生命周期相关
这里还是以多任务中启动自由窗口为例,对比与桌面侧直接启动应用的生命周期
桌面侧直接启动应用的生命周期
java
1181 1181 I wm_on_top_resumed_lost_called: [235136609,com.android.launcher3.uioverrides.QuickstepLauncher,topStateChangedWhenResumed]
1181 1181 I wm_on_paused_called: [235136609,com.android.launcher3.uioverrides.QuickstepLauncher,performPause,0]
2765 2765 I wm_on_create_called: [227340519,com.android.messaging.ui.conversationlist.ConversationListActivity,performCreate,129]
2765 2765 I wm_on_start_called: [227340519,com.android.messaging.ui.conversationlist.ConversationListActivity,handleStartActivity,1]
2765 2765 I wm_on_resume_called: [227340519,com.android.messaging.ui.conversationlist.ConversationListActivity,RESUME_ACTIVITY,17]
2765 2765 I wm_on_top_resumed_gained_called: [227340519,com.android.messaging.ui.conversationlist.ConversationListActivity,topStateChangedWhenResumed]
1181 1181 I wm_on_stop_called: [235136609,com.android.launcher3.uioverrides.QuickstepLauncher,STOP_ACTIVITY_ITEM,6]从多任务启动自由窗口生命周期
java
//进入多任务
1181 1181 I wm_on_restart_called: [235136609,com.android.launcher3.uioverrides.QuickstepLauncher,performRestart,0]
1181 1181 I wm_on_start_called: [235136609,com.android.launcher3.uioverrides.QuickstepLauncher,handleStartActivity,10]
1181 1181 I wm_on_resume_called: [235136609,com.android.launcher3.uioverrides.QuickstepLauncher,RESUME_ACTIVITY,11]
1181 1181 I wm_on_top_resumed_gained_called: [235136609,com.android.launcher3.uioverrides.QuickstepLauncher,topStateChangedWhenResumed]
//启动自由窗口
2073 2073 I wm_on_paused_called: [162074025,com.android.messaging.ui.conversationlist.ConversationListActivity,performPause,1]
1181 1181 I wm_on_top_resumed_lost_called: [235136609,com.android.launcher3.uioverrides.QuickstepLauncher,topStateChangedWhenResumed]
2073 2073 I wm_on_stop_called: [162074025,com.android.messaging.ui.conversationlist.ConversationListActivity,handleRelaunchActivity,0]
2073 2073 I wm_on_destroy_called: [162074025,com.android.messaging.ui.conversationlist.ConversationListActivity,performDestroy,0]
2073 2073 I wm_on_create_called: [162074025,com.android.messaging.ui.conversationlist.ConversationListActivity,performCreate,34]
2073 2073 I wm_on_start_called: [162074025,com.android.messaging.ui.conversationlist.ConversationListActivity,handleStartActivity,1]
2073 2073 I wm_on_resume_called: [162074025,com.android.messaging.ui.conversationlist.ConversationListActivity,RESUME_ACTIVITY,28]
2073 2073 I wm_on_top_resumed_gained_called: [162074025,com.android.messaging.ui.conversationlist.ConversationListActivity,topStateChangedWhenResumed]对比直接从桌面侧启动应用时的生命周期流程存在差异,即启动自由窗口时底层activity(launcher3)没有进行pause。
一般来说当一个应用启动,那么当前应用就会走pause流程,我们这里launcher3为什么没有走pause呢?
其实自由窗口的启动本质上来说就是启动一个具有特殊属性activity,因此我们需要回顾activity的启动流程中桌面的pause是如何确定的。
resumeTopActivity中pause流程分析
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/TaskFragment.java
java
final boolean resumeTopActivity(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options,
boolean deferPause) {
......
boolean pausing = !deferPause && taskDisplayArea.pauseBackTasks(next);先看这个resume流程,这会去判断是否需要pause。
这里deferPause的值是通过Task.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked方法中传递过来的,其值为false,因此!deferPause为true。
next指的是要启动的activity(我们这里是ConversationListActivity)。
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/TaskDisplayArea.java
java
/**
* Pause all activities in either all of the root tasks or just the back root tasks. This is
* done before resuming a new activity and to make sure that previously active activities are
* paused in root tasks that are no longer visible or in pinned windowing mode. This does not
* pause activities in visible root tasks, so if an activity is launched within the same root
* task, hen we should explicitly pause that root task's top activity.
