Flutter实战:从零实现俄罗斯方块(二)CustomPaint绘制游戏画面
文章目录
- Flutter实战:从零实现俄罗斯方块(二)CustomPaint绘制游戏画面
-
- 摘要
- 前言
- 一、CustomPaint是什么?
-
- [1.1 为什么游戏需要CustomPaint?](#1.1 为什么游戏需要CustomPaint?)
- [1.2 Canvas和Paint的基本概念](#1.2 Canvas和Paint的基本概念)
- [1.3 CustomPainter怎么写?](#1.3 CustomPainter怎么写?)
- 二、绘制游戏棋盘
-
- [2.1 创建GameBoardPainter类](#2.1 创建GameBoardPainter类)
- [2.2 先画背景和网格](#2.2 先画背景和网格)
- [2.3 画已经固定的方块](#2.3 画已经固定的方块)
- [2.4 画当前下落的方块](#2.4 画当前下落的方块)
- 三、绘制下一个方块预览
-
- [3.1 NextPiecePainter实现](#3.1 NextPiecePainter实现)
- [3.2 如何让方块居中显示?](#3.2 如何让方块居中显示?)
- 四、让画面更好看:颜色和特效
-
- [4.1 方块颜色系统](#4.1 方块颜色系统)
- [4.2 边框和高亮效果](#4.2 边框和高亮效果)
- [4.3 半透明效果怎么实现?](#4.3 半透明效果怎么实现?)
- 五、绘制性能优化
-
- [5.1 shouldRepaint的正确用法](#5.1 shouldRepaint的正确用法)
- [5.2 控制重绘频率](#5.2 控制重绘频率)
- [5.3 缓存Paint对象](#5.3 缓存Paint对象)
- 六、完整的游戏界面布局
-
- [6.1 响应式布局设计](#6.1 响应式布局设计)
- [6.2 控制按钮的实现](#6.2 控制按钮的实现)
- [6.3 游戏结束界面](#6.3 游戏结束界面)
- 七、游戏完成总结
- 参考资料
- 社区支持
摘要
这是我用Flutter开发俄罗斯方块游戏的第二篇文章,主要讲解如何用CustomPaint把上一篇设计的游戏数据渲染成可玩的游戏画面。我会分享我学习CustomPaint的过程,包括如何绘制游戏棋盘、如何绘制不同颜色的方块、如何实现方块预览功能,以及如何优化绘制性能。到这篇文章结束时,一个完整的俄罗斯方块游戏就基本完成了!
关键词:Flutter、CustomPaint、Canvas、游戏绘制、OpenHarmony、俄罗斯方块
前言
在上一篇文章中,我设计好了俄罗斯方块游戏的核心数据结构和算法。但光有逻辑还不够,游戏需要画面才能玩!
我最开始想的是直接用Flutter的常规Widget(Container、Row、Column)来拼凑游戏画面,但很快就发现不太合适:
- 游戏棋盘需要绘制20×10=200个格子
- 方块位置需要实时更新
- 需要精确控制每个像素的颜色
这时候我了解到Flutter有个CustomPaint Widget,可以直接在Canvas上绘制,非常适合游戏开发。这篇文章我就记录我学习CustomPaint的过程。
系列说明:这是Flutter俄罗斯方块游戏开发系列教程的第2篇(共3篇)。本文完成后,游戏核心功能已全部实现。
一、CustomPaint是什么?
1.1 为什么游戏需要CustomPaint?
