missing required variables: {missing_vars}")基本逻辑是:
- 定义必需变量集合:首先定义了一个必需变量集合
{"tools", "tool_names", "agent_scratchpad"},这些是 ReAct agent 运行所必需的三个变量。 - 获取提示模板中的变量:通过
prompt.input_variables和prompt.partial_variables获取提示模板中已有的变量,其中:prompt.input_variables是提示模板需要但尚未赋值的输入变量。prompt.partial_variables是提示模板中已经部分赋值的变量。
- 计算差集:使用
set.difference()方法计算必需变量集合与提示模板中实际存在的变量集合之间的差集,得到缺失的变量。 - 抛出异常:如果存在缺失的变量(即
missing_vars非空),则抛出ValueError异常,并指出缺少哪些必需变量。
绑定工具
如下代码完成工具的绑定:
python
prompt = prompt.partial(
tools=tools_renderer(list(tools)),
tool_names=", ".join([t.name for t in tools]),
)如果 create_react_agent 方法没有传入 tools_renderer 参数,则默认使用 render_text_description 方法绑定工具,render_text_description 方法定义如下:
python
def render_text_description(tools: list[BaseTool]) -> str:
descriptions = []
for tool in tools:
if hasattr(tool, "func") and tool.func:
sig = signature(tool.func)
description = f"{tool.name}{sig} - {tool.description}"
else:
description = f"{tool.name} - {tool.description}"
descriptions.append(description)
return "\n".join(descriptions)render_text_description 方法的主要逻辑:
- 遍历每个工具对象。
- 检查工具是否有func属性且不为空。
- 如果有func,则获取函数签名并格式化为"工具名(签名) - 描述"。
- 否则格式化为"工具名 - 描述"。
- 将所有描述用换行符连接返回。
最后使用 prompt.partial() 方法创建一个新的提示模板,其中 tools、tool_names 变量将会被被填充。
设置停止序列
如下代码完成停止序列的设置:
python
if stop_sequence:
stop = ["\nObservation"] if stop_sequence is True else stop_sequence
llm_with_stop = llm.bind(stop=stop)
else:
llm_with_stop = llmstop_sequence 参数的作用是控制语言模型何时停止生成文本,防止模型产生幻觉。
当设置为 True(默认值)时,大模型会在 "\nObservation" 处停止生成。这是因为在 ReAct 框架中,模型应该在生成 "Action" 和 "Action Input" 后等待工具执行结果(Observation)。如果没有停止序列,模型可能会自己编造 "Observation" 内容而不是等待真实的工具执行结果。
组装Agent链
如下代码完成 Agent 链的组装:
python
output_parser = output_parser or ReActSingleInputOutputParser()
agent = (
RunnablePassthrough.assign(
agent_scratchpad=lambda x: format_log_to_str(x["intermediate_steps"]),
)
| prompt
| llm_with_stop
| output_parser
)
return agent这里使用了LangChain表达式 (LCEL),将prompt、LLM、输出解析器组装成一条链。
在调用 create_react_agent 方法创建 Agent 时,如果没有传入 output_parser 参数,则默认使用 ReActSingleInputOutputParser 格式化大模型输出。ReActSingleInputOutputParser 需要单独进行说明,它对整个 Agent 能够正常运行至关重要。
ReActSingleInputOutputParser
ReActSingleInputOutputParser 是一个专门用于解析 ReAct Agent 输出的解析器类,它的主要作用是将语言模型生成的文本封装为 AgentAction 或 AgentFinish 对象。
ReActSingleInputOutputParser 能够正常工作的前提是------在 Prompt 中必须要求大模型按照指定格式输出。
当代理需要执行工具操作时,输出应采用以下格式:
plainText
Thought: agent thought here
Action: search
Action Input: what is the temperature in SF?解析器会生成一个 AgentAction 对象。
当代理准备给出最终答案时,输出应采用以下格式:
plainText
Thought: agent thought here
Final Answer: The temperature is 100 degrees解析器会生成一个 AgentFinish 对象。
ReActSingleInputOutputParser 的核心方法是 parse:
python
def parse(self, text: str) -> Union[AgentAction, AgentFinish]:
includes_answer = FINAL_ANSWER_ACTION in text
regex = (
r"Action\s*\d*\s*:[\s]*(.*?)[\s]*Action\s*\d*\s*Input\s*\d*\s*:[\s]*(.*)"
)
action_match = re.search(regex, text, re.DOTALL)
if action_match:
if includes_answer:
raise OutputParserException(
f"{FINAL_ANSWER_AND_PARSABLE_ACTION_ERROR_MESSAGE}: {text}"
)