*
* @param resuming The resuming activity.
* @return {@code true} if any activity was paused as a result of this call.
*/
boolean pauseBackTasks(ActivityRecord resuming) {
final int[] someActivityPaused = {0};
forAllLeafTasks(leafTask -> {
// Check if the direct child resumed activity in the leaf task needed to be paused if
// the leaf task is not a leaf task fragment.
//task fragment场景,暂不关注
if (!leafTask.isLeafTaskFragment()) {
final ActivityRecord top = topRunningActivity();
final ActivityRecord resumedActivity = leafTask.getResumedActivity();
if (resumedActivity != null && top.getTaskFragment() != leafTask) {
// Pausing the resumed activity because it is occluded by other task fragment.
if (leafTask.startPausing(false /* uiSleeping*/, resuming, "pauseBackTasks")) {
someActivityPaused[0]++;
}
}
}
//遍历所有leafTask节点,即最底端Task节点
leafTask.forAllLeafTaskFragments((taskFrag) -> {
final ActivityRecord resumedActivity = taskFrag.getResumedActivity();
//判断当前taskFrag是否有存在resumed的Activity,并且即将启动的Activity不能resumed
if (resumedActivity != null && !taskFrag.canBeResumed(resuming)) {
//暂停当前存在resumed的Activity
if (taskFrag.startPausing(false /* uiSleeping*/, resuming, "pauseBackTasks")) {
//记录暂停的Activity
someActivityPaused[0]++;
}
}
}, true /* traverseTopToBottom */);
}, true /* traverseTopToBottom */);
return someActivityPaused[0] > 0;
}这个方法会遍历TaskDisplayArea下的所有leafTask节点,即最底端Task节点
- 判断当前Task的Activity是否存在resumed状态,且即将启动的Activity不能被resumed
- 暂停当前存在resumed的Activity,若暂停成功,给参数
someActivityPaused计数
如下图圈的task节点是会遍历的task节点。
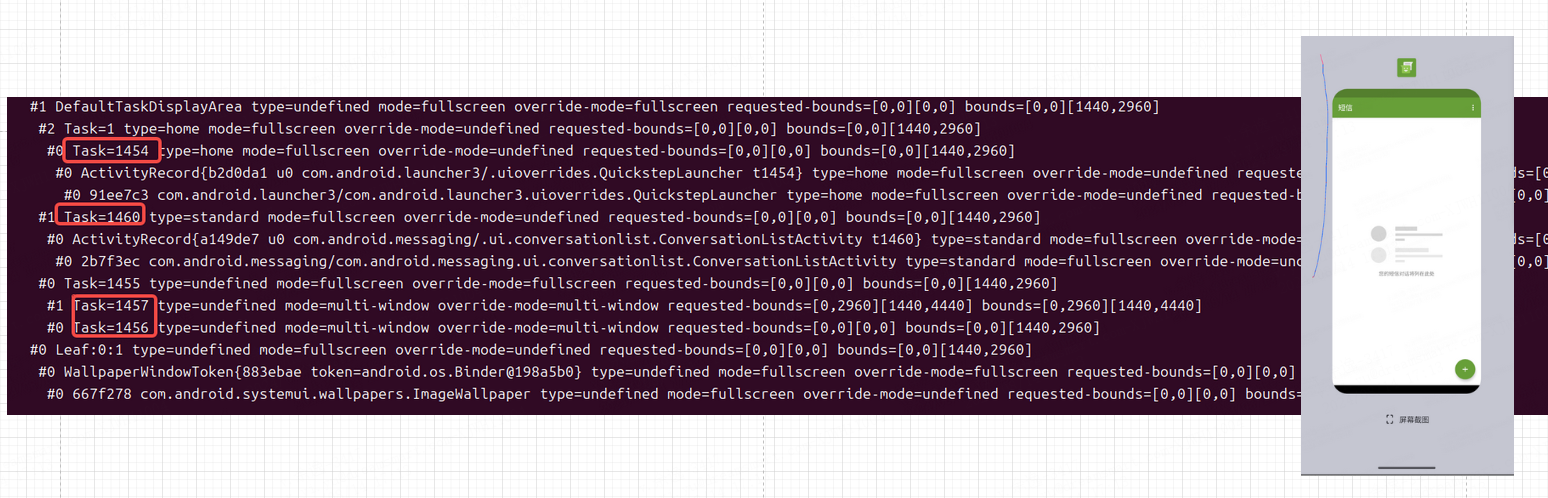
在该界面当我们点击启动自由窗口后开始条件判断resumedActivity != null && !taskFrag.canBeResumed(resuming)。
taskFrag.getResumedActivity()获取此时是resumed状态的task,当遍历到桌面Task时,由于我们要从多任务进入到自由窗口,而此时多任务界面为resumed状态,存在resumed状态的Activity,因此参数resumedActivity不为空。
这里resumedActivity != null为true,再来看看!taskFrag.canBeResumed(resuming)其中参数resuming指的是即将启动的Activity(ConversationListActivity)。
canBeResumed
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/TaskFragment.java
java
/**
* Returns {@code true} is the activity in this TaskFragment can be resumed.
