要使 AI Agent 真正有效且有目的性,它们不仅需要处理信息或使用工具的能力,还需要明确的方向感和判断自身是否真正成功的方法。这就是目标设定和监控模式发挥作用的地方。该模式的核心是为Agent 提供具体的工作目标,并为其配备跟踪进度和确定这些目标是否已实现的手段。
目标设定和监控模式概述
设想规划一次旅行。你不会自发地出现在目的地。你需要决定想去哪里(目标状态),弄清楚从哪里开始(初 始状态),考虑可用选项(交通工具、路线、预算),然后制定一系列步骤:订票、打包行李、前往机场/车站、 登机/上车、抵达、找住宿等。这个逐步的过程,通常考虑依赖关系和约束条件,从根本上就是我们在 Agent 系统中所说的规划。
在 AI Agent 的上下文中,规划通常涉及 Agent 接受高级目标,并自主或半自主地生成一系列中间步骤或子目标。这些步骤可以按顺序执行,或以更复杂的流程执行,可能涉及其他模式,如工具使用、路由或多 Agent 协作。规划机制可能涉及复杂的搜索算法、逻辑推理,或越来越多地利用大型语言模型(LLM)的能力,根 据其训练数据和对任务的理解生成合理且有效的计划。
良好的规划能力使 Agent 能够处理非简单的单步查询问题。它使 Agent 能够处理多方面的请求,通过重新规 划适应不断变化的情况,并编排复杂的工作流。这是支撑许多高级 Agent 行为的基础模式,将简单的反应系 统转变为能够主动朝着定义目标工作的系统。
实际应用和用例
目标设定和监控模式对于构建能够在复杂的现实场景中自主可靠运行的 Agent 至关重要。以下是一些实际应用:
-
**・ 客户支持自动化:**Agent的目标可能是"解决客户的账单查询"。它监控对话,检查数据库条目,并使 用工具调整账单。通过确认账单更改并收到客户的积极反馈来监控成功。如果问题未解决,它会升级 处理。
-
**・ 个性化学习系统:**学习Agent可能有"提高学生对代数的理解"的目标。它监控学生在练习中的进度, 调整教学材料,并跟踪准确性和完成时间等性能指标,如果学生遇到困难则调整其方法。
-
**・ 项目管理助手:**可以为Agent分配"确保项目里程碑X在Y日期前完成"的任务。它监控任务状态、团 队沟通和资源可用性,如果目标面临风险则标记延迟并建议纠正措施。
-
**・ 自动交易机器人:**交易Agent的目标可能是"在保持风险承受范围内最大化投资组合收益"。它持续监 控市场数据、当前投资组合价值和风险指标,在条件符合其目标时执行交易,并在突破风险阈值时调 整策略。
-
**・ 机器人和自动驾驶车辆:**自动驾驶车辆的主要目标是"安全地将乘客从A点运送到B点"。它不断监控 其环境(其他车辆、行人、交通信号)、自身状态(速度、燃料)以及沿规划路线的进度,调整其驾驶 行为以安全高效地实现目标。
-
**・ 内容审核:**Agent的目标可能是"识别并从平台X中删除有害内容"。它监控传入的内容,应用分类模 型,并跟踪误报/漏报等指标,调整其过滤标准或将模糊案例升级给人工审查员。
此模式对于需要可靠运行、实现特定成果并适应动态条件的 Agent 至关重要,为智能自我管理提供了必要的框架。
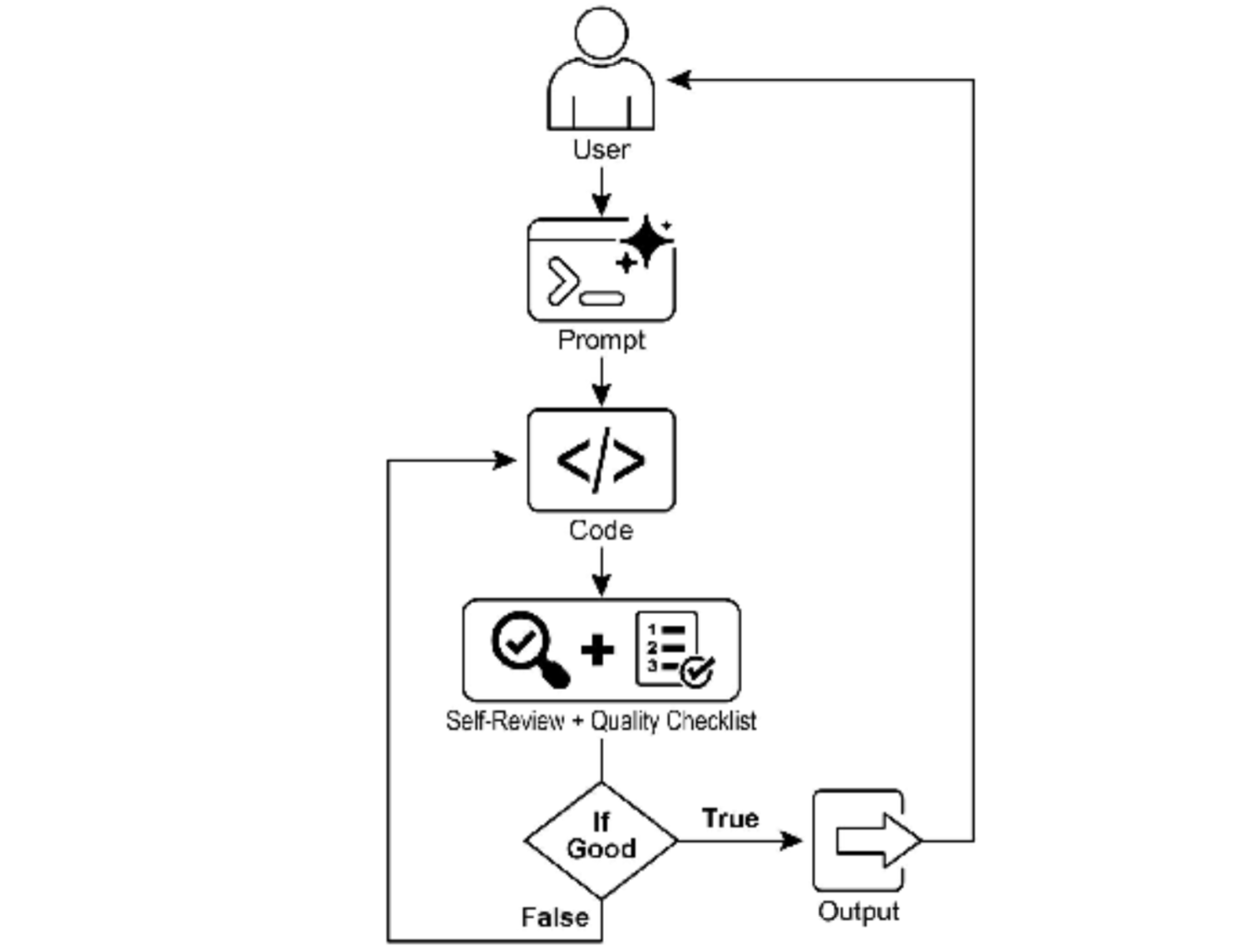
- 图 1:目标设定和监控示例
-
有这样的一个任务,AI 程序员开始工作并产生其第一个代码草稿。然而,它没有立即提交这个初始版本,而是暂停执行一个关键步骤:严格的自我审查。它仔细地将自己的创作与你提供的质量检查清单上的每一项进行比 较,充当自己的质量保证检查员。在这次检查之后,它对自己的进度做出一个简单、无偏见的判断:"True" 如果工作满足所有标准,或"False"如果它不满足标准。
如果判断是"False",AI 不会放弃。它进入深思熟虑的修订阶段,使用自我批评的见解来确定弱点并智能地 重写代码。这个起草、自我审查和完善的循环继续进行,每次迭代都旨在更接近目标。这个过程重复进行, 直到 AI 最终通过满足每个要求而达到"True"状态,或直到它达到预定义的尝试次数限制,就像开发人员在截止日期前工作一样。一旦代码通过了这次最终检查,脚本就会打包打磨好的解决方案,添加有用的注释并将其保存到一个干净的新文件中,准备使用。
注意事项和考虑因素:重要的是要注意,这是一个示例性的说明,而不是生产就绪的代码。对于实际应用, 必须考虑几个因素。LLM 可能无法完全理解目标的预期含义,并可能错误地评估其性能为成功。即使目标被 很好地理解,模型也可能产生幻觉。当同一个 LLM 既负责编写代码又负责判断其质量时,它可能更难发现自己走向错误的方向。
-
最终,LLM 不会魔法般地产生完美的代码;你仍然需要运行和测试生成的代码。此外,简单示例中的"监控"是基础的,并造成了进程可能永远运行的潜在风险。
-
充当一位对产生清晰、正确和简单代码有着深刻承诺的专家代码审查员。
−− 识别和纠正错误:指出任何逻辑缺陷、错误或潜在的运行时错误。
−− 简化和重构:建议使代码更易读、高效和可维护的更改,而不牺牲正确性。
−− 提供清晰的解释:对于每个建议的更改,解释为什么它是改进,引用清晰代码、性能或安全性的原则 。
-
−− 提供更正后的代码 : 显示建议更改的"之前"和"之后",以便改进清晰可见 。
你的反馈应该是直接的、建设性的,并始终旨在提高代码质量。
-
更健壮的方法涉及通过为 Agent 团队分配特定角色来分离这些关注点。例如,我使用 Gemini 构建了一个个人 AI Agent 团队,其中每个都有特定的角色:
**・ 同伴程序员:**帮助编写和头脑风暴代码。
-
・ 代码审查员: 捕获错误并建议改进。
・ 文档编写员: 生成清晰简洁的文档。
**・ 测试编写员:**创建全面的单元测试。**・ 提示词优化器:**优化与AI的交互。
在这个多 Agent 系统中,作为独立实体的代码审查员与程序员 Agent 分开,具有与示例中的判断者类似的提示词,这显著提高了客观评估。这种结构自然导致更好的实践,因为测试编写员 Agent 可以满足为同伴程序员产生的代码编写单元测试的需求。
概览
是什么:
AI Agent 通常缺乏明确的方向,阻碍了它们超越简单反应性任务的有目的行动。如果没有定义的目 标,它们无法独立处理复杂的多步骤问题或编排复杂的工作流。此外,它们缺乏固有的机制来确定其行动是 否导致成功的结果。这限制了它们的自主性,并阻止它们在仅执行任务不足的动态现实世界场景中真正有效。
为什么:
目标设定和监控模式通过将目的感和自我评估嵌入 Agent 系统来提供标准化的解决方案。它涉及明 确定义 Agent 要实现的清晰、可衡量的目标。同时,它建立了一个监控机制,持续跟踪 Agent 的进度和其环 境的状态与这些目标的对比。这创建了一个关键的反馈循环,使 Agent 能够评估其性能,纠正其路线,并在 偏离成功之路时调整其计划。通过实施此模式,开发人员可以将简单的反应 Agent 转变为能够自主和可靠运 行的主动的、以目标为导向的系统。
经验法则:
当 AI Agent 必须自主执行多步骤任务、适应动态条件并在没有持续人工干预的情况下可靠地实现 特定的高级目标时,使用此模式。
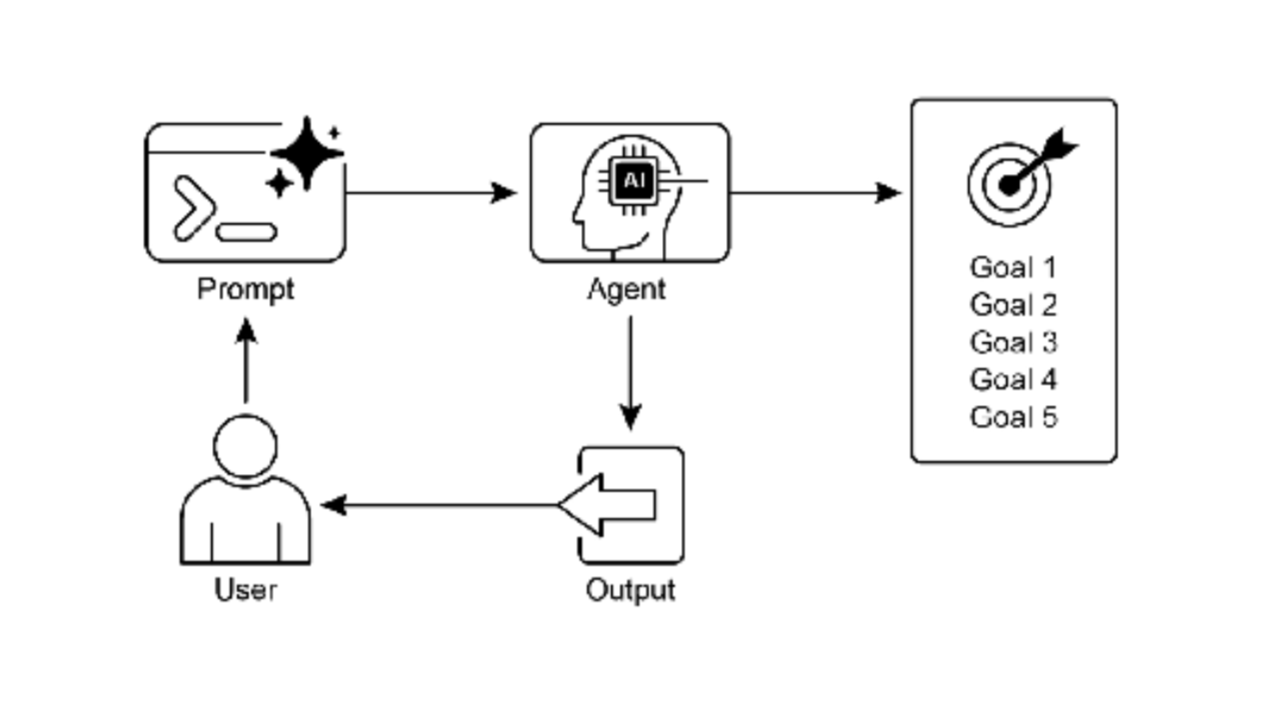
图 2:目标设计模式
关键要点
关键要点包括:
・ 目标设定和监控为Agent配备目的和跟踪进度的机制。
・ 目标应该是具体的、可衡量的、可实现的、相关的和有时限的(SMART)。
・ 清楚地定义指标和成功标准对于有效监控至关重要。
・ 监控涉及观察Agent的行动、环境状态和工具输出。
・ 来自监控的反馈循环允许Agent调整、修订计划或升级问题。
・ 在Google的ADK中,目标通常通过Agent指令传达,监控通过状态管理和工具交互完成。
实际应用和用例DEMO
以上面实际应用和用例中的"客户支持自动化"为例,构建一个简单的Java Agent Demo。该Agent的目标是"解决客户的账单查询"。我们将模拟以下步骤:
-
1、Agent接收用户查询,理解用户意图。
-
2、Agent使用工具(例如查询账单数据库、调整账单)来解决问题。
-
3、Agent监控对话,根据用户反馈判断问题是否解决,若未解决则升级处理。
由于这是一个演示,我们将简化实际场景,但保留关键要素。
步骤:
-
1、定义Agent需要的工具:查询账单、调整账单、升级问题。
-
2、定义Agent,它能够根据用户输入规划步骤,调用工具,并根据工具结果和用户反馈决定下一步。
-
3、模拟一个简单的用户交互场景。
我们将使用 LangChain4j 来构建这个Agent。LangChain4j 提供了工具调用和Agent的基本框架。
注意:为了简化,我们不会连接真实的数据库,而是用内存中的模拟数据。
AI Agent 规划能力 Java DEMO 实现
一、项目架构与基础设置
1.1 Maven 项目配置
XML
<!-- pom.xml -->
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot 基础 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- LangChain4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>dev.langchain4j</groupId>
<artifactId>langchain4j</artifactId>
<version>0.31.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>dev.langchain4j</groupId>
<artifactId>langchain4j-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>0.31.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 工具类 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>1.2 应用配置
XML
# application.yml
spring:
application:
name: ai-agent-planning-demo
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:mem:agentdb
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
username: sa
password:
h2:
console:
enabled: true
path: /h2-console
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true
langchain4j:
open-ai:
chat-model:
api-key: ${OPENAI_API_KEY}
model-name: gpt-4
temperature: 0.3
max-tokens: 2000
streaming-chat-model:
api-key: ${OPENAI_API_KEY}
model-name: gpt-4
app:
agents:
max-retries: 3
timeout-seconds: 60二、核心 Agent 规划架构
2.1 规划器接口与实现
java
// PlanningStrategy.java - 规划策略接口
public interface PlanningStrategy {
/**
* 为目标生成执行计划
*/
ExecutionPlan generatePlan(AgentGoal goal, AgentContext context);
/**
* 根据执行结果调整计划
*/
ExecutionPlan adaptPlan(ExecutionPlan currentPlan,
ExecutionResult result,
AgentContext context);
/**
* 评估计划可行性
*/
PlanFeasibility assessFeasibility(ExecutionPlan plan, AgentContext context);
}
// LLMBasedPlanner.java - 基于LLM的规划器
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LLMBasedPlanner implements PlanningStrategy {
@Autowired
private ChatLanguageModel llm;
@Autowired
private ToolRegistry toolRegistry;
private final ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
public ExecutionPlan generatePlan(AgentGoal goal, AgentContext context) {
log.info("为目标生成计划: {}", goal);
// 构建规划提示词
String prompt = buildPlanningPrompt(goal, context);
// 调用LLM生成计划
String planJson = llm.generate(prompt);
try {
// 解析LLM返回的规划
return parsePlanFromJson(planJson, goal, context);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("解析计划失败,使用默认计划", e);
return createDefaultPlan(goal, context);
}
}
@Override
public ExecutionPlan adaptPlan(ExecutionPlan currentPlan,
ExecutionResult result,
AgentContext context) {
log.info("根据结果调整计划: {}", result);
if (result.getStatus() == ExecutionStatus.SUCCESS) {
return currentPlan; // 计划成功,无需调整
}
// 构建重新规划提示词
String prompt = buildReplanningPrompt(currentPlan, result, context);
String newPlanJson = llm.generate(prompt);
try {
ExecutionPlan newPlan = parsePlanFromJson(newPlanJson,
currentPlan.getGoal(), context);
newPlan.setPreviousPlanId(currentPlan.getId());
return newPlan;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("重新规划失败", e);
return createFallbackPlan(currentPlan, result, context);
}
}
@Override
public PlanFeasibility assessFeasibility(ExecutionPlan plan, AgentContext context) {
String prompt = buildFeasibilityPrompt(plan, context);
String assessment = llm.generate(prompt);
return PlanFeasibility.builder()
.planId(plan.getId())
.assessment(assessment)
.confidence(extractConfidence(assessment))
.timestamp(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
}
private String buildPlanningPrompt(AgentGoal goal, AgentContext context) {
return String.format("""
你是一个AI规划专家。请根据以下信息制定执行计划:
目标:%s
目标描述:%s
优先级:%s
截止时间:%s
可用工具:
%s
约束条件:
%s
历史上下文:
%s
请生成一个详细的执行计划,包含以下内容:
1. 主要步骤序列
2. 每个步骤需要的工具
3. 预期输出
4. 依赖关系
5. 风险评估
返回格式必须是有效的JSON:
{
"planId": "唯一标识",
"goalId": "%s",
"steps": [
{
"stepId": "步骤ID",
"description": "步骤描述",
"action": "执行动作",
"requiredTool": "所需工具",
"expectedInput": "期望输入",
"expectedOutput": "期望输出",
"dependencies": ["依赖的步骤ID"],
"estimatedDuration": 预估分钟数,
"retryPolicy": {
"maxRetries": 最大重试次数,
"backoffSeconds": 回退秒数
}
}
],
"alternativeSteps": [
// 备用步骤
],
"monitoringMetrics": ["监控指标"],
"successCriteria": ["成功标准"],
"riskMitigation": ["风险缓解措施"]
}
""",
goal.getId(),
goal.getDescription(),
goal.getPriority(),
goal.getDeadline(),
toolRegistry.getAvailableToolsInfo(),
goal.getConstraints(),
context.getHistorySummary(),
goal.getId()
);
}
private ExecutionPlan parsePlanFromJson(String json, AgentGoal goal, AgentContext context) {
try {
JsonNode root = mapper.readTree(json);
List<PlanStep> steps = new ArrayList<>();
JsonNode stepsNode = root.get("steps");
if (stepsNode.isArray()) {
for (JsonNode stepNode : stepsNode) {
PlanStep step = PlanStep.builder()
.stepId(stepNode.get("stepId").asText())
.description(stepNode.get("description").asText())
.action(stepNode.get("action").asText())
.requiredTool(stepNode.get("requiredTool").asText())
.expectedInput(stepNode.get("expectedInput").asText())
.expectedOutput(stepNode.get("expectedOutput").asText())
.dependencies(parseStringArray(stepNode.get("dependencies")))
.estimatedDuration(stepNode.get("estimatedDuration").asInt())
.retryPolicy(parseRetryPolicy(stepNode.get("retryPolicy")))
.build();
steps.add(step);
}
}
return ExecutionPlan.builder()
