实际场景的Agent 调用链路
让我用一个具体例子带你从头到尾走一遍!
场景示例
假设用户问:"北京今天天气怎么样?顺便帮我搜索一下明天的航班"
系统会:
- 调用天气查询工具获取北京天气
- 调用航班搜索工具查询明天航班
- 整合结果返回给用户
完整调用流程图
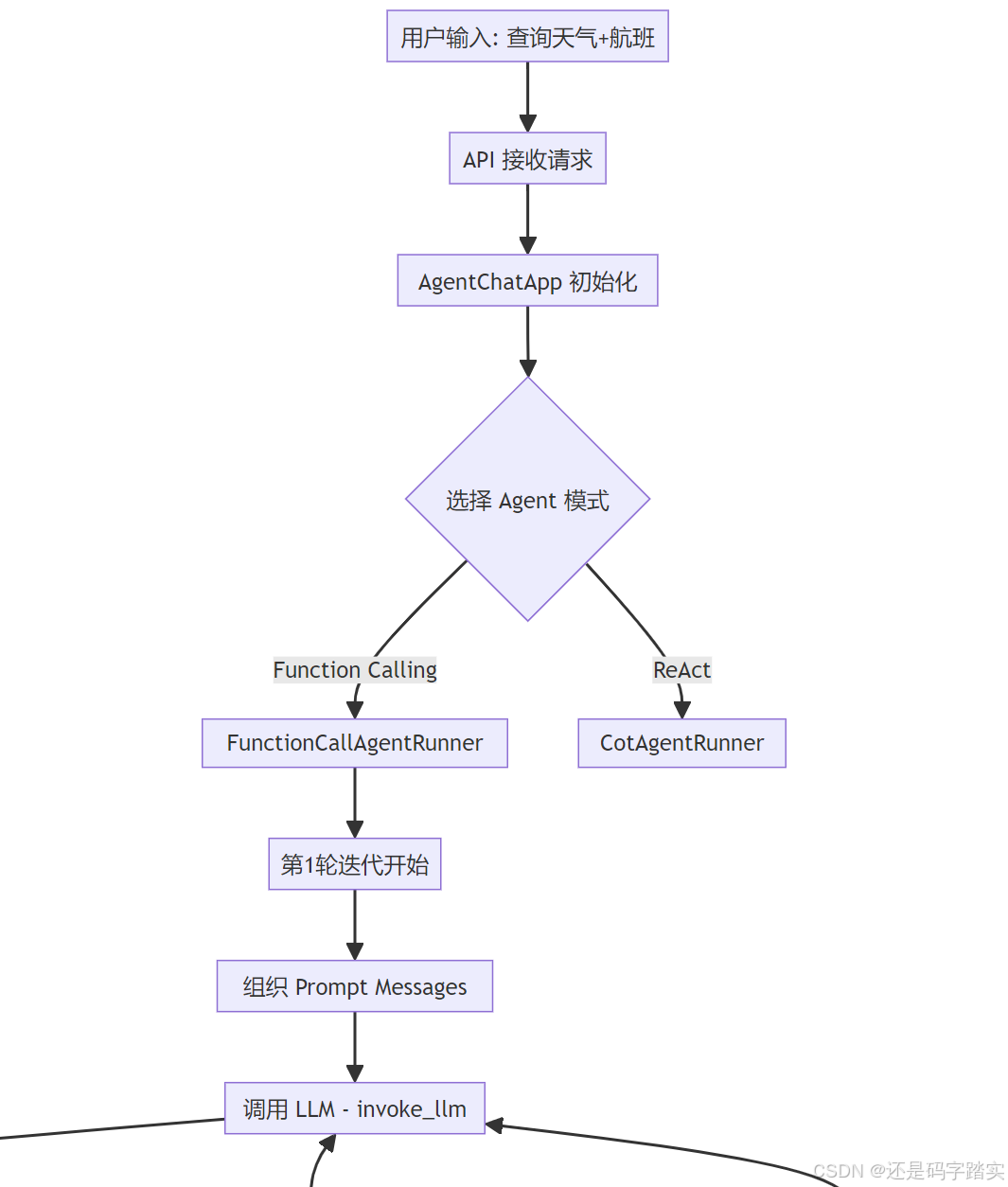
第一部分:请求入口与初始化
用户请求到达 API
python
# 假设用户通过 HTTP POST 发送请求
# POST /v1/chat-messages
{
"query": "北京今天天气怎么样?顺便帮我搜索一下明天的航班",
"user": "user_123",
"conversation_id": "conv_456"
}AgentChatApp 接收请求
系统会创建一个 FunctionCallAgentRunner 实例(假设使用 Function Calling 模式):
python
# 伪代码 - 展示初始化过程
agent_runner = FunctionCallAgentRunner(
tenant_id="tenant_789",
conversation=conversation_obj,
app_config=app_config, # 包含 Agent 配置、工具列表
model_config=model_config, # GPT-4 配置
config=agent_entity, # max_iteration=10
# ... 其他参数
)让我们看看初始化时发生了什么:
python
class BaseAgentRunner(AppRunner):
def __init__(
self,
*,
tenant_id: str,
application_generate_entity: AgentChatAppGenerateEntity,
conversation: Conversation,
app_config: AgentChatAppConfig,
model_config: ModelConfigWithCredentialsEntity,
config: AgentEntity,
queue_manager: AppQueueManager,
message: Message,
user_id: str,
model_instance: ModelInstance,
memory: TokenBufferMemory | None = None,
prompt_messages: list[PromptMessage] | None = None,
):
self.tenant_id = tenant_id
self.application_generate_entity = application_generate_entity
self.conversation = conversation
self.app_config = app_config
self.model_config = model_config
self.config = config
self.queue_manager = queue_manager
self.message = message
self.user_id = user_id
self.memory = memory
# 🔍 关键:组织历史对话记录
self.history_prompt_messages = self.organize_agent_history(prompt_messages=prompt_messages or [])
self.model_instance = model_instance
# init callback
# 🔍 Agent 工具调用的回调处理器
self.agent_callback = DifyAgentCallbackHandler()
# init dataset tools
# 🔍 如果配置了知识库,初始化检索工具
hit_callback = DatasetIndexToolCallbackHandler(
queue_manager=queue_manager,
app_id=self.app_config.app_id,
message_id=message.id,
user_id=user_id,
invoke_from=self.application_generate_entity.invoke_from,
)
self.dataset_tools = DatasetRetrieverTool.get_dataset_tools(
tenant_id=tenant_id,
dataset_ids=app_config.dataset.dataset_ids if app_config.dataset else [],
retrieve_config=app_config.dataset.retrieve_config if app_config.dataset else None,
return_resource=(
app_config.additional_features.show_retrieve_source if app_config.additional_features else False
),
invoke_from=application_generate_entity.invoke_from,
hit_callback=hit_callback,
user_id=user_id,
inputs=cast(dict, application_generate_entity.inputs),
)
# 🔍 统计已创建的 AgentThought 数量(用于排序)
# get how many agent thoughts have been created
self.agent_thought_count = (
db.session.query(MessageAgentThought)
.where(
MessageAgentThought.message_id == self.message.id,
)
.count()
)
db.session.close()
# 🔍 检查模型是否支持流式工具调用
# check if model supports stream tool call
llm_model = cast(LargeLanguageModel, model_instance.model_type_instance)
model_schema = llm_model.get_model_schema(model_instance.model, model_instance.credentials)
features = model_schema.features if model_schema and model_schema.features else []
self.stream_tool_call = ModelFeature.STREAM_TOOL_CALL in features
self.files = application_generate_entity.files if ModelFeature.VISION in features else []
self.query: str | None = ""
self._current_thoughts: list[PromptMessage] = []关键注释解读:
organize_agent_history:把之前的对话转成 Prompt 格式agent_callback:记录工具调用的开始/结束/错误dataset_tools:如果配置了知识库,这里会创建检索工具stream_tool_call:判断是用流式还是阻塞式调用
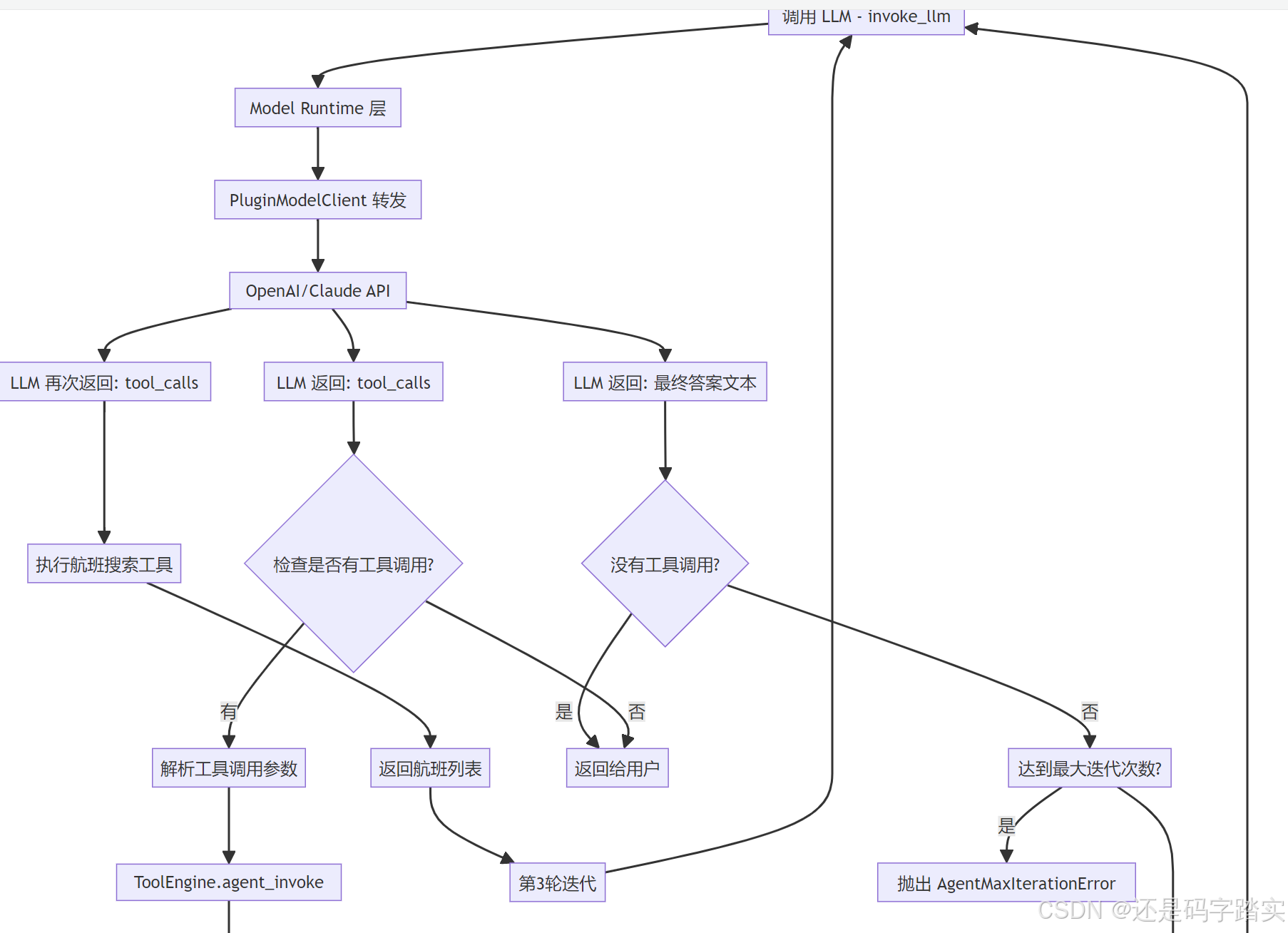
第二部分:第一轮迭代 - 调用 LLM
FunctionCallAgentRunner.run() 开始执行
python
class FunctionCallAgentRunner(BaseAgentRunner):
def run(self, message: Message, query: str, **kwargs: Any) -> Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None]:
"""
Run FunctionCall agent application
"""
# 🔍 保存用户的查询
self.query = query
app_generate_entity = self.application_generate_entity
app_config = self.app_config
assert app_config is not None, "app_config is required"
assert app_config.agent is not None, "app_config.agent is required"
# 🔍 【重要】初始化工具列表
# convert tools into ModelRuntime Tool format
tool_instances, prompt_messages_tools = self._init_prompt_tools()
assert app_config.agent
# 🔍 设置迭代参数
iteration_step = 1 # 当前是第几轮
max_iteration_steps = min(app_config.agent.max_iteration, 99) + 1 # 最多99轮
# 🔍 循环控制变量
# continue to run until there is not any tool call
function_call_state = True # 是否还有工具调用
llm_usage: dict[str, LLMUsage | None] = {"usage": None} # Token 统计
final_answer = ""
prompt_messages: list = [] # Initialize prompt_messages
# get tracing instance
trace_manager = app_generate_entity.trace_manager
# 🔍 Token 累加函数
def increase_usage(final_llm_usage_dict: dict[str, LLMUsage | None], usage: LLMUsage):
if not final_llm_usage_dict["usage"]:
final_llm_usage_dict["usage"] = usage
else:
llm_usage = final_llm_usage_dict["usage"]
llm_usage.prompt_tokens += usage.prompt_tokens
llm_usage.completion_tokens += usage.completion_tokens
llm_usage.total_tokens += usage.total_tokens
llm_usage.prompt_price += usage.prompt_price
llm_usage.completion_price += usage.completion_price
llm_usage.total_price += usage.total_price
model_instance = self.model_instance
# 🔍 【核心循环】持续执行直到没有工具调用
while function_call_state and iteration_step <= max_iteration_steps:
function_call_state = False # 默认本轮没有工具调用
# 🔍 如果是最后一轮,移除所有工具(强制模型输出答案)
if iteration_step == max_iteration_steps:
# the last iteration, remove all tools
prompt_messages_tools = []
message_file_ids: list[str] = []
# 🔍 创建 AgentThought 记录(用于前端展示推理过程)
agent_thought_id = self.create_agent_thought(
message_id=message.id, message="", tool_name="", tool_input="", messages_ids=message_file_ids
)
# 🔍 【关键】组织 Prompt 消息
# recalc llm max tokens
prompt_messages = self._organize_prompt_messages()
self.recalc_llm_max_tokens(self.model_config, prompt_messages)
# 🔍 【核心】调用 LLM
# invoke model
chunks: Union[Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None], LLMResult] = model_instance.invoke_llm(
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
model_parameters=app_generate_entity.model_conf.parameters,
tools=prompt_messages_tools, # 传入工具列表
stop=app_generate_entity.model_conf.stop,
stream=self.stream_tool_call,
user=self.user_id,
callbacks=[],
)可视化示例 - 第一轮迭代的 Prompt:
json
// prompt_messages 的内容
[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "你是一个智能助手,可以调用工具帮助用户完成任务"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "北京今天天气怎么样?顺便帮我搜索一下明天的航班"
}
]
// prompt_messages_tools (传给 LLM 的工具定义)
[
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "查询指定城市的天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {"type": "string", "description": "城市名称"}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
},
{
"name": "search_flights",
"description": "搜索航班信息",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"date": {"type": "string", "description": "日期 YYYY-MM-DD"}
},
"required": ["date"]
}
}
]_organize_prompt_messages
这个函数负责把历史对话、当前问题、工具调用结果组合成完整的 Prompt:
python
def _organize_prompt_messages(self):
# 🔍 获取系统提示词模板
prompt_template = self.app_config.prompt_template.simple_prompt_template or ""
# 🔍 初始化系统消息
self.history_prompt_messages = self._init_system_message(prompt_template, self.history_prompt_messages)
# 🔍 组织用户查询(可能包含图片等文件)
query_prompt_messages = self._organize_user_query(self.query or "", [])
# 🔍 使用 AgentHistoryPromptTransform 整合历史记录
self.history_prompt_messages = AgentHistoryPromptTransform(
model_config=self.model_config,
prompt_messages=[*query_prompt_messages, *self._current_thoughts],
history_messages=self.history_prompt_messages,
memory=self.memory,
).get_prompt()
# 🔍 最终的 Prompt = 历史 + 当前问题 + 当前思考
prompt_messages = [*self.history_prompt_messages, *query_prompt_messages, *self._current_thoughts]
if len(self._current_thoughts) != 0:
# 🔍 第二轮后需要清理图片消息(避免重复发送)
# clear messages after the first iteration
prompt_messages = self._clear_user_prompt_image_messages(prompt_messages)
return prompt_messages第三部分:模型调用与响应解析
LLM 层 - LargeLanguageModel.invoke()
这是统一的模型调用入口:
python
def invoke(
self,
model: str,
credentials: dict,
prompt_messages: list[PromptMessage],
model_parameters: dict | None = None,
tools: list[PromptMessageTool] | None = None,
stop: list[str] | None = None,
stream: bool = True,
user: str | None = None,
callbacks: list[Callback] | None = None,
) -> Union[LLMResult, Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None]]:
"""
Invoke large language model
调用大语言模型
:param model: 模型名称(如 "gpt-4")
:param credentials: 模型凭证(API Key 等)
:param prompt_messages: Prompt 消息列表
:param model_parameters: 模型参数(temperature, max_tokens 等)
:param tools: 工具列表(Function Calling 使用)
:param stop: 停止词
:param stream: 是否流式返回
:param user: 用户 ID
:param callbacks: 回调函数
:return: 流式结果生成器 或 完整结果
"""
# 🔍 参数验证
if model_parameters is None:
model_parameters = {}
# 🔍 记录开始时间(用于计算延迟)
self.started_at = time.perf_counter()
callbacks = callbacks or []
if dify_config.DEBUG:
callbacks.append(LoggingCallback())
# 🔍 触发调用前回调(用于日志、监控)
# trigger before invoke callbacks
self._trigger_before_invoke_callbacks(
model=model,
credentials=credentials,
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
model_parameters=model_parameters,
tools=tools,
stop=stop,
stream=stream,
user=user,
callbacks=callbacks,
)
result: Union[LLMResult, Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None]]
try:
# 🔍 【核心】通过插件系统调用实际的 LLM
from core.plugin.impl.model import PluginModelClient
plugin_model_manager = PluginModelClient()
result = plugin_model_manager.invoke_llm(
tenant_id=self.tenant_id,
user_id=user or "unknown",
plugin_id=self.plugin_id,
provider=self.provider_name, # 如 "openai"
model=model, # 如 "gpt-4"
credentials=credentials,
model_parameters=model_parameters,
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
tools=tools,
stop=list(stop) if stop else None,
stream=stream,
)时序图 - LLM 调用流程:
OpenAI API PluginModelClient LargeLanguageModel FunctionCallAgentRunner OpenAI API PluginModelClient LargeLanguageModel FunctionCallAgentRunner 记录调用开始 发送请求 包含 tools 定义 流式返回 包含 tool_calls 处理流式响应 累计 token 使用量 逐块接收 检查 tool_calls invoke_llm(prompt, tools) _trigger_before_invoke_callbacks() invoke_llm(provider="openai") POST /v1/chat/completions Stream Response Generator[LLMResultChunk] _invoke_result_generator() yield LLMResultChunk
解析 LLM 返回的 tool_calls
回到 FunctionCallAgentRunner,继续处理响应:
python
tool_calls: list[tuple[str, str, dict[str, Any]]] = []
# 🔍 保存模型的完整响应
# save full response
response = ""
# 🔍 保存工具调用的名称和参数
# save tool call names and inputs
tool_call_names = ""
tool_call_inputs = ""
current_llm_usage = None
# 🔍 如果是流式响应
if isinstance(chunks, Generator):
is_first_chunk = True
for chunk in chunks:
if is_first_chunk:
# 🔍 发布 AgentThought 事件(前端开始显示思考过程)
self.queue_manager.publish(
QueueAgentThoughtEvent(agent_thought_id=agent_thought_id), PublishFrom.APPLICATION_MANAGER
)
is_first_chunk = False
# 🔍 【关键】检查是否有工具调用
# check if there is any tool call
if self.check_tool_calls(chunk):
function_call_state = True # 标记有工具调用,需要下一轮迭代
tool_calls.extend(self.extract_tool_calls(chunk) or [])
tool_call_names = ";".join([tool_call[1] for tool_call in tool_calls])
try:
# 🔍 序列化工具调用参数
tool_call_inputs = json.dumps(
