深度详解Spring Context
每个Spring开发者都离不开Context,但你真的了解它吗?
引言:Spring Context 的核心地位
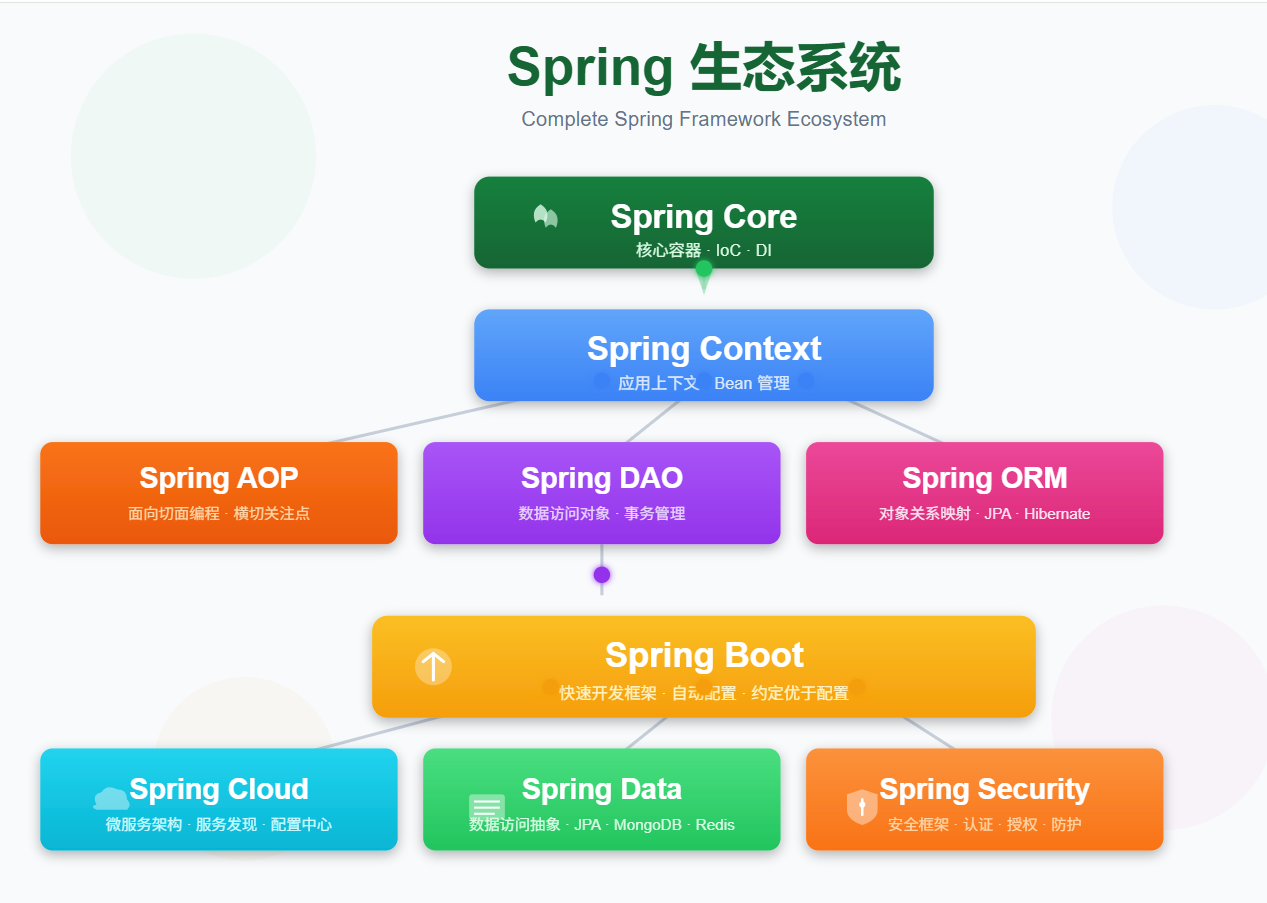
Spring Context作为Spring框架的核心组件,是IoC容器的具体实现。它就像一个巨大的工厂,负责管理所有的Bean对象,控制它们的生命周期,并解决它们之间的依赖关系。
什么是Spring Context?