.id(UUID.randomUUID().toString())
.goal(goal)
.steps(steps)
.createdAt(LocalDateTime.now())
.status(PlanStatus.PENDING)
.monitoringMetrics(parseStringArray(root.get("monitoringMetrics")))
.successCriteria(parseStringArray(root.get("successCriteria")))
.riskMitigation(parseStringArray(root.get("riskMitigation")))
.context(context)
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new PlanningException("解析计划JSON失败", e);
}
}
private List<String> parseStringArray(JsonNode node) {
if (node == null || !node.isArray()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
node.forEach(item -> list.add(item.asText()));
return list;
}
private RetryPolicy parseRetryPolicy(JsonNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return RetryPolicy.defaultPolicy();
}
return RetryPolicy.builder()
.maxRetries(node.get("maxRetries").asInt())
.backoffSeconds(node.get("backoffSeconds").asInt())
.build();
}
}2.2 Agent 核心类
java
// IntelligentAgent.java - 智能Agent基类
@Component
@Slf4j
public abstract class IntelligentAgent {
@Autowired
protected PlanningStrategy planningStrategy;
@Autowired
protected ToolRegistry toolRegistry;
@Autowired
protected ExecutionMonitor executionMonitor;
@Autowired
protected ChatLanguageModel llm;
protected final String agentId;
protected final String agentName;
protected final AgentType agentType;
protected AgentContext currentContext;
protected ExecutionPlan currentPlan;
protected AgentGoal currentGoal;
protected IntelligentAgent(String agentId, String agentName, AgentType agentType) {
this.agentId = agentId;
this.agentName = agentName;
this.agentType = agentType;
this.currentContext = AgentContext.initialContext(agentId);
}
/**
* 接受目标并开始规划执行
*/
public synchronized AgentResponse acceptGoal(AgentGoal goal) {
log.info("Agent {} 接受目标: {}", agentName, goal);
this.currentGoal = goal;
updateContext("接受新目标: " + goal.getDescription());
try {
// 步骤1: 生成初始计划
this.currentPlan = planningStrategy.generatePlan(goal, currentContext);
logPlan("初始计划生成完成", currentPlan);
// 步骤2: 评估计划可行性
PlanFeasibility feasibility = planningStrategy.assessFeasibility(currentPlan, currentContext);
if (feasibility.getConfidence() < 0.5) {
log.warn("计划可行性置信度低: {}", feasibility.getConfidence());
return AgentResponse.warning("计划可行性评估结果不理想", feasibility);
}
// 步骤3: 开始执行计划
ExecutionResult result = executePlan(currentPlan);
return AgentResponse.success("目标接受并开始执行", result);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("接受目标失败", e);
return AgentResponse.error("接受目标失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 执行计划
*/
protected ExecutionResult executePlan(ExecutionPlan plan) {
log.info("开始执行计划: {}", plan.getId());
plan.setStatus(PlanStatus.EXECUTING);
plan.setStartedAt(LocalDateTime.now());
ExecutionResult.Builder resultBuilder = ExecutionResult.builder()
.planId(plan.getId())
.goalId(plan.getGoal().getId())
.startTime(LocalDateTime.now());
Map<String, StepResult> stepResults = new LinkedHashMap<>();
List<PlanStep> executedSteps = new ArrayList<>();
try {
// 按依赖顺序执行步骤
List<PlanStep> executableSteps = findExecutableSteps(plan.getSteps(), stepResults);
while (!executableSteps.isEmpty()) {
for (PlanStep step : executableSteps) {
log.info("执行步骤: {} - {}", step.getStepId(), step.getDescription());
StepResult stepResult = executeStep(step, plan);
stepResults.put(step.getStepId(), stepResult);
executedSteps.add(step);
updateContext(String.format("完成步骤[%s]: %s, 结果: %s",
step.getStepId(), step.getDescription(), stepResult.getStatus()));
// 如果步骤失败,根据重试策略处理
if (stepResult.getStatus() == StepStatus.FAILED) {
handleStepFailure(step, stepResult, plan);
}
// 实时监控和调整
if (shouldReplan(stepResults, plan)) {
log.info("检测到需要重新规划");
ExecutionResult partialResult = resultBuilder
.stepResults(stepResults)
.status(ExecutionStatus.PARTIAL)
.build();
ExecutionPlan newPlan = planningStrategy.adaptPlan(plan, partialResult, currentContext);
return executePlan(newPlan); // 递归执行新计划
}
}
// 寻找下一批可执行步骤
executableSteps = findExecutableSteps(plan.getSteps(), stepResults);
}
// 所有步骤执行完成
plan.setStatus(PlanStatus.COMPLETED);
plan.setCompletedAt(LocalDateTime.now());
// 评估最终结果
ExecutionStatus finalStatus = evaluateFinalStatus(stepResults, plan);
return resultBuilder
.stepResults(stepResults)
.status(finalStatus)
.endTime(LocalDateTime.now())
.message("计划执行完成")
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("执行计划时发生异常", e);
plan.setStatus(PlanStatus.FAILED);
return resultBuilder
.stepResults(stepResults)
.status(ExecutionStatus.FAILED)
.endTime(LocalDateTime.now())
.errorMessage("执行异常: " + e.getMessage())
.build();
}
}
/**
* 执行单个步骤
*/
protected StepResult executeStep(PlanStep step, ExecutionPlan plan) {
StepResult.Builder resultBuilder = StepResult.builder()
.stepId(step.getStepId())
.startTime(LocalDateTime.now());
try {
// 检查步骤依赖是否满足
if (!areDependenciesSatisfied(step, plan)) {
return resultBuilder
.status(StepStatus.BLOCKED)
.message("依赖步骤未完成")
.build();
}
// 获取所需工具
Tool tool = toolRegistry.getTool(step.getRequiredTool());
if (tool == null) {
return resultBuilder
.status(StepStatus.FAILED)
.message("工具不可用: " + step.getRequiredTool())
.build();
}
// 准备输入参数
Map<String, Object> inputs = prepareStepInputs(step, plan);
// 执行工具调用
ToolExecutionResult toolResult = tool.execute(inputs);
// 评估工具执行结果
StepStatus status = evaluateToolResult(toolResult, step);
return resultBuilder
.status(status)
.output(toolResult.getOutput())
.metadata(toolResult.getMetadata())
.endTime(LocalDateTime.now())
.message(toolResult.getMessage())
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("执行步骤失败: {}", step.getStepId(), e);
return resultBuilder
.status(StepStatus.FAILED)
.endTime(LocalDateTime.now())
.errorMessage("步骤执行异常: " + e.getMessage())
.build();
}
}
/**
* 判断是否需要重新规划
*/
protected boolean shouldReplan(Map<String, StepResult> stepResults, ExecutionPlan plan) {
// 规则1: 关键步骤失败
long failedCriticalSteps = stepResults.values().stream()
.filter(r -> r.getStatus() == StepStatus.FAILED)
.count();
if (failedCriticalSteps > 0) {
return true;
}
// 规则2: 执行时间超预期
int totalEstimated = plan.getSteps().stream()
.mapToInt(PlanStep::getEstimatedDuration)
.sum();
long actualMinutes = Duration.between(plan.getStartedAt(), LocalDateTime.now()).toMinutes();
if (actualMinutes > totalEstimated * 1.5) {
return true;
}
// 规则3: 监控指标异常
List<String> anomalies = executionMonitor.detectAnomalies(plan, stepResults);
if (!anomalies.isEmpty()) {
log.warn("检测到监控异常: {}", anomalies);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 抽象方法 - 由具体Agent实现
*/
protected abstract Map<String, Object> prepareStepInputs(PlanStep step, ExecutionPlan plan);
protected abstract StepStatus evaluateToolResult(ToolExecutionResult result, PlanStep step);
protected abstract boolean areDependenciesSatisfied(PlanStep step, ExecutionPlan plan);
protected abstract List<PlanStep> findExecutableSteps(List<PlanStep> allSteps,
Map<String, StepResult> completedSteps);
protected abstract ExecutionStatus evaluateFinalStatus(Map<String, StepResult> stepResults,
ExecutionPlan plan);
/**
* 处理步骤失败
*/
protected void handleStepFailure(PlanStep step, StepResult result, ExecutionPlan plan) {
RetryPolicy retryPolicy = step.getRetryPolicy();
if (retryPolicy.getCurrentRetries() < retryPolicy.getMaxRetries()) {
log.info("步骤失败,尝试重试 {}/{}",
retryPolicy.getCurrentRetries() + 1,
retryPolicy.getMaxRetries());
retryPolicy.incrementRetries();
// 等待回退时间
try {
Thread.sleep(retryPolicy.getBackoffSeconds() * 1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
} else {
log.warn("步骤已达到最大重试次数: {}", step.getStepId());
}
}
private void updateContext(String message) {
currentContext.addEvent(new AgentEvent(
agentId,
AgentEventType.INFO,
message,
LocalDateTime.now()
));
}
private void logPlan(String message, ExecutionPlan plan) {
log.info("{} - 计划ID: {}", message, plan.getId());
plan.getSteps().forEach(step ->
log.info(" 步骤: {} - {}", step.getStepId(), step.getDescription()));
}
}2.3 数据模型定义
java
// AgentGoal.java - Agent目标
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class AgentGoal {
private String id;
private String description;
private GoalPriority priority;
private LocalDateTime deadline;
private Map<String, Object> parameters;
private List<String> constraints;
private Map<String, Object> successCriteria;
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
public enum GoalPriority {
CRITICAL, HIGH, MEDIUM, LOW
}
}
// ExecutionPlan.java - 执行计划
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ExecutionPlan {
private String id;
private String previousPlanId; // 前一个计划的ID(用于重新规划)
private AgentGoal goal;
private List<PlanStep> steps;
private List<String> alternativeSteps;
private PlanStatus status;
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
private LocalDateTime startedAt;
private LocalDateTime completedAt;
private List<String> monitoringMetrics;
