文章目录
- 前言
- [一、 @Cacheable bean 加载](#一、 @Cacheable bean 加载)
- 二、缓存查询
-
- [2.1 切面通知器进入](#2.1 切面通知器进入)
- [2.2 缓存查询:](#2.2 缓存查询:)
- 总结
前言
我们在开发中有时会使用到 @Cacheable 来缓存结果,这样在下一次请求进入后,可以先从缓存中获取结果,如果缓存中没有在进入原方法,最后将获取到的结果放入到缓存中,以便下次请求可以直接使用。那么 @Cacheable 它是如何实现的呢?
一、 @Cacheable bean 加载
spring 在创建单例bean 的时候,有一个步骤就是判断 是否需要为改bean 创建一个代理的bean 来进行业务的增强。
bean 的代理类过程:
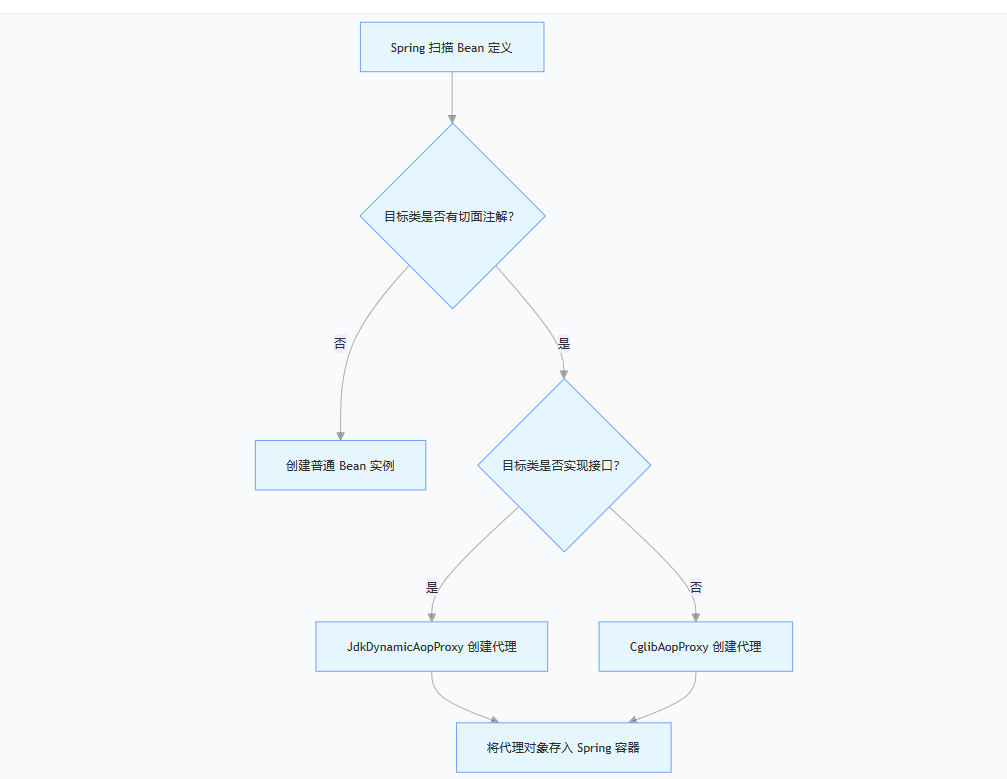
- Spring 启动时,AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator(自动代理创建器)会扫描所有 Bean;
- 若 Bean 有切面相关注解(如 @Cacheable/@Transactional/@Aspect), 获取当前 Bean 匹配的所有通知(Advice),为其创建动态代理bean;
AbstractAutoProxyCreator,核心方法是 postProcessAfterInitialization(Bean 初始化后处理):
java
// AbstractAutoProxyCreator 核心方法(简化版)
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
// 1. 为 Bean 生成唯一键(类名 + beanName)
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
// 2. 检查是否已创建过代理,避免重复创建
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
// 3. 核心:判断是否需要创建代理,需要则创建
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
// 核心逻辑:判断是否需要创建代理
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 步骤1:获取当前 Bean 匹配的所有通知(Advice)
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
// 步骤2:若有匹配的通知,创建代理
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 步骤3:创建代理对象(核心!)
