🔥我的主页: 九转苍翎
⭐️个人专栏: 《Java SE 》 《Java集合框架系统精讲》 《MySQL高手之路:从基础到高阶 》 《计算机网络 》 《Java工程师核心能力体系构建》
天行健,君子以自强不息。
Java JDK版本:Oracle OpenJDK 17.0.9
SpringBoot版本:3.5.9
- Spring Web
- Lombok
- Spring for RabbitMQ
1.可靠传输
RabbitMQ在实际使用中,消息传输可能遇到多种问题。以下是三种典型且关键的"可能出现问题的情况",涵盖了从生产、传输到消费的完整生命周期:
- 生产者消息丢失:消息从生产者应用程序发出后,未能成功到达RabbitMQ Broker
- RabbitMQ Broker自身消息丢失:消息已经成功到达RabbitMQ Broker,但由于某些非正常原因(如服务器宕机),消息在被消费者消费之前,消息从队列中丢失了
- 消费者处理失败 :消息成功从队列投递给消费者,但消费者未能成功处理,或处理结果不满足业务要求
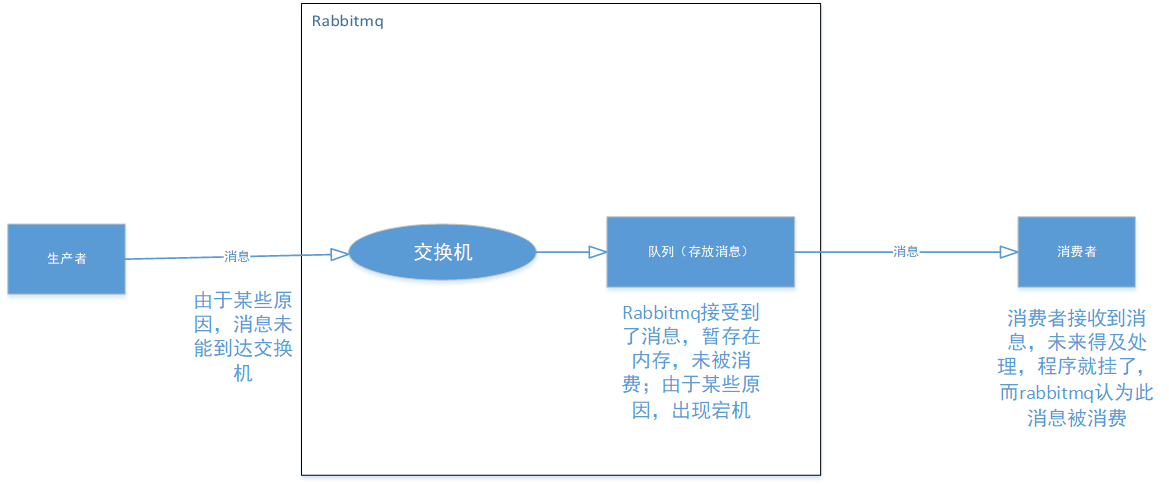
针对上述三种情况,RabbitMQ通过以下三种核心手段分别解决消息传输不同阶段的问题,用于实现消息可靠传输
- 生产者确认机制(Publisher Confirms):解决消息从生产者到Broker的可靠性问题
- 消息持久化(Message Durability):解决RabbitMQ Broker出现异常时导致消息丢失 的问题
- 消费者手动确认(Manual Acknowledgement):解决消费者处理失败导致消息丢失问题
1.1 生产者确认
生产者确认机制由Confirm确认模式 和Return退回模式组成,这两种模式可以且应该配合使用,分别解决:
- Confirm模式:确保消息到达RabbitMQ Broker的交换机
- Return模式:确保消息正确路由到队列(当mandatory=true时)
配置文件如下
yaml
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1:8080 # RabbitMQ服务器的IP地址
port: 5672
username: study
password: study
virtual-host: extension
publisher-confirm-type: correlated # 开启RabbitMQ的Publisher Confirm机制,实现异步消息接收确认1.1.1 confirm
生产者在发送消息的时候,会在发送端设置一个ConfirmCallback监听,无论消息是否到达交换机,这个监听都会被执行。如果消息成功到达交换机,ACK(Acknowledge character,确认字符)设置为true,否则为false
-
声明和配置交换器、队列和绑定关系
javaimport org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class RabbitMQConfig { @Bean("confirmQueue") public Queue confirmQueue(){ return QueueBuilder.durable(Constants.CONFIRM_QUEUE).build(); } @Bean("confirmExchange") public DirectExchange confirmExchange(){ return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange(Constants.CONFIRM_EXCHANGE).build(); } @Bean("confirmBinding") public Binding confirmBinding(@Qualifier("confirmExchange") DirectExchange directExchange,@Qualifier("confirmQueue") Queue queue){ return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(directExchange).with("confirm"); } } -