private List<String> successCriteria;
private List<String> riskMitigation;
private AgentContext context;
public enum PlanStatus {
PENDING, EXECUTING, COMPLETED, FAILED, CANCELLED
}
}
// PlanStep.java - 计划步骤
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class PlanStep {
private String stepId;
private String description;
private String action;
private String requiredTool;
private String expectedInput;
private String expectedOutput;
private List<String> dependencies;
private int estimatedDuration; // 分钟
private RetryPolicy retryPolicy;
}
// RetryPolicy.java - 重试策略
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class RetryPolicy {
@Builder.Default
private int maxRetries = 3;
@Builder.Default
private int backoffSeconds = 5;
@Builder.Default
private int currentRetries = 0;
public static RetryPolicy defaultPolicy() {
return RetryPolicy.builder().build();
}
public void incrementRetries() {
this.currentRetries++;
}
public boolean canRetry() {
return currentRetries < maxRetries;
}
}
// ExecutionResult.java - 执行结果
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ExecutionResult {
private String planId;
private String goalId;
private ExecutionStatus status;
private Map<String, StepResult> stepResults;
private LocalDateTime startTime;
private LocalDateTime endTime;
private String message;
private String errorMessage;
public enum ExecutionStatus {
SUCCESS, PARTIAL, FAILED, CANCELLED
}
}
// StepResult.java - 步骤结果
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class StepResult {
private String stepId;
private StepStatus status;
private Object output;
private Map<String, Object> metadata;
private LocalDateTime startTime;
private LocalDateTime endTime;
private String message;
private String errorMessage;
public enum StepStatus {
PENDING, EXECUTING, SUCCESS, FAILED, SKIPPED, BLOCKED
}
}
// AgentContext.java - Agent上下文
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class AgentContext {
private String agentId;
private List<AgentEvent> history;
private Map<String, Object> state;
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
private LocalDateTime lastUpdated;
public static AgentContext initialContext(String agentId) {
return AgentContext.builder()
.agentId(agentId)
.history(new ArrayList<>())
.state(new HashMap<>())
.createdAt(LocalDateTime.now())
.lastUpdated(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
}
public void addEvent(AgentEvent event) {
history.add(event);
lastUpdated = LocalDateTime.now();
}
public String getHistorySummary() {
if (history.isEmpty()) {
return "无历史记录";
}
return history.stream()
.limit(10)
.map(e -> String.format("[%s] %s", e.getTimestamp(), e.getMessage()))
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
}
}
// AgentEvent.java - Agent事件
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class AgentEvent {
private String agentId;
private AgentEventType type;
private String message;
private LocalDateTime timestamp;
private Map<String, Object> metadata;
public enum AgentEventType {
INFO, WARNING, ERROR, DECISION, ACTION, RESULT
}
}三、实际应用案例实现
3.1 客户支持自动化 Agent
java
// CustomerSupportAgent.java
@Service
@Slf4j
public class CustomerSupportAgent extends IntelligentAgent {
@Autowired
private CustomerRepository customerRepository;
@Autowired
private BillingService billingService;
private final Map<String, Object> conversationState = new HashMap<>();
public CustomerSupportAgent() {
super("customer-support-001", "客户支持助手", AgentType.CUSTOMER_SUPPORT);
}
/**
* 处理客户账单查询
*/
public AgentResponse handleBillingInquiry(String customerId, String inquiry) {
log.info("处理客户账单查询: {} - {}", customerId, inquiry);
// 构建目标
AgentGoal goal = AgentGoal.builder()
.id("billing-inquiry-" + System.currentTimeMillis())
.description("解决客户" + customerId + "的账单查询: " + inquiry)
.priority(AgentGoal.GoalPriority.HIGH)
.deadline(LocalDateTime.now().plusHours(1))
.parameters(Map.of(
"customerId", customerId,
"inquiry", inquiry
))
.constraints(List.of(
"必须遵循公司隐私政策",
"必须在1小时内解决",
"需要客户确认解决方案"
))
.successCriteria(Map.of(
"customerSatisfied", true,
"issueResolved", true,
"withinSLA", true
))
.createdAt(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
return acceptGoal(goal);
}
@Override
protected Map<String, Object> prepareStepInputs(PlanStep step, ExecutionPlan plan) {
Map<String, Object> inputs = new HashMap<>();
AgentGoal goal = plan.getGoal();
String customerId = (String) goal.getParameters().get("customerId");
String inquiry = (String) goal.getParameters().get("inquiry");
switch (step.getRequiredTool()) {
case "customer_lookup_tool":
inputs.put("customerId", customerId);
break;
case "billing_query_tool":
inputs.put("customerId", customerId);
inputs.put("inquiryType", extractInquiryType(inquiry));
break;
case "issue_classifier_tool":
inputs.put("inquiryText", inquiry);
inputs.put("customerData", conversationState.get("customerData"));
break;
case "billing_adjustment_tool":
Map<String, Object> issueDetails = (Map<String, Object>)
conversationState.get("issueDetails");
inputs.putAll(issueDetails);
inputs.put("customerId", customerId);
break;
case "confirmation_tool":
String solution = (String) conversationState.get("proposedSolution");
inputs.put("customerId", customerId);
inputs.put("solution", solution);
break;
case "escalation_tool":
String reason = (String) conversationState.get("escalationReason");
inputs.put("customerId", customerId);
inputs.put("reason", reason);
inputs.put("priority", "HIGH");
break;
}
return inputs;
}
@Override
protected StepStatus evaluateToolResult(ToolExecutionResult result, PlanStep step) {
// 保存工具执行结果到状态
conversationState.put(step.getStepId() + "_result", result.getOutput());
switch (step.getRequiredTool()) {
case "customer_lookup_tool":
Map<String, Object> customerData = (Map<String, Object>) result.getOutput();
conversationState.put("customerData", customerData);
return customerData != null ? StepStatus.SUCCESS : StepStatus.FAILED;
case "billing_query_tool":
Map<String, Object> billingData = (Map<String, Object>) result.getOutput();
conversationState.put("billingData", billingData);
boolean hasIssues = (boolean) billingData.getOrDefault("hasIssues", false);
return hasIssues ? StepStatus.SUCCESS : StepStatus.SUCCESS; // 即使没问题也是成功
case "issue_classifier_tool":
Map<String, Object> issueDetails = (Map<String, Object>) result.getOutput();
conversationState.put("issueDetails", issueDetails);
conversationState.put("issueType", issueDetails.get("type"));
return StepStatus.SUCCESS;
case "billing_adjustment_tool":
Map<String, Object> adjustment = (Map<String, Object>) result.getOutput();
boolean adjustmentSuccess = (boolean) adjustment.getOrDefault("success", false);
if (adjustmentSuccess) {
conversationState.put("proposedSolution", adjustment.get("solution"));
}
return adjustmentSuccess ? StepStatus.SUCCESS : StepStatus.FAILED;
case "confirmation_tool":
Map<String, Object> confirmation = (Map<String, Object>) result.getOutput();
boolean confirmed = (boolean) confirmation.getOrDefault("confirmed", false);
conversationState.put("customerConfirmed", confirmed);
return confirmed ? StepStatus.SUCCESS : StepStatus.FAILED;
case "escalation_tool":
return StepStatus.SUCCESS; // 升级总是成功的
default:
return StepStatus.SUCCESS;
}
}
@Override
protected boolean areDependenciesSatisfied(PlanStep step, ExecutionPlan plan) {
if (step.getDependencies() == null || step.getDependencies().isEmpty()) {
return true;
}
// 检查所有依赖步骤是否成功完成
return step.getDependencies().stream()
.allMatch(depId -> {
StepResult result = (StepResult) conversationState.get(depId + "_result");
return result != null && result.getStatus() == StepStatus.SUCCESS;
});
}
@Override
protected List<PlanStep> findExecutableSteps(List<PlanStep> allSteps,
Map<String, StepResult> completedSteps) {
return allSteps.stream()
.filter(step -> {
// 步骤尚未执行
if (completedSteps.containsKey(step.getStepId())) {
return false;
}
// 依赖已满足
return areDependenciesSatisfied(step, completedSteps);
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
@Override
protected ExecutionStatus evaluateFinalStatus(Map<String, StepResult> stepResults,
ExecutionPlan plan) {
// 检查客户是否确认
Boolean customerConfirmed = (Boolean) conversationState.get("customerConfirmed");
if (customerConfirmed != null && customerConfirmed) {
return ExecutionStatus.SUCCESS;
}
// 检查是否已升级
boolean escalated = stepResults.values().stream()
.anyMatch(r -> r.getMetadata() != null &&
"escalation".equals(r.getMetadata().get("type")));
if (escalated) {
return ExecutionStatus.PARTIAL; // 部分成功,已升级处理
}
// 计算成功率
long successfulSteps = stepResults.values().stream()
.filter(r -> r.getStatus() == StepStatus.SUCCESS)
.count();
double successRate = (double) successfulSteps / stepResults.size();
return successRate > 0.7 ? ExecutionStatus.PARTIAL : ExecutionStatus.FAILED;
}
