一、MyBatis 缓存核心原理深度解析
1.1 缓存架构全景图
java
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Spring Boot 应用 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Service 层 (Spring Cache) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Mapper 层 (MyBatis 二级缓存) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ SqlSession 层 (MyBatis 一级缓存) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 数据库连接池 (HikariCP) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────┘1.2 缓存查询完整流程
java
// 企业级缓存查询流程图
public Object executeQuery(Object param) {
// 1. 检查Spring Cache(如果有)
// 2. 检查MyBatis二级缓存(开启且命中)
// 3. 检查MyBatis一级缓存(当前SqlSession内)
// 4. 执行SQL查询数据库
// 5. 填充一级缓存
// 6. 事务提交时刷入二级缓存
// 7. 更新Spring Cache(如果有)
}二、Spring 整合下的"一级缓存陷阱"深度剖析
2.1 Spring 事务管理对一级缓存的影响
2.1.1 核心机制
java
// Spring事务管理下的SqlSession生命周期
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheTransactionAnalysis {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
/**
* 场景1:Spring事务中的一级缓存行为
*/
@Test
void testCacheWithTransaction() {
// 开启事务(默认REQUIRED)
userService.getUserInTransaction(1L);
// 事务提交,SqlSession关闭,一级缓存失效
}
/**
* 场景2:非事务环境下的缓存行为
*/
@Test
void testCacheWithoutTransaction() {
// 每次Mapper调用都创建新SqlSession
User user1 = userService.getUser(1L); // SqlSession1
User user2 = userService.getUser(1L); // SqlSession2
// 无法命中一级缓存!
}
}
@Service
@Slf4j
class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 事务方法 - 一级缓存有效
*/
@Transactional
public User getUserInTransaction(Long id) {
log.info("事务开始,创建SqlSession");
// 第一次查询,访问数据库
User user1 = userMapper.selectById(id);
log.info("第一次查询完成,一级缓存: {}",
System.identityHashCode(user1));
// 第二次查询,命中一级缓存(同一个SqlSession)
User user2 = userMapper.selectById(id);
log.info("第二次查询完成,一级缓存命中: {}",
System.identityHashCode(user2));
// 验证缓存命中(同一个对象)
log.info("是否为同一对象: {}", user1 == user2); // true
return user2;
}
/**
* 非事务方法 - 一级缓存失效
*/
public User getUser(Long id) {
// 每次调用都会创建新的SqlSession
return userMapper.selectById(id);
}
}2.1.2 生产环境配置优化
java
# application.yml - 一级缓存优化配置
mybatis:
configuration:
# 关键配置:控制一级缓存作用域
local-cache-scope: SESSION # 生产环境推荐SESSION
# Spring整合下的特殊配置
default-executor-type: REUSE # 重用Statement,提升性能
# 连接超时设置
default-statement-timeout: 30000
# 自动映射行为
auto-mapping-behavior: FULL2.1.3 一级缓存失效场景检测
java
@Component
@Slf4j
public class FirstLevelCacheMonitor {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
/**
* 检测一级缓存命中率
*/
public void monitorCacheHitRate() {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
Configuration config = sqlSession.getConfiguration();
// 模拟多次查询
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sqlSession.selectOne("com.example.UserMapper.selectById", 1L);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查询耗时: {}ms", end - start);
// 一级缓存特性:后续查询几乎0耗时
}
}
/**
* 检测Spring事务对缓存的影响
*/
public void testSpringTransactionCache() {
// 模拟不同传播行为
// REQUIRED(默认):加入现有事务或创建新事务
// REQUIRES_NEW:总是创建新事务,新SqlSession
// NESTED:嵌套事务,特殊的一级缓存行为
// 重点:不同传播级别会影响SqlSession的生命周期
}
}2.2 一级缓存最佳实践
java
// 一级缓存使用规范
@Service
@Slf4j
class CacheBestPracticeService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private OrderMapper orderMapper;
/**
* 场景1:事务内批量查询 - 充分利用一级缓存
*/
@Transactional
public void batchProcess(Long userId) {
// 同一个事务,同一个SqlSession
User user = userMapper.selectById(userId); // 首次查询
// 后续多次查询同一数据(命中缓存)
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User cachedUser = userMapper.selectById(userId); // 命中一级缓存
processUser(cachedUser);
}
}
/**
* 场景2:避免跨事务缓存依赖
*/
public void crossTransactionIssue() {
// ❌ 错误示例:依赖跨事务缓存
User user1 = getUserInNewTransaction(1L); // 事务1
User user2 = getUserInNewTransaction(1L); // 事务2,重新查询
// ✅ 正确做法:事务外部缓存
User user = getFromExternalCache(1L); // 使用Redis等外部缓存
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public User getUserInNewTransaction(Long id) {
return userMapper.selectById(id);
}
}三、二级缓存"提交才生效"机制深度解析
3.1 二级缓存写入时机详解
java
/**
* 二级缓存生命周期演示
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class SecondLevelCacheLifecycle {
@Autowired
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
/**
* 演示二级缓存写入时机
*/
public void demonstrateCacheWriteTiming() {
log.info("=== 二级缓存写入时机演示 ===");
// 场景1:没有提交,二级缓存不写入
SqlSession session1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
UserMapper mapper1 = session1.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
log.info("第一次查询(Session1)");
User user1 = mapper1.selectById(1L); // 查询数据库
// ❌ 重要:此时二级缓存还没有数据!
