背景
最近由于增长团队的持续买量,业务在逐步增长,与此同时逐渐开始收到一些timewait超过阈值的告警。通过这次tw的调查,对go-redis有了更多的理解和学习。
我用的redis client是github.com/redis/go-redis/v9 v9.7.1
结论
通过调整redis的xTimeout配置,tw变成了0(2000左右 -> 0),etb变成了200(130左右 -> 200)。
变更如下:
从
c
PoolSize = 200
MinIdleConns = 50
ReadTimeout = "30ms"
WriteTimeout = "20ms"
DialTimeout = "20ms"
PoolTimeout = "10ms"变成
c
PoolSize = 200
MinIdleConns = 50
ReadTimeout = "2s"
WriteTimeout = "2s"
DialTimeout = "3s"
PoolTimeout = "2s"staleConn:
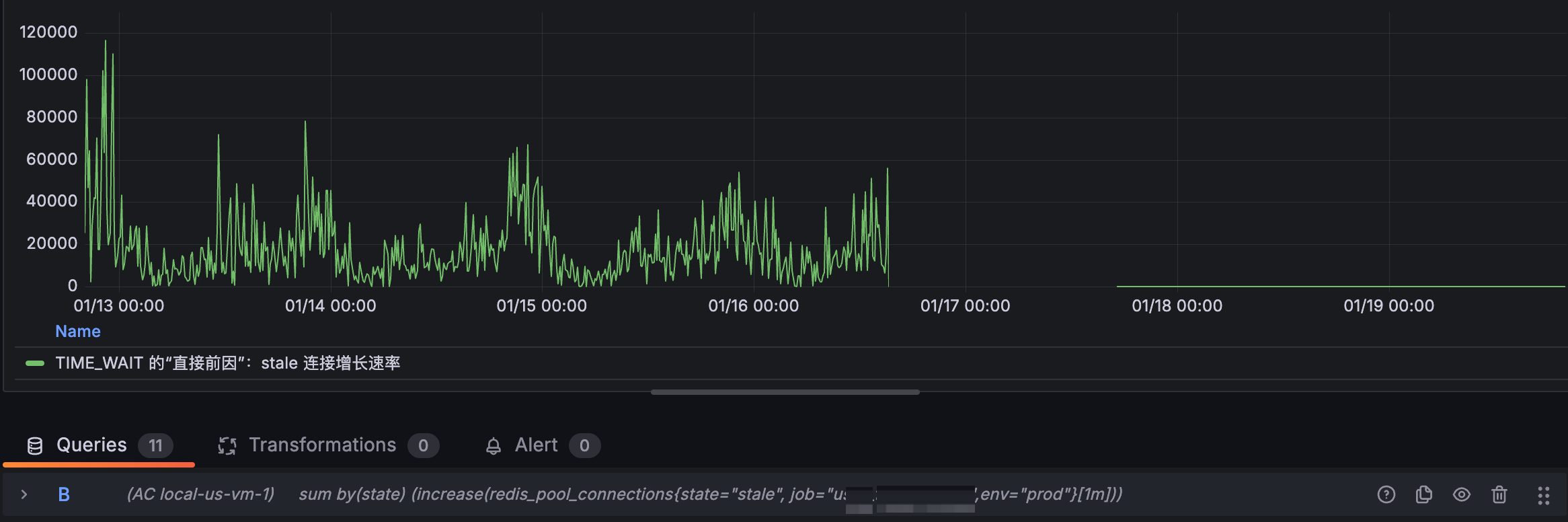
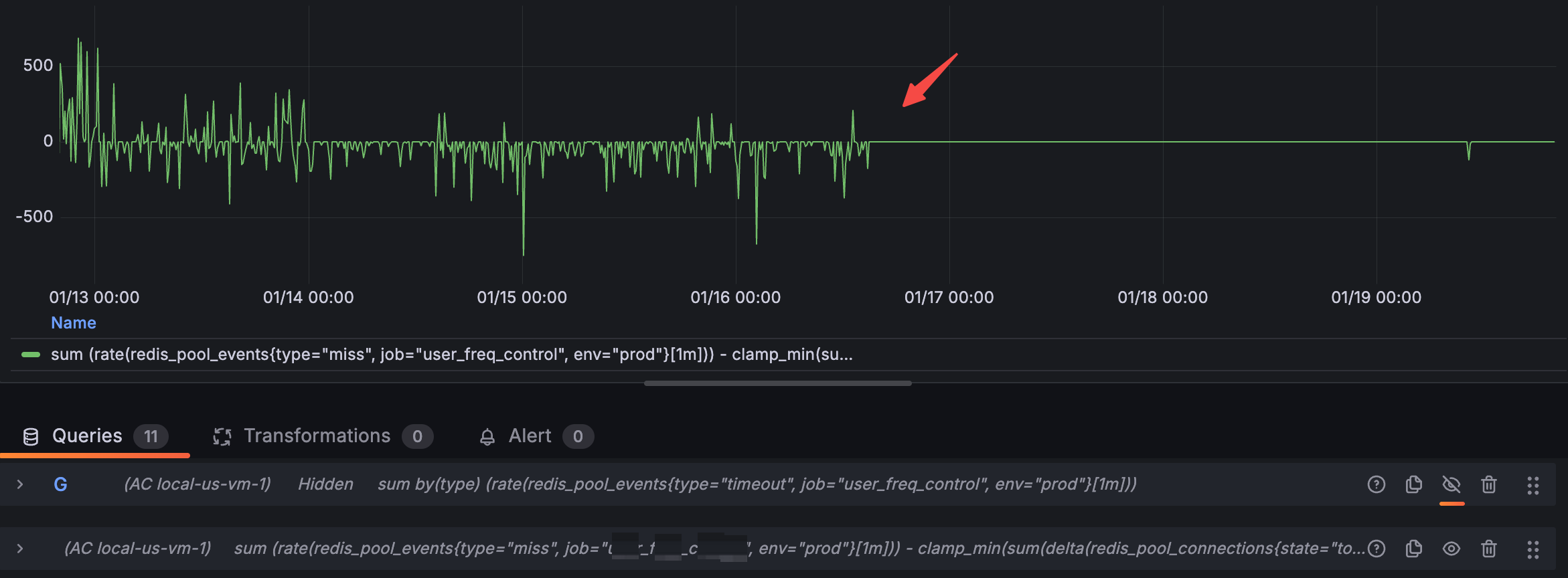
sum (rate(redis_pool_events{type="miss", env="prod"}[1m]))-clamp_min(sum(delta(redis_pool_connections{state="total", env="prod"}[1m])), 0)
调查tw
登录实例,通过netstat -apn就可以直接看出成片的跟6379的连接都是tw状态。大概tw有2000左右,而etb有150左右。
bash
root@abc-864774d65d-4gx68:~/etc# netstat -apn | grep 172.0.10.1:6379 | awk '{print $6}' | sort | uniq -c
109 ESTABLISHED
2350 TIME_WAIT
root@abc-864774d65d-4gx68:~/etc# netstat -apn | grep 172.0.10.1:6379 | awk '{print $6}' | sort | uniq -c
116 ESTABLISHED
1447 TIME_WAIT
root@abc-864774d65d-4gx68:~/etc# netstat -apn | grep 172.0.10.1:6379 | awk '{print $6}' | sort | uniq -c
123 ESTABLISHED
1273 TIME_WAIT
root@abc-864774d65d-4gx68:~/etc# netstat -apn | grep 172.0.10.1:6379 | awk '{print $6}' | sort | uniq -c
123 ESTABLISHED
1 FIN_WAIT1
1336 TIME_WAIT