我先解释一下为什么普通的Widget不够用。
普通Widget的问题:
dart
// 如果用Container表示每个格子
Column(
children: [
for (int y = 0; y < 20; y++)
Row(
children: [
for (int x = 0; x < 10; x++)
Container(
width: 20,
height: 20,
color: board[y][x] != 0 ? Colors.blue : Colors.grey,
),
],
),
],
)这样做有几个问题:
- 性能差:200个Container嵌套,每次更新都要重建整个Widget树
- 不灵活:很难实现特殊效果(渐变、边框、阴影)
- 代码复杂:大量的嵌套结构,难以维护
CustomPaint的优势:
| 方面 | 普通Widget | CustomPaint |
|---|---|---|
| 性能 | 较慢(需要重建Widget树) | 快速(直接绘制到Canvas) |
| 灵活性 | 受限 | 完全控制每个像素 |
| 代码复杂度 | 高(大量嵌套) | 低(集中绘制逻辑) |
| 适用场景 | UI界面 | 游戏画面、图表 |
1.2 Canvas和Paint的基本概念
Canvas:就像一块画布,提供了各种绘制方法。
Paint:就像画笔,定义了颜色、线条粗细、样式等属性。
dart
// 基本使用
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
final paint = Paint()
..color = Colors.blue // 蓝色
..style = PaintingStyle.fill // 填充模式
..strokeWidth = 2.0; // 线宽2像素
// 在Canvas上画一个矩形
canvas.drawRect(Rect.fromLTWH(10, 10, 50, 50), paint);
}常用Canvas方法:
dart
canvas.drawRect(rect, paint); // 画矩形
canvas.drawCircle(center, radius, paint); // 画圆形
canvas.drawLine(p1, p2, paint); // 画线条
canvas.drawPath(path, paint); // 画路径1.3 CustomPainter怎么写?
CustomPainter是自定义绘制的基类,需要实现两个方法:
dart
class GameBoardPainter extends CustomPainter {
// 1. 构造函数:接收需要绘制的数据
final List<List<int>> board;
GameBoardPainter(this.board);
// 2. paint方法:在这里实现绘制逻辑
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
// 绘制代码...
}
// 3. shouldRepaint方法:决定是否需要重绘
@override
bool shouldRepaint(covariant CustomPainter oldDelegate) {
return true; // true表示需要重绘
}
}使用CustomPaint Widget:
dart
CustomPaint(
size: Size(300, 600), // 指定绘制区域大小
painter: GameBoardPainter(board), // 传入自定义Painter
)二、绘制游戏棋盘
2.1 创建GameBoardPainter类
我先创建一个专门绘制游戏棋盘的Painter:
dart
class GameBoardPainter extends CustomPainter {
final List<List<int>> board; // 棋盘数据
final List<List<int>>? currentPiece; // 当前下落的方块
final int currentX; // 当前方块的X坐标
final int currentY; // 当前方块的Y坐标
GameBoardPainter(
this.board, {
this.currentPiece,
this.currentX = 0,
this.currentY = 0,
});
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
// 绘制逻辑在下几节实现
}
@override
bool shouldRepaint(covariant CustomPainter oldDelegate) => true;
}2.2 先画背景和网格
我先把背景和网格线画好:
dart
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
// 计算每个格子的尺寸
final cellWidth = size.width / board[0].length; // 例如:300/10 = 30
final cellHeight = size.height / board.length; // 例如:600/20 = 30
// 1. 画深灰色背景
final bgPaint = Paint()..color = Colors.grey[900]!;
canvas.drawRect(
Rect.fromLTWH(0, 0, size.width, size.height),
bgPaint,
);
// 2. 画网格线
final gridPaint = Paint()
..color = Colors.grey[800]!
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeWidth = 0.5;
for (int y = 0; y < board.length; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < board[y].length; x++) {
final rect = Rect.fromLTWH(
x * cellWidth,
y * cellHeight,
cellWidth,
cellHeight,
);
canvas.drawRect(rect, gridPaint);
}
}
}效果图 (想象一下):
2.3 画已经固定的方块
接下来画已经固定在棋盘上的方块:
dart
// 在paint方法中继续添加...
