👨⚕️ 主页: gis分享者
👨⚕️ 感谢各位大佬 点赞👍 收藏⭐ 留言📝 加关注✅!
文章目录
- 一、🍀前言
-
- [1.1 ☘️THREE.ShaderMaterial](#1.1 ☘️THREE.ShaderMaterial)
-
- [1.1.1 ☘️注意事项](#1.1.1 ☘️注意事项)
- [1.1.2 ☘️构造函数](#1.1.2 ☘️构造函数)
- [1.1.3 ☘️属性](#1.1.3 ☘️属性)
- [1.1.4 ☘️方法](#1.1.4 ☘️方法)
- 二、🍀实现发光信息流效果
-
- [1. ☘️实现思路](#1. ☘️实现思路)
- [2. ☘️代码样例](#2. ☘️代码样例)
一、🍀前言
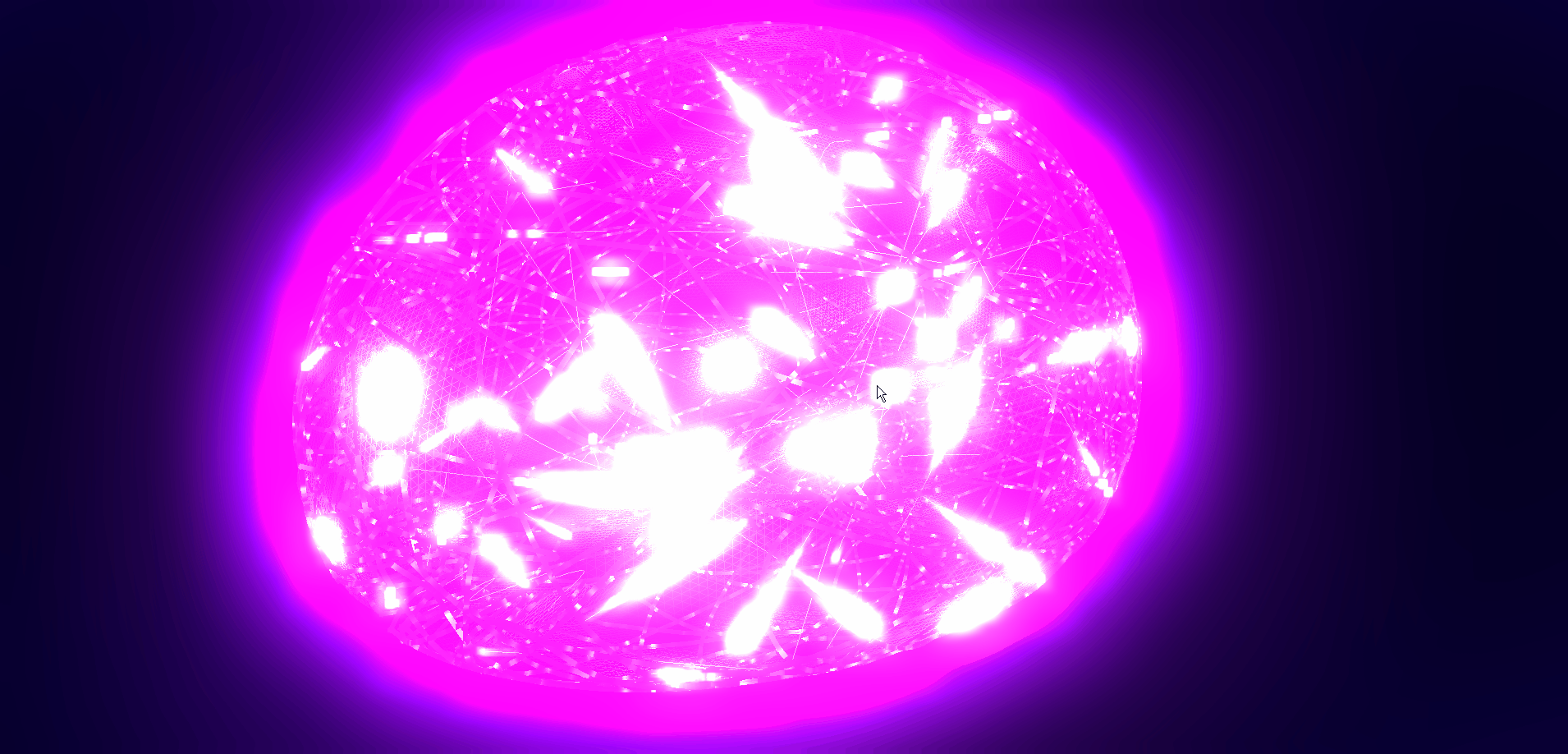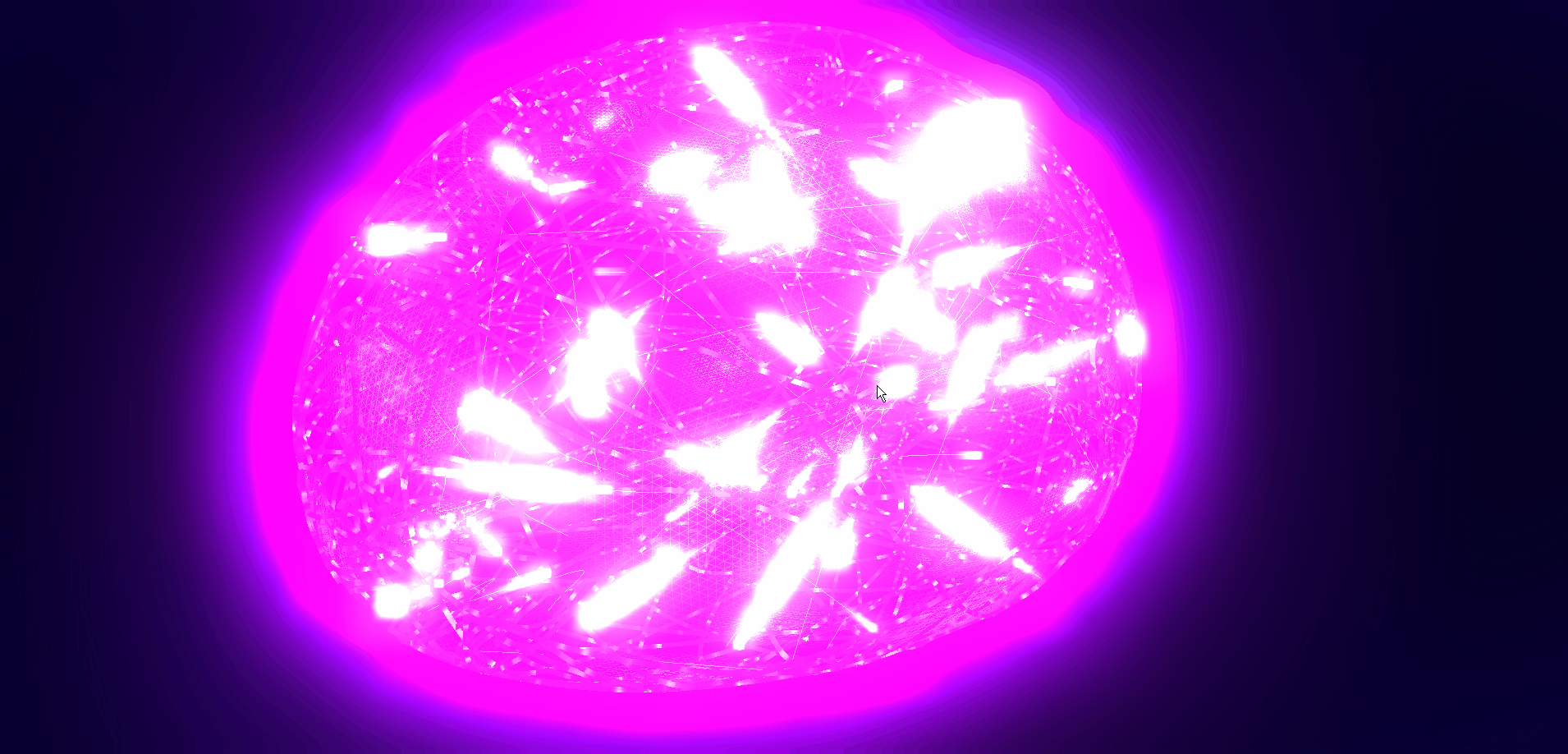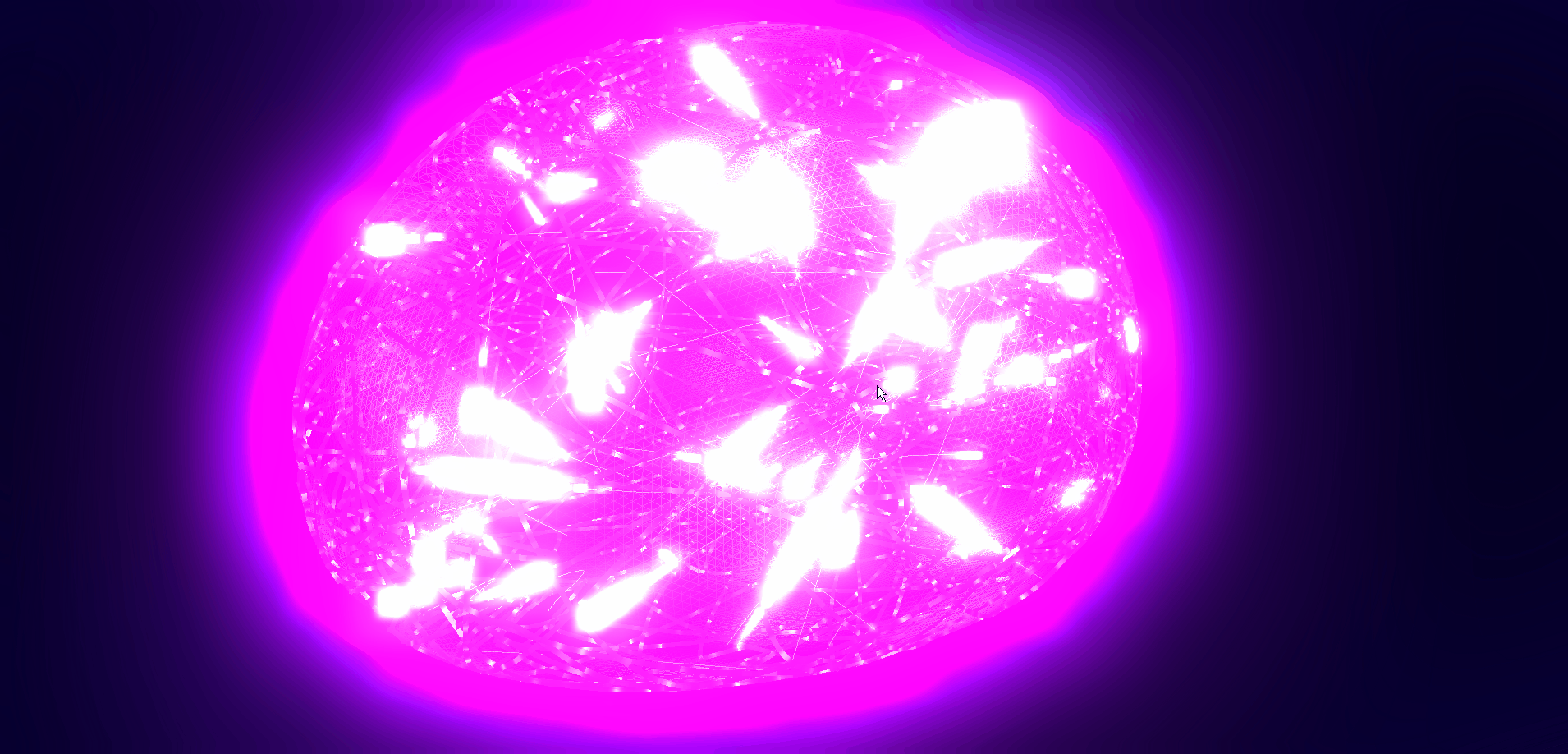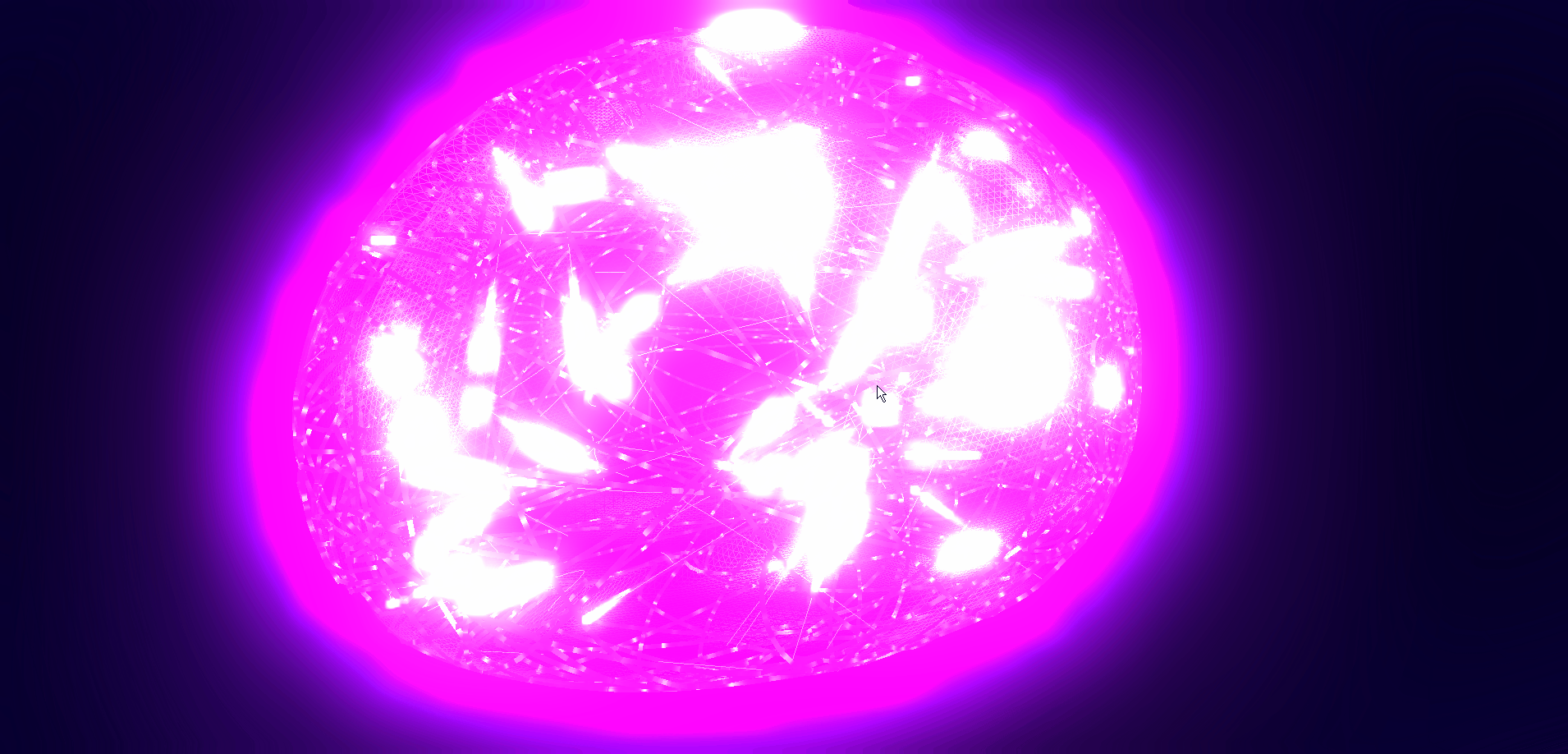
