线程中断
一个线程不应该由其他的线程来强制中断或停止,而是应该由线程自己自行停止,自己来决定自己的命运 。
中断只是一种协商机制,Java没有给中断增加任何语法,中断的过程完全需要程序员自己实现。
每个线程对象中都有一个中断标志位,用于表示线程是否被中断,该标志位为true表示中断,为false为未中断,通过调用线程对象的interrupt方法将该线程的标志位设为true;可以在别的线程中调用,也可以在自己的线程中调用。

中断相关的API方法之三大方法说明
| 函数签名 | 相关作用 |
|---|---|
| public void interrupt() | 实例方法:仅仅是设置线程的中断状态为true,发起一个协商而不会立刻停止线程 |
| public static boolean interrupted() | j静态方法:Thread.interrupted();判断线程是否被中断并清除当前的中断状态。这个方法主要干了两件事:1.返回当前线程的中断状态,测试当前线程是否已被中断;2.将当前线程的中断状态清零并重新设置为false,清除线程的中断状态 |
| public boolean isInterrupted() | 实例方法:判断当前线程是否被中断(通过检查中断标志位) |

如何停止中断运行中的线程?
通过一个volatile变量实现
java
package com.sgm.springboottest.demos.web;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 线程中断demo演示
*/
public class InterruptedDemo {
static volatile boolean isStop=false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