root@abc-864774d65d-4gx68:~/etc# netstat -apn | grep 172.0.10.1:6379 | awk '{print $6}' | sort | uniq -c
116 ESTABLISHED
1676 TIME_WAITtw经常出现在主动关闭的一方,那也就是说我的服务在大量的关闭与redis的连接。
虽然使用了redis的连接池,从现象看就像是短连接一样。我又确认了一下确实使用了连接池。
那大概率是连接池的使用方式有问题。
连接池配置
我的redis连接池配置如下:
PoolSize = 200
MinIdleConns = 50
ReadTimeout = "30ms"
WriteTimeout = "20ms"
DialTimeout = "20ms"
PoolTimeout = "10ms"我有很多疑问,为什么达不到200个etb;主调方给我的ctx超时时间是50ms,为什么30ms都没有读完。
日志
从我的服务错误日志上看,有大量的context cancel和context deadline exceeded的错误。也就是超时了,主调方取消了。
redis stat监控
redis的版本是:github.com/redis/go-redis/v9 v9.7.1
redis有几个监控指标:
go
type Stats struct {
Hits uint32 // number of times free connection was found in the pool
Misses uint32 // number of times free connection was NOT found in the pool
Timeouts uint32 // number of times a wait timeout occurred
TotalConns uint32 // number of total connections in the pool
IdleConns uint32 // number of idle connections in the pool
StaleConns uint32 // number of stale connections removed from the pool
}指标分为两部分,一部分是事件类型(hits/misses/timeouts),一部分是连接数类型(totalConns/idleConns/staleConns)
hits:发起请求,并且拿到了空闲且healthy 的连接的计数
misses:发起请求,没有拿到空闲切healthy 的连接的计数
timeouts:发起请求,在PoolTimeout内没有拿到连接的计数
totalConns:总连接数
idleConns:空闲且healthy的连接数
staleConns:销毁的连接数
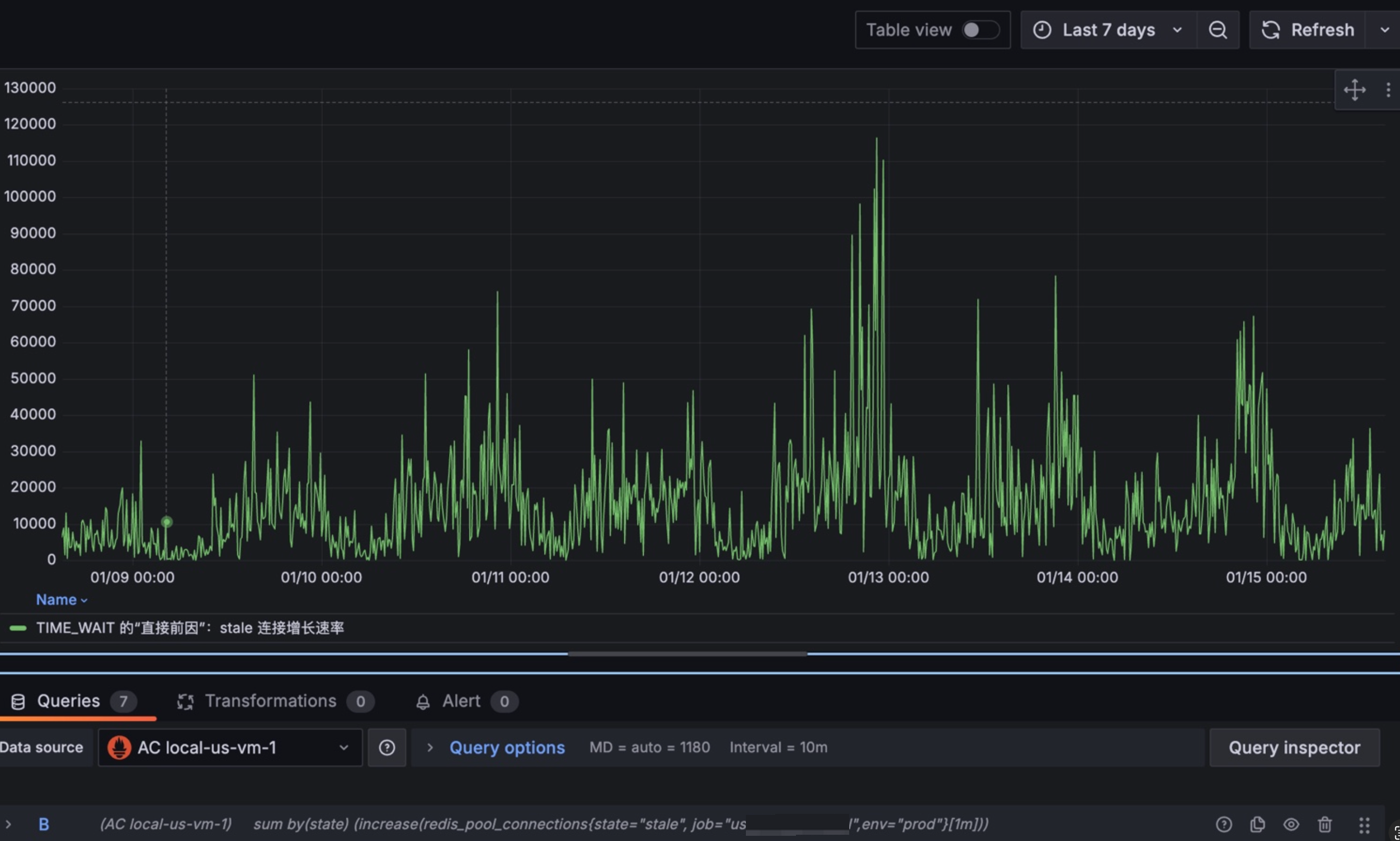
有几个明显的视图:
1/ stale的数量很多
2/ miss的数量也是有的
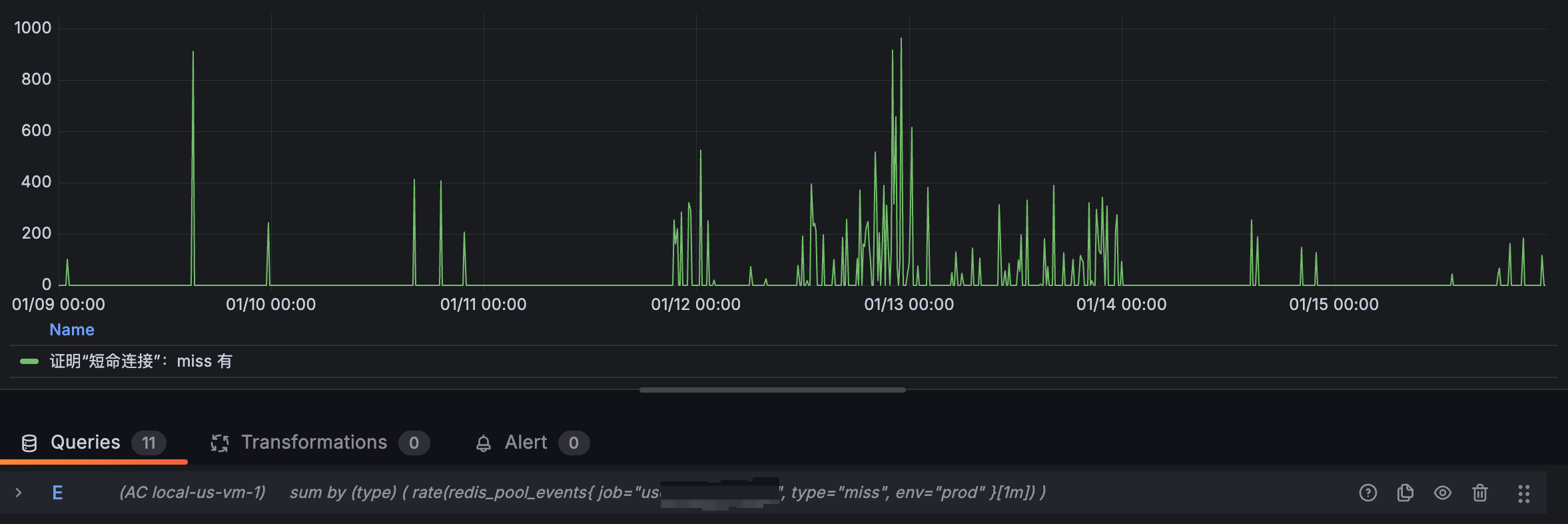
并且miss的数量跟请求量是正相关的,每当业务高峰期就会产生大量的miss。
3/ 我们的timeouts是没有图像的,说明我们并没有从池子中获取连接而超时。
那我们来分析一下:
1/ stale是怎么产生的
2/ miss是怎么产生的
顺着统计值反查stale的逻辑大致如下:
NewClient -> c.init -> c.initHooks -> c.baseClient.process -> c._process -> c.withConn -> c.releaseConn -> isBadConn -> c.connPool.Remove -> p.removeConnInternal -> p.removeConn -> atomic.AddUint32(&p.stats.StaleConns, 1)
p.stat.StaleConns是在要移除Conn的时候,会有一个原子加1。
这里有一个关键的方法,决定是否要Remove这个Conn。这个方法就是isBadConn:
c
位置:github.com/redis/go-redis/v9@v9.7.1/error.go: 81
func isBadConn(err error, allowTimeout bool, addr string) bool {
if err == nil {
return false
}
// Check for context errors (works with wrapped errors)
if errors.Is(err, context.Canceled) || errors.Is(err, context.DeadlineExceeded) {
return true
}
// Check for pool timeout errors (works with wrapped errors)
if errors.Is(err, pool.ErrConnUnusableTimeout) {
return true
}
if isRedisError(err) {
switch {
case isReadOnlyError(err):
// Close connections in read only state in case domain addr is used
// and domain resolves to a different Redis Server. See #790.
return true
case isMovedSameConnAddr(err, addr):
// Close connections when we are asked to move to the same addr
// of the connection. Force a DNS resolution when all connections