log.info("查询完成,但未提交,二级缓存为空");
// session1.close(); // 关闭也会触发写入
} finally {
session1.rollback(); // 回滚,二级缓存不写入
}
// 场景2:提交后,二级缓存才有数据
SqlSession session2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
UserMapper mapper2 = session2.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
log.info("第二次查询(Session2,新会话)");
User user2 = mapper2.selectById(1L); // 仍然查数据库
log.info("说明:没有提交,二级缓存未生效");
// 提交事务,写入二级缓存
session2.commit();
log.info("提交成功,数据已写入二级缓存");
} finally {
session2.close();
}
// 场景3:新会话命中二级缓存
SqlSession session3 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
UserMapper mapper3 = session3.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
log.info("第三次查询(Session3)");
User user3 = mapper3.selectById(1L); // 命中二级缓存
log.info("二级缓存命中成功!");
} finally {
session3.close();
}
}
}3.2 二级缓存配置的黄金法则
java
<!-- mybatis-config.xml 二级缓存企业级配置 -->
<configuration>
<!-- 全局缓存设置 -->
<settings>
<!-- 开启缓存(默认true) -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<!-- 本地缓存作用域 -->
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/>
</settings>
<!-- 缓存配置模板 -->
<cache-template id="defaultCache">
<!-- 回收策略:LRU最近最少使用 -->
<property name="eviction" value="LRU"/>
<!-- 刷新间隔:5分钟 -->
<property name="flushInterval" value="300000"/>
<!-- 缓存大小:1000个对象 -->
<property name="size" value="1000"/>
<!-- 只读缓存(性能最好) -->
<property name="readOnly" value="true"/>
<!-- 序列化策略:Kryo(可选) -->
<!-- <property name="serializer" value="org.mybatis.caches.kryo.KryoCacheSerializer"/> -->
</cache-template>
</configuration>
<!-- UserMapper.xml - 企业级配置示例 -->
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.UserMapper">
<!-- 继承默认模板,可覆盖属性 -->
<cache-ref namespace="defaultCache"/>
<!-- 或者自定义配置 -->
<cache
eviction="LRU"
flushInterval="300000"
size="1000"
readOnly="true"
blocking="false" <!-- 防止缓存击穿 -->
type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache">
<!-- Ehcache 特有配置 -->
<property name="memoryStoreEvictionPolicy" value="LRU"/>
<property name="maxEntriesLocalHeap" value="1000"/>
<property name="timeToLiveSeconds" value="300"/>
<property name="timeToIdleSeconds" value="180"/>
</cache>
<!-- 查询语句配置 -->
<select id="selectById" resultType="User" useCache="true">
SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
<!-- 企业级规范:所有DML操作必须清空缓存 -->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="User" flushCache="true">
UPDATE user
SET name = #{name},
updated_at = NOW()
WHERE id = #{id}
</update>
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="User" flushCache="true">
INSERT INTO user (name, email)
VALUES (#{name}, #{email})
</insert>
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="Long" flushCache="true">
DELETE FROM user WHERE id = #{id}
</delete>
</mapper>3.3 生产环境二级缓存监控
java
/**
* 二级缓存监控与统计
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class SecondLevelCacheMonitor {
@Autowired
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
/**
* 获取缓存统计信息
*/
public CacheStats getCacheStats(String namespace) {
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
Cache cache = configuration.getCache(namespace);
if (cache == null) {
return null;
}
CacheStats stats = new CacheStats();
stats.setNamespace(namespace);
stats.setCacheSize(cache.getSize());
stats.setCacheType(cache.getClass().getSimpleName());
// 如果是Ehcache,获取更多信息
if (cache instanceof EhcacheCache) {
EhcacheCache ehcache = (EhcacheCache) cache;
net.sf.ehcache.Ehcache underlyingCache = ehcache.getEhcache();
stats.setMemoryStoreSize(underlyingCache.getMemoryStoreSize());
stats.setDiskStoreSize(underlyingCache.getDiskStoreSize());
stats.setHitCount(underlyingCache.getStatistics().cacheHitCount());
stats.setMissCount(underlyingCache.getStatistics().cacheMissCount());
stats.setHitRatio(underlyingCache.getStatistics().cacheHitRatio());
}
return stats;
}
/**
* 清理指定命名空间缓存
*/
public void clearCache(String namespace) {
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
Cache cache = configuration.getCache(namespace);
if (cache != null) {
cache.clear();
log.info("已清理缓存: {}", namespace);
}
}
/**
* 批量清理缓存
*/
public void batchClearCache(Set<String> namespaces) {
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
Collection<Cache> caches = configuration.getCaches();
for (Cache cache : caches) {
String cacheId = cache.getId();
if (namespaces.contains(cacheId)) {
cache.clear();
log.info("已清理缓存: {}", cacheId);
}
}
}
@Data
public static class CacheStats {
private String namespace;
private int cacheSize;
private String cacheType;
private long memoryStoreSize;
private long diskStoreSize;
private long hitCount;
private long missCount;
private double hitRatio;
}
}四、二级缓存 Key 结构深度解析与优化
4.1 CacheKey 组成原理
java
/**
* MyBatis CacheKey 结构分析
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheKeyAnalyzer {
@Autowired
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
/**
* 分析缓存Key的组成
*/
public void analyzeCacheKey(String statementId, Object parameter) {
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
// 模拟创建CacheKey的过程
CacheKey cacheKey = ms.getCacheKey(
parameter,
RowBounds.DEFAULT,
ms.getBoundSql(parameter)
);
log.info("=== CacheKey 结构分析 ===");
log.info("MappedStatement ID: {}", ms.getId());
log.info("SQL: {}", ms.getBoundSql(parameter).getSql());
log.info("参数: {}", parameter);
log.info("RowBounds: {}", RowBounds.DEFAULT);
log.info("Environment ID: {}", configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
// 获取hashcode(MyBatis用于比较的hash)
log.info("CacheKey HashCode: {}", cacheKey.hashCode());
log.info("CacheKey UpdateCount: {}", cacheKey.getUpdateCount());
// 重要结论:以下情况会产生不同的CacheKey
// 1. SQL语句不同(即使一个空格差异)
// 2. 参数值不同
// 3. 分页参数不同
// 4. 不同的Mapper方法
}
/**
* 演示动态SQL对缓存的影响
*/
public void demonstrateDynamicSqlCacheIssue() {
// 场景:动态SQL会产生大量不同的CacheKey
// SELECT * FROM users WHERE 1=1
// AND name = ? --> CacheKey1
// AND age > ? --> CacheKey2
// AND name=? AND age>? --> CacheKey3
// 解决方案:使用固定SQL或控制参数组合
}
}4.2 缓存碎片化问题解决方案
java
<!-- 优化前:动态SQL导致缓存碎片 -->
<select id="searchUsers" parameterType="UserQuery" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM users WHERE 1=1
<if test="name != null">
AND name LIKE CONCAT('%', #{name}, '%')