while (true){
if(isStop){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t isStop的值被修改为true,程序停止");
break;
}
System.out.println("t1 ========hello volatile");
}
},"t1").start();
//20毫秒睡眠
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
isStop=true;
},"t2").start();
}
}运行效果:
通过AtomicBoolean实现
java
package com.sgm.springboottest.demos.web;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
/**
* 线程中断demo演示
*/
public class InterruptedDemo {
static volatile boolean isStop=false;
static AtomicBoolean atomicBoolean=new AtomicBoolean(false);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//原子类实现
new Thread(()->{
while (true){
if(atomicBoolean.get()){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t isStop的值被修改为true,程序停止");
break;
}
System.out.println("t1 ========hello atomicBoolean");
}
},"t1").start();
//20毫秒睡眠
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
atomicBoolean.set(true);
},"t2").start();
}
/**
* volatile 方法
*/
private static void m1_volatile() {
new Thread(()->{
while (true){
if(isStop){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t isStop的值被修改为true,程序停止");
break;
}
System.out.println("t1 ========hello volatile");
}
},"t1").start();
//20毫秒睡眠
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
isStop=true;
},"t2").start();
}
}运行结果:
通过Thread类自带的中断API实例方法实现
在需要中断的线程中不断监听中断状态,一旦发生中断,就执行相应的中断处理业务逻辑stop线程
java
package com.sgm.springboottest.demos.web;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
/**
* 线程中断demo演示
*/
public class InterruptedDemo {
static volatile boolean isStop=false;