action = action_match.group(1).strip()
action_input = action_match.group(2)
tool_input = action_input.strip(" ")
tool_input = tool_input.strip('"')
return AgentAction(action, tool_input, text)
elif includes_answer:
return AgentFinish(
{"output": text.split(FINAL_ANSWER_ACTION)[-1].strip()}, text
)
if not re.search(r"Action\s*\d*\s*:[\s]*(.*?)", text, re.DOTALL):
raise OutputParserException(
f"Could not parse LLM output: `{text}`",
observation=MISSING_ACTION_AFTER_THOUGHT_ERROR_MESSAGE,
llm_output=text,
send_to_llm=True,
)
elif not re.search(
r"[\s]*Action\s*\d*\s*Input\s*\d*\s*:[\s]*(.*)", text, re.DOTALL
):
raise OutputParserException(
f"Could not parse LLM output: `{text}`",
observation=MISSING_ACTION_INPUT_AFTER_ACTION_ERROR_MESSAGE,
llm_output=text,
send_to_llm=True,
)
else:
raise OutputParserException(f"Could not parse LLM output: `{text}`")逻辑非常简单:
- 判断LLM输出中是否包含最终答案(
Final Answer:) - 检测是否存在可解析的动作指令(
Action:和Action Input:) - 根据检测结果返回相应的对象或抛出异常
从上述代码可以看出,LangChain v0.3 提供的 ReAct 实现要求 TAO 循环中每次调用大模型要么返回调用工具,要么给出最终答案,否则会抛出异常。
这和之前梳理的 OpenManus Agent 的实现有所不同(参考OpenManus 原理浅析(一)------Agent 基本原理),在 OpenManus 的每次 TAO 循环中,是判断了大模型是否返回需要调用工具,如果不要需要,则继续进行循环,直到终止Agent工具被调用,才结束循环。
AgentExecutor
AgentExecutor 本质是一个循环,一直执行直到 Agent 认为已经找到了答案。
调用方法
_call 是关键方法,agent_executor.invoke 最终就是调用 _call 方法获取输出:
python
def _call(
self,
inputs: Dict[str, str],
run_manager: Optional[CallbackManagerForChainRun] = None,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Run text through and get agent response."""
# Construct a mapping of tool name to tool for easy lookup
name_to_tool_map = {tool.name: tool for tool in self.tools}
# We construct a mapping from each tool to a color, used for logging.
color_mapping = get_color_mapping(
[tool.name for tool in self.tools], excluded_colors=["green", "red"]
)
intermediate_steps: List[Tuple[AgentAction, str]] = []
# Let's start tracking the number of iterations and time elapsed
iterations = 0
time_elapsed = 0.0
start_time = time.time()
# We now enter the agent loop (until it returns something).
while self._should_continue(iterations, time_elapsed):
next_step_output = self._take_next_step(
name_to_tool_map,
color_mapping,
inputs,
intermediate_steps,
run_manager=run_manager,
)
if isinstance(next_step_output, AgentFinish):
return self._return(
next_step_output, intermediate_steps, run_manager=run_manager
)
intermediate_steps.extend(next_step_output)
if len(next_step_output) == 1:
next_step_action = next_step_output[0]
# See if tool should return directly
tool_return = self._get_tool_return(next_step_action)
if tool_return is not None:
return self._return(
tool_return, intermediate_steps, run_manager=run_manager
)
iterations += 1
time_elapsed = time.time() - start_time
output = self._action_agent.return_stopped_response(
self.early_stopping_method, intermediate_steps, **inputs
)
return self._return(output, intermediate_steps, run_manager=run_manager)_call 方法中,主要通过一个 while 循环,不断调用 _take_next_step 方法获取每一步的执行结果,直至 _take_next_step 返回 AgentFinish 类型的结果,或者达到终止条件。
是否应该继续循环?