</if>
<if test="age != null">
AND age > #{age}
</if>
<if test="email != null">
AND email = #{email}
</if>
<!-- 问题:参数组合爆炸,缓存命中率极低 -->
</select>
<!-- 优化方案1:固定SQL,应用层过滤 -->
<select id="searchAllUsers" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM users
WHERE created_at > DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 30 DAY)
<!-- 限制数据量,缓存全部数据 -->
</select>
<!-- 优化方案2:关键查询单独缓存 -->
<select id="searchUsersByName" parameterType="String" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM users
WHERE name LIKE CONCAT('%', #{name}, '%')
<!-- 单独缓存,命中率高 -->
</select>
<!-- 优化方案3:参数标准化 -->
<select id="searchUsersByStandardQuery" parameterType="StandardQuery" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM users
WHERE
<choose>
<when test="queryType == 'RECENT'">
created_at > DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 7 DAY)
</when>
<when test="queryType == 'ACTIVE'">
last_login > DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 30 DAY)
</when>
<otherwise>
1=1
</otherwise>
</choose>
<!-- 标准化查询类型,减少参数组合 -->
</select>
/**
* 缓存Key优化策略
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class CacheKeyOptimizationService {
/**
* 方法1:参数标准化
*/
public List<User> searchUsers(UserQuery query) {
// 标准化参数
StandardizedQuery stdQuery = standardizeQuery(query);
// 使用标准化参数查询
return userMapper.searchWithStandardQuery(stdQuery);
}
private StandardizedQuery standardizeQuery(UserQuery query) {
StandardizedQuery stdQuery = new StandardizedQuery();
// 标准化名称查询(忽略大小写,trim)
if (query.getName() != null) {
stdQuery.setName(query.getName().trim().toLowerCase());
}
// 标准化年龄查询(按年龄段)
if (query.getAge() != null) {
stdQuery.setAgeGroup(calculateAgeGroup(query.getAge()));
}
// 标准化分页(固定分页大小)
stdQuery.setPageSize(20);
stdQuery.setPageNum(query.getPageNum() != null ? query.getPageNum() : 1);
return stdQuery;
}
/**
* 方法2:查询结果二次过滤
*/
public List<User> searchWithPostFilter(UserQuery query) {
// 1. 获取基础数据集(缓存友好)
List<User> allUsers = userMapper.getRecentUsers(1000);
// 2. 应用层过滤
return allUsers.stream()
.filter(user -> matchesQuery(user, query))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}五、二级缓存不适用场景全解析
5.1 禁止使用二级缓存的场景清单
java
/**
* 二级缓存禁用场景检测器
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheSuitabilityChecker {
/**
* 检查是否适合使用二级缓存
*/
public CacheSuitability checkSuitability(String mapperName, CacheConfig config) {
CacheSuitability result = new CacheSuitability();
result.setMapperName(mapperName);
// 规则1:高并发写场景
if (config.getWriteQps() > 100) { // QPS > 100
result.setSuitable(false);
result.addReason("高并发写场景,缓存失效频繁");
}
// 规则2:强一致性要求
if (config.isStrongConsistency()) {
result.setSuitable(false);
result.addReason("强一致性要求,缓存可能导致脏读");
}
// 规则3:数据频繁变更
if (config.getUpdateFrequency() == UpdateFrequency.SECONDS) {
result.setSuitable(false);
result.addReason("数据秒级变更,缓存价值低");
}
// 规则4:大结果集查询
if (config.getAvgResultSize() > 1000) {
result.setSuitable(false);
result.addReason("结果集过大,内存压力大");
}
// 规则5:动态SQL复杂
if (config.isDynamicSql()) {
result.setSuitable(false);
result.addReason("动态SQL导致缓存碎片化");
}
// 规则6:分页查询多变
if (config.isPaginationVolatile()) {
result.setSuitable(false);
result.addReason("分页参数多变,缓存命中率低");
}
return result;
}
/**
* 适合使用缓存的场景
*/
public List<String> getSuitableScenarios() {
return Arrays.asList(
"1. 配置表/字典表(极少变更)",
"2. 地区信息表(只读)",
"3. 商品分类表(低频变更)",
"4. 用户角色权限(低频变更)",
"5. 历史数据查询(只读)",
"6. 统计结果缓存(定时更新)"
);
}
@Data
public static class CacheSuitability {
private String mapperName;
private boolean suitable;
private List<String> reasons = new ArrayList<>();
public void addReason(String reason) {
reasons.add(reason);
}
}
public enum UpdateFrequency {
SECONDS, MINUTES, HOURS, DAYS, MONTHS
}
@Data
public static class CacheConfig {
private int writeQps; // 写入QPS
private boolean strongConsistency; // 强一致性要求
private UpdateFrequency updateFrequency; // 更新频率
private int avgResultSize; // 平均结果集大小
private boolean dynamicSql; // 是否动态SQL
private boolean paginationVolatile; // 分页是否多变
}
}5.2 生产环境缓存决策矩阵
java
/**
* 企业级缓存决策框架
*/
@Service
public class CacheDecisionFramework {
private static final Map<CacheScenario, CacheStrategy> DECISION_MATRIX = new HashMap<>();
static {
// 初始化决策矩阵
DECISION_MATRIX.put(CacheScenario.CONFIG_TABLE,
CacheStrategy.SECOND_LEVEL_CACHE);
DECISION_MATRIX.put(CacheScenario.HOT_DATA,
CacheStrategy.REDIS_CACHE);
DECISION_MATRIX.put(CacheScenario.TRANSACTIONAL_DATA,
CacheStrategy.NO_CACHE);
DECISION_MATRIX.put(CacheScenario.REPORT_QUERY,
CacheStrategy.QUERY_CACHE);
DECISION_MATRIX.put(CacheScenario.USER_SESSION,
CacheStrategy.REDIS_CACHE);
}
/**
* 根据场景选择缓存策略
*/
public CacheStrategy decideStrategy(CacheScenario scenario, CacheMetrics metrics) {
CacheStrategy baseStrategy = DECISION_MATRIX.get(scenario);
// 根据指标动态调整
if (metrics != null) {
if (metrics.getHitRatio() < 0.3) {
// 命中率太低,考虑禁用缓存
return CacheStrategy.NO_CACHE;
}
if (metrics.getMemoryUsage() > 0.8) {
// 内存使用率高,考虑使用外部缓存
return CacheStrategy.REDIS_CACHE;
}
}
return baseStrategy;
}
public enum CacheScenario {
CONFIG_TABLE, // 配置表
HOT_DATA, // 热点数据
TRANSACTIONAL_DATA,// 事务数据
REPORT_QUERY, // 报表查询
USER_SESSION, // 用户会话
PRODUCT_CATALOG // 商品目录
}
public enum CacheStrategy {
NO_CACHE, // 不使用缓存
FIRST_LEVEL_CACHE, // 仅一级缓存
SECOND_LEVEL_CACHE, // MyBatis二级缓存
REDIS_CACHE, // Redis缓存
QUERY_CACHE, // 查询结果缓存
HYBRID_CACHE // 混合缓存
}
@Data
public static class CacheMetrics {
private double hitRatio; // 命中率
private double memoryUsage; // 内存使用率
private long qps; // 查询QPS
private long updateQps; // 更新QPS
}
}六、MyBatis 二级缓存 vs Spring Cache 架构对比
6.1 技术栈对比分析
java
/**
* 缓存技术栈对比分析
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheStackComparison {
/**
* 技术选型对比表
*/
public void compareCacheStacks() {
CacheComparison mybatisCache = new CacheComparison("MyBatis二级缓存");
CacheComparison springCache = new CacheComparison("Spring Cache");
CacheComparison redisDirect = new CacheComparison("直接Redis操作");
// MyBatis二级缓存特点
mybatisCache.setInvasionLevel("DAO层");
mybatisCache.setGranularity("SQL级别");
mybatisCache.setConsistency("弱一致性");
mybatisCache.setDistributedSupport("不支持");
mybatisCache.setLearningCurve("简单");