本文详细介绍如何基于threejs在三维场景中实现发光信息流效果,亲测可用。希望能帮助到您。一起学习,加油!加油!
1.1 ☘️THREE.ShaderMaterial
THREE.ShaderMaterial使用自定义shader渲染的材质。 shader是一个用GLSL编写的小程序 ,在GPU上运行。
1.1.1 ☘️注意事项
- ShaderMaterial 只有使用 WebGLRenderer 才可以绘制正常, 因为 vertexShader 和
fragmentShader 属性中GLSL代码必须使用WebGL来编译并运行在GPU中。 - 从 THREE r72开始,不再支持在ShaderMaterial中直接分配属性。 必须使用
BufferGeometry实例,使用BufferAttribute实例来定义自定义属性。 - 从 THREE r77开始,WebGLRenderTarget 或 WebGLCubeRenderTarget
实例不再被用作uniforms。 必须使用它们的texture 属性。 - 内置attributes和uniforms与代码一起传递到shaders。
如果您不希望WebGLProgram向shader代码添加任何内容,则可以使用RawShaderMaterial而不是此类。 - 您可以使用指令#pragma unroll_loop_start,#pragma unroll_loop_end
以便通过shader预处理器在GLSL中展开for循环。 该指令必须放在循环的正上方。循环格式必须与定义的标准相对应。 - 循环必须标准化normalized。
- 循环变量必须是i。
- 对于给定的迭代,值 UNROLLED_LOOP_INDEX 将替换为 i 的显式值,并且可以在预处理器语句中使用。
javascript
#pragma unroll_loop_start
for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i ++ ) {
// ...