Spring Context是Spring框架的核心容器,它继承自BeanFactory接口,但在其基础上增加了企业级应用所需的功能:
- 国际化支持
- 事件传播机制
- 资源加载
- AOP集成
- 事务管理
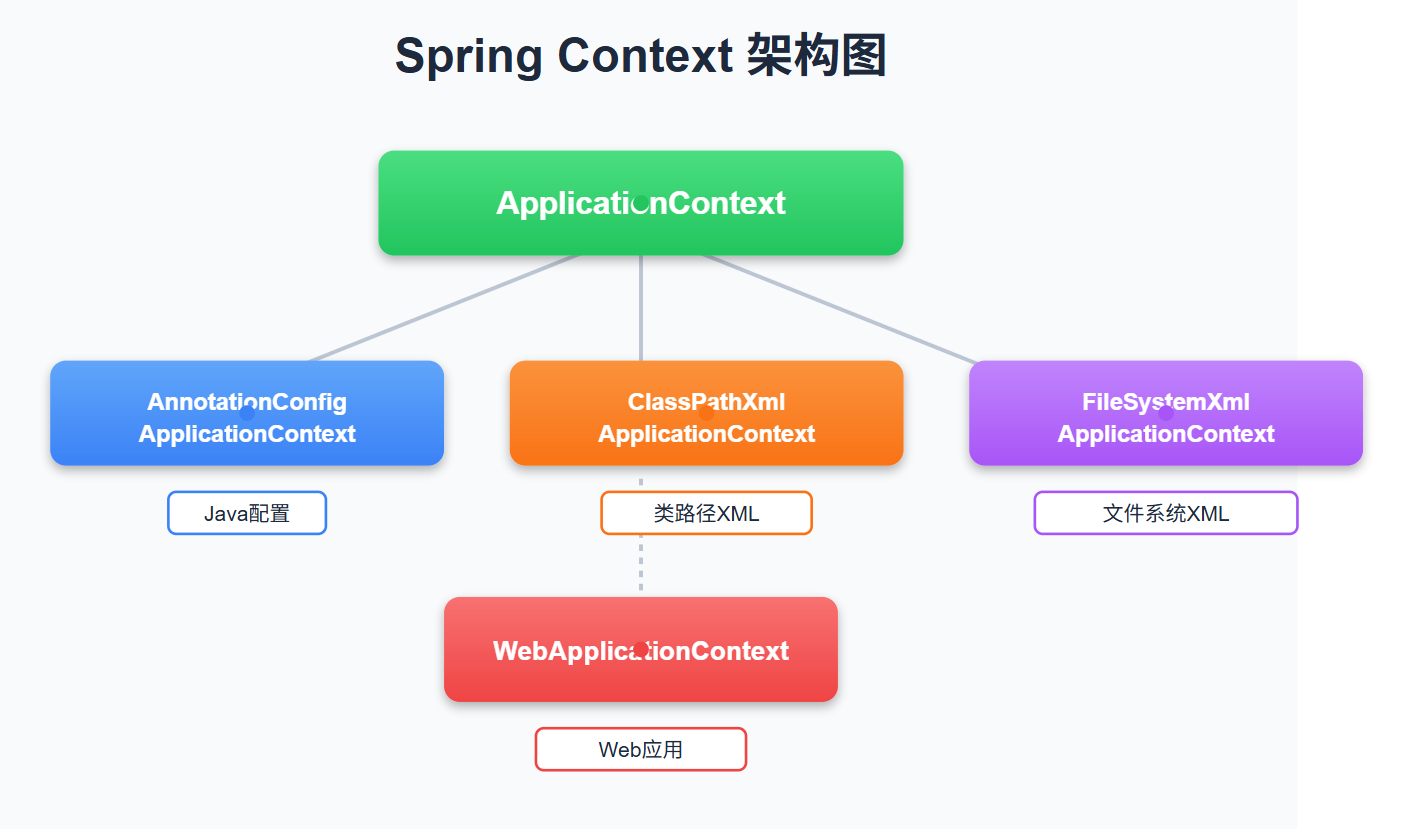
四大ApplicationContext全解析
1️⃣ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext - Java配置的王者
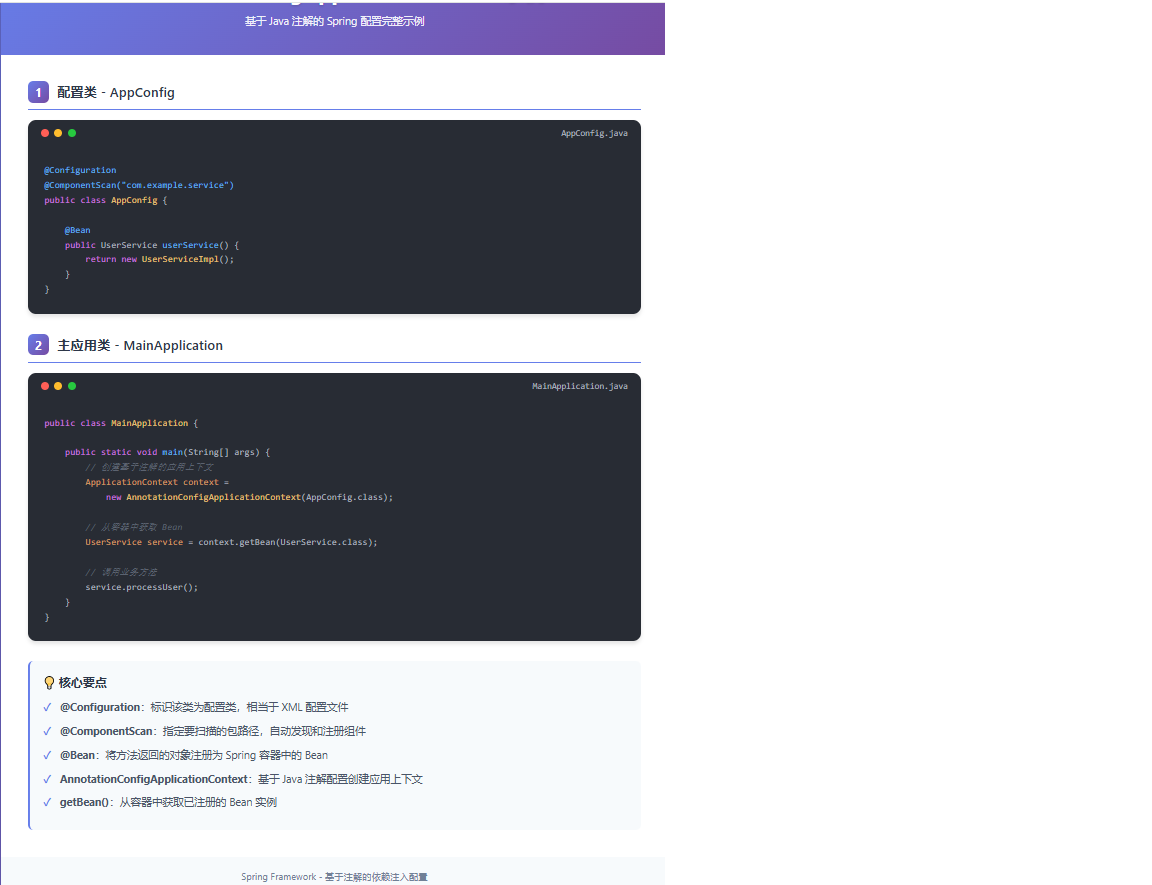
适用场景:
- 现代Spring Boot应用
- 纯Java配置的项目
- 需要类型安全的配置
核心特点:
- 完全基于注解的配置方式
- 支持Java 8的Lambda表达式
- 与Spring Boot无缝集成
实战代码示例:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.example.service")
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class AppConfig {
@Value("${app.name}")
private String appName;
@Bean
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public UserService userService() {
return new UserServiceImpl();
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
HikariDataSource dataSource = new HikariDataSource();
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("password");
return dataSource;
}
}
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建上下文
ApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// 获取Bean
UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
DataSource dataSource = context.getBean(DataSource.class);
// 使用服务
userService.processUser();
}
}生产环境应用: 在Spring Boot项目中,我们通常通过@SpringBootApplication注解自动创建AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}2️⃣ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext - 类路径XML配置

适用场景:
- 传统Spring应用
- 需要与XML配置兼容
- 类路径资源管理
核心特点:
- 从类路径加载XML配置文件
- 支持通配符配置
- 兼容性好
实战代码示例:
public class XmlConfigApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 基础用法
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 2. 多配置文件
String[] configLocations = {
"spring-datasource.xml",
"spring-service.xml",
"spring-mvc.xml"
};
ApplicationContext context2 =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(configLocations);
// 3. 使用通配符
ApplicationContext context3 =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath*:spring/*.xml");
// 获取Bean
UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
}
}XML配置文件示例:
<!-- applicationContext.xml -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!-- 组件扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example"/>
<!-- 属性文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:application.properties"/>
