用Qwen3-VL模型实现端到端检测,无需额外训练检测器,通过自然语言提示词约束模型输出。
文章详细介绍了transformers和vLLM两种实现版本,包括模型初始化、图像处理、推理流程、结果清理和格式转换等关键环节。

基于 Qwen3-VL 模型的物体检测,支持对指定类别的物体进行批量检测,并输出 LabelMe 标准格式的标注文件与可视化结果。
- 基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的物体检测 依托 Qwen3-VL-4B 模型实现端到端检测,无需额外训练检测器,直接通过自然语言提示词约束模型输出指定类别的物体信息,兼顾检测灵活性与易用性。
- 标准化输出与可视化 检测结果自动转换为 LabelMe 标注格式,可直接用于标注工具导入与二次编辑;同时支持可视化渲染,在图像上绘制检测框和类别标签,直观展示检测效果。
- 强容错的结果处理流程 针对 VLM 生成文本可能存在的格式不规范、JSON 截断等问题,设计了多级响应清理机制:移除代码块标记、补全缺失括号、修复多余逗号、单双引号转换,搭配容错式 JSON 解析,大幅提升结果有效性。
Qwen3-VL有多种不同大小的模型:
参考官网:https://huggingface.co/collections/Qwen/qwen3-vl
开源代码:https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3-VL
目录
1、Qwen3-VL目标检测(transformers版本)
2.1、关键代码1:init_vllm_engine、prepare_vllm_input
1、Qwen3-VL目标检测(transformers版本)
整体关键流程:模型初始化 → 图像批量读取 → VLM 模型推理 → JSON 结果清理 / 修复 → 坐标校验 → LabelMe 格式转换 → 可视化保存。
1.1、关键函数1:call_vlm
-
核心作用 :使用****HuggingFace transformers,调用VLM模型,基于输入的图像和提示词生成并返回文本响应。
-
关键处理:对图像 / 文本输入格式化、张量转换,禁用梯度加速推理,裁剪并解码生成的文本 ID。
-
异常处理:捕获调用过程中的异常,失败时打印错误信息并返回空字符串。
def call_vlm(image_path, prompt):
"""
调用VLM(视觉语言模型)推理,返回文本响应
:param image_path: 图像文件路径
:param prompt: 推理提示词
:return: 模型生成的文本响应
"""
try:
# 打开图像并转换为RGB格式
image = Image.open(image_path).convert("RGB")
# 构造模型输入的对话格式
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "image"}, {"type": "text", "text": prompt}]}]
# 应用对话模板,生成模型输入文本
text = processor.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
# 处理输入(文本+图像),转换为张量并移至模型所在设备
inputs = processor(text=text, images=image, return_tensors="pt", padding=True).to(model.device)# 禁用梯度计算,提升推理速度并节省显存 with torch.no_grad(): # 模型推理生成文本,调大max_new_tokens避免JSON结果截断 generated_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=4096, do_sample=False, num_beams=1) # 裁剪掉输入部分,只保留生成的文本ID generated_ids_trimmed = generated_ids[:, inputs.input_ids.shape[1]:] # 解码生成的ID为文本 output_text = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids_trimmed, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)[0] return output_text except Exception as e: print(f"VLM调用失败: {str(e)}") return ""
1.2、关键函数2:detect_objects
- 核心作用:调用 VLM 检测指定类别物体,处理响应并返回含合法类别和有效像素级 bbox 的结果列表。
- 关键处理 :格式化提示词约束 JSON 输出、清理解析响应、转换并校验 bbox 坐标、过滤无效结果。
- 异常与容错:捕获全流程异常,对非标准响应 / 格式错误结果做容错处理,异常时返回空列表。
python
def detect_objects(image_path):
"""
核心检测函数:调用VLM检测图像中的目标物体
:param image_path: 图像路径
:return: 有效检测结果列表(包含类别和bbox)
"""
# 优化后的提示词:强制模型仅输出标准JSON格式,无多余内容
prompt = f"""
严格按照以下要求检测图像中{NODE_SPACE}类别的所有物体:
1. 仅输出JSON数组,不添加任何解释、说明、备注文字;
2. 每个数组元素是包含"category"(类别)和"bbox"([x1,y1,x2,y2],整数像素)的JSON对象;
3. 只检测{NODE_SPACE}中的类别,忽略其他所有类别;
4. 确保JSON格式完全合法(属性名用双引号,逗号分隔,括号匹配);
5. 每个对象必须包含完整的"category"和"bbox"字段,缺一不可。
输出示例(仅输出此格式,无其他内容):
[
{{
"category": "cup",
"bbox": [97, 203, 176, 282]
}},
{{
"category": "table",
"bbox": [10, 318, 639, 474]
}}
]
"""
try:
# 获取图像尺寸(用于后续坐标转换)
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
w_img, h_img = img.size
print("调用VLM检测物体...")
time_start = time.time()
# 调用VLM模型获取原始响应
raw_response = call_vlm(image_path, prompt)
print(f'VLM推理耗时:{time.time() - time_start:.2f}s')
if not raw_response:
print("VLM返回空响应")
return []
# 打印原始响应前800字符(方便排查问题)
print(f"原始VLM响应(前800字符):\n{raw_response[:800]}...")
# 清理模型响应,提取有效JSON
cleaned_response = clean_vlm_response(raw_response)
if not cleaned_response:
print("清理后无有效JSON内容")
return []
# 容错式解析JSON
objects_data = safe_json_loads(cleaned_response)
# 确保结果为列表格式
if not isinstance(objects_data, list):
print(f"响应非列表格式,已转换为列表: {objects_data}")
objects_data = [] if objects_data is None else [objects_data]
valid_objects = []
# 过滤并验证检测结果
for i, obj in enumerate(objects_data):
# 跳过非字典格式的结果
if not isinstance(obj, dict):
print(f"跳过非对象结果 #{i+1}: {obj}")
continue
# 提取类别和bbox
category = obj.get('category')
bbox = obj.get('bbox', [])
# 过滤无效类别或不完整的bbox
if category not in NODE_SPACE or len(bbox) != 4:
print(f"跳过无效结果 #{i+1}: 类别={category}, bbox={bbox}")
continue
try:
# 转换bbox坐标为图像像素值(处理归一化坐标)
x1_norm, y1_norm, x2_norm, y2_norm = map(float, bbox)
x1 = int(round(x1_norm / 1000 * w_img))
y1 = int(round(y1_norm / 1000 * h_img))
x2 = int(round(x2_norm / 1000 * w_img))
y2 = int(round(y2_norm / 1000 * h_img))
# 边界校验:确保坐标在图像范围内
x1 = max(0, min(x1, w_img - 1))
y1 = max(0, min(y1, h_img - 1))
x2 = max(x1 + 1, min(x2, w_img - 1))
y2 = max(y1 + 1, min(y2, h_img - 1))
# 添加有效结果到列表
valid_objects.append({"category": category, "bbox": [x1, y1, x2, y2]})
except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
print(f"坐标格式错误 #{i+1}: {e}, bbox={bbox}")
continue
print(f"有效检测结果:{len(valid_objects)} 个")
return valid_objects
except Exception as e:
print(f"检测失败: {str(e)}")
return []1.3、整体代码的流程图
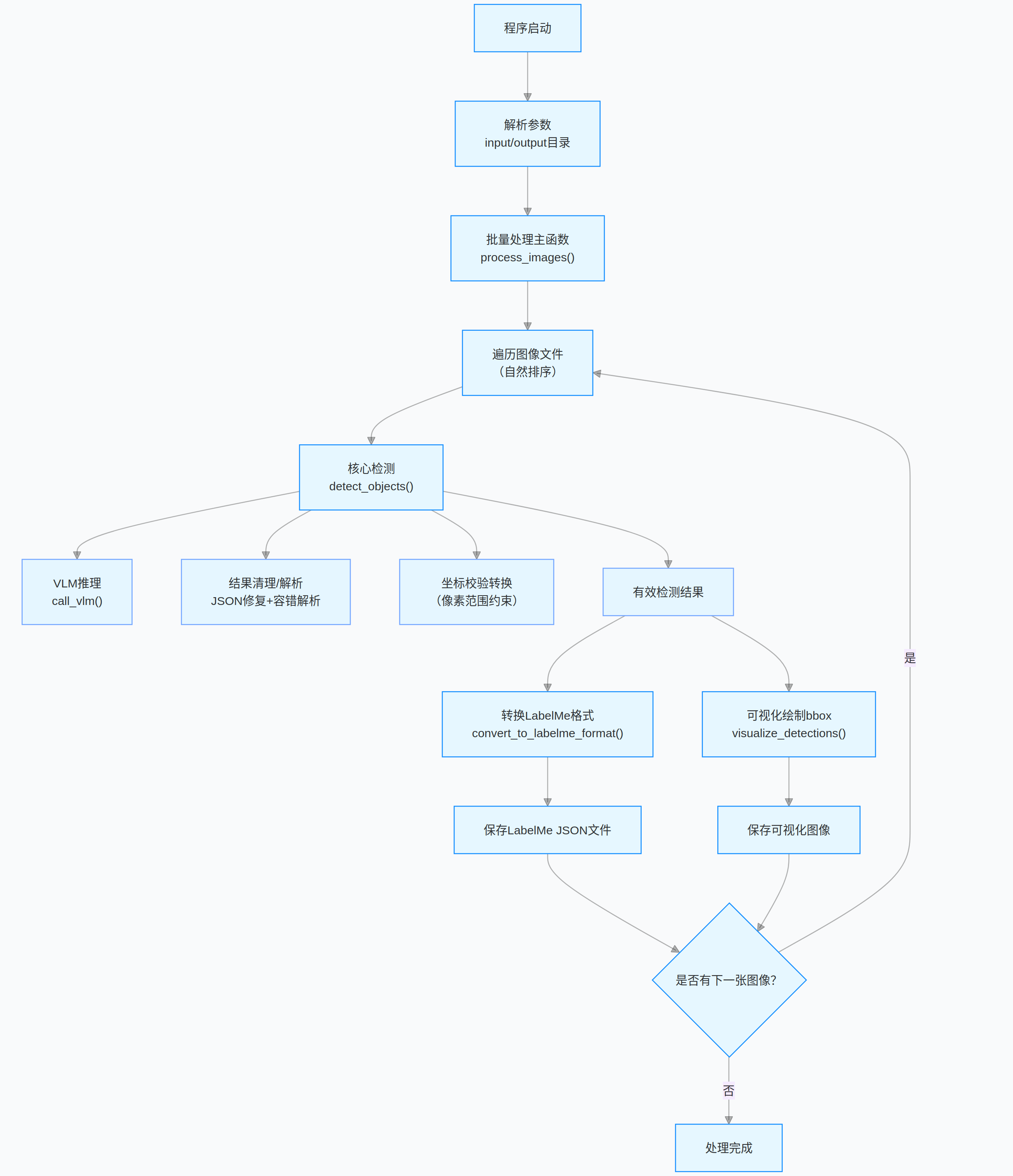
1.4、完整代码
python
# 导入所需基础库
import os
import json
import glob
import re
import torch
import time
from PIL import Image # 图像处理库
import cv2 # OpenCV库,用于图像可视化
# 导入HuggingFace Transformers库中的Qwen3-VL模型相关类
from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModelForImageTextToText
from tqdm import tqdm # 进度条显示库
# --- 基础配置 ---
# 量化后的Qwen3-VL-4B模型路径
QUANTIZED_MODEL_PATH = "/home/user/lgp_dev/model_path/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct"
# 输入图像目录(RGB图像)
input_dir = "./rgb/"
# 输出目录(存储检测结果和可视化图片)
output_dir = "./output_vis_labelme"
# 需要检测的目标类别列表
NODE_SPACE = [
'table', # 桌子
'cup', # 杯子
'bottle', # 瓶子
'chair', # 椅子
'robot', # 机器人
'garbage can', # 垃圾桶
'shelf', # 架子
'tissue box', # 纸巾盒
'potted plant', # 盆栽
'television', # 电视
'food', # 食物
'beverage', # 饮料
'daily_necessities', # 日用品
'computer mainframe', # 电脑主机
'coffee machine' # 咖啡机
]
# 全局初始化模型/处理器(仅初始化一次,提升效率)
print(f"加载量化Qwen3-VL-4B模型:{QUANTIZED_MODEL_PATH}...")
try:
# 加载预训练的Qwen3-VL模型,自动分配设备(CPU/GPU)
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained(
QUANTIZED_MODEL_PATH,
device_map="auto", # 自动分配模型到可用设备
trust_remote_code=True # 信任远程代码(Qwen3-VL需要)
)
# 加载模型对应的处理器(处理图像和文本输入)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(QUANTIZED_MODEL_PATH)
print("模型加载成功!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"模型加载失败:{str(e)}")
exit(1) # 模型加载失败则退出程序
def call_vlm(image_path, prompt):
"""
调用VLM(视觉语言模型)推理,返回文本响应
:param image_path: 图像文件路径
:param prompt: 推理提示词
:return: 模型生成的文本响应
"""
try:
# 打开图像并转换为RGB格式
image = Image.open(image_path).convert("RGB")
# 构造模型输入的对话格式
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "image"}, {"type": "text", "text": prompt}]}]
# 应用对话模板,生成模型输入文本
text = processor.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
# 处理输入(文本+图像),转换为张量并移至模型所在设备
inputs = processor(text=text, images=image, return_tensors="pt", padding=True).to(model.device)
# 禁用梯度计算,提升推理速度并节省显存
with torch.no_grad():
# 模型推理生成文本,调大max_new_tokens避免JSON结果截断
generated_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=4096, do_sample=False, num_beams=1)
# 裁剪掉输入部分,只保留生成的文本ID
generated_ids_trimmed = generated_ids[:, inputs.input_ids.shape[1]:]
# 解码生成的ID为文本
output_text = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids_trimmed, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)[0]
return output_text
except Exception as e:
print(f"VLM调用失败: {str(e)}")
return ""
def fix_truncated_json(cleaned_response):
"""
修复被截断的JSON字符串,补全缺失的括号/逗号
:param cleaned_response: 初步清理后的响应文本
:return: 修复后的JSON字符串
"""
if not cleaned_response:
return ""
# 统计各类括号数量,判断是否缺失闭合括号
open_braces = cleaned_response.count('{')
close_braces = cleaned_response.count('}')
open_brackets = cleaned_response.count('[')
close_brackets = cleaned_response.count(']')
# 补全缺失的对象闭合括号
if open_braces > close_braces:
cleaned_response += '}' * (open_braces - close_braces)
# 补全缺失的数组闭合括号
if open_brackets > close_brackets:
cleaned_response += ']' * (open_brackets - close_brackets)
# 移除末尾多余的逗号(避免JSON解析错误)
cleaned_response = re.sub(r',\s*$', '', cleaned_response)
return cleaned_response
def clean_vlm_response(response):
"""
清理VLM模型响应,提取有效JSON并修复格式错误
:param response: 模型原始响应文本
:return: 清理后的JSON字符串
"""
if not response:
return ""
# 1. 移除首尾空白和代码块标记(```json/```)
cleaned = response.strip().replace('```json', '').replace('```', '').strip()
# 2. 提取JSON数组核心部分(匹配[]包裹的内容)
json_match = re.search(r'\[.*\]', cleaned, re.DOTALL)
if json_match:
cleaned = json_match.group(0)
else:
# 未匹配到完整数组时,取开头到最后一个}的部分并补全数组格式
last_brace = cleaned.rfind('}')
if last_brace != -1:
cleaned = '[' + cleaned[:last_brace+1] + ']'
# 3. 修复常见格式错误
cleaned = cleaned.replace("'", '"') # 单引号替换为双引号(JSON标准)
cleaned = re.sub(r',\s*]', ']', cleaned) # 移除数组末尾多余逗号
cleaned = re.sub(r',\s*}', '}', cleaned) # 移除对象末尾多余逗号
# 4. 修复截断的JSON(补全括号)
cleaned = fix_truncated_json(cleaned)
return cleaned
def safe_json_loads(json_str):
"""
容错式JSON解析,兼容格式不完整的情况
:param json_str: 待解析的JSON字符串
:return: 解析后的列表/字典,解析失败返回空列表
"""
try:
# 常规JSON解析
return json.loads(json_str)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
# 解析失败时,尝试提取所有{}包裹的独立对象
try:
obj_matches = re.findall(r'\{[^}]+\}', json_str)
objects = []
for obj_str in obj_matches:
# 补全对象闭合括号
if not obj_str.endswith('}'):
obj_str += '}'
# 解析单个对象并加入列表
obj = json.loads(obj_str)
objects.append(obj)
return objects
except:
# 终极容错:返回空列表
return []
def detect_objects(image_path):
"""
核心检测函数:调用VLM检测图像中的目标物体
:param image_path: 图像路径
:return: 有效检测结果列表(包含类别和bbox)
"""
# 优化后的提示词:强制模型仅输出标准JSON格式,无多余内容
prompt = f"""
严格按照以下要求检测图像中{NODE_SPACE}类别的所有物体:
1. 仅输出JSON数组,不添加任何解释、说明、备注文字;
2. 每个数组元素是包含"category"(类别)和"bbox"([x1,y1,x2,y2],整数像素)的JSON对象;
3. 只检测{NODE_SPACE}中的类别,忽略其他所有类别;
4. 确保JSON格式完全合法(属性名用双引号,逗号分隔,括号匹配);
5. 每个对象必须包含完整的"category"和"bbox"字段,缺一不可。
输出示例(仅输出此格式,无其他内容):
[
{{
"category": "cup",
"bbox": [97, 203, 176, 282]
}},
{{
"category": "table",
"bbox": [10, 318, 639, 474]
}}
]
"""
try:
# 获取图像尺寸(用于后续坐标转换)
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
w_img, h_img = img.size
print("调用VLM检测物体...")
time_start = time.time()
# 调用VLM模型获取原始响应
raw_response = call_vlm(image_path, prompt)
print(f'VLM推理耗时:{time.time() - time_start:.2f}s')
if not raw_response:
print("VLM返回空响应")
return []
# 打印原始响应前800字符(方便排查问题)
print(f"原始VLM响应(前800字符):\n{raw_response[:800]}...")
# 清理模型响应,提取有效JSON
cleaned_response = clean_vlm_response(raw_response)
if not cleaned_response:
print("清理后无有效JSON内容")
return []
# 容错式解析JSON
objects_data = safe_json_loads(cleaned_response)
# 确保结果为列表格式
if not isinstance(objects_data, list):
print(f"响应非列表格式,已转换为列表: {objects_data}")
objects_data = [] if objects_data is None else [objects_data]
valid_objects = []
# 过滤并验证检测结果
for i, obj in enumerate(objects_data):
# 跳过非字典格式的结果
if not isinstance(obj, dict):
print(f"跳过非对象结果 #{i+1}: {obj}")
continue
# 提取类别和bbox
category = obj.get('category')
bbox = obj.get('bbox', [])
# 过滤无效类别或不完整的bbox
if category not in NODE_SPACE or len(bbox) != 4:
print(f"跳过无效结果 #{i+1}: 类别={category}, bbox={bbox}")
continue
try:
# 转换bbox坐标为图像像素值(处理归一化坐标)
x1_norm, y1_norm, x2_norm, y2_norm = map(float, bbox)
x1 = int(round(x1_norm / 1000 * w_img))
y1 = int(round(y1_norm / 1000 * h_img))
x2 = int(round(x2_norm / 1000 * w_img))
y2 = int(round(y2_norm / 1000 * h_img))
# 边界校验:确保坐标在图像范围内
x1 = max(0, min(x1, w_img - 1))
y1 = max(0, min(y1, h_img - 1))
x2 = max(x1 + 1, min(x2, w_img - 1))
y2 = max(y1 + 1, min(y2, h_img - 1))
# 添加有效结果到列表
valid_objects.append({"category": category, "bbox": [x1, y1, x2, y2]})
except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
print(f"坐标格式错误 #{i+1}: {e}, bbox={bbox}")
continue
print(f"有效检测结果:{len(valid_objects)} 个")
return valid_objects
except Exception as e:
print(f"检测失败: {str(e)}")
return []
def convert_to_labelme_format(image_path, detected_objects):
"""
将检测结果转换为LabelMe标注工具的JSON格式
:param image_path: 图像路径
:param detected_objects: 检测结果列表
:return: LabelMe格式的字典,失败返回None
"""
try:
# 获取图像尺寸
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
image_width, image_height = img.size
# 初始化LabelMe格式数据
labelme_data = {
"version": "5.1.1", # LabelMe版本
"flags": {}, # 自定义标记
"shapes": [], # 标注形状列表
"imagePath": os.path.basename(image_path), # 图像文件名
"imageData": None, # 图像二进制数据(None即可)
"imageHeight": image_height, # 图像高度
"imageWidth": image_width # 图像宽度
}
# 遍历检测结果,构造标注形状
for obj in detected_objects:
category = obj['category']
x1, y1, x2, y2 = obj['bbox']
shape = {
"label": category, # 标注类别
"points": [[x1, y1], [x2, y2]], # 矩形对角点
"group_id": None, # 分组ID
"shape_type": "rectangle", # 形状类型(矩形)
"flags": {} # 形状标记
}
labelme_data["shapes"].append(shape)
return labelme_data
except Exception as e:
print(f"转换为LabelMe格式失败: {str(e)}")
return None
def visualize_detections(image_path, detected_objects, output_path):
"""
可视化检测结果:在图像上绘制bbox和类别标签
:param image_path: 输入图像路径
:param detected_objects: 检测结果列表
:param output_path: 可视化结果保存路径
"""
try:
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
if image is None:
print(f"无法读取图像: {image_path}")
return
h, w = image.shape[:2]
# 遍历检测结果,绘制矩形框和标签
for obj in detected_objects:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = obj['bbox']
category = obj['category']
# 绘制矩形框(绿色,线宽2)
cv2.rectangle(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 绘制类别标签背景和文字
label = category
(text_w, text_h), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
# 调整标签位置(避免超出图像边界)
y_label = y1 - 10 if y1 - 10 > 10 else y1 + text_h + 10
# 绘制标签背景矩形
cv2.rectangle(image, (x1, y_label - text_h - 2), (x1 + text_w, y_label + 2), (0, 255, 0), -1)
# 绘制标签文字(黑色)
cv2.putText(image, label, (x1, y_label), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1)
# 保存可视化结果
cv2.imwrite(output_path, image)
print(f"可视化结果保存至: {output_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"可视化失败: {str(e)}")
def print_detection_results(detected_objects):
"""打印检测结果(仅显示类别和bbox,便于调试)"""
if not detected_objects:
print("未检测到任何物体")
return
print("\n--- 原始检测结果 ---")
for i, obj in enumerate(detected_objects):
print(f"物体 #{i+1}: 类别={obj['category']}, bbox={obj['bbox']}")
print("--- 结果结束 ---\n")
def natural_sort_key(filename):
"""
生成自然排序的键值,用于文件名按数字顺序排序
:param filename: 文件名
:return: 排序键列表
"""
return [int(t) if t.isdigit() else t.lower() for t in re.split(r'(\d+)', os.path.basename(filename))]
def process_images(input_dir, output_dir):
"""
批量处理图像的主函数:检测物体 + 转换为LabelMe格式 + 可视化结果
:param input_dir: 输入图像目录
:param output_dir: 输出结果目录
"""
try:
# 创建输出目录(不存在则创建)
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 检测结果(LabelMe格式)保存目录
detections_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, "detections_labelme")
# 可视化结果保存目录
viz_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, "visualizations")
os.makedirs(detections_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(viz_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 支持的图像格式
image_ext = ['*.jpg', '*.jpeg', '*.png', '*.bmp']
image_files = []
# 遍历所有图像格式,收集图像文件路径
for ext in image_ext:
image_files.extend(glob.glob(os.path.join(input_dir, ext)))
# 按自然顺序排序图像文件
image_files = sorted(image_files, key=natural_sort_key)
if not image_files:
print(f"输入目录 {input_dir} 未找到图像")
return
# 批量处理图像,显示进度条
for img_path in tqdm(image_files, desc="Processing Images", unit="image"):
img_name = os.path.basename(img_path)
print(f"\n===== 处理 {img_name} =====")
# 检测图像中的物体
det_results = detect_objects(img_path)
# 打印检测结果
print_detection_results(det_results)
# 构造LabelMe格式JSON文件名
json_filename = os.path.splitext(img_name)[0] + ".json"
json_output_path = os.path.join(detections_dir, json_filename)
# 转换检测结果为LabelMe格式
labelme_json_data = convert_to_labelme_format(img_path, det_results)
# 保存LabelMe格式JSON文件
if labelme_json_data:
try:
with open(json_output_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(labelme_json_data, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
print(f"LabelMe格式的JSON已保存至: {json_output_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"保存JSON失败: {str(e)}")
# 构造可视化结果保存路径
viz_path = os.path.join(viz_dir, os.path.splitext(img_name)[0] + "_viz.jpg")
# 可视化检测结果并保存
visualize_detections(img_path, det_results, viz_path)
print("\n所有图像处理完成!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"批量处理失败: {str(e)}")
# 程序主入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 导入命令行参数解析库
import argparse
# 创建参数解析器
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Qwen3-VL物体检测,并输出LabelMe格式结果')
parser.add_argument('--input_dir', type=str, default=input_dir, help='输入图像目录')
parser.add_argument('--output_dir', type=str, default=output_dir, help='输出目录')
# 解析命令行参数
args = parser.parse_args()
# 执行批量图像处理
process_images(args.input_dir, args.output_dir)- 程序首先加载预训练的 VLM 模型与处理器,读取输入目录下的图像文件;
- 通过定制化提示词引导模型输出 JSON 格式的检测结果,再经格式清理、容错解析、坐标校验等步骤筛选有效检测框;
- 最后将结果转换为 LabelMe 标注格式保存,并生成带检测框的可视化图像。
2、Qwen3-VL目标检测(vLLM版本)
基于 vLLM 加速的 Qwen3-VL 多模态物体检测工具,可批量处理 RGB 图像,自动检测指定类别的物体,输出 LabelMe 格式的标注文件并生成可视化检测结果。
- 替换原生 transformers 模型调用逻辑,采用 vLLM 引擎实现高吞吐量、低延迟的多模态推理,支持多 GPU 张量并行。
- 保留提示词引导的结构化输出:强制模型输出标准 JSON 格式的检测结果,包含物体类别与边界框坐标。
- 内置JSON 格式容错修复:自动处理模型响应的截断、格式错误问题,提升结果解析稳定性。
- 支持LabelMe 格式转换 与检测结果可视化:一键生成可直接用于标注工具的 JSON 文件,以及带检测框的可视化图像。
2.1、关键代码1:init_vllm_engine、prepare_vllm_input
init_vllm_engine函数核心特点:vLLM 引擎初始化逻辑封装为独立函数,仅由主函数调用,规避全局作用域初始化引发的多进程启动冲突,符合 Python 多进程编程规范。prepare_vllm_input函数核心特点:统一处理文本 + 图像 / 视频输入,转换成 vLLM 引擎可直接识别的格式,适配 Qwen3-VL 多模态模型的输入要求
python
def init_vllm_engine():
"""
初始化vllm引擎(放在函数内,由主函数调用)
"""
global processor, llm_engine, sampling_config
print(f"加载vllm引擎和Qwen3-VL-4B模型:{QUANTIZED_MODEL_PATH}...")
try:
# 加载模型处理器
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(
QUANTIZED_MODEL_PATH,
trust_remote_code=True,
torch_dtype=torch.float16 # 指定半精度,节省显存
)
# 初始化vllm推理引擎(调整多卡配置,降低显存占用)
llm_engine = LLM(
model=QUANTIZED_MODEL_PATH,
tensor_parallel_size=torch.cuda.device_count(), # 自动适配GPU数量
gpu_memory_utilization=0.8, # GPU显存利用率(可根据显存调整)
seed=42, # 固定随机种子,保证结果可复现
trust_remote_code=True,
dtype=torch.bfloat16 # 匹配原模型精度
)
# 配置vllm生成参数
sampling_config = SamplingParams(
temperature=0.0,
max_tokens=1024,
stop_token_ids=[],
top_p=1.0
)
print("vllm引擎和模型加载成功!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"模型加载失败:{str(e)}")
raise e # 抛出异常,让主函数退出
def prepare_vllm_input(messages, processor):
"""
预处理多模态输入,转换成vllm可直接使用的格式
"""
# 1. 处理文本
prompt_text = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
# 2. 处理视觉信息
image_data, video_data, video_kwargs = process_vision_info(
messages,
image_patch_size=processor.image_processor.patch_size,
return_video_kwargs=True,
return_video_metadata=True
)
# 3. 整理多模态数据
multi_modal_data = {}
if image_data is not None:
multi_modal_data['image'] = image_data
if video_data is not None:
multi_modal_data['video'] = video_data
return {
'prompt': prompt_text,
'multi_modal_data': multi_modal_data,
'mm_processor_kwargs': video_kwargs
}2.2、关键代码2:detect_objects
- 采用精准的提示词模板,明确要求模型仅输出包含指定类别和 bbox 的标准 JSON 数组,禁用多余解释性文字,从源头约束输出格式,适配后续自动化解析需求。
- 自动读取图像尺寸,将模型返回的归一化坐标(按 1000 缩放)转换为实际像素坐标;
- 对转换后的坐标做严格边界校验,确保 x1/y1/x2/y2 均在图像像素范围内,且 x2>x1、y2>y1,避免出现无效 / 反向的边界框。
python
def detect_objects(image_path):
"""核心检测函数"""
prompt = f"""
严格按照以下要求检测图像中{NODE_SPACE}类别的所有物体:
1. 仅输出JSON数组,不添加任何解释、说明、备注文字;
2. 每个数组元素是包含"category"(类别)和"bbox"([x1,y1,x2,y2],整数像素)的JSON对象;
3. 只检测{NODE_SPACE}中的类别,忽略其他所有类别;
4. 确保JSON格式完全合法(属性名用双引号,逗号分隔,括号匹配);
5. 每个对象必须包含完整的"category"和"bbox"字段,缺一不可。
输出示例(仅输出此格式,无其他内容):
[
{{
"category": "cup",
"bbox": [97, 203, 176, 282]
}},
{{
"category": "table",
"bbox": [10, 318, 639, 474]
}}
]
"""
try:
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
w_img, h_img = img.size
print("调用VLM检测物体...")
time_start = time.time()
raw_response = call_vlm(image_path, prompt)
print(f'VLM推理耗时:{time.time() - time_start:.2f}s')
if not raw_response:
print("VLM返回空响应")
return []
cleaned_response = clean_vlm_response(raw_response)
if not cleaned_response:
print("清理后无有效JSON内容")
return []
objects_data = safe_json_loads(cleaned_response)
if not isinstance(objects_data, list):
print(f"响应非列表格式,已转换为列表: {objects_data}")
objects_data = [] if objects_data is None else [objects_data]
valid_objects = []
for i, obj in enumerate(objects_data):
if not isinstance(obj, dict):
print(f"跳过非对象结果 #{i+1}: {obj}")
continue
category = obj.get('category')
bbox = obj.get('bbox', [])
if category not in NODE_SPACE or len(bbox) != 4:
print(f"跳过无效结果 #{i+1}: 类别={category}, bbox={bbox}")
continue
try:
x1_norm, y1_norm, x2_norm, y2_norm = map(float, bbox)
x1 = int(round(x1_norm / 1000 * w_img))
y1 = int(round(y1_norm / 1000 * h_img))
x2 = int(round(x2_norm / 1000 * w_img))
y2 = int(round(y2_norm / 1000 * h_img))
x1 = max(0, min(x1, w_img - 1))
y1 = max(0, min(y1, h_img - 1))
x2 = max(x1 + 1, min(x2, w_img - 1))
y2 = max(y1 + 1, min(y2, h_img - 1))
valid_objects.append({"category": category, "bbox": [x1, y1, x2, y2]})
except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
print(f"坐标格式错误 #{i+1}: {e}, bbox={bbox}")
continue
print(f"有效检测结果:{len(valid_objects)} 个")
return valid_objects
except Exception as e:
print(f"检测失败: {str(e)}")
return []2.3、完整代码的流程图
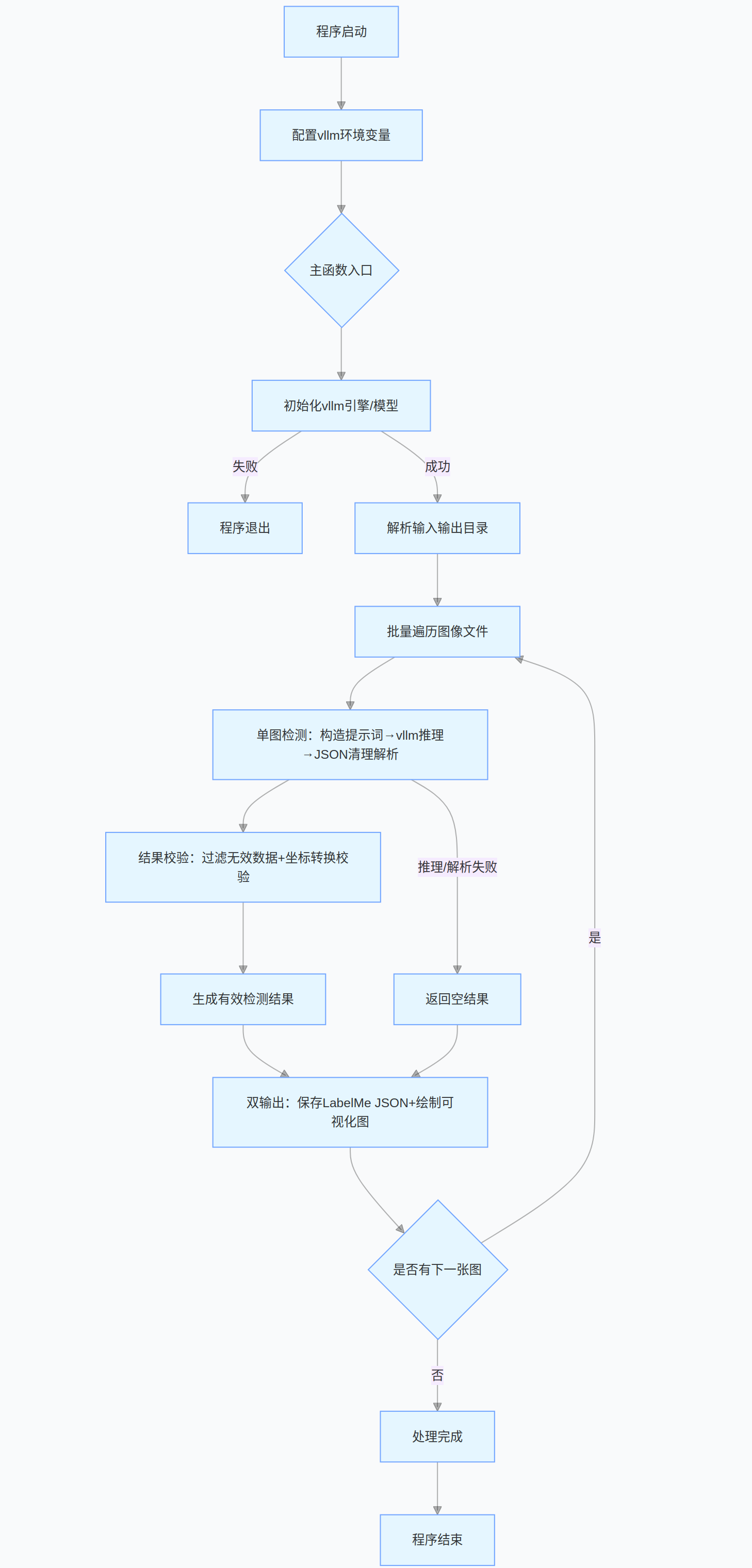
2.4、完整代码
python
# 先设置vllm环境变量
import os
os.environ['VLLM_WORKER_MULTIPROC_METHOD'] = 'spawn'
os.environ['PYTHONWARNINGS'] = 'ignore' # 屏蔽无关警告
# 导入所需基础库
import json
import glob
import re
import torch
import time
from PIL import Image # 图像处理库
import cv2 # OpenCV库,用于图像可视化
# 导入vllm和Qwen3-VL相关依赖
from transformers import AutoProcessor
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
from qwen_vl_utils import process_vision_info
from tqdm import tqdm # 进度条显示库
# --- 基础配置 ---
# 量化后的Qwen3-VL-4B模型路径
QUANTIZED_MODEL_PATH = "/home/user/lgp_dev/model_path/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct"
# 输入图像目录(RGB图像)
input_dir = "./rgb/"
# 输出目录(存储检测结果和可视化图片)
output_dir = "./output_vis_labelme_VLLM"
# 需要检测的目标类别列表
NODE_SPACE = [
'table', # 桌子
'cup', # 杯子
'bottle', # 瓶子
'chair', # 椅子
'robot', # 机器人
'garbage can', # 垃圾桶
'shelf', # 架子
'tissue box', # 纸巾盒
'potted plant', # 盆栽
'television', # 电视
'food', # 食物
'beverage', # 饮料
'daily_necessities', # 日用品
'computer mainframe', # 电脑主机
'coffee machine' # 咖啡机
]
# 全局变量(仅声明,不初始化)
processor = None
llm_engine = None
sampling_config = None
def init_vllm_engine():
"""
初始化vllm引擎(放在函数内,由主函数调用)
"""
global processor, llm_engine, sampling_config
print(f"加载vllm引擎和Qwen3-VL-4B模型:{QUANTIZED_MODEL_PATH}...")
try:
# 加载模型处理器
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(
QUANTIZED_MODEL_PATH,
trust_remote_code=True,
torch_dtype=torch.float16 # 指定半精度,节省显存
)
# 初始化vllm推理引擎(调整多卡配置,降低显存占用)
llm_engine = LLM(
model=QUANTIZED_MODEL_PATH,
tensor_parallel_size=torch.cuda.device_count(), # 自动适配GPU数量
gpu_memory_utilization=0.8, # GPU显存利用率(可根据显存调整)
seed=42, # 固定随机种子,保证结果可复现
trust_remote_code=True,
dtype=torch.bfloat16 # 匹配原模型精度
)
# 配置vllm生成参数
sampling_config = SamplingParams(
temperature=0.0,
max_tokens=1024,
stop_token_ids=[],
top_p=1.0
)
print("vllm引擎和模型加载成功!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"模型加载失败:{str(e)}")
raise e # 抛出异常,让主函数退出
def prepare_vllm_input(messages, processor):
"""
预处理多模态输入,转换成vllm可直接使用的格式
"""
# 1. 处理文本
prompt_text = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
# 2. 处理视觉信息
image_data, video_data, video_kwargs = process_vision_info(
messages,
image_patch_size=processor.image_processor.patch_size,
return_video_kwargs=True,
return_video_metadata=True
)
# 3. 整理多模态数据
multi_modal_data = {}
if image_data is not None:
multi_modal_data['image'] = image_data
if video_data is not None:
multi_modal_data['video'] = video_data
return {
'prompt': prompt_text,
'multi_modal_data': multi_modal_data,
'mm_processor_kwargs': video_kwargs
}
def call_vlm(image_path, prompt):
"""
调用VLM(视觉语言模型)推理(基于vllm)
"""
try:
# 构造对话输入
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": image_path},
{"type": "text", "text": prompt}
]
}
]
# 预处理输入
vllm_inputs = [prepare_vllm_input(messages, processor)]
# 执行推理
outputs = llm_engine.generate(vllm_inputs, sampling_params=sampling_config)
# 解析结果
generated_text = outputs[0].outputs[0].text
return generated_text
except Exception as e:
print(f"VLM调用失败: {str(e)}")
return ""
def fix_truncated_json(cleaned_response):
"""修复被截断的JSON字符串"""
if not cleaned_response:
return ""
open_braces = cleaned_response.count('{')
close_braces = cleaned_response.count('}')
open_brackets = cleaned_response.count('[')
close_brackets = cleaned_response.count(']')
if open_braces > close_braces:
cleaned_response += '}' * (open_braces - close_braces)
if open_brackets > close_brackets:
cleaned_response += ']' * (open_brackets - close_brackets)
cleaned_response = re.sub(r',\s*$', '', cleaned_response)
return cleaned_response
def clean_vlm_response(response):
"""清理VLM模型响应,提取有效JSON"""
if not response:
return ""
cleaned = response.strip().replace('```json', '').replace('```', '').strip()
json_match = re.search(r'\[.*\]', cleaned, re.DOTALL)
if json_match:
cleaned = json_match.group(0)
else:
last_brace = cleaned.rfind('}')
if last_brace != -1:
cleaned = '[' + cleaned[:last_brace+1] + ']'
cleaned = cleaned.replace("'", '"')
cleaned = re.sub(r',\s*]', ']', cleaned)
cleaned = re.sub(r',\s*}', '}', cleaned)
cleaned = fix_truncated_json(cleaned)
return cleaned
def safe_json_loads(json_str):
"""容错式JSON解析"""
try:
return json.loads(json_str)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
try:
obj_matches = re.findall(r'\{[^}]+\}', json_str)
objects = []
for obj_str in obj_matches:
if not obj_str.endswith('}'):
obj_str += '}'
obj = json.loads(obj_str)
objects.append(obj)
return objects
except:
return []
def detect_objects(image_path):
"""核心检测函数"""
prompt = f"""
严格按照以下要求检测图像中{NODE_SPACE}类别的所有物体:
1. 仅输出JSON数组,不添加任何解释、说明、备注文字;
2. 每个数组元素是包含"category"(类别)和"bbox"([x1,y1,x2,y2],整数像素)的JSON对象;
3. 只检测{NODE_SPACE}中的类别,忽略其他所有类别;
4. 确保JSON格式完全合法(属性名用双引号,逗号分隔,括号匹配);
5. 每个对象必须包含完整的"category"和"bbox"字段,缺一不可。
输出示例(仅输出此格式,无其他内容):
[
{{
"category": "cup",
"bbox": [97, 203, 176, 282]
}},
{{
"category": "table",
"bbox": [10, 318, 639, 474]
}}
]
"""
try:
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
w_img, h_img = img.size
print("调用VLM检测物体...")
time_start = time.time()
raw_response = call_vlm(image_path, prompt)
print(f'VLM推理耗时:{time.time() - time_start:.2f}s')
if not raw_response:
print("VLM返回空响应")
return []
cleaned_response = clean_vlm_response(raw_response)
if not cleaned_response:
print("清理后无有效JSON内容")
return []
objects_data = safe_json_loads(cleaned_response)
if not isinstance(objects_data, list):
print(f"响应非列表格式,已转换为列表: {objects_data}")
objects_data = [] if objects_data is None else [objects_data]
valid_objects = []
for i, obj in enumerate(objects_data):
if not isinstance(obj, dict):
print(f"跳过非对象结果 #{i+1}: {obj}")
continue
category = obj.get('category')
bbox = obj.get('bbox', [])
if category not in NODE_SPACE or len(bbox) != 4:
print(f"跳过无效结果 #{i+1}: 类别={category}, bbox={bbox}")
continue
try:
x1_norm, y1_norm, x2_norm, y2_norm = map(float, bbox)
x1 = int(round(x1_norm / 1000 * w_img))
y1 = int(round(y1_norm / 1000 * h_img))
x2 = int(round(x2_norm / 1000 * w_img))
y2 = int(round(y2_norm / 1000 * h_img))
x1 = max(0, min(x1, w_img - 1))
y1 = max(0, min(y1, h_img - 1))
x2 = max(x1 + 1, min(x2, w_img - 1))
y2 = max(y1 + 1, min(y2, h_img - 1))
valid_objects.append({"category": category, "bbox": [x1, y1, x2, y2]})
except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
print(f"坐标格式错误 #{i+1}: {e}, bbox={bbox}")
continue
print(f"有效检测结果:{len(valid_objects)} 个")
return valid_objects
except Exception as e:
print(f"检测失败: {str(e)}")
return []
def convert_to_labelme_format(image_path, detected_objects):
"""转换为LabelMe格式"""
try:
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
image_width, image_height = img.size
labelme_data = {
"version": "5.1.1",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [],
"imagePath": os.path.basename(image_path),
"imageData": None,
"imageHeight": image_height,
"imageWidth": image_width
}
for obj in detected_objects:
category = obj['category']
x1, y1, x2, y2 = obj['bbox']
shape = {
"label": category,
"points": [[x1, y1], [x2, y2]],
"group_id": None,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {}
}
labelme_data["shapes"].append(shape)
return labelme_data
except Exception as e:
print(f"转换为LabelMe格式失败: {str(e)}")
return None
def visualize_detections(image_path, detected_objects, output_path):
"""可视化检测结果"""
try:
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
if image is None:
print(f"无法读取图像: {image_path}")
return
h, w = image.shape[:2]
for obj in detected_objects:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = obj['bbox']
category = obj['category']
cv2.rectangle(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
label = category
(text_w, text_h), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
y_label = y1 - 10 if y1 - 10 > 10 else y1 + text_h + 10
cv2.rectangle(image, (x1, y_label - text_h - 2), (x1 + text_w, y_label + 2), (0, 255, 0), -1)
cv2.putText(image, label, (x1, y_label), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1)
cv2.imwrite(output_path, image)
print(f"可视化结果保存至: {output_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"可视化失败: {str(e)}")
def print_detection_results(detected_objects):
"""打印检测结果"""
if not detected_objects:
print("未检测到任何物体")
return
print("\n--- 原始检测结果 ---")
for i, obj in enumerate(detected_objects):
print(f"物体 #{i+1}: 类别={obj['category']}, bbox={obj['bbox']}")
print("--- 结果结束 ---\n")
def natural_sort_key(filename):
"""自然排序键"""
return [int(t) if t.isdigit() else t.lower() for t in re.split(r'(\d+)', os.path.basename(filename))]
def process_images(input_dir, output_dir):
"""批量处理图像"""
try:
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
detections_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, "detections_labelme")
viz_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, "visualizations")
os.makedirs(detections_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(viz_dir, exist_ok=True)
image_ext = ['*.jpg', '*.jpeg', '*.png', '*.bmp']
image_files = []
for ext in image_ext:
image_files.extend(glob.glob(os.path.join(input_dir, ext)))
image_files = sorted(image_files, key=natural_sort_key)
if not image_files:
print(f"输入目录 {input_dir} 未找到图像")
return
for img_path in tqdm(image_files, desc="Processing Images", unit="image"):
img_name = os.path.basename(img_path)
print(f"\n===== 处理 {img_name} =====")
time1 = time.time()
det_results = detect_objects(img_path)
time2 = time.time()
print("## Time VLM infer:", time2-time1)
print_detection_results(det_results)
json_filename = os.path.splitext(img_name)[0] + ".json"
json_output_path = os.path.join(detections_dir, json_filename)
labelme_json_data = convert_to_labelme_format(img_path, det_results)
if labelme_json_data:
try:
with open(json_output_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(labelme_json_data, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
print(f"LabelMe格式的JSON已保存至: {json_output_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"保存JSON失败: {str(e)}")
viz_path = os.path.join(viz_dir, os.path.splitext(img_name)[0] + "_viz.jpg")
visualize_detections(img_path, det_results, viz_path)
print("\n所有图像处理完成!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"批量处理失败: {str(e)}")
# 程序主入口(关键:所有初始化都放在这里)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 导入命令行参数解析库
import argparse
# 第一步:初始化vllm引擎(必须在主函数内)
try:
init_vllm_engine()
except Exception as e:
print(f"引擎初始化失败,程序退出:{e}")
exit(1)
# 第二步:解析命令行参数
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Qwen3-VL物体检测(vllm加速),并输出LabelMe格式结果')
parser.add_argument('--input_dir', type=str, default=input_dir, help='输入图像目录')
parser.add_argument('--output_dir', type=str, default=output_dir, help='输出目录')
args = parser.parse_args()
# 第三步:执行批量处理
process_images(args.input_dir, args.output_dir)核心是将原 transformers 原生调用的 VLM 模型替换为 vLLM 推理引擎,在保留完整检测功能的同时,大幅提升模型推理速度,尤其适用于多 GPU 批量处理场景。
运行信息:
===== 处理 431023.png =====
调用VLM检测物体...
Adding requests: 100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 87.00it/s]
Processed prompts: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 1/1 [00:01<00:00, 1.45s/it, est. speed input: 457.91 toks/s, output: 145.51 toks/s]
VLM推理耗时:1.48s 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 1/1 [00:01<00:00, 1.45s/it, est. speed input: 457.91 toks/s, output: 145.51 toks/s]
有效检测结果:6 个
Time VLM infer: 1.48121976852417
--- 原始检测结果 ---
物体 #1: 类别=table, bbox=[452, 117, 639, 310]
物体 #2: 类别=chair, bbox=[339, 97, 456, 278]
物体 #3: 类别=robot, bbox=[516, 0, 639, 267]
物体 #4: 类别=shelf, bbox=[146, 0, 456, 133]
物体 #5: 类别=tissue box, bbox=[325, 9, 353, 47]
物体 #6: 类别=computer mainframe, bbox=[64, 0, 163, 169]
--- 结果结束 ---
LabelMe格式的JSON已保存至: ./output_vis_labelme_VLLM/detections_labelme/431023.json
可视化结果保存至: ./output_vis_labelme_VLLM/visualizations/431023_viz.jpg
Processing Images: 66%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▍ | 176/268 [06:27<02:05, 1.36s/image]
3、LabelMe格式转为COCO数据格式
适配多类别标注的 LabelMe → COCO 格式转换,专为上游视觉检测任务输出的 多种类物体标注(桌子、杯子、机器人等)设计,可批量将 LabelMe 标注文件转换为标准 COCO 格式。
- 灵活的多类别适配能力: 基于
NODE_SPACE列表实现动态类别管理,自动为 15 个指定类别分配唯一 ID(0 开始递增),无需手动维护类别与 ID 的映射关系;新增 / 删除类别仅需修改列表,适配性极强,完全匹配上游检测环节的类别体系。 - 严格的数据类型校验与转换:针对 COCO 格式 JSON 序列化易出错的问题,强制将所有数值(宽高、坐标、面积、边界框参数等)从 numpy 类型转换为 Python 原生 int/float 类型,同时将多边形坐标数组转为标准列表格式,彻底避免序列化失败。

完整代码的流程图:
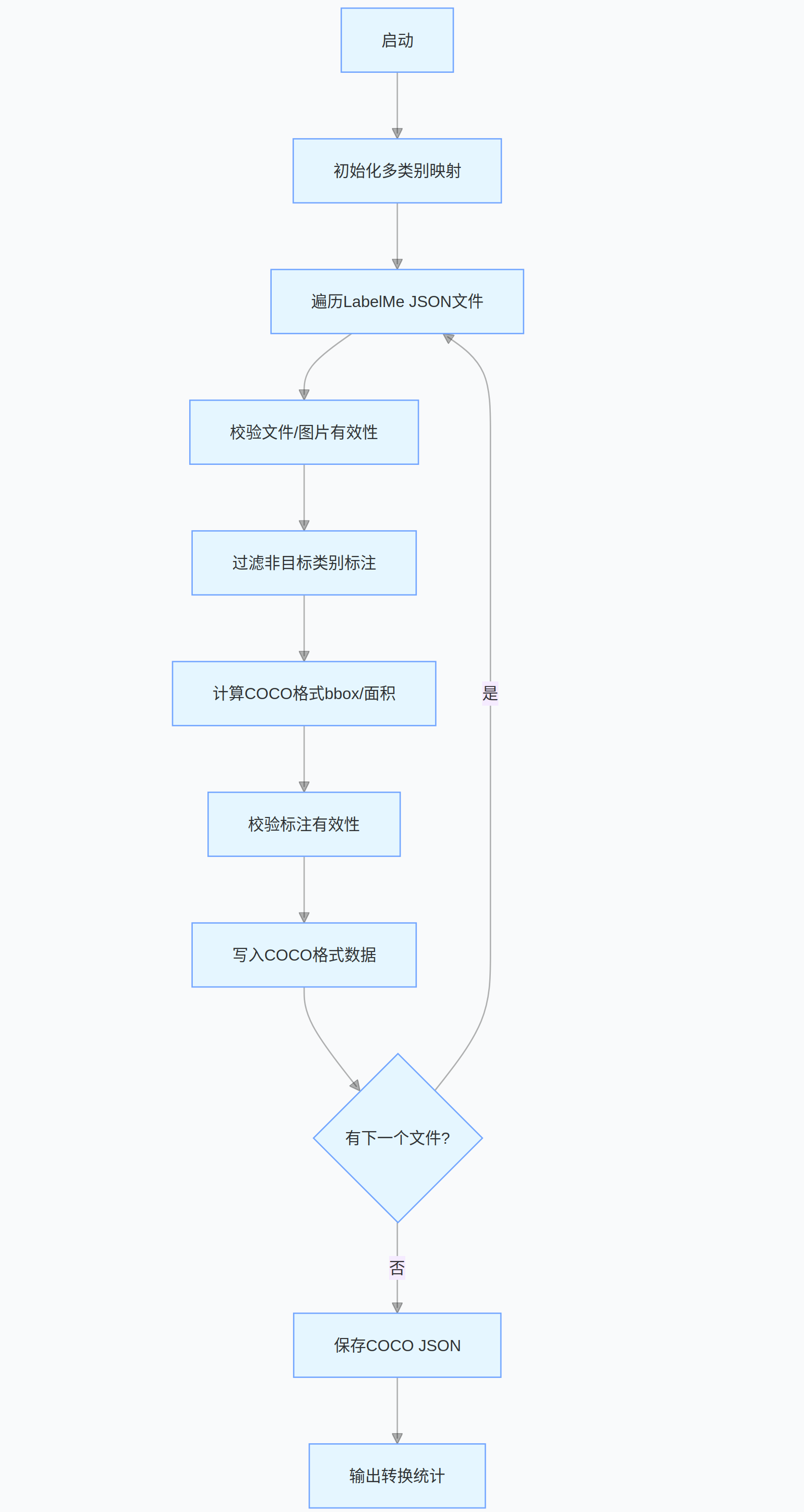
源代码:
python
import os
import json
import cv2
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
# 需要检测的目标类别列表(与检测环节保持一致)
NODE_SPACE = [
'table', # 桌子
'cup', # 杯子
'bottle', # 瓶子
'chair', # 椅子
'robot', # 机器人
'garbage can', # 垃圾桶
'shelf', # 架子
'tissue box', # 纸巾盒
'potted plant', # 盆栽
'television', # 电视
'food', # 食物
'beverage', # 饮料
'daily_necessities', # 日用品
'computer mainframe', # 电脑主机
'coffee machine' # 咖啡机
]
# 生成类别ID映射(类别名: ID),ID从0开始递增
CATEGORY_MAPPING = {name: idx for idx, name in enumerate(NODE_SPACE)}
def labelme_to_coco(image_dir, json_dir, output_json):
"""
将LabelMe标注转换为COCO格式(支持多类别,修复类型错误和空文件问题)
:param image_dir: 图片文件夹路径
:param json_dir: LabelMe JSON标注文件夹路径
:param output_json: 输出的COCO格式JSON文件路径
"""
# COCO格式结构初始化(动态生成多类别)
coco = {
"images": [],
"annotations": [],
"categories": [{"id": idx, "name": name} for name, idx in CATEGORY_MAPPING.items()]
}
img_id = 0
ann_id = 0
# 遍历所有JSON标注文件
for json_filename in os.listdir(json_dir):
if not json_filename.endswith(".json"):
continue
json_path = os.path.join(json_dir, json_filename)
# 处理空JSON文件或读取失败的情况
try:
with open(json_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
# 尝试解析JSON,空文件会抛出异常
labelme_data = json.load(f)
except (json.JSONDecodeError, UnicodeDecodeError):
print(f"警告:{json_filename} 为空或格式错误,跳过")
continue
# 检查必要字段是否存在
if "shapes" not in labelme_data or "imagePath" not in labelme_data:
print(f"警告:{json_filename} 缺少关键字段,跳过")
continue
# 获取图片路径和基本信息
img_filename = labelme_data["imagePath"]
img_path = os.path.join(image_dir, img_filename)
# 检查图片是否存在
if not os.path.exists(img_path):
print(f"警告:图片 {img_path} 不存在,跳过该标注")
continue
# 获取图片宽高(优先从JSON读取,失败则从图片读取)
try:
img_width = labelme_data["imageWidth"]
img_height = labelme_data["imageHeight"]
except KeyError:
try:
with Image.open(img_path) as img:
img_width, img_height = img.size
except Exception as e:
print(f"警告:无法获取 {img_filename} 的尺寸,跳过(错误:{e})")
continue
# 添加图片信息到COCO(确保为Python原生类型)
coco["images"].append({
"id": img_id,
"file_name": img_filename,
"width": int(img_width), # 强制转换为int
"height": int(img_height)
})
# 处理每个标注形状(shapes)
for shape in labelme_data["shapes"]:
# 过滤不在NODE_SPACE中的类别
label = shape["label"]
if label not in CATEGORY_MAPPING:
print(f"警告:{json_filename} 中包含未定义类别 {label},跳过该标注")
continue
# 提取多边形坐标(确保为numpy数组)
try:
points = np.array(shape["points"], dtype=np.float32)
if points.size == 0:
raise ValueError("空坐标")
except Exception as e:
print(f"警告:{json_filename} 中 {label} 坐标格式错误,跳过(错误:{e})")
continue
# 计算边界框(x,y,w,h),转换为Python原生float
x_min = float(np.min(points[:, 0]))
y_min = float(np.min(points[:, 1]))
x_max = float(np.max(points[:, 0]))
y_max = float(np.max(points[:, 1]))
bbox_width = float(x_max - x_min)
bbox_height = float(y_max - y_min)
# 过滤无效边界框
if bbox_width <= 0 or bbox_height <= 0:
print(f"警告:{json_filename} 中 {label} 存在无效边界框,跳过")
continue
# 计算面积
area = float(bbox_width * bbox_height)
# 添加标注信息到COCO(所有数值转换为Python原生类型)
coco["annotations"].append({
"id": ann_id,
"image_id": img_id,
"category_id": CATEGORY_MAPPING[label], # 动态获取类别ID
"bbox": [x_min, y_min, bbox_width, bbox_height],
"area": area,
"iscrowd": 0,
# 将numpy数组转换为Python列表(确保元素为float)
"segmentation": [list(map(float, points.flatten().tolist()))]
})
ann_id += 1
img_id += 1
print(f"处理完成:{json_filename}(图片ID: {img_id-1})")
# 保存COCO格式JSON
with open(output_json, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(coco, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
print(f"\n转换完成!")
print(f"- 共处理 {img_id} 张图片")
print(f"- 共生成 {ann_id} 个标注")
print(f"- 支持的类别数量:{len(CATEGORY_MAPPING)}")
print(f"- 结果保存至:{output_json}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 配置路径(根据实际情况修改)
IMAGE_DIR = "rebelme_data/rgb" # LabelMe图片所在文件夹
JSON_DIR = "rebelme_data/json" # LabelMe JSON标注所在文件夹
OUTPUT_JSON = "coco_annotations_multi_class.json" # 输出的COCO格式标注文件
# 执行转换
labelme_to_coco(IMAGE_DIR, JSON_DIR, OUTPUT_JSON)- 程序首先基于预设的
NODE_SPACE类别列表动态生成类别 - ID 映射,遍历指定目录下的 LabelMe JSON 标注文件后,先校验文件完整性、图片有效性及关键字段; - 再过滤非目标类别标注,提取有效标注的坐标信息,计算 COCO 格式所需的边界框、面积等参数,并严格转换数据类型以适配 JSON 序列化;
- 最后过滤无效标注,按 COCO 规范整理图片和标注信息并保存为 JSON 文件。
分享完成~