一.获取Cookie,Session,Header
在处理http请求时,先明白http协议 是"无状态" 的(指服务器默认不会保留 客户端请求之间的任何信息。)会导致用户登录状态、购物车内容等连续性功能无法直接实现。解决该问题据需要用到Cookie和Session,接下来进行解释:
1.Cookie 和 Session 基本概念
1.1 什么是 Cookie?
Cookie 是服务器发送到用户浏览器并保存在本地的一小块数据(最大 4KB),浏览器会在后续请求中自动携带它。
用一个登录请求说明:
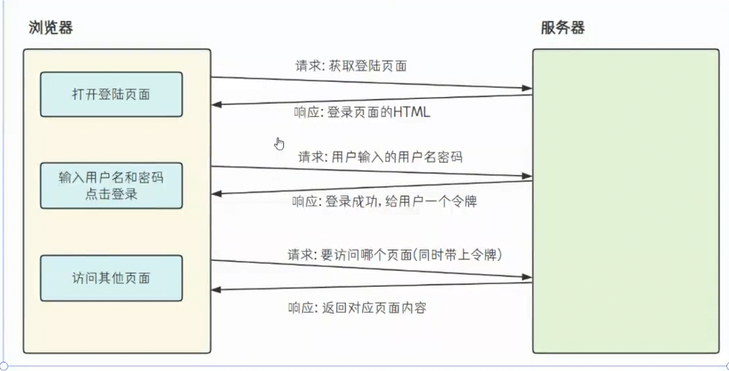
因为http协议是无状态 的,服务器通过给客户端发送一个令牌, 下次客户端请求时带上令牌,服务器通过令牌 就能够识别客户端,这个令牌就是Cookie
1.2 什么是 Session?
Session 是服务器端存储的用户会话数据,通常用 Session ID 标识,Session ID 通过 Cookie 在客户端存储。
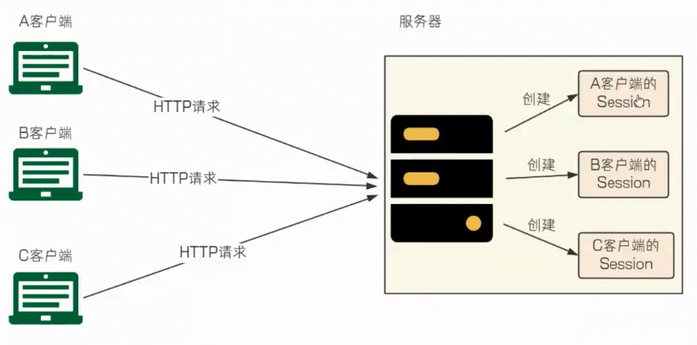
Session 的核心机制就是服务器为每个独立的客户端在服务器端创建并维护一个专属的、隔离的数据存储空间,以解决 HTTP 协议无状态的问题。
-
服务器创建 Session
-
对于首次访问 或新会话 的客户端(如图中的 A、B、C),服务器会在其内存或专用数据库中创建一个新的、唯一的 Session 对象。
-
这个 Session 对象就像服务器端的一个"私人档案袋",用于存放该用户在这次会话中的状态信息(如用户 ID、登录状态、购物车商品等)。
-
-
关联客户端与 Session:
-
服务器在创建 Session 的同时,会生成一个唯一的标识符,即 Session ID。
-
服务器在响应中,会通过 Set-Cookie 头部将这个 Session ID 发送给客户端。
-
客户端(浏览器)会保存这个 Cookie(包含 Session ID)。
-
-
后续请求的身份识别:
-
此后,该客户端发出的每一个 HTTP 请求,浏览器都会自动在请求头(Cookie 头部)中带上这个 Session ID。
-
