文章目录
- [1. 前言](#1. 前言)
- [2. ARM64 虚拟地址空间布局图](#2. ARM64 虚拟地址空间布局图)
1. 前言
限于作者能力水平,本文可能存在谬误,因此而给读者带来的损失,作者不做任何承诺。
2. ARM64 虚拟地址空间布局图
ARM64 不支持全部 64-bit VA 寻址,目前支持最大 52-bit VA 寻址,可寻址 4096TB 虚拟地址空间。更常见的配置是 48-bit VA,可寻址 512TB 虚拟地址空间。本文展示 48-bit VA 寻址下的 ARM64 虚拟地址空间的典型布局:
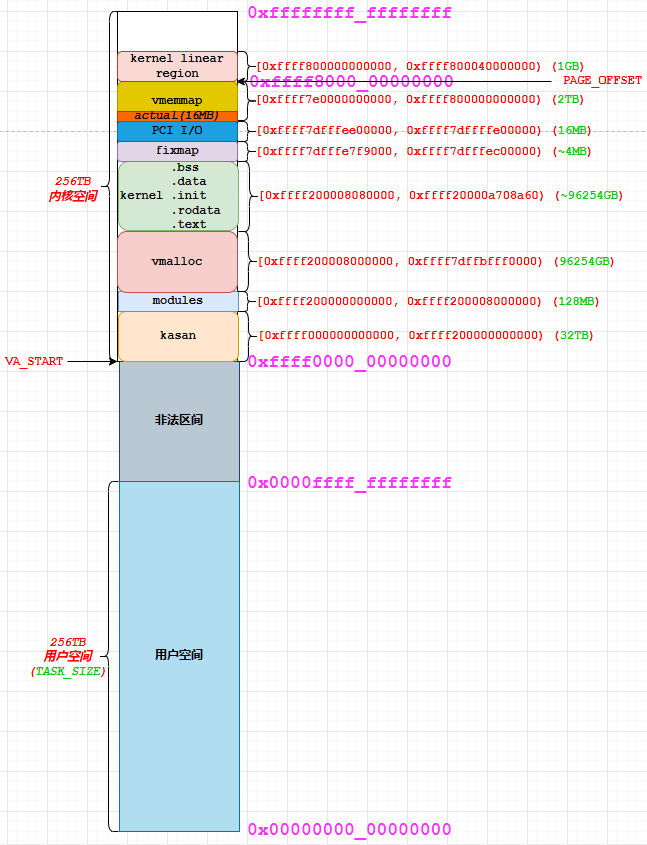
[0x0000000000000000, 0x0000ffffffffffff]:用户空间,总大小为256TB[0xffff000000000000, 0xffffffffffffffff]:内核空间,总大小256TB[0xffff000000000000, 0xffff200000000000):ksan shadow region,总大小32TB[0xffff200000000000, 0xffff200008000000):modules,总大小128MB[0xffff200008000000, 0xffff7dffbfff0000):vmalloc,总大小96254GB0xffff200008080000, 0xffff20000a708a60: 内核镜像区间,包含.text, .rodata, .init, .data, .bss子区间,最大可支持约96254GB[0xffff7dfffe7f9000, 0xffff7dfffec00000):fixmap区间,总大小约4MB[0xffff7dfffee00000, 0xffff7dffffe00000):PCI I/O区间,总大小16MB[0xffff7e0000000000, 0xffff800000000000):vmemmap区间,最大支持2TB,实际使用大小和系统配置的物理内存有关[0xffff800000000000, 0xffff800040000000):内核线性映射区间,1GB
上述布局取自 Linux 4.14.113 内核,不同的内核版本、不同的硬件架构下,该布局会有所不同。Linux 内核日志打印这些区间的具体分布:
bash
[ 0.000000] Virtual kernel memory layout:
[ 0.000000] kasan : 0xffff000000000000 - 0xffff200000000000 ( 32768 GB)
[ 0.000000] modules : 0xffff200000000000 - 0xffff200008000000 ( 128 MB)
[ 0.000000] vmalloc : 0xffff200008000000 - 0xffff7dffbfff0000 ( 96254 GB)
[ 0.000000] .text : 0xffff200008080000 - 0xffff200008ea0000 ( 14464 KB)
[ 0.000000] .rodata : 0xffff200008ea0000 - 0xffff200009650000 ( 7872 KB)
[ 0.000000] .init : 0xffff200009650000 - 0xffff2000097e0000 ( 1600 KB)
[ 0.000000] .data : 0xffff2000097e0000 - 0xffff200009e6da00 ( 6711 KB)
[ 0.000000] .bss : 0xffff200009e6da00 - 0xffff20000a708a60 ( 8813 KB)
[ 0.000000] fixed : 0xffff7dfffe7f9000 - 0xffff7dfffec00000 ( 4124 KB)
[ 0.000000] PCI I/O : 0xffff7dfffee00000 - 0xffff7dffffe00000 ( 16 MB)
[ 0.000000] vmemmap : 0xffff7e0000000000 - 0xffff800000000000 ( 2048 GB maximum)