{tool_call[1]: tool_call[2] for tool_call in tool_calls}, ensure_ascii=False
)
except TypeError:
# fallback: force ASCII to handle non-serializable objects
tool_call_inputs = json.dumps({tool_call[1]: tool_call[2] for tool_call in tool_calls})
# 🔍 累积模型的文本回复
if chunk.delta.message and chunk.delta.message.content:
if isinstance(chunk.delta.message.content, list):
for content in chunk.delta.message.content:
response += content.data
else:
response += str(chunk.delta.message.content)
# 🔍 累计 Token 使用量
if chunk.delta.usage:
increase_usage(llm_usage, chunk.delta.usage)
current_llm_usage = chunk.delta.usage
# 🔍 向前端流式推送结果
yield chunk
else:
# 🔍 非流式响应的处理逻辑(类似)
result = chunks
# check if there is any tool call
if self.check_blocking_tool_calls(result):
function_call_state = True
tool_calls.extend(self.extract_blocking_tool_calls(result) or [])
tool_call_names = ";".join([tool_call[1] for tool_call in tool_calls])
try:
tool_call_inputs = json.dumps(
{tool_call[1]: tool_call[2] for tool_call in tool_calls}, ensure_ascii=False
)
except TypeError:
# fallback: force ASCII to handle non-serializable objects
tool_call_inputs = json.dumps({tool_call[1]: tool_call[2] for tool_call in tool_calls})
if result.usage:
increase_usage(llm_usage, result.usage)
current_llm_usage = result.usage
if result.message and result.message.content:
if isinstance(result.message.content, list):
for content in result.message.content:
response += content.data
else:
response += str(result.message.content)
if not result.message.content:
result.message.content = ""
self.queue_manager.publish(
QueueAgentThoughtEvent(agent_thought_id=agent_thought_id), PublishFrom.APPLICATION_MANAGER
)
yield LLMResultChunk(
model=model_instance.model,
prompt_messages=result.prompt_messages,
system_fingerprint=result.system_fingerprint,
delta=LLMResultChunkDelta(
index=0,
message=result.message,
usage=result.usage,
),
)可视化示例 - LLM 返回的 tool_calls:
json
// 第一轮 LLM 返回
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": null, // 没有文本回复
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_abc123",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"city\": \"北京\"}"
}
}
]
}
// extract_tool_calls 解析后
tool_calls = [
("call_abc123", "get_weather", {"city": "北京"})
// (tool_call_id, tool_name, tool_args)
]第四部分:执行工具调用
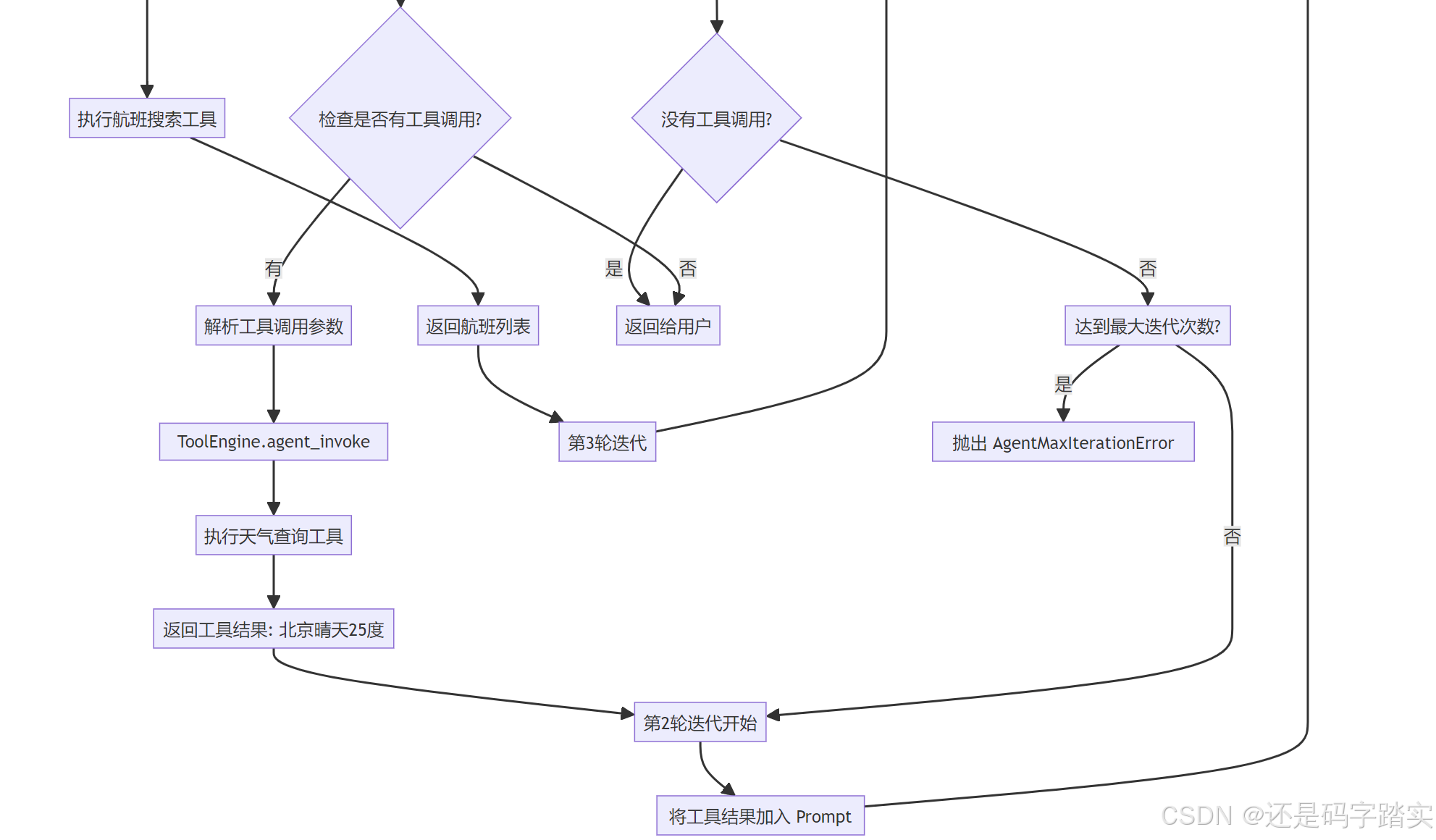
遍历 tool_calls 并执行
python
# 🔍 【核心】调用工具
# call tools
tool_responses = []
for tool_call_id, tool_call_name, tool_call_args in tool_calls:
# 🔍 从工具实例字典中获取工具
tool_instance = tool_instances.get(tool_call_name)
if not tool_instance:
# 🔍 工具不存在,返回错误信息
tool_response = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"tool_call_name": tool_call_name,
"tool_response": f"there is not a tool named {tool_call_name}",
"meta": ToolInvokeMeta.error_instance(f"there is not a tool named {tool_call_name}").to_dict(),
}
else:
# 🔍 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐【重要】调用 ToolEngine 执行工具
# invoke tool
tool_invoke_response, message_files, tool_invoke_meta = ToolEngine.agent_invoke(
tool=tool_instance,
tool_parameters=tool_call_args,
user_id=self.user_id,
tenant_id=self.tenant_id,
message=self.message,
invoke_from=self.application_generate_entity.invoke_from,
agent_tool_callback=self.agent_callback,
trace_manager=trace_manager,
app_id=self.application_generate_entity.app_config.app_id,
message_id=self.message.id,
conversation_id=self.conversation.id,
)
# 🔍 发布工具生成的文件(如图片)
# publish files
for message_file_id in message_files:
# publish message file
self.queue_manager.publish(
QueueMessageFileEvent(message_file_id=message_file_id), PublishFrom.APPLICATION_MANAGER
)
# add message file ids
message_file_ids.append(message_file_id)
tool_response = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"tool_call_name": tool_call_name,
"tool_response": tool_invoke_response,
"meta": tool_invoke_meta.to_dict(),
}
tool_responses.append(tool_response)
# 🔍 将工具结果添加到 _current_thoughts(下一轮会加入 Prompt)
if tool_response["tool_response"] is not None:
self._current_thoughts.append(
ToolPromptMessage(
content=str(tool_response["tool_response"]),
tool_call_id=tool_call_id,
name=tool_call_name,
)
)ToolEngine.agent_invoke 详解
这是工具执行的核心引擎:
python
@staticmethod
def agent_invoke(
tool: Tool,
tool_parameters: Union[str, dict],
user_id: str,
tenant_id: str,
message: Message,
invoke_from: InvokeFrom,
agent_tool_callback: DifyAgentCallbackHandler,
trace_manager: TraceQueueManager | None = None,
conversation_id: str | None = None,
app_id: str | None = None,
message_id: str | None = None,
) -> tuple[str, list[str], ToolInvokeMeta]:
"""
Agent invokes the tool with the given arguments.
Agent 调用工具
"""
# 🔍 【Step 1】参数类型转换
# check if arguments is a string
if isinstance(tool_parameters, str):
# 🔍 如果工具只有一个参数,直接用字符串
# check if this tool has only one parameter
parameters = [
parameter
for parameter in tool.get_runtime_parameters()
if parameter.form == ToolParameter.ToolParameterForm.LLM
]
if parameters and len(parameters) == 1:
tool_parameters = {parameters[0].name: tool_parameters}
else:
# 🔍 否则尝试解析 JSON
with contextlib.suppress(Exception):
tool_parameters = json.loads(tool_parameters)
if not isinstance(tool_parameters, dict):
raise ValueError(f"tool_parameters should be a dict, but got a string: {tool_parameters}")
try:
# 🔍 【Step 2】触发工具调用开始回调
# hit the callback handler
agent_tool_callback.on_tool_start(tool_name=tool.entity.identity.name, tool_inputs=tool_parameters)
# 🔍 【Step 3】执行工具的 _invoke 方法
messages = ToolEngine._invoke(tool, tool_parameters, user_id, conversation_id, app_id, message_id)
invocation_meta_dict: dict[str, ToolInvokeMeta] = {}
# 🔍 【Step 4】处理工具返回的消息
def message_callback(
invocation_meta_dict: dict, messages: Generator[ToolInvokeMessage | ToolInvokeMeta, None, None]
):
for message in messages:
if isinstance(message, ToolInvokeMeta):
invocation_meta_dict["meta"] = message
else:
yield message
# 🔍 【Step 5】转换工具消息(处理文件上传等)
messages = ToolFileMessageTransformer.transform_tool_invoke_messages(
messages=message_callback(invocation_meta_dict, messages),
user_id=user_id,
tenant_id=tenant_id,
conversation_id=message.conversation_id,
)
message_list = list(messages)
# 🔍 【Step 6】提取二进制文件(图片、音频等)
# extract binary data from tool invoke message
binary_files = ToolEngine._extract_tool_response_binary_and_text(message_list)
# 🔍 【Step 7】创建消息文件记录
# create message file
message_files = ToolEngine._create_message_files(
tool_messages=binary_files, agent_message=message, invoke_from=invoke_from, user_id=user_id
)
# 🔍 【Step 8】转换为纯文本(给 LLM 看的)
plain_text = ToolEngine._convert_tool_response_to_str(message_list)
meta = invocation_meta_dict["meta"]
# 🔍 【Step 9】触发工具调用结束回调
# hit the callback handler
agent_tool_callback.on_tool_end(
tool_name=tool.entity.identity.name,
tool_inputs=tool_parameters,
tool_outputs=plain_text,
message_id=message.id,
trace_manager=trace_manager,
)
# 🔍 【Step 10】返回结果
# transform tool invoke message to get LLM friendly message
return plain_text, message_files, meta可视化示例 - 工具执行结果:
python
# 天气查询工具返回
plain_text = "北京今天天气:晴,温度25°C,湿度60%,风力3级"
message_files = [] # 没有文件
tool_invoke_meta = {
"time_cost": 0.234, # 耗时 234ms
"error": None,
"tool_config": {
"tool_name": "get_weather",
"tool_provider": "weather_api"
}
}第五部分:第二轮迭代与最终答案
将工具结果加入 Prompt 后重新调用 LLM
python
if len(tool_responses) > 0:
# 🔍 保存工具调用结果到数据库
# save agent thought
self.save_agent_thought(
agent_thought_id=agent_thought_id,
tool_name="",
tool_input="",
thought="",
tool_invoke_meta={
tool_response["tool_call_name"]: tool_response["meta"] for tool_response in tool_responses
},
observation={
tool_response["tool_call_name"]: tool_response["tool_response"]
for tool_response in tool_responses
},
answer="",
messages_ids=message_file_ids,
)
self.queue_manager.publish(
QueueAgentThoughtEvent(agent_thought_id=agent_thought_id), PublishFrom.APPLICATION_MANAGER
)
# 🔍 更新工具的 Prompt 定义(某些工具参数可能动态变化)
# update prompt tool
for prompt_tool in prompt_messages_tools:
self.update_prompt_message_tool(tool_instances[prompt_tool.name], prompt_tool)
# 🔍 【关键】迭代计数器加1,回到 while 循环开始
iteration_step += 1第二轮迭代的 Prompt 示例:
json
[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "你是一个智能助手,可以调用工具帮助用户完成任务"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "北京今天天气怎么样?顺便帮我搜索一下明天的航班"
},
// ===== 新增:第一轮的工具调用记录 =====
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_abc123",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"city\": \"北京\"}"
}
}
]
},
// ===== 新增:工具执行结果 =====
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": "call_abc123",
"name": "get_weather",
"content": "北京今天天气:晴,温度25°C,湿度60%,风力3级"
}
]LLM 看到工具结果后,可能继续调用航班搜索工具,或者直接返回最终答案。
循环终止与最终答案
python
# 🔍 循环结束后,发布最终结果
# publish end event
self.queue_manager.publish(
QueueMessageEndEvent(
llm_result=LLMResult(
model=model_instance.model,
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
message=AssistantPromptMessage(content=final_answer),
usage=llm_usage["usage"] or LLMUsage.empty_usage(),
system_fingerprint="",
)
),
PublishFrom.APPLICATION_MANAGER,
)完整时序图
数据库 天气工具 ToolEngine OpenAI API PluginModelClient LargeLanguageModel FunctionCallAgentRunner API 层 用户 数据库 天气工具 ToolEngine OpenAI API PluginModelClient LargeLanguageModel FunctionCallAgentRunner API 层 用户 第1轮迭代开始 发现调用 get_weather 第2轮迭代开始 类似流程调用航班搜索工具 第3轮迭代 POST 查询天气+航班 1 run(query) 2 _init_prompt_tools() 初始化工具列表 3 _organize_prompt_messages() 组织 Prompt 4 create_agent_thought() 创建思考记录 5 invoke_llm(prompt, tools) 6 invoke_llm() 7 POST /v1/chat/completions 8 Stream: tool_calls 9 LLMResultChunk 10 yield chunk 11 extract_tool_calls() 解析工具调用 12 agent_invoke(get_weather, {city: 北京}) 13 _invoke({city: 北京}) 14 晴 25°C 15 create_message_files() 保存文件(如有) 16 (plain_text, files, meta) 17 _current_thoughts.append(ToolPromptMessage) 18 save_agent_thought() 保存工具结果 19 _organize_prompt_messages() 包含工具结果 20 invoke_llm(prompt+tool_result, tools) 21 invoke_llm() 22 POST /v1/chat/completions 23 Stream: tool_calls (search_flights) 24 invoke_llm(...) 25 Stream: 最终答案(无 tool_calls) 26 function_call_state = False 退出循环 27 QueueMessageEndEvent 28 返回完整答案 29
关键数据结构可视化
AgentThought(推理步骤记录)
python
# 数据库中存储的每一步推理
{
"id": "thought_001",
"message_id": "msg_123",
"position": 1, # 第1步
# 模型的思考
"thought": "", # Function Calling 模式下通常为空
# 调用的工具
"tool": "get_weather",
"tool_input": '{"city": "北京"}',
# 工具返回
"observation": "晴 25°C",
# Token 消耗
"message_token": 150, # Prompt tokens
"answer_token": 30, # Completion tokens
"total_price": 0.0027, # 费用
# 元数据
"tool_meta_str": '{"time_cost": 0.234}',
"created_at": "2024-01-20 10:30:00"
}PromptMessage 类型
python
# 第二轮迭代的完整 Prompt 结构
prompt_messages = [
SystemPromptMessage(content="你是智能助手..."),
UserPromptMessage(content="北京天气+航班"),
# 第一轮 LLM 响应
AssistantPromptMessage(
content=None,
tool_calls=[
ToolCall(
id="call_abc",
function=ToolCallFunction(
name="get_weather",
arguments='{"city":"北京"}'
)
)
]
),
# 工具执行结果
ToolPromptMessage(
tool_call_id="call_abc",
name="get_weather",
content="晴 25°C"
)
]安全机制可视化
死循环防护
python
# 配置
max_iteration = 10
# 执行流程
iteration_step = 1
while function_call_state and iteration_step <= 11: # max+1
if iteration_step == 11:
# 🚨 最后一轮,强制终止
prompt_messages_tools = [] # 移除所有工具
# ... 调用 LLM ...
if iteration_step == 11 and tool_calls:
# 🚨 模型还想调用工具,抛出异常
raise AgentMaxIterationError(10)
iteration_step += 1
# 正常情况:function_call_state 变为 False,退出循环Token 计费追踪
python
# 每轮累加
llm_usage = {
"prompt_tokens": 0,
"completion_tokens": 0,
"total_price": 0.0
}
# 第1轮:150 + 30 = 180 tokens
# 第2轮:200 + 40 = 240 tokens
# 第3轮:180 + 100 = 280 tokens
# 总计:700 tokens,费用 $0.0105抽象工厂模式 --- 模型适配器层标准化
生活类比:外卖平台
想象你在用美团外卖点餐:
- 你(用户):想吃披萨
- 美团(抽象工厂):帮你找餐厅
- 不同餐厅(OpenAI/Claude/DeepSeek):各有自己的做法
- 统一接口:你不管哪家餐厅,都通过美团下单,格式统一
Dify 的模型层就是这个"美团平台"!
场景示例:调用 GPT-4 生成文本
假设 Agent 需要调用 GPT-4 来思考下一步操作:
python
# 用户代码(简化版)
response = model_instance.invoke_llm(
prompt_messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "北京今天天气如何?"}
],
tools=[weather_tool], # 可用的工具
stream=True
)完整调用链路图
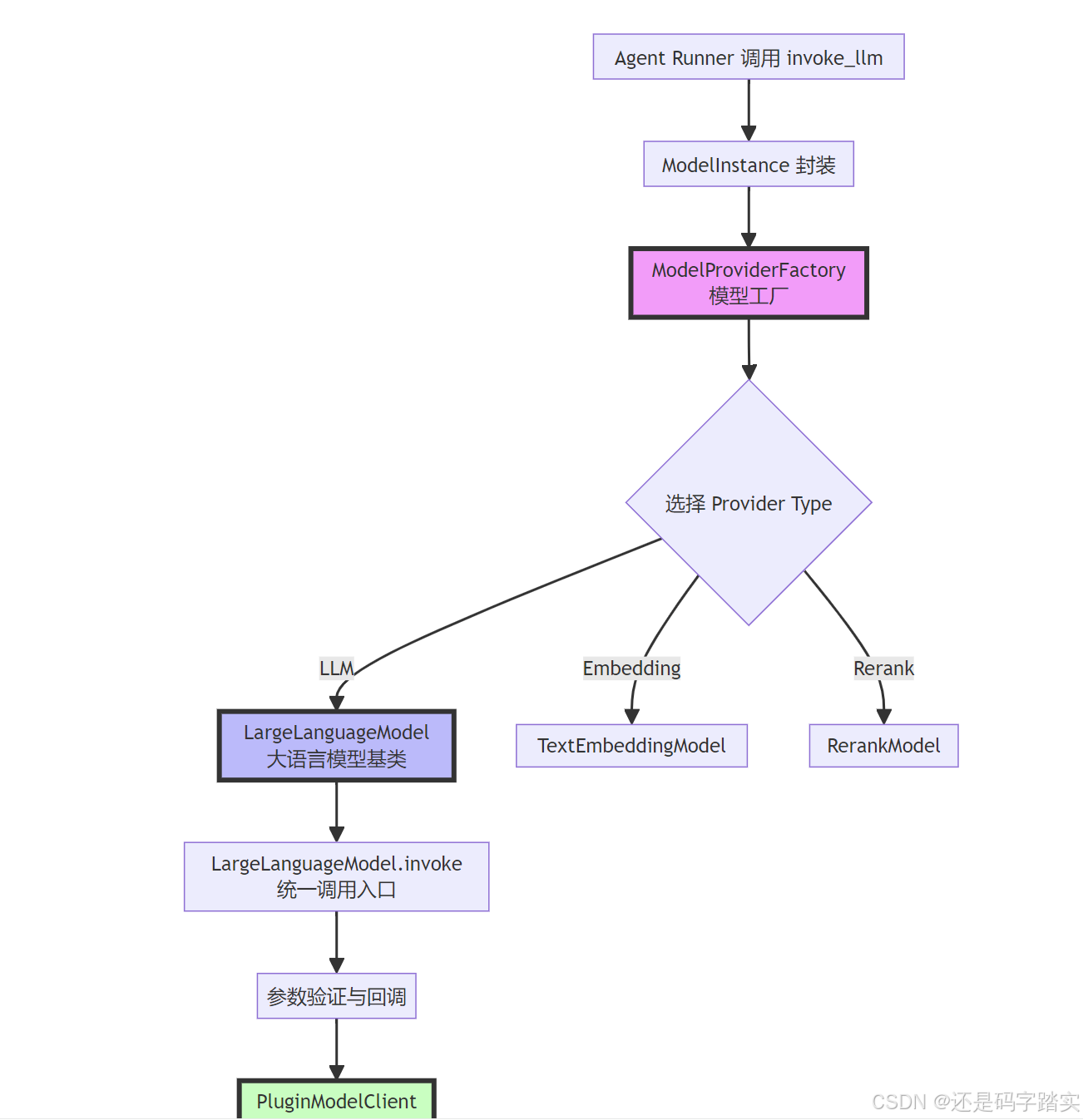
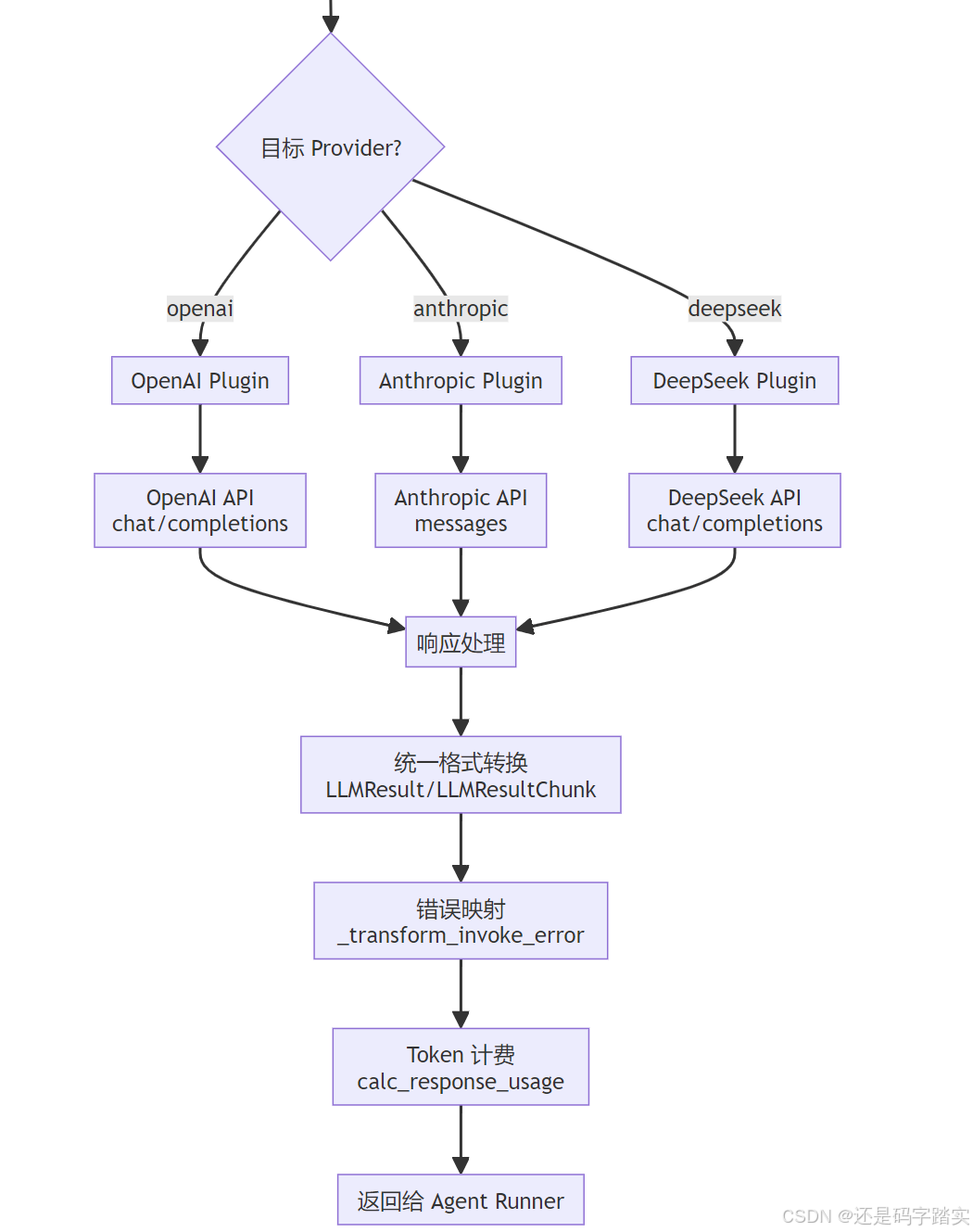
工厂创建 - ModelProviderFactory
Agent 需要获取一个 LLM 实例
python
# 在 Agent 初始化时
factory = ModelProviderFactory(tenant_id="tenant_123")
llm_instance = factory.get_model_type_instance(
provider="openai", # 指定供应商
model_type=ModelType.LLM # 指定类型
)源码是如何实现的:
api/core/model_runtime/model_providers/model_provider_factory.py
python
def get_model_type_instance(self, provider: str, model_type: ModelType) -> AIModel:
"""
Get model type instance by provider name and model type
根据供应商名称和模型类型获取模型实例
:param provider: provider name (如 "openai", "anthropic")
:param model_type: model type (如 ModelType.LLM, ModelType.TEXT_EMBEDDING)
:return: model type instance (返回对应的模型实例)
"""
# 🔍 【Step 1】解析 provider 字符串
# 分离出 plugin_id 和 provider_name
# 例如:"openai" -> ("builtin", "openai")
plugin_id, provider_name = self.get_plugin_id_and_provider_name_from_provider(provider)
# 🔍 【Step 2】准备初始化参数
init_params = {
"tenant_id": self.tenant_id, # 租户 ID(多租户隔离)
"plugin_id": plugin_id, # 插件 ID
"provider_name": provider_name, # 供应商名称
"plugin_model_provider": self.get_plugin_model_provider(provider), # 供应商配置
}
# 🔍 【Step 3】根据模型类型创建对应实例(工厂模式核心)
if model_type == ModelType.LLM:
return LargeLanguageModel.model_validate(init_params)
elif model_type == ModelType.TEXT_EMBEDDING:
return TextEmbeddingModel.model_validate(init_params)
elif model_type == ModelType.RERANK:
return RerankModel.model_validate(init_params)
elif model_type == ModelType.SPEECH2TEXT:
return Speech2TextModel.model_validate(init_params)
elif model_type == ModelType.MODERATION:
return ModerationModel.model_validate(init_params)
elif model_type == ModelType.TTS:
return TTSModel.model_validate(init_params)关键注释解读:
- plugin_id 解析 :Dify 使用插件系统,每个模型供应商都是一个插件
builtin/openai→ 内置的 OpenAI 插件custom/my-model→ 用户自定义插件
- 工厂模式体现 :根据
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">model_type</font>返回不同的类实例,但它们都继承自<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">AIModel</font>基类 - Pydantic 验证 :
model_validate(init_params)会自动验证参数并创建实例
可视化示例
python
# 输入
provider = "openai"
model_type = ModelType.LLM
# 内部处理
plugin_id = "builtin"
provider_name = "openai"
# 输出
llm_instance = LargeLanguageModel(
tenant_id="tenant_123",
plugin_id="builtin",
provider_name="openai",
model_type=ModelType.LLM,
plugin_model_provider=<PluginModelProviderEntity>
)统一基类 - AIModel
所有模型实例都继承自 AIModel,它定义了通用能力:
api/core/model_runtime/model_providers/__base/ai_model.py
python
class AIModel(BaseModel):
"""
Base class for all models.
所有模型的基类
"""
# 🔍 【属性定义】每个模型实例都有这些属性
tenant_id: str = Field(description="Tenant ID")
model_type: ModelType = Field(description="Model type")
plugin_id: str = Field(description="Plugin ID")
provider_name: str = Field(description="Provider")
plugin_model_provider: PluginModelProviderEntity = Field(description="Plugin model provider")
started_at: float = Field(description="Invoke start time", default=0)
# pydantic configs
model_config = ConfigDict(protected_namespaces=())
@property
def _invoke_error_mapping(self) -> dict[type[Exception], list[type[Exception]]]:
"""
Map model invoke error to unified error
将模型调用错误映射为统一错误
The key is the error type thrown to the caller
键是抛给调用者的错误类型
The value is the error type thrown by the model,
which needs to be converted into a unified error type for the caller.
值是模型抛出的错误类型,需要转换为统一的错误类型
:return: Invoke error mapping
"""
from core.plugin.entities.plugin_daemon import PluginDaemonInnerError
# 🔍 【错误映射表】不同 API 的错误统一转换
return {
InvokeConnectionError: [InvokeConnectionError], # 连接错误
InvokeServerUnavailableError: [InvokeServerUnavailableError], # 服务不可用
InvokeRateLimitError: [InvokeRateLimitError], # 速率限制
InvokeAuthorizationError: [InvokeAuthorizationError], # 认证错误
InvokeBadRequestError: [InvokeBadRequestError], # 请求错误
PluginDaemonInnerError: [PluginDaemonInnerError], # 插件内部错误
ValueError: [ValueError],
}
def _transform_invoke_error(self, error: Exception) -> Exception:
"""
Transform invoke error to unified error
转换调用错误为统一错误
:param error: model invoke error (模型调用错误)
:return: unified error (统一错误)
"""
# 🔍 【错误转换逻辑】遍历映射表,找到匹配的错误类型
for invoke_error, model_errors in self._invoke_error_mapping.items():
if isinstance(error, tuple(model_errors)):
# 🔍 特殊处理认证错误,添加供应商信息
if invoke_error == InvokeAuthorizationError:
return InvokeAuthorizationError(
description=(
f"[{self.provider_name}] Incorrect model credentials provided, please check and try again."