在 _call 方法中,声明循环次数 iterations 和耗时 time_elapsed。在 while 循环中判断循环次数或执行时间是否超过上限,只要有一个超过上限,就停止执行。
_should_continue 函数的逻辑如下:
python
def _should_continue(self, iterations: int, time_elapsed: float) -> bool:
if self.max_iterations is not None and iterations >= self.max_iterations:
return False
if (
self.max_execution_time is not None
and time_elapsed >= self.max_execution_time
):
return False
return Truemax_iterations 默认是 15,max_execution_time 默认是 None。
每次循环
步骤
每次循环中,方法调用链路:_take_next_step -> _consume_next_step -> _iter_next_step -> _perform_agent_action。
其中:
_take_next_step和_consume_next_step并不承接 Agent 的实际逻辑,只是处理_iter_next_step的返回。_iter_next_step实现Agent单步执行逻辑,包括调用LLM,以及处理LLM的返回。- 如果LLM返回需要调用工具,则交由
_perform_agent_action方法执行工具。
_iter_next_step
_iter_next_step 实现 Agent 单步执行逻辑。
源码
python
def _iter_next_step(
self,
name_to_tool_map: Dict[str, BaseTool],
color_mapping: Dict[str, str],
inputs: Dict[str, str],
intermediate_steps: List[Tuple[AgentAction, str]],
run_manager: Optional[CallbackManagerForChainRun] = None,
) -> Iterator[Union[AgentFinish, AgentAction, AgentStep]]:
"""Take a single step in the thought-action-observation loop.
Override this to take control of how the agent makes and acts on choices.
"""
try:
intermediate_steps = self._prepare_intermediate_steps(intermediate_steps)
# Call the LLM to see what to do.
output = self._action_agent.plan(
intermediate_steps,
callbacks=run_manager.get_child() if run_manager else None,
**inputs,
)
except OutputParserException as e:
# ...
text = str(e)
# ...
# 将错误信息进行封装,下次循环有机会让大模型重新尝试生成正确的格式
output = AgentAction("_Exception", observation, text)
observation = ExceptionTool().run(
output.tool_input,
verbose=self.verbose,
color=None,
callbacks=run_manager.get_child() if run_manager else None,
**tool_run_kwargs,
)
yield AgentStep(action=output, observation=observation)
return
# If the tool chosen is the finishing tool, then we end and return.
if isinstance(output, AgentFinish):
yield output
return
actions: List[AgentAction]
if isinstance(output, AgentAction):
actions = [output]
else:
actions = output
for agent_action in actions:
yield agent_action
for agent_action in actions:
yield self._perform_agent_action(
name_to_tool_map, color_mapping, agent_action, run_manager
)返回类型
_iter_next_step 是一个迭代器,准确来说是一个 generator 函数,每次迭代会返回如下三种元素之一:
AgentAction:表示 Agent 应该执行某个操作,包含要执行的工具名称及需传递的输入参数。
python
AgentAction(
tool='ask_fruit_unit_price',
tool_input='apple',
log='To find the total price, I need to know the price per kilogram for both apples and bananas. I will first ask for the price of apples and then for the price of bananas.\n\nAction: ask_fruit_unit_price \nAction Input: "apple"'
)AgentStep:运行 AgentAction 的结果。
python
AgentStep(
action=AgentAction(
tool='ask_fruit_unit_price',
tool_input='apple',
log='To find the total price, I need to know the price per kilogram for both apples and bananas. I will first ask for the price of apples and then for the price of bananas.\n\nAction: ask_fruit_unit_price \nAction Input: "apple"'
),
observation='Apple unit price is 10/kg'
)AgentFinish:Agent 在达到停止条件时返回。
python
AgentFinish(
return_values={'output': 'The total price of 3 kg of apple and 2 kg of banana is 42.'},
log='I now know the final answer \nFinal Answer: The total price of 3 kg of apple and 2 kg of banana is 42.'