*
* @param starting The currently starting activity or {@code null} if there is none.
*/
boolean canBeResumed(@Nullable ActivityRecord starting) {
// No need to resume activity in TaskFragment that is not visible.
return isTopActivityFocusable()
&& getVisibility(starting) == TASK_FRAGMENT_VISIBILITY_VISIBLE;
}isTopActivityFocusable()判断顶部Activity是否可聚焦,一般为true,这里主要关注getVisibility(starting)方法,通样传递starting即将启动的的Activity (ConversationListActivity)。
java
/**
* Returns the visibility state of this TaskFragment.
*
* @param starting The currently starting activity or null if there is none.
*/
@TaskFragmentVisibility
int getVisibility(ActivityRecord starting) {
......
//根据上述代码流程,这里this指的是桌面task,因此此时getParent获取的是桌面task的task
final WindowContainer<?> parent = getParent();
......
// This TaskFragment is only considered visible if all its parent TaskFragments are
// considered visible, so check the visibility of all ancestor TaskFragment first.
//判断parent是否是task或者TaskFragment
if (parent.asTaskFragment() != null) {
//递归调用getVisibility,直到parent为TaskDisplayArea(不是task)为止。
//其目的是为了能够遍历到TaskDisplayArea下所有task节点
final int parentVisibility = parent.asTaskFragment().getVisibility(starting);
if (parentVisibility == TASK_FRAGMENT_VISIBILITY_INVISIBLE) {
// Can't be visible if parent isn't visible
return TASK_FRAGMENT_VISIBILITY_INVISIBLE;
} else if (parentVisibility == TASK_FRAGMENT_VISIBILITY_VISIBLE_BEHIND_TRANSLUCENT) {
// Parent is behind a translucent container so the highest visibility this container
// can get is that.
gotTranslucentFullscreen = true;
}
}
final List<TaskFragment> adjacentTaskFragments = new ArrayList<>();
//逆序遍历parent下的task,即优先最前台,从大到小遍历
for (int i = parent.getChildCount() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
final WindowContainer other = parent.getChildAt(i);
if (other == null) continue;
//判断other是否是运行中的Activity
final boolean hasRunningActivities = hasRunningActivity(other);
//other和this相同则中断循环,做后续处理
if (other == this) {
......
// Should be visible if there is no other fragment occluding it, unless it doesn't
// have any running activities, not starting one and not home stack.
shouldBeVisible = hasRunningActivities
|| (starting != null && starting.isDescendantOf(this))
|| isActivityTypeHome();
break;
}
if (!hasRunningActivities) {
continue;
}
//根据other的WindowingMode判断返回值
final int otherWindowingMode = other.getWindowingMode();
if (otherWindowingMode == WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN) {
if (isTranslucent(other, starting)) {
// Can be visible behind a translucent fullscreen TaskFragment.
gotTranslucentFullscreen = true;
continue;
}
return TASK_FRAGMENT_VISIBILITY_INVISIBLE;
} else if (otherWindowingMode == WINDOWING_MODE_MULTI_WINDOW
&& other.matchParentBounds()) {
if (isTranslucent(other, starting)) {
// Can be visible behind a translucent TaskFragment.
gotTranslucentFullscreen = true;
continue;
}
// Multi-window TaskFragment that matches parent bounds would occlude other children
return TASK_FRAGMENT_VISIBILITY_INVISIBLE;
}
......