static AtomicBoolean atomicBoolean=new AtomicBoolean(false);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//thread中断API
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t isInterrupted的值被修改为true,程序停止");
break;
}
System.out.println("t1 ========hello interrupt api");
}
}, "t1");
t1.start();
//20毫秒睡眠
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
t1.interrupt();
},"t2").start();
}
}运行结果
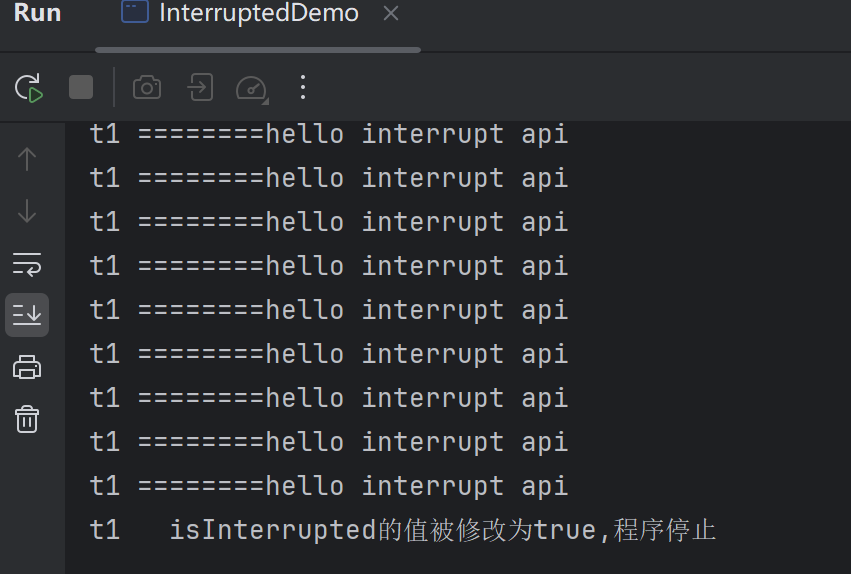
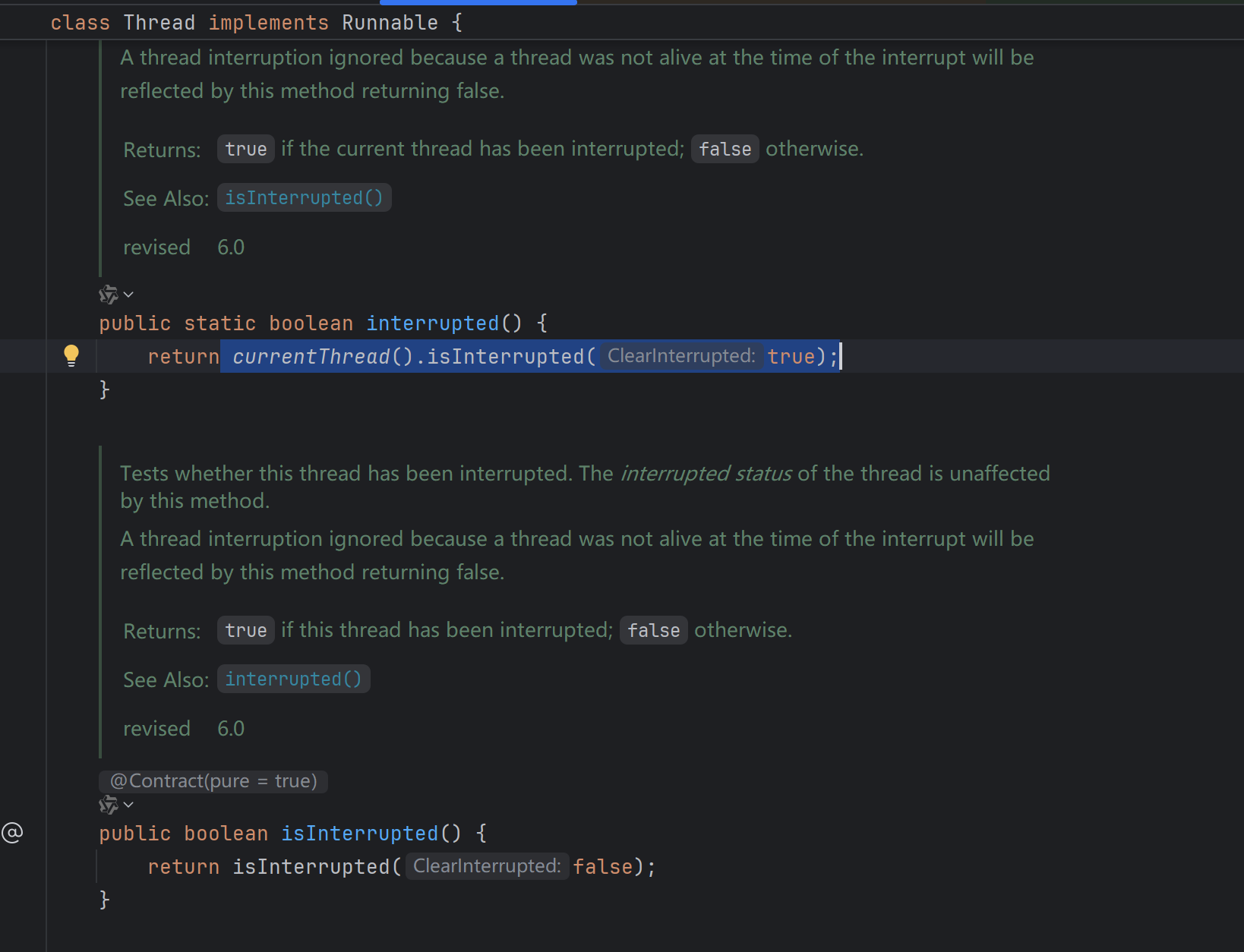
public void interrupt()的源码
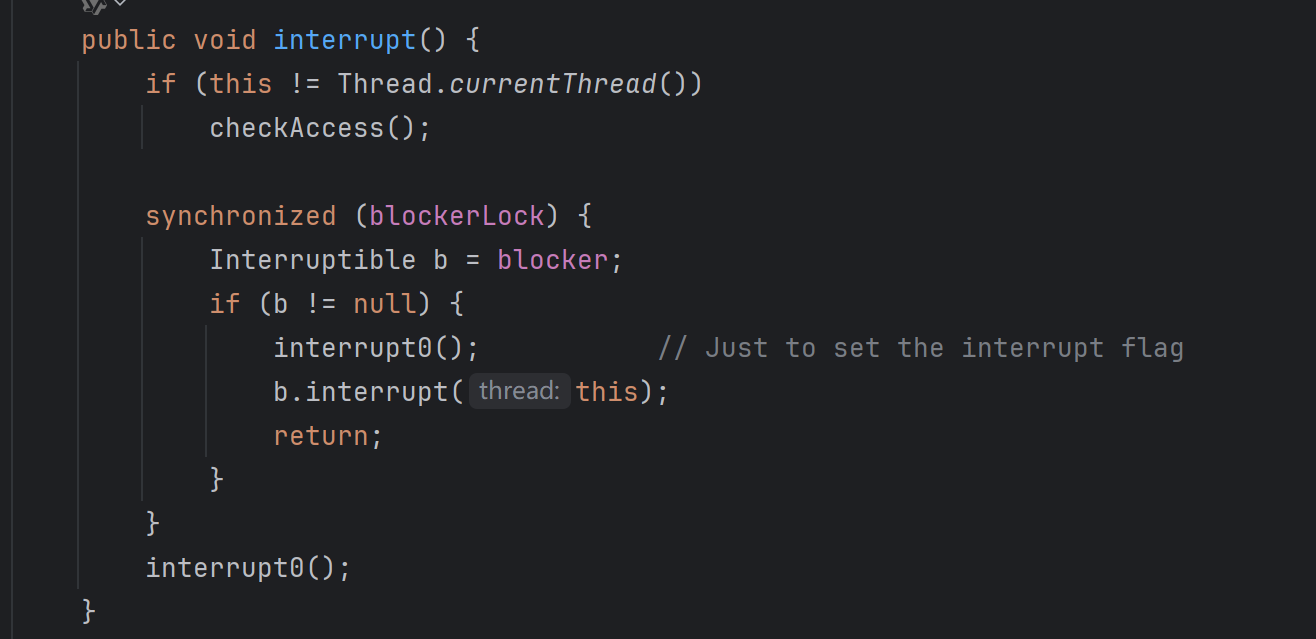
native方法 private native void interrupt0();
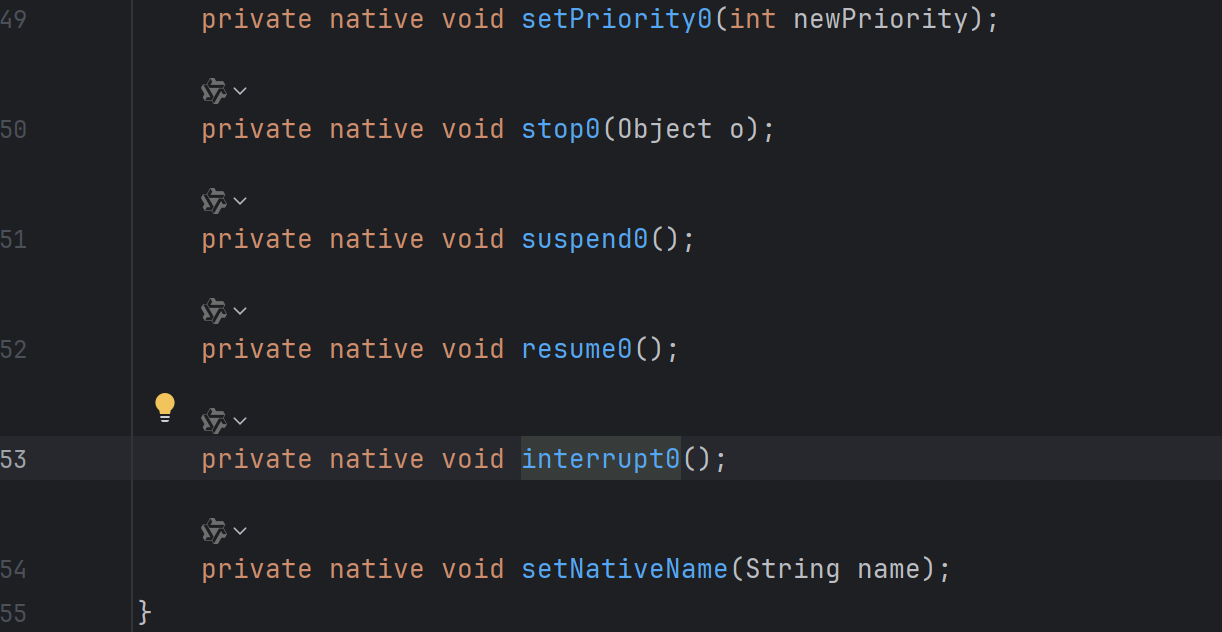
源码中解析这个方法的作用以及注意点
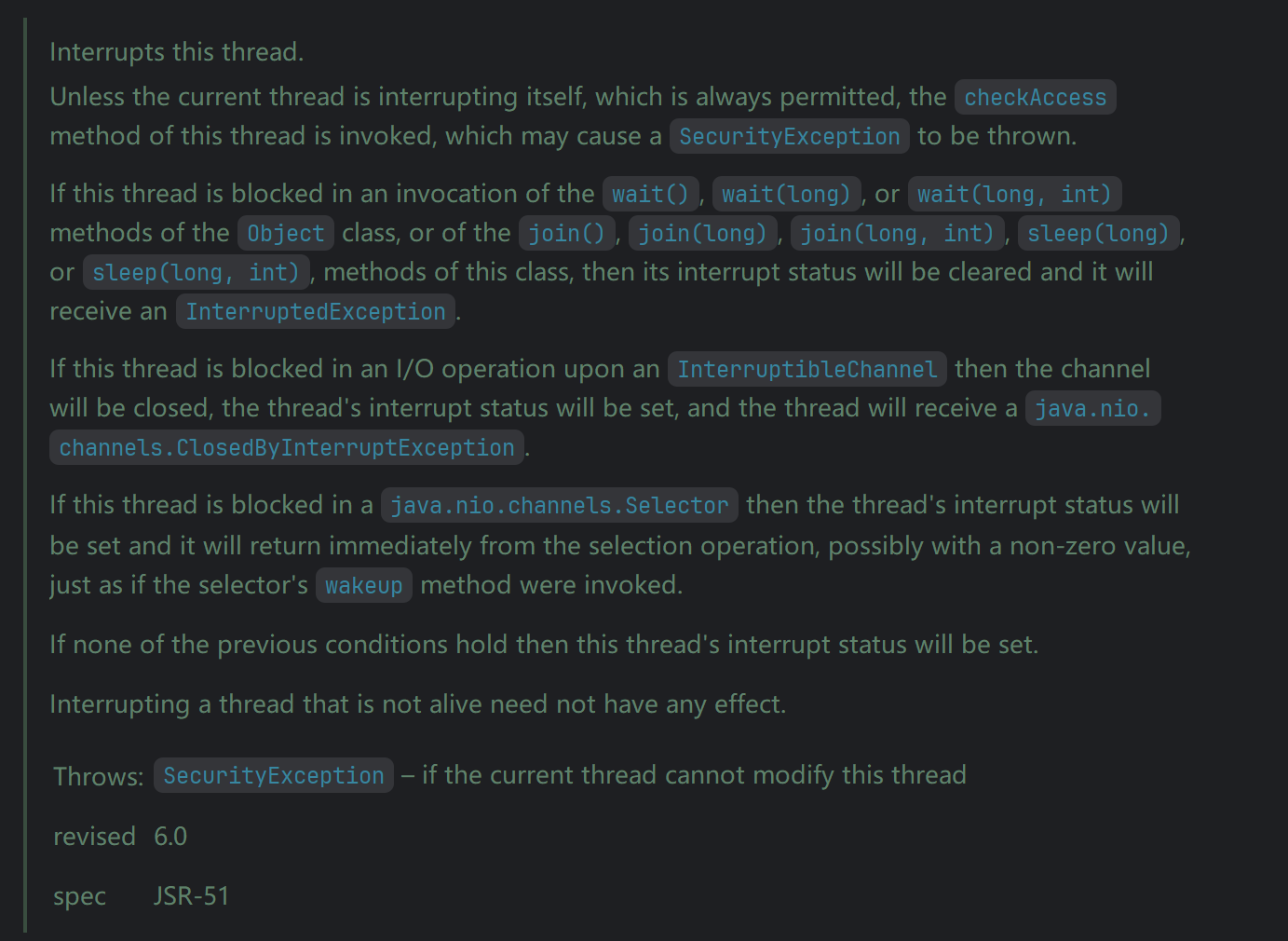

public boolean isInterrupted ()的源码说明
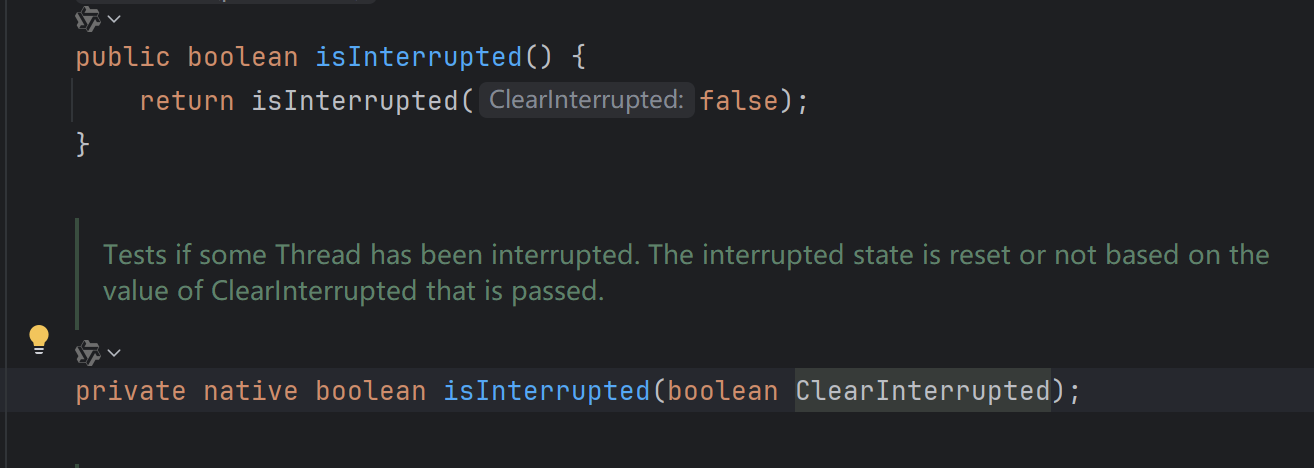
总结一下

当前线程的中断标识为true,是不是线程立刻停止?