mybatisCache.setPerformance("中等");
// Spring Cache特点
springCache.setInvasionLevel("Service层");
springCache.setGranularity("方法级别");
springCache.setConsistency("可配置");
springCache.setDistributedSupport("支持");
springCache.setLearningCurve("中等");
springCache.setPerformance("高");
// 直接Redis操作特点
redisDirect.setInvasionLevel("任意层");
redisDirect.setGranularity("业务级别");
redisDirect.setConsistency("强一致性");
redisDirect.setDistributedSupport("原生支持");
redisDirect.setLearningCurve("较高");
redisDirect.setPerformance("最高");
log.info("=== 缓存技术栈对比 ===");
log.info("1. MyBatis二级缓存: 适合简单的DAO层优化");
log.info("2. Spring Cache: 企业级推荐,灵活可控");
log.info("3. 直接Redis: 高性能要求,完全控制");
}
@Data
static class CacheComparison {
private String name;
private String invasionLevel; // 侵入层次
private String granularity; // 控制粒度
private String consistency; // 一致性
private String distributedSupport; // 分布式支持
private String learningCurve; // 学习曲线
private String performance; // 性能
public CacheComparison(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
/**
* 生产环境推荐方案
*/
public RecommendedSolution getRecommendedSolution() {
RecommendedSolution solution = new RecommendedSolution();
// 分层缓存架构
solution.setLayer1("Caffeine/Guava本地缓存 - 毫秒级热点数据");
solution.setLayer2("Redis集群 - 秒级业务数据");
solution.setLayer3("MySQL + MyBatis一级缓存 - 基础数据源");
// 使用策略
solution.setStrategy("Spring Cache抽象层 + 多级缓存实现");
// 监控体系
solution.setMonitoring("缓存命中率监控 + 内存使用告警 + 一致性检查");
return solution;
}
@Data
static class RecommendedSolution {
private String layer1;
private String layer2;
private String layer3;
private String strategy;
private String monitoring;
}
}6.2 混合缓存架构实现
java
/**
* 企业级混合缓存架构
*/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
@Slf4j
public class HybridCacheConfig {
/**
* 一级缓存:Caffeine(本地缓存)
*/
@Bean
public CacheManager caffeineCacheManager() {
CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager();
// 配置不同的缓存策略
cacheManager.setCaffeine(Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES) // 写后10分钟过期
.maximumSize(1000) // 最大1000个条目
.recordStats()); // 记录统计信息
return cacheManager;
}
/**
* 二级缓存:Redis(分布式缓存)
*/
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(30)) // 30分钟过期
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()))
.disableCachingNullValues(); // 不缓存null值
return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.transactionAware() // 支持事务
.build();
}
/**
* MyBatis二级缓存:Ehcache(可选)
*/
@Bean
public EhCacheManagerFactoryBean ehCacheManagerFactoryBean() {
EhCacheManagerFactoryBean factoryBean = new EhCacheManagerFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setConfigLocation(new ClassPathResource("ehcache.xml"));
factoryBean.setShared(true); // 共享缓存实例
return factoryBean;
}
/**
* 统一的缓存抽象层
*/
@Component
@Primary
public class UnifiedCacheService {
@Autowired
private CacheManager caffeineCacheManager;
@Autowired
private CacheManager redisCacheManager;
@Autowired
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
/**
* 智能缓存获取
*/
public <T> T getWithSmartCache(String key, Class<T> type,
Supplier<T> loader, CacheLevel level) {
// L1: 检查本地缓存
Cache localCache = caffeineCacheManager.getCache("local");
T value = localCache.get(key, type);
if (value != null) {
log.debug("L1缓存命中: {}", key);
return value;
}
// L2: 检查Redis缓存
Cache redisCache = redisCacheManager.getCache("redis");
value = redisCache.get(key, type);
if (value != null) {
log.debug("L2缓存命中: {}", key);
// 回填本地缓存
localCache.put(key, value);
return value;
}
// L3: 检查MyBatis二级缓存(如果适用)
if (level == CacheLevel.DAO) {
// 这里可以集成MyBatis二级缓存检查
}
// 都没有命中,从数据源加载
value = loader.get();
// 写入缓存
if (value != null) {
switch (level) {
case LOCAL:
localCache.put(key, value);
break;
case DISTRIBUTED:
redisCache.put(key, value);
break;
case DAO:
// 依赖MyBatis自动缓存
break;
}
}
return value;
}
public enum CacheLevel {
LOCAL, // 仅本地缓存
DISTRIBUTED, // 分布式缓存
DAO // DAO层缓存
}
}
}七、Redis 二级缓存生产级实现
7.1 安全的 Redis 缓存实现
java
/**
* 生产级 Redis 缓存实现
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ProductionRedisCache implements Cache {
private final String id;
private final String namespace;
private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
private final ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
// 缓存配置
private static final long DEFAULT_EXPIRE = 3600; // 默认1小时
private static final String KEY_PREFIX = "mybatis:cache:";
public ProductionRedisCache(String id) {
this.id = id;
this.namespace = extractNamespace(id);
ApplicationContext context = ApplicationContextHolder.getContext();
this.redisTemplate = context.getBean("redisTemplate", RedisTemplate.class);
log.info("初始化Redis缓存: {}, namespace: {}", id, namespace);
}
private String extractNamespace(String mapperId) {
// 从Mapper ID提取命名空间
// com.example.mapper.UserMapper -> user
String[] parts = mapperId.split("\\.");
String className = parts[parts.length - 1];
return className.replace("Mapper", "").toLowerCase();
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return this.id;
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
if (value == null) {
return;
}
readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
String redisKey = buildRedisKey(key);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
redisKey,
value,
DEFAULT_EXPIRE,
TimeUnit.SECONDS
);
// 记录缓存Key,便于管理
String cacheKeyList = KEY_PREFIX + namespace + ":keys";
redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(cacheKeyList, redisKey);
log.debug("缓存写入成功: {}", redisKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("缓存写入失败: {}", key, e);
// 生产环境:降级处理,不影响主流程
} finally {
readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
readWriteLock.readLock().lock();
try {
String redisKey = buildRedisKey(key);
Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(redisKey);
if (value != null) {
log.debug("缓存命中: {}", redisKey);
// 续期(可选)
redisTemplate.expire(redisKey, DEFAULT_EXPIRE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
return value;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("缓存读取失败: {}", key, e);
return null; // 降级:返回null,走数据库查询
} finally {
readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