服务器收到请求后,通过解析请求中的 Session ID,就能快速找到之前在服务器端为该客户端创建的专属 Session 对象,从而"认出"用户,并读取或修改其中的状态信息。
-
1.3 Cookie和Session的区别
- 两者都保存用户信息 ,但是Cookie 是客户端 保存信息的机制,Session 是服务端保存信息的机制
- 两者主要通过SessionID关联起来的
- 两者经常一起搭配使用,但不是必须的
- SessionId 不一定非得靠Set-Cookie传输,也可以通过url传输
- 可以用Cookie来保存数据在客户端
1.4获取cookie
(1)传统获取
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/request")
public class RequestControl {
@RequestMapping("/getCookie")
public String getCookie(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
//HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response
//http请求内容,http响应内容
//两者为内置对象,不需要额外创建
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
if(cookies != null){
for(Cookie cookie : cookies){
System.out.println(cookie.getName()+":"+cookie.getValue());
}
}
return "获取成功";
}
}浏览器输入网址127.0.0.1:8080/request/getCookie得到结果:
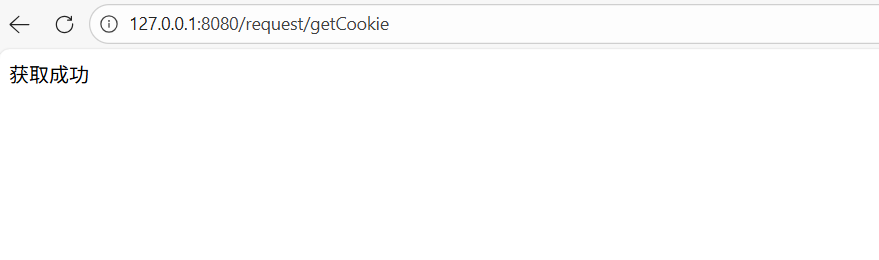
除此之外,cookie中不一定存储用户信息,并且可以伪造:
在浏览器中使用F12,向cookie传送bite:666
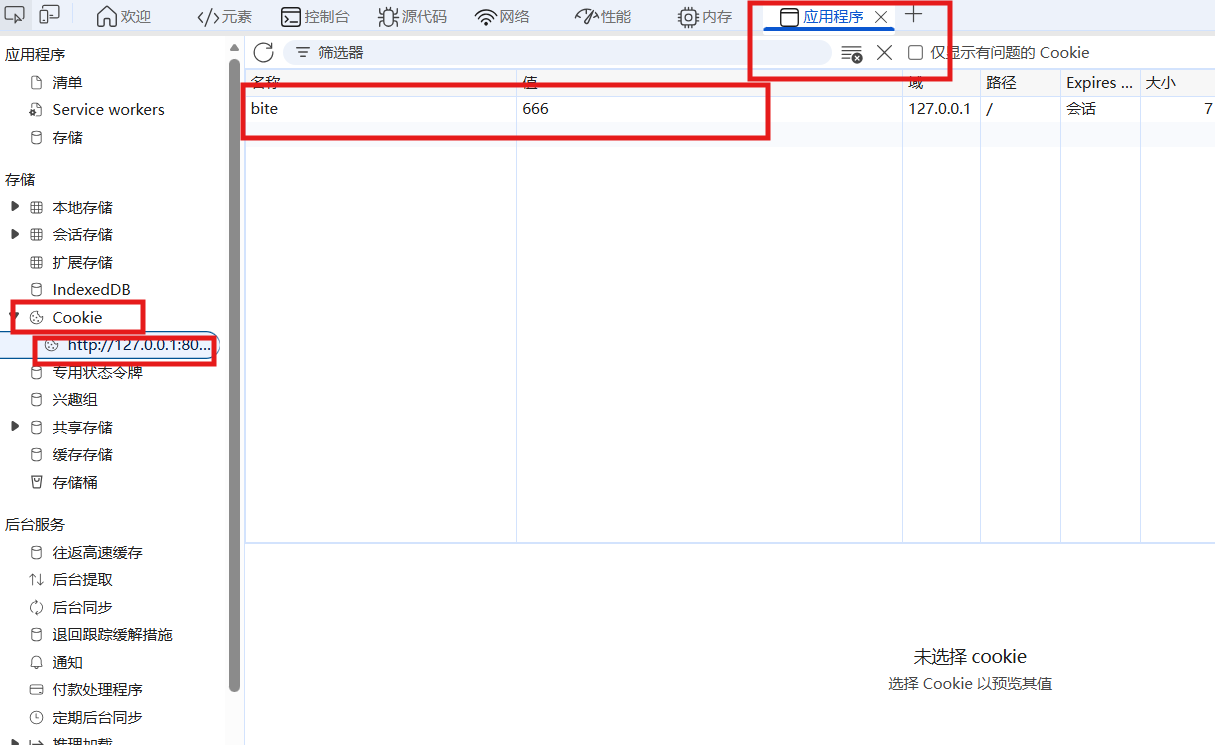