配置RabbitTemplate
javaimport lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.ConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @Slf4j public class RabbitTemplateConfig { @Bean("confirmRabbitTemplate") public RabbitTemplate confirmRabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory){ RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory); // 设置确认回调函数 rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback((correlationData, ack, cause) -> { if (ack){ if (correlationData != null) { log.info("消息接收成功, id:{}", correlationData.getId()); } }else { if (correlationData != null) { log.info("消息接收失败, id:{}, cause:{}", correlationData.getId(), cause); } } }); return rabbitTemplate; } }RabbitTemplate类是Spring AMQP框架中最核心的类,它封装了RabbitMQ客户端的操作,简化了与RabbitMQ的交互 -
发送消息
javaimport jakarta.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/producer") public class ProducerController { @Resource(name = "confirmRabbitTemplate") private RabbitTemplate confirmRabbitTemplate; @RequestMapping("/confirm") public String confirm(){ CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData("1"); confirmRabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.CONFIRM_EXCHANGE, "confirm", "confirm",correlationData); return "发送成功"; } }当指定不存在的交换机时,会发生以下错误

1.1.2 returns
消息到达交换机之后,会根据路由规则匹配把消息放入队列中。在此过程中,如果
存在消息无法被任何队列消费(即没有队列与消息的路由键匹配或队列不存在等),可以选择把消息退回给发送者。RabbitMQ把消息退回给发送者时,可以设置一个返回回调方法对消息进行处理
-
配置RabbitTemplate