String redisKey = buildRedisKey(key);
Object oldValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue().getAndDelete(redisKey);
// 从Key集合中移除
String cacheKeyList = KEY_PREFIX + namespace + ":keys";
redisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(cacheKeyList, redisKey);
log.debug("缓存删除成功: {}", redisKey);
return oldValue;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("缓存删除失败: {}", key, e);
return null;
} finally {
readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public void clear() {
readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
// 批量删除该命名空间下的所有Key
String pattern = KEY_PREFIX + namespace + ":*";
Set<String> keys = redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
if (keys != null && !keys.isEmpty()) {
redisTemplate.delete(keys);
log.info("清理缓存命名空间: {}, 删除 {} 个Key", namespace, keys.size());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("缓存清理失败: {}", namespace, e);
} finally {
readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
readWriteLock.readLock().lock();
try {
String cacheKeyList = KEY_PREFIX + namespace + ":keys";
Long size = redisTemplate.opsForSet().size(cacheKeyList);
return size != null ? size.intValue() : 0;
} finally {
readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return readWriteLock;
}
/**
* 构建安全的Redis Key
*/
private String buildRedisKey(Object key) {
// 格式:mybatis:cache:{namespace}:{keyHash}
return KEY_PREFIX + namespace + ":" + String.valueOf(key).hashCode();
}
/**
* 缓存统计信息
*/
public CacheStats getStats() {
CacheStats stats = new CacheStats();
stats.setNamespace(namespace);
stats.setSize(getSize());
// 获取内存使用情况(需要Redis info命令)
// 这里可以扩展获取更多Redis统计信息
return stats;
}
@Data
public static class CacheStats {
private String namespace;
private int size;
private long memoryUsage;
private double hitRatio;
}
}7.2 Redis 缓存管理控制台
java
/**
* Redis 缓存管理端点
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/cache")
@Slf4j
public class CacheManagementController {
@Autowired
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 获取所有缓存统计
*/
@GetMapping("/stats")
public Map<String, Object> getCacheStats() {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
Collection<Cache> caches = configuration.getCaches();
List<Map<String, Object>> cacheList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Cache cache : caches) {
Map<String, Object> cacheInfo = new HashMap<>();
cacheInfo.put("id", cache.getId());
cacheInfo.put("size", cache.getSize());
cacheInfo.put("type", cache.getClass().getSimpleName());
cacheList.add(cacheInfo);
}
result.put("caches", cacheList);
result.put("total", cacheList.size());
// Redis全局统计
Properties info = redisTemplate.getRequiredConnectionFactory()
.getConnection().info();
result.put("redisInfo", info);
return result;
}
/**
* 清理指定缓存
*/
@PostMapping("/clear/{namespace}")
public ApiResponse clearCache(@PathVariable String namespace) {
try {
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
Cache cache = configuration.getCache(namespace);
if (cache != null) {
cache.clear();
log.info("手动清理缓存: {}", namespace);
return ApiResponse.success("缓存清理成功");
} else {
return ApiResponse.error("缓存不存在");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("清理缓存失败", e);
return ApiResponse.error("缓存清理失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 预热缓存
*/
@PostMapping("/warmup/{namespace}")
public ApiResponse warmupCache(@PathVariable String namespace) {
// 根据业务逻辑预热缓存
// 例如:加载热点数据到缓存中
return ApiResponse.success("缓存预热开始");
}
@Data
public static class ApiResponse {
private boolean success;
private String message;
private Object data;
public static ApiResponse success(String message) {
ApiResponse response = new ApiResponse();
response.setSuccess(true);
response.setMessage(message);
return response;
}
public static ApiResponse error(String message) {
ApiResponse response = new ApiResponse();
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setMessage(message);
return response;
}
}
}八、线程安全与并发控制
8.1 生产环境线程安全配置
java
/**
* 线程安全的缓存配置
*/
@Configuration
public class ThreadSafeCacheConfig {
/**
* 线程安全的Cache实现
*/
@Bean
public CacheFactory cacheFactory() {
return new ThreadSafeCacheFactory();
}
/**
* 自定义Cache工厂,确保线程安全
*/
public static class ThreadSafeCacheFactory implements CacheFactory {
@Override
public Cache getCache(String id) {
// 根据id返回相应的Cache实现
// 确保每个Cache都有独立的锁
return new ThreadSafeCacheImpl(id);
}
}
/**
* 线程安全的Cache实现
*/
public static class ThreadSafeCacheImpl implements Cache {
private final String id;
private final Map<Object, Object> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final ReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
// 统计信息(线程安全)
private final AtomicLong hitCount = new AtomicLong(0);
private final AtomicLong missCount = new AtomicLong(0);
private final AtomicLong putCount = new AtomicLong(0);
private final AtomicLong evictionCount = new AtomicLong(0);
public ThreadSafeCacheImpl(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
lock.writeLock().lock();
try {
cache.put(key, value);
putCount.incrementAndGet();
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
lock.readLock().lock();
try {
Object value = cache.get(key);
if (value != null) {
hitCount.incrementAndGet();
} else {
missCount.incrementAndGet();
}
return value;
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
lock.writeLock().lock();
try {
evictionCount.incrementAndGet();
return cache.remove(key);
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public void clear() {
lock.writeLock().lock();
try {
cache.clear();
evictionCount.addAndGet(cache.size());
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
lock.readLock().lock();
try {
return cache.size();
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return lock;
}
/**
* 获取缓存统计信息
*/
public CacheStats getStats() {
CacheStats stats = new CacheStats();
stats.setHitCount(hitCount.get());
stats.setMissCount(missCount.get());
stats.setPutCount(putCount.get());
stats.setEvictionCount(evictionCount.get());
stats.setSize(getSize());
long total = hitCount.get() + missCount.get();
stats.setHitRatio(total > 0 ?
