Haproxy 算法实验

本文档整理并补全了各类负载均衡算法(静态/动态/混合)在实验环境下的配置、行为与验证方法,保留了原始实验中的截图与命令输出,便于复现与学习。
目录
- 实验拓扑(说明)
- 公共说明(healthcheck / weight / stats socket)
- 静态算法
- static-rr(静态加权轮询)
- first(优先/首选)
- 动态算法
- roundrobin(动态轮询)
- leastconn(最少连接)
- 混合/一致性哈希类
- source(基于源 IP)
- uri(基于请求 URI)
- url_param���基于 URL 参数)
- hdr(基于请求头)
- 常见问题与注意事项
- 常用命令速查
实验拓扑(说明)
实验环境同前:haproxy(双网卡调度器)前端 IP 为 172.25.254.100:80,后端两台 webserver:192.168.0.10 与 192.168.0.20。后端用简单的 index.html 返回标识文本。
(原图:static-rr 用图示)
公共说明(healthcheck / weight / stats socket)
- health check 常用参数说明:
- check:启用健康检查
- inter 3s:每 3s 检查一次
- fall N:连续 N 次失败判定为 DOWN
- rise N:连续 N 次成功判定为 UP
- weight:配置在 server 行上,表示权重(影响算法行为,详见各算法)
- stats socket(用于运行时查询/修改):
- 示例:
echo "get weight webcluster/haha" | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats - 修改权重(动态支持的算法):
echo "set weight webcluster/haha 1" | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats - 注意:某些静态算法(例如 static-rr)限制通过 stats socket 修改权重(只接受 0% / 100% 或根本不接受),输出会提示原因。
- 示例:
校验配置语法:
haproxy -c -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
重启服务:
systemctl restart haproxy
静态算法
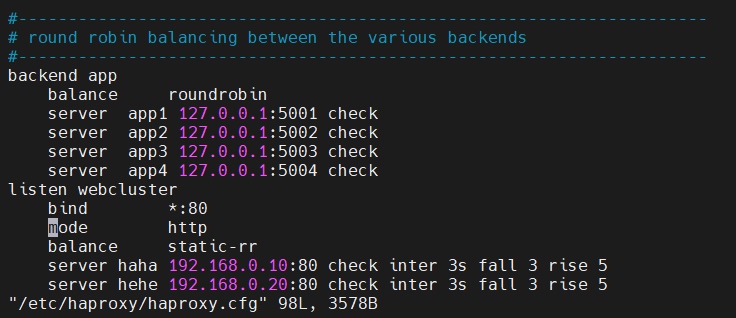
1. static-rr(静态加权轮询)
描述:
- static-rr 是"静态轮询",权重在启动或配置载入时生效,属于静态分配。运行时不接受任意百分比的权重更新(通常只允许 0%/100% 或完全不接受),因此不适合需要动态调整权重的场景。
配置示例:
haproxy
listen webcluster
bind *:80
balance static-rr
server haha 192.168.0.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server hehe 192.168.0.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 1重启并测试:
bash
systemctl restart haproxy.service
# 测试(示例)
for i in {1..10}; do curl 172.25.254.100; done
# 输出示例(webserver1 比 webserver2 多两倍)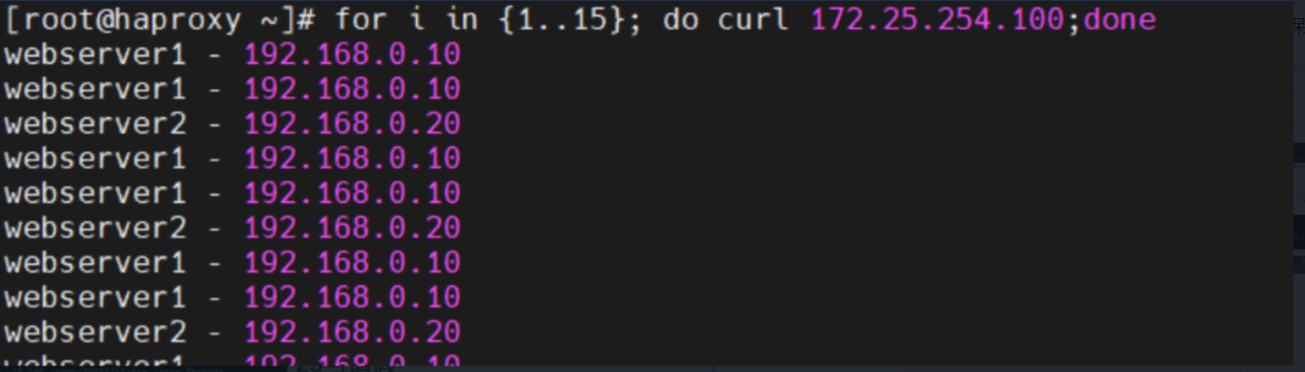
运行时权重查询/修改示例(会提示限制):
bash
echo "get weight webcluster/haha" | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
# 2 (initial 2)
echo "set weight webcluster/haha 1" | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
# Backend is using a static LB algorithm and only accepts weights '0%' and '100%'要点:
- 启动后权重是固定的,不能像动态算法那样平滑调整。