)中间步骤裁剪
_prepare_intermediate_steps 用于裁剪中间步骤,中间步骤可以先理解为 Agent 每次循环的结果。
python
def _prepare_intermediate_steps(
self, intermediate_steps: List[Tuple[AgentAction, str]]
) -> List[Tuple[AgentAction, str]]:
if (
isinstance(self.trim_intermediate_steps, int)
and self.trim_intermediate_steps > 0
):
return intermediate_steps[-self.trim_intermediate_steps :]
elif callable(self.trim_intermediate_steps):
return self.trim_intermediate_steps(intermediate_steps)
else:
return intermediate_steps大致逻辑是:
- 如果
trim_intermediate_steps是正整数,则只保留最后N个步骤。 - 如果
trim_intermediate_steps是可调用对象,则调用该函数处理步骤列表。 - 否则返回原始步骤列表。
trim_intermediate_steps是实例化 AgentExecutor 时的可选参数,默认是 -1,即不裁剪中间步骤。
调用大模型
在 _iter_next_step 中会调用 _action_agent(可以简单理解为实例化 AgentExecutor 时传入的 agent 参数,详见后文)的 plan 方法,这一步会请求大模型。
plan 方法可能会返回 AgentAction 或 AgentFinish 或 List[AgentAction]。
处理大模型返回
如果是 AgentFinish 类型返回,代表 Agent 在达到停止条件,直接将 AgentFinish 作为 _iter_next_step 的返回结果。
非 AgentFinish 类型返回,不管是 AgentAction 还是 List[AgentAction],最终都会组装成 List[AgentAction]。
_iter_next_step 会遍历两次 List[AgentAction]:
- 第一次是将列表中所有的
AgentActionyield 出去。 - 第二次是调用
_perform_agent_action执行所有的AgentAction。
需要注意,对比 OpenManus,LangChain reAct 没有处理大模型的返回既不是 AgentAction,也不是 AgentFinish 的场景。只是 _action_agent.plan() 方法被定义为只能返回这两种类型。
_perform_agent_action
_perform_agent_action 方法用于执行Agent的动作。
源码
python
def _perform_agent_action(
self,
name_to_tool_map: Dict[str, BaseTool],
color_mapping: Dict[str, str],
agent_action: AgentAction,
run_manager: Optional[CallbackManagerForChainRun] = None,
) -> AgentStep:
if run_manager:
run_manager.on_agent_action(agent_action, color="green")
# Otherwise we lookup the tool
if agent_action.tool in name_to_tool_map:
tool = name_to_tool_map[agent_action.tool]
return_direct = tool.return_direct
color = color_mapping[agent_action.tool]
tool_run_kwargs = self._action_agent.tool_run_logging_kwargs()
if return_direct:
tool_run_kwargs["llm_prefix"] = ""
# We then call the tool on the tool input to get an observation
observation = tool.run(
agent_action.tool_input,
verbose=self.verbose,
color=color,
callbacks=run_manager.get_child() if run_manager else None,
**tool_run_kwargs,
)
else:
tool_run_kwargs = self._action_agent.tool_run_logging_kwargs()
observation = InvalidTool().run(
{
"requested_tool_name": agent_action.tool,
"available_tool_names": list(name_to_tool_map.keys()),
},
verbose=self.verbose,
color=None,
callbacks=run_manager.get_child() if run_manager else None,
**tool_run_kwargs,
)
return AgentStep(action=agent_action, observation=observation)调用工具
_perform_agent_action 方法最关键的操作就是判断本次要执行工具是实现定义好的工具,调用工具的 run 方法执行工具,然后将 AgentAction 和 工具执行结果封装成 AgentStep 实例返回出去。
_take_next_step
_take_next_step 方法的作用是:
- 调用
_iter_next_step生成器方法,逐个获取下一步动作(AgentAction); - 将生成器返回的所有动作收集为列表;
- 调用
_consume_next_step方法处理该列表,决定是继续执行还是结束(返回AgentFinish或新的中间步骤列表)。
源码
python
def _take_next_step(
self,
name_to_tool_map: Dict[str, BaseTool],
color_mapping: Dict[str, str],
inputs: Dict[str, str],
intermediate_steps: List[Tuple[AgentAction, str]],
run_manager: Optional[CallbackManagerForChainRun] = None,
) -> Union[AgentFinish, List[Tuple[AgentAction, str]]]:
return self._consume_next_step(
[
a
for a in self._iter_next_step(
name_to_tool_map,
color_mapping,
inputs,
intermediate_steps,
run_manager,
)
]
)逻辑