}
#pragma unroll_loop_end代码示例
javascript
const material = new THREE.ShaderMaterial( {
uniforms: {
time: { value: 1.0 },
resolution: { value: new THREE.Vector2() }
},
vertexShader: document.getElementById( 'vertexShader' ).textContent,
fragmentShader: document.getElementById( 'fragmentShader' ).textContent
} );1.1.2 ☘️构造函数
ShaderMaterial( parameters : Object )
parameters - (可选)用于定义材质外观的对象,具有一个或多个属性。 材质的任何属性都可以从此处传入(包括从Material继承的任何属性)。
1.1.3 ☘️属性
共有属性请参见其基类Material。
.clipping : Boolean
定义此材质是否支持剪裁; 如果渲染器传递clippingPlanes uniform,则为true。默认值为false。
.defaultAttributeValues : Object
当渲染的几何体不包含这些属性但材质包含这些属性时,这些默认值将传递给shaders。这可以避免在缓冲区数据丢失时出错。
javascript
this.defaultAttributeValues = {
'color': [ 1, 1, 1 ],
'uv': [ 0, 0 ],
'uv2': [ 0, 0 ]
};.defines : Object
使用 #define 指令在GLSL代码为顶点着色器和片段着色器定义自定义常量;每个键/值对产生一行定义语句:
javascript
defines: {
FOO: 15,
BAR: true
}这将在GLSL代码中产生如下定义语句:
javascript
#define FOO 15
#define BAR true.extensions : Object
一个有如下属性的对象:
javascript
this.extensions = {
derivatives: false, // set to use derivatives
fragDepth: false, // set to use fragment depth values
drawBuffers: false, // set to use draw buffers
shaderTextureLOD: false // set to use shader texture LOD
};.fog : Boolean
定义材质颜色是否受全局雾设置的影响; 如果将fog uniforms传递给shader,则为true。默认值为false。
.fragmentShader : String
片元着色器的GLSL代码。这是shader程序的实际代码。在上面的例子中, vertexShader 和 fragmentShader 代码是从DOM(HTML文档)中获取的; 它也可以作为一个字符串直接传递或者通过AJAX加载。
.glslVersion : String
定义自定义着色器代码的 GLSL 版本。仅与 WebGL 2 相关,以便定义是否指定 GLSL 3.0。有效值为 THREE.GLSL1 或 THREE.GLSL3。默认为空。
.index0AttributeName : String
如果设置,则调用gl.bindAttribLocation 将通用顶点索引绑定到属性变量。默认值未定义。
.isShaderMaterial : Boolean
只读标志,用于检查给定对象是否属于 ShaderMaterial 类型。
.lights : Boolean
材质是否受到光照的影响。默认值为 false。如果传递与光照相关的uniform数据到这个材质,则为true。默认是false。
.linewidth : Float
控制线框宽度。默认值为1。
由于OpenGL Core Profile与大多数平台上WebGL渲染器的限制,无论如何设置该值,线宽始终为1。
.flatShading : Boolean
定义材质是否使用平面着色进行渲染。默认值为false。
.uniforms : Object
如下形式的对象:
javascript
{ "uniform1": { value: 1.0 }, "uniform2": { value: 2 } }指定要传递给shader代码的uniforms;键为uniform的名称,值(value)是如下形式:
javascript
{ value: 1.0 }这里 value 是uniform的值。名称必须匹配 uniform 的name,和GLSL代码中的定义一样。 注意,uniforms逐帧被刷新,所以更新uniform值将立即更新GLSL代码中的相应值。
.uniformsNeedUpdate : Boolean
可用于在 Object3D.onBeforeRender() 中更改制服时强制进行制服更新。默认为假。
.vertexColors : Boolean
定义是否使用顶点着色。默认为假。
.vertexShader : String
顶点着色器的GLSL代码。这是shader程序的实际代码。 在上面的例子中,vertexShader 和 fragmentShader 代码是从DOM(HTML文档)中获取的; 它也可以作为一个字符串直接传递或者通过AJAX加载。
.wireframe : Boolean
将几何体渲染为线框(通过GL_LINES而不是GL_TRIANGLES)。默认值为false(即渲染为平面多边形)。
.wireframeLinewidth : Float
控制线框宽度。默认值为1。
由于OpenGL Core Profile与大多数平台上WebGL渲染器的限制,无论如何设置该值,线宽始终为1。
1.1.4 ☘️方法
共有方法请参见其基类Material。
.clone () : ShaderMaterial this : ShaderMaterial
创建该材质的一个浅拷贝。需要注意的是,vertexShader和fragmentShader使用引用拷贝; attributes的定义也是如此; 这意味着,克隆的材质将共享相同的编译WebGLProgram; 但是,uniforms 是 值拷贝,这样对不同的材质我们可以有不同的uniforms变量。
二、🍀实现发光信息流效果
1. ☘️实现思路
通过threejs的ShaderMaterial自定义着色器实现发光信息流效果。具体代码参考下面代码样例。
2. ☘️代码样例
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body {
overflow: hidden;
margin: 0;
}
#info {
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
top: 50%;
text-align: center;
font-family: 'Orbitron', sans-serif;
font-size: 2vh;
color: black;
}
</style>
<script type="importmap">
{
"imports": {
"three": "https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/three.js/0.163.0/three.module.min.js",
"three/addons/": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/three@0.163.0/examples/jsm/"
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="info">patience... we're deforming the spheres</div>
<script type="x-shader/x-vertex" id="vertexshader">
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * modelViewMatrix * vec4( position, 1.0 );
}
</script>
<script type="x-shader/x-fragment" id="fragmentshader">
uniform sampler2D baseTexture;
uniform sampler2D bloomTexture;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_FragColor = ( texture2D( baseTexture, vUv ) + vec4( 1.0 ) * texture2D( bloomTexture, vUv ) );
}
</script>
<script>
const noiseV3 = `
vec4 permute(vec4 x){return mod(((x*34.0)+1.0)*x, 289.0);}
float permute(float x){return floor(mod(((x*34.0)+1.0)*x, 289.0));}
vec4 taylorInvSqrt(vec4 r){return 1.79284291400159 - 0.85373472095314 * r;}
float taylorInvSqrt(float r){return 1.79284291400159 - 0.85373472095314 * r;}
vec4 grad4(float j, vec4 ip){
const vec4 ones = vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0);
vec4 p,s;
p.xyz = floor( fract (vec3(j) * ip.xyz) * 7.0) * ip.z - 1.0;
p.w = 1.5 - dot(abs(p.xyz), ones.xyz);
s = vec4(lessThan(p, vec4(0.0)));
p.xyz = p.xyz + (s.xyz*2.0 - 1.0) * s.www;
return p;
}
float snoise(vec4 v){
const vec2 C = vec2( 0.138196601125010504, // (5 - sqrt(5))/20 G4