[ 0.000000] 0xffff7e0000000000 - 0xffff7e0001000000 ( 16 MB actual)
[ 0.000000] memory : 0xffff800000000000 - 0xffff800040000000 ( 1024 MB)ARM64 Linux 虚拟地址空间主要来自于一下架构相关头文件
c
arch/arm64/include/asm/memory.h
arch/arm64/include/asm/processor.h
arch/arm64/include/asm/fixmap.h的静态定义,以及内存初始化期间一些动态设置。这里简单的看下头文件的静态定义:
c
// arch/arm64/include/asm/memory.h
#define UL(x) _AC(x, UL)
#define PCI_IO_SIZE SZ_16M
#define STRUCT_PAGE_MAX_SHIFT 6
#define VMEMMAP_SIZE (UL(1) << (VA_BITS - PAGE_SHIFT - 1 + STRUCT_PAGE_MAX_SHIFT))
/*
* PAGE_OFFSET - the virtual address of the start of the linear map (top
* (VA_BITS - 1))
* KIMAGE_VADDR - the virtual address of the start of the kernel image
* VA_BITS - the maximum number of bits for virtual addresses.
* VA_START - the first kernel virtual address.
*/
#define VA_BITS (CONFIG_ARM64_VA_BITS)
#define VA_START (UL(0xffffffffffffffff) - \
(UL(1) << VA_BITS) + 1)
#define PAGE_OFFSET (UL(0xffffffffffffffff) - \
(UL(1) << (VA_BITS - 1)) + 1)
#define KIMAGE_VADDR (MODULES_END)
#define MODULES_END (MODULES_VADDR + MODULES_VSIZE)
#define MODULES_VADDR (VA_START + KASAN_SHADOW_SIZE)
#define MODULES_VSIZE (SZ_128M)
#define VMEMMAP_START (PAGE_OFFSET - VMEMMAP_SIZE)
#define PCI_IO_END (VMEMMAP_START - SZ_2M)
#define PCI_IO_START (PCI_IO_END - PCI_IO_SIZE)
#define FIXADDR_TOP (PCI_IO_START - SZ_2M)
#define KERNEL_START _text
#define KERNEL_END _end
/*
* KASAN requires 1/8th of the kernel virtual address space for the shadow
* region. KASAN can bloat the stack significantly, so double the (minimum)
* stack size when KASAN is in use.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_KASAN
#define KASAN_SHADOW_SIZE (UL(1) << (VA_BITS - 3))
#define KASAN_THREAD_SHIFT 1
#else
#define KASAN_SHADOW_SIZE (0)
#define KASAN_THREAD_SHIFT 0
#endif
c
// arch/arm64/include/asm/processor.h
/*
* TASK_SIZE - the maximum size of a user space task.