javaimport lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.ConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @Slf4j public class RabbitTemplateConfig { @Bean("confirmRabbitTemplate") public RabbitTemplate confirmRabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory){ RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory); // 设置确认回调函数 rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback((correlationData, ack, cause) -> { if (ack){ if (correlationData != null) { log.info("消息接收成功, id:{}", correlationData.getId()); } }else { if (correlationData != null) { log.info("消息接收失败, id:{}, cause:{}", correlationData.getId(), cause); } } }); // 当消息无法路由到任何队列时,RabbitMQ会将消息返回给生产者 rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true); rabbitTemplate.setReturnsCallback(returned -> log.info("消息被退回:{}", returned)); return rabbitTemplate; } } -
发送消息
javaimport jakarta.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/producer") public class ProducerController { @Resource(name = "confirmRabbitTemplate") private RabbitTemplate confirmRabbitTemplate; @RequestMapping("/returns") public String returns(){ CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData("2"); confirmRabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.CONFIRM_EXCHANGE, "confirm", "confirm",correlationData); return "发送成功"; } }当路由键设置错误时
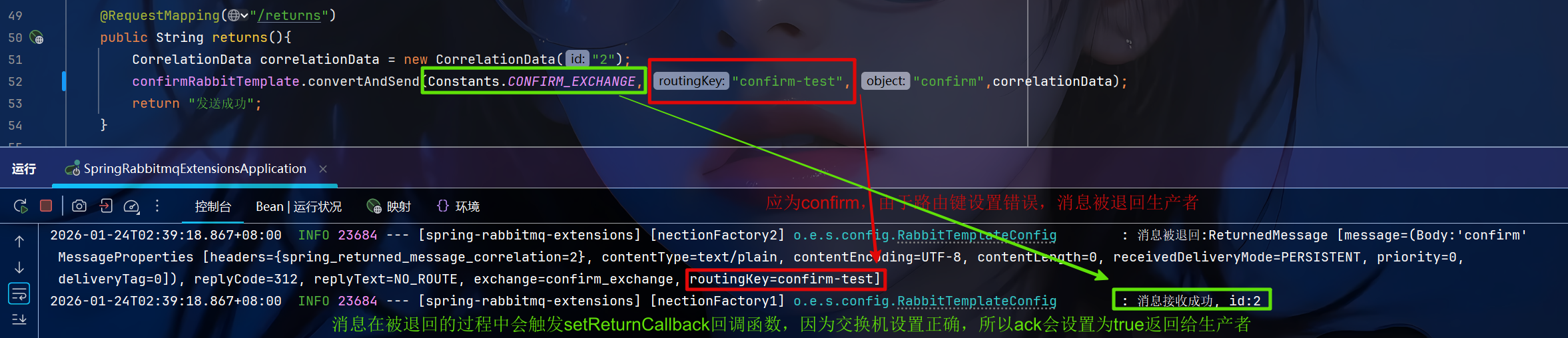
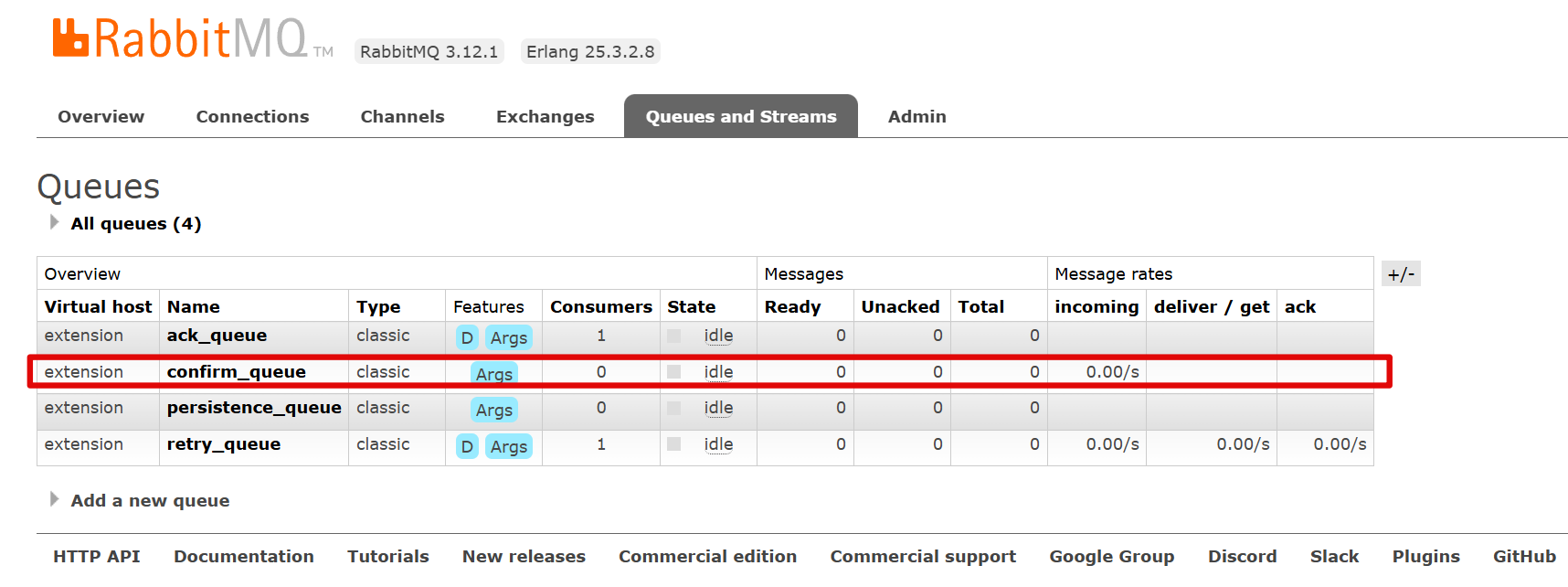
消息不会到达队列
1.2 消息持久化
RabbitMQ消息持久化需要三个层面的配合才能完整生效
- 交换器持久化(Exchange Durability):确保交换器在RabbitMQ重启后仍然存在
- 队列持久化(Queue Durability):确保队列在RabbitMQ重启后仍然存在
- 消息持久化(Message Persistence):确保消息内容被写入磁盘
RabbitMQ 持久化机制需要理解各组件之间的关系,以下重点需要注意:
- 队列持久化是消息持久化的前提条件
- 当队列设置为非持久化时,RabbitMQ重启后队列本身会被删除,即使其中的消息设置了持久化属性
- 设置了持久化的消息确实会被写入磁盘,但依附于队列存在。队列消失后,其关联的磁盘存储文件也会被清理