_take_next_step 遍历 _iter_next_step 这个迭代器,将遍历的结果作为 _consume_next_step 方法的入参。
也就是说,_consume_next_step 的入参是一个列表,可能有如下三种形式:
- 如果调用大模型返回
AgentAction类型,则入参列表为:
python
[AgentAction, AgentStep]- 如果调用大模型返回
List[AgentAction]类型,则入参列表为:
python
[AgentAction, AgentAction, ..., AgentStep, AgentStep, ...]此时列表中包含数量相同的 AgentAction 与 AgentStep,且 AgentAction 在前,AgentStep 在后,AgentAction 和 AgentStep 按顺序一一对应。
- 如果调用大模型返回
AgentFinish类型,则入参列表为:
python
[AgentFinish]此时列表中仅有一个 AgentFinish 类型元素。
_take_next_step 会直接返回 _consume_next_step 方法的结果。
_consume_next_step
源码
python
def _consume_next_step(
self, values: NextStepOutput
) -> Union[AgentFinish, List[Tuple[AgentAction, str]]]:
if isinstance(values[-1], AgentFinish):
assert len(values) == 1
return values[-1]
else:
return [
(a.action, a.observation) for a in values if isinstance(a, AgentStep)
]逻辑
_consume_next_step 方法先检查最后一个值是否为 AgentFinish 类型,如果是则断言整个 values 列表长度为1,直接返回该 AgentFinish 对象。当最后一个值是 AgentFinish 类型但 values 长度不为1时,会抛出一个 AssertionError 异常。
如果不是结束状态,则遍历 values 列表,筛选出 AgentStep 类型的元素,将其 action 和 observation 属性组合成元组列表返回。
处理 _take_next_step 调用结果
综上,在每次循环中,调用 _take_next_step 方法,返回 AgentFinish 或 List[Tuple[AgentAction, str]] 类型的结果。
如果是 AgentFinish 类型,则将 AgentFinish 对象的 return_values 参数作为结果返回并结束循环,_call 方法执行完成。
return_values 参数形如:
python
{'output': 'The total price of 3 kg of apple and 2 kg of banana is 42.'},如果是由 AgentAction 和工具调用结果组成的元组列表,则将其添加到中间步骤结果列表 intermediate_steps 中,即 intermediate_steps 的类型是 List[Tuple[AgentAction, str]]。
最后更新循环次数与执行时间。
循环结束条件
循环有两种结束条件:
-
某次循环中,
_take_next_step方法返回了AgentFinish类型的结果,此时AgentFinish对象的return_values参数会被作为_call方法的结果返回,并结束循环。 -
循环次数或执行时间超过限制,也就是说,每次循环
_take_next_step返回的结果都不是AgentFinish类型,Agent 并没有达到结束条件。此时会返回一个固定的结束响应:- 如果
early_stopping_method为"force",则返回预设的完成信息,此时_call方法的返回为:
python{"output": "Agent stopped due to iteration limit or time limit."}- 否则抛出异常表示不支持该停止方法。
- 如果
plan方法
在 _iter_next_step 中会调用 _action_agent 的 plan 方法,这一步会请求大模型。之前简单将 _action_agent 理解为实例化 AgentExecutor 时的 agent 入参,实际两者还不是一回事。
实例化 AgentExecutor 时的 agent 入参经过一点处理才成为 _action_agent。
模型验证器
在 AgentExecutor 是源码中,可以找到如下代码:
python
@model_validator(mode="before")
@classmethod
def validate_runnable_agent(cls, values: Dict) -> Any:
"""Convert runnable to agent if passed in.
Args:
values: Values to validate.
Returns:
Dict: Validated values.
"""
agent = values.get("agent")
if agent and isinstance(agent, Runnable):
try:
output_type = agent.OutputType
except Exception as _:
multi_action = False
else:
multi_action = output_type == Union[List[AgentAction], AgentFinish]
stream_runnable = values.pop("stream_runnable", True)
if multi_action:
values["agent"] = RunnableMultiActionAgent(
runnable=agent, stream_runnable=stream_runnable
)
else:
values["agent"] = RunnableAgent(
runnable=agent, stream_runnable=stream_runnable
)
return valuesAgentExecutor 继承自 Chain,Chain 的继承关系又可以追溯到 BaseModel。BaseModel 是 Pydantic 库的核心基类,用于创建数据模型,并且提供了数据验证功能。
validate_runnable_agent 就是一个模型验证器,负责在 AgentExecutor 实例化时,将传入的 agent 参数转换为适当的 Agent 类型。如果 agent 是 Runnable 类型,则根据其输出类型决定是否支持多动作,进而封装成 RunnableMultiActionAgent 或 RunnableAgent。不管是 RunnableMultiActionAgent 还是 RunnableAgent,它们都定义了 plan 方法。
属性定义
在 AgentExecutor 中找到 _action_agent 属性的定义:
python
@property
def _action_agent(self) -> Union[BaseSingleActionAgent, BaseMultiActionAgent]:
"""Type cast self.agent.