// 3. 画已固定的方块
for (int y = 0; y < board.length; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < board[y].length; x++) {
if (board[y][x] != 0) { // 如果该位置有方块
final rect = Rect.fromLTWH(
x * cellWidth,
y * cellHeight,
cellWidth - 1, // 减1留出小间隙
cellHeight - 1,
);
// 填充颜色
final cellPaint = Paint()
..color = _getColor(board[y][x])
..style = PaintingStyle.fill;
canvas.drawRect(rect, cellPaint);
// 画半透明白色边框(增加立体感)
final borderPaint = Paint()
..color = Colors.white.withValues(alpha: 0.3)
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeWidth = 1;
canvas.drawRect(rect, borderPaint);
}
}
}
// 颜色映射函数
Color _getColor(int value) {
switch (value) {
case 1: return Colors.cyan; // I
case 2: return Colors.blue; // O
case 3: return Colors.orange; // T
case 4: return Colors.yellow; // S
case 5: return Colors.green; // Z
case 6: return Colors.purple; // J
case 7: return Colors.red; // L
default: return Colors.transparent;
}
}2.4 画当前下落的方块
当前下落的方块不在board数组里,需要单独画:
dart
// 4. 画当前下落的方块
if (currentPiece != null) {
for (int py = 0; py < currentPiece!.length; py++) {
for (int px = 0; px < currentPiece![py].length; px++) {
if (currentPiece![py][px] != 0) {
// 计算在棋盘上的绝对位置
final boardX = currentX + px;
final boardY = currentY + py;
// 边界检查
if (boardY >= 0 && boardY < board.length &&
boardX >= 0 && boardX < board[0].length) {
final rect = Rect.fromLTWH(
boardX * cellWidth,
boardY * cellHeight,
cellWidth - 1,
cellHeight - 1,
);
// 填充颜色
final cellPaint = Paint()
..color = _getColor(currentPiece![py][px])
..style = PaintingStyle.fill;
canvas.drawRect(rect, cellPaint);
// 画更亮的边框(突出当前方块)
final borderPaint = Paint()
..color = Colors.white.withValues(alpha: 0.6) // 更亮
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeWidth = 2; // 更粗
canvas.drawRect(rect, borderPaint);
}
}
}
}
}视觉效果对比:
- 已固定的方块:边框透明度0.3,线宽1像素
- 当前方块:边框透明度0.6,线宽2像素
这样一眼就能看出哪个是正在操作的方块!
三、绘制下一个方块预览
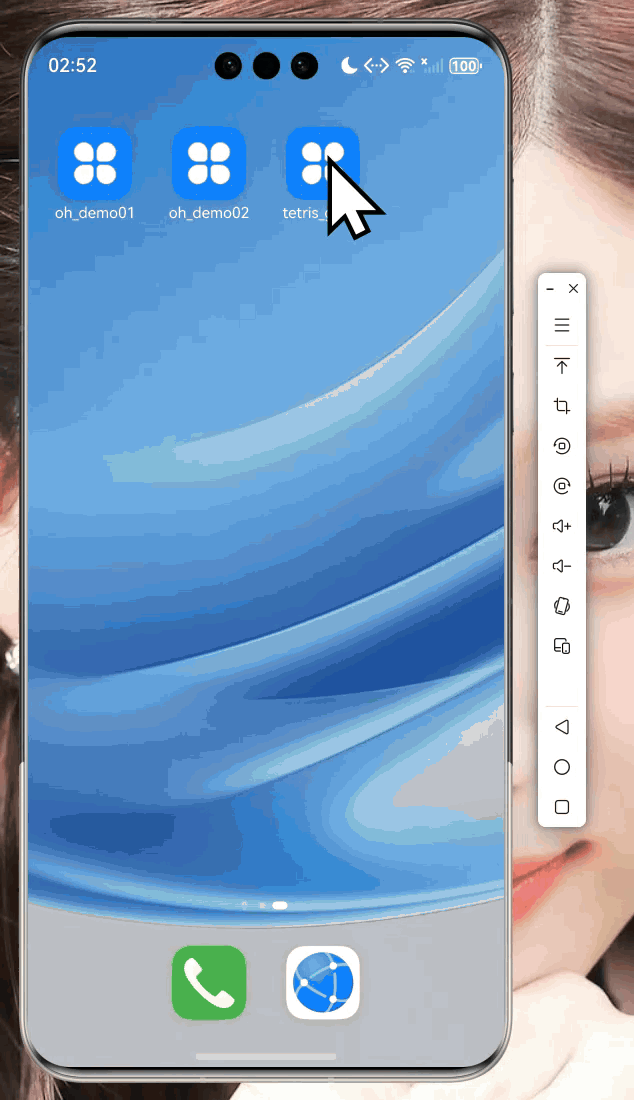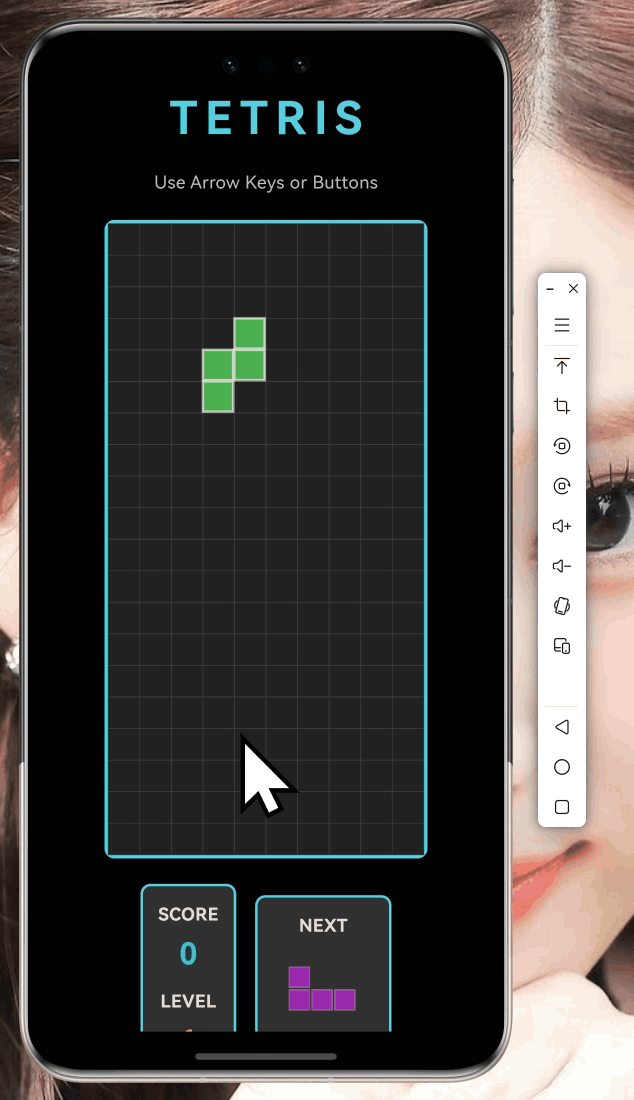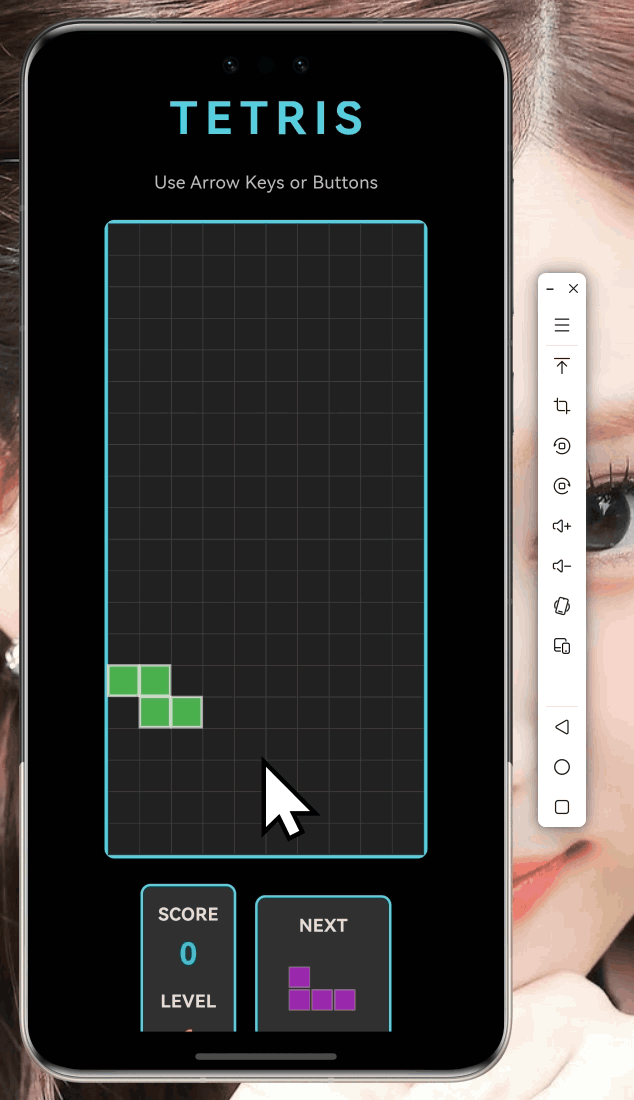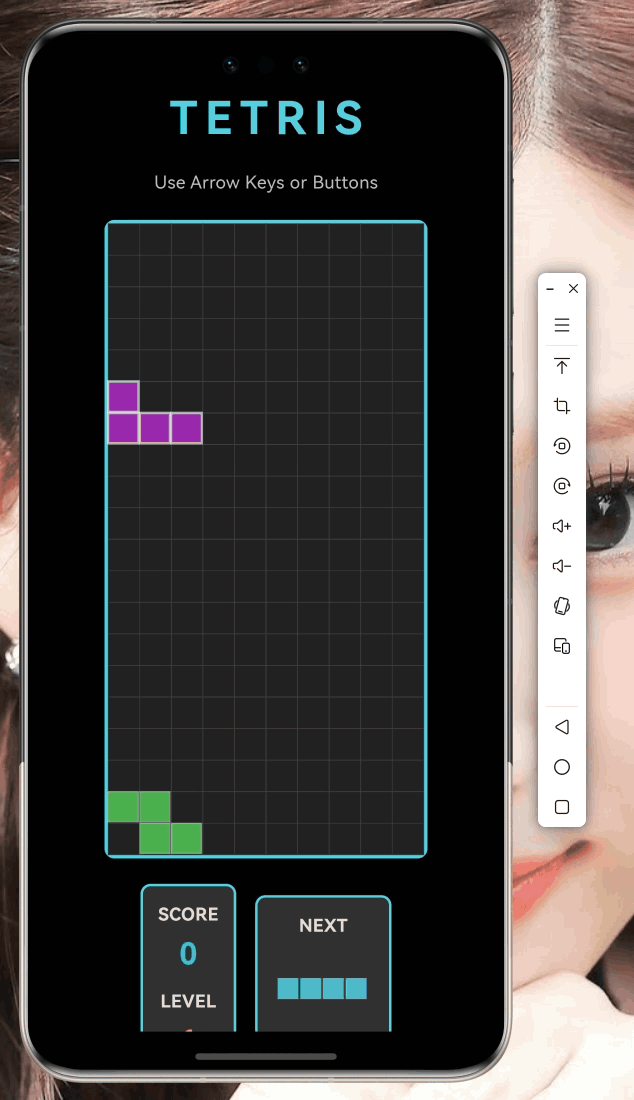
3.1 NextPiecePainter实现
游戏右侧需要显示下一个方块预览,我创建了一个专门的Painter:
dart
class NextPiecePainter extends CustomPainter {
final List<List<int>>? piece;
NextPiecePainter(this.piece);
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
if (piece == null) return;
final cellSize = 18.0; // 固定格子大小
// 绘制方块
for (int y = 0; y < piece!.length; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < piece![y].length; x++) {
if (piece![y][x] != 0) {
final rect = Rect.fromLTWH(
x * cellSize,
y * cellSize,
cellSize - 2,
cellSize - 2,
);
// 填充
final paint = Paint()
..color = _getColor(piece![y][x])
..style = PaintingStyle.fill;
canvas.drawRect(rect, paint);
// 边框
final borderPaint = Paint()
..color = Colors.white.withValues(alpha: 0.3)
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeWidth = 1;
canvas.drawRect(rect, borderPaint);
}
}
}
}
Color _getColor(int value) {
// 同上面的颜色映射
}
@override
bool shouldRepaint(covariant CustomPainter oldDelegate) => true;
}3.2 如何让方块居中显示?