- 交换器、队列、消息的持久化相互独立
- 每个组件的持久化配置独立生效,互不影响
- 当交换器或队列设置为非持久化时,无论与其他组件是否存在绑定关系,在 RabbitMQ 重启后该组件都会被删除。这点容易与Java中的规则相混淆,Java中的变量或对象只要存在外部引用,就不会被回收
- 绑定关系的特殊性
- 绑定关系的持久化自动继承自队列和交换器,它本身没有单独的持久化设置
- 只要队列和交换器都是持久化的,它们之间的绑定关系在重启后会自动重建
-
声明和配置交换器、队列和绑定关系
javaimport org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class RabbitMQConfig { @Bean("persistenceQueue") public Queue persistenceQueue(){ return QueueBuilder.nonDurable(Constants.PERSISTENCE_QUEUE).build(); } @Bean("persistenceExchange") public DirectExchange persistenceExchange(){ return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange(Constants.PERSISTENCE_EXCHANGE).durable(false).build(); } @Bean("persistenceBinding") public Binding persistenceBinding(@Qualifier("persistenceExchange") DirectExchange directExchange,@Qualifier("persistenceQueue") Queue queue){ return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(directExchange).with("persistence"); } } -
配置RabbitTemplate
javaimport lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.ConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @Slf4j public class RabbitTemplateConfig { @Bean("rabbitTemplate") public RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) { return new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory); } } -
发送消息
javaimport jakarta.annotation.Resource; import org.example.springrabbitmqextensions.constant.Constants; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message; import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageDeliveryMode; import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageProperties; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/producer") public