在代码运行结果中发现得到了cookie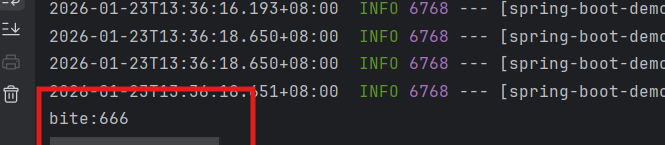
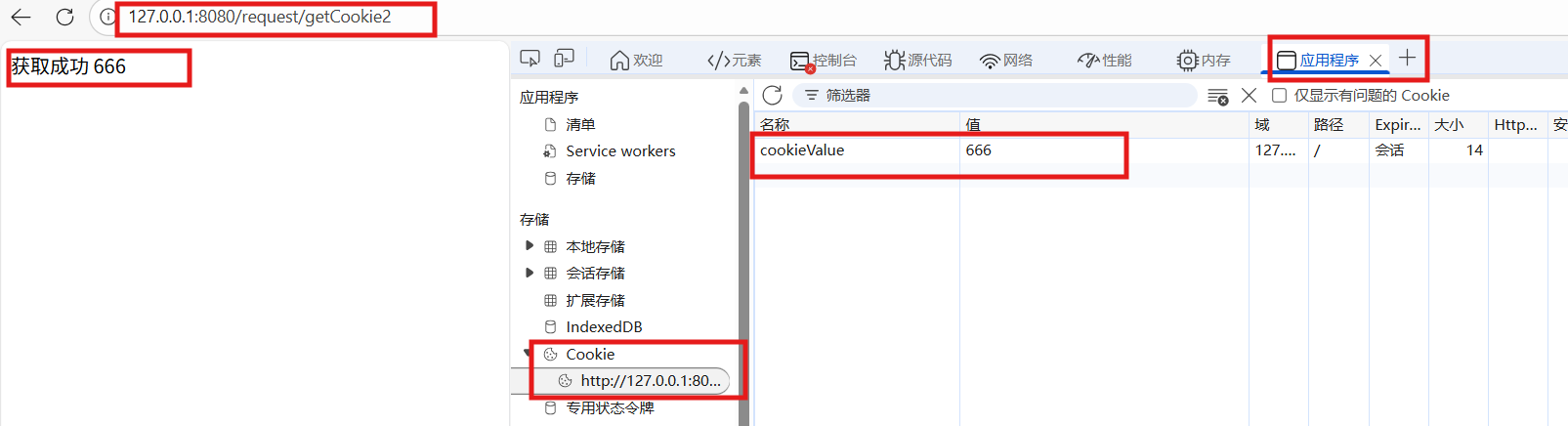
(2)简洁获取
@RequestMapping("/getCookie2")
public String getCookie2(@CookieValue String cookieValue){
return "获取成功 "+cookieValue;
}
1.5获取session
(1)存储和获取
存储
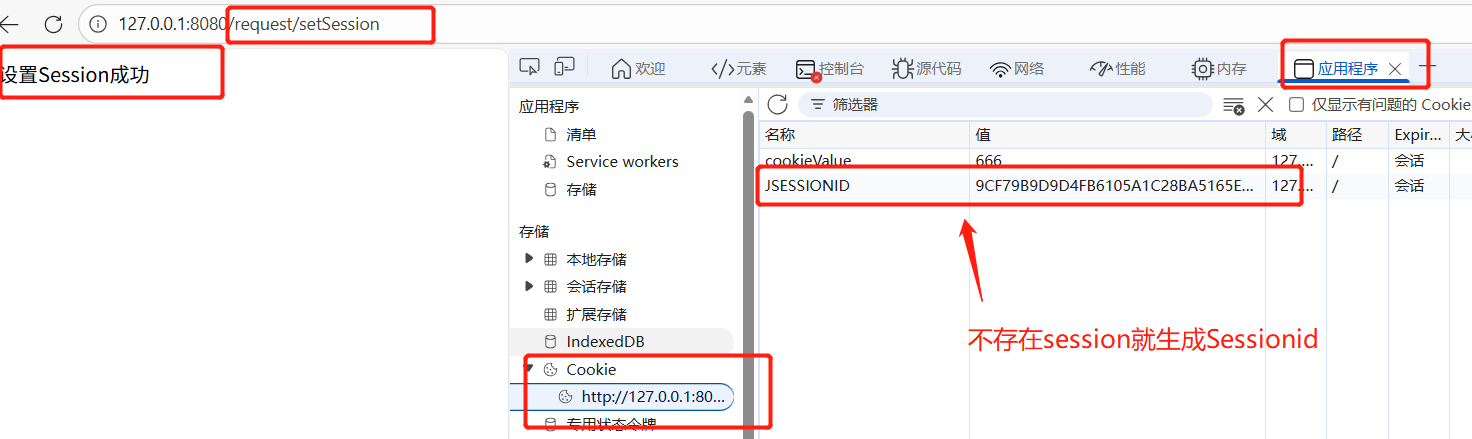
//存储Session
@RequestMapping("/setSession")
public String setSession(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
//获取session对象
HttpSession session=request.getSession();
//getSession()方法参数为True=>未获取到Session对象,则创建一个
// false=>为获取到Session对象,返回null
//无参默认为true
session.setAttribute("name","zhangsan");
session.setAttribute("age",30);
session.setAttribute("user",new Person("lisi",20,"男"));
return "设置Session成功";
}
获取
//获取Session
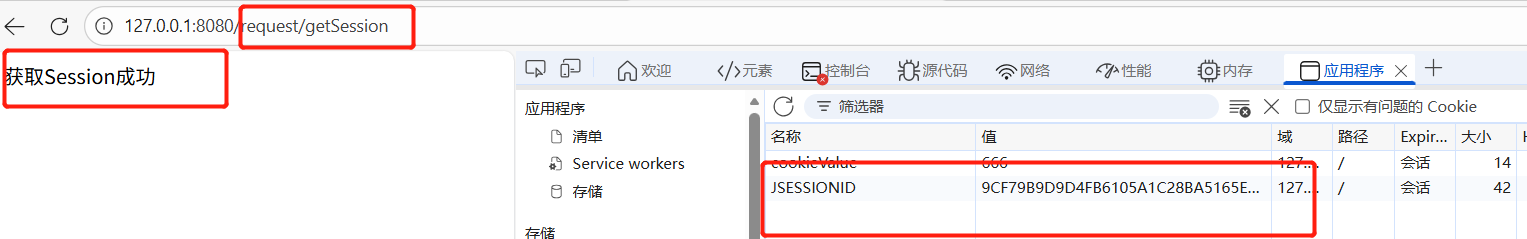
@RequestMapping("/getSession")
public String getSession(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
//获取session对象
HttpSession session=request.getSession();
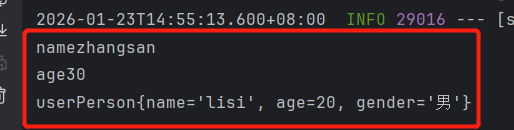
