引言
在前后端分离、微服务架构中,接口交互需统一数据格式(主流为 JSON)。通过序列化将 Java 对象转为 JSON 字符串,才能通过 HTTP/HTTPs 等协议跨服务、跨终端传输,确保前端能正确解析数据。
在 SpringBoot 中,默认内置了 Jackson 框架,处理 Java 对象序列化为 JSON 字符串。在spring-boot-starter-web模块中,默认引入jackson-databind、jackson-core、jackson-annotations三个核心依赖,无需手动添加。在 spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar 包中,有一个 JacksonAutoConfiguration,该类会自动向容器中注入ObjectMapper实例和MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(HTTP消息转换器,负责接口响应的JSON序列化),从而实现"零配置"的JSON处理能力。
Jackson 序列化实现原理
服务端响应客户端的请求时,返回给客户端的数据通过序列化,将 Java 对象转换为 JSON 字符串。
2.1 创建一个 JsonSerializer 对象
在返回数据之前,先获取对应 Java 对象处理的 Serializer 对象。如果是 Bean 对象,则创建 BeanSerializer 对象。
1)通过反射,解析 Java 对象,获取对象中的属性/方法
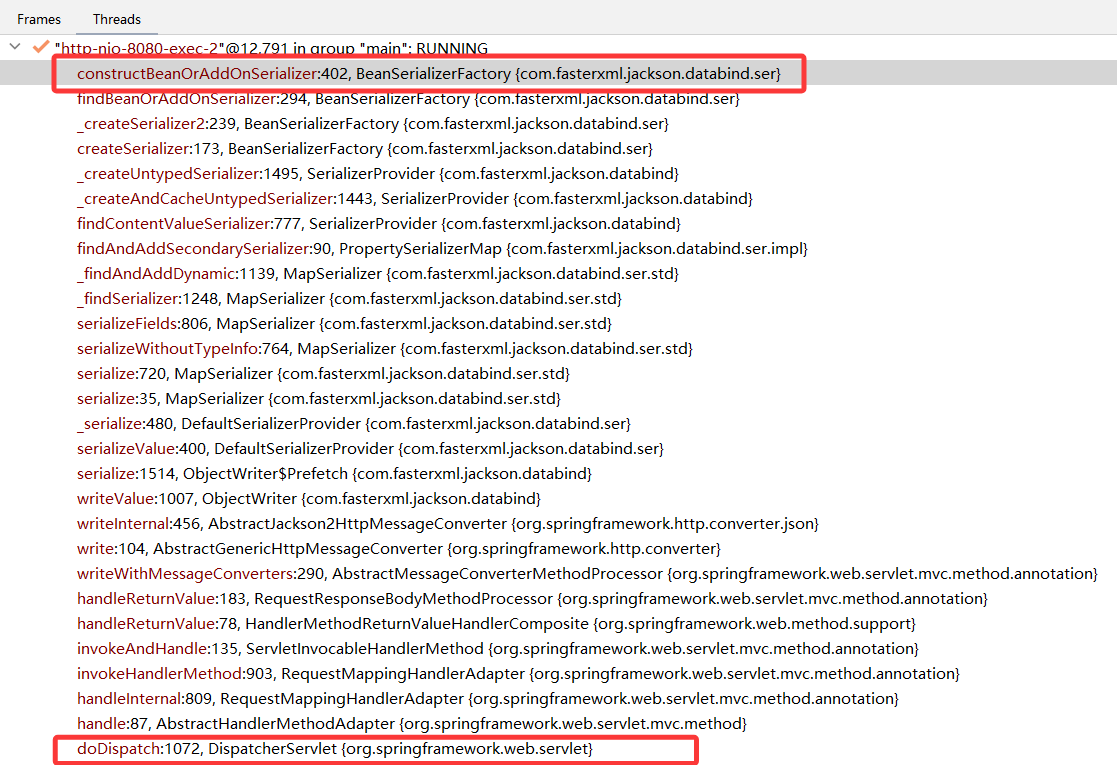
在 BeanSerializerFactory.constructBeanOrAddOnSerializer() 方法中,通过 findBeanProperties() 方法,使用反射获取 Java 对象的属性,每个属性封装成一个 BeanPropertyWriter 对象。