If the `agent` attribute is a Runnable, it will be converted one of
RunnableAgentType in the validate_runnable_agent root_validator.
To support instantiating with a Runnable, here we explicitly cast the type
to reflect the changes made in the root_validator.
"""
if isinstance(self.agent, Runnable):
return cast(RunnableAgentType, self.agent)
else:
return self.agent这段代码定义了一个名为 _action_agent 的属性方法,该方法在运行时访问 self._action_agent 时调用。
该方法主要用于类型转换,它检查 self.agent 是否为 Runnable 类型------如果是,则将其显式转换为 RunnableAgentType 类型(RunnableAgent 与 RunnableMultiActionAgent 的联合类型);否则直接返回原对象。
这样做的原因是:
- 虽然经过
validate_runnable_agent验证器处理后,如果原始agent是Runnable类型,它实际上已经被转换成了RunnableAgent或RunnableMultiActionAgent。 - 但由于类型系统的限制,类型检查器不知道这一点,仍然认为它是
Runnable类型。 - 使用
cast(RunnableAgentType, self.agent)告诉类型检查器:虽然静态分析认为这是Runnable,但在运行时它实际上是RunnableAgentType(即Union[RunnableAgent, RunnableMultiActionAgent])
RunnableAgent继承自BaseSingleActionAgent,所以_action_agent的返回类型是Union[BaseSingleActionAgent, BaseMultiActionAgent]。
RunnableAgent
以 RunnableAgent 为例,其 plan 方法很简单:
python
def plan(
self,
intermediate_steps: List[Tuple[AgentAction, str]],
callbacks: Callbacks = None,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> Union[AgentAction, AgentFinish]:
"""Based on past history and current inputs, decide what to do.
Args:
intermediate_steps: Steps the LLM has taken to date,
along with the observations.
callbacks: Callbacks to run.
**kwargs: User inputs.
Returns:
Action specifying what tool to use.
"""
inputs = {**kwargs, **{"intermediate_steps": intermediate_steps}}
final_output: Any = None
if self.stream_runnable:
# Use streaming to make sure that the underlying LLM is invoked in a
# streaming
# fashion to make it possible to get access to the individual LLM tokens
# when using stream_log with the Agent Executor.
# Because the response from the plan is not a generator, we need to
# accumulate the output into final output and return that.
for chunk in self.runnable.stream(inputs, config={"callbacks": callbacks}):
if final_output is None:
final_output = chunk
else:
final_output += chunk
else:
final_output = self.runnable.invoke(inputs, config={"callbacks": callbacks})
return final_output其中:
intermediate_steps入参就是每次循环后记录的中间结果,只不过会根据实例化AgentExecutor时传入的trim_intermediate_steps参数进行裁剪。runnable就是create_react_agent返回的、由 Prompt、llm、输出解析器组成的 Agent 链。
在 plan 方法中判断若启用流式处理,则逐块累积输出;否则直接调用执行。最终返回动作或完成信号。
总结
TAO循环
Thought
在每次 TAO 循环中,会将工具的描述插入到 prompt 中供 LLM 决策,LLM 返回的结果会被解析为不同的类型,有的类型表示需要调用工具,有的类型表示最终结果。
Action
如果需要调用工具,则执行具体的工具。
Observation
每次执行工具后,都会将 LLM 的返回、工具执行结果添加到中间步骤的结果中。下一次 TAO 循环中,会将裁剪后的中间步骤结果作为上下文传递给LLM,由LLM根据执行情况决定下一步操作。
循环终止条件
LanChain reAct 的 TAO 循环有两种终止条件:
- 循环次数或执行时长达到限制,循环次数默认最大 15 次,执行市场默认是没有限制。
- 每次循环中,调用大模型的结果会被解析器处理成两种类实例,分别是 AgentFinish 和 AgentAction。如果某次调用大模型返回的是 AgentFinish 实例,则视为任务完成,跳出循环。