System.out.println("name"+session.getAttribute("name"));
System.out.println("age"+session.getAttribute("age"));
System.out.println("user"+session.getAttribute("user"));
return "获取Session成功";
}结果展示
(2)简洁获取1
@RequestMapping("/getSession2")
public String getSession2(@SessionAttribute String name){
//获取session对象
return "获取Session成功 name:"+name;
}(3)简洁获取2
@RequestMapping("/getSession3")
public String getSession3(HttpSession session){
//获取session对象
return "获取Session成功 name:"+session.getAttribute("name");
}2.获取Header
(1)传统获取
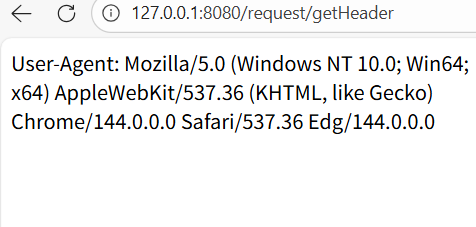
@RequestMapping("/getHeader")
public String getHeader(HttpServletRequest request){
String header = request.getHeader("User-Agent");
return "User-Agent: "+header;
}
(2)简洁获取
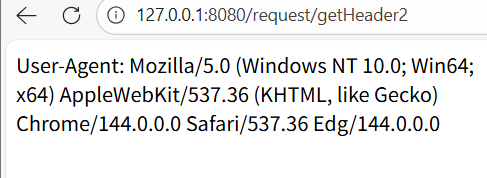
@RequestMapping("/getHeader2")
public String getHeader2(@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String header){
return "User-Agent: "+header;
}
二.响应
1.返回静态页面
@Control=>返回视图
@RestControl=>返回数据