private String extractInquiryType(String inquiry) {
if (inquiry.contains("费用") || inquiry.contains("金额") || inquiry.contains("账单")) {
return "charge_inquiry";
} else if (inquiry.contains("错误") || inquiry.contains("问题")) {
return "issue_report";
} else if (inquiry.contains("解释") || inquiry.contains("说明")) {
return "explanation";
}
return "general";
}
}3.2 客户支持工具实现
java
// CustomerSupportTools.java
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CustomerSupportTools {
@Autowired
private CustomerRepository customerRepository;
@Autowired
private BillingRecordRepository billingRepository;
@Tool(name = "customer_lookup_tool", description = "根据客户ID查询客户信息")
public Map<String, Object> lookupCustomer(
@P("客户ID") String customerId) {
try {
Optional<Customer> customerOpt = customerRepository.findById(customerId);
if (customerOpt.isEmpty()) {
return Map.of(
"error", "客户不存在",
"customerId", customerId
);
}
Customer customer = customerOpt.get();
return Map.of(
"customerId", customer.getId(),
"name", customer.getName(),
"email", customer.getEmail(),
"phone", customer.getPhone(),
"customerTier", customer.getTier(),
"joinDate", customer.getJoinDate(),
"status", customer.getStatus()
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("查询客户信息失败", e);
return Map.of("error", "查询失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Tool(name = "billing_query_tool", description = "查询客户账单信息")
public Map<String, Object> queryBilling(
@P("客户ID") String customerId,
@P("查询类型") String inquiryType) {
try {
List<BillingRecord> records = billingRepository.findByCustomerId(customerId);
if (records.isEmpty()) {
return Map.of(
"hasIssues", false,
"message", "未找到账单记录",
"customerId", customerId
);
}
// 分析账单记录
List<Map<String, Object>> billingDetails = records.stream()
.map(record -> Map.of(
"billingId", record.getId(),
"period", record.getBillingPeriod(),
"amount", record.getAmount(),
"status", record.getStatus(),
"dueDate", record.getDueDate(),
"paidDate", record.getPaidDate()
))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 检测潜在问题
List<String> issues = new ArrayList<>();
BigDecimal totalOutstanding = BigDecimal.ZERO;
for (BillingRecord record : records) {
if ("OVERDUE".equals(record.getStatus())) {
issues.add("账单" + record.getId() + "已逾期");
totalOutstanding = totalOutstanding.add(record.getAmount());
}
if (record.getAmount().compareTo(BigDecimal.valueOf(10000)) > 0) {
issues.add("账单" + record.getId() + "金额异常偏高");
}
}
return Map.of(
"hasIssues", !issues.isEmpty(),
"issues", issues,
"totalOutstanding", totalOutstanding,
"billingDetails", billingDetails,
"customerId", customerId
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("查询账单失败", e);
return Map.of(
"error", "查询失败: " + e.getMessage(),
"customerId", customerId
);
}
}
@Tool(name = "issue_classifier_tool", description = "分类和分析客户问题")
public Map<String, Object> classifyIssue(
@P("问题描述") String inquiryText,
@P("客户数据") Map<String, Object> customerData) {
try {
// 使用规则+LLM进行问题分类
String classificationPrompt = String.format("""
请分析以下客户问题并分类:
客户等级:%s
问题描述:%s
请返回JSON格式:
{
"type": "问题类型",
"severity": "严重程度",
"category": ["类别1", "类别2"],
"requiresManualReview": true/false,
"suggestedActions": ["建议操作1", "建议操作2"]
}
""",
customerData.get("customerTier"),
inquiryText
);
// 这里应该调用LLM,简化实现使用规则
Map<String, Object> classification = classifyByRules(inquiryText);
return Map.of(
"type", classification.get("type"),
"severity", classification.get("severity"),
"category", classification.get("category"),
"requiresManualReview", classification.get("requiresManualReview"),
"suggestedActions", classification.get("suggestedActions"),
"analysisTimestamp", LocalDateTime.now()
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("问题分类失败", e);
return Map.of("error", "分类失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Tool(name = "billing_adjustment_tool", description = "调整客户账单")
public Map<String, Object> adjustBilling(
@P("客户ID") String customerId,
@P("调整类型") String adjustmentType,
@P("调整金额") BigDecimal amount,
@P("调整原因") String reason,
@P("备注") String notes) {
try {
// 验证调整权限
if (!isAdjustmentAllowed(customerId, adjustmentType, amount)) {
return Map.of(
"success", false,
"error", "调整未授权",
"customerId", customerId
);
}
// 创建调整记录
BillingAdjustment adjustment = BillingAdjustment.builder()
.id(UUID.randomUUID().toString())
.customerId(customerId)
.adjustmentType(adjustmentType)
.amount(amount)
.reason(reason)
.notes(notes)
.status("PENDING")
.createdBy("customer_support_agent")
.createdAt(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
// 保存调整记录
billingAdjustmentRepository.save(adjustment);
// 应用调整到账单
boolean applied = applyBillingAdjustment(customerId, adjustment);
if (applied) {
return Map.of(
"success", true,
"adjustmentId", adjustment.getId(),
"solution", String.format("已为客户%s调整账单,调整金额:%s,原因:%s",
customerId, amount, reason),
"timestamp", LocalDateTime.now()
);
} else {
return Map.of(
"success", false,
"error", "调整应用失败",
"adjustmentId", adjustment.getId()
);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("账单调整失败", e);
return Map.of(
"success", false,
"error", "调整失败: " + e.getMessage(),
"customerId", customerId
);
}
}
@Tool(name = "confirmation_tool", description = "获取客户确认")
public Map<String, Object> getCustomerConfirmation(
@P("客户ID") String customerId,
@P("解决方案") String solution) {
try {
// 这里应该实际联系客户获取确认
// 简化实现:模拟客户响应
boolean confirmed = simulateCustomerResponse(customerId, solution);
return Map.of(
"confirmed", confirmed,
"customerId", customerId,
"solution", solution,
"confirmationTime", confirmed ? LocalDateTime.now() : null,
"message", confirmed ? "客户已确认解决方案" : "客户未确认解决方案"
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("获取客户确认失败", e);
return Map.of(
"confirmed", false,
"error", "确认失败: " + e.getMessage()
);
}
}
@Tool(name = "escalation_tool", description = "升级问题到人工处理")
public Map<String, Object> escalateIssue(
@P("客户ID") String customerId,
@P("升级原因") String reason,
@P("优先级") String priority) {
try {
// 创建升级工单
EscalationTicket ticket = EscalationTicket.builder()
.id(UUID.randomUUID().toString())
.customerId(customerId)
.reason(reason)
.priority(priority)
.status("OPEN")
.createdBy("customer_support_agent")
.createdAt(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
escalationTicketRepository.save(ticket);
log.info("问题已升级: ticketId={}, customerId={}, reason={}",
ticket.getId(), customerId, reason);
return Map.of(
"success", true,
"ticketId", ticket.getId(),
"message", "问题已成功升级到人工处理",
"escalationTime", LocalDateTime.now(),
"type", "escalation"
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("问题升级失败", e);
return Map.of(
"success", false,
"error", "升级失败: " + e.getMessage()
);
}
}
private Map<String, Object> classifyByRules(String inquiryText) {
// 简化的规则分类
if (inquiryText.contains("错误收费") || inquiryText.contains("多扣钱")) {
return Map.of(
"type", "BILLING_ERROR",
"severity", "HIGH",
"category", List.of("BILLING", "ERROR"),
"requiresManualReview", false,
"suggestedActions", List.of("verify_charges", "adjust_billing", "refund_if_needed")
);
} else if (inquiryText.contains("解释") || inquiryText.contains("不明白")) {
return Map.of(
"type", "EXPLANATION_REQUEST",
"severity", "LOW",
"category", List.of("INFORMATION"),
"requiresManualReview", false,
"suggestedActions", List.of("explain_charges", "provide_breakdown")
);
} else {
return Map.of(
"type", "GENERAL_INQUIRY",
"severity", "MEDIUM",
"category", List.of("GENERAL"),
"requiresManualReview", true,
"suggestedActions", List.of("review_manually")
);
}
}
private boolean isAdjustmentAllowed(String customerId, String type, BigDecimal amount) {
// 简化的授权检查
if (amount.compareTo(BigDecimal.valueOf(1000)) > 0) {
return false; // 大额调整需要人工审批
}
if ("REFUND".equals(type)) {
return false; // 退款需要特殊授权
}
return true;
}
private boolean applyBillingAdjustment(String customerId, BillingAdjustment adjustment) {
// 简化实现
log.info("应用账单调整: {} for customer {}", adjustment.getId(), customerId);
return true;
}
private boolean simulateCustomerResponse(String customerId, String solution) {
// 模拟80%的确认率
return Math.random() > 0.2;
}
}3.3 项目管理助手 Agent
java
// ProjectManagementAgent.java
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ProjectManagementAgent extends IntelligentAgent {
@Autowired
private ProjectRepository projectRepository;
@Autowired
private TaskRepository taskRepository;
@Autowired
private TeamMemberRepository teamMemberRepository;
public ProjectManagementAgent() {
super("project-mgmt-001", "项目管理助手", AgentType.PROJECT_MANAGEMENT);
}
/**
* 监控项目里程碑
*/
public AgentResponse monitorMilestone(String projectId, String milestoneId, LocalDateTime targetDate) {
log.info("监控项目里程碑: project={}, milestone={}, target={}",
projectId, milestoneId, targetDate);
AgentGoal goal = AgentGoal.builder()
.id("milestone-monitor-" + milestoneId)
.description(String.format("确保项目%s的里程碑%s在%s前完成",