// of the pool are recycled
return true
default:
return false
}
}
if allowTimeout {
// Check for network timeout errors (works with wrapped errors)
var netErr net.Error
if errors.As(err, &netErr) && netErr.Timeout() {
return false
}
}
return true
}该方法中对超时的判断:errors.Is(err, context.Canceled) || errors.Is(err, context.DeadlineExceeded)就是我遇到的tw的主要原因。
由于我们的readTimeout和ctxTimeout设置的比较短,readTimeout是30ms,主调方调我的服务的context超时时间是50ms,以至于产生大量的context.Canceled或context.DeadlineExceeded,进而RemoveConn,导致tw。
效果
ok,这里是我们tw的原因所在。那么我们尝试调整xTimeouts后,tw得到巨大的改善,甚至修复。
从
c
PoolSize = 200
MinIdleConns = 50
ReadTimeout = "30ms"
WriteTimeout = "20ms"
DialTimeout = "20ms"
PoolTimeout = "10ms"变成
c
PoolSize = 200
MinIdleConns = 50
ReadTimeout = "2s"
WriteTimeout = "2s"
DialTimeout = "3s"
PoolTimeout = "2s"效果如下:
staleConn:

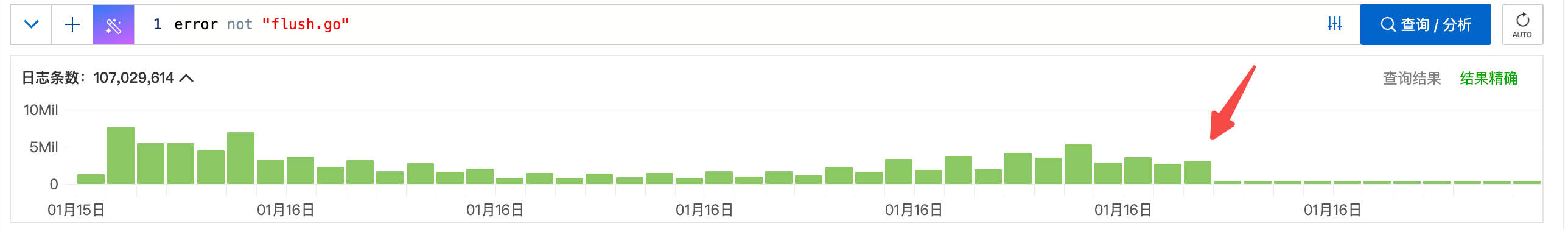
c
容器上没有tw了
root@abc-6c4ffc8864-4q7nc:~# netstat -apn | grep 172.0.10.1:6379 | awk '{print $6}' | sort | uniq -c
200 ESTABLISHED
root@abc-6c4ffc8864-4q7nc:~# netstat -apn | grep 172.0.10.1:6379 | awk '{print $6}' | sort | uniq -c
200 ESTABLISHED
root@abc-6c4ffc8864-4q7nc:~# netstat -apn | grep 172.0.10.1:6379 | awk '{print $6}' | sort | uniq -c
200 ESTABLISHED参考
source: https://uptrace.dev/blog/golang-context-timeout
内容如下:
You probably should avoid ctx.WithTimeout or ctx.WithDeadline with code that makes network calls. Here is why.
Using context for cancellation
Typically, context.Context is used to cancel operations like this:
c
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, time.Second)
defer cancel()
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
fmt.Println(ctx.Err())
fmt.Println("cancelling...")
}
}Later, you can use such context with, for example, Redis client:
c
import "github.com/go-redis/redis/v8"
rdb := redis.NewClient(...)
ctx := context.Background()
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 3*time.Second)
defer cancel()
val, err := rdb.Get(ctx, "redis-key").Result()At first glance, the code above works fine. But what happens when rdb.Get operation exceeds the timeout?
Context deadline exceeded
When context is cancelled, go-redis and most other database clients (including database/sql) must do the following:
Close the connection, because it can't be safely reused.
Open a new connection.
Perform TLS handshake using the new connection.
Optionally, pass some authentication checks, for example, using Redis AUTH command.
Effectively, your application does not use the connection pool any more which makes each operation slower and increases the chance of exceeding the timeout again. The result can be disastrous.
Technically, this problem is not caused by context.Context and using small deadlines with net.Conn can cause similar issues. But because context.Context imposes a single timeout on all operations that use the context, each individual operation has a random timeout which depends on timings of previous operations.
What to do instead?
Your first option is to use fixed net.Conn deadlines:
c
var cn net.Conn
cn.SetDeadline(time.Now().Add(3 * time.Second))With go-redis, you can use ReadTimeout and WriteTimeout options which control net.Conn deadlines:
c
rdb := redis.NewClient(&redis.Options{
ReadTimeout: 3 * time.Second,
WriteTimeout: 3 * time.Second,
})Alternatively, you can also use a separate context timeout for each operation:
c
ctx := context.Background()
op1(ctx.WithTimeout(ctx, time.Second))
op2(ctx.WithTimeout(ctx, time.Second))You should also avoid timeouts smaller than 1 second, because they have the same problem. If you must deliver a SLA no matter what, you can make sure to generate a response in time but let the operation to continue in background:
c
func handler(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
// Process asynchronously in a goroutine.
ch := process(req)
select {
case res := <-ch:
// success
case <-time.After(time.Second):
// unknown result
}
}