不同方块尺寸不同(2×2到4×4),需要居中显示:
dart
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
if (piece == null) return;
final cellSize = 18.0;
// 计算居中偏移量
final offsetX = (size.width - piece![0].length * cellSize) / 2;
final offsetY = (size.height - piece!.length * cellSize) / 2;
for (int y = 0; y < piece!.length; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < piece![y].length; x++) {
if (piece![y][x] != 0) {
final rect = Rect.fromLTWH(
offsetX + x * cellSize, // 加上偏移量
offsetY + y * cellSize,
cellSize - 2,
cellSize - 2,
);
// 绘制...
}
}
}
}四、让画面更好看:颜色和特效
4.1 方块颜色系统
我使用了经典俄罗斯方块的配色方案:
dart
Color _getColor(int value) {
const colors = {
1: Color(0xFF00BCD4), // I - 青色
2: Color(0xFF2196F3), // O - 蓝色
3: Color(0xFFFF9800), // T - 橙色
4: Color(0xFFFFEB3B), // S - 黄色
5: Color(0xFF4CAF50), // Z - 绿色
6: Color(0xFF9C27B0), // J - 紫色
7: Color(0xFFF44336), // L - 红色
};
return colors[value] ?? Colors.transparent;
}颜色方案对比:
| 方案 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 经典配色 | 玩家熟悉 | 可能单调 |
| 霓虹配色 | 视觉冲击强 | 不适合长时间玩 |
| 柔和配色 | 护眼 | 缺乏对比度 |
我选择了经典配色,因为大家最熟悉。
4.2 边框和高亮效果
边框让方块更有立体感:
dart
// 方案1:单色边框(当前实现)
final borderPaint = Paint()
..color = Colors.white.withValues(alpha: 0.6)
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeWidth = 2;
// 方案2:渐变边框(进阶)
final gradient = LinearGradient(
begin: Alignment.topLeft,
end: Alignment.bottomRight,
colors: [
Colors.white.withValues(alpha: 0.8),
Colors.white.withValues(alpha: 0.2),
],
).createShader(rect);
final borderPaint = Paint()
..shader = gradient
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeWidth = 2;4.3 半透明效果怎么实现?