projectId, milestoneId, targetDate))
.priority(AgentGoal.GoalPriority.HIGH)
.deadline(targetDate)
.parameters(Map.of(
"projectId", projectId,
"milestoneId", milestoneId,
"targetDate", targetDate
))
.constraints(List.of(
"不能超过项目预算",
"必须保证交付质量",
"需要团队协作完成"
))
.successCriteria(Map.of(
"milestoneCompleted", true,
"onTime", true,
"withinBudget", true,
"qualityMet", true
))
.createdAt(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
return acceptGoal(goal);
}
/**
* 风险检测和缓解
*/
public AgentResponse detectAndMitigateRisks(String projectId) {
log.info("检测和缓解项目风险: project={}", projectId);
AgentGoal goal = AgentGoal.builder()
.id("risk-mitigation-" + projectId)
.description("识别和缓解项目" + projectId + "的风险")
.priority(AgentGoal.GoalPriority.MEDIUM)
.deadline(LocalDateTime.now().plusDays(7))
.parameters(Map.of("projectId", projectId))
.constraints(List.of(
"不能影响现有进度",
"必须符合风险管理政策",
"需要利益相关者沟通"
))
.successCriteria(Map.of(
"risksIdentified", true,
"mitigationPlansCreated", true,
"riskLevelReduced", true
))
.createdAt(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
return acceptGoal(goal);
}
@Override
protected Map<String, Object> prepareStepInputs(PlanStep step, ExecutionPlan plan) {
Map<String, Object> inputs = new HashMap<>();
AgentGoal goal = plan.getGoal();
String projectId = (String) goal.getParameters().get("projectId");
switch (step.getRequiredTool()) {
case "project_status_tool":
inputs.put("projectId", projectId);
break;
case "task_analysis_tool":
inputs.put("projectId", projectId);
inputs.put("milestoneId", goal.getParameters().get("milestoneId"));
break;
case "resource_check_tool":
inputs.put("projectId", projectId);
inputs.put("resourceType", step.getExpectedInput());
break;
case "risk_detection_tool":
inputs.put("projectId", projectId);
inputs.put("analysisDepth", "DEEP");
break;
case "mitigation_planning_tool":
Map<String, Object> risks = (Map<String, Object>)
currentContext.getState().get("detectedRisks");
inputs.put("projectId", projectId);
inputs.put("risks", risks);
break;
case "notification_tool":
String message = (String) currentContext.getState().get("alertMessage");
inputs.put("recipients", getProjectStakeholders(projectId));
inputs.put("subject", "项目风险警报");
inputs.put("message", message);
inputs.put("priority", "HIGH");
break;
case "schedule_adjustment_tool":
Map<String, Object> scheduleData = (Map<String, Object>)
currentContext.getState().get("scheduleAnalysis");
inputs.put("projectId", projectId);
inputs.put("currentSchedule", scheduleData);
inputs.put("adjustmentReason", "风险缓解");
break;
}
return inputs;
}
@Override
protected StepStatus evaluateToolResult(ToolExecutionResult result, PlanStep step) {
Map<String, Object> output = (Map<String, Object>) result.getOutput();
switch (step.getRequiredTool()) {
case "project_status_tool":
currentContext.getState().put("projectStatus", output);
boolean isOnTrack = (boolean) output.getOrDefault("onTrack", false);
return isOnTrack ? StepStatus.SUCCESS : StepStatus.SUCCESS; // 即使有问题也需要继续
case "task_analysis_tool":
currentContext.getState().put("taskAnalysis", output);
int delayedTasks = (int) output.getOrDefault("delayedTasks", 0);
return delayedTasks == 0 ? StepStatus.SUCCESS : StepStatus.SUCCESS;
case "resource_check_tool":
currentContext.getState().put("resourceStatus", output);
boolean resourcesAvailable = (boolean) output.getOrDefault("available", true);
return resourcesAvailable ? StepStatus.SUCCESS : StepStatus.FAILED;
case "risk_detection_tool":
currentContext.getState().put("detectedRisks", output);
int riskCount = (int) output.getOrDefault("riskCount", 0);
return riskCount >= 0 ? StepStatus.SUCCESS : StepStatus.FAILED;
case "mitigation_planning_tool":
currentContext.getState().put("mitigationPlans", output);
boolean plansCreated = (boolean) output.getOrDefault("plansCreated", false);
return plansCreated ? StepStatus.SUCCESS : StepStatus.FAILED;
case "notification_tool":
boolean notified = (boolean) output.getOrDefault("notified", false);
return notified ? StepStatus.SUCCESS : StepStatus.FAILED;
case "schedule_adjustment_tool":
boolean adjusted = (boolean) output.getOrDefault("adjusted", false);
return adjusted ? StepStatus.SUCCESS : StepStatus.FAILED;
default:
return StepStatus.SUCCESS;
}
}
@Override
protected boolean areDependenciesSatisfied(PlanStep step, ExecutionPlan plan) {
// 项目管理中的依赖关系
if ("mitigation_planning_tool".equals(step.getRequiredTool())) {
return currentContext.getState().containsKey("detectedRisks");
}
if ("notification_tool".equals(step.getRequiredTool())) {
return currentContext.getState().containsKey("alertMessage");
}
if ("schedule_adjustment_tool".equals(step.getRequiredTool())) {
return currentContext.getState().containsKey("scheduleAnalysis");
}
return true;
}
@Override
protected List<PlanStep> findExecutableSteps(List<PlanStep> allSteps,
Map<String, StepResult> completedSteps) {
return allSteps.stream()
.filter(step -> {
// 步骤尚未执行
if (completedSteps.containsKey(step.getStepId())) {
return false;
}
// 检查工具特定的前置条件
return areDependenciesSatisfied(step, null);
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
@Override
protected ExecutionStatus evaluateFinalStatus(Map<String, StepResult> stepResults,
ExecutionPlan plan) {
AgentGoal goal = plan.getGoal();
String goalType = goal.getDescription();
if (goalType.contains("监控")) {
// 里程碑监控目标
Map<String, Object> projectStatus = (Map<String, Object>)
currentContext.getState().get("projectStatus");
if (projectStatus != null) {
boolean milestoneAchieved = (boolean) projectStatus.getOrDefault(
"milestoneAchieved", false);
boolean onTime = (boolean) projectStatus.getOrDefault("onTime", false);
if (milestoneAchieved && onTime) {
return ExecutionStatus.SUCCESS;
} else if (milestoneAchieved && !onTime) {
return ExecutionStatus.PARTIAL; // 完成但延期
}
}
return ExecutionStatus.FAILED;
} else if (goalType.contains("风险")) {
// 风险管理目标
Map<String, Object> mitigationPlans = (Map<String, Object>)
currentContext.getState().get("mitigationPlans");
if (mitigationPlans != null) {
boolean plansCreated = (boolean) mitigationPlans.getOrDefault(
"plansCreated", false);
int risksMitigated = (int) mitigationPlans.getOrDefault(
"risksMitigated", 0);
if (plansCreated && risksMitigated > 0) {
return ExecutionStatus.SUCCESS;
} else if (plansCreated) {
return ExecutionStatus.PARTIAL; // 有计划但未实施
}
}
return ExecutionStatus.FAILED;
}
// 默认评估
long successfulSteps = stepResults.values().stream()
.filter(r -> r.getStatus() == StepStatus.SUCCESS)
.count();
double successRate = (double) successfulSteps / stepResults.size();
if (successRate >= 0.9) return ExecutionStatus.SUCCESS;
if (successRate >= 0.6) return ExecutionStatus.PARTIAL;
return ExecutionStatus.FAILED;
}
private List<String> getProjectStakeholders(String projectId) {
// 获取项目相关方
Optional<Project> project = projectRepository.findById(projectId);
if (project.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<String> stakeholders = new ArrayList<>();
stakeholders.add(project.get().getProjectManager());
stakeholders.addAll(project.get().getStakeholders());
return stakeholders.stream()
.filter(email -> email != null && !email.isEmpty())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}3.4 项目管理工具
java
// ProjectManagementTools.java
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ProjectManagementTools {
@Autowired
private ProjectRepository projectRepository;
@Autowired
private TaskRepository taskRepository;
@Autowired
private RiskRepository riskRepository;
@Tool(name = "project_status_tool", description = "获取项目状态和进度")
public Map<String, Object> getProjectStatus(
@P("项目ID") String projectId) {
try {
Optional<Project> projectOpt = projectRepository.findById(projectId);
if (projectOpt.isEmpty()) {
return Map.of("error", "项目不存在", "projectId", projectId);
}
Project project = projectOpt.get();
// 计算项目进度
List<Task> tasks = taskRepository.findByProjectId(projectId);
long totalTasks = tasks.size();
long completedTasks = tasks.stream()
.filter(task -> "COMPLETED".equals(task.getStatus()))
.count();
double progress = totalTasks > 0 ? (double) completedTasks / totalTasks * 100 : 0;
// 检查里程碑
List<Milestone> milestones = project.getMilestones();
List<Map<String, Object>> milestoneStatus = new ArrayList<>();
for (Milestone milestone : milestones) {
boolean achieved = milestone.getAchievedDate() != null;
boolean onTime = !achieved ||
!milestone.getTargetDate().isBefore(milestone.getAchievedDate());
milestoneStatus.add(Map.of(
"id", milestone.getId(),
"name", milestone.getName(),
"targetDate", milestone.getTargetDate(),
"achieved", achieved,
"achievedDate", milestone.getAchievedDate(),
"onTime", onTime
));
}
// 检测问题
List<String> issues = new ArrayList<>();
if (progress < project.getExpectedProgress()) {
issues.add("项目进度落后于计划");
}