}
if (!shouldBeVisible) {
return TASK_FRAGMENT_VISIBILITY_INVISIBLE;
}
// Lastly - check if there is a translucent fullscreen TaskFragment on top.
return gotTranslucentFullscreen
? TASK_FRAGMENT_VISIBILITY_VISIBLE_BEHIND_TRANSLUCENT
: TASK_FRAGMENT_VISIBILITY_VISIBLE;
}简单来说这个方法就是判断当前启动之后的activity的WindowingMode如果不是 WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN或者WINDOWING_MODE_MULTI_WINDOW那么就返回TASK_FRAGMENT_VISIBILITY_VISIBLE,使后台应用可见,不进入到pause流程。
因此启动自由窗口时底层activity(launcher3)不会进行pause。
保持顶部显示方法
当我们启动了一个自由窗口后,即使启动了其他的应用也希望这个窗口一直保持在顶部。
回顾自由窗口启动流程中桌面侧会设置相应的ActivityOptions给需要启动为自由窗口activity。
activityOptions在Launcher侧设置
代码路径:packages/apps/Launcher3/quickstep/src/com/android/quickstep/TaskShortcutFactory.java
java
class FreeformSystemShortcut extends SystemShortcut<BaseDraggingActivity> {
......
private ActivityOptions makeLaunchOptions(Activity activity) {
ActivityOptions activityOptions = ActivityOptions.makeBasic();
activityOptions.setLaunchWindowingMode(WINDOWING_MODE_FREEFORM);
// Arbitrary bounds only because freeform is in dev mode right now
final View decorView = activity.getWindow().getDecorView();
final WindowInsets insets = decorView.getRootWindowInsets();
final Rect r = new Rect(0, 0, decorView.getWidth() / 2, decorView.getHeight() / 2);
r.offsetTo(insets.getSystemWindowInsetLeft() + 50,
insets.getSystemWindowInsetTop() + 50);
activityOptions.setLaunchBounds(r);
/* 添加保持在顶部的options start */
activityOptions.setTaskAlwaysOnTop(true);
/* end */
return activityOptions;
}
}修改后发现进入到自由窗口之后,启动其他应用仍然会被覆盖,因此我们需要确认activityOptions.setTaskAlwaysOnTop(true);在桌面侧设置的参数是否在system_server端生效。
activityOptions在system_server侧的设置
回顾TaskDisplayArea.getOrCreateRootTask方法
java
/**
* When two level tasks are required for given windowing mode and activity type, returns an
* existing compatible root task or creates a new one.
* For one level task, the candidate task would be reused to also be the root task or create
* a new root task if no candidate task.
*
* @param windowingMode The windowing mode the root task should be created in.
* @param activityType The activityType the root task should be created in.
* @param onTop If true the root task will be created at the top of the display,
* else at the bottom.
* @param candidateTask The possible task the activity might be launched in. Can be null.
* @param sourceTask The task requesting to start activity. Used to determine which of the
* adjacent roots should be launch root of the new task. Can be null.
* @param options The activity options used to the launch. Can be null.
* @param launchFlags The launch flags for this launch.
* @return The root task to use for the launch.
* @see #getRootTask(int, int)
*/
Task getOrCreateRootTask(int windowingMode, int activityType, boolean onTop,
@Nullable Task candidateTask, @Nullable Task sourceTask,
@Nullable ActivityOptions options, int launchFlags) {
//我们这里windowingMode传递的是WINDOWING_MODE_FREEFORM,
//因此resolvedWindowingMode为WINDOWING_MODE_FREEFORM
final int resolvedWindowingMode =
windowingMode == WINDOWING_MODE_UNDEFINED ? getWindowingMode() : windowingMode;
// Need to pass in a determined windowing mode to see if a new root task should be created,
// so use its parent's windowing mode if it is undefined.