* TASK_UNMAPPED_BASE - the lower boundary of the mmap VM area.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
#define TASK_SIZE_32 UL(0x100000000)
#define TASK_SIZE (test_thread_flag(TIF_32BIT) ? \
TASK_SIZE_32 : TASK_SIZE_64)
#define TASK_SIZE_OF(tsk) (test_tsk_thread_flag(tsk, TIF_32BIT) ? \
TASK_SIZE_32 : TASK_SIZE_64)
#else
#define TASK_SIZE TASK_SIZE_64
#endif /* CONFIG_COMPAT */
#define TASK_UNMAPPED_BASE (PAGE_ALIGN(TASK_SIZE / 4))
#define STACK_TOP_MAX TASK_SIZE_64
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
#define AARCH32_VECTORS_BASE 0xffff0000
#define STACK_TOP (test_thread_flag(TIF_32BIT) ? \
AARCH32_VECTORS_BASE : STACK_TOP_MAX)
#else
#define STACK_TOP STACK_TOP_MAX
#endif /* CONFIG_COMPAT */
c
// arch/arm64/include/asm/fixmap.h
/*
* Here we define all the compile-time 'special' virtual
* addresses. The point is to have a constant address at
* compile time, but to set the physical address only
* in the boot process.
*
* These 'compile-time allocated' memory buffers are
* page-sized. Use set_fixmap(idx,phys) to associate
* physical memory with fixmap indices.
*
*/
enum fixed_addresses {
FIX_HOLE,
/*
* Reserve a virtual window for the FDT that is 2 MB larger than the
* maximum supported size, and put it at the top of the fixmap region.
* The additional space ensures that any FDT that does not exceed
* MAX_FDT_SIZE can be mapped regardless of whether it crosses any
* 2 MB alignment boundaries.
*
* Keep this at the top so it remains 2 MB aligned.
*/
#define FIX_FDT_SIZE (MAX_FDT_SIZE + SZ_2M)
FIX_FDT_END,
FIX_FDT = FIX_FDT_END + FIX_FDT_SIZE / PAGE_SIZE - 1,
FIX_EARLYCON_MEM_BASE,
FIX_TEXT_POKE0,
#ifdef CONFIG_ACPI_APEI_GHES
/* Used for GHES mapping from assorted contexts */
FIX_APEI_GHES_IRQ,
FIX_APEI_GHES_NMI,
#endif /* CONFIG_ACPI_APEI_GHES */
#ifdef CONFIG_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0
FIX_ENTRY_TRAMP_DATA,
FIX_ENTRY_TRAMP_TEXT,
#define TRAMP_VALIAS (__fix_to_virt(FIX_ENTRY_TRAMP_TEXT))
#endif /* CONFIG_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0 */
__end_of_permanent_fixed_addresses,
/*
* Temporary boot-time mappings, used by early_ioremap(),
* before ioremap() is functional.
*/
#define NR_FIX_BTMAPS (SZ_256K / PAGE_SIZE)
#define FIX_BTMAPS_SLOTS 7
#define TOTAL_FIX_BTMAPS (NR_FIX_BTMAPS * FIX_BTMAPS_SLOTS)
FIX_BTMAP_END = __end_of_permanent_fixed_addresses,
FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN = FIX_BTMAP_END + TOTAL_FIX_BTMAPS - 1,
/*
* Used for kernel page table creation, so unmapped memory may be used
* for tables.
*/
FIX_PTE,
FIX_PMD,
FIX_PUD,
FIX_PGD,
__end_of_fixed_addresses
};
#define FIXADDR_SIZE (__end_of_permanent_fixed_addresses << PAGE_SHIFT)
#define FIXADDR_START (FIXADDR_TOP - FIXADDR_SIZE)对于内存初始化期间一些动态设置,本文不做涉及,有机会再和大家探讨。