)
)
elif isinstance(invoke_error, InvokeError):
return InvokeError(description=f"[{self.provider_name}] {invoke_error.description}, {str(error)}")
else:
return error
# 🔍 如果没有匹配的,返回通用错误
return InvokeError(description=f"[{self.provider_name}] Error: {str(error)}")关键能力:
- 统一属性 :所有模型都有
tenant_id、provider_name等 - 错误标准化 :不同 API 的错误(OpenAI 429、Anthropic 529)统一转为
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">InvokeRateLimitError</font> - 多租户支持 :通过
tenant_id隔离不同租户的调用
价格计算标准化
python
def get_price(self, model: str, credentials: dict, price_type: PriceType, tokens: int) -> PriceInfo:
"""
Get price for given model and tokens
根据模型和 Token 数计算价格
:param model: model name (模型名称,如 "gpt-4")
:param credentials: model credentials (模型凭证)
:param price_type: price type (价格类型:INPUT 或 OUTPUT)
:param tokens: number of tokens (Token 数量)
:return: price info (价格信息)
"""
# 🔍 【Step 1】获取模型配置信息
# get model schema
model_schema = self.get_model_schema(model, credentials)
# 🔍 【Step 2】从配置中提取价格信息
# get price info from predefined model schema
price_config: PriceConfig | None = None
if model_schema and model_schema.pricing:
price_config = model_schema.pricing
# 🔍 【Step 3】获取单价
# get unit price
unit_price = None
if price_config:
if price_type == PriceType.INPUT:
unit_price = price_config.input # 输入 Token 单价
elif price_type == PriceType.OUTPUT and price_config.output is not None:
unit_price = price_config.output # 输出 Token 单价
# 🔍 【Step 4】如果没有价格信息,返回免费
if unit_price is None:
return PriceInfo(
unit_price=decimal.Decimal("0.0"),
unit=decimal.Decimal("0.0"),
total_amount=decimal.Decimal("0.0"),
currency="USD",
)
# 🔍 【Step 5】计算总费用
# calculate total amount
if not price_config:
raise ValueError(f"Price config not found for model {model}")
total_amount = tokens * unit_price * price_config.unit
# 🔍 保留7位小数,四舍五入
total_amount = total_amount.quantize(decimal.Decimal("0.0000001"), rounding=decimal.ROUND_HALF_UP)
return PriceInfo(
unit_price=unit_price,
unit=price_config.unit,
total_amount=total_amount,
currency=price_config.currency,
)可视化示例 - 价格计算:
python
# 假设 GPT-4 价格配置
price_config = {
"input": 0.00003, # $0.03 / 1K tokens
"output": 0.00006, # $0.06 / 1K tokens
"unit": 0.001, # 单位是 1K tokens
"currency": "USD"
}
# 输入:1500 tokens
input_price = 1500 * 0.00003 * 0.001 = $0.000045
# 输出:500 tokens
output_price = 500 * 0.00006 * 0.001 = $0.00003
# 总费用:$0.000075LLM 调用入口 - LargeLanguageModel.invoke
这是所有 LLM 调用的统一入口!
api/core/model_runtime/model_providers/__base/large_language_model.py
python
def invoke(
self,
model: str,
credentials: dict,
prompt_messages: list[PromptMessage],
model_parameters: dict | None = None,
tools: list[PromptMessageTool] | None = None,
stop: list[str] | None = None,
stream: bool = True,
user: str | None = None,
callbacks: list[Callback] | None = None,
) -> Union[LLMResult, Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None]]:
"""
Invoke large language model
调用大语言模型
:param model: model name (模型名称,如 "gpt-4-turbo")
:param credentials: model credentials (凭证,如 API Key)
:param prompt_messages: prompt messages (Prompt 消息列表)
:param model_parameters: model parameters (模型参数:temperature 等)
:param tools: tools for tool calling (Function Calling 的工具列表)
:param stop: stop words (停止词)
:param stream: is stream response (是否流式返回)
:param user: unique user id (用户 ID,用于追踪)
:param callbacks: callbacks (回调函数列表)
:return: full response or stream response chunk generator result
"""
# 🔍 【Step 1】参数初始化
# validate and filter model parameters
if model_parameters is None:
model_parameters = {}
# 🔍 记录开始时间(用于计算延迟)
self.started_at = time.perf_counter()
callbacks = callbacks or []
# 🔍 调试模式下添加日志回调
if dify_config.DEBUG:
callbacks.append(LoggingCallback())
# 🔍 【Step 2】触发调用前回调
# trigger before invoke callbacks
self._trigger_before_invoke_callbacks(
model=model,
credentials=credentials,
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
model_parameters=model_parameters,
tools=tools,
stop=stop,
stream=stream,
user=user,
callbacks=callbacks,
)
result: Union[LLMResult, Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None]]
try:
# 🔍 【Step 3】通过插件客户端调用实际的 LLM
from core.plugin.impl.model import PluginModelClient
plugin_model_manager = PluginModelClient()
result = plugin_model_manager.invoke_llm(
tenant_id=self.tenant_id,
user_id=user or "unknown",
plugin_id=self.plugin_id,
provider=self.provider_name,
model=model,
credentials=credentials,
model_parameters=model_parameters,
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
tools=tools,
stop=list(stop) if stop else None,
stream=stream,
)
# 🔍 【Step 4】处理非流式响应
if not stream:
content = ""
content_list = []
usage = LLMUsage.empty_usage()
system_fingerprint = None
tools_calls: list[AssistantPromptMessage.ToolCall] = []
# 🔍 从流式结果中提取完整响应
for chunk in result:
if isinstance(chunk.delta.message.content, str):
content += chunk.delta.message.content
elif isinstance(chunk.delta.message.content, list):
content_list.extend(chunk.delta.message.content)
if chunk.delta.message.tool_calls:
_increase_tool_call(chunk.delta.message.tool_calls, tools_calls)
usage = chunk.delta.usage or LLMUsage.empty_usage()
system_fingerprint = chunk.system_fingerprint
break
# 🔍 组装成 LLMResult
result = LLMResult(
model=model,
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
message=AssistantPromptMessage(
content=content or content_list,
tool_calls=tools_calls,
),
usage=usage,
system_fingerprint=system_fingerprint,
)
except Exception as e:
# 🔍 【Step 5】错误处理
self._trigger_invoke_error_callbacks(
model=model,
ex=e,
credentials=credentials,
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
model_parameters=model_parameters,
tools=tools,
stop=stop,
stream=stream,
user=user,
callbacks=callbacks,
)
# 🔍 转换为统一错误格式
# TODO
raise self._transform_invoke_error(e)
# 🔍 【Step 6】返回结果
if stream and isinstance(result, Generator):
# 🔍 流式响应:返回生成器
return self._invoke_result_generator(
model=model,
result=result,
credentials=credentials,
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
model_parameters=model_parameters,
tools=tools,
stop=stop,
stream=stream,
user=user,
callbacks=callbacks,
)
elif isinstance(result, LLMResult):
# 🔍 非流式响应:直接返回结果
self._trigger_after_invoke_callbacks(
model=model,
result=result,
credentials=credentials,
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
model_parameters=model_parameters,
tools=tools,
stop=stop,
stream=stream,
user=user,
callbacks=callbacks,
)
# 🔍 确保 prompt_messages 被保存
# Following https://github.com/langgenius/dify/issues/17799,
# we removed the prompt_messages from the chunk on the plugin daemon side.
# To ensure compatibility, we add the prompt_messages back here.
result.prompt_messages = prompt_messages
return result
raise NotImplementedError("unsupported invoke result type", type(result))时序图 - invoke 方法调用流程
OpenAI/Claude API PluginModelClient Callbacks LargeLanguageModel Agent Runner OpenAI/Claude API PluginModelClient Callbacks LargeLanguageModel Agent Runner Step 1: 参数初始化 Step 2: 触发前置回调 Step 3: 调用插件客户端 loop [每个 chunk] alt [流式响应] [非流式响应] Step 4: 错误处理 alt [发生错误] invoke(model, prompt, tools) 1 started_at = time.perf_counter() 2 _trigger_before_invoke_callbacks() 3 记录日志/监控 4 invoke_llm(provider, model, prompt) 5 HTTP POST /v1/chat/completions 6 SSE Stream 7 Generator[LLMResultChunk] 8 _invoke_result_generator() 9 on_new_chunk() 10 yield chunk 11 _trigger_after_invoke_callbacks() 12 JSON Response 13 LLMResult 14 _trigger_after_invoke_callbacks() 15 return result 16 Error (429/500/etc) 17 Exception 18 _transform_invoke_error() 19 _trigger_invoke_error_callbacks() 20 raise InvokeError 21
插件系统 - PluginModelClient
这一层负责将请求转发给具体的模型插件:
api/core/plugin/impl/model.py
python
# 伪代码展示插件客户端的核心逻辑
class PluginModelClient:
def invoke_llm(
self,
tenant_id: str,
plugin_id: str,
provider: str, # "openai"
model: str, # "gpt-4"
credentials: dict,
prompt_messages: list[PromptMessage],
tools: list[PromptMessageTool] | None,
stream: bool
):
# 🔍 【Step 1】找到对应的插件
plugin = self._get_plugin(plugin_id, provider)
# 🔍 【Step 2】将 Dify 的标准格式转换为插件格式
plugin_request = self._convert_to_plugin_format(
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
tools=tools,
model_parameters=model_parameters
)
# 🔍 【Step 3】通过 RPC/HTTP 调用插件
if plugin.type == "remote":
response = self._call_remote_plugin(plugin.url, plugin_request)
else:
response = self._call_local_plugin(plugin, plugin_request)
# 🔍 【Step 4】将插件响应转换为 Dify 标准格式
return self._convert_from_plugin_format(response, stream)插件隔离的好处
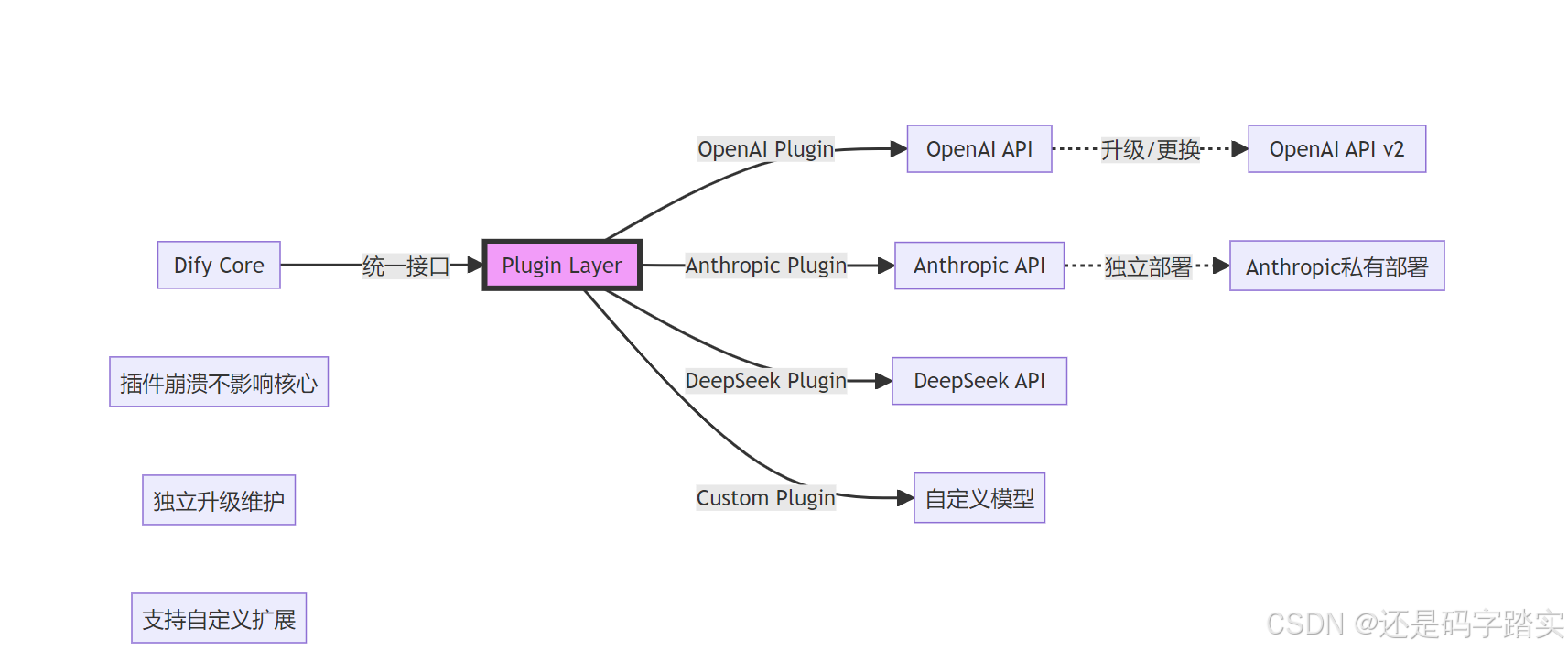
响应标准化
统一的响应格式 - LLMResult
api/core/model_runtime/entities/llm_entities.py
python
# 所有模型的响应都转换为这个格式
class LLMResult:
model: str # 实际使用的模型
prompt_messages: list[PromptMessage] # 输入的 Prompt
message: AssistantPromptMessage # 模型的回复
usage: LLMUsage # Token 使用情况
system_fingerprint: str | None # 系统指纹流式响应 - LLMResultChunk
python
class LLMResultChunk:
model: str
prompt_messages: list[PromptMessage]
delta: LLMResultChunkDelta # 增量内容
system_fingerprint: str | None
class LLMResultChunkDelta:
index: int # 序号
message: AssistantPromptMessage # 增量消息
usage: LLMUsage | None # Token 使用(最后一块才有)Token 使用统计
python
class LLMUsage:
prompt_tokens: int # 输入 Token 数
completion_tokens: int # 输出 Token 数
total_tokens: int # 总计
prompt_unit_price: Decimal # 输入单价
prompt_price_unit: Decimal # 价格单位
prompt_price: Decimal # 输入费用
completion_unit_price: Decimal # 输出单价
completion_price_unit: Decimal
completion_price: Decimal # 输出费用
total_price: Decimal # 总费用
currency: str # 货币单位
latency: float # 延迟(秒)完整示例:从输入到输出
输入示例
python
# Agent 调用
model_instance.invoke_llm(
prompt_messages=[
SystemPromptMessage(content="你是智能助手"),
UserPromptMessage(content="北京今天天气如何?")
],
tools=[
PromptMessageTool(
name="get_weather",
description="查询天气",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
)
],
model_parameters={"temperature": 0.7},
stream=True
)中间处理流程
OpenAI API OpenAI Plugin PluginModelClient LargeLanguageModel ModelProviderFactory Agent OpenAI API OpenAI Plugin PluginModelClient LargeLanguageModel ModelProviderFactory Agent 准备调用参数 Dify 格式 → OpenAI 格式 OpenAI API 处理 OpenAI 格式 → Dify 格式 loop [每个 chunk] get_model_type_instance("openai", LLM) 1 解析 plugin_id 和 provider 2 LargeLanguageModel 实例 3 invoke(model="gpt-4", prompt, tools) 4 记录开始时间 5 _trigger_before_invoke_callbacks() 6 invoke_llm(provider="openai") 7 查找 OpenAI 插件 8 转换为 OpenAI 格式 9 RPC 调用插件 10 POST /v1/chat/completions 11 SSE Stream 12 Generator[PluginResponse] 13 Generator[LLMResultChunk] 14 _trigger_new_chunk_callbacks() 15 yield LLMResultChunk 16 calc_response_usage() 17 _trigger_after_invoke_callbacks() 18
输出示例(流式)
python
# 第1个 chunk
LLMResultChunk(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
delta=LLMResultChunkDelta(
index=0,
message=AssistantPromptMessage(
content=None,
tool_calls=[
ToolCall(
id="call_abc123",
function=ToolCallFunction(
name="get_weather",
arguments='{"city":'
)
)
]
)
)
)
# 第2个 chunk(继续)
LLMResultChunkDelta(
message=AssistantPromptMessage(
tool_calls=[
ToolCall(
id="call_abc123",
function=ToolCallFunction(
arguments=' "北京"}' # 补全参数
)
)
]
)
)
# 最后一个 chunk(包含 usage)
LLMResultChunkDelta(
message=AssistantPromptMessage(content=""),
usage=LLMUsage(
prompt_tokens=150,
completion_tokens=25,
total_tokens=175,
total_price=0.00525, # $0.00525
currency="USD",
latency=1.234
)
)关键设计模式解析
抽象工厂模式(Abstract Factory)
python
# 抽象产品
class AIModel(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def invoke(self, ...):
pass
# 具体产品
class LargeLanguageModel(AIModel):
def invoke(self, ...):
# LLM 专属实现
pass
class TextEmbeddingModel(AIModel):
def invoke(self, ...):
# Embedding 专属实现
pass
# 工厂
class ModelProviderFactory:
def get_model_type_instance(self, model_type):
if model_type == ModelType.LLM:
return LargeLanguageModel(...)
elif model_type == ModelType.TEXT_EMBEDDING:
return TextEmbeddingModel(...)好处:
- ✅ 新增模型类型只需添加新的产品类
- ✅ 客户端代码不依赖具体类
- ✅ 符合开闭原则(对扩展开放,对修改封闭)
策略模式(Strategy)
不同的 Provider(OpenAI、Claude)是不同的策略:
python
# 策略接口(通过插件实现)
class ModelProviderPlugin(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def invoke_llm(self, prompt, tools):
pass
# 具体策略
class OpenAIPlugin(ModelProviderPlugin):
def invoke_llm(self, prompt, tools):
# 调用 OpenAI API
return openai.ChatCompletion.create(...)
class AnthropicPlugin(ModelProviderPlugin):
def invoke_llm(self, prompt, tools):
# 调用 Anthropic API
return anthropic.messages.create(...)
# 上下文
class PluginModelClient:
def invoke_llm(self, provider, ...):
plugin = self._get_plugin(provider)
return plugin.invoke_llm(...) # 动态选择策略模板方法模式(Template Method)
LargeLanguageModel.invoke 定义了调用模板:
python
def invoke(self, ...):
# 1. 前置处理(模板固定)
self._trigger_before_invoke_callbacks(...)
try:
# 2. 实际调用(子类实现)
result = self._do_invoke(...)
