
notion
难点-创建 Notion 集成
-
访问 Notion Developers 页面。
-
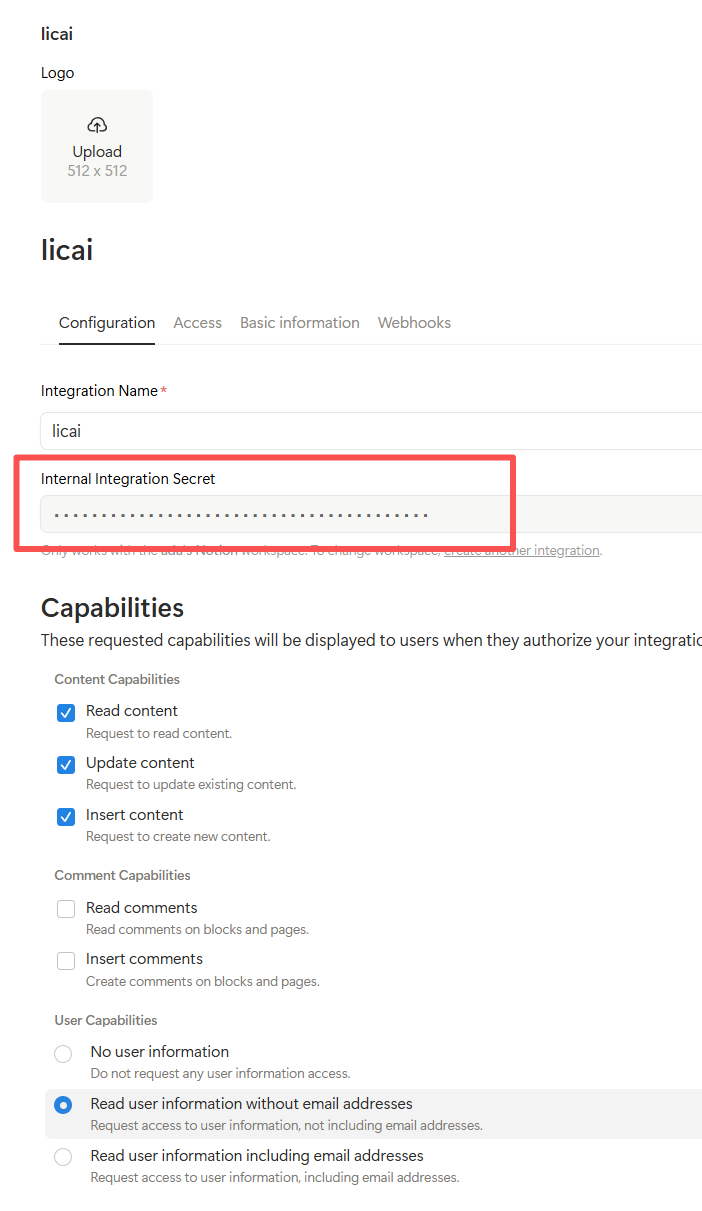
创建一个新的集成,并获得 API 密钥(integration token)。
-
将集成添加到你要操作的工作区,并获取相关权限。
代码解释:
-
NOTION_API_URL : 用于访问 Notion API 的 URL。这个不要动!官方的。
-
NOTION_TOKEN: 你的 Notion API token(集成密钥)。
-
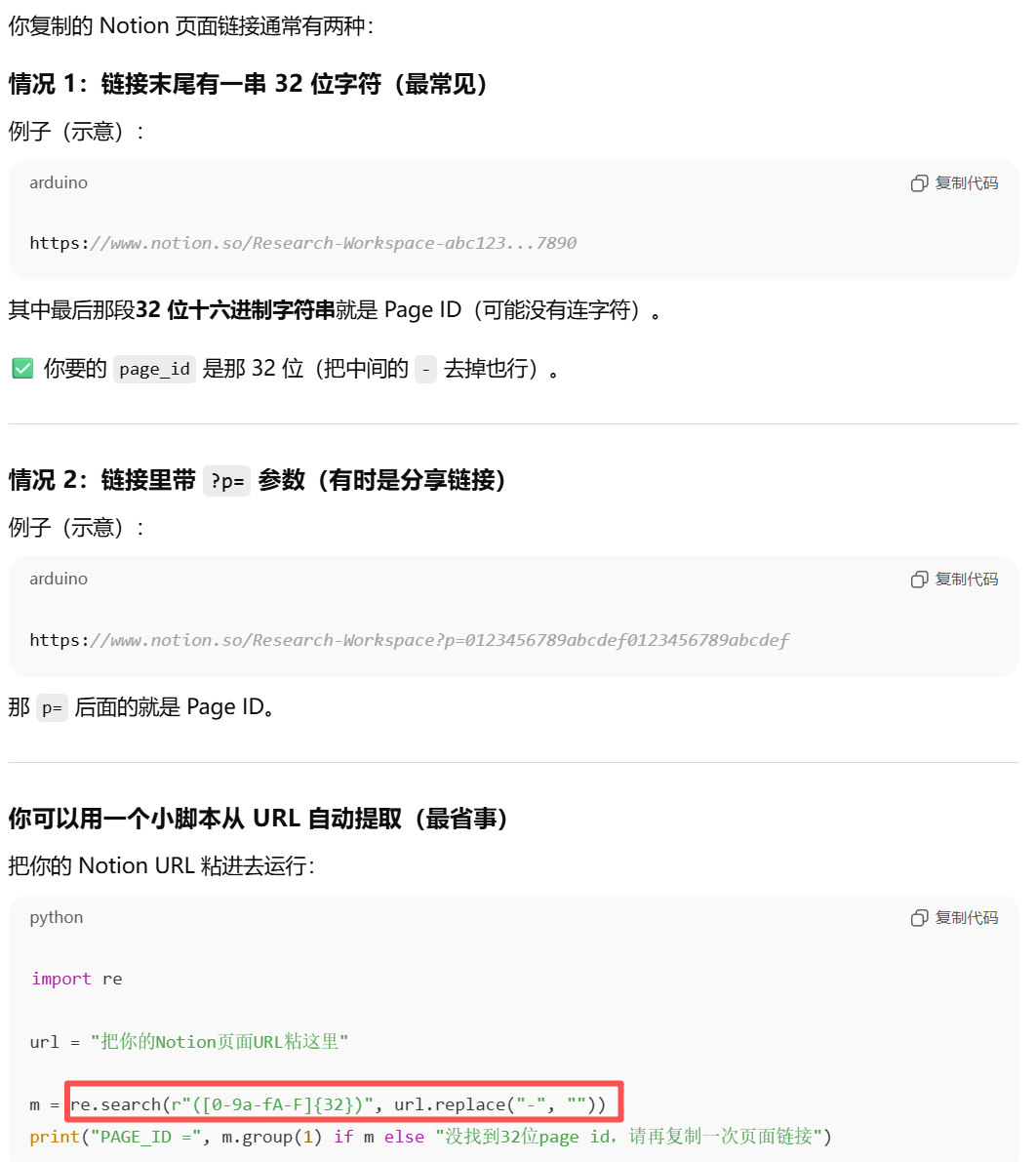
DATABASE_PARENT_PAGE_ID: 你想要将这些数据库放入的页面 ID。可以在 Notion 中右键页面并选择"复制链接",然后从链接中提取 ID。
-
create_database : 创建数据库的函数,接收数据库名称和属性作为参数,使用
requests.post()发送 API 请求。 -
databases: 定义了每个数据库的名称和属性(表头列名)。每个数据库会有不同的列,根据你的要求设置了列类型(例如文本、日期、URL等)。
-
循环创建数据库 : 遍历
databases字典,为每个数据库调用create_database函数,并打印响应。
运行代码:
-
你需要在 Notion 中创建一个集成,并获取 API 密钥。
-
用你的 API 密钥替换代码中的
NOTION_TOKEN,并将你想要添加数据库的页面 ID 填入DATABASE_PARENT_PAGE_ID。 -
运行代码,它会为你创建 6 个数据库,并按要求配置列。
注意事项:
- 小编悲伤地发现,一开始没理解意思,自己按照
python
import requests
import json
# 定义 Notion API 访问的 URL 和 token
NOTION_API_URL = "https://api.notion.com/v1/databases"
NOTION_TOKEN = "your_notion_api_token_here" # 将此替换为你的API密钥
DATABASE_PARENT_PAGE_ID = "your_parent_page_id_here" # 填写你的父页面 ID
# 请求头
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {NOTION_TOKEN}",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Notion-Version": "2022-06-28", # 确保使用适当的版本
}
# 创建数据库的函数
def create_database(database_name, properties):
data = {
"parent": {"type": "page_id", "page_id": DATABASE_PARENT_PAGE_ID},
"title": [{"type": "text", "text": {"content": database_name}}],
"properties": properties
}
response = requests.post(NOTION_API_URL, headers=headers, json=data)
return response.json()
# 配置每个数据库的结构和列
# 确保每个数据库至少有一个 `title` 属性
databases = {
"Company Brief": {
"Title": {"title": {}}, # 这里是必填字段
"Company": {"rich_text": {}},
"Code": {"rich_text": {}},
"Business": {"rich_text": {}},
"Competitors": {"rich_text": {}},
"Key Products": {"rich_text": {}}
},
"Source Library": {
"Title": {"title": {}}, # 这里是必填字段
"Annual Report": {"rich_text": {}},
"Announcements": {"rich_text": {}},
"Earnings Call": {"rich_text": {}},
"Broker Reports": {"rich_text": {}},
"Industry Materials": {"rich_text": {}}
},
"Industry Map": {
"Title": {"title": {}}, # 这里是必填字段
"Industry Chain": {"rich_text": {}},
"Key Links": {"rich_text": {}},
"Policy": {"rich_text": {}},