if (project.getActualCost().compareTo(project.getBudget()) > 0) {
issues.add("项目超出预算");
}
// 计算关键路径
List<Task> criticalPath = calculateCriticalPath(tasks);
return Map.of(
"projectId", projectId,
"projectName", project.getName(),
"progress", progress,
"completedTasks", completedTasks,
"totalTasks", totalTasks,
"budgetStatus", calculateBudgetStatus(project),
"milestoneStatus", milestoneStatus,
"issues", issues,
"criticalPath", criticalPath.stream()
.map(Task::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList()),
"onTrack", issues.isEmpty() && progress >= project.getExpectedProgress(),
"lastUpdated", LocalDateTime.now()
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("获取项目状态失败", e);
return Map.of("error", "获取失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Tool(name = "task_analysis_tool", description = "分析任务状态和依赖")
public Map<String, Object> analyzeTasks(
@P("项目ID") String projectId,
@P("里程碑ID") String milestoneId) {
try {
List<Task> tasks = taskRepository.findByProjectId(projectId);
// 过滤关联到特定里程碑的任务
List<Task> milestoneTasks = tasks.stream()
.filter(task -> milestoneId.equals(task.getMilestoneId()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 分析任务状态
Map<String, Long> statusCount = milestoneTasks.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Task::getStatus, Collectors.counting()));
// 检测延迟任务
List<Task> delayedTasks = milestoneTasks.stream()
.filter(task -> {
if (task.getDueDate() == null || "COMPLETED".equals(task.getStatus())) {
return false;
}
return LocalDateTime.now().isAfter(task.getDueDate());
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 分析依赖关系
List<Map<String, Object>> dependencyAnalysis = new ArrayList<>();
for (Task task : milestoneTasks) {
if (task.getDependencies() != null && !task.getDependencies().isEmpty()) {
List<String> blockingDependencies = task.getDependencies().stream()
.filter(depId -> {
Optional<Task> depTask = taskRepository.findById(depId);
return depTask.isPresent() &&
!"COMPLETED".equals(depTask.get().getStatus());
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
if (!blockingDependencies.isEmpty()) {
dependencyAnalysis.add(Map.of(
"taskId", task.getId(),
"taskName", task.getName(),
"blockingDependencies", blockingDependencies
));
}
}
}
return Map.of(
"milestoneId", milestoneId,
"totalTasks", milestoneTasks.size(),
"statusCount", statusCount,
"delayedTasks", delayedTasks.size(),
"delayedTaskDetails", delayedTasks.stream()
.map(t -> Map.of("id", t.getId(), "name", t.getName(), "dueDate", t.getDueDate()))
.collect(Collectors.toList()),
"dependencyIssues", dependencyAnalysis,
"analysisTime", LocalDateTime.now()
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("任务分析失败", e);
return Map.of("error", "分析失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Tool(name = "risk_detection_tool", description = "检测项目风险")
public Map<String, Object> detectRisks(
@P("项目ID") String projectId,
@P("分析深度") String analysisDepth) {
try {
List<Risk> existingRisks = riskRepository.findByProjectId(projectId);
// 检测新风险
List<Map<String, Object>> newRisks = detectNewRisks(projectId, analysisDepth);
// 评估风险等级
Map<String, Object> riskAssessment = assessRisks(existingRisks, newRisks);
return Map.of(
"projectId", projectId,
"existingRiskCount", existingRisks.size(),
"newRiskCount", newRisks.size(),
"newRisks", newRisks,
"riskAssessment", riskAssessment,
"overallRiskLevel", calculateOverallRiskLevel(riskAssessment),
"detectionTime", LocalDateTime.now()
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("风险检测失败", e);
return Map.of("error", "检测失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Tool(name = "mitigation_planning_tool", description = "制定风险缓解计划")
public Map<String, Object> planMitigations(
@P("项目ID") String projectId,
@P("风险列表") Map<String, Object> risks) {
try {
List<Map<String, Object>> newRisks = (List<Map<String, Object>>)
risks.get("newRisks");
List<MitigationPlan> mitigationPlans = new ArrayList<>();
for (Map<String, Object> risk : newRisks) {
String riskId = (String) risk.get("id");
String description = (String) risk.get("description");
String severity = (String) risk.get("severity");
MitigationPlan plan = createMitigationPlan(projectId, riskId,
description, severity);
mitigationPlans.add(plan);
riskRepository.saveMitigationPlan(plan);
}
return Map.of(
"projectId", projectId,
"plansCreated", true,
"mitigationPlans", mitigationPlans.stream()
.map(p -> Map.of(
"id", p.getId(),
"riskId", p.getRiskId(),
"actions", p.getActions(),
"owner", p.getOwner(),
"deadline", p.getDeadline()
))
.collect(Collectors.toList()),
"risksMitigated", mitigationPlans.size(),
"planningTime", LocalDateTime.now()
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("制定缓解计划失败", e);
return Map.of("error", "计划制定失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Tool(name = "notification_tool", description = "发送项目通知")
public Map<String, Object> sendProjectNotification(
@P("收件人") List<String> recipients,
@P("主题") String subject,
@P("消息内容") String message,
@P("优先级") String priority) {
try {
// 简化实现:记录日志代替实际发送
log.info("发送项目通知: subject={}, recipients={}, priority={}",
subject, recipients, priority);
log.info("消息内容: {}", message);
// 模拟发送延迟
Thread.sleep(1000);
return Map.of(
"notified", true,
"recipientCount", recipients.size(),
"subject", subject,
"sentTime", LocalDateTime.now()
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("发送通知失败", e);
return Map.of("error", "发送失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Tool(name = "schedule_adjustment_tool", description = "调整项目计划")
public Map<String, Object> adjustSchedule(
@P("项目ID") String projectId,
@P("当前计划") Map<String, Object> currentSchedule,
@P("调整原因") String adjustmentReason) {
try {
// 获取项目
Optional<Project> projectOpt = projectRepository.findById(projectId);
if (projectOpt.isEmpty()) {
return Map.of("error", "项目不存在");
}
Project project = projectOpt.get();
// 创建计划调整记录
ScheduleAdjustment adjustment = ScheduleAdjustment.builder()
.id(UUID.randomUUID().toString())
.projectId(projectId)
.reason(adjustmentReason)
.originalEndDate(project.getEndDate())
.proposedEndDate(calculateNewEndDate(project))
.status("PROPOSED")
.createdAt(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
scheduleAdjustmentRepository.save(adjustment);
log.info("项目计划调整建议已创建: {}", adjustment.getId());
return Map.of(
"adjusted", true,
"adjustmentId", adjustment.getId(),
"originalEndDate", adjustment.getOriginalEndDate(),
"proposedEndDate", adjustment.getProposedEndDate(),
"reason", adjustmentReason,
"adjustmentTime", LocalDateTime.now()
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("调整计划失败", e);
return Map.of("error", "调整失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private List<Map<String, Object>> detectNewRisks(String projectId, String analysisDepth) {
List<Map<String, Object>> newRisks = new ArrayList<>();
// 模拟风险检测逻辑
newRisks.add(Map.of(
"id", "RISK-" + UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8),
"description", "关键路径任务延迟风险",
"severity", "HIGH",
"probability", 0.7,
"impact", "项目延期",
"detectionMethod", "SCHEDULE_ANALYSIS"
));
newRisks.add(Map.of(
"id", "RISK-" + UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8),
"description", "预算超支风险",
"severity", "MEDIUM",
"probability", 0.5,
"impact", "成本增加",
"detectionMethod", "BUDGET_ANALYSIS"
));
if ("DEEP".equals(analysisDepth)) {
newRisks.add(Map.of(
"id", "RISK-" + UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8),
"description", "关键资源依赖风险",
"severity", "MEDIUM",
"probability", 0.4,
"impact", "进度阻塞",
"detectionMethod", "RESOURCE_ANALYSIS"
));
}
return newRisks;
}
private Map<String, Object> assessRisks(List<Risk> existingRisks,
List<Map<String, Object>> newRisks) {
Map<String, Object> assessment = new HashMap<>();
long highRisks = newRisks.stream()
.filter(r -> "HIGH".equals(r.get("severity")))
.count();
long mediumRisks = newRisks.stream()
.filter(r -> "MEDIUM".equals(r.get("severity")))
.count();
long lowRisks = newRisks.stream()
.filter(r -> "LOW".equals(r.get("severity")))
.count();
assessment.put("highRiskCount", highRisks);
assessment.put("mediumRiskCount", mediumRisks);
assessment.put("lowRiskCount", lowRisks);
assessment.put("requiresImmediateAction", highRisks > 0);
assessment.put("recommendedPriority", highRisks > 0 ? "HIGH" : "MEDIUM");
return assessment;
}
private MitigationPlan createMitigationPlan(String projectId, String riskId,
String description, String severity) {
List<String> actions = new ArrayList<>();
if ("HIGH".equals(severity)) {
actions.add("立即通知项目负责人");
actions.add("制定应急计划");
actions.add("分配专门资源");
} else if ("MEDIUM".equals(severity)) {
actions.add("周会讨论");
actions.add("分配解决责任人");
actions.add("监控风险指标");
} else {
actions.add("记录风险登记册");
actions.add("定期检查");
}
return MitigationPlan.builder()
.id(UUID.randomUUID().toString())
.projectId(projectId)