示例:
java
public class Member {
@JsonFormat(shape = JsonFormat.Shape.STRING)
private Long id;
}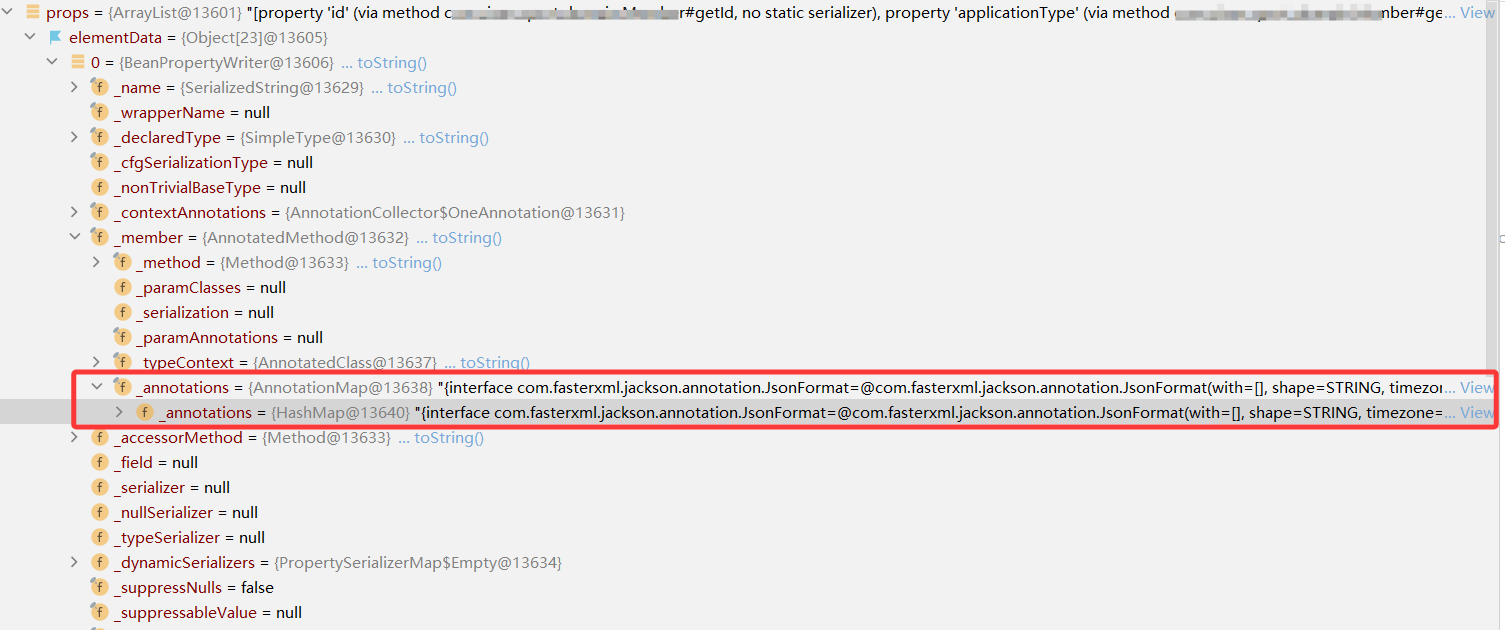
Java 对象解析后的每个属性对应的 BeanPropertyWriter 对象中的 _annotations 会记录该属性添加的注解。
2)创建 BeanSerializer 对象
如果是 Bean 对象,在执行 BeanSerializerFactory.constructBeanOrAddOnSerializer()方法中,通过BeanSerializerBuilder.build(),创建一个 BeanSerializer 对象。
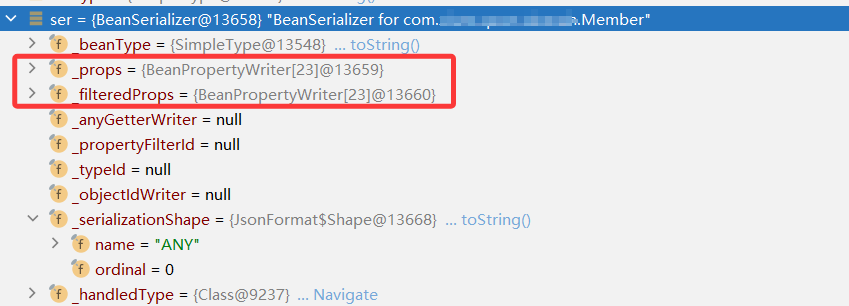
3)加入 SerializerCache 缓存
创建 BeanSerializer 对象之后,会将该序列化对象保存到 SerializerCache 缓存中。在加入缓存前,会再次遍历所有的属性,即 BeanPropertyWriter 对象,查找满足对应类型的序列化对象。
4)@JsonFormat 实现原理
不同类型的属性在 BeanPropertyWriter 对象中,关联一个对应的 _serializer ,如果是数字的属性,如 Integer、Long 等,为 NumberSerializers。执行 serializer 的 createContextual() 方法。
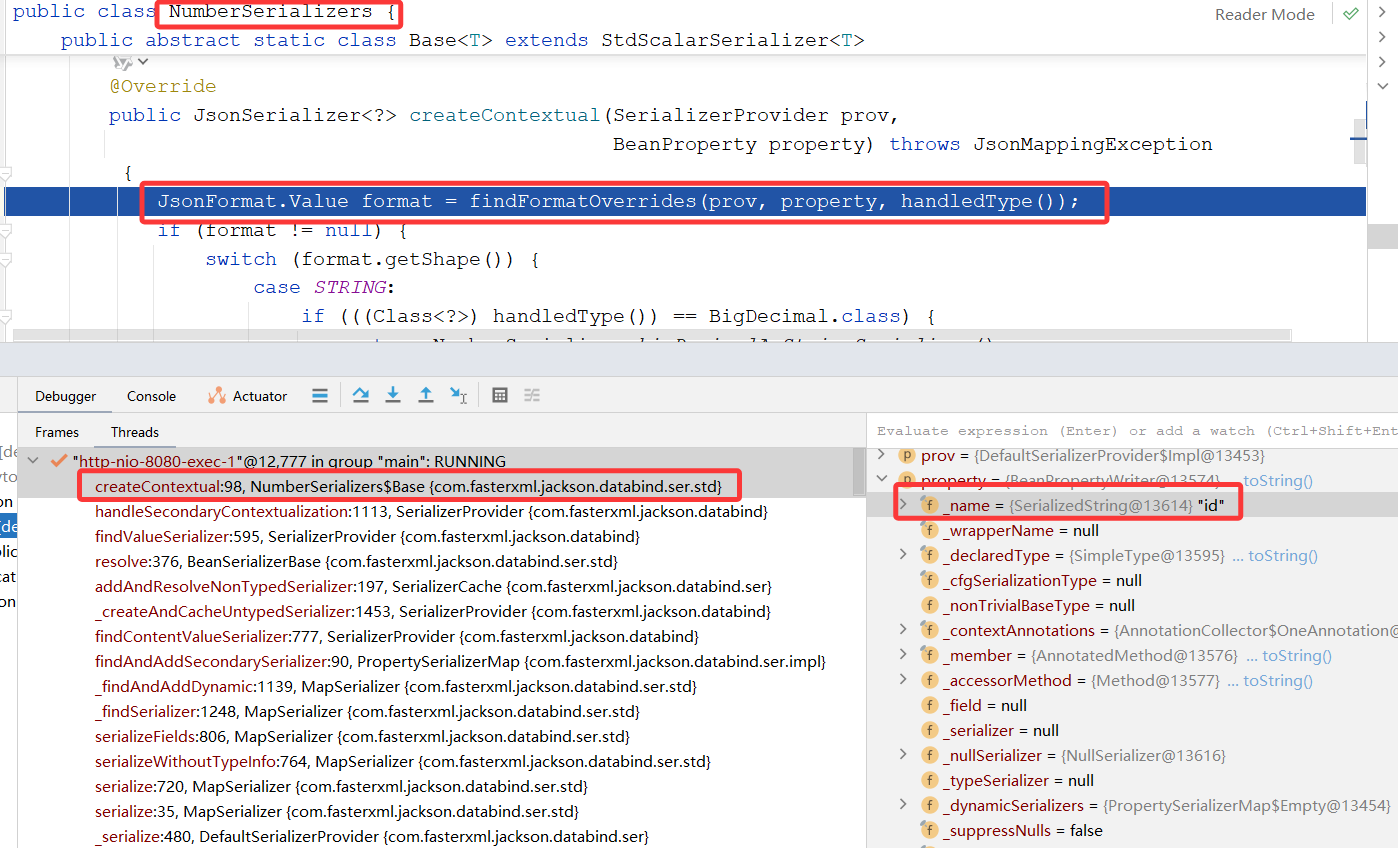
如 NumberSerializers 的 createContextual() 方法,源码如下:
java
@Override
public JsonSerializer<?> createContextual(SerializerProvider prov,
BeanProperty property) throws JsonMappingException
{
JsonFormat.Value format = findFormatOverrides(prov, property, handledType());
if (format != null) {
switch (format.getShape()) {
case STRING:
if (((Class<?>) handledType()) == BigDecimal.class) {
return NumberSerializer.bigDecimalAsStringSerializer();
}
return ToStringSerializer.instance;
default:
}
}
return this;
}如果属性添加了 @JsonFormat 注解,且 shape 为 STRING,则返回 ToStringSerializer 序列化对象。否则返回 NumberSerializer。
返回的 serializer 对象会保存到对应属性的 BeanPropertyWriter._serializer 对象中。
5)@JsonSerialize 实现原理
在创建某个数据的序列化对象时,会调用 JacksonAnnotationIntrospector.findSerializationConverter() 方法,判断对应属性或类是否添加了 @JsonSerialize 注解。
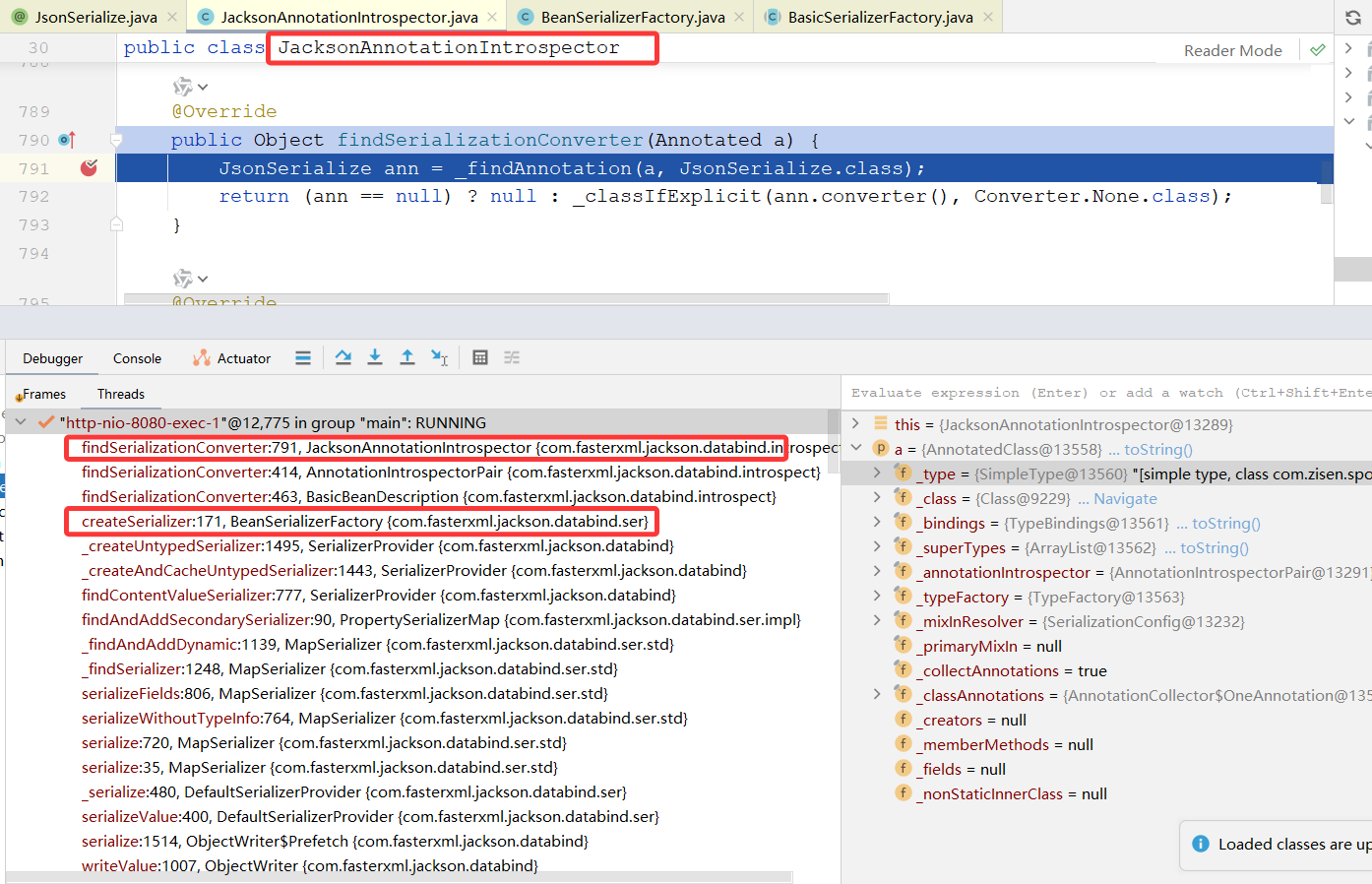
2.2 序列化
执行 JsonSerializer.serialize() 进行序列化。
1)Bean 对象序列化
Bean 对象的序列化对象为 BeanSerializer,核心代码如下:
java
public class BeanSerializer extends BeanSerializerBase{
/**
* @param bean 要序列化的 Java 对象
* @param gen 默认为 UTF8JsonGenerator
* @param provider 序列化上下文,提供查找 serializer、处理配置等能力
**/
@Override
public final void serialize(Object bean, JsonGenerator gen, SerializerProvider provider)
throws IOException
{
if (_objectIdWriter != null) {
gen.setCurrentValue(bean); // [databind#631]
_serializeWithObjectId(bean, gen, provider, true);
return;
}
// 输出 {
gen.writeStartObject(bean);
// 过滤情况,如果类上有 @JsonFilter("myFilter"),则 _propertyFilterId = "myFilter"
if (_propertyFilterId != null) {
serializeFieldsFiltered(bean, gen, provider);
} else {
// 序列化 bean 对象的属性信息
serializeFields(bean, gen, provider);
}
// 输出 }
gen.writeEndObject();
}
// 父类 BeanSerializerBase 中的方法
protected void serializeFields(Object bean, JsonGenerator gen, SerializerProvider provider)
throws IOException
{
final BeanPropertyWriter[] props;
if (_filteredProps != null && provider.getActiveView() != null) {
props = _filteredProps;
} else {
props = _props;
}
int i = 0;
try {
// 遍历每个属性,将数据序列化到 输出流
for (final int len = props.length; i < len; ++i) {
BeanPropertyWriter prop = props[i];
if (prop != null) { // can have nulls in filtered list
prop.serializeAsField(bean, gen, provider);
}
}
if (_anyGetterWriter != null) {
_anyGetterWriter.getAndSerialize(bean, gen, provider);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
String name = (i == props.length) ? "[anySetter]" : props[i].getName();
wrapAndThrow(provider, e, bean, name);
} catch (StackOverflowError e) {
// 04-Sep-2009, tatu: Dealing with this is tricky, since we don't have many
// stack frames to spare... just one or two; can't make many calls.
// 10-Dec-2015, tatu: and due to above, avoid "from" method, call ctor directly:
//JsonMappingException mapE = JsonMappingException.from(gen, "Infinite recursion (StackOverflowError)", e);
DatabindException mapE = new JsonMappingException(gen, "Infinite recursion (StackOverflowError)", e);
String name = (i == props.length) ? "[anySetter]" : props[i].getName();
mapE.prependPath(bean, name);
throw mapE;
}
}
} 在 serializeFields() 方法中,遍历 Bean 中的 BeanPropertyWriter 对象,即属性信息,执行 prop.serializeAsField() 方法,通过反射获取对象的值,使用序列化对象,将值写入到输出流中。
java
public void serializeAsField(Object bean, JsonGenerator gen,
SerializerProvider prov) throws Exception {
// inlined 'get()'
// 获取对象的属性值
final Object value = (_accessorMethod == null) ? _field.get(bean)
: _accessorMethod.invoke(bean, (Object[]) null);
// Null handling is bit different, check that first
if (value == null) {
if (_nullSerializer != null) {
gen.writeFieldName(_name);
_nullSerializer.serialize(null, gen, prov);
}
return;
}
// then find serializer to use
// 获取属性的序列化对象
JsonSerializer<Object> ser = _serializer;
if (ser == null) {
Class<?> cls = value.getClass();
PropertySerializerMap m = _dynamicSerializers;
ser = m.serializerFor(cls);
if (ser == null) {
ser = _findAndAddDynamic(m, cls, prov);
}
}
// and then see if we must suppress certain values (default, empty)
if (_suppressableValue != null) {
if (MARKER_FOR_EMPTY == _suppressableValue) {
if (ser.isEmpty(prov, value)) {
return;
}
} else if (_suppressableValue.equals(value)) {
return;
}
}
// For non-nulls: simple check for direct cycles
if (value == bean) {
// four choices: exception; handled by call; pass-through or write null
if (_handleSelfReference(bean, gen, prov, ser)) {
return;
}
}
// 写入属性的名称
gen.writeFieldName(_name);
if (_typeSerializer == null) {
// 执行序列化
ser.serialize(value, gen, prov);
} else {
ser.serializeWithType(value, gen, prov, _typeSerializer);
}
}2)String 序列化
String对象的序列化对象为 ToStringSerializer,其 serialize() 方法在父类 ToStringSerializerBase 中,核心代码如下:
java
public abstract class ToStringSerializerBase extends StdSerializer<Object> {
/**
* @param value 属性的值
* @param gen 默认为 UTF8JsonGenerator
* @param provider 序列化上下文,提供查找 serializer、处理配置等能力
**/
@Override
public void serialize(Object value, JsonGenerator gen, SerializerProvider provider)
throws IOException
{
// 获取 value 的字符串值,使用 gen 写入到输出流
gen.writeString(valueToString(value));
}
} 其中,valueToString() 在子类 ToStringSerializer 中实现。返回 value.toString() 字符串信息。
3)数据写入输出流 UTF8JsonGenerator
默认使用 UTF8JsonGenerator 将响应信息写入到输出流中。如 writeString() 方法源码如下:
java
public class UTF8JsonGenerator extends JsonGeneratorImpl {
/**
* @param text 输出的文本信息
**/
public void writeString(String text) throws IOException {
// 验证当前是否可以写入值
this._verifyValueWrite("write a string");
// 写入 null
if (text == null) {
this._writeNull();
} else {
int len = text.length();
// 如果长度太长,需要分断处理
if (len > this._outputMaxContiguous) {
this._writeStringSegments(text, true);
} else {
// 检查缓冲区剩余空间是否足够容纳整个字符串 + 两个引号
if (this._outputTail + len >= this._outputEnd) {
// 缓冲区满,先刷出到 OutputStream
this._flushBuffer();
}
// 写入开头的双引号(_quoteChar 通常是 '"')
this._outputBuffer[this._outputTail++] = this._quoteChar;
// 将字符串内容写入缓冲区
this._writeStringSegment((String)text, 0, len);
// 如果写完后缓冲区满了,再刷一次
if (this._outputTail >= this._outputEnd) {
this._flushBuffer();
}
// 写入结尾的双引号
this._outputBuffer[this._outputTail++] = this._quoteChar;
}
}
}
public void writeNumber(BigDecimal value) throws IOException {
this._verifyValueWrite("write a number");
if (value == null) {
this._writeNull();
} else if (this._cfgNumbersAsStrings) {
// 如果启用了全局配置 WRITE_NUMBERS_AS_STRINGS
// 则将 BigDecimal 转为字符串,并用双引号包裹后写入(即输出为 JSON 字符串)
// _asString(),调用 value.toString() 获取字符串
this._writeQuotedRaw(this._asString(value));
} else {
// 否则,将 BigDecimal 转为字符串后,不加引号直接写入,作为 JSON 数字输出。
this.writeRaw(this._asString(value));
}
}
private final void _writeQuotedRaw(String value) throws IOException {
// 检查缓冲区是否已满,若满则刷新
if (this._outputTail >= this._outputEnd) {
this._flushBuffer();
}
// 写入开头的双引号
this._outputBuffer[this._outputTail++] = this._quoteChar;
// 写入原始字符串内容
this.writeRaw(value);
// 再次检查缓冲区是否满(写完内容后可能刚好满)
if (this._outputTail >= this._outputEnd) {
this._flushBuffer();
}
// 写入结尾的双引号
this._outputBuffer[this._outputTail++] = this._quoteChar;
}
} UTF8JsonGenerator 方法的特点:
a)所有输出直接写入字节缓冲区 _outputBuffer,不创建任何中间的 String 或 byte[] 对象;
b)使用固定大小的 _outputBuffer,默认为 8KB。所有写操作先写入 buffer,满时才调用 _flushBuffer() ,刷到 OutputStream 中,减少系统调用,提升 I/O 效率;
小结
以上为本篇分享的全部内容,以下做一个小结:
1)SpringBoot 响应请求时,如果返回的时 application/json 格式的数据,返回的数据会进行序列化处理;
2)序列化时,会先获取一个 Serializer 对象。不同类型数据会创建对应的 Serializer 对象,并加入到 SerializerCache 缓存;
a)如 Bean 对象,创建 BeanSerializer 对象;
b)String 对象,使用 ToStringSerializer 对象;
3)可以通过 @JsonFormat 或 @JsonSerialize,指定某个属性要使用的序列化对象;
a)通过@JsonFormat(shape = JsonFormat.Shape.STRING),可以强制属性的返回值为字符串。如 长整型 强制返回 String,解决前端失去精度的问题;
b)通过@JsonSerialize(using = ToStringSerializer.class),指定属性使用的序列化对象,可自定义序列化对象。如自定义序列化器,如果是默认值 -1,返回特定的信息;
4)通过 Serializer 对象的 serialize() 方法,进行数据的序列化。默认调用 UTF8JsonGenerator 将数据写入输出流;
a)所有输出直接写入字节缓冲区 _outputBuffer,不创建任何中间的 String 或 byte[] 对象;
b)使用固定大小的 _outputBuffer,默认为 8KB。所有写操作先写入 buffer,满时才调用 _flushBuffer() ,刷到 OutputStream 中,减少系统调用,提升 I/O 效率;
关于本篇内容你有什么自己的想法或独到见解,欢迎在评论区一起交流探讨下吧。