<!-- 数据源配置 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${db.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${db.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${db.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${db.password}"/>
</bean>
<!-- JPA配置 -->
<bean id="entityManagerFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="packagesToScan" value="com.example.entity"/>
<property name="jpaVendorAdapter">
<bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter"/>
</property>
<property name="jpaProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager">
<property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory"/>
</bean>
<!-- 启用事务注解 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>3️⃣ FileSystemXmlApplicationContext - 文件系统XML配置

适用场景:
- 外部配置文件管理
- 开发环境快速配置
- 多环境部署
核心特点:
- 从文件系统加载配置文件
- 支持绝对路径
- 便于外部配置管理
实战代码示例:
public class FileSystemConfigApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 使用绝对路径
ApplicationContext context1 =
new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(
"C:/config/spring/applicationContext.xml");
// 2. 使用多个配置文件
String[] configPaths = {
"/opt/spring/config/datasource.xml",
"/opt/spring/config/service.xml"
};
ApplicationContext context2 =
new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(configPaths);
// 3. 相对路径(不推荐,路径不明确)
ApplicationContext context3 =
new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("config/spring.xml");
// 使用上下文
UserService userService = context1.getBean(UserService.class);
}
}最佳实践:
public class ConfigManager {
private static final String CONFIG_DIR = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/config";
public static ApplicationContext createApplicationContext(String profile) {
String configPath = CONFIG_DIR + "/application-" + profile + ".xml";
return new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(configPath);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 根据环境创建不同的上下文
String env = System.getProperty("spring.profiles.active", "dev");
ApplicationContext context = createApplicationContext(env);
}
}4️⃣ WebApplicationContext - Web应用的守护神

适用场景:
- Web应用开发
- Spring MVC应用
- Servlet容器集成
核心特点:
- 继承自ApplicationContext
- 提供Web特有的功能
- 支持Servlet生命周期集成
Web.xml配置示例:
<!-- web.xml -->
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!-- Spring Context配置 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml
/WEB-INF/spring/app-config.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- 监听器 -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- Spring MVC配置 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/servlet-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web.xml>Servlet集成示例:
// 自定义Servlet
@WebServlet("/api/users")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
// 获取WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext context =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(
getServletContext());
// 手动注入(不推荐,应该使用注解)
if (userService == null) {
userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
List<User> users = userService.getAllUsers();
// 返回JSON响应
}
}
// 使用注解的控制器
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ApiController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/users")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> getUsers() {
return userService.getAllUsers();
}
}生产环境实战:微服务架构中的Spring Context
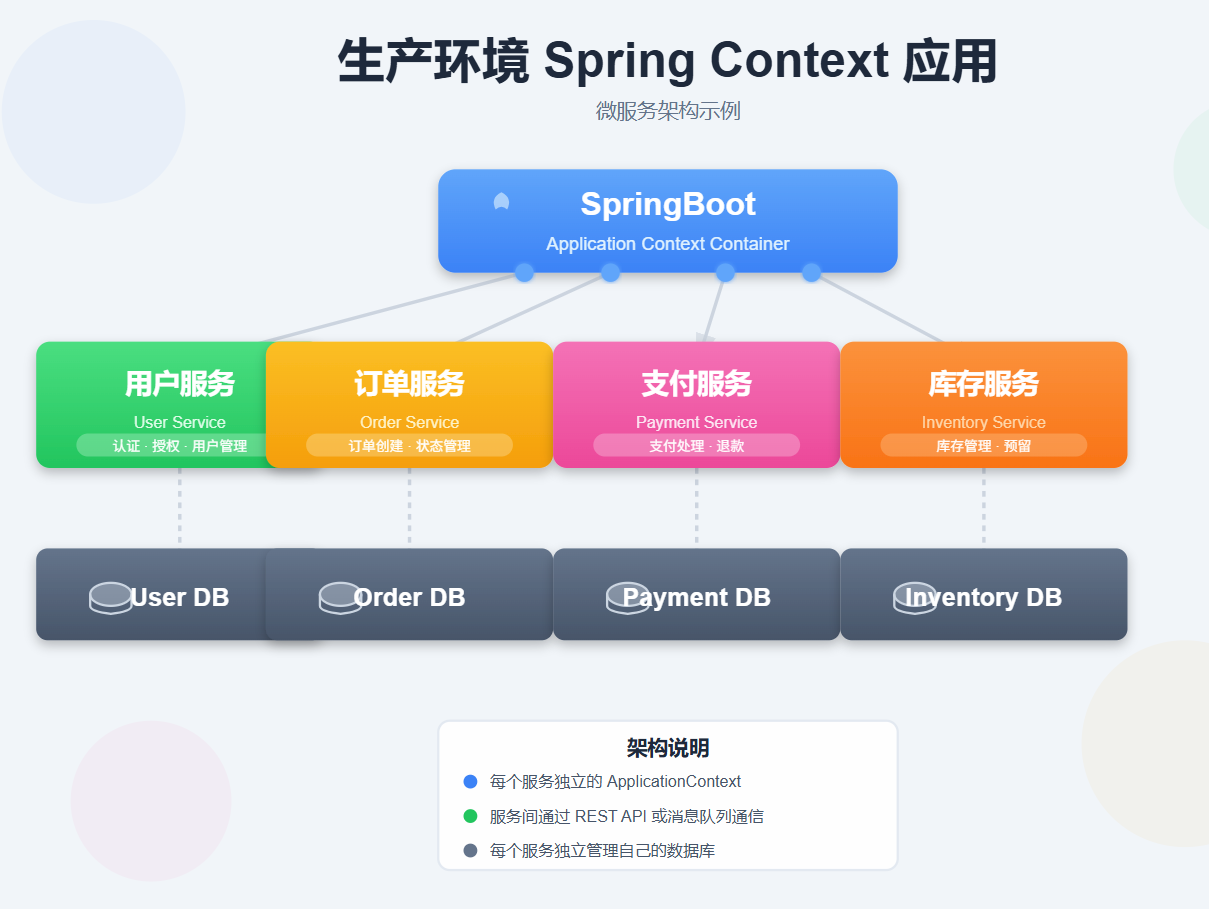
微服务集成示例
// 用户服务
@Configuration
@EnableEurekaClient
@ComponentScan("com.example.user")
public class UserServiceProvider {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(UserServiceProvider.class, args);
}
}
// 订单服务
@Configuration
@EnableEurekaClient
@ComponentScan("com.example.order")
public class OrderServiceProvider {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceProvider.class, args);
}
}
// 公共配置
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:application-common.properties")
public class CommonConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
return LettuceConnectionFactory.builder()
.host("redis-server")
.port(6379)
.build();
}
}Spring Boot与Spring Cloud整合
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableCircuitBreaker
public class MicroserviceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MicroserviceApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext() {
return new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
}
}
// 服务实现类
@Service
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Autowired
private UserClient userClient;
@Autowired
private PaymentClient paymentClient;
@Autowired
private InventoryClient inventoryClient;
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "createOrderFallback")