- 适用于需要非常简单且启动时即可确定分配比例的场景。
2. first
描述:
- first 算法会依次尝试按 server 配置顺序选择第一个可用服务器,当该服务器达到 maxconn(或不可用)时才会选择下一个。它更"倾向"于前面的服务器,通常用于主/备或优先级场景。
示例配置:
haproxy
listen webcluster
bind *:80
balance first
server haha 192.168.0.10:80 maxconn 1 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server hehe 192.168.0.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 1验证(观察行为):
- 在一个终端持续发送请求到 haproxy(curl 循环),会发现大多数请求都分配到"首选"可用服务器(server hehe,或取决于哪个先满足条件)。
- 当首选达到 maxconn 或不可用时,才会回退到下一台。
要点:
- 适合主/备或"优先前端"的部署。
- 注意 maxconn 的设置决定何时切换到下一个服务器。
动态算法(支持运行时权重修改)
3. roundrobin(轮询)
描述:
- 动态轮询,按顺序轮流选择后端;支持权重,且支持通过 stats socket 在运行时调整权重,影响后续请求分配。
配置示例:
haproxy
listen webcluster
bind *:80
balance roundrobin
server haha 192.168.0.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server hehe 192.168.0.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 1动态权重调整示例:
bash
# 查看初始权重
echo "get weight webcluster/haha" | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
# 2 (initial 2)
# 设置新的权重
echo "set weight webcluster/haha 1" | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
# 验证新权重
echo "get weight webcluster/haha" | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
# 1 (initial 2)测试效果(权重变化后的请求分配):
- 修改权重后再次循环 curl,分发会按新权重反映(更接近 1:1 或按新权重比例)。
要点:
- 支持在线调整,适合需要根据后端真实负载调整流量的场景。
4. leastconn(最少连接)
描述:
- 将新请求分配给当前连接数最少的后端服务器(动态),对于长连接或连接时间差异较大的场景效果更好。
配置示例:
haproxy
listen webcluster
bind *:80
balance leastconn
server haha 192.168.0.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server hehe 192.168.0.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 1测试示例:
- 在短请求场景可能看起来像是交替分配;在并发长连接场景最少连接效果明显。
要点:
- 适用于连接保持时间不一致或长连接服务(例如 WebSocket、长轮询)场景。
混合 / 一致性哈希类算法
说明:这些算法通常通过某个请求属性(源 IP / URI / 参数 / header)做哈希,从而将同一类请求路由到同一后端(常用于会话粘性或缓存命中率优化)。可与 hash-type consistent 配合以降低节点变更时的抖动。
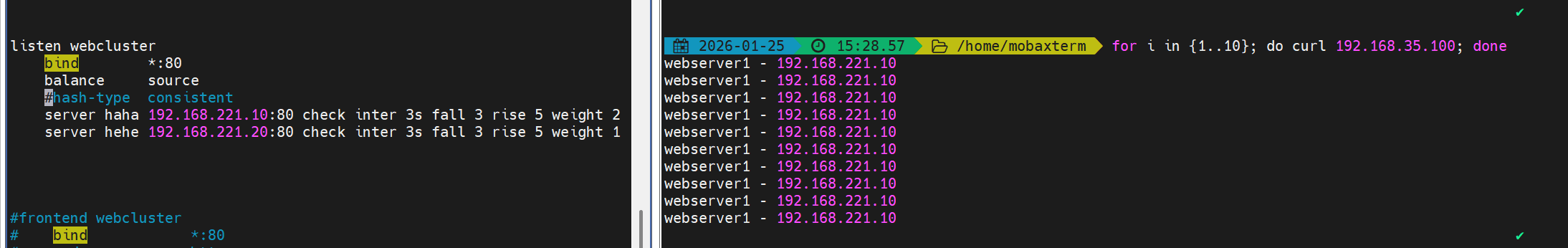
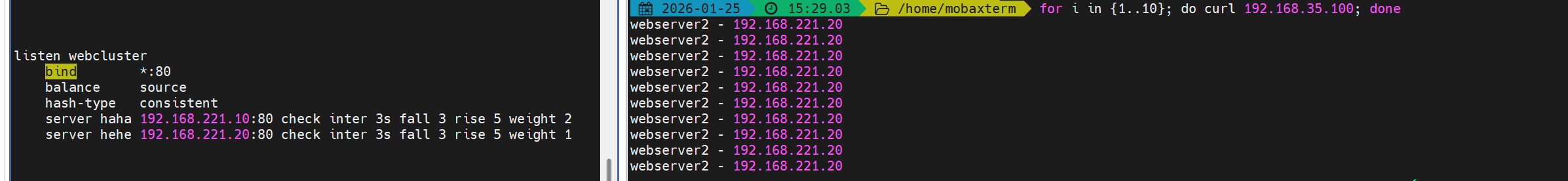
5. source(基于源 IP)
描述:
- 基于客户端源 IP 的哈希来决定后端,使同一客户端 IP 一般会被分配到同一后端。默认行为为简单散列,若要更稳定(在后端变动时尽量少变),可以启用一致性哈希。
示例(默认):
haproxy
listen webcluster
bind *:80
balance source
server haha 192.168.0.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server hehe 192.168.0.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 1示例(启用一致性哈希):
haproxy
listen webcluster
bind *:80
balance source
hash-type consistent
server haha 192.168.0.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server hehe 192.168.0.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 1测试(示例):
- 多次 curl 会发现相同客户端 IP 保持到同一后端。
要点:
- 适合需要客户端粘性但不想做 cookie/session 的场景(局限:同一公网出口的多个客户端会被视为同一 IP)。
(原图)
6. uri(基于 URI)
描述:
- 根据请求 URI(path + query 部分)进行哈希,能把相同资源请求路由到相同后端,常用于缓存或资源分片策略。
配置示例:
haproxy
listen webcluster
bind *:80
balance uri
hash-type consistent
server haha 192.168.0.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server hehe 192.168.0.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 1实验准备(主备示例):
bash
# webserver1:
echo "RS1 - 192.168.0.10" > /var/www/html/index1.html
echo "RS1 - 192.168.0.10" > /var/www/html/index2.html
# webserver2:
echo "RS2 - 192.168.0.20" > /var/www/html/index1.html
echo "RS2 - 192.168.0.20" > /var/www/html/index2.html测试示例:
bash
# /index.html 全部命中 RS1
for i in {1..10}; do curl 172.25.254.100/index.html; done
# 多次结果均为 webserver1 - 192.168.0.10
# /index2.html 全部命中 RS2
for i in {1..10}; do curl 172.25.254.100/index2.html; done
# 多次结果均为 webserver2 - 192.168.0.20要点:
- 可用于把不同 URI 的请求固定路由到指定后端(便于缓存命中或资源定位)。
(原图)
7. url_param(基于 URL 参数)
描述:
- 根据 URL 中指定参数名的值进行哈希(例如 ?name=xxx),非常适合按用户标识或会话参数做粘性路由。
配置示例:
haproxy
listen webcluster
bind *:80
balance url_param name
hash-type consistent
server haha 192.168.0.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server hehe 192.168.0.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 1测试示例:
bash
for i in {1..10}; do curl "172.25.254.100/index.html?name=lee"; done
# 多次命中同一后端(例如 webserver2)
for i in {1..10}; do curl "172.25.254.100/index.html?name=redhat"; done