"Upstream/Downstream": {"rich_text": {}},
"Price/Cycle Variables": {"rich_text": {}}
},
"Moat & Competition": {
"Title": {"title": {}}, # 这里是必填字段
"Scorecard": {"rich_text": {}},
"Evidence Link": {"url": {}}
},
"Risks & Bear Case": {
"Title": {"title": {}}, # 这里是必填字段
"Risk Item": {"rich_text": {}},
"Trigger Indicator": {"rich_text": {}},
"Evidence": {"rich_text": {}}
},
"Research Log": {
"Title": {"title": {}}, # 这里是必填字段
"Date": {"date": {}},
"Content": {"rich_text": {}},
"Conclusion": {"rich_text": {}},
"Questions": {"rich_text": {}},
"Next Steps": {"rich_text": {}}
}
}
# 创建所有数据库
for database_name, properties in databases.items():
response = create_database(database_name, properties)
print(f"Created database: {database_name} | Response: {response}")Excel 工作簿,自动添加
代码解释:
-
数据结构创建:
-
每个表的数据使用 Python 字典表示,列名作为键,数据作为值。
-
使用
pandas.DataFrame()将这些字典转换为 DataFrame 对象。
-
-
Excel 写入:
-
使用
pd.ExcelWriter()配合openpyxl引擎将 DataFrame 写入 Excel 文件中。 -
每个表格都会被写入一个单独的工作表,工作表的名称会根据你的需求设置为 "Inputs"、"IS"、"BS"、"CF" 等。
-
-
输出文件 :最终生成的 Excel 文件将保存为
financial_model.xlsx
python
import pandas as pd
from openpyxl import Workbook
# 创建一个新的 Excel 工作簿
wb = Workbook()
# 创建 Inputs 工作表
inputs_data = {
"假设名称": ["增长率", "折现率", "税率", "长期增长率"],
"当前值": ["", "", "", ""], # 初始值可以是空的,后期填充
"备注": ["", "", "", ""]
}
inputs_df = pd.DataFrame(inputs_data)
# 创建 IS(利润表)工作表
is_data = {
"年份": ["2022", "2023", "2024", "2025", "2026"],
"收入": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"成本": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"毛利": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"运营费用": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"EBIT": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"利息": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"税前利润": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"税后利润": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"净利润": ["", "", "", "", ""]
}
is_df = pd.DataFrame(is_data)
# 创建 BS(资产负债表)工作表
bs_data = {
"年份": ["2022", "2023", "2024", "2025", "2026"],