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}二、缓存查询
当访问后端资源时,会先获取到改资源对应的 通知 责任链,然后依次进行调用;本文 中 spring-boot-starter-cache 版本为 4.0.1
2.1 切面通知器进入
ReflectiveMethodInvocation 中的invocation.proceed() 是执行通知链的核心,采用「责任链模式」依次执行每个通知:
java
// ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed() 核心源码(简化版)
@Override
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// 1. 如果所有通知都执行完了,执行原始方法
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint(); // 调用原始方法:method.invoke(target, args)
}
// 2. 获取下一个要执行的通知(如 CacheInterceptor)
Object interceptor = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
// 3. 执行当前通知,并递归调用 proceed() 执行后续通知
if (interceptor instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// 动态匹配的通知(如根据方法参数匹配)
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptor;
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
} else {
return proceed(); // 不匹配则跳过,执行下一个通知
}
} else {
// 普通通知:执行通知逻辑(如 CacheInterceptor.invoke())
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptor).invoke(this);
}
}- currentInterceptorIndex 记录当前执行到的通知索引;
- 每个通知执行时,会调用 invocation.proceed() 触发下一个通知的执行;
- 最后一个通知执行完后,调用 invokeJoinpoint() 执行原始方法 ------ 这就是「环绕通知」能控制是否执行原始方法的底层原因。
缓存切面的通知实现:CacheInterceptor
@Cacheable 的核心是 CacheInterceptor(实现了 MethodInterceptor),其 invoke() 方法就是通知逻辑:
java
// CacheInterceptor.invoke() 核心源码
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 调用父类逻辑:先查缓存,未命中则执行原始方法
return execute(invocation, invocation.getThis(), invocation.getMethod(), invocation.getArguments());
}2.2 缓存查询:
CacheInterceptor # invoke 进行缓存查询 ,本文以redis 实现为例 ,对应spring-context 为7.0.1
CacheAspectSupport #execute -》 该方法是否有缓存的注解-》有缓存的注解-》findCachedValue 获取缓存中的数据-》如果命中缓存则直接将数据返回-》 如果没有命中缓存则调用原始的方法, 将获取到的数据进行缓存-》 返回数据
(1) 缓存获取:
java
@Override
public @Nullable Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 调用的目标方法
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
// 封装原始方法执行逻辑:调用 invocation.proceed() 执行业务方法
CacheOperationInvoker aopAllianceInvoker = () -> {
try {
return invocation.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper(ex);
}
};
Object target = invocation.getThis();
Assert.state(target != null, "Target must not be null");
try {
// 用父类 CacheAspectSupport 的 execute 方法
return execute(aopAllianceInvoker, target, method, invocation.getArguments());
}
catch (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper th) {
throw th.getOriginal();
}
}execute 获取缓存数据
bash
private @Nullable Object execute(CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts) {
// sync 同步注解处理
if (contexts.isSynchronized()) {
// Special handling of synchronized invocation
return executeSynchronized(invoker, method, contexts);
}
// Process any early evictions
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), true,
CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
// Check if we have a cached value matching the conditions
// 获取缓存数据
Object cacheHit = findCachedValue(invoker, method, contexts);
if (cacheHit == null || cacheHit instanceof Cache.ValueWrapper) {
// 没有命中缓存 则调用原始的方法并获取结果数据后 放入到缓存中
return evaluate(cacheHit, invoker, method, contexts);
}
return cacheHit;
}
private @Nullable Object findCachedValue(CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts) {
for (CacheOperationContext context : contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class)) {
// 遍历有缓存的操作
if (isConditionPassing(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT)) {
// 生成缓存对应 的key
Object key = generateKey(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
// 获取缓存数据
Object cached = findInCaches(context, key, invoker, method, contexts);
if (cached != null) {
// 命中缓存数据则直接返回
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Cache entry for key '" + key + "' found in cache(s) " + context.getCacheNames());
}
return cached;
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No cache entry for key '" + key + "' in cache(s) " + context.getCacheNames());
}
}
}
}
// 没有名中缓存数据则返回null
return null;
}
(2) 没有名中缓存
当从缓存中获取的数据为null 时,则调用原始方法,获取数据,并进行缓存
bash
private @Nullable Object evaluate(@Nullable Object cacheHit, CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method,
CacheOperationContexts contexts) {
// Re-invocation in reactive pipeline after late cache hit determination?
if (contexts.processed) {
return cacheHit;
}
Object cacheValue;
Object returnValue;
if (cacheHit != null && !hasCachePut(contexts)) {
// If there are no put requests, just use the cache hit
cacheValue = unwrapCacheValue(cacheHit);
returnValue = wrapCacheValue(method, cacheValue);
}
else {
// Invoke the method if we don't have a cache hit
// 通过反射调用原始的方法
returnValue = invokeOperation(invoker);
cacheValue = unwrapReturnValue(returnValue);
}
// Collect puts from any @Cacheable miss, if no cached value is found
List<CachePutRequest> cachePutRequests = new ArrayList<>(1);
if (cacheHit == null) {
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class), cacheValue, cachePutRequests);
}
// Collect any explicit @CachePuts
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class), cacheValue, cachePutRequests);
// Process any collected put requests, either from @CachePut or a @Cacheable miss
for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) {
// 最终调用 doPut(cache, key, value); 将结果缓存
Object returnOverride = cachePutRequest.apply(cacheValue);
if (returnOverride != null) {
returnValue = returnOverride;
}
}
// Process any late evictions
Object returnOverride = processCacheEvicts(
contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), false, returnValue);
if (returnOverride != null) {
returnValue = returnOverride;
}
// Mark as processed for re-invocation after late cache hit determination
contexts.processed = true;
// 返回结果数据
return returnValue;
}总结
本文对Cacheable 缓存的获取过程进行记录。