class ProducerController { @Resource(name = "rabbitTemplate") private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; @RequestMapping("/persistence") public String persistence(){ Message message = new Message("This is a persistent message".getBytes(),new MessageProperties()); message.getMessageProperties().setDeliveryMode(MessageDeliveryMode.PERSISTENT); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.PERSISTENCE_EXCHANGE, "persistence", message); return "发送成功"; } }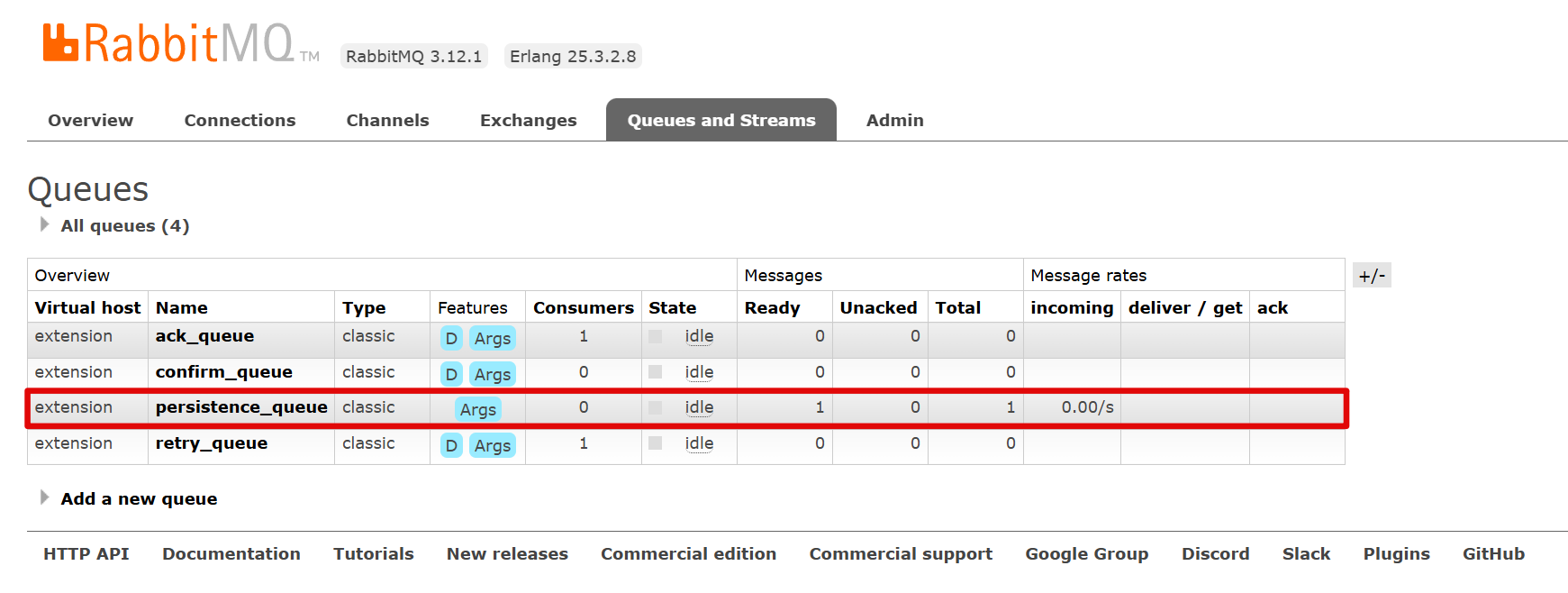
-
重启RabbitMQ服务器,并停止SpringBoot应用程序
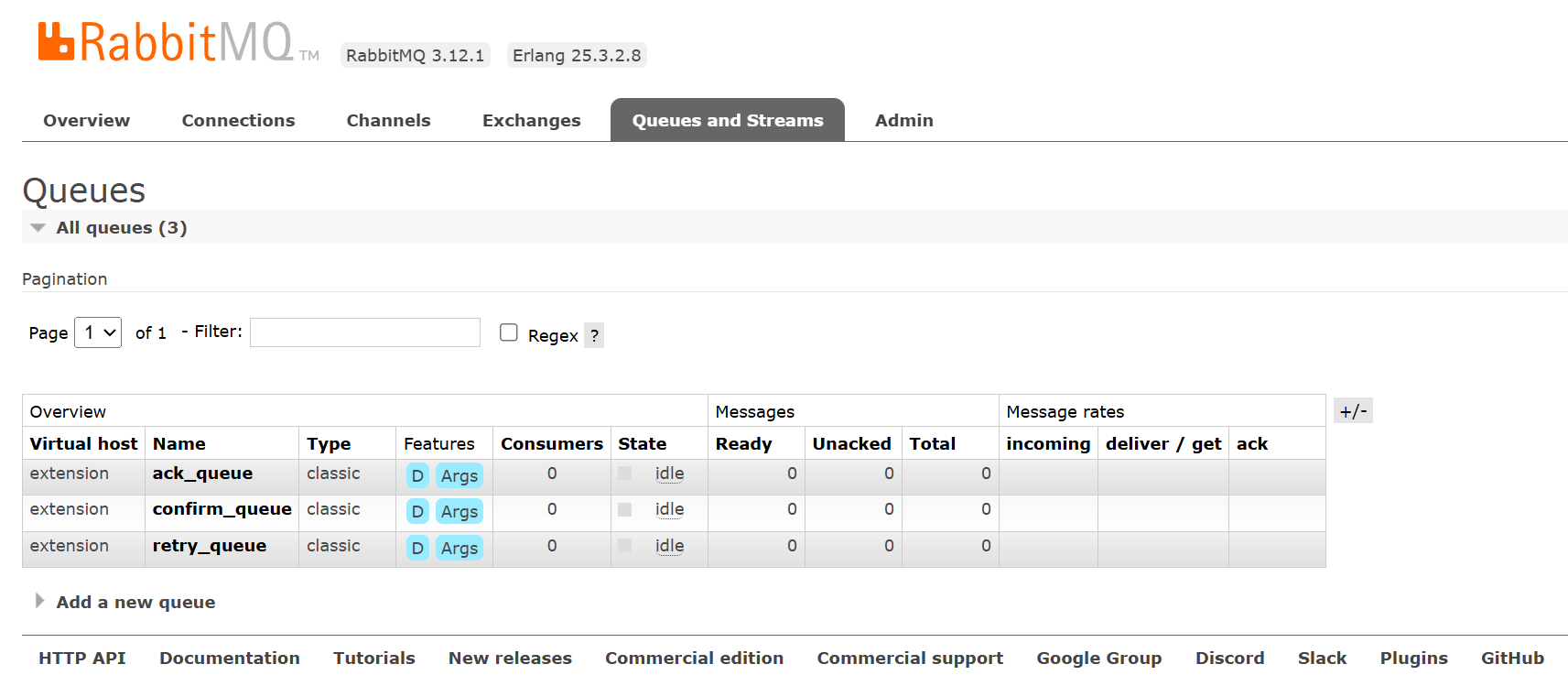
1.3 消费者确认
1.3.1 消息确认机制
消费者在订阅队列时,可以指定autoAck参数,根据这个参数消息确认机制分为以下两种
- 自动确认机制(Auto Acknowledge):消息一旦发送给消费者,RabbitMQ立即将其标记为已确认,然后立即从队列中删除该消息,无论消费者处理是否成功,消息都无法重新投递
- 手动确认机制(Manual Acknowledge):消费者处理完成后才发送确认,只有收到确认后才从队列删除消息,处理失败可拒绝消息,让其重新投递或进入死信队列
1.3.2 手动确认机制
-
肯定确认
java// 处理成功,从队列删除消息 channel.basicAck(deliveryTag, multiple); // deliveryTag: 消息唯一标识 // multiple: false=只确认本条,true=确认deliveryTag之前的所有消息 -
否定确认
java// requeue=true: 重新放回队列(可能无限循环) // requeue=false: 不重新入队(进入死信队列或丢弃) channel.basicReject(deliveryTag, requeue); -
批量否定确认
java// 推荐使用 channel.basicNack(deliveryTag, multiple, requeue);
1.3.3 Spring-AMQP消息确认机制
Spring-AMQP 在原生RabbitMQ确认机制基础上进行了封装和扩展,提供了更简洁、更强大的确认机制
- acknowledge-mode.none:消息一旦投递给消费者,不管消费者是否成功处理了消息,RabbitMQ 就会自动确认消息,然后从队列中移除消息(与原生RabbitMQ自动确认机制相同)
- acknowledge-mode.auto(默认):消费者在消息处理成功时会自动确认消息,但如果处理失败,则不会确认消息
- acknowledge-mode.manual:消费者必须在成功处理消息后显式调用 basicAck 方法来确认消息. 如果消息未被确认, RabbitMQ 会认为消息尚未被成功处理, 并且会在消费者可用时重新投递该消息
-
配置文件如下