"资产": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"负债": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"股东权益": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"流动资产": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"非流动资产": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"流动负债": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"非流动负债": ["", "", "", "", ""]
}
bs_df = pd.DataFrame(bs_data)
# 创建 CF(现金流量表)工作表
cf_data = {
"年份": ["2022", "2023", "2024", "2025", "2026"],
"经营活动现金流": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"投资活动现金流": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"融资活动现金流": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"净现金流": ["", "", "", "", ""]
}
cf_df = pd.DataFrame(cf_data)
# 创建 KPIs(关键指标自动计算)工作表
kpis_data = {
"指标名称": ["毛利率", "净利率", "ROE"],
"计算公式": ["毛利/收入", "净利润/收入", "净利润/股东权益"],
"当前值": ["", "", ""],
"历史值": ["", "", ""]
}
kpis_df = pd.DataFrame(kpis_data)
# 创建 DCF(折现现金流)工作表
dcf_data = {
"年份": ["2022", "2023", "2024", "2025", "2026"],
"自由现金流": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"终值": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"折现率": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"折现因子": ["", "", "", "", ""],
"折现后现金流": ["", "", "", "", ""]
}
dcf_df = pd.DataFrame(dcf_data)
# 创建 Comps(同业可比)工作表
comps_data = {
"公司": ["公司A", "公司B", "公司C"],
"P/E": ["", "", ""],
"EV/EBITDA": ["", "", ""],
"P/B": ["", "", ""],
"其他估值倍数": ["", "", ""],
"估值区间": ["", "", ""]
}
comps_df = pd.DataFrame(comps_data)
# 写入工作表
with pd.ExcelWriter('financial_model.xlsx', engine='openpyxl') as writer:
inputs_df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Inputs", index=False)
is_df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="IS", index=False)
bs_df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="BS", index=False)
cf_df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="CF", index=False)
kpis_df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="KPIs", index=False)
dcf_df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="DCF", index=False)
comps_df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Comps", index=False)
print("Excel 文件已创建并保存为 'financial_model.xlsx'")目前没心思静下来研究功能!mark
Notion MCP + Claude Code 完美结合教程 - 让大模型自动管理你的知识库_notion claude code-CSDN博客
广告打得飞起,文章写得垃圾,但是mark一下,Notion MCP + Claude Code看上去很好的模式