0.309016994374947451); // (sqrt(5) - 1)/4 F4
// First corner
vec4 i = floor(v + dot(v, C.yyyy) );
vec4 x0 = v - i + dot(i, C.xxxx);
vec4 i0;
vec3 isX = step( x0.yzw, x0.xxx );
vec3 isYZ = step( x0.zww, x0.yyz );
// i0.x = dot( isX, vec3( 1.0 ) );
i0.x = isX.x + isX.y + isX.z;
i0.yzw = 1.0 - isX;
// i0.y += dot( isYZ.xy, vec2( 1.0 ) );
i0.y += isYZ.x + isYZ.y;
i0.zw += 1.0 - isYZ.xy;
i0.z += isYZ.z;
i0.w += 1.0 - isYZ.z;
// i0 now contains the unique values 0,1,2,3 in each channel
vec4 i3 = clamp( i0, 0.0, 1.0 );
vec4 i2 = clamp( i0-1.0, 0.0, 1.0 );
vec4 i1 = clamp( i0-2.0, 0.0, 1.0 );
// x0 = x0 - 0.0 + 0.0 * C
vec4 x1 = x0 - i1 + 1.0 * C.xxxx;
vec4 x2 = x0 - i2 + 2.0 * C.xxxx;
vec4 x3 = x0 - i3 + 3.0 * C.xxxx;
vec4 x4 = x0 - 1.0 + 4.0 * C.xxxx;
// Permutations
i = mod(i, 289.0);
float j0 = permute( permute( permute( permute(i.w) + i.z) + i.y) + i.x);
vec4 j1 = permute( permute( permute( permute (
i.w + vec4(i1.w, i2.w, i3.w, 1.0 ))
+ i.z + vec4(i1.z, i2.z, i3.z, 1.0 ))
+ i.y + vec4(i1.y, i2.y, i3.y, 1.0 ))
+ i.x + vec4(i1.x, i2.x, i3.x, 1.0 ));
// Gradients
// ( 7*7*6 points uniformly over a cube, mapped onto a 4-octahedron.)
// 7*7*6 = 294, which is close to the ring size 17*17 = 289.
vec4 ip = vec4(1.0/294.0, 1.0/49.0, 1.0/7.0, 0.0) ;
vec4 p0 = grad4(j0, ip);
vec4 p1 = grad4(j1.x, ip);
vec4 p2 = grad4(j1.y, ip);
vec4 p3 = grad4(j1.z, ip);
vec4 p4 = grad4(j1.w, ip);
// Normalise gradients
vec4 norm = taylorInvSqrt(vec4(dot(p0,p0), dot(p1,p1), dot(p2, p2), dot(p3,p3)));
p0 *= norm.x;
p1 *= norm.y;
p2 *= norm.z;
p3 *= norm.w;
p4 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p4,p4));
// Mix contributions from the five corners
vec3 m0 = max(0.6 - vec3(dot(x0,x0), dot(x1,x1), dot(x2,x2)), 0.0);
vec2 m1 = max(0.6 - vec2(dot(x3,x3), dot(x4,x4) ), 0.0);
m0 = m0 * m0;
m1 = m1 * m1;
return 49.0 * ( dot(m0*m0, vec3( dot( p0, x0 ), dot( p1, x1 ), dot( p2, x2 )))
+ dot(m1*m1, vec2( dot( p3, x3 ), dot( p4, x4 ) ) ) ) ;
}
`;
const noise = `
// https://gist.github.com/patriciogonzalezvivo/670c22f3966e662d2f83
/*float rand(vec2 c){
return fract(sin(dot(c.xy ,vec2(12.9898,78.233))) * 43758.5453);
}*/
float noise(vec2 p, float freq ){
float unit = 2.; //screenWidth/freq;
vec2 ij = floor(p/unit);
vec2 xy = mod(p,unit)/unit;
//xy = 3.*xy*xy-2.*xy*xy*xy;
xy = .5*(1.-cos(PI*xy));
float a = rand((ij+vec2(0.,0.)));
float b = rand((ij+vec2(1.,0.)));
float c = rand((ij+vec2(0.,1.)));
float d = rand((ij+vec2(1.,1.)));
float x1 = mix(a, b, xy.x);
float x2 = mix(c, d, xy.x);
return mix(x1, x2, xy.y);
}
float pNoise(vec2 p, int res){
float persistance = .5;
float n = 0.;
float normK = 0.;
float f = 4.;
float amp = 1.;
int iCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i<50; i++){
n+=amp*noise(p, f);
f*=2.;
normK+=amp;
amp*=persistance;
if (iCount == res) break;
iCount++;
}
float nf = n/normK;
return nf*nf*nf*nf;
}
`;
const flVert = `
#include <common>
#include <color_pars_vertex>
#include <fog_pars_vertex>
#include <logdepthbuf_pars_vertex>
#include <clipping_planes_pars_vertex>
uniform float linewidth;
uniform vec2 resolution;
attribute vec3 instanceStart;
attribute vec3 instanceEnd;
attribute vec3 instanceColorStart;
attribute vec3 instanceColorEnd;
#ifdef WORLD_UNITS
varying vec4 worldPos;
varying vec3 worldStart;
varying vec3 worldEnd;
varying vec2 vUv;
#else
varying vec2 vUv;
#endif
attribute float instanceDistanceStart;
attribute float instanceDistanceEnd;
varying float vLineDistance;
void trimSegment( const in vec4 start, inout vec4 end ) {
// trim end segment so it terminates between the camera plane and the near plane
// conservative estimate of the near plane
float a = projectionMatrix[ 2 ][ 2 ]; // 3nd entry in 3th column
float b = projectionMatrix[ 3 ][ 2 ]; // 3nd entry in 4th column
float nearEstimate = - 0.5 * b / a;
float alpha = ( nearEstimate - start.z ) / ( end.z - start.z );
end.xyz = mix( start.xyz, end.xyz, alpha );
}
void main() {
#ifdef USE_COLOR
vColor.xyz = ( position.y < 0.5 ) ? instanceColorStart : instanceColorEnd;
#endif
vLineDistance = ( position.y < 0.5 ) ? instanceDistanceStart : instanceDistanceEnd;
vUv = uv;
float aspect = resolution.x / resolution.y;
// camera space
vec4 start = modelViewMatrix * vec4( instanceStart, 1.0 );
vec4 end = modelViewMatrix * vec4( instanceEnd, 1.0 );
#ifdef WORLD_UNITS
worldStart = start.xyz;
worldEnd = end.xyz;
#else
vUv = uv;
#endif
// special case for perspective projection, and segments that terminate either in, or behind, the camera plane
// clearly the gpu firmware has a way of addressing this issue when projecting into ndc space
// but we need to perform ndc-space calculations in the shader, so we must address this issue directly