yamlspring: application: name: spring-rabbitmq-extensions rabbitmq: host: 127.0.0.1:8080 # RabbitMQ服务器的IP地址 port: 5672 username: study password: study virtual-host: extension listener: simple: acknowledge-mode: none # 消费者确认机制 # acknowledge-mode: auto # 消费者确认机制 # acknowledge-mode: manual # 消费者确认机制 -
声明和配置交换器、队列和绑定关系
javaimport org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class RabbitMQConfig { @Bean("ackQueue") public Queue ackQueue(){ return QueueBuilder.durable(Constants.ACK_QUEUE).build(); } @Bean("ackExchange") public DirectExchange ackExchange(){ return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange(Constants.ACK_EXCHANGE).build(); } @Bean("ackBinding") public Binding ackBinding(@Qualifier("ackExchange") DirectExchange directExchange,@Qualifier("ackQueue") Queue ackQueue){ return BindingBuilder.bind(ackQueue).to(directExchange).with("ack"); } }
1.3.3.1 none
-
配置消费者
javaimport lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.example.springrabbitmqextensions.constant.Constants; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; @Component @Slf4j public class AckListener { @RabbitListener(queues = Constants.ACK_QUEUE) public void handMessage(Message message) { long deliveryTag = message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(); log.info("接收到消息:{},deliveryTag:{}", new String(message.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8), deliveryTag); int num = 3/ 0; log.info("处理成功"); } } -
发送消息
java@RequestMapping("/ack") public String ack(){ rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.ACK_EXCHANGE, "ack", "ack"); return "发送成功"; }抛出算数异常
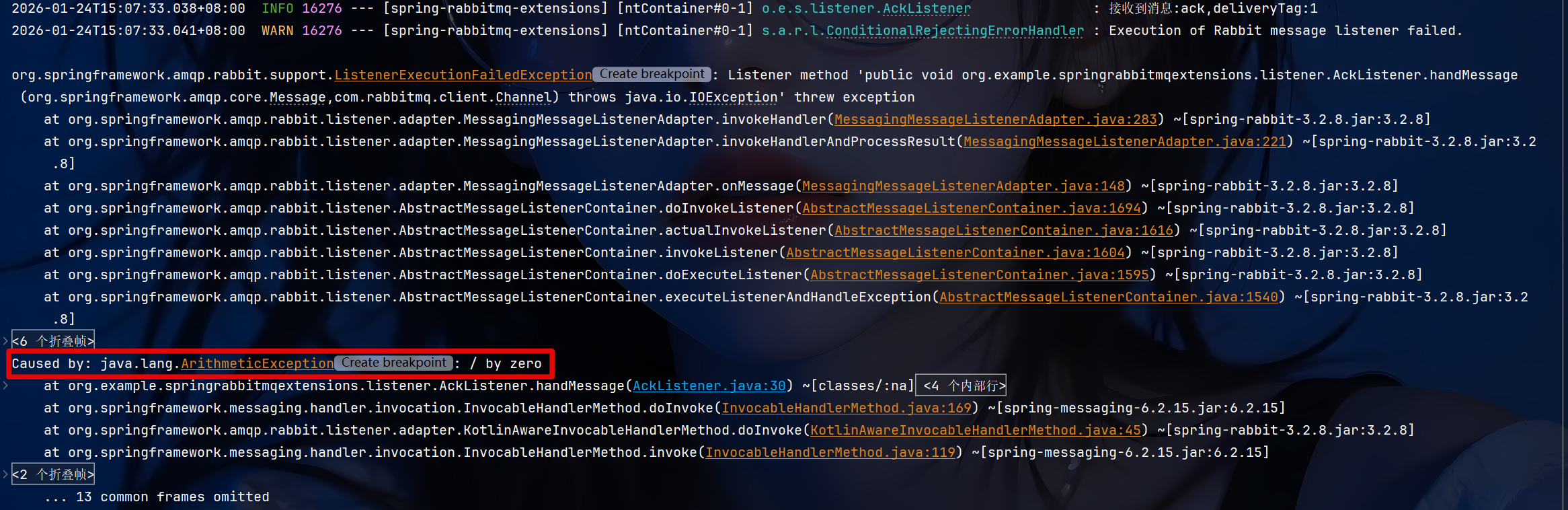
但仍然成功确认
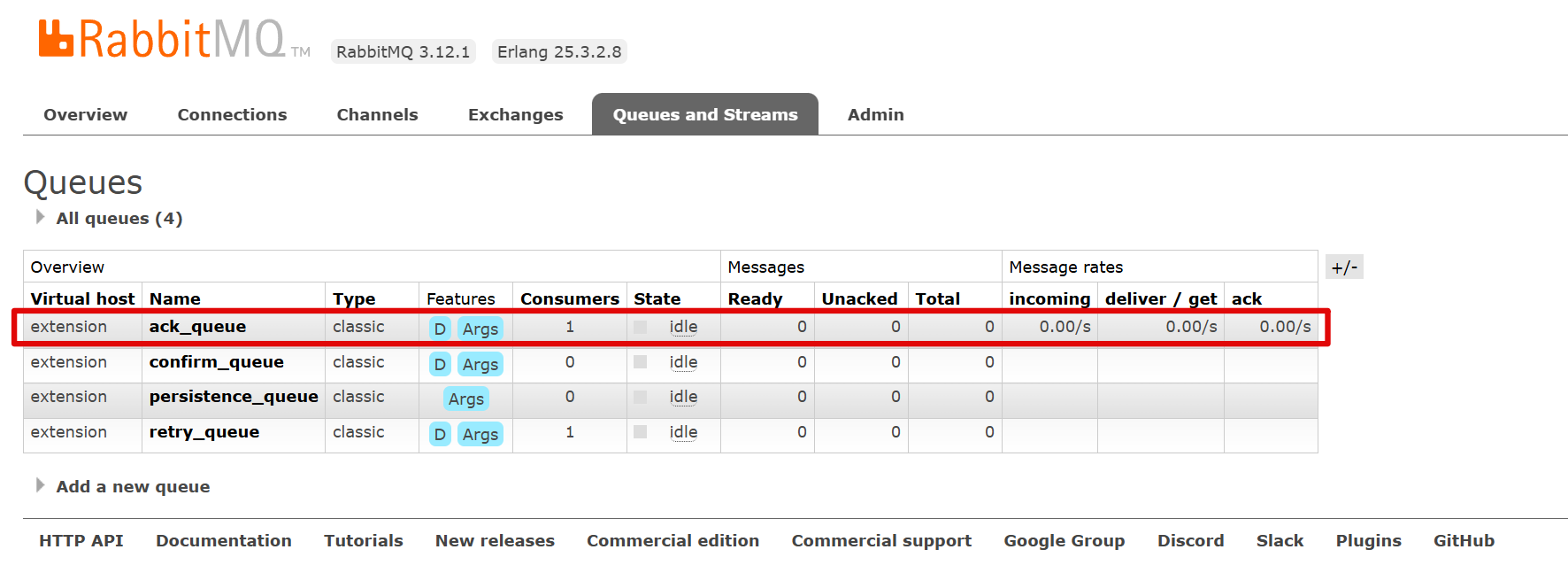
1.3.3.2 auto
代码同上(none),在抛出算数异常后消息不会被确认,但会重新投入队列不断重发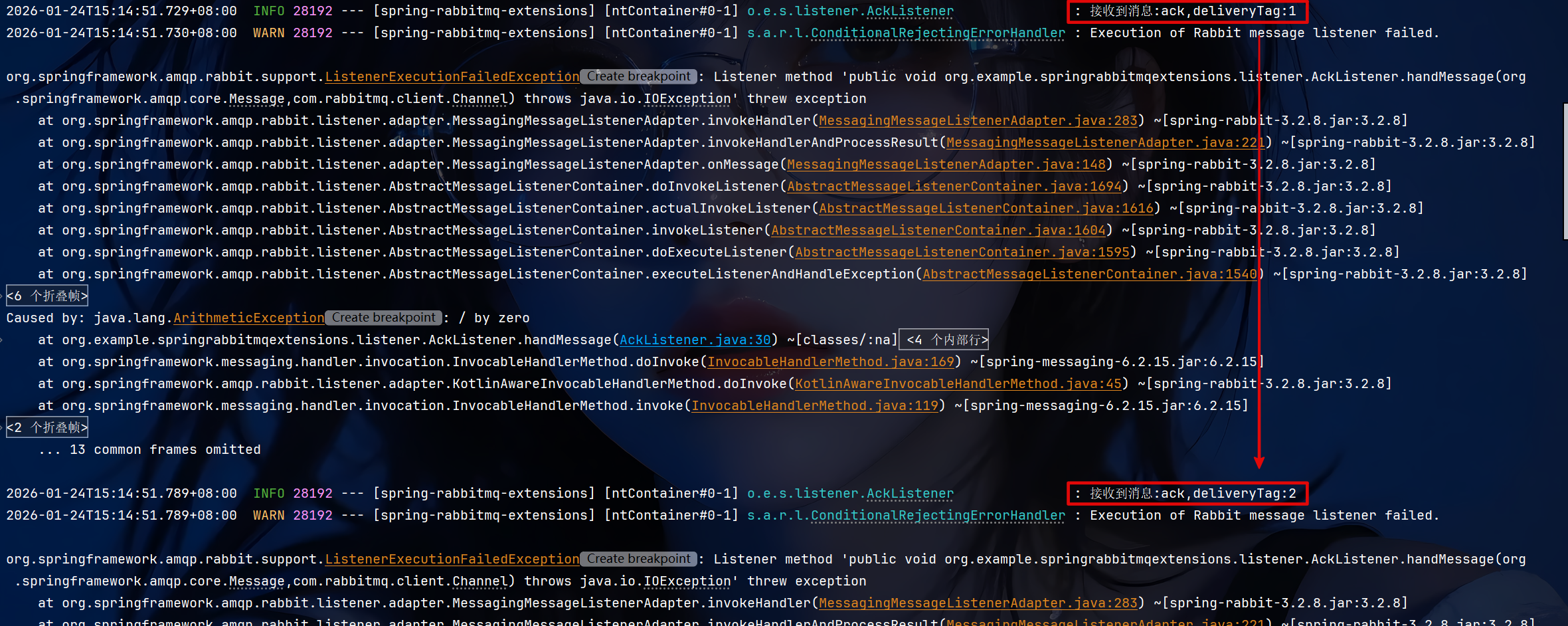