t1.interrupt() 实例方法仅仅是设置中断状态标志位为true,不会停止线程
代码
java
package com.sgm.springboottest.demos.web;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
/**
* 线程中断demo演示
*/
public class InterruptedDemo {
static volatile boolean isStop=false;
static AtomicBoolean atomicBoolean=new AtomicBoolean(false);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//t1.interrupt() 实例方法仅仅是设置中断状态标志位为true,不会停止线程
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) {
System.out.println("=========> "+i);
}
System.out.println("t1.interrupt()后的中断标志位02:"+Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()); //true
}, "t1");
t1.start();
System.out.println("t1的默认中断标志位:"+t1.isInterrupted()); //false
//2毫秒睡眠
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t1.interrupt();//true
System.out.println("t1.interrupt()后的中断标志位01:"+t1.isInterrupted()); //true
//2秒睡眠
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2*1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("t1.interrupt()后的中断标志位03:"+t1.isInterrupted()); //false 中断不活跃的线程,不会有任何影响
}
}Thread.sleep() 睡眠对于中断的影响
没有说明时的效果
java
package com.sgm.springboottest.demos.web;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
/**
* 线程中断demo演示
*/
public class InterruptedDemo {
static volatile boolean isStop=false;
static AtomicBoolean atomicBoolean=new AtomicBoolean(false);
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true){
if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 中断标志位为:" +Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()+",程序终止");
break;
}
System.out.println("====>hello");
}
}, "t1");
t1.start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
t1.interrupt();
},"t2").start();
}
}代码结果
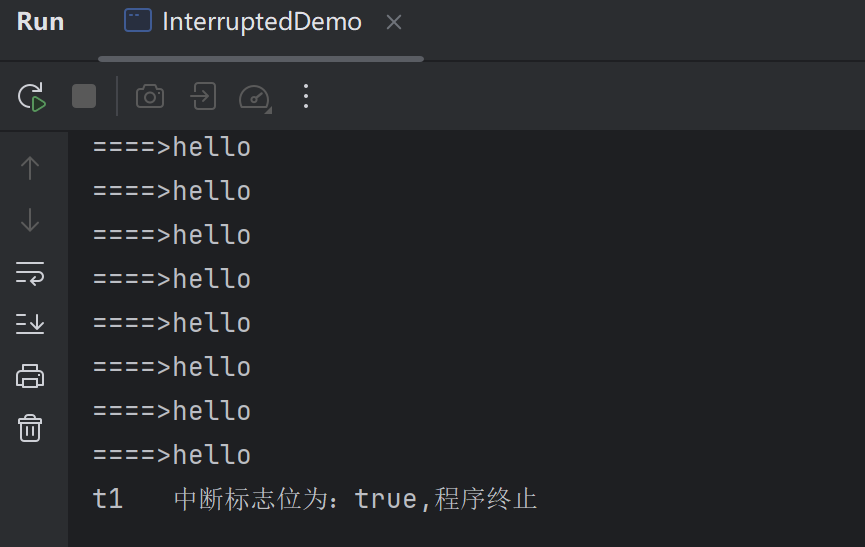
t1 线程引入睡眠后
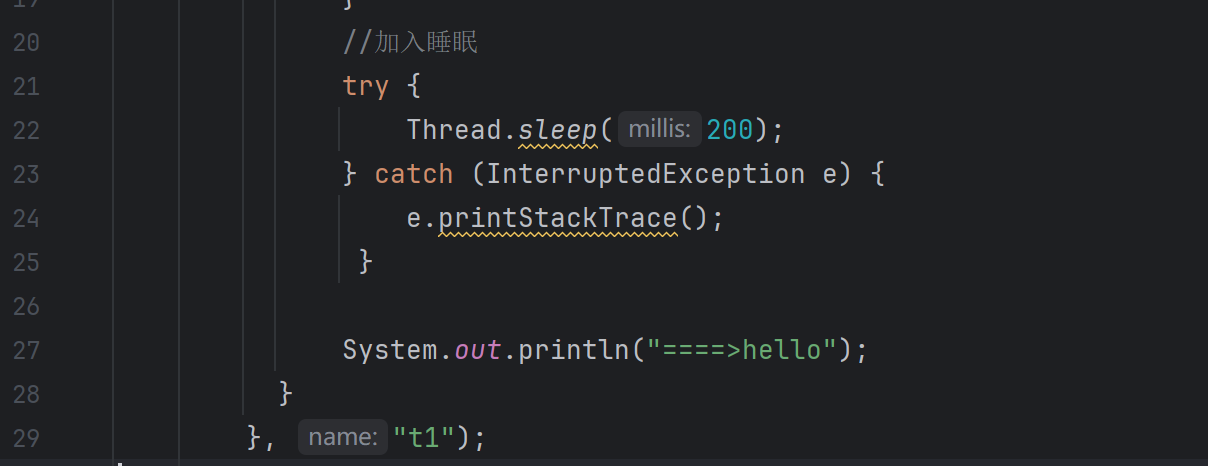
代码运行效果是没有终止,死循环的执行
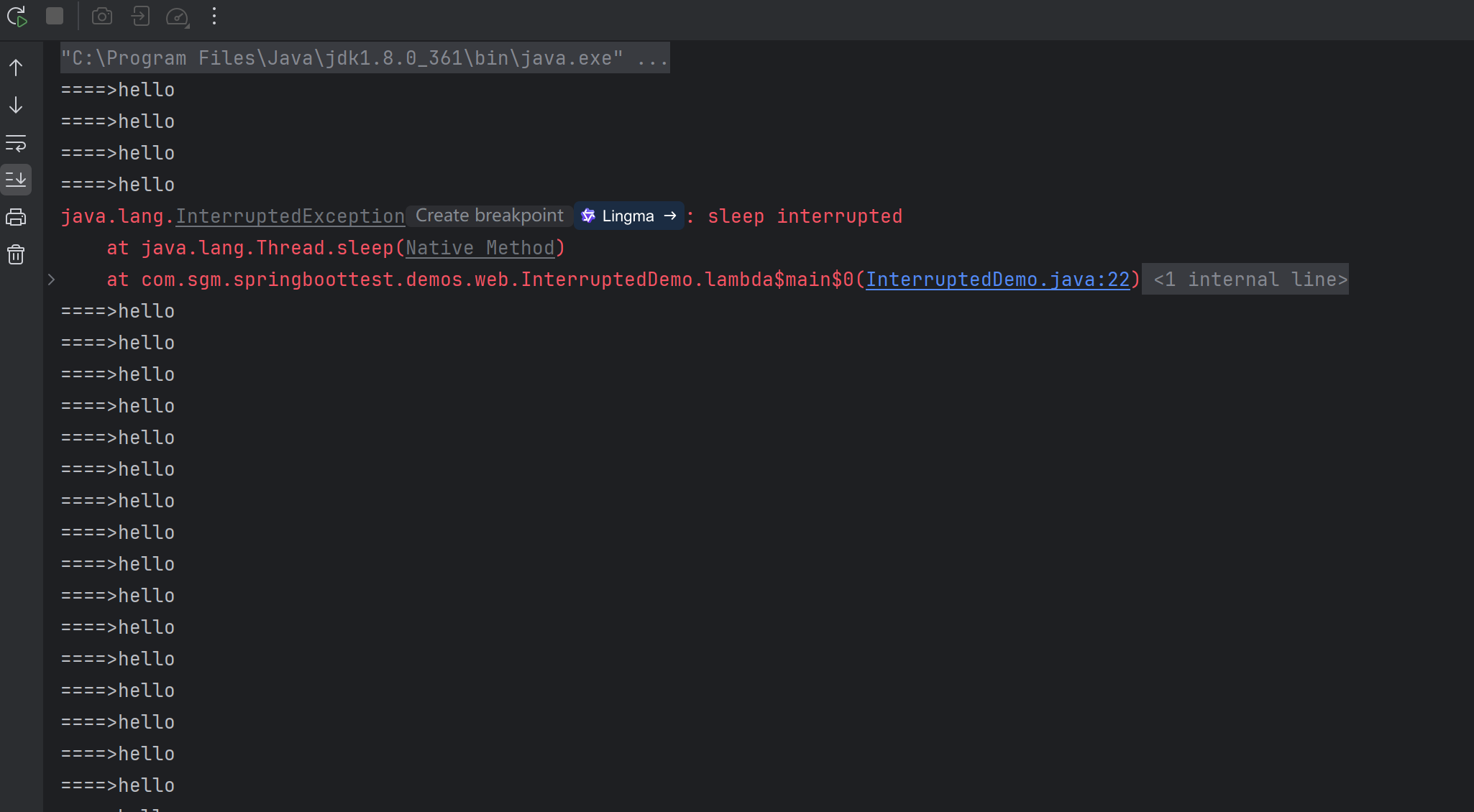
这种情况需要重新设置中断标志位
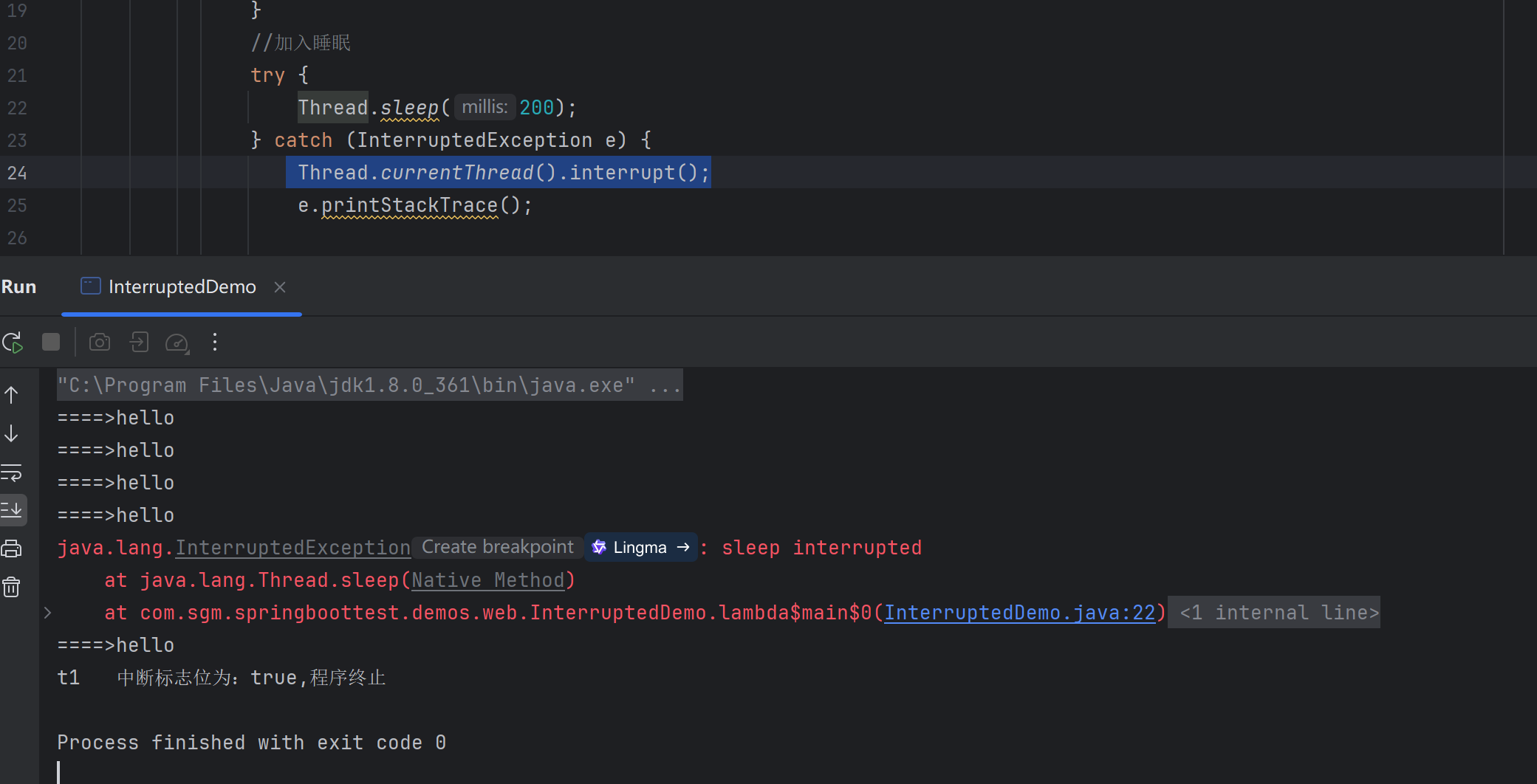
原因分析:

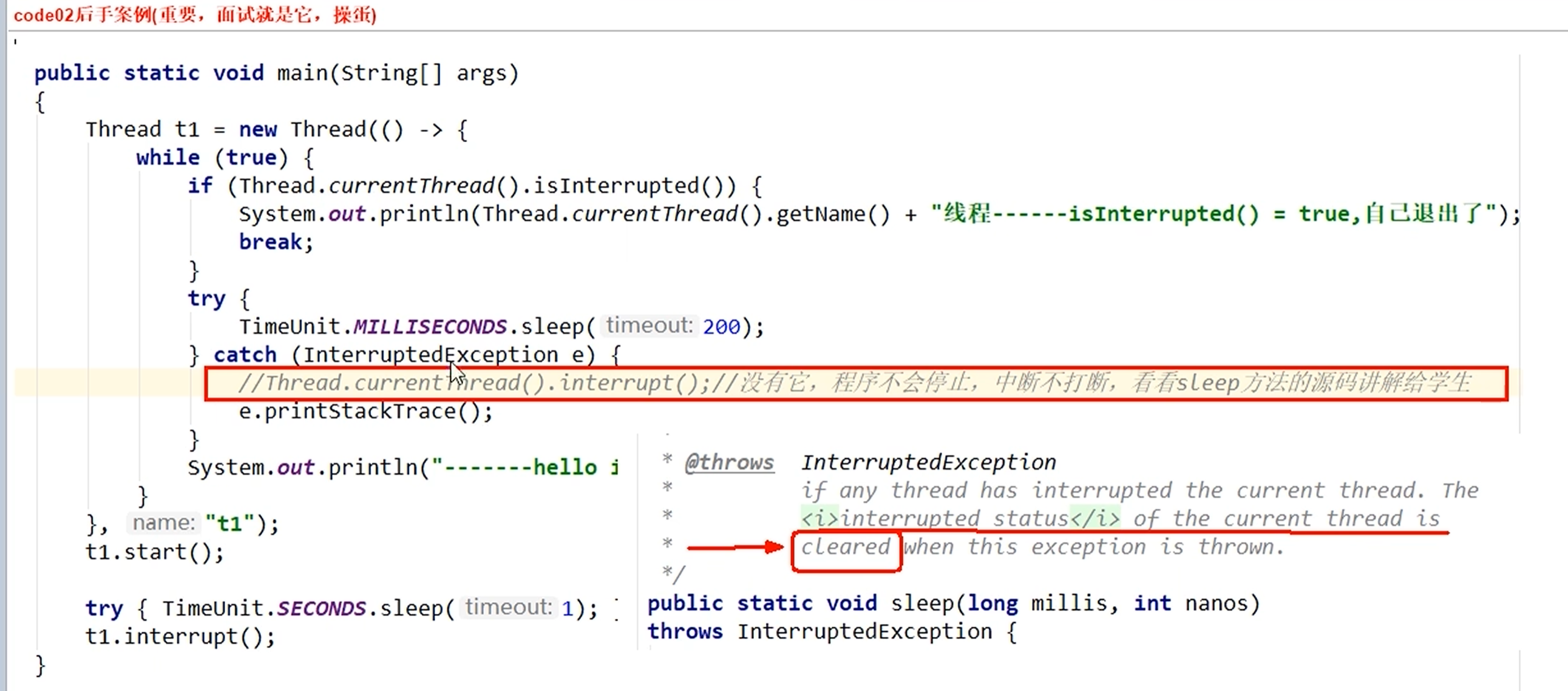
Thread.sleep() 源码 说明
InterruptedException -- if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The interrupted status of the current thread is cleared when this exception is thrown.
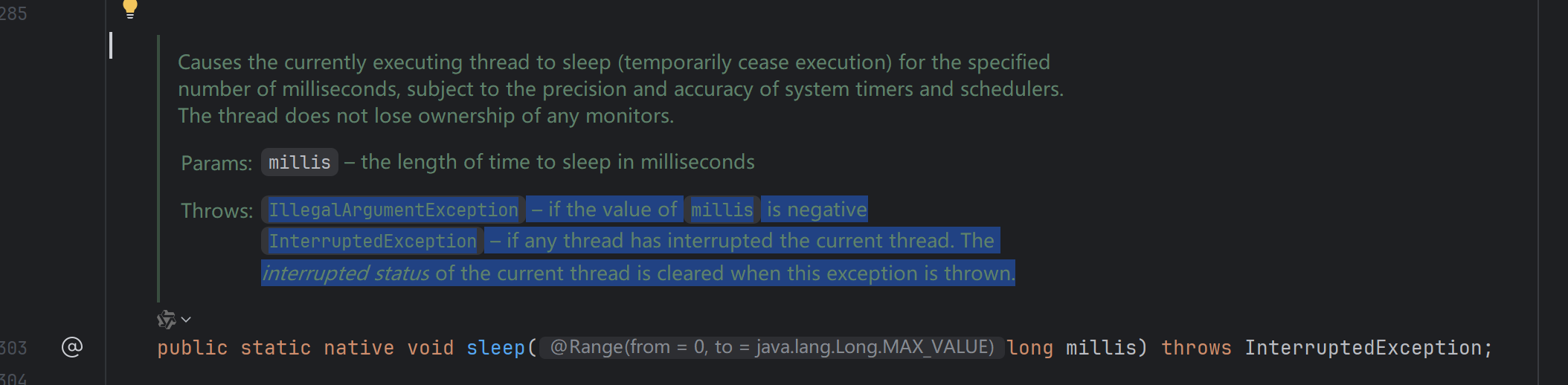
总结

中断只是一种协商机制,修改中断标志位仅此而已,不是立刻stop打断
静态方法Thread.interrupted(),谈谈你的理解。

代码演示
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 中断标志位:" +Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 中断标志位:" +Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("==>1");
//执行静态中断
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("==>2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 中断标志位:" +Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 中断标志位:" +Thread.interrupted());
}执行结果
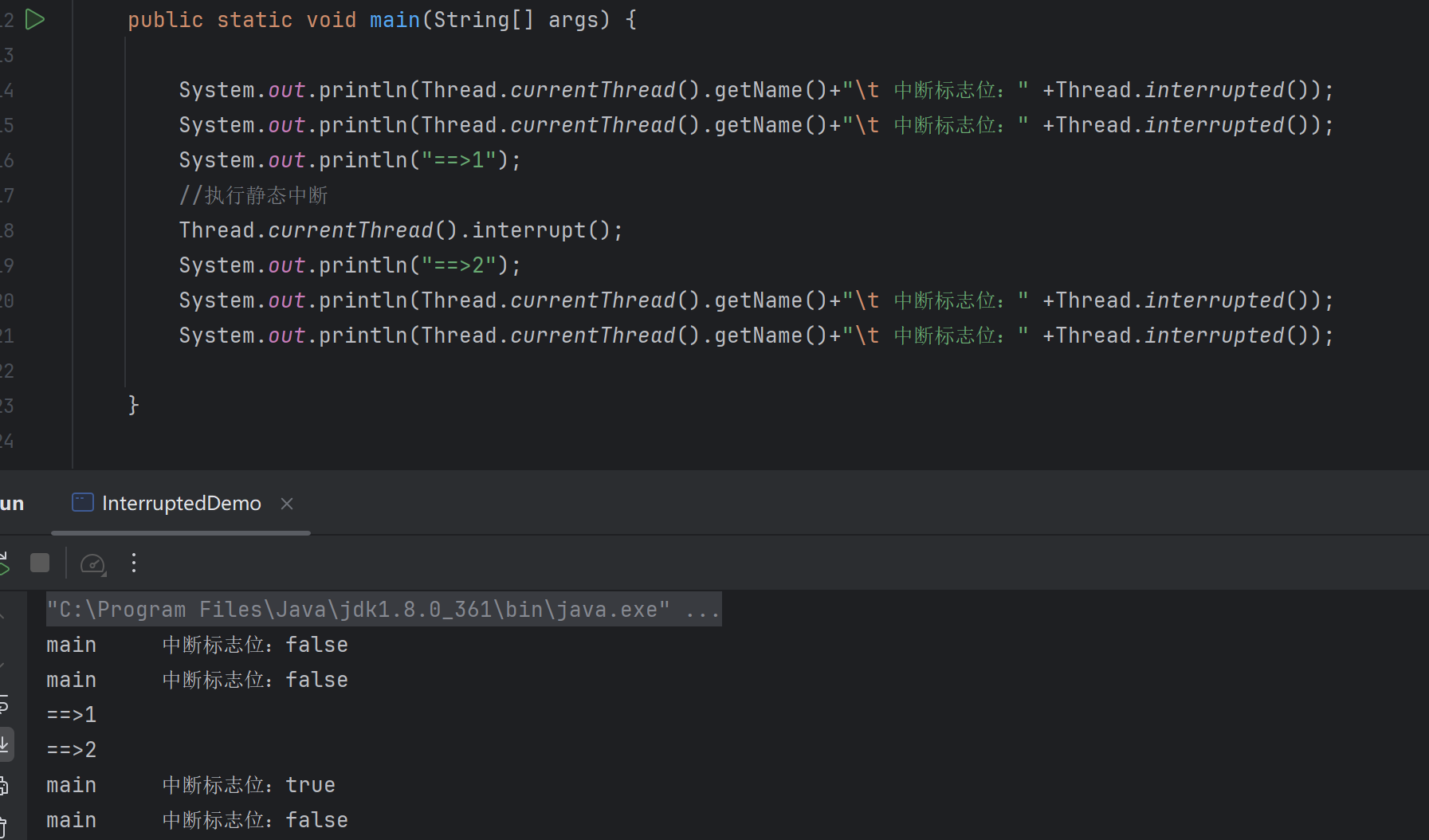
源码底层调用同一个方法,一个是true清除,一个是false