# 多次命中另一个后端(例如 webserver1)要点:
- 参数名必须存在,若不存在可能会用空值或落入其他分配策略(具体行为请根据 haproxy 版本确认)。
- 注意对 URL 编码与特殊字符的处理。
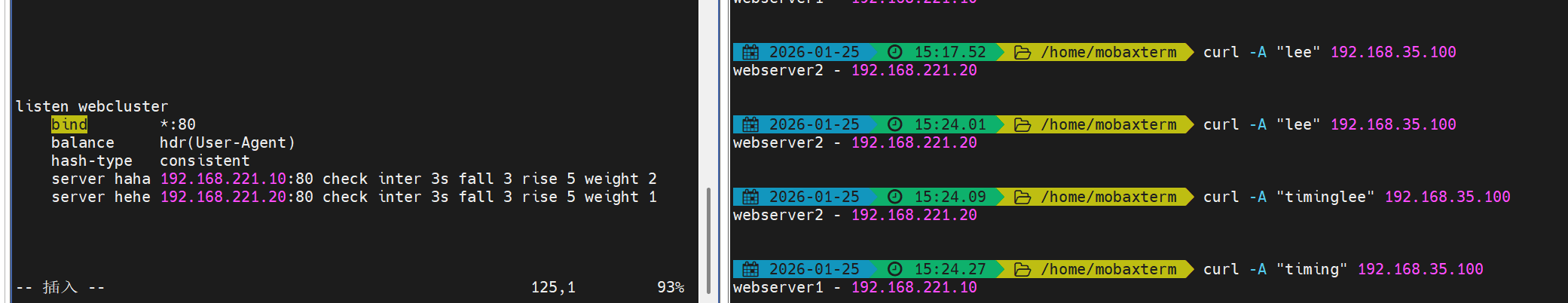
8. hdr(基于请求头)
描述:
- 根据指定请求头的值做哈希,例如
User-Agent、Cookie等,实现基于头部的路由与粘性。
正确语法示例(注意半角符号):
haproxy
listen webcluster
bind *:80
balance hdr(User-Agent)
hash-type consistent
server haha 192.168.0.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server hehe 192.168.0.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 1测试示例:
bash
curl -A "lee" 172.25.254.100 # User-Agent: lee
curl -A "timing" 172.25.254.100
curl -A "timinglee" 172.25.254.100
# 不同 User-Agent 的哈希值不同,可能会命中不同后端(原图)
常见问题与注意事项
- 配置文件语法:使用
haproxy -c -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg检查配置。 - stats socket:用于运行时监控与某些可动态调整的设置(如 roundrobin 的 weight)。不是所有算法/参数在运行时都支持修改。
- static-rr 的运行时限制:许多实现不允许对权重进行任意实时修改(仅允许 0%/100% 或拒绝),因为分配是静态计算好的。
- hash-type consistent:在使用基于 hash 的算法(source/uri/url_param/hdr)时建议配合使用
hash-type consistent,减少集群成员变更时的分流抖动。 - hdr/uri/url_param 等算法对字符串的处理可能与 haproxy 版本有关(如是否忽略 query 排序、编码处理等),测试时请以实际版本为准。
- 首选(first)与 maxconn:first 算法强烈依赖 server 顺序与 maxconn 的设置以控制"何时换后端"。
- healthcheck 太严格/太宽松会导致后端频繁上下线或误判,按真实服务响应速度设置 inter/fall/rise。
常用命令速查
- 检查配置:haproxy -c -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
- 重启服务:systemctl restart haproxy
- 查看状态:systemctl status haproxy
- 查看日志:journalctl -u haproxy -f
- stats socket 查询权重:echo "get weight /" | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
- stats socket 设置权重(动态算法):echo "set weight / " | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
- 测试后端可达性:curl -I http://192.168.0.10/ 或 telnet 192.168.0.10 80
temctl status haproxy
- 查看日志:journalctl -u haproxy -f
- stats socket 查询权重:echo "get weight /" | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
- stats socket 设置权重(动态算法):echo "set weight / " | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
- 测试后端可达性:curl -I http://192.168.0.10/ 或 telnet 192.168.0.10 80