消息一直处于未确认状态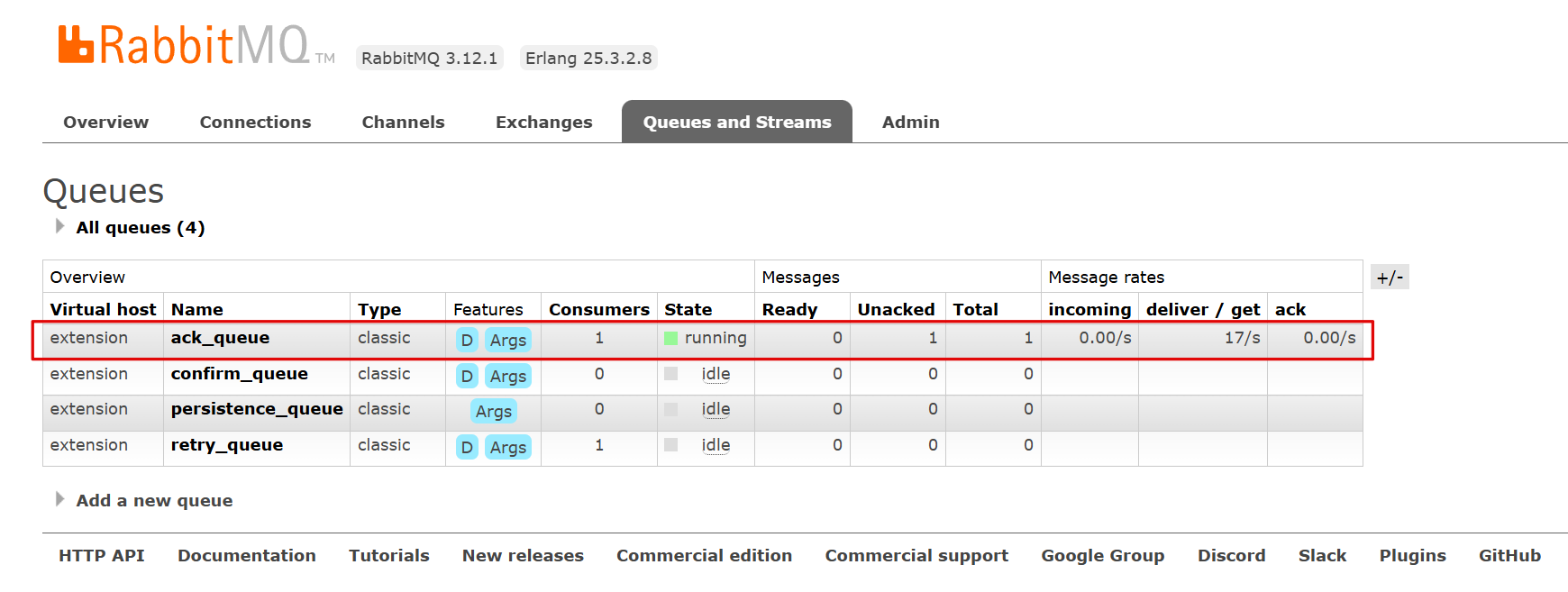
1.3.3.3 manual
-
配置消费者
javaimport com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.example.springrabbitmqextensions.constant.Constants; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; @Component @Slf4j public class AckListener { @RabbitListener(queues = Constants.ACK_QUEUE) public void handMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException { long deliveryTag = message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(); try{ log.info("接收到消息:{},deliveryTag:{}", new String(message.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8), deliveryTag); int num = 3/ 0; log.info("处理成功"); channel.basicAck(deliveryTag, true); }catch(Exception e){ channel.basicNack(deliveryTag,true,true); } } } -
发送消息代码同上(none、auto),在抛出算数异常后情况和auto一样
2.Spring-AMQP消息重传机制
Spring-AMQP提供了重试机制,允许消息在处理失败后重新发送
-
配置文件如下:配置的重传次数仅在
auto模式下生效yamlspring: application: name: spring-rabbitmq-extensions rabbitmq: host: 127.0.0.1:8080 # RabbitMQ服务器的IP地址 port: 5672 username: study password: study virtual-host: extension listener: simple: acknowledge-mode: auto # 消费者确认机制 retry: enabled: true # 开启消费者失败重试 initial-interval: 3000ms # 初始失败等待时长为3秒 max-attempts: 3 # 最大重试次数 -
声明和配置交换器、队列和绑定关系
java@Bean("retryQueue") public Queue retryQueue(){ return QueueBuilder.durable(Constants.RETRY_QUEUE).build(); } @Bean("retryExchange") public DirectExchange retryExchange(){ return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange(Constants.RETRY_EXCHANGE).build(); } @Bean("retryBinding") public Binding retryBinding(@Qualifier("retryExchange") DirectExchange directExchange,@Qualifier("retryQueue") Queue queue){ return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(directExchange).with("retry"); } -