(double) hitCount.get() / total : 0.0);
return stats;
}
@Data
public static class CacheStats {
private long hitCount;
private long missCount;
private long putCount;
private long evictionCount;
private int size;
private double hitRatio;
}
}
}8.2 并发场景下的缓存策略
java
/**
* 并发缓存策略
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ConcurrentCacheStrategy {
@Autowired
private CacheManager cacheManager;
/**
* 防止缓存击穿:互斥锁
*/
public <T> T getWithMutex(String key, Class<T> type,
Supplier<T> loader, long expireSeconds) {
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache("default");
// 1. 尝试从缓存获取
T value = cache.get(key, type);
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
// 2. 获取分布式锁
String lockKey = "lock:" + key;
boolean locked = acquireLock(lockKey, 3000); // 3秒超时
if (locked) {
try {
// 双重检查
value = cache.get(key, type);
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
// 3. 加载数据
value = loader.get();
if (value != null) {
// 4. 写入缓存
cache.put(key, value);
} else {
// 缓存空值,防止缓存穿透
cache.put(key, new NullValue(), expireSeconds);
}
return value;
} finally {
releaseLock(lockKey);
}
} else {
// 获取锁失败,等待重试或返回默认值
log.warn("获取缓存锁失败: {}", key);
return null;
}
}
/**
* 防止缓存雪崩:随机过期时间
*/
public void putWithRandomExpire(String key, Object value) {
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache("default");
// 基础过期时间 + 随机偏移(防止同时过期)
long baseExpire = 3600; // 1小时
long randomOffset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(300); // 0-5分钟随机
long expireTime = baseExpire + randomOffset;
// 使用带过期时间的put方法
// 注意:Spring Cache默认不支持,需要自定义Cache实现
}
/**
* 缓存预热:启动时加载热点数据
*/
@PostConstruct
public void warmUpCache() {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
List<Callable<Void>> tasks = Arrays.asList(
() -> { warmUpUserCache(); return null; },
() -> { warmUpProductCache(); return null; },
() -> { warmUpConfigCache(); return null; }
);
try {
executor.invokeAll(tasks);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("缓存预热被中断", e);
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} finally {
executor.shutdown();
}
}
private boolean acquireLock(String lockKey, long timeout) {
// 使用Redis分布式锁
// 实现略...
return true;
}
private void releaseLock(String lockKey) {
// 释放锁
}
// 空值标记类
private static class NullValue implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
}
}九、监控、告警与故障处理
9.1 缓存监控体系
java
# prometheus.yml - 缓存监控指标
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'mybatis-cache'
metrics_path: '/actuator/prometheus'
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:8080']
- job_name: 'redis-cache'
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:9121'] # Redis Exporter
# 关键监控指标
# mybatis_cache_hit_total{namespace="UserMapper"}
# mybatis_cache_miss_total{namespace="UserMapper"}
# mybatis_cache_size{namespace="UserMapper"}
# redis_memory_used_bytes
# redis_connected_clients
java
/**
* 缓存监控端点
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheMetricsCollector {
@Autowired
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Autowired
private MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
private final Map<String, CacheMetrics> metricsMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 定时收集缓存指标
*/
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 60000) // 每分钟收集一次
public void collectCacheMetrics() {