# 3. 结果处理(模板固定)
if stream:
return self._invoke_result_generator(...)
else:
return result
except Exception as e:
# 4. 错误处理(模板固定)
self._trigger_invoke_error_callbacks(...)
raise self._transform_invoke_error(e)
finally:
# 5. 后置处理(模板固定)
self._trigger_after_invoke_callbacks(...)架构优势可视化
添加新模型供应商
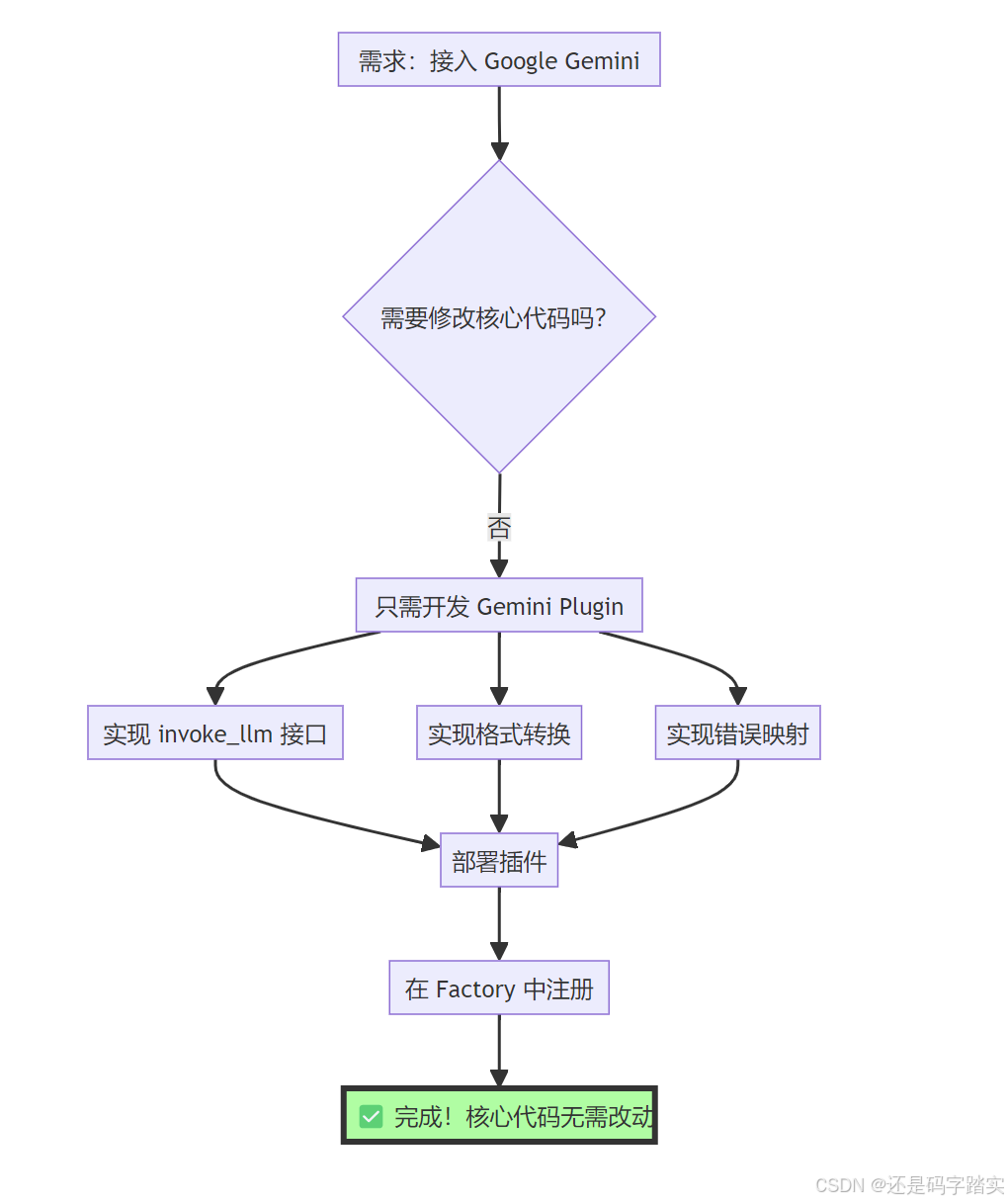
模型切换无缝化
python
# 用户代码完全不变
response = model_instance.invoke_llm(
prompt_messages=[...],
tools=[...]
)
# 只需修改配置
# config.yaml
model:
# provider: "openai" # 旧配置
provider: "anthropic" # 新配置
# model: "gpt-4"
model: "claude-3-opus"
# 所有错误处理、Token 统计、回调逻辑自动适配!关键优势
| 传统方式 | Dify 抽象工厂模式 |
|---|---|
| 代码耦合各 API | 插件隔离,核心解耦 |
| 切换模型需大改代码 | 改配置文件即可 |
| 错误处理各不相同 | 统一错误映射 |
| Token 统计逻辑分散 | 统一计费逻辑 |
| 新增模型影响全局 | 只需添加插件 |
ReAct vs Function Calling 深度对比
测试场景
用户提问 :"帮我查一下北京天气,如果是晴天就推荐一个景点"
模式对比总览
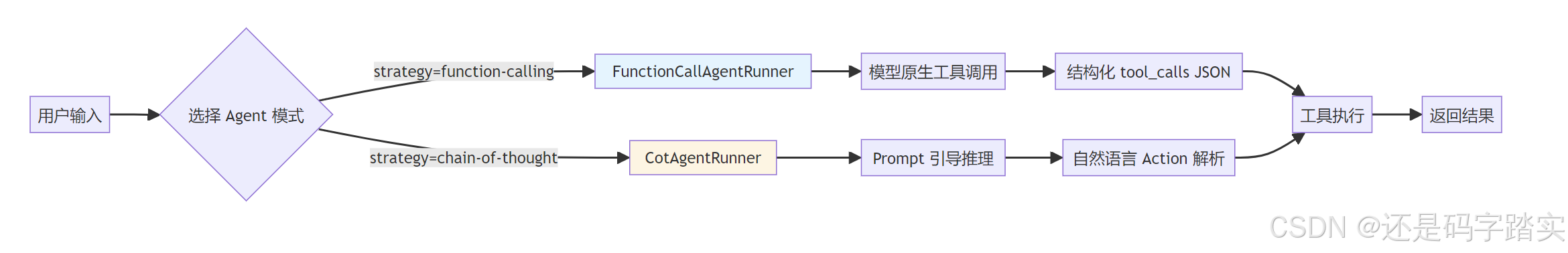
| 对比维度 | Function Calling | ReAct (CoT) |
|---|---|---|
| 适用模型 | GPT-4, Claude 3+, Gemini Pro | 任意文本生成模型 |
| 工具传递方式 | JSON Schema(<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">tools</font> 参数) |
自然语言 Prompt 模板 |
| 模型输出 | 结构化 <font style="color:#DF2A3F;">tool_calls</font> 对象 |
自然语言 "Action: xxx\nAction Input: yyy" |
| 解析方式 | 直接提取 JSON | 正则表达式 + 文本解析 |
| 推理透明度 | 黑盒(模型内部决策) | 白盒(可见 Thought 过程) |
| 可靠性 | 高(格式保证) | 中(依赖 Prompt 质量) |
| Stop 序列 | 无需特殊处理 | 必须添加 "Observation" |
模式一:Function Calling 详细链路
步骤 1:初始化工具列表(两种模式相同)
python
# 位置:BaseAgentRunner._init_prompt_tools()
def _init_prompt_tools(self) -> tuple[dict[str, Tool], list[PromptMessageTool]]:
"""
初始化工具
返回:(工具实例字典, Prompt 工具列表)
"""
tool_instances = {}
prompt_messages_tools = []
# 🔍 遍历配置的工具列表
for tool in self.app_config.agent.tools or []:
try:
# 🔍⭐⭐⭐⭐【关键】转换为 PromptMessageTool
prompt_tool, tool_entity = self._convert_tool_to_prompt_message_tool(tool)
except Exception:
continue
tool_instances[tool.tool_name] = tool_entity
prompt_messages_tools.append(prompt_tool)
return tool_instances, prompt_messages_tools工具转换函数
python
def _convert_tool_to_prompt_message_tool(self, tool: AgentToolEntity) -> tuple[PromptMessageTool, Tool]:
"""
convert tool to prompt message tool
将 AgentToolEntity 转为 PromptMessageTool(LLM 能理解的格式)
"""
# 🔍 获取工具的运行时实例
tool_entity = ToolManager.get_agent_tool_runtime(
tenant_id=self.tenant_id,
app_id=self.app_config.app_id,
agent_tool=tool,
invoke_from=self.application_generate_entity.invoke_from,
)
assert tool_entity.entity.description
# 🔍 【关键】创建 PromptMessageTool(OpenAI Function 格式)
message_tool = PromptMessageTool(
name=tool.tool_name,
description=tool_entity.entity.description.llm,
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {},
"required": [],
},
)
# 🔍 遍历工具参数,构建 JSON Schema
parameters = tool_entity.get_merged_runtime_parameters()
for parameter in parameters:
if parameter.form != ToolParameter.ToolParameterForm.LLM:
continue
parameter_type = parameter.type.as_normal_type()
# 🔍 跳过文件类型参数
if parameter.type in {
ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.SYSTEM_FILES,
ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.FILE,
ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.FILES,
}:
continue
enum = []
if parameter.type == ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.SELECT:
enum = [option.value for option in parameter.options] if parameter.options else []
# 🔍 添加参数到 properties
message_tool.parameters["properties"][parameter.name] = (
{
"type": parameter_type,
"description": parameter.llm_description or "",
}
if parameter.input_schema is None
else parameter.input_schema
)
if len(enum) > 0:
message_tool.parameters["properties"][parameter.name]["enum"] = enum
# 🔍 标记必需参数
if parameter.required:
message_tool.parameters["required"].append(parameter.name)
return message_tool, tool_entity可视化工具示例 - PromptMessageTool 结构:
json
// Function Calling 模式下的工具定义
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "查询指定城市的实时天气信息",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称,例如:北京、上海"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"description": "温度单位",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]
}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
}步骤 2:组织 Prompt 并调用 LLM
python
def _organize_prompt_messages(self):
# 🔍 获取系统提示词模板
prompt_template = self.app_config.prompt_template.simple_prompt_template or ""
# 🔍 初始化系统消息
self.history_prompt_messages = self._init_system_message(prompt_template, self.history_prompt_messages)
# 🔍 组织用户查询(可能包含图片等文件)
query_prompt_messages = self._organize_user_query(self.query or "", [])
# 🔍 使用 AgentHistoryPromptTransform 整合历史记录
self.history_prompt_messages = AgentHistoryPromptTransform(
model_config=self.model_config,
prompt_messages=[*query_prompt_messages, *self._current_thoughts],
history_messages=self.history_prompt_messages,
memory=self.memory,
).get_prompt()
# 🔍 最终的 Prompt = 历史 + 当前问题 + 当前思考
prompt_messages = [*self.history_prompt_messages, *query_prompt_messages, *self._current_thoughts]
if len(self._current_thoughts) != 0:
# clear messages after the first iteration
prompt_messages = self._clear_user_prompt_image_messages(prompt_messages)
return prompt_messages第一轮调用示例:
json
# 发送给 OpenAI 的请求
{
"model": "gpt-4",
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "你是一个智能助手,可以使用工具帮助用户完成任务。"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "帮我查一下北京天气,如果是晴天就推荐一个景点"
}
],
"tools": [ // 🔍 【关键】工具定义作为参数传递
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "查询城市天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "recommend_attraction",
"description": "推荐景点",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {"type": "string"},
"weather": {"type": "string"}
}
}
}
}
],
"stream": true
}步骤 3:解析模型返回的 tool_calls
python
def check_tool_calls(self, llm_result_chunk: LLMResultChunk) -> bool:
"""
Check if there is any tool call in llm result chunk
检查流式结果中是否有工具调用
"""
if llm_result_chunk.delta.message.tool_calls:
return True
return False
def check_blocking_tool_calls(self, llm_result: LLMResult) -> bool:
"""
Check if there is any blocking tool call in llm result
检查阻塞式结果中是否有工具调用
"""
if llm_result.message.tool_calls:
return True
return False
def extract_tool_calls(self, llm_result_chunk: LLMResultChunk) -> list[tuple[str, str, dict[str, Any]]]:
"""
Extract tool calls from llm result chunk
从流式结果中提取工具调用
Returns:
List[Tuple[str, str, Dict[str, Any]]]: [(tool_call_id, tool_call_name, tool_call_args)]
"""
tool_calls = []
for prompt_message in llm_result_chunk.delta.message.tool_calls:
args = {}
# 🔍 解析 JSON 参数
if prompt_message.function.arguments != "":
args = json.loads(prompt_message.function.arguments)
tool_calls.append(
(
prompt_message.id,
prompt_message.function.name,
args,
)
)
return tool_callsOpenAI 返回示例:
json
// Stream 响应
{
"id": "chatcmpl-xxx",
"object": "chat.completion.chunk",
"choices": [{
"index": 0,
"delta": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": null, // 🔍 无文本内容
"tool_calls": [ // 🔍 【关键】结构化工具调用
{
"index": 0,
"id": "call_abc123",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"city\":\"北京\"}"
}
}
]
}
}]
}
// extract_tool_calls 解析后
[
("call_abc123", "get_weather", {"city": "北京"})
]模式二:ReAct (Chain of Thought) 详细链路
步骤 1:初始化 ReAct 特有状态
python
def run(
self,
message: Message,
query: str,
inputs: Mapping[str, str],
) -> Generator:
"""
Run Cot agent application
"""
app_generate_entity = self.application_generate_entity
self._repack_app_generate_entity(app_generate_entity)
# 🔍 ⭐⭐⭐【关键】初始化 ReAct 状态
self._init_react_state(query)
trace_manager = app_generate_entity.trace_manager
# 🔍 【重要】检查并添加 "Observation" 到 stop 序列
# check model mode
if "Observation" not in app_generate_entity.model_conf.stop:
if app_generate_entity.model_conf.provider not in self._ignore_observation_providers:
app_generate_entity.model_conf.stop.append("Observation")
app_config = self.app_config
assert app_config.agent
# 🔍 初始化指令(填充变量)
# init instruction
inputs = inputs or {}
instruction = app_config.prompt_template.simple_prompt_template or ""
self._instruction = self._fill_in_inputs_from_external_data_tools(instruction, inputs)
iteration_step = 1
max_iteration_steps = min(app_config.agent.max_iteration, 99) + 1
python
def _init_react_state(self, query):
"""
init agent scratchpad
初始化 Agent 推理记录本
"""
self._query = query
self._agent_scratchpad = [] # 🔍 存储每一轮的推理过程
self._historic_prompt_messages = self._organize_historic_prompt_messages()!!!步骤 2:组织 ReAct Prompt(关键差异!)
ReAct 模式需要将工具转换为自然语言描述:
python
# 伪代码示例 - ReAct Prompt 模板
prompt = f"""
Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:
get_weather: 查询城市天气,参数:city (string) - 城市名称
recommend_attraction: 推荐景点,参数:city (string), weather (string)
Use the following format:
Thought: 你应该思考接下来要做什么
Action: 要调用的工具名称
Action Input: 工具的输入参数(JSON格式)
Observation: 工具的执行结果
... (重复 Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation 可以多次)
Thought: 我现在知道最终答案了
Final Answer: 最终答案
Begin!
Question: {self._query}
Thought:"""步骤 3:调用 LLM 并解析响应
python
# 🔍 组织 Prompt
prompt_messages = self._organize_prompt_messages()
self.recalc_llm_max_tokens(self.model_config, prompt_messages)
# 🔍 【关键】调用 LLM(不传 tools 参数!)
# invoke model
chunks = model_instance.invoke_llm(
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
model_parameters=app_generate_entity.model_conf.parameters,
tools=[], # 🔍 空列表!