//我们这里resolvedWindowingMode是WINDOWING_MODE_FREEFORM
//activityType是ACTIVITY_TYPE_STANDARD,因此alwaysCreateRootTask为true
//这取反为false,因此不进入该逻辑
if (!alwaysCreateRootTask(resolvedWindowingMode, activityType)) {
Task rootTask = getRootTask(resolvedWindowingMode, activityType);
if (rootTask != null) {
return rootTask;
}
} else if (candidateTask != null) {
final int position = onTop ? POSITION_TOP : POSITION_BOTTOM;
//这里getLaunchRootTask是同options获取,我们这里options没有设置过mLaunchRootTask,因此为null
final Task launchParentTask = getLaunchRootTask(resolvedWindowingMode, activityType,
options, sourceTask, launchFlags, candidateTask);
//launchParentTask为null不进入该流程
if (launchParentTask != null) {
if (candidateTask.getParent() == null) {
launchParentTask.addChild(candidateTask, position);
} else if (candidateTask.getParent() != launchParentTask) {
candidateTask.reparent(launchParentTask, position);
}
//candidateTask.getDisplayArea()和this都是默认的TaskDisplayArea,即DefaultTaskDisplayArea
//两者相同,即candidateTask.getDisplayArea() != this 为false,因此不进入该流程
} else if (candidateTask.getDisplayArea() != this
|| candidateTask.getRootTask().mReparentLeafTaskIfRelaunch) {
if (candidateTask.getParent() == null) {
addChild(candidateTask, position);
} else {
candidateTask.reparent(this, onTop);
}
}
// Update windowing mode if necessary, e.g. launch into a different windowing mode.
//windowingMode传递的是WINDOWING_MODE_FREEFORM
//candidateTask自身就是rootTask
//candidateTask前后windowingMode有发生变化
if (windowingMode != WINDOWING_MODE_UNDEFINED && candidateTask.isRootTask()
&& candidateTask.getWindowingMode() != windowingMode) {
//ShellTransitions调用collect处理
candidateTask.mTransitionController.collect(candidateTask);
//设置task窗口模式
candidateTask.setWindowingMode(windowingMode);
}
//返回candidateTask的rootTask
return candidateTask.getRootTask();
}
return new Task.Builder(mAtmService)
.setWindowingMode(windowingMode)
.setActivityType(activityType)
.setOnTop(onTop)
.setParent(this)
.setSourceTask(sourceTask)
.setActivityOptions(options)
.setLaunchFlags(launchFlags)
.build();
}在自由窗口启动流程中,我们讲到,其最主要的操作在该流程中进行。
java
if (windowingMode != WINDOWING_MODE_UNDEFINED && candidateTask.isRootTask()
&& candidateTask.getWindowingMode() != windowingMode) {
candidateTask.mTransitionController.collect(candidateTask);
candidateTask.setWindowingMode(windowingMode);
}
return candidateTask.getRootTask();但是从代码中我们可以看到,这里并没有进行给task设置AlwaysOnTop,所以不会在最顶端显示。
修改
方案一:直接在上述代码中添加设置AlwaysOnTop
java
if (windowingMode != WINDOWING_MODE_UNDEFINED && candidateTask.isRootTask()
&& candidateTask.getWindowingMode() != windowingMode) {
candidateTask.mTransitionController.collect(candidateTask);
candidateTask.setWindowingMode(windowingMode);
/* 添加保持在顶部的options start */
candidateTask.setTaskAlwaysOnTop(true);
/* end */
}
return candidateTask.getRootTask();这种改法可以把桌面端设置TaskAlwaysOnTop给去掉,但是比较局限,不太推荐
方案二:在最开始调用anyTaskForId方法获取task的位置修改
java
int startActivityFromRecents(int callingPid, int callingUid, int taskId,
SafeActivityOptions options) {
......
synchronized (mService.mGlobalLock) {
......
try {
task = mRootWindowContainer.anyTaskForId(taskId,
MATCH_ATTACHED_TASK_OR_RECENT_TASKS_AND_RESTORE, activityOptions, ON_TOP);
/* 添加保持在顶部的options start */
//判断task是否是自由窗口模式
if(task.inFreeformWindowingMode()){
//获取桌面侧设置的TaskAlwaysOnTop状态
task.setAlwaysOnTop(activityOptions.getTaskAlwaysOnTop());
}
/* end */
if (task == null) {
mWindowManager.executeAppTransition();
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"startActivityFromRecents: Task " + taskId + " not found.");
}
if (moveHomeTaskForward) {
// We always want to return to the home activity instead of the recents
// activity from whatever is started from the recents activity, so move
// the home root task forward.
// TODO (b/115289124): Multi-display supports for recents.
mRootWindowContainer.getDefaultTaskDisplayArea().moveHomeRootTaskToFront(
"startActivityFromRecents");
}
......这个改法比较推荐,在anyTaskForId整个流程完成之后再进行判断设置,比较稳健。