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/response")
public class ResponseControl {
@RequestMapping("/returnHtml")
public String returnHtml(){
return "/index.html";
}
}
//index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
我是欢迎页
</body>
</html>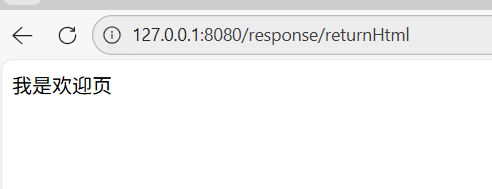
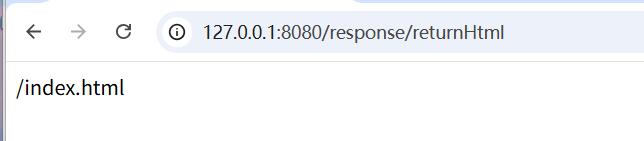
使用@RestControl=>返回字符串"/index.html"
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/response")
public class ResponseControl {
@RequestMapping("/returnHtml")
public String returnHtml(){
return "/index.html";
}
}
2.返回数据@ResponseBody
将数据写入http响应体中
加在类上=>所有方法返回数据
加在方法上=>该方法返回数据
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/response")
public class ResponseControl {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/returnHtml")
public String returnHtml(){
return "/index.html";
}
}
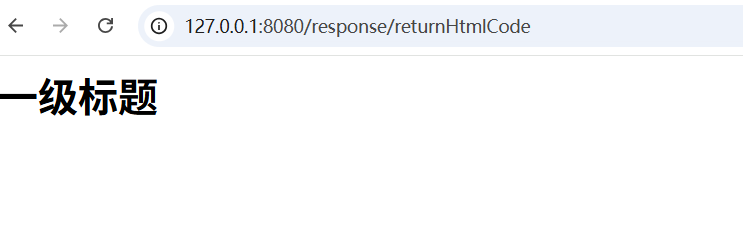
3.返回HTML代码片段
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/returnHtmlCode")