Configuration config = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
Collection<Cache> caches = config.getCaches();
for (Cache cache : caches) {
String cacheId = cache.getId();
CacheMetrics metrics = getOrCreateMetrics(cacheId);
// 收集指标
metrics.setSize(cache.getSize());
// 发布到监控系统
Gauge.builder("mybatis.cache.size", metrics, CacheMetrics::getSize)
.tags("namespace", cacheId)
.register(meterRegistry);
Counter.builder("mybatis.cache.hit")
.tags("namespace", cacheId)
.register(meterRegistry)
.increment(metrics.getHitCount());
// 计算命中率
double hitRatio = calculateHitRatio(metrics);
Gauge.builder("mybatis.cache.hit.ratio", () -> hitRatio)
.tags("namespace", cacheId)
.register(meterRegistry);
}
}
/**
* 缓存健康检查
*/
@Component
public class CacheHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {
@Override
public Health health() {
Map<String, Object> details = new HashMap<>();
Configuration config = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
boolean healthy = true;
List<String> issues = new ArrayList<>();
// 检查所有缓存
Collection<Cache> caches = config.getCaches();
for (Cache cache : caches) {
String cacheId = cache.getId();
int size = cache.getSize();
details.put(cacheId + ".size", size);
// 检查缓存大小是否异常
if (size > 10000) {
issues.add(cacheId + "缓存过大: " + size);
healthy = false;
}
}
if (healthy) {
return Health.up().withDetails(details).build();
} else {
return Health.down()
.withDetail("issues", issues)
.withDetails(details)
.build();
}
}
}
/**
* 缓存告警规则
*/
@Component
public class CacheAlertRules {
private static final double HIT_RATIO_THRESHOLD = 0.3; // 命中率低于30%告警
private static final int SIZE_THRESHOLD = 10000; // 缓存大小超过10000告警
@Autowired
private AlertService alertService;
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 300000) // 每5分钟检查一次
public void checkCacheAlerts() {
Configuration config = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
for (Cache cache : config.getCaches()) {
String cacheId = cache.getId();
CacheMetrics metrics = getOrCreateMetrics(cacheId);
// 规则1:命中率过低
double hitRatio = calculateHitRatio(metrics);
if (hitRatio < HIT_RATIO_THRESHOLD) {
alertService.sendAlert(
"CACHE_LOW_HIT_RATIO",
String.format("缓存%s命中率过低: %.2f%%",
cacheId, hitRatio * 100)
);
}
// 规则2:缓存过大
int size = cache.getSize();
if (size > SIZE_THRESHOLD) {
alertService.sendAlert(
"CACHE_SIZE_TOO_LARGE",
String.format("缓存%s大小异常: %d", cacheId, size)
);
}
}
}
}
@Data
public static class CacheMetrics {
private String namespace;
private int size;
private long hitCount;
private long missCount;
private long putCount;
private long evictionCount;
}
}9.2 缓存故障处理预案
java
/**
* 缓存故障降级方案
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheFailureHandler {
@Autowired
private CircuitBreakerFactory circuitBreakerFactory;
/**
* 带熔断的缓存操作
*/
public <T> T getWithCircuitBreaker(String key, Supplier<T> supplier) {
CircuitBreaker cb = circuitBreakerFactory.create("cache-circuit");
return cb.run(
() -> {
// 正常缓存操作
return getFromCache(key, supplier);
},
throwable -> {
// 降级处理
log.error("缓存操作失败,执行降级", throwable);
return fallback(key, supplier);
}
);
}
/**
* 多级降级策略
*/
private <T> T fallback(String key, Supplier<T> supplier) {
try {
// 降级1:尝试本地内存缓存
T value = getFromLocalMemory(key);
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
// 降级2:直接访问数据库(限流)
return supplier.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 降级3:返回默认值