@Override
public Order createOrder(OrderDTO orderDTO) {
// 1. 检查用户
User user = userClient.getUser(orderDTO.getUserId());
// 2. 检查库存
inventoryClient.checkInventory(orderDTO.getItems());
// 3. 创建订单
Order order = new Order();
// ... 设置订单信息
// 4. 处理支付
PaymentResult payment = paymentClient.processPayment(order);
return orderRepository.save(order);
}
public Order createOrderFallback(OrderDTO orderDTO) {
// 降级处理
Order order = new Order();
order.setStatus("FAILED");
return order;
}
}性能优化与最佳实践
1. 上下文加载优化
// 延迟加载
@Configuration
public class OptimizedConfig {
@Lazy
@Bean
public HeavyService heavyService() {
return new HeavyService();
}
@Bean
@Primary
@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON,
proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
public ExpensiveService expensiveService() {
return new ExpensiveService();
}
}2. 内存管理
// 配置JVM参数
// 在启动脚本中添加:
// -XX:+UseG1GC -Xms512m -Xmx1024m -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=256m
// 配置Bean生命周期
@Configuration
public class LifecycleConfig {
@Bean(destroyMethod = "cleanup")
public ResourceCleanup resourceCleanup() {
return new ResourceCleanup();
}
@Bean
@DependsOn("resourceCleanup")
public MainService mainService() {
return new MainService();
}
}3. 多环境配置
// application-dev.properties
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://dev-db:3306/mydb
spring.datasource.username=dev_user
spring.datasource.password=dev_pass
// application-prod.properties
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://prod-db:3306/mydb
spring.datasource.username=prod_user
spring.datasource.password=${PROD_DB_PASSWORD}
// application-test.properties
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://test-db:3306/mydb
spring.datasource.username=test_user
spring.datasource.password=test_pass
// 激活不同环境
java -jar app.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod总结
四种ApplicationContext各有其适用场景:
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext - 现代Java配置的首选
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext - 传统XML配置的可靠选择
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext - 外部配置管理的灵活方案
- WebApplicationContext - Web应用的专用容器
在实际开发中,推荐根据项目需求和技术栈选择合适的ApplicationContext实现方式,并注意性能优化和最佳实践的应用。
记住,Spring Context是Spring框架的核心,掌握它的使用将让你在Spring开发的道路上更加游刃有余!