// perhaps there is a more elegant solution -- WestLangley
bool perspective = ( projectionMatrix[ 2 ][ 3 ] == - 1.0 ); // 4th entry in the 3rd column
if ( perspective ) {
if ( start.z < 0.0 && end.z >= 0.0 ) {
trimSegment( start, end );
} else if ( end.z < 0.0 && start.z >= 0.0 ) {
trimSegment( end, start );
}
}
// clip space
vec4 clipStart = projectionMatrix * start;
vec4 clipEnd = projectionMatrix * end;
// ndc space
vec3 ndcStart = clipStart.xyz / clipStart.w;
vec3 ndcEnd = clipEnd.xyz / clipEnd.w;
// direction
vec2 dir = ndcEnd.xy - ndcStart.xy;
// account for clip-space aspect ratio
dir.x *= aspect;
dir = normalize( dir );
#ifdef WORLD_UNITS
// get the offset direction as perpendicular to the view vector
vec3 worldDir = normalize( end.xyz - start.xyz );
vec3 offset;
if ( position.y < 0.5 ) {
offset = normalize( cross( start.xyz, worldDir ) );
} else {
offset = normalize( cross( end.xyz, worldDir ) );
}
// sign flip
if ( position.x < 0.0 ) offset *= - 1.0;
float forwardOffset = dot( worldDir, vec3( 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 ) );
// don't extend the line if we're rendering dashes because we
// won't be rendering the endcaps
#ifndef USE_DASH
// extend the line bounds to encompass endcaps
start.xyz += - worldDir * linewidth * 0.5;
end.xyz += worldDir * linewidth * 0.5;
// shift the position of the quad so it hugs the forward edge of the line
offset.xy -= dir * forwardOffset;
offset.z += 0.5;
#endif
// endcaps
if ( position.y > 1.0 || position.y < 0.0 ) {
offset.xy += dir * 2.0 * forwardOffset;
}
// adjust for linewidth
offset *= linewidth * 0.5;
// set the world position
worldPos = ( position.y < 0.5 ) ? start : end;
worldPos.xyz += offset;
// project the worldpos
vec4 clip = projectionMatrix * worldPos;
// shift the depth of the projected points so the line
// segements overlap neatly
vec3 clipPose = ( position.y < 0.5 ) ? ndcStart : ndcEnd;
clip.z = clipPose.z * clip.w;
#else
vec2 offset = vec2( dir.y, - dir.x );
// undo aspect ratio adjustment
dir.x /= aspect;
offset.x /= aspect;
// sign flip
if ( position.x < 0.0 ) offset *= - 1.0;
// endcaps
if ( position.y < 0.0 ) {
offset += - dir;
} else if ( position.y > 1.0 ) {
offset += dir;
}
// adjust for linewidth
offset *= linewidth;
// adjust for clip-space to screen-space conversion // maybe resolution should be based on viewport ...
offset /= resolution.y;
// select end
vec4 clip = ( position.y < 0.5 ) ? clipStart : clipEnd;
// back to clip space
offset *= clip.w;
clip.xy += offset;
#endif
gl_Position = clip;
vec4 mvPosition = ( position.y < 0.5 ) ? start : end; // this is an approximation
#include <logdepthbuf_vertex>
#include <clipping_planes_vertex>
#include <fog_vertex>
}
`;
const flFrag = `
uniform float time;
uniform float bloom;
uniform vec3 diffuse;
uniform float opacity;
uniform float linewidth;
#ifdef USE_DASH
uniform float dashOffset;
uniform float dashSize;
uniform float gapSize;
#endif
varying float vLineDistance;
#ifdef WORLD_UNITS
varying vec4 worldPos;
varying vec3 worldStart;
varying vec3 worldEnd;
varying vec2 vUv;
#else
varying vec2 vUv;
#endif
#include <common>
#include <color_pars_fragment>
#include <fog_pars_fragment>
#include <logdepthbuf_pars_fragment>
#include <clipping_planes_pars_fragment>
vec2 closestLineToLine(vec3 p1, vec3 p2, vec3 p3, vec3 p4) {
float mua;
float mub;
vec3 p13 = p1 - p3;
vec3 p43 = p4 - p3;
vec3 p21 = p2 - p1;
float d1343 = dot( p13, p43 );
float d4321 = dot( p43, p21 );
float d1321 = dot( p13, p21 );
float d4343 = dot( p43, p43 );
float d2121 = dot( p21, p21 );
float denom = d2121 * d4343 - d4321 * d4321;
float numer = d1343 * d4321 - d1321 * d4343;
mua = numer / denom;
mua = clamp( mua, 0.0, 1.0 );
mub = ( d1343 + d4321 * ( mua ) ) / d4343;
mub = clamp( mub, 0.0, 1.0 );
return vec2( mua, mub );
}
${noise}
void main() {
#include <clipping_planes_fragment>
#ifdef USE_DASH
if ( vUv.y < - 1.0 || vUv.y > 1.0 ) discard; // discard endcaps
if ( mod( vLineDistance + dashOffset, dashSize + gapSize ) > dashSize ) discard; // todo - FIX
#endif
float alpha = opacity;
#ifdef WORLD_UNITS
// Find the closest points on the view ray and the line segment
vec3 rayEnd = normalize( worldPos.xyz ) * 1e5;
vec3 lineDir = worldEnd - worldStart;
vec2 params = closestLineToLine( worldStart, worldEnd, vec3( 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 ), rayEnd );
vec3 p1 = worldStart + lineDir * params.x;
vec3 p2 = rayEnd * params.y;
vec3 delta = p1 - p2;
float len = length( delta );
float norm = len / linewidth;
#ifndef USE_DASH
#ifdef USE_ALPHA_TO_COVERAGE
float dnorm = fwidth( norm );
alpha = 1.0 - smoothstep( 0.5 - dnorm, 0.5 + dnorm, norm );
#else