stop=app_generate_entity.model_conf.stop, # 🔍 包含 "Observation"
stream=True,
user=self.user_id,
callbacks=[],
)
usage_dict: dict[str, LLMUsage | None] = {}
# 🔍 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐【核心】使用 CotAgentOutputParser 解析自然语言输出
react_chunks = CotAgentOutputParser.handle_react_stream_output(chunks, usage_dict)
# 🔍 创建 Scratchpad(推理记录本)
scratchpad = AgentScratchpadUnit(
agent_response="",
thought="",
action_str="",
observation="",
action=None,
)
# publish agent thought if it's first iteration
if iteration_step == 1:
self.queue_manager.publish(
QueueAgentThoughtEvent(agent_thought_id=agent_thought_id), PublishFrom.APPLICATION_MANAGER
)
# 🔍 【关键】逐块解析模型输出
for chunk in react_chunks:
if isinstance(chunk, AgentScratchpadUnit.Action):
# 🔍 检测到 Action
action = chunk
assert scratchpad.agent_response is not None
scratchpad.agent_response += json.dumps(chunk.model_dump())
scratchpad.action_str = json.dumps(chunk.model_dump())
scratchpad.action = action
else:
# 🔍 普通文本(Thought)
assert scratchpad.agent_response is not None
scratchpad.agent_response += chunk
assert scratchpad.thought is not None
scratchpad.thought += chunk
# 🔍 流式返回给用户
yield LLMResultChunk(
model=self.model_config.model,
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
system_fingerprint="",
delta=LLMResultChunkDelta(index=0, message=AssistantPromptMessage(content=chunk), usage=None),
)步骤 4:CotAgentOutputParser 解析详解
python
@classmethod
def handle_react_stream_output(
cls, llm_response: Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None], usage_dict: dict
) -> Generator[Union[str, AgentScratchpadUnit.Action], None, None]:
# 🔍 【内部函数】解析 Action JSON
def parse_action(action) -> Union[str, AgentScratchpadUnit.Action]:
action_name = None
action_input = None
if isinstance(action, str):
try:
action = json.loads(action, strict=False)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
return action or ""
# cohere always returns a list
if isinstance(action, list) and len(action) == 1:
action = action[0]
# 🔍 从 JSON 中提取 action 和 action_input
for key, value in action.items():
if "input" in key.lower():
action_input = value
else:
action_name = value
if action_name is not None and action_input is not None:
return AgentScratchpadUnit.Action(
action_name=action_name,
action_input=action_input,
)
else:
return json.dumps(action)解析状态机:
python
# 🔍 状态变量
code_block_cache = "" # 代码块缓存
code_block_delimiter_count = 0 # ```计数器
in_code_block = False # 是否在代码块内
json_cache = "" # JSON 缓存
json_quote_count = 0 # { } 计数器
in_json = False # 是否在 JSON 内
got_json = False # 是否获取到完整 JSON
action_cache = "" # "action:" 缓存
action_str = "action:" # 要匹配的字符串
action_idx = 0 # 匹配到第几个字符
thought_cache = "" # "thought:" 缓存
thought_str = "thought:"
thought_idx = 0解析流程:
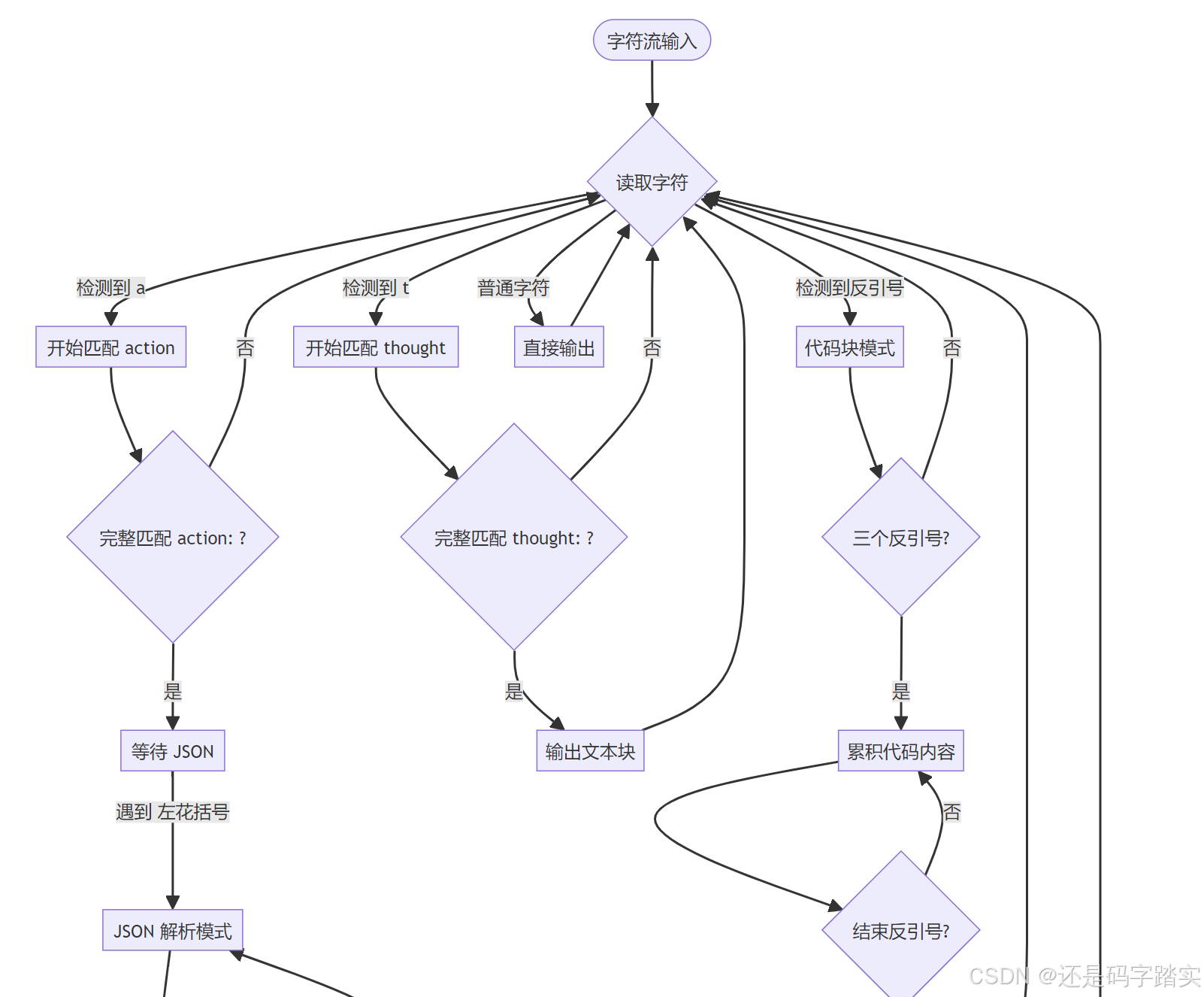
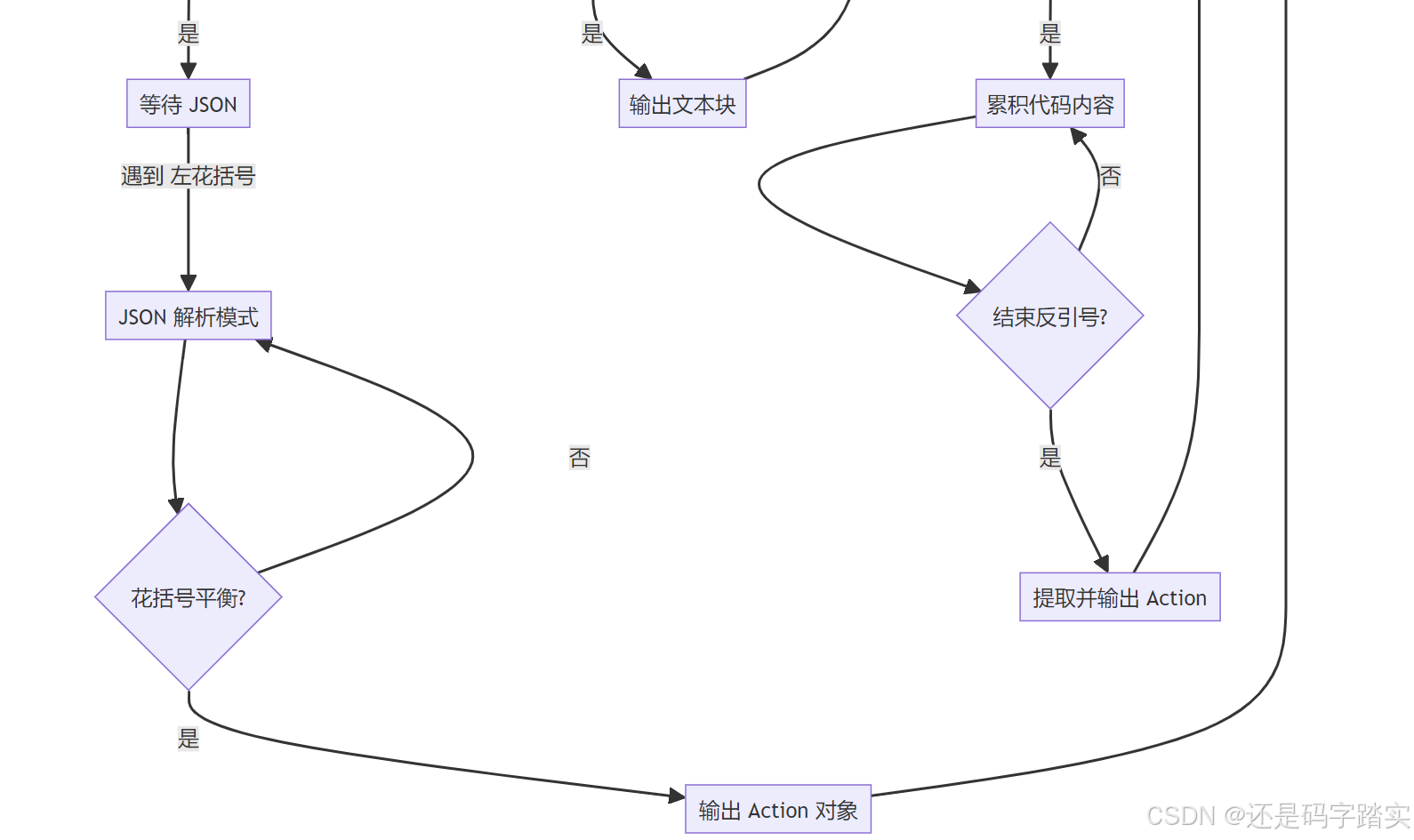
LLM 输出示例(ReAct 格式):
latex
Thought: 用户想知道北京天气,如果是晴天还要推荐景点。首先我需要查询北京的天气。
Action: get_weather
Action Input: {"city": "北京"}
Observation: // 🔍 模型会在这里停止(因为 stop=["Observation"])解析结果:
python
# CotAgentOutputParser 输出的 chunks
[
"Thought: 用户想知道北京天气,如果是晴天还要推荐景点。首先我需要查询北京的天气。\n\n",
"Action: ",
AgentScratchpadUnit.Action(
action_name="get_weather",
action_input={"city": "北京"}
)
]步骤 5:执行工具并格式化 Observation
python
function_call_state = True
# 🔍 调用工具
# action is tool call, invoke tool
tool_invoke_response, tool_invoke_meta = self._handle_invoke_action(
action=scratchpad.action,
tool_instances=tool_instances,
message_file_ids=message_file_ids,
trace_manager=trace_manager,
)
# 🔍 将结果保存为 Observation
scratchpad.observation = tool_invoke_response
scratchpad.agent_response = tool_invoke_response
# 🔍 保存到数据库
self.save_agent_thought(
agent_thought_id=agent_thought_id,
tool_name=scratchpad.action.action_name,
tool_input={scratchpad.action.action_name: scratchpad.action.action_input},
thought=scratchpad.thought or "",
observation={scratchpad.action.action_name: tool_invoke_response},
tool_invoke_meta={scratchpad.action.action_name: tool_invoke_meta.to_dict()},
answer=scratchpad.agent_response,
messages_ids=message_file_ids,
llm_usage=usage_dict["usage"],
)步骤 6:构建下一轮 Prompt
python
def _format_assistant_message(self, agent_scratchpad: list[AgentScratchpadUnit]) -> str:
"""
format assistant message
格式化助手消息(将推理过程转为文本)
"""
message = ""
for scratchpad in agent_scratchpad:
if scratchpad.is_final():
# 🔍 最终答案
message += f"Final Answer: {scratchpad.agent_response}"
else:
# 🔍 推理步骤
message += f"Thought: {scratchpad.thought}\n\n"
if scratchpad.action_str:
message += f"Action: {scratchpad.action_str}\n\n"
if scratchpad.observation:
message += f"Observation: {scratchpad.observation}\n\n"
return message第二轮 Prompt 示例:
latex
Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:
get_weather: 查询城市天气,参数:city (string) - 城市名称
recommend_attraction: 推荐景点,参数:city (string), weather (string)
Use the following format:
Thought: 你应该思考接下来要做什么
Action: 要调用的工具名称
Action Input: 工具的输入参数(JSON格式)
Observation: 工具的执行结果
...
Begin!
Question: 帮我查一下北京天气,如果是晴天就推荐一个景点
Thought: 用户想知道北京天气,如果是晴天还要推荐景点。首先我需要查询北京的天气。
Action: get_weather
Action Input: {"city": "北京"}
Observation: 北京今天天气晴朗,温度25°C,湿度60%
Thought: // 🔍 模型从这里继续生成完整时序图对比
Function Calling 时序图
WeatherTool ToolEngine OpenAI API LargeLanguageModel FunctionCallAgentRunner 用户 WeatherTool ToolEngine OpenAI API LargeLanguageModel FunctionCallAgentRunner 用户 第1轮迭代 模型内部决策 第2轮迭代 ... 继续迭代 ... "查天气+推荐景点" 1 _init_prompt_tools() 转为 PromptMessageTool 2 _organize_prompt_messages() 3 invoke_llm(messages, tools=[...]) 4 POST with tools parameter 5 tool_calls=[{name: "get_weather", args: {...}}] 6 LLMResultChunk with tool_calls 7 extract_tool_calls() 直接提取 JSON 8 agent_invoke(get_weather, {"city": "北京"}) 9 _invoke({"city": "北京"}) 10 "晴 25°C" 11 plain_text, files, meta 12 _current_thoughts.append( ToolPromptMessage) 13 _organize_prompt_messages() 包含工具结果 14 invoke_llm(messages+tool_result) 15 POST 16 tool_calls=[{name: "recommend_attraction"}] 17 content="推荐您去故宫..." 无 tool_calls 18 function_call_state=False 19 最终答案 20
ReAct 时序图
WeatherTool ToolEngine GPT-3.5 API LargeLanguageModel CotAgentOutputParser CotAgentRunner 用户 WeatherTool ToolEngine GPT-3.5 API LargeLanguageModel CotAgentOutputParser CotAgentRunner 用户 第1轮迭代 生成自然语言推理 loop [逐字符解析] 第2轮迭代 继续推理 ... 继续迭代 ... "查天气+推荐景点" 1 _init_react_state() 2 构建 ReAct Prompt 工具描述为文本 3 invoke_llm(prompt, tools=[], stop=["Observation"]) 4 POST (无 tools 参数) 5 Stream: "Thought: 需要查询天气\n\nAction: get_weather\nAction Input: {\"city\":\"北京\"}\nObservation:" 6 LLMResultChunk (文本流) 7 handle_react_stream_output(chunks) 8 检测 "thought:" 9 yield "Thought: 需要查询天气\n\n" 10 检测 "action:" 11 检测 JSON { 12 累积直到 } 13 yield Action(name="get_weather", input={...}) 14 保存到 scratchpad 15 agent_invoke(get_weather, {"city": "北京"}) 16 _invoke({"city": "北京"}) 17 "晴 25°C" 18 plain_text 19 scratchpad.observation = "晴 25°C" 20 _format_assistant_message() 格式化为 "Thought...Action...Observation..." 21 invoke_llm(prompt+历史) 22 "Thought: 天气是晴天,推荐景点\nAction: recommend_attraction..." 23 "Thought: 已完成\nFinal Answer: 推荐故宫..." 24 scratchpad.is_final() = True 25 最终答案 26
!!!关键差异代码对比
差异点 1:工具传递方式:ReAct不需要传递工具列表
Function Calling:
python
# fc_agent_runner.py line 93
chunks = model_instance.invoke_llm(
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
tools=prompt_messages_tools, # 🔍 传递结构化工具列表
stop=app_generate_entity.model_conf.stop,
stream=self.stream_tool_call,
)ReAct:
python
# cot_agent_runner.py line 119
chunks = model_instance.invoke_llm(
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
tools=[], # 🔍 空列表!
stop=app_generate_entity.model_conf.stop, # 🔍 包含 "Observation"
stream=True,
)差异点 2:Stop 序列:ReAct使用Observation
Function Calling:
python
# 不需要特殊 stop 序列
stop = ["<|im_end|>"] # 默认值ReAct:
python
# cot_agent_runner.py line 56-59
if "Observation" not in app_generate_entity.model_conf.stop:
if app_generate_entity.model_conf.provider not in self._ignore_observation_providers:
# 🔍 【关键】添加 "Observation" 作为停止词
app_generate_entity.model_conf.stop.append("Observation")差异点 3:响应解析:是否需要专门的解析器
Function Calling:
python
# fc_agent_runner.py line 123-126
if self.check_tool_calls(chunk):
function_call_state = True
# 🔍 直接提取 tool_calls
tool_calls.extend(self.extract_tool_calls(chunk) or [])ReAct:
python
# cot_agent_runner.py line 130
# 🔍 使用专门的解析器
react_chunks = CotAgentOutputParser.handle_react_stream_output(chunks, usage_dict)
# line 145-157
for chunk in react_chunks:
if isinstance(chunk, AgentScratchpadUnit.Action):
# 🔍 解析出的 Action 对象
action = chunk
scratchpad.action = action
else:
# 🔍 普通文本(Thought)
scratchpad.thought += chunk差异点 4:历史记录格式:ChatML或文本格式
Function Calling:
python
# 使用标准的 ChatML 格式
[
AssistantPromptMessage(
content=None,
tool_calls=[ToolCall(...)]
),
ToolPromptMessage(
tool_call_id="xxx",
name="get_weather",
content="晴 25°C"
)
]ReAct:
python
# 转为文本格式
[
AssistantPromptMessage(
content="""
Thought: 需要查询天气
Action: get_weather
Action Input: {"city": "北京"}
Observation: 晴 25°C
Thought: 天气是晴天...