Flutter提供了多种创建半透明颜色的方法:
dart
// 方法1:使用withValues(推荐)
Colors.white.withValues(alpha: 0.5)
// 方法2:使用withOpacity(已弃用)
Colors.white.withOpacity(0.5)
// 方法3:使用Color.fromARGB
Color.fromARGB(128, 255, 255, 255)
// 方法4:使用Color.fromRGBO
Color.fromRGBO(255, 255, 255, 0.5)我推荐用withValues,因为它是新的API。
透明度速查表:
| Alpha值 | 效果 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 完全透明 | 不可见 |
| 0.3 | 微弱 | 固定方块边框 |
| 0.6 | 明显 | 当前方块边框 |
| 1.0 | 不透明 | 方块填充 |
五、绘制性能优化
5.1 shouldRepaint的正确用法
我一开始写成总是返回true,这样性能不好:
dart
// 不好:每次都重绘
@override
bool shouldRepaint(covariant CustomPainter oldDelegate) {
return true;
}
// 好:只在数据变化时重绘
@override
bool shouldRepaint(covariant GameBoardPainter oldDelegate) {
return board != oldDelegate.board ||
currentPiece != oldDelegate.currentPiece ||
currentX != oldDelegate.currentX ||
currentY != oldDelegate.currentY;
}5.2 控制重绘频率
游戏需要频繁更新,但可以优化:
dart
// 在游戏逻辑中
void tick() {
if (gameOver || paused) return;
bool changed = false;
if (!_checkCollision(_currentX, _currentY + 1, _currentPiece!)) {
_currentY++;
changed = true;
} else {
_mergePiece();
changed = true;
}
// 只有数据真正变化时才通知UI更新
if (changed) {
updateCallback();
}
}5.3 缓存Paint对象
Paint对象可以复用:
dart
class GameBoardPainter extends CustomPainter {
// 静态缓存Paint对象
static final _gridPaint = Paint()
..color = Colors.grey[800]!
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeWidth = 0.5;
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
// 直接使用缓存的Paint
canvas.drawRect(rect, _gridPaint);
}
}六、完整的游戏界面布局
6.1 响应式布局设计
我用了LayoutBuilder实现响应式:
dart
LayoutBuilder(
builder: (context, constraints) {
final isSmallScreen = constraints.maxWidth < 700;
final boardSize = isSmallScreen ? 250.0 : 300.0;
return isSmallScreen
? Column( // 小屏幕:垂直布局
children: [
CustomPaint(...), // 游戏棋盘
ScorePanel(), // 分数
Controls(), // 按钮
],
)
: Row( // 大屏幕:水平布局
children: [
CustomPaint(...), // 游戏棋盘
Column( // 侧边栏
children: [
ScorePanel(),
NextPiecePanel(),
Controls(),
],
),
],
);
},
)6.2 控制按钮的实现
dart
Widget _buildControlButton(String label, double size, VoidCallback onPressed) {
return SizedBox(
width: size,
height: size,
child: ElevatedButton(
onPressed: onPressed,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
backgroundColor: Colors.cyan[700],
shape: RoundedRectangleBorder(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(8),
),
),
child: FittedBox(
child: Text(
label,
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 20,
color: Colors.white,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
),
),
);
}6.3 游戏结束界面
dart
if (_game.gameOver)
Container(
color: Colors.black.withValues(alpha: 0.85),
child: Center(
child: Column(
children: [
Text('GAME OVER', style: TextStyle(fontSize: 32, color: Colors.red)),
Text('Score: ${_game.score}'),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
_game.reset();
setState(() {});
},
child: Text('Play Again'),
),
],
),
),
)
七、游戏完成总结
到这篇文章为止,一个完整的俄罗斯方块游戏就基本完成了!
已完成的功能
- 数据结构:方块、棋盘、游戏状态
- 核心算法:碰撞检测、旋转、消行
- 游戏绘制:CustomPaint绘制棋盘和方块
- 交互控制:键盘和触摸按钮控制
- 游戏循环:Timer驱动的游戏主循环
- 计分系统:分数、等级、最高分
- UI界面:响应式布局、暂停、游戏结束
项目结构
后续优化方向
虽然游戏已经可以玩了,但还可以优化:
- 性能优化:使用DevTools分析性能瓶颈
- 代码优化:算法优化、异步处理
- APK构建:混淆、压缩、签名
这些内容我会在下一篇文章中详细讲解。
系列说明:这是Flutter俄罗斯方块游戏开发系列教程的第2篇(共4篇)。到本文为止,游戏核心功能已全部实现。第3篇将介绍交互控制的细节,第4篇将讲解性能优化和部署流程。
参考资料
社区支持
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:
- 社区论坛 :开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
- 技术交流:参与讨论,分享经验
如果本文对你有帮助,欢迎点赞、收藏、评论!