配置消费者
javaimport lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.example.springrabbitmqextensions.constant.Constants; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; @Component @Slf4j public class RetryListener { @RabbitListener(queues = Constants.RETRY_QUEUE) public void handMessage(Message message) { log.info("接收到消息:{},deliveryTag:{}", new String(message.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8), message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag()); int num = 3/ 0; log.info("处理成功"); } } -
发送消息
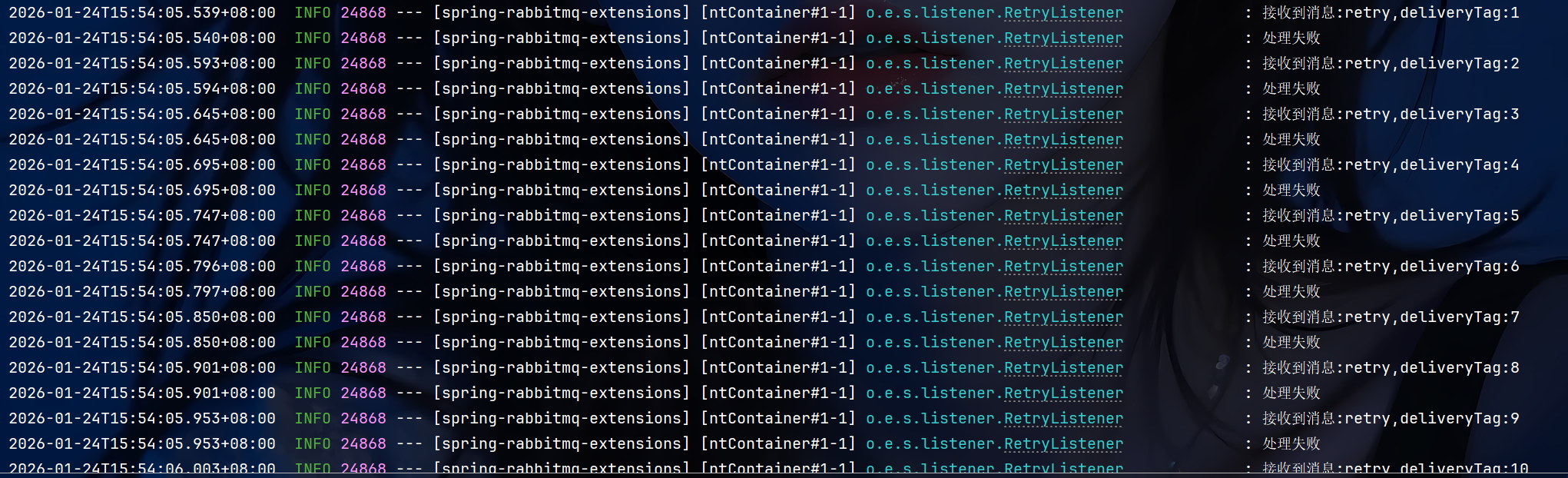
java@RequestMapping("/retry") public String retry(){ rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.RETRY_EXCHANGE, "retry", "retry"); return "发送成功"; }在消息重传过程中,消息处于未确认状态
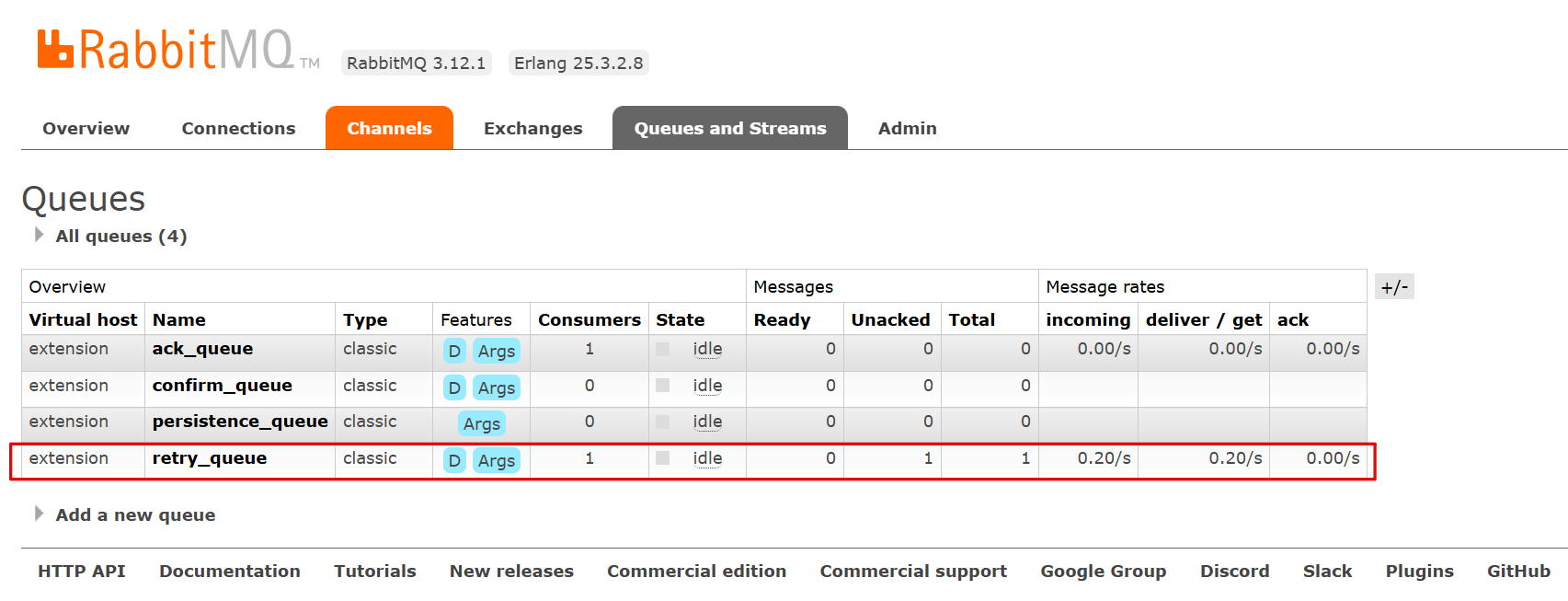
重试次数用尽后,消息被丢弃
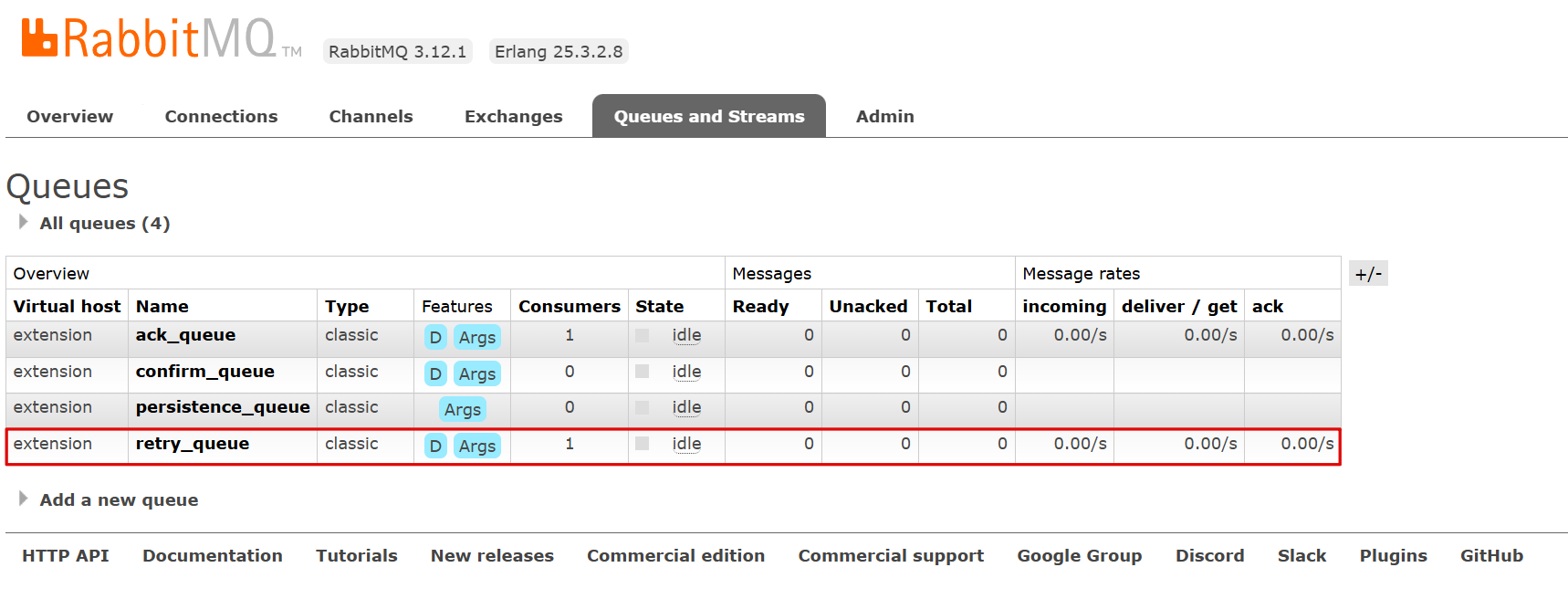
如果设置为manual模式,那么配置的重试次数和间隔时间将不会生效
java
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.example.springrabbitmqextensions.constant.Constants;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class RetryListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = Constants.RETRY_QUEUE)
public void handMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws Exception {
log.info("接收到消息:{},deliveryTag:{}",
new String(message.getBody(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8),
message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag());
try{
int num = 3/ 0;
log.info("处理成功");
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), true);
}catch(Exception e){
log.info("处理失败");
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), true,true);
}
}
}