"""
)
]性能与可靠性对比
| 指标 | Function Calling | ReAct |
|---|---|---|
| 首次响应延迟 | 低(直接返回 tool_calls) | 高(需生成 Thought) |
| Token 消耗 | 低(工具定义在系统层) | 高(工具定义在 Prompt 中) |
| 解析成功率 | 99%+(结构化保证) | 85-95%(依赖 Prompt 质量) |
| 调试难度 | 高(黑盒决策) | 低(可见思考过程) |
| 多轮对话 Token | 增长慢 | 增长快(历史记录更长) |
| 错误恢复 | 难(需重新调用) | 易(可通过 Prompt 引导) |
实战选择建议
使用 Function Calling 当:高可靠性的生产环境
✅ 需要高可靠性的生产环境
✅ 工具数量多(>10个)
✅ 使用 GPT-4、Claude 3+ 等高端模型
✅ 对延迟敏感
使用 ReAct 当:透明的推理过程
✅ 需要透明的推理过程(教育/研究)
✅ 模型不支持 Function Calling
✅ 需要细粒度控制推理流程
✅ 成本敏感(可用更便宜的模型)
调试技巧
Function Calling 调试
python
# 查看模型返回的原始 tool_calls
for chunk in chunks:
if chunk.delta.message.tool_calls:
print(f"Tool calls: {chunk.delta.message.tool_calls}")ReAct 调试
python
# 查看解析器的输出
for chunk in react_chunks:
if isinstance(chunk, AgentScratchpadUnit.Action):
print(f"🎯 Detected Action: {chunk.action_name}")
print(f" Input: {chunk.action_input}")
else:
print(f"💭 Thought: {chunk}")工具调用链路
整体架构图
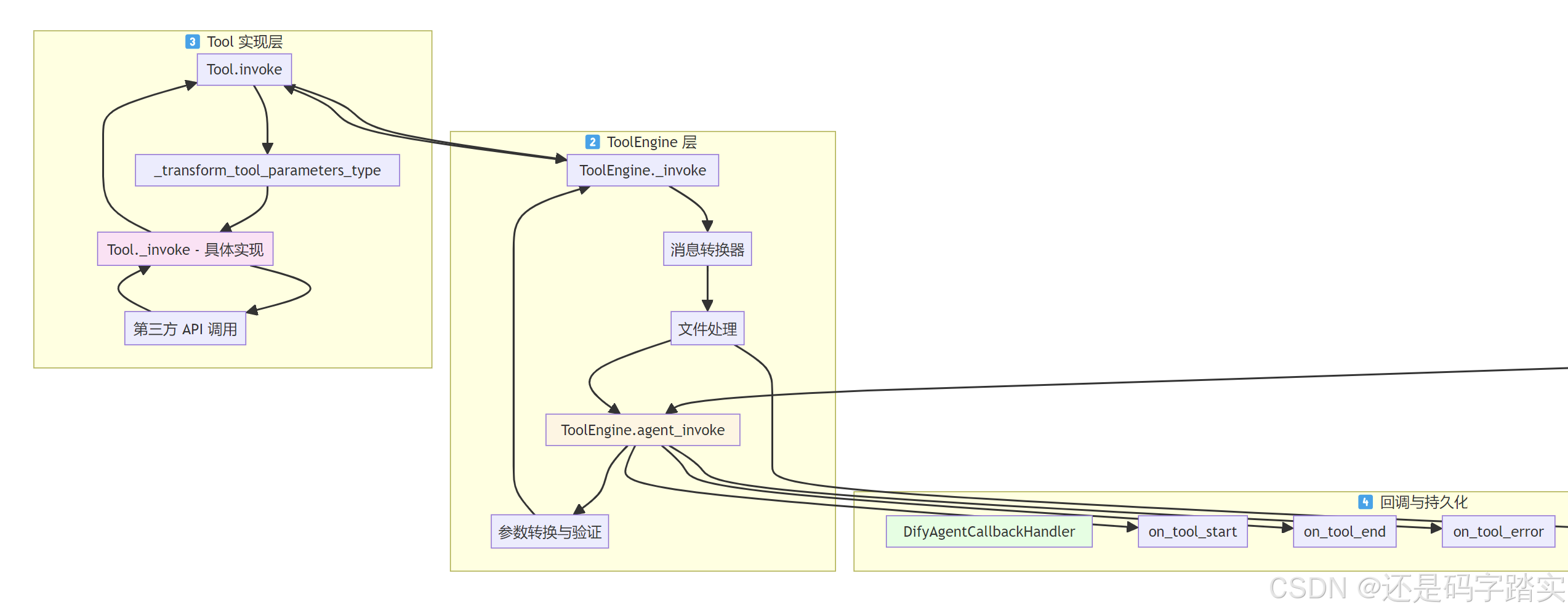
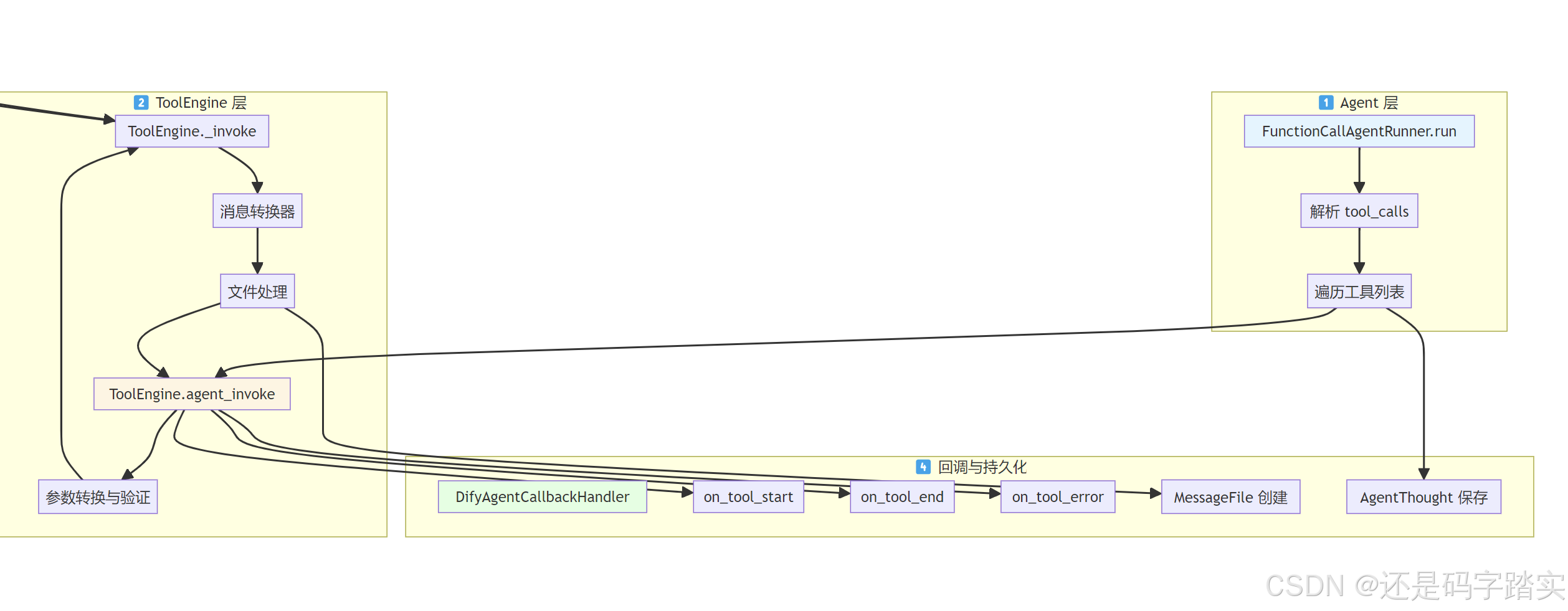
Agent 层发起工具调用
场景设定
用户问:"北京今天天气怎么样?"
LLM 返回:tool_calls = [{"id": "call_1", "name": "get_weather", "arguments": '{"city": "北京"}'}]
遍历 tool_calls
代码解读(文件: api/core/agent/fc_agent_runner.py:230-307):
python
# 🔍 步骤1:遍历 LLM 返回的所有 tool_calls
# tool_calls = [("call_1", "get_weather", {"city": "北京"})]
for tool_call_id, tool_call_name, tool_call_args in tool_calls:
# 🔍 步骤2:从初始化的工具字典中获取工具实例
# tool_instances = {"get_weather": WeatherTool对象, "search_flights": FlightTool对象}
tool_instance = tool_instances.get(tool_call_name)
if not tool_instance:
# ❌ 工具不存在,返回错误
tool_response = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"tool_call_name": tool_call_name,
"tool_response": f"there is not a tool named {tool_call_name}",
"meta": ToolInvokeMeta.error_instance(...).to_dict(),
}
else:
# ✅ 工具存在,调用 ToolEngine
# ⭐⭐⭐⭐ 这里是关键!进入 ToolEngine 层
tool_invoke_response, message_files, tool_invoke_meta = ToolEngine.agent_invoke(
tool=tool_instance, # 工具实例
tool_parameters=tool_call_args, # {"city": "北京"}
user_id=self.user_id,
tenant_id=self.tenant_id,
message=self.message,
invoke_from=self.application_generate_entity.invoke_from,
agent_tool_callback=self.agent_callback, # 回调处理器
trace_manager=trace_manager,
# ... 其他上下文信息
)
# 🔍 步骤3:处理工具返回的文件(如图片)
for message_file_id in message_files:
self.queue_manager.publish(
QueueMessageFileEvent(message_file_id=message_file_id),
PublishFrom.APPLICATION_MANAGER
)
# 🔍 步骤4:构造工具响应
tool_response = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"tool_call_name": tool_call_name,
"tool_response": tool_invoke_response, # "北京:晴 25°C"
"meta": tool_invoke_meta.to_dict(), # {"time_cost": 0.234}
}
# 🔍 步骤5:将工具响应添加到列表
tool_responses.append(tool_response)
# 🔍 步骤6:将工具结果添加到 _current_thoughts
# 下一轮 LLM 调用时会包含在 Prompt 中
if tool_response["tool_response"] is not None:
self._current_thoughts.append(
ToolPromptMessage(
content=str(tool_response["tool_response"]),
tool_call_id=tool_call_id,
name=tool_call_name,
)
)
# 🔍 步骤7:保存所有工具调用结果到数据库
if len(tool_responses) > 0:
self.save_agent_thought(
agent_thought_id=agent_thought_id,
tool_name="",
tool_input="",
thought="",
tool_invoke_meta={...}, # 元数据
observation={...}, # 工具返回值
answer="",
messages_ids=message_file_ids,
)ToolEngine 层 - 工具执行引擎
ToolEngine.agent_invoke
代码解读(文件: api/core/tools/tool_engine.py:45-146):
python
@staticmethod
def agent_invoke(
tool: Tool, # 工具实例
tool_parameters: Union[str, dict], # 可能是字符串或字典
# ... 其他参数
) -> tuple[str, list[str], ToolInvokeMeta]:
"""
🎯 核心功能:统一的工具调用入口
📤 返回:(纯文本结果, 文件ID列表, 元数据)
"""
# ====== 阶段1:参数转换 ======
# 🔍 处理字符串参数的情况
# 如果 LLM 返回的是字符串而不是 JSON 对象
if isinstance(tool_parameters, str):
# 🔍 获取工具的参数定义
parameters = [
parameter
for parameter in tool.get_runtime_parameters()
if parameter.form == ToolParameter.ToolParameterForm.LLM
]
# 🔍 如果工具只有1个参数,直接用字符串值
if parameters and len(parameters) == 1:
tool_parameters = {parameters[0].name: tool_parameters}
else:
# 🔍 否则尝试解析为 JSON
with contextlib.suppress(Exception):
tool_parameters = json.loads(tool_parameters)
if not isinstance(tool_parameters, dict):
raise ValueError(f"tool_parameters should be a dict...")
try:
# ====== 阶段2:触发开始回调 ======
# 🔍 通知:工具开始执行
agent_tool_callback.on_tool_start(
tool_name=tool.entity.identity.name, # "get_weather"
tool_inputs=tool_parameters # {"city": "北京"}
)
# ====== 阶段3:执行工具 ======
# 🎯⭐⭐⭐⭐ 调用 _invoke(下一个关键函数)
messages = ToolEngine._invoke(
tool, tool_parameters, user_id,
conversation_id, app_id, message_id
)
# messages 是一个生成器,产出 ToolInvokeMessage 或 ToolInvokeMeta
invocation_meta_dict: dict[str, ToolInvokeMeta] = {}
# ====== 阶段4:消息处理回调 ======
# 🔍 从生成器中分离出元数据
def message_callback(invocation_meta_dict, messages):
for message in messages:
if isinstance(message, ToolInvokeMeta):
invocation_meta_dict["meta"] = message # 保存元数据
else:
yield message # 转发普通消息
# ====== 阶段5:文件消息转换 ======
# 🔍 处理工具返回的文件(图片、文档等)
messages = ToolFileMessageTransformer.transform_tool_invoke_messages(
messages=message_callback(invocation_meta_dict, messages),
user_id=user_id,
tenant_id=tenant_id,
conversation_id=message.conversation_id,
)
# 🔍 消费生成器,获取所有消息
message_list = list(messages)
# ====== 阶段6:提取二进制文件 ======
# 🔍 从消息中提取图片、音频等二进制文件
binary_files = ToolEngine._extract_tool_response_binary_and_text(message_list)
# ====== 阶段7:创建文件记录 ======
# 🔍 将二进制文件保存到数据库
message_files = ToolEngine._create_message_files(
tool_messages=binary_files,
agent_message=message,
invoke_from=invoke_from,
user_id=user_id
)
# message_files = ["file_id_1", "file_id_2"]
# ====== 阶段8:转换为纯文本 ======
# 🔍⭐⭐⭐⭐ 将所有消息转为 LLM 可读的文本
plain_text = ToolEngine._convert_tool_response_to_str(message_list)
# plain_text = "北京:晴 25°C"
# 🔍 获取元数据
meta = invocation_meta_dict["meta"]
# ====== 阶段9:触发结束回调 ======
agent_tool_callback.on_tool_end(
tool_name=tool.entity.identity.name,
tool_inputs=tool_parameters,
tool_outputs=plain_text,
message_id=message.id,
trace_manager=trace_manager,
)
# ====== 阶段10:返回结果 ======
return plain_text, message_files, meta
except ToolProviderCredentialValidationError as e:
# ❌ 凭证错误
error_response = "Please check your tool provider credentials"
agent_tool_callback.on_tool_error(e)
except (ToolNotFoundError, ToolNotSupportedError, ...) as e:
# ❌ 工具不存在
error_response = f"there is not a tool named {tool.entity.identity.name}"
agent_tool_callback.on_tool_error(e)
# ... 其他异常处理
return error_response, [], ToolInvokeMeta.error_instance(error_response)核心方法:ToolEngine._invoke
代码解读(文件: api/core/tools/tool_engine.py:192-224):
python
@staticmethod
def _invoke(
tool: Tool,
tool_parameters: dict,
user_id: str,
# ...
) -> Generator[ToolInvokeMessage | ToolInvokeMeta, None, None]:
"""
🎯 功能:包装工具调用,添加计时和元数据
📤 返回:生成器,产出消息和元数据
"""
# 🔍 记录开始时间
started_at = datetime.now(UTC)
# 🔍 初始化元数据对象
meta = ToolInvokeMeta(
time_cost=0.0,
error=None,
tool_config={
"tool_name": tool.entity.identity.name, # "get_weather"
"tool_provider": tool.entity.identity.provider, # "weather_api"
"tool_provider_type": tool.tool_provider_type().value,
"tool_parameters": deepcopy(tool.runtime.runtime_parameters),
"tool_icon": tool.entity.identity.icon,
},
)
try:
# ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐关键:调用工具的 invoke 方法(进入 Tool 层)
# yield from 会逐个转发工具产生的消息
yield from tool.invoke(
user_id,
tool_parameters, # {"city": "北京"}
conversation_id,
app_id,
message_id
)
except Exception as e:
# ❌ 捕获工具执行异常
meta.error = str(e)
raise ToolEngineInvokeError(meta)
finally:
# 🔍 无论成功失败,都计算耗时
ended_at = datetime.now(UTC)
meta.time_cost = (ended_at - started_at).total_seconds()
# 🔍 最后产出元数据
yield metaTool 层 - 具体工具实现
Tool 基类的 invoke 方法
代码解读(文件: api/core/tools/__base/tool.py:47-105):
python
def invoke(
self,
user_id: str,
tool_parameters: dict[str, Any],
# ...
) -> Generator[ToolInvokeMessage]:
"""
🎯 功能:Tool 基类的 invoke,处理参数转换
📤 返回:消息生成器
"""
# 🔍 步骤1:合并运行时参数
# runtime_parameters 是工具配置的固定参数
# 例如:API Key、Base URL 等
if self.runtime and self.runtime.runtime_parameters:
tool_parameters.update(self.runtime.runtime_parameters)
# 🔍 ⭐⭐⭐步骤2:参数类型转换
# 将字符串转为正确的类型(int, float, bool 等)
tool_parameters = self._transform_tool_parameters_type(tool_parameters)
# 🎯⭐⭐⭐ 步骤3:调用子类实现的 _invoke 方法
result = self._invoke(
user_id=user_id,
tool_parameters=tool_parameters,
conversation_id=conversation_id,
app_id=app_id,
message_id=message_id,
)
# 🔍 步骤4:统一返回格式为生成器
if isinstance(result, ToolInvokeMessage):
# 单个消息 → 包装为生成器
def single_generator() -> Generator[ToolInvokeMessage, None, None]:
yield result
return single_generator()
elif isinstance(result, list):
# 消息列表 → 包装为生成器
def generator() -> Generator[ToolInvokeMessage, None, None]:
yield from result
return generator()
else:
# 已经是生成器 → 直接返回
return result
def _transform_tool_parameters_type(self, tool_parameters: dict[str, Any]) -> dict[str, Any]:
"""
🎯 功能:参数类型转换
📝 示例:
输入:{"temperature": "25", "humidity": "60"}
参数定义:temperature=int, humidity=int
输出:{"temperature": 25, "humidity": 60}
"""
result = deepcopy(tool_parameters)
for parameter in self.entity.parameters or []:
if parameter.name in tool_parameters:
# 🔍 使用参数定义的类型进行转换
result[parameter.name] = parameter.type.cast_value(
tool_parameters[parameter.name]
)
return result
@abstractmethod
def _invoke(
self,
user_id: str,
tool_parameters: dict[str, Any],
# ...
) -> ToolInvokeMessage | list[ToolInvokeMessage] | Generator[ToolInvokeMessage, None, None]:
"""
🎯 抽象方法:由子类实现具体的工具逻辑
"""
pass具体工具实现示例:WorkflowTool
读取一个真实的工具实现:
代码解读(文件: api/core/tools/workflow_as_tool/tool.py:67-127):
python
def _invoke(
self,
user_id: str,
tool_parameters: dict[str, Any],
# ...
) -> Generator[ToolInvokeMessage, None, None]:
"""
🎯 功能:WorkflowTool 的具体实现
📝 场景:将一个工作流封装为工具供 Agent 调用
"""
# 🔍 步骤1:获取工作流应用
app = self._get_app(app_id=self.workflow_app_id)
workflow = self._get_workflow(app_id=self.workflow_app_id, version=self.version)
# 🔍 步骤2:转换参数(可能包含文件)
tool_parameters, files = self._transform_args(tool_parameters=tool_parameters)
# 🔍 步骤3:初始化工作流生成器
from core.app.apps.workflow.app_generator import WorkflowAppGenerator
generator = WorkflowAppGenerator()
# 🔍 步骤4:获取用户信息
user = self._resolve_user(user_id=user_id)
if user is None:
raise ToolInvokeError("User not found")
self._latest_usage = LLMUsage.empty_usage()
# 🎯⭐⭐⭐⭐ 步骤5:执行工作流
result = generator.generate(
app_model=app,
workflow=workflow,
user=user,
args={"inputs": tool_parameters, "files": files},
invoke_from=self.runtime.invoke_from,
streaming=False,
call_depth=self.workflow_call_depth + 1, # 防止递归调用
)
# 🔍 步骤6:检查错误
assert isinstance(result, dict)
data = result.get("data", {})
if err := data.get("error"):
raise ToolInvokeError(err)
# 🔍 步骤7:处理输出
outputs = data.get("outputs")
if outputs is None:
outputs = {}
else:
# 🔍 提取文件输出
outputs, files = self._extract_files(outputs)
for file in files:
# 📤 产出文件消息
yield self.create_file_message(file)
# 🔍 步骤8:遍历所有输出变量
for key, value in outputs.items():
if key not in {"text", "json", "files"}:
# 📤 产出变量消息
yield self.create_variable_message(
variable_name=key,
variable_value=value
)
# 🔍 步骤9:记录 Token 使用量
self._latest_usage = self._derive_usage_from_result(data)
# 🔍 步骤10:产出文本和 JSON 消息
# 📤 产出文本消息(给 LLM 看)
yield self.create_text_message(json.dumps(outputs, ensure_ascii=False))
# 📤 产出 JSON 消息(结构化数据,不显示在文本输出中)
yield self.create_json_message(outputs, suppress_output=True)消息转换与文件处理
消息转换为纯文本
代码解读(文件: api/core/tools/tool_engine.py:226-265):
python
@staticmethod
def _convert_tool_response_to_str(tool_response: list[ToolInvokeMessage]) -> str:
"""
🎯 功能:将工具返回的各种消息类型转换为 LLM 可读的纯文本
📝 示例输入:[TextMessage("晴"), ImageMessage("weather.jpg"), JsonMessage({...})]
📤 输出:"晴。image has been created and sent to user already..."