if ( norm > 0.5 ) {
discard;
}
#endif
#endif
#else
#ifdef USE_ALPHA_TO_COVERAGE
// artifacts appear on some hardware if a derivative is taken within a conditional
float a = vUv.x;
float b = ( vUv.y > 0.0 ) ? vUv.y - 1.0 : vUv.y + 1.0;
float len2 = a * a + b * b;
float dlen = fwidth( len2 );
if ( abs( vUv.y ) > 1.0 ) {
alpha = 1.0 - smoothstep( 1.0 - dlen, 1.0 + dlen, len2 );
}
#else
if ( abs( vUv.y ) > 1.0 ) {
float a = vUv.x;
float b = ( vUv.y > 0.0 ) ? vUv.y - 1.0 : vUv.y + 1.0;
float len2 = a * a + b * b;
if ( len2 > 1.0 ) discard;
}
#endif
#endif
float pn1 = abs(pNoise(vec2(vLineDistance * 0.05, time), 3)) * 0.75;
float pn2 = pNoise(vec2(vLineDistance * 25. + time * 4., 0.123), 10) * 0.5 + 0.5;
pn2 = clamp(pow(pn2, 4.), 0., 1.);
vec3 c = mix(vec3(0, 0, 0.25), diffuse, pn1);
c = mix(c, diffuse, pn2);
vec4 diffuseColor = vec4( c, alpha );
#include <logdepthbuf_fragment>
#include <color_fragment>
gl_FragColor = vec4( diffuseColor.rgb, alpha );
#include <tonemapping_fragment>
#include <encodings_fragment>
#include <fog_fragment>
#include <premultiplied_alpha_fragment>
vec3 col = gl_FragColor.rgb;
gl_FragColor.rgb = mix(gl_FragColor.rgb, vec3(0), bloom);
gl_FragColor.rgb = mix(gl_FragColor.rgb, mix(vec3(1), col, bloom), pn2);
}
`;
</script>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from "three";
import { OrbitControls } from "three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js";
import { ImprovedNoise } from 'three/addons/math/ImprovedNoise.js';
import { Line2 } from "three/addons/lines/Line2.js";
import { LineMaterial } from "three/addons/lines/LineMaterial.js";
import { LineGeometry } from "three/addons/lines/LineGeometry.js";
import { EffectComposer } from 'three/addons/postprocessing/EffectComposer.js';
import { RenderPass } from 'three/addons/postprocessing/RenderPass.js';
import { ShaderPass } from 'three/addons/postprocessing/ShaderPass.js';
import { UnrealBloomPass } from 'three/addons/postprocessing/UnrealBloomPass.js';
const perlin = new ImprovedNoise();
let v3 = new THREE.Vector3();
let scene = new THREE.Scene();
let camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, innerWidth / innerHeight, 1, 5000);
camera.position.set(5, 2, 5).setLength(12);
let renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true });
renderer.setSize(innerWidth, innerHeight);
renderer.toneMapping = THREE.ReinhardToneMapping;
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
window.addEventListener("resize", () => {
camera.aspect = innerWidth / innerHeight;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
renderer.setSize(innerWidth, innerHeight);
m.resolution.set(innerWidth, innerHeight);
bloomPass.resolution.set(innerWidth, innerHeight);
})
let controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
controls.enablePan = false;
controls.enableDamping = true;
controls.minDistance = 1;
controls.maxDistance = 15;
// <CURVE>
let curvePts = new Array(200).fill().map(p => {
return new THREE.Vector3().randomDirection();
})
let curve = new THREE.CatmullRomCurve3(curvePts, true);
let pts = curve.getSpacedPoints(200);
pts.shift();
curve = new THREE.CatmullRomCurve3(pts, true);
pts = curve.getSpacedPoints(10000);
pts.forEach(p => { p.setLength(4) });
let n = new THREE.Vector3();
let s = new THREE.Vector3(0.5, 0.5, 1.);
pts.forEach(p => {
deform(p);
})
let fPts = [];
pts.forEach(p => { fPts.push(p.x, p.y, p.z) });
let g = new LineGeometry();
g.setPositions(fPts);
let globalUniforms = {
time: { value: 0 },
bloom: { value: 0 }
}
let m = new LineMaterial({
color: "magenta",
worldUnits: true,
linewidth: 0.0375,
alphaToCoverage: true,
onBeforeCompile: shader => {
shader.uniforms.time = globalUniforms.time;
shader.uniforms.bloom = globalUniforms.bloom;
shader.vertexShader = flVert;
shader.fragmentShader = flFrag;
}
});
m.resolution.set(innerWidth, innerHeight);
let l = new Line2(g, m);
l.computeLineDistances();
scene.add(l);
// </CURVE>
// <SPHERE>
let sg = new THREE.IcosahedronGeometry(1, 70);
for (let i = 0; i < sg.attributes.position.count; i++) {
v3.fromBufferAttribute(sg.attributes.position, i);
deform(v3);
sg.attributes.position.setXYZ(i, v3.x, v3.y, v3.z);
}
let sm = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x7f00ff,
wireframe: true,
transparent: true,
onBeforeCompile: shader => {
shader.uniforms.bloom = globalUniforms.bloom;
shader.uniforms.time = globalUniforms.time;
shader.vertexShader = `
varying vec3 vN;
${shader.vertexShader}
`.replace(
`#include <begin_vertex>`,
`#include <begin_vertex>
vN = normal;
`
);
//console.log(shader.vertexShader);
shader.fragmentShader = `
uniform float bloom;
uniform float time;
varying vec3 vN;
${noiseV3}
${shader.fragmentShader}