public String returnHtmlCode(){
return "<h1>一级标题<h1>";
}
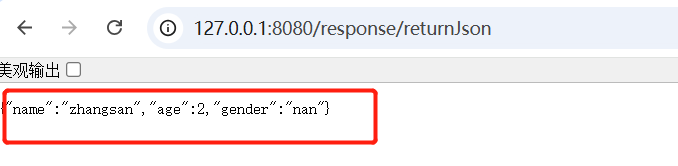
4.返回JSON
spring自动将对象转化为json
//返回json
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/returnJson")
public Person returnJson(){
return new Person("zhangsan",2,"nan");
}
5.设置状态码
Spring Mvc会根据返回结果自动设置响应状态码,可通过HttpServletResponse提供的方法手动设置
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/response")
public class ResponseControl {
@RequestMapping("/custom")
public String customStatus(HttpServletResponse response) {
// 设置自定义状态码
response.setStatus(418); // I'm a teapot
return "我是一个茶壶";
}
@RequestMapping("/redirect")
public void redirect(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// 302 重定向
response.sendRedirect("/response/success");
}
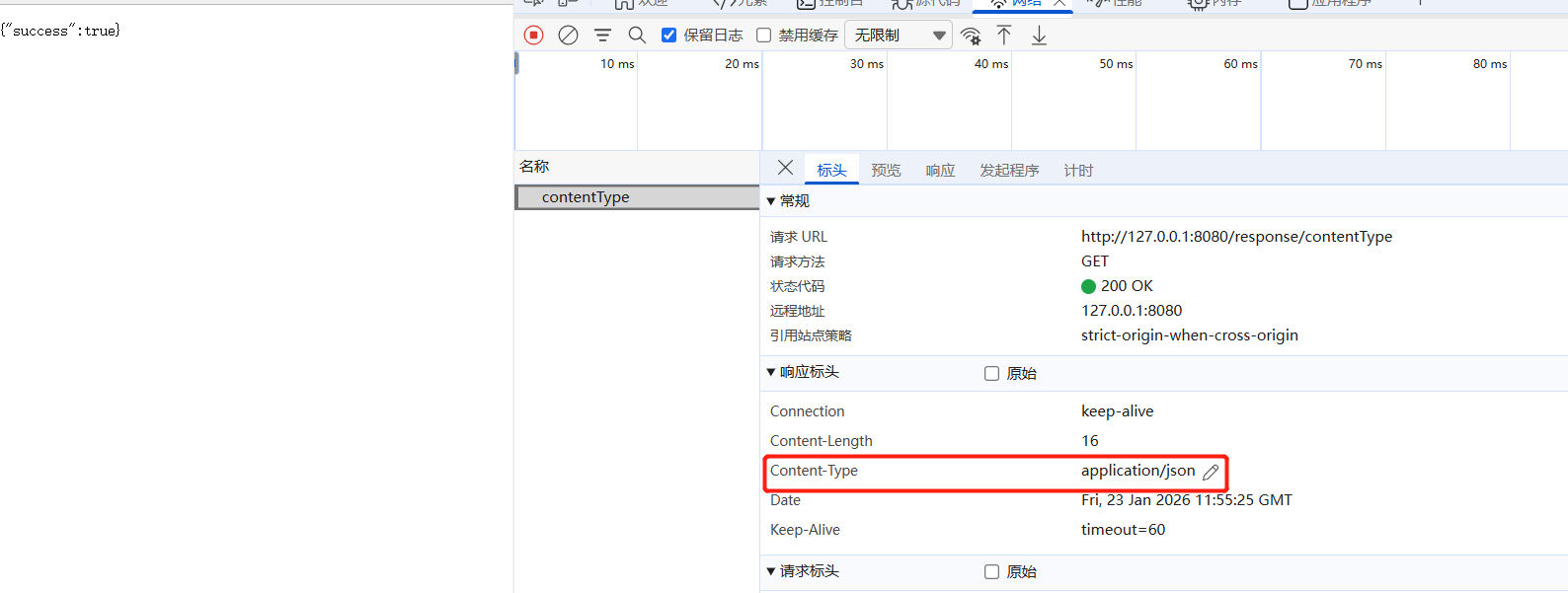
}6.设置Header
通过produces修改Content-Type
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/contentType",produces = "application/json")
public String contentType(){
return "{\"success\":true}" ;
}