log.error("所有降级策略都失败", e);
return getDefaultValue();
}
}
/**
* 缓存重建策略
*/
public <T> T rebuildCache(String key, Supplier<T> loader) {
// 1. 标记缓存正在重建
markRebuilding(key);
try {
// 2. 异步重建缓存
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(loader)
.thenAccept(value -> {
// 3. 更新缓存
updateCache(key, value);
// 4. 清除重建标记
clearRebuildingMark(key);
})
.exceptionally(throwable -> {
log.error("缓存重建失败", throwable);
clearRebuildingMark(key);
return null;
});
// 5. 返回旧数据或null
return getOldValue(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
clearRebuildingMark(key);
throw e;
}
}
/**
* 缓存一致性检查
*/
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 2 * * ?") // 每天凌晨2点执行
public void checkCacheConsistency() {
log.info("开始缓存一致性检查");
// 1. 采样检查
List<String> sampleKeys = getSampleKeys();
for (String key : sampleKeys) {
Object cacheValue = getFromCache(key);
Object dbValue = getFromDatabase(key);
if (!Objects.equals(cacheValue, dbValue)) {
log.warn("缓存不一致: key={}, cache={}, db={}",
key, cacheValue, dbValue);
// 自动修复
fixInconsistency(key, dbValue);
}
}
}
}十、企业级缓存架构总结与最佳实践
10.1 缓存架构决策树
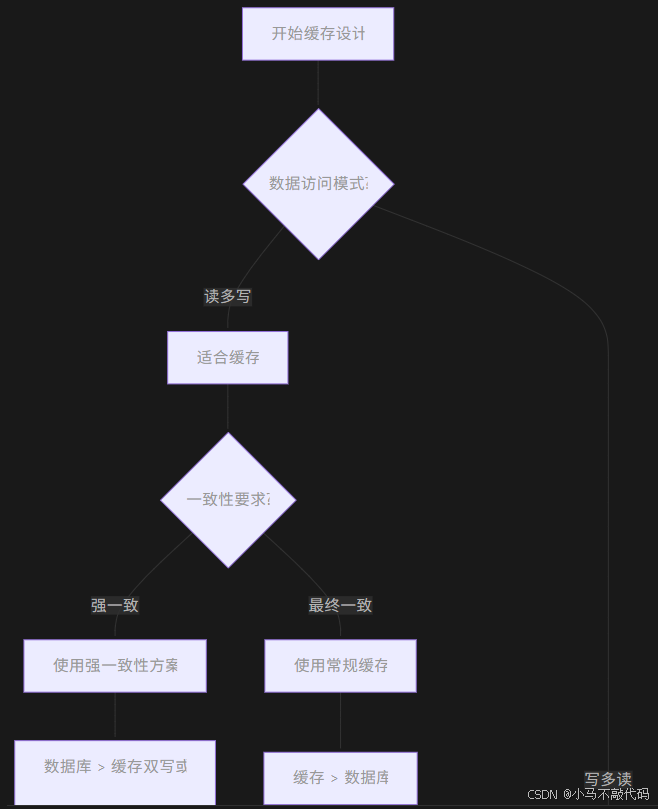
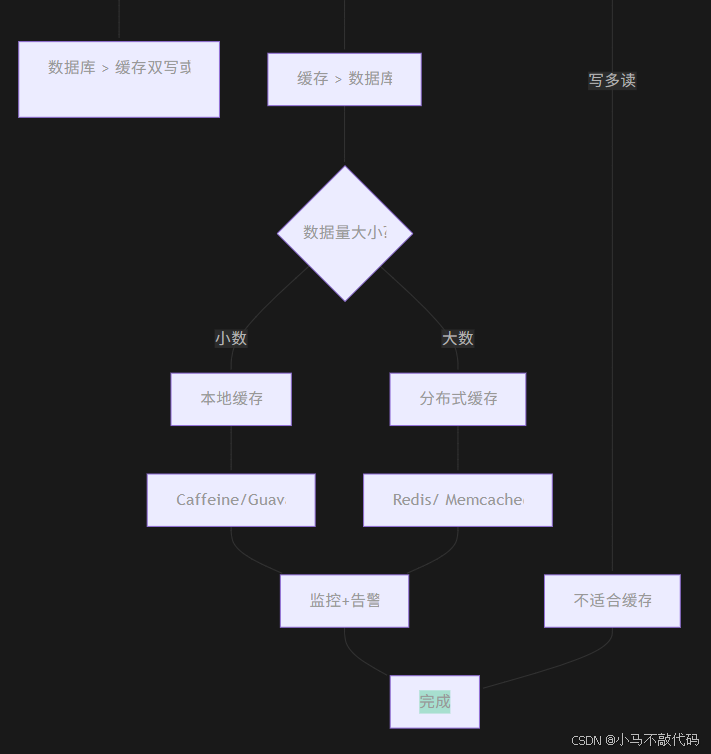
10.2 缓存使用黄金法则
java
/**
* 企业级缓存使用规范
*/
public class CacheGoldenRules {
/**
* 法则1:明确缓存目的
*/
public static final class Rule1 {
// ❌ 不要为了缓存而缓存
// ✅ 明确缓存要解决的问题:降低延迟、减少数据库压力、提升吞吐量
}
/**
* 法则2:选择合适的缓存粒度
*/
public static final class Rule2 {
// ❌ 大对象整体缓存
// ✅ 按需缓存,精细控制
}
/**
* 法则3:设置合理的过期时间
*/
public static final class Rule3 {
// ❌ 永久缓存
// ✅ 根据业务特点设置TTL
// ✅ 热数据长TTL,冷数据短TTL
}
/**
* 法则4:处理缓存失效
*/
public static final class Rule4 {
// ❌ 忽略缓存失效
// ✅ 有降级方案
// ✅ 有重建策略
}
/**
* 法则5:监控一切
*/
public static final class Rule5 {
// ❌ 无监控上线
// ✅ 监控命中率、内存使用、响应时间
// ✅ 设置告警阈值
}
/**
* 法则6:容量规划
*/
public static final class Rule6 {
// ❌ 无限制使用内存
// ✅ 根据业务量规划容量
// ✅ 设置淘汰策略
}
/**
* 法则7:线程安全
*/
public static final class Rule7 {
// ❌ 忽略并发问题
// ✅ 读写锁保护
// ✅ 避免缓存击穿
}
/**
* 法则8:可观测性
*/
public static final class Rule8 {
// ❌ 黑盒缓存
// ✅ 详细日志
// ✅ 统计信息
// ✅ 管理接口
}
}10.3 各层级缓存推荐方案
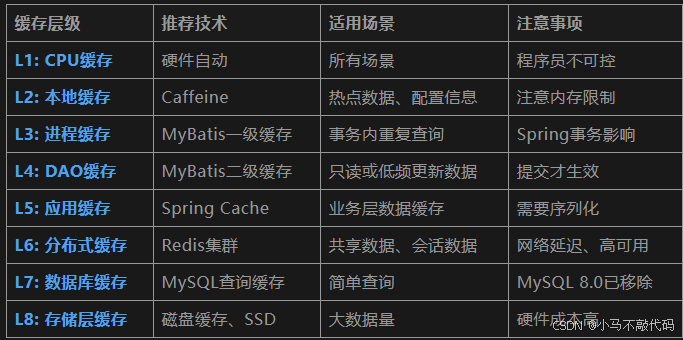
10.4 工程级结论与建议
MyBatis 缓存体系工程实践总结
核心理念
1. 缓存是补偿机制,不是架构核心
• 优先优化数据库和业务逻辑
• 缓存是用来弥补其他组件不足的
2. 分层缓存,各司其职
• 本地缓存解决热点数据
• 分布式缓存解决数据共享
• MyBatis缓存作为DAO层优化
3. 数据一致性高于性能
• 宁可慢,不能错
• 最终一致性要有明确预期
生产环境建议
针对MyBatis缓存:
• ✅ 一级缓存:默认开启,无需特殊关注
• ⚠️ 二级缓存:谨慎使用,仅适合特定场景
• ❌ 动态SQL缓存:避免使用,缓存碎片严重
企业级缓存架构:
• 推荐方案:Spring Cache + Redis + Caffeine 多级缓存
• 监控体系:命中率、内存使用、响应时间
• 降级方案:缓存失效时的业务降级策略
团队规范:
- 新项目默认禁用MyBatis二级缓存
- 使用缓存必须添加监控
- 重要数据必须有降级方案
- 定期进行缓存一致性检查
性能数据参考(仅供参考)
• 一级缓存:纳秒级访问,命中率>99%(事务内)
• 二级缓存:微秒级访问,命中率30%-80%
• Redis缓存:毫秒级访问,命中率>95%
• 数据库查询:10ms-100ms
缓存能提升性能,但也增加复杂度。
在添加缓存前,先问自己:
- 真的需要缓存吗?
- 数据一致性如何保证?
- 缓存失效怎么办?
- 如何监控和告警?
附录:完整配置示例
java
application-production.yml
mybatis:
configuration:
cache-enabled: false # 生产环境默认关闭二级缓存
local-cache-scope: SESSION
lazy-loading-enabled: true
aggressive-lazy-loading: false
# 日志配置
log-prefix: MYBATIS
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.slf4j.Slf4jImpl
# 缓存配置
cache:
multi-level:
enabled: true
levels:
- name: local
type: caffeine
spec: maximumSize=1000,expireAfterWrite=10m
- name: redis
type: redis
ttl: 30m
key-prefix: app:cache:
use-key-prefix: true
# 缓存预热
warmup:
enabled: true
cron: "0 0 6 * * ?" # 每天6点预热
batch-size: 100
# 监控
monitor:
enabled: true
export-metrics: true
alert-thresholds:
hit-ratio: 0.3
memory-usage: 0.8