.riskId(riskId)
.actions(actions)
.owner("project_manager")
.deadline(LocalDateTime.now().plusDays(7))
.createdAt(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
}
private LocalDateTime calculateNewEndDate(Project project) {
// 简单逻辑:延后2周
return project.getEndDate().plusWeeks(2);
}
private List<Task> calculateCriticalPath(List<Task> tasks) {
// 简化实现:返回持续时间最长的任务链
return tasks.stream()
.filter(task -> task.getDurationDays() != null && task.getDurationDays() > 5)
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Task::getDurationDays).reversed())
.limit(5)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private Map<String, Object> calculateBudgetStatus(Project project) {
BigDecimal budget = project.getBudget();
BigDecimal actualCost = project.getActualCost();
BigDecimal remaining = budget.subtract(actualCost);
double usageRate = budget.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) > 0 ?
actualCost.divide(budget, 2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP).doubleValue() * 100 : 0;
return Map.of(
"budget", budget,
"actualCost", actualCost,
"remaining", remaining,
"usageRate", usageRate,
"status", usageRate > 90 ? "OVER_BUDGET" : usageRate > 70 ? "WARNING" : "OK"
);
}
}四、多 Agent 协作示例
java
// MultiAgentOrchestrator.java
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MultiAgentOrchestrator {
@Autowired
private CustomerSupportAgent customerSupportAgent;
@Autowired
private ProjectManagementAgent projectManagementAgent;
@Autowired
private ChatLanguageModel llm;
private final Map<String, List<AgentGoal>> agentGoals = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Map<String, List<AgentResponse>> agentResponses = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 处理复杂跨领域请求
*/
public ComplexResponse handleComplexRequest(ComplexRequest request) {
log.info("处理复杂请求: {}", request.getDescription());
String requestId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
agentGoals.put(requestId, new ArrayList<>());
agentResponses.put(requestId, new ArrayList<>());
try {
// 步骤1: 分解请求到多个Agent目标
List<AgentGoal> decomposedGoals = decomposeRequest(request);
agentGoals.put(requestId, decomposedGoals);
// 步骤2: 并行执行Agent目标
List<CompletableFuture<AgentResponse>> futures = decomposedGoals.stream()
.map(goal -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
executeGoalWithAgent(goal, requestId)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 步骤3: 等待所有结果
CompletableFuture<Void> allFutures = CompletableFuture.allOf(
futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0]));
allFutures.join();
// 步骤4: 收集结果
List<AgentResponse> responses = futures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
agentResponses.put(requestId, responses);
// 步骤5: 综合结果
ComplexResponse finalResponse = synthesizeResponses(responses, request);
log.info("复杂请求处理完成: {}", requestId);
return finalResponse;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("处理复杂请求失败", e);
return ComplexResponse.error("处理失败: " + e.getMessage(), requestId);
}
}
/**
* 使用LLM分解复杂请求
*/
private List<AgentGoal> decomposeRequest(ComplexRequest request) {
String decompositionPrompt = String.format("""
请将以下复杂请求分解为多个可独立执行的Agent目标:
请求描述:%s
请求类型:%s
优先级:%s
截止时间:%s
可用Agent类型:
1. 客户支持Agent:处理客户咨询、账单问题、技术支持
2. 项目管理Agent:监控项目进度、风险检测、资源协调
3. 数据分析Agent:数据提取、分析报告、趋势预测
请为每个子目标指定:
1. 目标描述
2. 负责Agent类型
3. 优先级
4. 预期输出
5. 依赖关系
返回JSON格式:
{
"goals": [
{
"description": "目标描述",
"agentType": "Agent类型",
"priority": "HIGH/MEDIUM/LOW",
"expectedOutput": "预期输出",
"dependencies": ["依赖目标索引"],
"parameters": {
// 目标参数
}
}
]
}
""",
request.getDescription(),
request.getType(),
request.getPriority(),
request.getDeadline()
);
String decompositionJson = llm.generate(decompositionPrompt);
try {
return parseDecomposition(decompositionJson, request);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("分解请求失败,使用默认分解", e);
return createDefaultDecomposition(request);
}
}
/**
* 执行单个Agent目标
*/
private AgentResponse executeGoalWithAgent(AgentGoal goal, String requestId) {
String agentType = (String) goal.getParameters().get("agentType");
try {
AgentResponse response;
switch (agentType) {
case "CUSTOMER_SUPPORT":
response = executeCustomerSupportGoal(goal);
break;
case "PROJECT_MANAGEMENT":
response = executeProjectManagementGoal(goal);
break;
default:
response = AgentResponse.error("不支持的Agent类型: " + agentType);
}
// 记录结果
log.info("Agent目标执行完成: {} -> {}", goal.getDescription(),
response.getStatus());
return response;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("执行Agent目标失败", e);
return AgentResponse.error("执行失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 综合多个Agent的结果
*/
private ComplexResponse synthesizeResponses(List<AgentResponse> responses,
ComplexRequest request) {
// 分析所有结果
long successCount = responses.stream()
.filter(r -> r.getStatus() == AgentResponse.Status.SUCCESS)
.count();
long partialCount = responses.stream()
.filter(r -> r.getStatus() == AgentResponse.Status.PARTIAL)
.count();
long failedCount = responses.stream()
.filter(r -> r.getStatus() == AgentResponse.Status.FAILED)
.count();
// 构建综合报告
StringBuilder summary = new StringBuilder();
summary.append(String.format("""
复杂请求处理完成
总目标数: %d
成功: %d
部分成功: %d
失败: %d
成功率: %.1f%%
详细结果:
""",
responses.size(),
successCount,
partialCount,
failedCount,
(double) (successCount + partialCount * 0.5) / responses.size() * 100
));
for (int i = 0; i < responses.size(); i++) {
AgentResponse response = responses.get(i);
summary.append(String.format("%d. %s: %s\n",
i + 1,
response.getMessage(),
response.getStatus()
));
}
// 生成建议
String recommendations = generateRecommendations(responses);
return ComplexResponse.builder()
.requestId(request.getRequestId())
.status(calculateOverallStatus(successCount, partialCount, failedCount))
.summary(summary.toString())
.recommendations(recommendations)
.timestamp(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
}
private AgentResponse executeCustomerSupportGoal(AgentGoal goal) {
Map<String, Object> params = goal.getParameters();
String customerId = (String) params.get("customerId");
String inquiry = (String) params.get("inquiry");
return customerSupportAgent.handleBillingInquiry(customerId, inquiry);
}
private AgentResponse executeProjectManagementGoal(AgentGoal goal) {
Map<String, Object> params = goal.getParameters();
String projectId = (String) params.get("projectId");
if (goal.getDescription().contains("里程碑")) {
String milestoneId = (String) params.get("milestoneId");
LocalDateTime targetDate = (LocalDateTime) params.get("targetDate");
return projectManagementAgent.monitorMilestone(projectId, milestoneId, targetDate);
} else if (goal.getDescription().contains("风险")) {
return projectManagementAgent.detectAndMitigateRisks(projectId);
}
return AgentResponse.error("未知的项目管理目标类型");
}
private String generateRecommendations(List<AgentResponse> responses) {
// 基于结果生成建议
if (responses.stream().anyMatch(r -> r.getStatus() == AgentResponse.Status.FAILED)) {
return """
建议:
1. 重新评估失败的目标,可能需要调整策略
2. 考虑人工干预处理复杂情况
3. 更新Agent的知识库以改进未来表现
""";
}
if (responses.stream().anyMatch(r -> r.getStatus() == AgentResponse.Status.PARTIAL)) {
return """
建议:
1. 对部分成功的目标进行跟踪
2. 安排后续跟进以确保完全解决
3. 分析部分成功原因以优化流程
""";
}
return """
建议:
1. 所有目标已成功完成,无需进一步操作
2. 可以考虑自动化类似流程
3. 记录成功经验供未来参考
""";
}
private ComplexResponse.Status calculateOverallStatus(long success, long partial, long failed) {
if (failed > 0) return ComplexResponse.Status.FAILED;
if (partial > 0) return ComplexResponse.Status.PARTIAL;
return ComplexResponse.Status.SUCCESS;
}
}五、监控与执行引擎
java
// ExecutionMonitor.java
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ExecutionMonitor {
@Autowired
private PlanningStrategy planningStrategy;
@Autowired
private MetricsCollector metricsCollector;
private final Map<String, ExecutionTracker> activeExecutions = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 监控执行过程
*/
public void monitorExecution(String executionId, ExecutionPlan plan,
Map<String, StepResult> stepResults) {
ExecutionTracker tracker = activeExecutions.computeIfAbsent(executionId,
id -> new ExecutionTracker(id, plan));
tracker.update(stepResults);
// 检测异常
List<String> anomalies = detectAnomalies(tracker);
if (!anomalies.isEmpty()) {
log.warn("检测到执行异常: {}", anomalies);
handleAnomalies(executionId, tracker, anomalies);
}
// 收集指标
metricsCollector.recordExecutionMetrics(tracker);
}
/**
* 检测异常
*/
public List<String> detectAnomalies(ExecutionPlan plan,
Map<String, StepResult> stepResults) {
List<String> anomalies = new ArrayList<>();
// 1. 检测执行时间异常
long totalEstimated = plan.getSteps().stream()
.mapToInt(PlanStep::getEstimatedDuration)
.sum();
long actualMinutes = Duration.between(plan.getStartedAt(), LocalDateTime.now())
.toMinutes();
if (actualMinutes > totalEstimated * 2) {
anomalies.add("执行时间严重超预期");
}
// 2. 检测步骤失败率
long failedSteps = stepResults.values().stream()
.filter(r -> r.getStatus() == StepStatus.FAILED)
.count();
double failureRate = (double) failedSteps / stepResults.size();
if (failureRate > 0.3) {
anomalies.add("步骤失败率过高: " + String.format("%.1f%%", failureRate * 100));
}
// 3. 检测资源使用异常
if (isResourceUsageExcessive(plan, stepResults)) {
anomalies.add("资源使用异常");
}
return anomalies;
}
/**
* 处理异常
*/
private void handleAnomalies(String executionId, ExecutionTracker tracker,
List<String> anomalies) {
// 记录异常
tracker.addAnomalies(anomalies);
// 根据异常严重程度采取行动
if (anomalies.contains("执行时间严重超预期")) {
log.warn("执行超时,考虑终止或调整计划");
// 可以触发重新规划
}
if (anomalies.contains("步骤失败率过高")) {
log.warn("失败率过高,可能需要人工干预");
// 可以发送警报
}
}
private boolean isResourceUsageExcessive(ExecutionPlan plan,
Map<String, StepResult> stepResults) {
// 简化实现:检查内存使用
long freeMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory();
long totalMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory();
double memoryUsage = (double) (totalMemory - freeMemory) / totalMemory;
return memoryUsage > 0.9;
}
/**
* 生成执行报告
*/
public ExecutionReport generateReport(String executionId) {
ExecutionTracker tracker = activeExecutions.get(executionId);
if (tracker == null) {
return ExecutionReport.notFound(executionId);
}
return ExecutionReport.builder()
.executionId(executionId)
.planId(tracker.getPlan().getId())
.goalId(tracker.getPlan().getGoal().getId())
.status(tracker.getStatus())
.startTime(tracker.getStartTime())
.endTime(tracker.getEndTime())
.totalSteps(tracker.getTotalSteps())
.completedSteps(tracker.getCompletedSteps())
.failedSteps(tracker.getFailedSteps())
.successRate(tracker.getSuccessRate())
.anomalies(tracker.getAnomalies())
.performanceMetrics(tracker.getPerformanceMetrics())
.recommendations(generateRecommendations(tracker))
.build();
}
}
// ExecutionTracker.java
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
class ExecutionTracker {
private String executionId;
private ExecutionPlan plan;
private ExecutionStatus status;
private LocalDateTime startTime;
private LocalDateTime endTime;
private Map<String, StepResult> stepResults;
private List<String> anomalies;
private Map<String, Object> performanceMetrics;
@Builder.Default
private int totalSteps = 0;
@Builder.Default
private int completedSteps = 0;
@Builder.Default
private int failedSteps = 0;
public ExecutionTracker(String executionId, ExecutionPlan plan) {
this.executionId = executionId;
this.plan = plan;
this.status = ExecutionStatus.RUNNING;
this.startTime = LocalDateTime.now();
this.stepResults = new LinkedHashMap<>();
this.anomalies = new ArrayList<>();
this.performanceMetrics = new HashMap<>();
this.totalSteps = plan.getSteps().size();
}
public void update(Map<String, StepResult> newResults) {
this.stepResults.putAll(newResults);
// 更新统计
this.completedSteps = (int) stepResults.values().stream()
.filter(r -> r.getStatus() == StepStatus.SUCCESS ||
r.getStatus() == StepStatus.FAILED)
.count();
this.failedSteps = (int) stepResults.values().stream()
.filter(r -> r.getStatus() == StepStatus.FAILED)
.count();
// 更新状态
if (completedSteps == totalSteps) {
this.status = failedSteps == 0 ? ExecutionStatus.SUCCESS : ExecutionStatus.PARTIAL;
this.endTime = LocalDateTime.now();
}
// 更新性能指标
updatePerformanceMetrics();
}
public void addAnomalies(List<String> newAnomalies) {
this.anomalies.addAll(newAnomalies);
}
public double getSuccessRate() {
if (completedSteps == 0) return 0;
return (double) (completedSteps - failedSteps) / completedSteps;
}
private void updatePerformanceMetrics() {
long executionTime = Duration.between(startTime, LocalDateTime.now()).toSeconds();
performanceMetrics.put("executionTimeSeconds", executionTime);
performanceMetrics.put("stepsPerSecond",
completedSteps > 0 ? (double) completedSteps / executionTime : 0);
performanceMetrics.put("successRate", getSuccessRate());
performanceMetrics.put("timestamp", LocalDateTime.now());
}
}六、测试和演示
java
// AgentDemoApplication.java
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class AgentDemoApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private CustomerSupportAgent customerSupportAgent;
@Autowired
private ProjectManagementAgent projectManagementAgent;
@Autowired
private MultiAgentOrchestrator multiAgentOrchestrator;
@Autowired
private ExecutionMonitor executionMonitor;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AgentDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) {
log.info("🚀 AI Agent 规划能力演示开始");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("\n请选择演示场景:");
System.out.println("1. 客户支持自动化 - 处理账单查询");
System.out.println("2. 项目管理助手 - 监控里程碑");
System.out.println("3. 项目管理助手 - 风险检测");
System.out.println("4. 多Agent协作 - 复杂请求处理");
System.out.println("5. 查看执行报告");
System.out.println("0. 退出");
System.out.print("请输入选择: ");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine(); // 消耗换行符
switch (choice) {
case 1:
demoCustomerSupport(scanner);
break;
case 2:
demoProjectManagement(scanner);
break;
case 3:
demoRiskManagement(scanner);
break;
case 4:
demoMultiAgentCollaboration(scanner);
break;
case 5:
viewExecutionReports(scanner);
break;
case 0:
log.info("演示结束");
return;
default:
System.out.println("无效选择");
}
}
}
private void demoCustomerSupport(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.println("\n=== 客户支持自动化演示 ===");
System.out.print("请输入客户ID: ");
String customerId = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入查询内容: ");
String inquiry = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("\n🤖 客户支持Agent开始工作...");
AgentResponse response = customerSupportAgent.handleBillingInquiry(customerId, inquiry);
System.out.println("\n📋 处理结果:");
System.out.println("状态: " + response.getStatus());
System.out.println("消息: " + response.getMessage());
if (response.getData() != null) {
System.out.println("数据: " + response.getData());
}
}
private void demoProjectManagement(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.println("\n=== 项目管理助手演示 ===");
System.out.print("请输入项目ID: ");
String projectId = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入里程碑ID: ");
String milestoneId = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入目标日期 (yyyy-MM-dd): ");
String dateStr = scanner.nextLine();
LocalDateTime targetDate = LocalDate.parse(dateStr).atStartOfDay();
System.out.println("\n📊 项目管理Agent开始监控...");
AgentResponse response = projectManagementAgent.monitorMilestone(
projectId, milestoneId, targetDate);
System.out.println("\n📋 监控结果:");
System.out.println("状态: " + response.getStatus());
System.out.println("消息: " + response.getMessage());
}
private void demoRiskManagement(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.println("\n=== 项目风险管理演示 ===");
System.out.print("请输入项目ID: ");
String projectId = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("\n⚠️ 项目管理Agent开始风险检测...");
AgentResponse response = projectManagementAgent.detectAndMitigateRisks(projectId);
System.out.println("\n📋 风险管理结果:");
System.out.println("状态: " + response.getStatus());
System.out.println("消息: " + response.getMessage());
}
private void demoMultiAgentCollaboration(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.println("\n=== 多Agent协作演示 ===");
System.out.print("请输入复杂请求描述: ");
String description = scanner.nextLine();
ComplexRequest request = ComplexRequest.builder()
.requestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString())
.description(description)
.type("MULTI_DOMAIN")
.priority("HIGH")
.deadline(LocalDateTime.now().plusDays(1))
.build();
System.out.println("\n🤝 多Agent协作开始...");
ComplexResponse response = multiAgentOrchestrator.handleComplexRequest(request);
System.out.println("\n📋 协作处理结果:");
System.out.println("请求ID: " + response.getRequestId());
System.out.println("状态: " + response.getStatus());
System.out.println("\n摘要:");
System.out.println(response.getSummary());
System.out.println("\n建议:");
System.out.println(response.getRecommendations());
}
private void viewExecutionReports(Scanner scanner) {
System.out.println("\n=== 执行报告查看 ===");
// 实现报告查看逻辑
System.out.println("执行报告功能开发中...");
}
}七、总结
这个DEMO展示了AI Agent规划能力的完整实现,包括:
核心特性:
-
智能规划:基于LLM生成和调整执行计划
-
多Agent协作:协调不同领域的Agent共同完成任务
-
执行监控:实时监控执行过程,检测和处理异常
-
自适应调整:根据执行结果动态调整策略
实现的应用场景:
-
客户支持自动化:处理账单查询,自动解决问题
-
项目管理助手:监控里程碑,检测和缓解风险
-
复杂任务分解:将复杂请求分解为多个Agent目标
-
多Agent协作:协调多个Agent完成跨领域任务
技术亮点:
-
模块化设计:每个组件职责清晰,易于扩展
-
类型安全:使用Java强类型系统确保代码可靠性
-
异步处理:支持并行执行提高效率
-
错误恢复:完善的异常处理和重试机制
-
监控和报告:完整的执行跟踪和报告生成
这个框架可以作为构建企业级AI Agent系统的基础,可以根据具体业务需求进行扩展和定制。
结论
本文重点介绍了目标设定和监控的关键范式。我们强调了这个概念如何将 AI Agent 从仅仅是反应系统转变为主动的、以目标为驱动的实体。文本强调了定义清晰、可衡量的目标以及建立严格的监控程序来跟踪进度的重要性。实际应用展示了这个范式如何支持在各个领域(包括客户服务和机器人)的可靠自主运行。编码示例说明了这些原则在结构化框架内的实现,使用 Agent 指令和状态管理来指导和评估 Agent 对其指定目标的实现。最终,为Agent 配备制定和监督目标的能力是构建真正智能和负责任的 AI 系统的基本步骤。
参考文献
- SMARTGoalsFramework.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SMART_criteria