"""
parts: list[str] = [] # 文本部分
json_parts: list[str] = [] # JSON 部分
for response in tool_response:
# 🔍 类型1:纯文本消息
if response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.TEXT:
parts.append(cast(ToolInvokeMessage.TextMessage, response.message).text)
# 直接添加文本内容
# 🔍 类型2:链接消息
elif response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.LINK:
parts.append(
f"result link: {cast(ToolInvokeMessage.TextMessage, response.message).text}."
+ " please tell user to check it."
)
# 转换为提示语,让 LLM 告诉用户点击链接
# 🔍 类型3:图片消息
elif response.type in {ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.IMAGE_LINK,
ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.IMAGE}:
parts.append(
"image has been created and sent to user already, "
+ "you do not need to create it, just tell the user to check it now."
)
# ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ 关键:告诉 LLM 图片已发送,避免 LLM 尝试生成图片描述
# 🔍 类型4:JSON 消息
elif response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.JSON:
json_message = cast(ToolInvokeMessage.JsonMessage, response.message)
if json_message.suppress_output:
continue # 跳过不需要展示的 JSON
json_parts.append(
json.dumps(
safe_json_value(json_message.json_object),
ensure_ascii=False,
)
)
# 🔍 类型5:其他类型
else:
parts.append(str(response.message))
# 🔍 合并 JSON 部分,避免重复
if json_parts:
existing_parts = set(parts)
parts.extend(p for p in json_parts if p not in existing_parts)
# 📤 拼接所有部分
return "".join(parts)完整时序图:从 Agent 到工具执行
数据层 Tool 层 ToolEngine 层 Agent 层 文件存储 数据库 第三方 API WeatherTool (子类) Tool (基类) ToolFileMessageTransformer DifyAgentCallbackHandler ToolEngine FunctionCallAgentRunner 文件存储 数据库 第三方 API WeatherTool (子类) Tool (基类) ToolFileMessageTransformer DifyAgentCallbackHandler ToolEngine FunctionCallAgentRunner LLM 返回 tool_calls tool_call = ("call_1", "get_weather", {"city": "北京"}) 文件: tool_engine.py:46 str → dict 转换 记录工具调用开始 文件: tool_engine.py:193 记录开始时间 文件: tool.py:47 添加 API Key 等配置 类型转换: "25" → 25 (int) 子类具体实现 处理文件消息 提取图片/音频等二进制文件 创建 MessageFile 记录 转换为纯文本 记录工具调用结束 下一轮 LLM 调用会包含此消息 保存推理步骤到 MessageAgentThought 表 准备下一轮迭代 遍历 tool_calls 1 agent_invoke(tool, parameters) 2 参数类型转换 3 on_tool_start("get_weather", {"city": "北京"}) 4 _invoke(tool, parameters) 5 创建 ToolInvokeMeta 6 tool.invoke(user_id, tool_parameters) 7 合并 runtime_parameters 8 _transform_tool_parameters_type() 9 _invoke(user_id, tool_parameters) 10 HTTP GET /weather?city=北京 11 {"temp": 25, "weather": "晴"} 12 构造 ToolInvokeMessage 13 yield TextMessage("北京:晴 25°C") 14 yield TextMessage(...) 15 计算 time_cost 16 yield ToolInvokeMeta(time_cost=0.234) 17 transform_tool_invoke_messages() 18 上传文件(如有) 19 file_url 20 转换后的消息列表 21 _extract_tool_response_binary_and_text() 22 _create_message_files() 23 message_file_ids = ["file_1"] 24 _convert_tool_response_to_str() 25 plain_text = "北京:晴 25°C" 26 on_tool_end("get_weather", plain_text) 27 return (plain_text, file_ids, meta) 28 构造 ToolPromptMessage 29 save_agent_thought() 30 _current_thoughts.append(ToolPromptMessage) 31
数据流转可视化
示例:天气查询工具完整数据流
plain
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 输入:LLM 返回的 tool_calls │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ tool_calls = [ │
│ ("call_abc123", "get_weather", {"city": "北京"}) │
│ ] │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 步骤1:Agent 层提取工具信息 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ tool_call_id = "call_abc123" │
│ tool_call_name = "get_weather" │
│ tool_call_args = {"city": "北京"} │
│ │
│ tool_instance = tool_instances["get_weather"] │
│ # → WeatherTool 对象 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 步骤2:ToolEngine.agent_invoke 参数处理 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 输入:tool_parameters = {"city": "北京"} │
│ │
│ ① 参数类型检查: │
│ isinstance(tool_parameters, dict) ✅ │
│ │
│ ② 触发回调: │
│ on_tool_start("get_weather", {"city": "北京"}) │
│ │
│ ③ 调用 _invoke: │
│ messages = ToolEngine._invoke(...) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 步骤3:ToolEngine._invoke 包装 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ started_at = datetime.now() # 2024-01-20 10:30:00.123 │
│ │
│ meta = ToolInvokeMeta( │
│ time_cost=0.0, │
│ error=None, │
│ tool_config={ │
│ "tool_name": "get_weather", │
│ "tool_provider": "weather_api", │
│ ... │
│ } │
│ ) │
│ │
│ yield from tool.invoke(...) # 进入 Tool 层 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 步骤4:Tool.invoke 基类处理 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ① 合并运行时参数: │
│ tool_parameters.update(self.runtime.runtime_parameters) │
│ # 添加 API Key: "abc123" │
│ │
│ ② 类型转换: │
│ tool_parameters = self._transform_tool_parameters_type( │
│ tool_parameters │
│ ) │
│ # 确保类型正确 │
│ │
│ ③ 调用子类实现: │
│ result = self._invoke(...) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 步骤5:WeatherTool._invoke 具体实现 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ① 调用第三方 API: │
│ response = requests.get( │
│ "https://api.weather.com/v1/current", │
│ params={"city": "北京", "key": "abc123"} │
│ ) │
│ │
│ ② API 返回: │
│ { │
│ "temperature": 25, │
│ "weather": "晴", │
│ "humidity": 60, │
│ "wind": "3级" │
│ } │
│ │
│ ③ 构造消息: │
│ text = f"{city}:{weather} {temperature}°C" │
│ message = self.create_text_message(text) │
│ │
│ ④ 产出消息: │
│ yield ToolInvokeMessage( │
│ type=MessageType.TEXT, │
│ message=TextMessage(text="北京:晴 25°C") │
│ ) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 步骤6:返回 ToolEngine._invoke │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ① 接收消息: │
│ messages = [ │
│ ToolInvokeMessage(type=TEXT, message="北京:晴 25°C") │
│ ] │
│ │
│ ② 计算耗时: │
│ ended_at = datetime.now() # 2024-01-20 10:30:00.357 │
│ meta.time_cost = (ended_at - started_at).total_seconds()│
│ # → 0.234 秒 │
│ │
│ ③ 产出元数据: │
│ yield meta │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 步骤7:ToolEngine.agent_invoke 后处理 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ① 消息回调: │
│ messages = [ToolInvokeMessage(...)] │
│ meta = ToolInvokeMeta(time_cost=0.234, error=None) │
│ │
│ ② 文件消息转换: │
│ messages = ToolFileMessageTransformer.transform(...) │
│ # 处理图片、文件等(本例无文件) │
│ │
│ ③ 提取二进制文件: │
│ binary_files = _extract_tool_response_binary(messages) │
│ # → [](无文件) │
│ │
│ ④ 创建文件记录: │
│ message_files = _create_message_files(binary_files) │
│ # → [](无文件) │
│ │
│ ⑤ 转换为纯文本: │
│ plain_text = _convert_tool_response_to_str(messages) │
│ # → "北京:晴 25°C" │
│ │
│ ⑥ 触发结束回调: │
│ on_tool_end("get_weather", plain_text) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 输出:返回给 Agent │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ tool_invoke_response = "北京:晴 25°C" │
│ message_files = [] │
│ tool_invoke_meta = ToolInvokeMeta( │
│ time_cost=0.234, │
│ error=None, │
│ tool_config={...} │
│ ) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 步骤8:Agent 处理工具结果 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ① 构造响应字典: │
│ tool_response = { │
│ "tool_call_id": "call_abc123", │
│ "tool_call_name": "get_weather", │
│ "tool_response": "北京:晴 25°C", │
│ "meta": {...} │
│ } │
│ │
│ ② 添加到 _current_thoughts: │
│ self._current_thoughts.append( │
│ ToolPromptMessage( │
│ content="北京:晴 25°C", │
│ tool_call_id="call_abc123", │
│ name="get_weather" │
│ ) │
│ ) │
│ │
│ ③ 保存到数据库: │
│ save_agent_thought( │
│ tool_name="get_weather", │
│ tool_input='{"city": "北京"}', │
│ observation="北京:晴 25°C", │
│ ... │
│ ) │
│ # → 插入 MessageAgentThought 表 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 最终:下一轮 LLM 调用的 Prompt │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ [ │
│ SystemPromptMessage(...), │
│ UserPromptMessage("北京天气怎么样?"), │
│ AssistantPromptMessage(tool_calls=[...]), │
│ ToolPromptMessage( ← 新增! │
│ content="北京:晴 25°C", │
│ tool_call_id="call_abc123", │
│ name="get_weather" │
│ ) │
│ ] │
│ │
│ LLM 看到工具结果后生成最终答案: │
│ "根据查询结果,北京今天天气晴朗,温度 25°C,非常适合外出。" │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘关键函数调用栈
plain
1. FunctionCallAgentRunner.run() [fc_agent_runner.py:35]
├─ 2. for tool_call in tool_calls [fc_agent_runner.py:232]
│ └─ 3. ToolEngine.agent_invoke() [tool_engine.py:46]
│ ├─ 4. 参数转换 (str → dict) [tool_engine.py:63-76]
│ ├─ 5. on_tool_start() 回调 [tool_engine.py:80]
│ ├─ 6. ToolEngine._invoke() [tool_engine.py:193]
│ │ ├─ 7. 创建 ToolInvokeMeta [tool_engine.py:205-215]
│ │ ├─ 8. Tool.invoke() [tool.py:47]
│ │ │ ├─ 9. 合并 runtime_parameters [tool.py:55-56]
│ │ │ ├─ 10. _transform_tool_parameters_type() [tool.py:59]
│ │ │ │ └─ 11. parameter.type.cast_value() [tool.py:92]
│ │ │ └─ 12. Tool._invoke() [tool.py:97] ← 抽象方法
│ │ │ └─ 13. WeatherTool._invoke() [具体实现]
│ │ │ ├─ 14. 调用第三方 API
│ │ │ ├─ 15. self.create_text_message()
│ │ │ └─ 16. yield ToolInvokeMessage
│ │ └─ 17. 计算 time_cost & yield meta [tool_engine.py:222-224]
│ ├─ 18. ToolFileMessageTransformer.transform() [tool_engine.py:94]
│ ├─ 19. _extract_tool_response_binary() [tool_engine.py:104]
│ ├─ 20. _create_message_files() [tool_engine.py:106]
│ │ └─ 21. db.session.add(MessageFile) [tool_engine.py:357]
│ ├─ 22. _convert_tool_response_to_str() [tool_engine.py:110]
│ │ └─ 23. 转换各种消息类型为文本 [tool_engine.py:234-265]
│ └─ 24. on_tool_end() 回调 [tool_engine.py:115]
├─ 25. _current_thoughts.append(ToolPromptMessage) [fc_agent_runner.py:274]
└─ 26. save_agent_thought() [fc_agent_runner.py:284]
└─ 27. db.session.add(MessageAgentThought) [base_agent_runner.py:316]类比总结
想象你去餐厅吃饭(调用工具):
- 服务员记录订单(Agent 解析 tool_calls)
- 传单到厨房(ToolEngine.agent_invoke)
- 厨师长检查食材(参数转换与验证)
- 通知开始做菜(on_tool_start 回调)
- 记录开始时间(ToolInvokeMeta)
- 炒菜师傅炒菜(Tool._invoke 具体实现)
- 调用冰箱取食材(第三方 API)
- 装盘(create_text_message)
- 记录做菜时间(time_cost)
- 拍照发朋友圈(文件处理)
- 写菜品说明(转换为纯文本)
- 通知做好了(on_tool_end 回调)
- 端菜给服务员(返回 Agent)
- 记录在账本上(save_agent_thought)
- 告诉顾客菜好了(添加到 _current_thoughts)
关键点:
- 生成器模式 :使用
yield流式返回结果,支持实时反馈 - 回调机制:在关键节点触发回调,用于日志、监控、追踪
- 参数转换:自动将字符串转为正确类型(int, float, bool)
- 文件处理:自动识别并保存工具返回的图片、文档等
- 消息标准化:统一转换为 LLM 可读的文本格式
- 持久化:每个工具调用都记录到数据库,可追溯
标准化回答话术(300字以内)
"在多模型环境下,如何设计一个既灵活又安全可靠的 Agent 调度系统?"
架构设计的三大支柱:模型标准化、工程化约束死循环、热切换降级策略
1. 抽象工厂模式实现模型标准化
"我会采用 Abstract Factory Pattern 屏蔽底层模型差异。具体来说:
- 统一接口层 :定义
LargeLanguageModel.invoke()作为所有模型的调用入口,接收标准化的PromptMessage和PromptMessageTool。 - 插件化提供商 :通过
ModelProviderFactory.get_model_type_instance()动态加载不同模型(OpenAI/Anthropic/DeepSeek),每个 Provider 实现相同的invoke接口但封装各自的 API 调用逻辑。 - 错误映射机制 :使用
_invoke_error_mapping将各家 API 的错误码(如 OpenAI 的 429、Anthropic 的 529)统一转换为InvokeRateLimitError、InvokeServerUnavailableError等标准异常,上层业务逻辑无需关心底层细节。
优势:
- 新增模型只需实现适配器,无需修改 Agent 调度逻辑
- 便于 A/B Testing 和成本优化(根据价格动态选择模型)
- 支持多租户场景下的模型隔离"
2. 工程化约束防止 Agent 死循环
Agent 的非确定性是把双刃剑,从三个层面设置 刹车系统:
硬性限制:
- 设置
max_iteration参数(默认 10,上限 99),通过while iteration_step <= max_iteration_steps强制终止循环。 - 最后一轮迭代时移除工具列表(
prompt_messages_tools = []),使模型无法继续调用工具。
异常抛出:
- 若达到最大迭代次数且模型仍返回
tool_calls,立即抛出AgentMaxIterationError,触发上层告警。
成本保护:
- 每轮迭代累计 Token 消耗(
increase_usage()),可在企业层设置预算上限(如单次对话不超过 100k tokens)。 - 记录每个
AgentThought的耗时和费用,便于追溯异常消耗。
自我纠错策略:
- 在 ReAct 模式中,通过 Prompt 引导模型在最后一步生成
Final Answer,避免陷入工具调用循环。 - 检测重复工具调用(如连续 3 次调用同一工具且参数相同)时提前终止。"
3. API 崩溃时的热切换降级策略
单点故障是分布式系统的常态:
多 Provider 配置:
- 为每个
tenant_id配置主备模型列表(如["openai/gpt-4", "anthropic/claude-3", "deepseek/chat"])。 - 在
ModelProviderFactory中实现invoke_with_fallback()方法。
错误分类处理:
- 可重试错误 (
InvokeRateLimitError、InvokeServerUnavailableError):采用 Exponential Backoff(1s、2s、4s),重试 3 次后切换备用模型。 - 不可重试错误 (
InvokeAuthorizationError):直接切换到下一个 Provider。
状态管理:
- 使用 Redis 记录每个 Provider 的健康状态(
provider:openai:status = {"available": false, "retry_after": 1705123456})。 - 健康检查线程定期探测各 Provider 的可用性,自动恢复故障节点。
Prompt 一致性:
- 切换模型时保持
prompt_messages和tools定义不变,依赖抽象工厂模式实现无缝切换。 - 若备用模型不支持 Function Calling,自动降级为 ReAct 模式。
监控告警:
- 每次 Fallback 触发时发送 Slack/PagerDuty 通知
- 按
provider和error_type维度统计失败率,超过阈值(如 5% 失败率)时人工介入"
进一步优化:架构演进思考
如果进一步优化,可以考虑:
- 智能路由:基于 Prompt 复杂度动态选择模型(简单问题用 GPT-3.5,复杂推理用 Claude Opus)。
- 缓存层 :对相同
prompt_messages+tools的调用结果缓存 10 分钟,减少 API 成本。 - 联邦学习:收集各模型在不同任务上的成功率,训练路由策略模型。
- 合规性:不同地区用户路由到符合当地法规的模型(如欧盟用户避免使用 OpenAI)。