`.replace(
`#include <dithering_fragment>`,
`#include <dithering_fragment>
float ns = snoise(vec4(vN * 1.5, time * 0.5));
ns = abs(ns);
vec3 col = mix(diffuse, vec3(0, 1, 1) * 0.5, ns);
gl_FragColor.rgb = mix(col, vec3(0), bloom);
gl_FragColor.a = ns;
gl_FragColor.rgb = mix(gl_FragColor.rgb, col, pow(ns, 16.));
`
);
}
});
let sphere = new THREE.Mesh(sg, sm);
scene.add(sphere);
// </SPHERE>
// <LINKS>
let LINK_COUNT = 50;
let linkPts = [];
for (let i = 0; i < LINK_COUNT; i++) {
let pS = new THREE.Vector3().randomDirection();
let pE = new THREE.Vector3().randomDirection();
let division = 100;
for (let j = 0; j < division; j++) {
let v1 = new THREE.Vector3().lerpVectors(pS, pE, j / division);
let v2 = new THREE.Vector3().lerpVectors(pS, pE, (j + 1) / division);
deform(v1, true);
deform(v2, true);
linkPts.push(v1, v2);
}
}
let linkG = new THREE.BufferGeometry().setFromPoints(linkPts);
let linkM = new THREE.LineDashedMaterial({
color: 0xffff00,
onBeforeCompile: shader => {
shader.uniforms.time = globalUniforms.time;
shader.uniforms.bloom = globalUniforms.bloom;
shader.fragmentShader = `
uniform float bloom;
uniform float time;
${shader.fragmentShader}
`.replace(
`if ( mod( vLineDistance, totalSize ) > dashSize ) {
discard;
}`,
``
)
.replace(
`#include <premultiplied_alpha_fragment>`,
`#include <premultiplied_alpha_fragment>
vec3 col = diffuse;
gl_FragColor.rgb = mix(col * 0.5, vec3(0), bloom);
float sig = sin((vLineDistance * 2. + time * 5.) * 0.5) * 0.5 + 0.5;
sig = pow(sig, 16.);
gl_FragColor.rgb = mix(gl_FragColor.rgb, col * 0.75, sig);
`
);
//console.log(shader.fragmentShader);
}
});
let link = new THREE.LineSegments(linkG, linkM);
link.computeLineDistances();
scene.add(link);
// </LINKS>
// <BACKGROUND>
let bg = new THREE.SphereGeometry(1000, 64, 32);
let bm = new THREE.ShaderMaterial({
side: THREE.BackSide,
uniforms: {
bloom: globalUniforms.bloom,
time: globalUniforms.time
},
vertexShader: `
varying vec3 vNormal;
void main() {
vNormal = normal;
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * modelViewMatrix * vec4( position, 1.0 );
}
`,
fragmentShader: `
uniform float bloom;
uniform float time;
varying vec3 vNormal;
${noiseV3}
void main() {
vec3 col = vec3(0.012, 0, 0.1);
float ns = snoise(vec4(vNormal, time * 0.1));
col = mix(col * 5., col, pow(abs(ns), 0.125));
col = mix(col, vec3(0), bloom);
gl_FragColor = vec4( col, 1.0 );
}
`
});
let bo = new THREE.Mesh(bg, bm);
scene.add(bo);
// </BACKGROUND>
// <BLOOM>
const params = {
exposure: 1,
bloomStrength: 7,
bloomThreshold: 0,
bloomRadius: 0
};
const renderScene = new RenderPass(scene, camera);
const bloomPass = new UnrealBloomPass(new THREE.Vector2(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight), 1.5, 0.4, 0.85);
bloomPass.threshold = params.bloomThreshold;
bloomPass.strength = params.bloomStrength;
bloomPass.radius = params.bloomRadius;
const bloomComposer = new EffectComposer(renderer);
bloomComposer.renderToScreen = false;
bloomComposer.addPass(renderScene);
bloomComposer.addPass(bloomPass);
const finalPass = new ShaderPass(
new THREE.ShaderMaterial({
uniforms: {
baseTexture: { value: null },
bloomTexture: { value: bloomComposer.renderTarget2.texture }
},
vertexShader: document.getElementById('vertexshader').textContent,
fragmentShader: document.getElementById('fragmentshader').textContent,
defines: {}
}), 'baseTexture'
);
finalPass.needsSwap = true;
const finalComposer = new EffectComposer(renderer);
finalComposer.addPass(renderScene);
finalComposer.addPass(finalPass);
// </BLOOM>
let clock = new THREE.Clock();
info.style.visibility = "hidden";
renderer.setAnimationLoop(() => {
let t = clock.getElapsedTime();
controls.update();
globalUniforms.time.value = t;
globalUniforms.bloom.value = 1;
//renderer.setClearColor(0x000000);
bloomComposer.render();
globalUniforms.bloom.value = 0;
//renderer.setClearColor(0x080032);
finalComposer.render();
//renderer.render(scene, camera);
})
function deform(p, useLength) {
let mainR = 5;
v3.copy(p).normalize();
let len = p.length();
let ns = perlin.noise(v3.x * 3, v3.y * 3, v3.z * 3);
ns = Math.pow(Math.abs(ns), 0.5) * 0.25;
let r = smoothstep(0.125, 0, Math.abs(v3.x)) - ns;
p.setLength(mainR - Math.pow(r, 2) * 1);
p.y *= 1 - 0.5 * smoothstep(0, -mainR, p.y);
p.y *= 0.75;
p.x *= 0.75;
p.y *= 1 - 0.125 * smoothstep(mainR * 0.25, -mainR, p.z);
p.x *= 1 - 0.125 * smoothstep(mainR * 0.25, -mainR, p.z);
if (useLength) {
p.multiplyScalar(len)
};
//p.y += 0.5;
}
//https://github.com/gre/smoothstep/blob/master/index.js
function smoothstep(min, max, value) {
var x = Math.max(0, Math.min(1, (value - min) / (max - min)));
return x * x * (3 - 2 * x);
};
</script>
</body>
</html>效果如下: