目录
题目范围
牛客练习输入,输出
逻辑题:牛客的中+难等级的题目
算法题:力扣:简单+中等的题目
题型
题型:三道题是简单+简单+中等难度的题型。第一二题可能会是循环、数组、字符串、栈这些,第三题会难一点,二分查找、动态规划、DFS、BFS这些。
参考资料
leetcode网的典型练习题目编号如下:
字符串:3,49,30
线性表:86,16,27,732
队列:641,406,899
栈:946,116,117,895
哈希表:61,729,25,554
dfs:105,112,98,494,547,1254
bfs:1091,1129,102,101,752
字符串
3.无重复字符串的最长子串
python
class Solution(object):
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
start = 0
max_length = 0
char_index_map = {}
for i, char in enumerate(s):
if char in char_index_map and char_index_map[char] >= start:
start = char_index_map[char] + 1
char_index_map[char] = i
current_length = i - start + 1
if current_length > max_length:
max_length = current_length
return max_length
str = input("Enter a string: ")
solution = Solution()
print("The longest substring without repeating characters is:", solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring(str))49.字母异位词分组.py
python
class Solution(object):
def groupAnagrams(self, strs):
"""
:type strs: List[str]
:rtype: List[List[str]]
"""
anagram_map = {}
for s in strs:
sorted_s = ''.join(sorted(s))
if sorted_s in anagram_map:
anagram_map[sorted_s].append(s)
else:
anagram_map[sorted_s] = [s]
return list(anagram_map.values())
strs = input("Enter a list of words separated by spaces: ").split()
solution = Solution()
print("Grouped anagrams:", solution.groupAnagrams(strs))30.串联所有单词的子串
python
from collections import Counter
class Solution(object):
def findSubstring(self, s, words):
"""
:type s: str
:type words: List[str]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = []
m, n, ls = len(words), len(words[0]), len(s)
for i in range(n):
if i + m * n > ls:
break
differ = Counter()
for j in range(m):
word = s[i + j * n: i + (j + 1) * n]
differ[word] += 1
for word in words:
differ[word] -= 1
if differ[word] == 0:
del differ[word]
for start in range(i, ls - m * n + 1, n):
if start != i:
word = s[start + (m - 1) * n: start + m * n]
differ[word] += 1
if differ[word] == 0:
del differ[word]
word = s[start - n: start]
differ[word] -= 1
if differ[word] == 0:
del differ[word]
if len(differ) == 0:
res.append(start)
return res
s = input("Enter a string: ")
words = input("Enter words separated by spaces: ").split()
solution = Solution()
print("Starting indices of substring concatenations are:", solution.findSubstring(s, words))线性表
86.分隔链表.py
python
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = int(val) if val is not None and val != '' else 0
self.next = next
@staticmethod
def from_list(values):
if not values:
return None
head = ListNode(values[0])
cur = head
for v in values[1:]:
cur.next = ListNode(v)
cur = cur.next
return head
def to_list(self):
out = []
node = self
while node:
out.append(node.val)
node = node.next
return out
def __repr__(self):
return '->'.join(str(x) for x in self.to_list())
class Solution(object):
def partition(self, head, x):
"""
:type head: Optional[ListNode]
:type x: int
:rtype: Optional[ListNode]
"""
small = ListNode(0)
smallHead = small
large = ListNode(0)
largeHead = large
while head:
if head.val < x:
small.next = head
small = small.next
else:
large.next = head
large = large.next
head = head.next
large.next = None
small.next = largeHead.next
return smallHead.next
head = ListNode.from_list([1,4,3,2,5,2])
x = 3
solution = Solution()
new_head = solution.partition(head, x)
print("Partitioned linked list:", new_head.to_list())16.最接近的三数之和
python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def threeSumClosest(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
nums.sort()
closest_sum = float('inf')
for i in range(len(nums) - 2):
left, right = i + 1, len(nums) - 1
while left < right:
current_sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]
if abs(current_sum - target) < abs(closest_sum - target):
closest_sum = current_sum
if current_sum < target:
left += 1
elif current_sum > target:
right -= 1
else:
return current_sum
return closest_sum
nums = list(map(int, input("Enter numbers separated by spaces: ").split()))
target = int(input("Enter the target sum: "))
solution = Solution()
result = solution.threeSumClosest(nums, target)
print("The sum of the three integers closest to the target is:", result)27.移除元素
python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def removeElement(self, nums: List[int], val: int) -> int:
i = 0
for j in range(len(nums)):
if nums[j] != val:
nums[i] = nums[j]
i += 1
return i
nums = list(map(int, input("Enter numbers separated by spaces: ").split(",")))
val = int(input("Enter the value to remove: "))
solution = Solution()
new_length = solution.removeElement(nums, val)
print("The new length of the array is:", new_length)
print("The modified array is:", nums[:new_length])732.我的日程安排
python
from sortedcontainers import SortedDict
class MyCalendarThree:
def __init__(self):
# 使用SortedDict存储时间点的变化量
self.diff = SortedDict()
self.max_k = 0
def book(self, startTime: int, endTime: int) -> int:
# 更新起点和终点
self.diff[startTime] = self.diff.get(startTime, 0) + 1
self.diff[endTime] = self.diff.get(endTime, 0) - 1
# 计算当前最大重叠次数
current = 0
for time in self.diff:
current += self.diff[time]
self.max_k = max(self.max_k, current)
return self.max_k
calendar = MyCalendarThree()
print(calendar.book(10, 20)) # 返回 1
print(calendar.book(50, 60)) # 返回 1
print(calendar.book(10, 40)) # 返回 2
print(calendar.book(5, 15)) # 返回 3
print(calendar.book(5, 10)) # 返回 3
print(calendar.book(25, 55)) # 返回 3队列
641.设计循环双端队列
python
class MyCircularDeque:
def __init__(self, k: int):
self.capacity = k
self.queue = [0] * k
self.front = 0
self.rear = 0
self.size = 0
def insertFront(self, value: int) -> bool:
if self.isFull():
return False
self.front = (self.front - 1) % self.capacity
self.queue[self.front] = value
self.size += 1
return True
def insertLast(self, value: int) -> bool:
if self.isFull():
return False
self.queue[self.rear] = value
self.rear = (self.rear + 1) % self.capacity
self.size += 1
return True
def deleteFront(self) -> bool:
if self.isEmpty():
return False
self.front = (self.front + 1) % self.capacity
self.size -= 1
return True
def deleteLast(self) -> bool:
if self.isEmpty():
return False
self.rear = (self.rear - 1) % self.capacity
self.size -= 1
return True
def getFront(self) -> int:
return -1 if self.isEmpty() else self.queue[self.front]
def getRear(self) -> int:
return -1 if self.isEmpty() else self.queue[(self.rear - 1) % self.capacity]
def isEmpty(self) -> bool:
return self.size == 0
def isFull(self) -> bool:
return self.size == self.capacity
deque = MyCircularDeque(3)
print(deque.insertLast(1)) # True
print(deque.insertLast(2)) # True
print(deque.insertFront(3)) # True
print(deque.insertFront(4)) # False (已满)
print(deque.getRear()) # 2
print(deque.isFull()) # True
print(deque.deleteLast()) # True
print(deque.insertFront(4)) # True
print(deque.getFront()) # 4406.根据身高重建队列
python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def reconstructQueue(self, people: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
# 排序:身高降序,k值升序
people.sort(key=lambda x: (-x[0], x[1]))
result = []
for p in people:
# 使用bisect找到插入位置
# 这里可以直接使用insert,因为已经排序了
result.insert(p[1], p)
return result
solution = Solution()
people1 = [[7,0],[4,4],[7,1],[5,0],[6,1],[5,2]]
result1 = solution.reconstructQueue(people1)
print("测试用例1:")
print("输入:", people1)
print("输出:", result1)
print("预期:", [[5,0],[7,0],[5,2],[6,1],[4,4],[7,1]])
print("正确?", result1 == [[5,0],[7,0],[5,2],[6,1],[4,4],[7,1]])
print()899.有序队列
python
class Solution:
def orderlyQueue(self, s: str, k: int) -> str:
if k == 1:
# 生成所有可能的旋转,取最小值
return min(s[i:] + s[:i] for i in range(len(s)))
else:
# 当k>1时,可以完全重新排列
return ''.join(sorted(s))
solution = Solution()
s1, k1 = "cba", 1
result1 = solution.orderlyQueue(s1, k1)
print(f"测试1: s='{s1}', k={k1}")
print(f"结果: '{result1}'")
print(f"预期: 'acb'")
print(f"正确: {result1 == 'acb'}")
print()栈
946.验证栈序列
python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def validateStackSequences(self, pushed: List[int], popped: List[int]) -> bool:
"""
使用栈模拟push和pop操作
思路:
1. 遍历pushed数组,将元素依次压入栈
2. 每次压入后,检查栈顶元素是否等于popped的当前元素
3. 如果相等则弹出,直到栈为空或栈顶元素不等于popped当前元素
4. 最后检查栈是否为空
"""
stack = []
pop_index = 0
for num in pushed:
# 压入当前元素
stack.append(num)
# 循环检查并弹出匹配的元素
while stack and stack[-1] == popped[pop_index]:
stack.pop()
pop_index += 1
# 如果栈为空,说明所有元素都正确弹出了
return len(stack) == 0
solution = Solution()
pushed1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
popped1 = [4, 5, 3, 2, 1]
result1 = solution.validateStackSequences(pushed1, popped1)
print(f"测试1: pushed={pushed1}, popped={popped1}")
print(f"结果: {result1}")
print(f"预期: True")
print(f"正确: {result1 == True}")895.最大频率栈
python
from collections import defaultdict
class FreqStack:
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化最大频率栈
需要维护三个数据结构:
1. freq: 记录每个值的频率
2. group: 记录每个频率对应的值列表(栈)
3. max_freq: 当前最大频率
"""
self.freq = defaultdict(int) # 值 -> 频率
self.group = defaultdict(list) # 频率 -> 值列表(栈)
self.max_freq = 0 # 当前最大频率
def push(self, val: int) -> None:
"""
将值推入栈中
"""
# 更新频率
self.freq[val] += 1
f = self.freq[val]
# 将值加入到对应频率的组中
self.group[f].append(val)
# 更新最大频率
if f > self.max_freq:
self.max_freq = f
def pop(self) -> int:
"""
弹出并返回出现频率最高的元素
如果有多个频率相同的元素,返回最接近栈顶的
"""
# 从最大频率对应的组中弹出元素
val = self.group[self.max_freq].pop()
# 更新该值的频率
self.freq[val] -= 1
# 如果最大频率对应的组为空,则减小最大频率
if not self.group[self.max_freq]:
self.max_freq -= 1
return val
freq_stack = FreqStack()
print("测试示例1:")
operations = ["push", "push", "push", "push", "push", "push", "pop", "pop", "pop", "pop"]
values = [5, 7, 5, 7, 4, 5, None, None, None, None]
results = []
for op, val in zip(operations, values):
if op == "push":
freq_stack.push(val)
results.append(None)
elif op == "pop":
results.append(freq_stack.pop())
print("操作序列:", operations)
print("值序列:", values)
print("结果:", results)
print("预期:", [None, None, None, None, None, None, 5, 7, 5, 4])
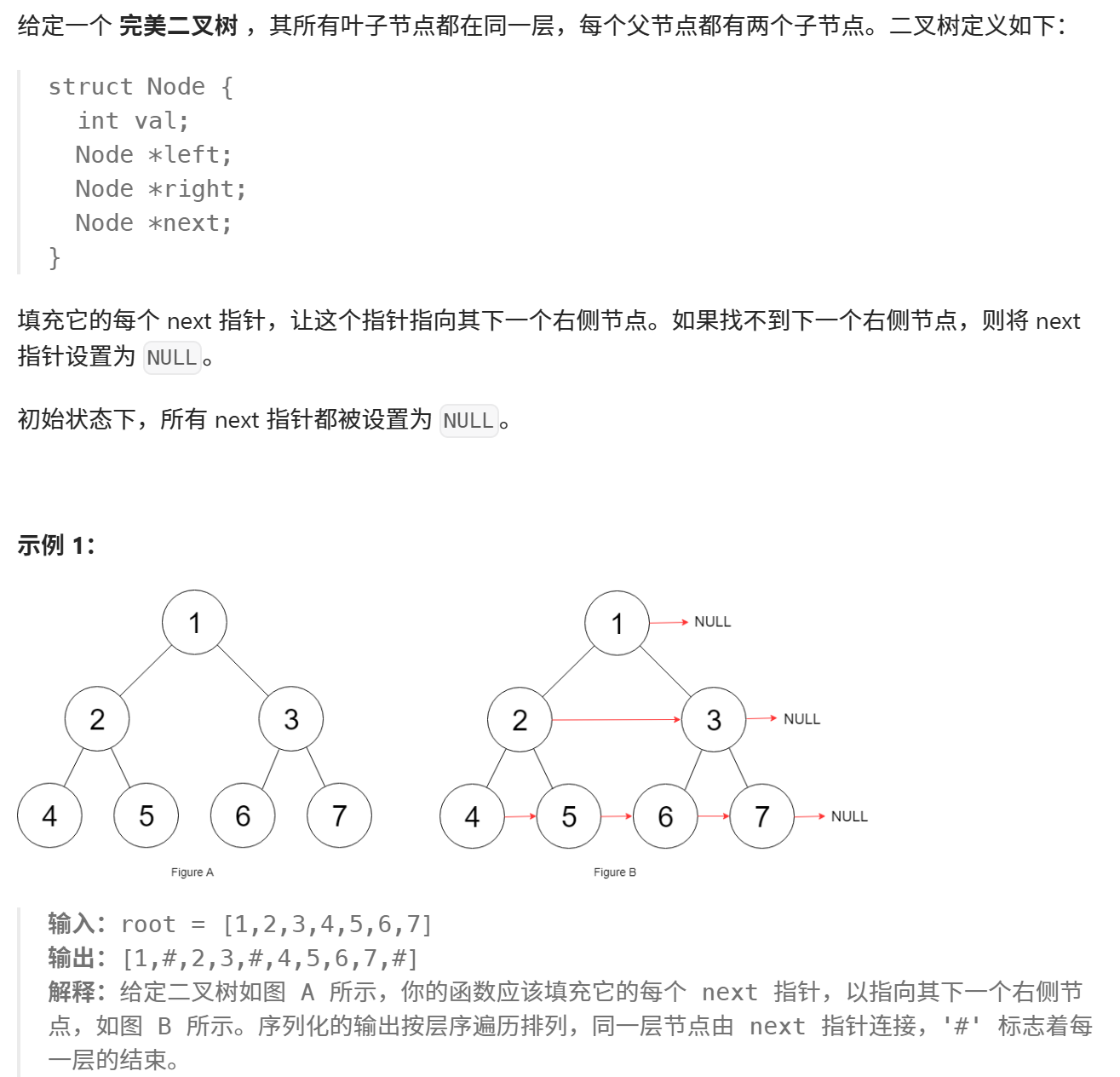
print("正确?", results == [None, None, None, None, None, None, 5, 7, 5, 4])116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
python
from typing import Optional
# Node类的定义
class Node:
def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left: 'Node' = None, right: 'Node' = None, next: 'Node' = None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
self.next = next
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':
"""
使用已建立的next指针进行层序遍历
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)(不考虑递归栈空间)
"""
if not root:
return root
# 从根节点开始
leftmost = root
# 当还有下一层时继续
while leftmost.left:
# 遍历当前层的节点,通过next指针横向移动
head = leftmost
while head:
# 连接1:连接同一个父节点的左右子节点
head.left.next = head.right
# 连接2:连接不同父节点的相邻子节点
if head.next:
head.right.next = head.next.left
# 移动到当前层的下一个节点
head = head.next
# 移动到下一层的最左边节点
leftmost = leftmost.left
return root
def print_tree_next(root):
"""打印每层的next指针"""
if not root:
return
leftmost = root
while leftmost:
current = leftmost
level_nodes = []
while current:
next_val = current.next.val if current.next else "NULL"
level_nodes.append(f"{current.val}->{next_val}")
current = current.next
print(" | ".join(level_nodes))
leftmost = leftmost.left
# 构建一个完美二叉树
def build_perfect_tree(nodes):
"""构建完美二叉树用于测试"""
if not nodes:
return None
from collections import deque
root = Node(nodes[0])
queue = deque([root])
i = 1
while queue and i < len(nodes):
node = queue.popleft()
if i < len(nodes):
node.left = Node(nodes[i])
queue.append(node.left)
i += 1
if i < len(nodes):
node.right = Node(nodes[i])
queue.append(node.right)
i += 1
return root
solution = Solution()
# 测试用例1
print("测试用例1:")
nodes1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
root1 = build_perfect_tree(nodes1)
root1 = solution.connect(root1)
print_tree_next(root1)
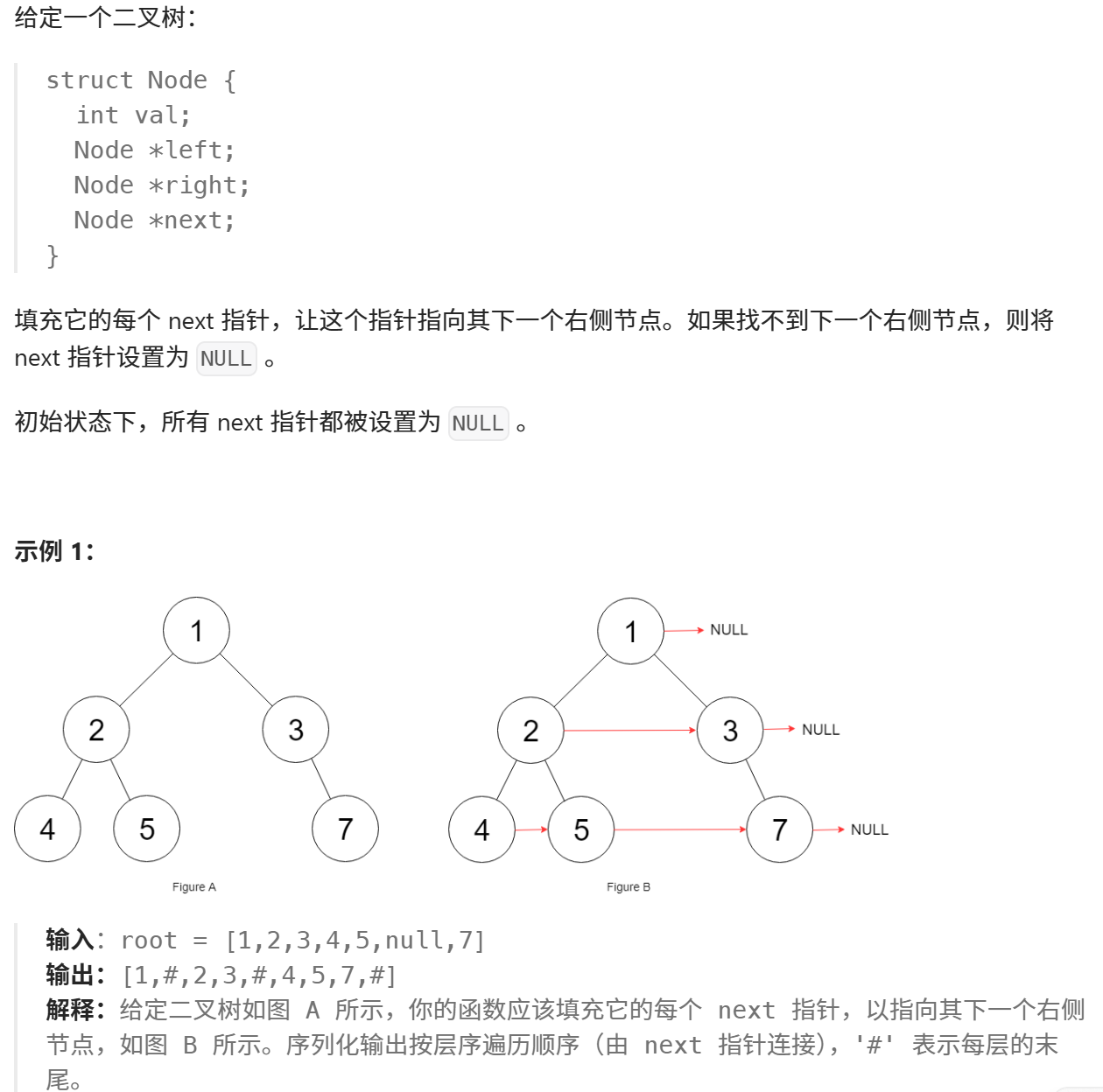
print()117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
python
class Node:
def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left: 'Node' = None, right: 'Node' = None, next: 'Node' = None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
self.next = next
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
"""
更简洁的迭代解法
"""
if not root:
return root
# 当前层头节点
head = root
while head:
# 为下一层创建虚拟头节点
dummy = Node(0)
tail = dummy
# 遍历当前层
current = head
while current:
# 处理左子节点
if current.left:
tail.next = current.left
tail = tail.next
# 处理右子节点
if current.right:
tail.next = current.right
tail = tail.next
# 移动到当前层的下一个节点
current = current.next
# 移动到下一层
head = dummy.next
return root
def print_tree_next(root):
"""打印每层的next指针"""
if not root:
return
leftmost = root
while leftmost:
current = leftmost
level_nodes = []
while current:
next_val = current.next.val if current.next else "NULL"
level_nodes.append(f"{current.val}->{next_val}")
current = current.next
print(" | ".join(level_nodes))
leftmost = leftmost.left
# 构建测试树
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.right = Node(7)
solution = Solution()
root = solution.connect(root)
print("测试用例:")
print_tree_next(root)哈希表
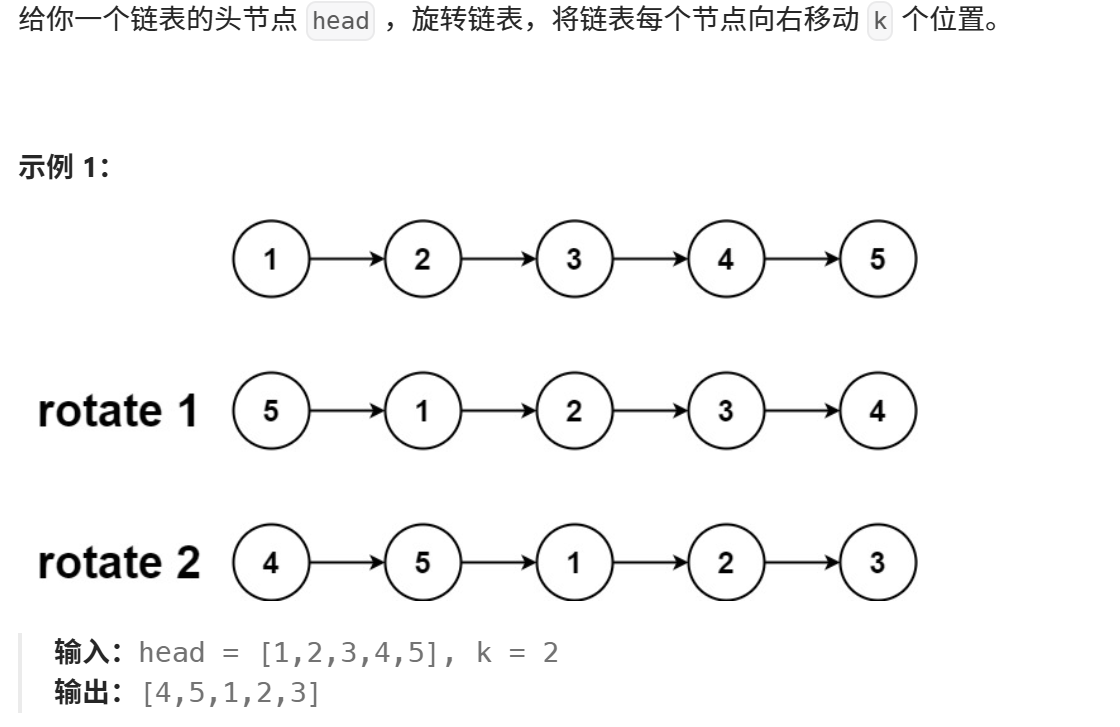
61.旋转链表
python
from typing import Optional
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def rotateRight(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
"""
旋转链表:将链表每个节点向右移动k个位置
思路:
1. 如果链表为空或只有一个节点,或者k=0,直接返回
2. 计算链表长度,并找到尾节点
3. 将链表连接成环
4. 计算实际需要移动的步数:k % n
5. 找到新的尾节点(从head开始移动n - k%n - 1步)
6. 断开环,返回新的头节点
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
"""
# 边界情况处理
if not head or not head.next or k == 0:
return head
# 1. 计算链表长度,并找到尾节点
n = 1 # 链表长度
tail = head
while tail.next:
tail = tail.next
n += 1
# 2. 计算实际需要移动的步数(避免重复旋转)
k = k % n
if k == 0: # 如果移动0步或移动整圈,直接返回
return head
# 3. 将链表连接成环
tail.next = head
# 4. 找到新的尾节点(第n-k个节点)
new_tail = head
for _ in range(n - k - 1):
new_tail = new_tail.next
# 5. 新的头节点是新的尾节点的下一个节点
new_head = new_tail.next
# 6. 断开环
new_tail.next = None
return new_head
solution = Solution()
head = ListNode(1, ListNode(2, ListNode(3, ListNode(4, ListNode(5)))))
k = 2
new_head = solution.rotateRight(head, k)
# 输出旋转后的链表
result = []
while new_head:
result.append(new_head.val)
new_head = new_head.next
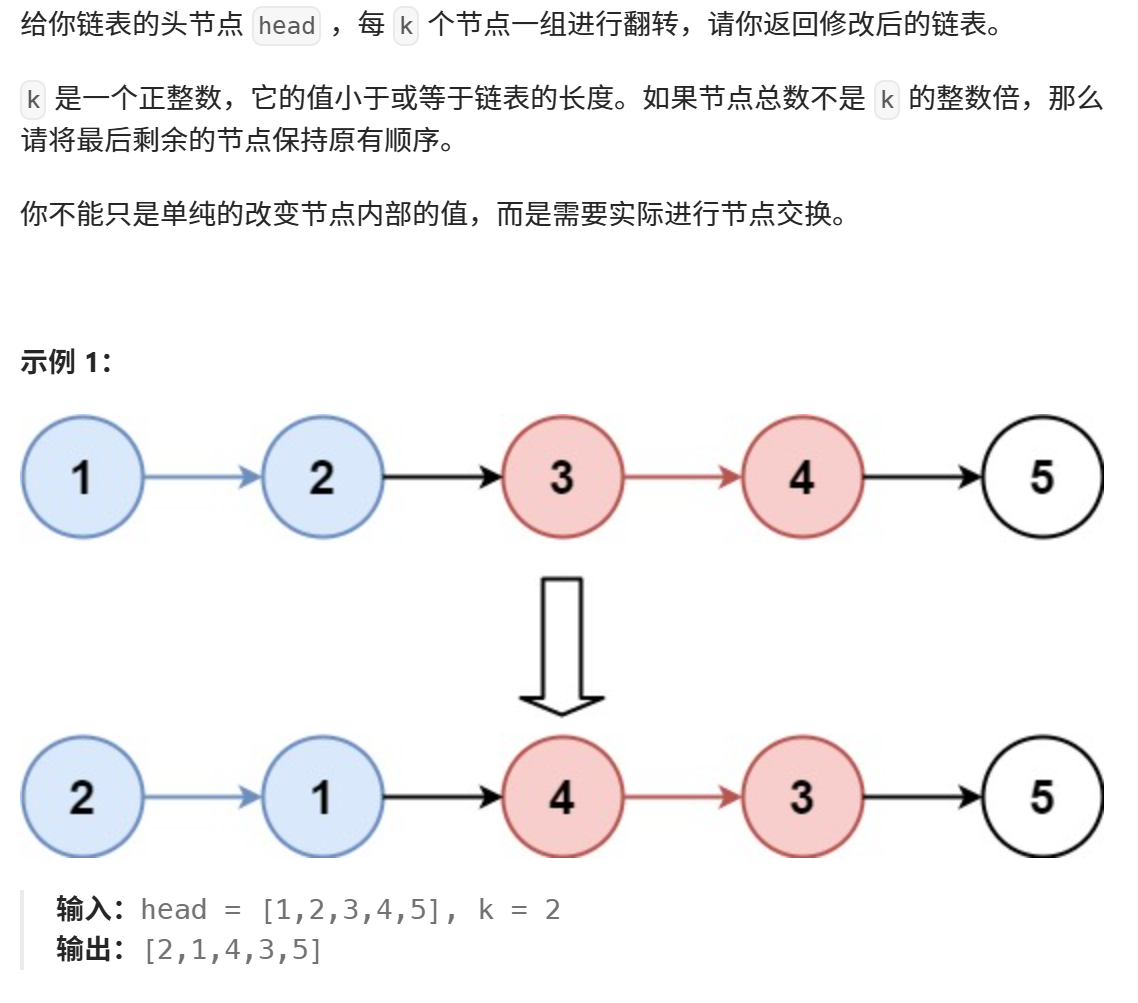
print("Rotated linked list:", result) # 预期输出: [4, 5, 1, 2, 3]25.K个一组翻转链表
python
from typing import Optional
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
"""
更简洁的迭代实现
"""
# 创建虚拟头节点
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
prev = dummy
while True:
# 检查剩余节点是否足够k个
check = prev
for _ in range(k):
if not check.next:
return dummy.next
check = check.next
# 翻转当前k个节点
# prev -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> next
# 翻转后:prev -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> next
# 记录当前组的第一个节点(翻转后将成为尾节点)
group_start = prev.next
# 记录当前组翻转后的尾节点
last = None
# 翻转k个节点
current = prev.next
for _ in range(k):
next_node = current.next
current.next = last
last = current
current = next_node
# 连接翻转后的组
prev.next = last # prev指向翻转后的头节点
group_start.next = current # 原组的第一个节点(现在是尾节点)指向下一组的头节点
# 更新prev为当前组的尾节点
prev = group_start
solution = Solution()
head = ListNode(1, ListNode(2, ListNode(3, ListNode(4, ListNode(5)))))
k = 2
new_head = solution.reverseKGroup(head, k)
# 输出翻转后的链表
result = []
while new_head:
result.append(new_head.val)
new_head = new_head.next
print("Reversed linked list in k-groups:", result)554.砖墙
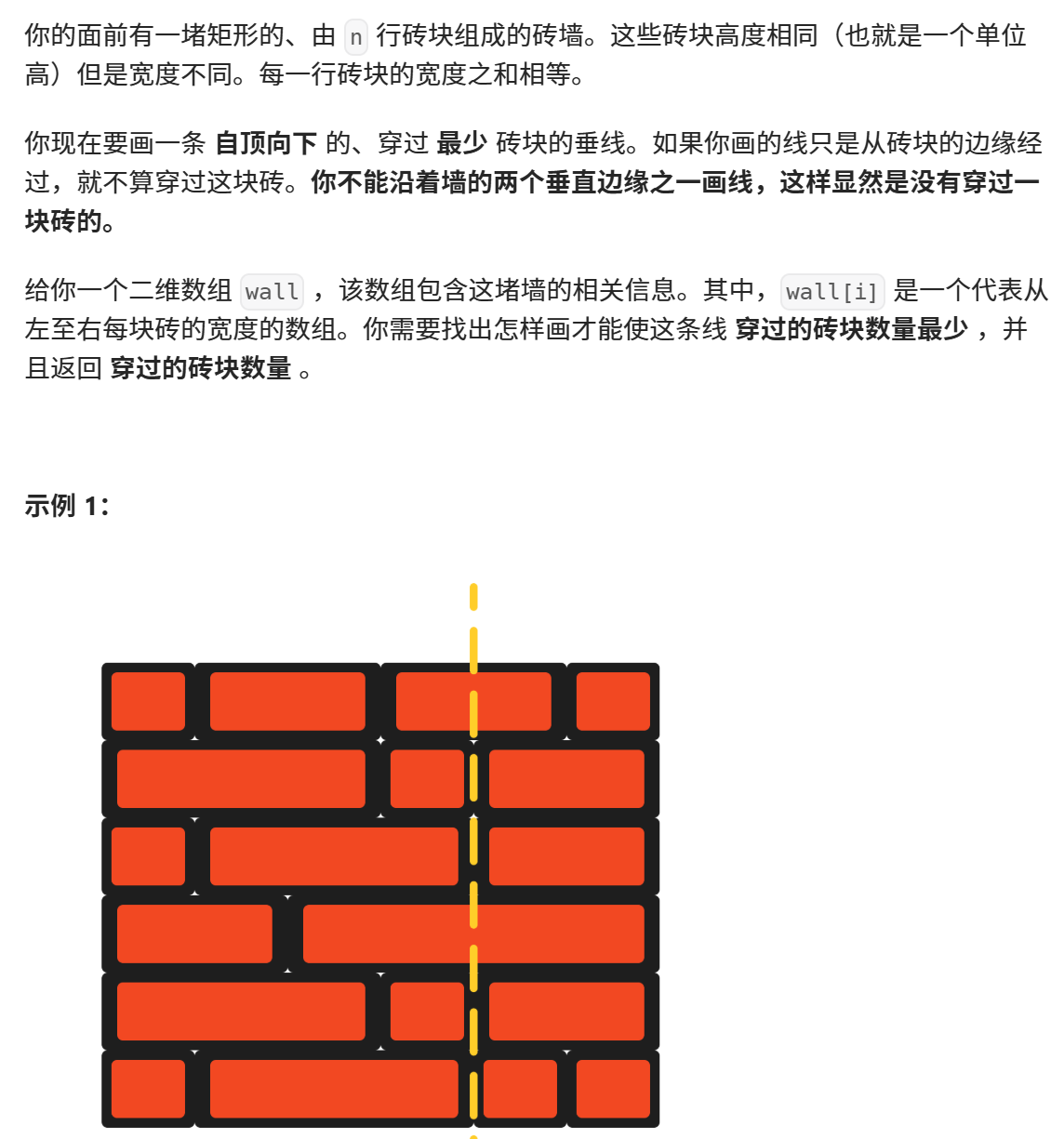

python
from typing import List
from collections import defaultdict
class Solution:
def leastBricks(self, wall: List[List[int]]) -> int:
"""
砖墙问题:找到穿过最少砖块的垂直线
思路:
1. 统计每个垂直缝隙的位置(前缀和)
2. 找到出现次数最多的缝隙位置
3. 最少的穿过砖块数 = 总行数 - 最多缝隙数量
时间复杂度:O(n×m),其中n是行数,m是每行的砖块数
空间复杂度:O(k),k是不同缝隙位置的数量
"""
if not wall:
return 0
# 使用字典统计每个缝隙位置出现的次数
gap_count = defaultdict(int)
# 遍历每一行砖块
for row in wall:
# 计算前缀和(缝隙位置)
prefix_sum = 0
# 注意:最后一个缝隙是墙的右边缘,不算有效缝隙
for brick in row[:-1]: # 不包括最后一块砖的右边缘
prefix_sum += brick
gap_count[prefix_sum] += 1
# 如果没有找到任何缝隙(比如每行只有一块砖)
if not gap_count:
return len(wall)
# 找到出现次数最多的缝隙
max_gaps = max(gap_count.values())
# 最少穿过砖块数 = 总行数 - 最多缝隙数
return len(wall) - max_gaps
solution = Solution()
# 测试用例1:题目示例
print("测试用例1:")
wall1 = [[1,2,2,1],[3,1,2],[1,3,2],[2,4],[3,1,2],[1,3,1]]
result1 = solution.leastBricks(wall1)
print(f"输入: wall = {wall1}")
print(f"输出: {result1}")
print(f"预期: 2")
print(f"正确: {result1 == 2}")729.我的日程安排表

python
import bisect
class MyCalendar:
def __init__(self):
"""
使用两个列表分别存储开始时间和结束时间,并保持有序
"""
self.starts = [] # 开始时间列表(有序)
self.ends = [] # 结束时间列表(对应有序)
def book(self, startTime: int, endTime: int) -> bool:
"""
使用二分查找找到插入位置,检查前后是否有重叠
"""
# 使用bisect找到startTime应该插入的位置
pos = bisect.bisect_right(self.starts, startTime)
# 检查与前一个区间是否重叠(如果pos > 0)
# 当前一个区间的结束时间 > startTime,则重叠
if pos > 0 and self.ends[pos-1] > startTime:
return False
# 检查与后一个区间是否重叠(如果pos < len(self.starts))
# 如果endTime > 后一个区间的开始时间,则重叠
if pos < len(self.starts) and endTime > self.starts[pos]:
return False
# 没有重叠,插入新区间
self.starts.insert(pos, startTime)
self.ends.insert(pos, endTime)
return True
print("测试用例1:")
calendar = MyCalendar()
print(calendar.book(10, 20)) # True
print(calendar.book(15, 25)) # False,与[10,20)重叠
print(calendar.book(20, 30)) # True,刚好相邻不重叠DFS
105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
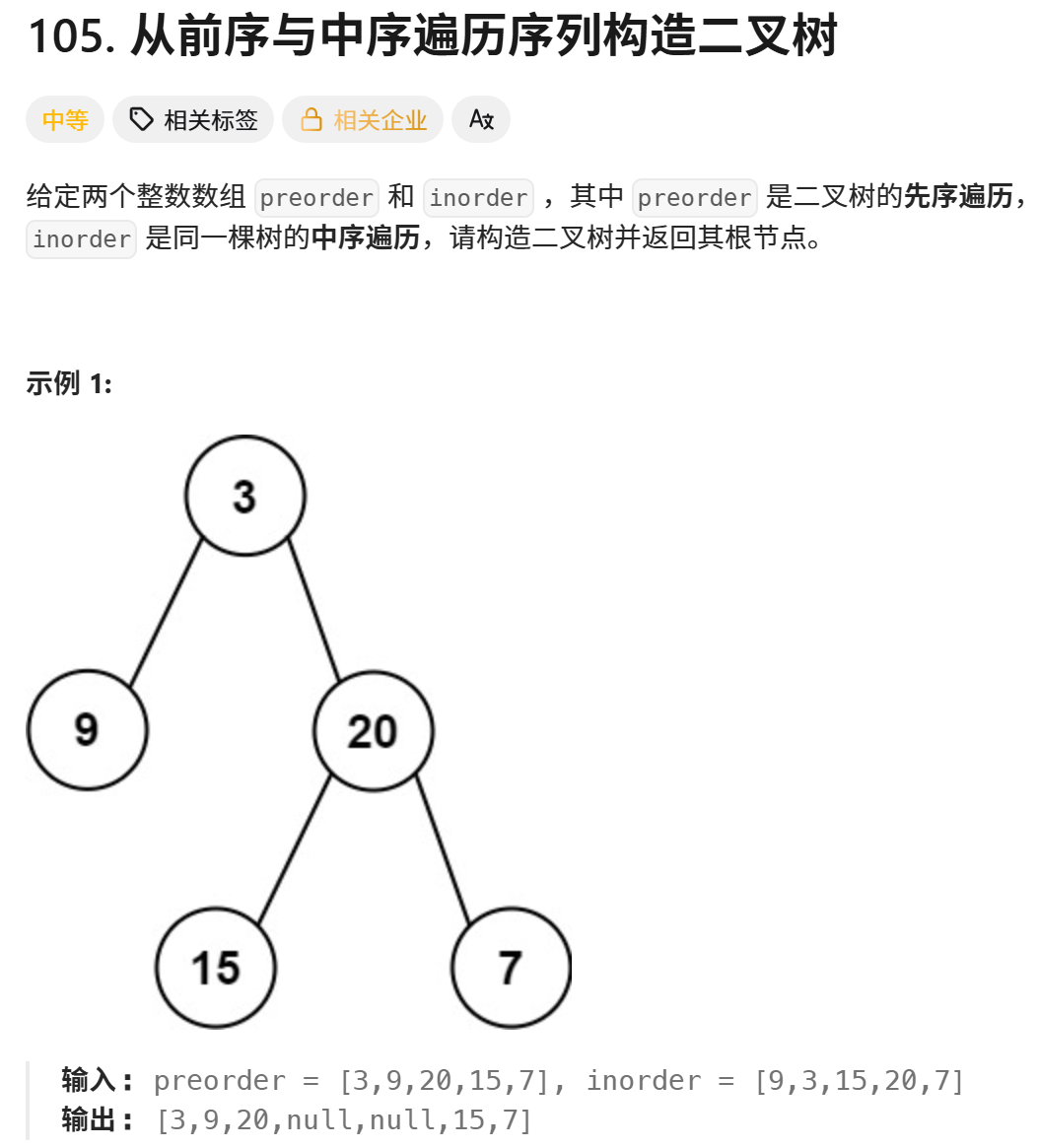
python
from typing import List, Optional
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
"""
更简洁的递归实现
"""
if not preorder or not inorder:
return None
# 前序遍历的第一个元素是根节点
root_val = preorder[0]
root = TreeNode(root_val)
# 在中序遍历中找到根节点的位置
root_index = inorder.index(root_val)
# 递归构建左右子树
# 左子树的前序遍历:preorder[1:root_index+1]
# 左子树的中序遍历:inorder[:root_index]
root.left = self.buildTree(preorder[1:root_index+1], inorder[:root_index])
# 右子树的前序遍历:preorder[root_index+1:]
# 右子树的中序遍历:inorder[root_index+1:]
root.right = self.buildTree(preorder[root_index+1:], inorder[root_index+1:])
return root
solution = Solution()
preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
root = solution.buildTree(preorder, inorder)
print("Root of the constructed tree:", root.val) # 输出根节点的值112.路径总和
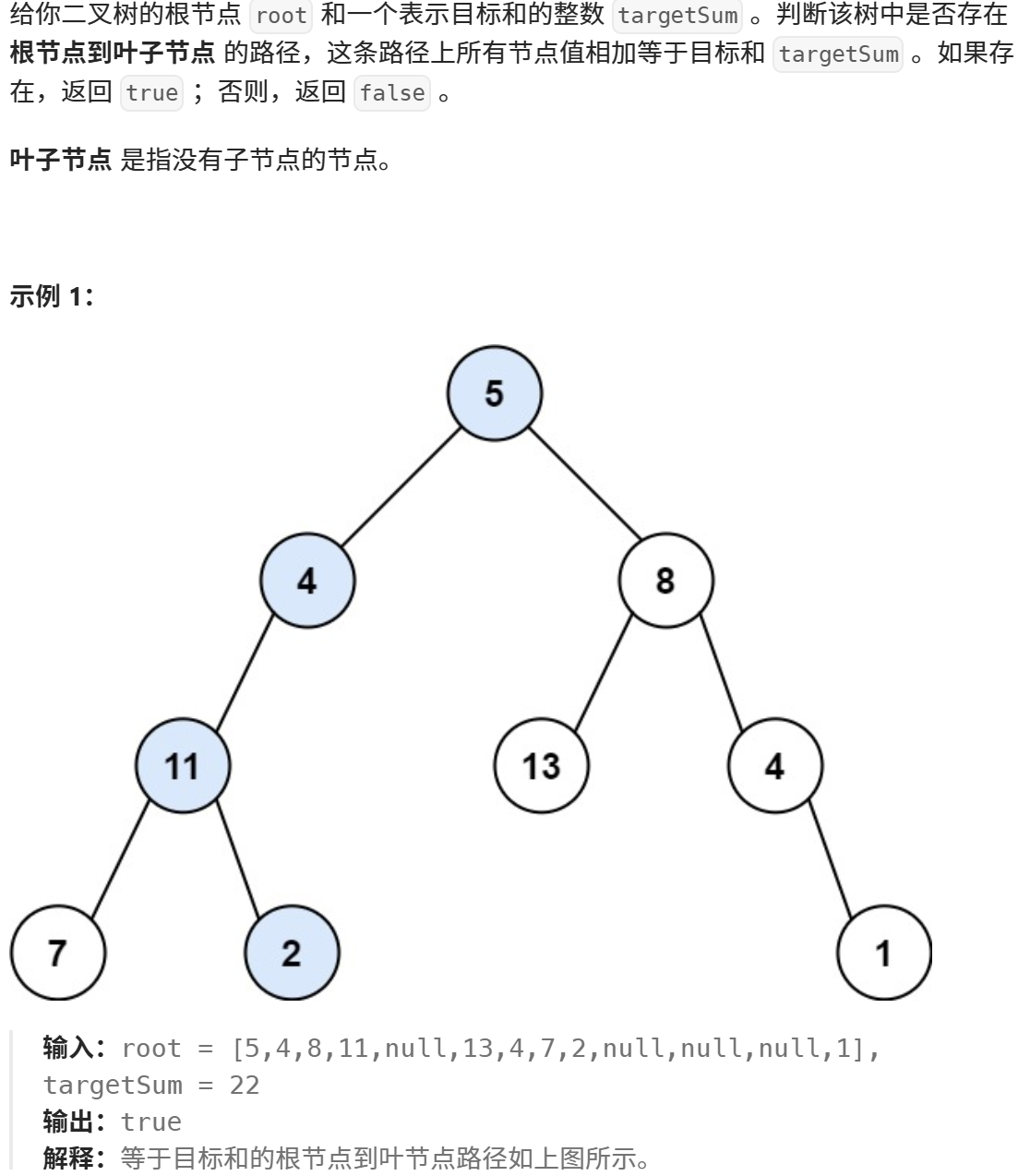
python
from typing import Optional
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
"""
非常简洁的递归实现(一行代码)
"""
if not root:
return False
if not root.left and not root.right:
return targetSum == root.val
return self.hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val)
# 示例用法
solution = Solution()
root = TreeNode(5)
root.left = TreeNode(4)
root.right = TreeNode(8)
root.left.left = TreeNode(11)
root.left.left.left = TreeNode(7)
root.left.left.right = TreeNode(2)
root.right.left = TreeNode(13)
root.right.right = TreeNode(4)
targetSum = 22
print("Has path sum:", solution.hasPathSum(root, targetSum)) # 输出: Has path sum: True98.验证二叉搜索树
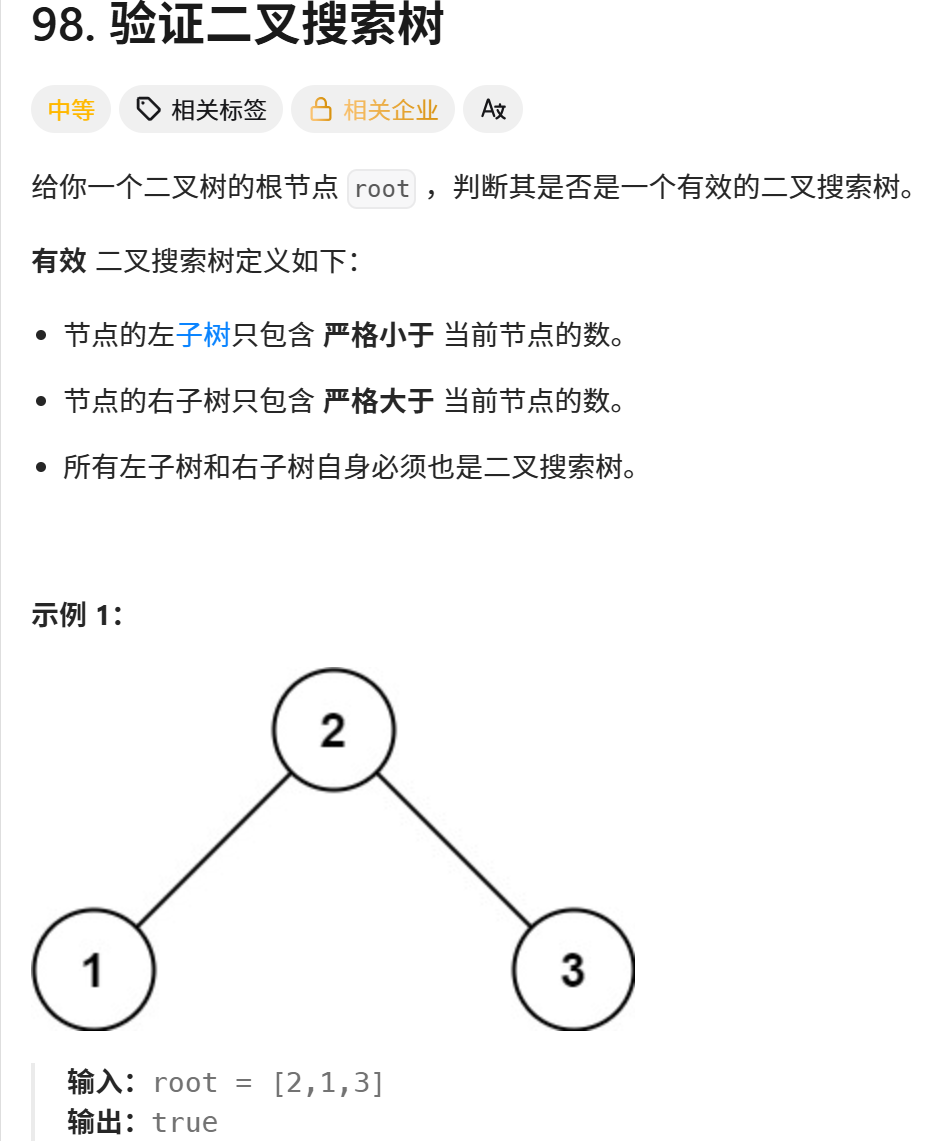
python
from typing import Optional
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
"""
验证二叉搜索树
方法一:递归传递范围
每个节点都有一个允许的值范围(min_val, max_val)
左子树的值必须在 (min_val, root.val) 范围内
右子树的值必须在 (root.val, max_val) 范围内
时间复杂度:O(n),每个节点访问一次
空间复杂度:O(h),递归栈空间,h为树的高度
"""
def validate(node: Optional[TreeNode], min_val: float, max_val: float) -> bool:
"""
递归验证节点是否在有效范围内
参数:
node: 当前节点
min_val: 允许的最小值(不包含)
max_val: 允许的最大值(不包含)
"""
# 空节点是有效的BST
if not node:
return True
# 检查当前节点值是否在允许范围内
if node.val <= min_val or node.val >= max_val:
return False
# 递归验证左子树和右子树
# 左子树的最大值不能超过当前节点值
# 右子树的最小值不能小于当前节点值
return (validate(node.left, min_val, node.val) and
validate(node.right, node.val, max_val))
# 初始调用,根节点的值可以是任意值,所以使用正负无穷大作为范围边界
return validate(root, float('-inf'), float('inf'))
# 示例用法
solution = Solution()
# 构建一个示例二叉树
# 2
# / \
# 1 3
root = TreeNode(2)
root.left = TreeNode(1)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
print("Is valid BST:", solution.isValidBST(root)) # 输出: Is valid BST: True494.目标和

python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def findTargetSumWays(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
"""
将问题转化为子集和问题
设添加'+'的数字和为p,添加'-'的数字和为q
则 p + q = sum, p - q = target
解得 p = (sum + target) // 2
问题转化为:从nums中选择若干数,使其和为p的组合数
"""
total_sum = sum(nums)
# 如果target的绝对值大于总和,不可能实现
if abs(target) > total_sum:
return 0
# 如果(sum + target)为奇数,不可能实现
if (total_sum + target) % 2 == 1:
return 0
# 计算目标和
target_sum = (total_sum + target) // 2
# 确保target_sum非负
if target_sum < 0:
return 0
# 动态规划:dp[i]表示和为i的组合数
dp = [0] * (target_sum + 1)
dp[0] = 1 # 和为0只有一种方式:不选任何数
for num in nums:
# 从后往前遍历,避免重复使用同一个数字
for i in range(target_sum, num - 1, -1):
dp[i] += dp[i - num]
return dp[target_sum]
# 示例用法
solution = Solution()
nums = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
target = 3
print("Number of ways:", solution.findTargetSumWays(nums, target)) # 输出: Number of ways: 5547.省份数量

python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def findCircleNum(self, isConnected: List[List[int]]) -> int:
"""
使用DFS求解省份数量
思路:
1. 创建一个访问标记数组
2. 对每个未访问的城市,进行DFS遍历所有相连的城市
3. 每次DFS开始计数一个省份
时间复杂度:O(n²)
空间复杂度:O(n)
"""
n = len(isConnected)
visited = [False] * n
provinces = 0
def dfs(city: int):
"""深度优先搜索,标记所有相连的城市"""
visited[city] = True
# 遍历所有其他城市
for neighbor in range(n):
# 如果两个城市相连且邻居城市未被访问
if isConnected[city][neighbor] == 1 and not visited[neighbor]:
dfs(neighbor)
# 遍历所有城市
for city in range(n):
if not visited[city]:
# 开始一个新的省份
provinces += 1
dfs(city)
return provinces
# 示例用法
solution = Solution()
isConnected = [
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1]
]
print("Number of provinces:", solution.findCircleNum(isConnected)) # 输出: Number of provinces: 21254.统计封闭岛屿的数目

python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def closedIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
"""
统计封闭岛屿的数量
思路:
1. 先处理边界上的岛屿(将它们标记为已访问,因为它们不是封闭的)
2. 然后遍历内部,统计剩余的岛屿数量
时间复杂度:O(m×n),其中m和n是网格的行数和列数
空间复杂度:O(m×n),最坏情况下递归栈空间
"""
if not grid or not grid[0]:
return 0
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
def dfs(i: int, j: int):
"""深度优先搜索,将相连的陆地标记为已访问"""
# 边界检查
if i < 0 or i >= m or j < 0 or j >= n:
return
# 如果是水域或已访问,返回
if grid[i][j] == 1:
return
# 标记为已访问(修改为1,表示水域)
grid[i][j] = 1
# 向四个方向搜索
dfs(i - 1, j) # 上
dfs(i + 1, j) # 下
dfs(i, j - 1) # 左
dfs(i, j + 1) # 右
# 步骤1:处理边界上的岛屿(将它们标记为水域)
# 因为边界上的岛屿不可能被完全包围
# 处理第一行和最后一行
for j in range(n):
if grid[0][j] == 0: # 第一行
dfs(0, j)
if grid[m - 1][j] == 0: # 最后一行
dfs(m - 1, j)
# 处理第一列和最后一列
for i in range(m):
if grid[i][0] == 0: # 第一列
dfs(i, 0)
if grid[i][n - 1] == 0: # 最后一列
dfs(i, n - 1)
# 步骤2:统计内部封闭岛屿的数量
count = 0
for i in range(1, m - 1):
for j in range(1, n - 1):
if grid[i][j] == 0:
count += 1
dfs(i, j)
return count
# 示例用法
solution = Solution()
grid = [
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0],
[1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0],
[1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0],
[1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1],
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0]
]
print("Number of closed islands:", solution.closedIsland(grid)) # 输出: Number of closed islands: 2BFS
1091.二进制矩阵中的最短路径
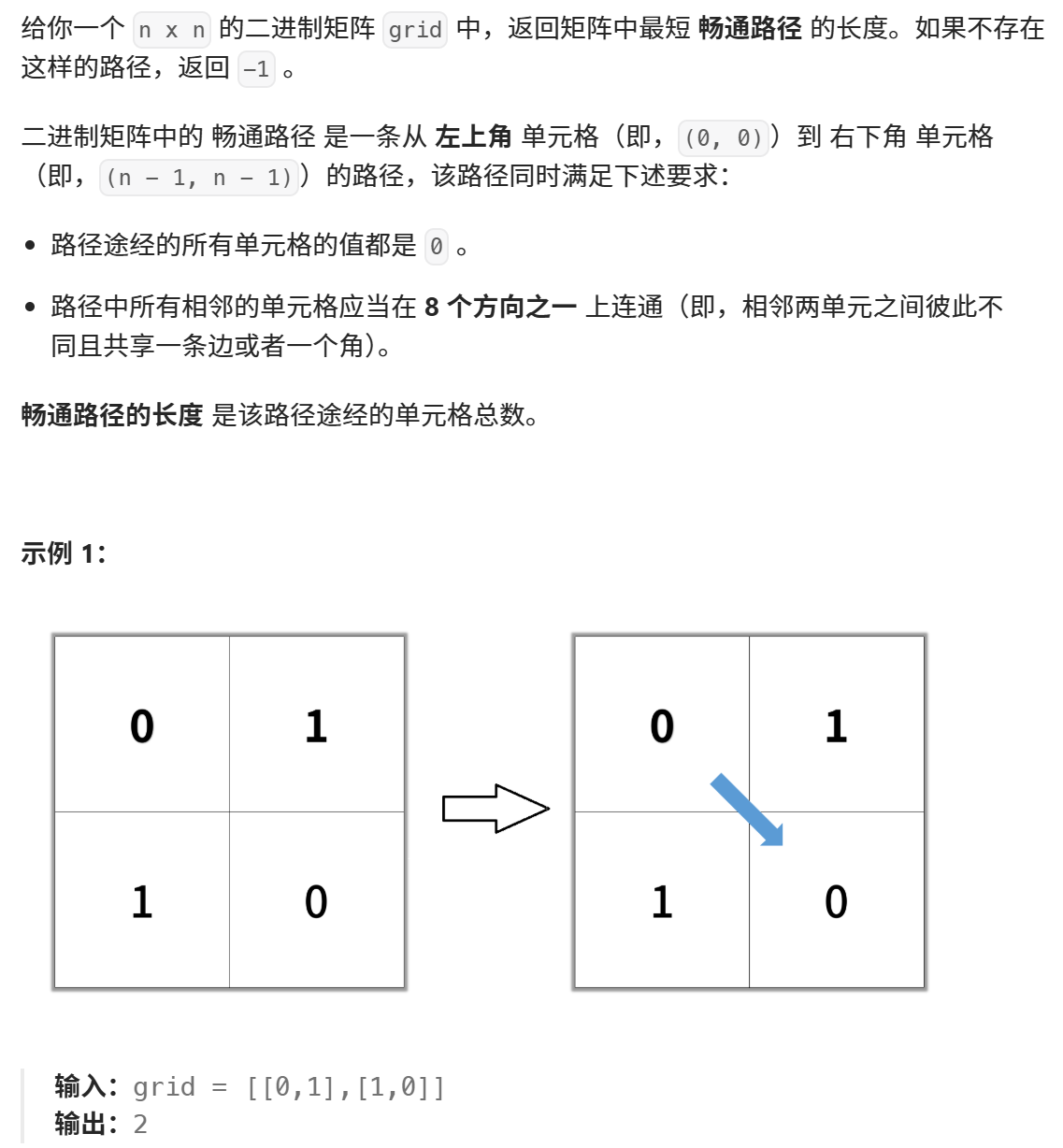
python
from typing import List
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
"""
在二进制矩阵中寻找最短畅通路径
思路:
1. 使用BFS寻找最短路径
2. 可以从8个方向移动
3. 路径必须全部由0组成
时间复杂度:O(n²),其中n是矩阵边长
空间复杂度:O(n²),用于存储队列和访问标记
"""
n = len(grid)
# 如果起点或终点是1,直接返回-1
if grid[0][0] == 1 or grid[n-1][n-1] == 1:
return -1
# 如果只有一个单元格且为0
if n == 1:
return 1
# 8个方向:上、下、左、右、左上、右上、左下、右下
directions = [
(-1, -1), (-1, 0), (-1, 1), # 左上、上、右上
(0, -1), (0, 1), # 左、右
(1, -1), (1, 0), (1, 1) # 左下、下、右下
]
# 使用队列进行BFS,存储(x, y, distance)
queue = deque()
queue.append((0, 0, 1)) # 起点,距离为1
# 标记已访问的单元格,避免重复访问
visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(n)]
visited[0][0] = True
while queue:
x, y, dist = queue.popleft()
# 尝试8个方向
for dx, dy in directions:
new_x, new_y = x + dx, y + dy
# 检查是否在边界内
if 0 <= new_x < n and 0 <= new_y < n:
# 如果是终点
if new_x == n-1 and new_y == n-1 and grid[new_x][new_y] == 0:
return dist + 1
# 如果是可访问的单元格且未访问过
if grid[new_x][new_y] == 0 and not visited[new_x][new_y]:
visited[new_x][new_y] = True
queue.append((new_x, new_y, dist + 1))
# 如果队列为空仍未到达终点,返回-1
return -1
# 示例用法
solution = Solution()
grid = [
[0, 1],
[1, 0]
]
print("Shortest path length:", solution.shortestPathBinaryMatrix(grid)) # 输出: Shortest path length: 21129.颜色交替的最短路径

python
from typing import List
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def shortestAlternatingPaths(self, n: int, redEdges: List[List[int]], blueEdges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
# 构建邻接表
red_adj = [[] for _ in range(n)]
blue_adj = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v in redEdges:
red_adj[u].append(v)
for u, v in blueEdges:
blue_adj[u].append(v)
# visited[i][0] 表示是否通过红色边到达过节点 i
# visited[i][1] 表示是否通过蓝色边到达过节点 i
visited = [[False, False] for _ in range(n)]
# 初始化答案数组,-1 表示不可达
answer = [-1] * n
answer[0] = 0 # 节点 0 到自身的距离为 0
# BFS 队列,元素为 (节点, 最后一条边的颜色, 步数)
# 颜色表示:0 表示红色,1 表示蓝色
queue = deque()
# 起点可以以两种颜色状态开始(表示第一条边可以是红色或蓝色)
queue.append((0, 0, 0)) # (节点, 颜色, 步数)
queue.append((0, 1, 0))
visited[0][0] = visited[0][1] = True
while queue:
node, color, steps = queue.popleft()
# 下一个需要交替的颜色
next_color = 1 - color
# 根据颜色选择邻接表
adj = red_adj if next_color == 0 else blue_adj
for neighbor in adj[node]:
if not visited[neighbor][next_color]:
visited[neighbor][next_color] = True
if answer[neighbor] == -1:
answer[neighbor] = steps + 1
queue.append((neighbor, next_color, steps + 1))
return answer
# 示例用法
solution = Solution()
n = 3
redEdges = [[0,1],[1,2]]
blueEdges = []
print("Shortest alternating paths:", solution.shortestAlternatingPaths(n, redEdges, blueEdges)) # 输出: Shortest alternating paths: [0, 1, -1]102.二叉树的层序遍历
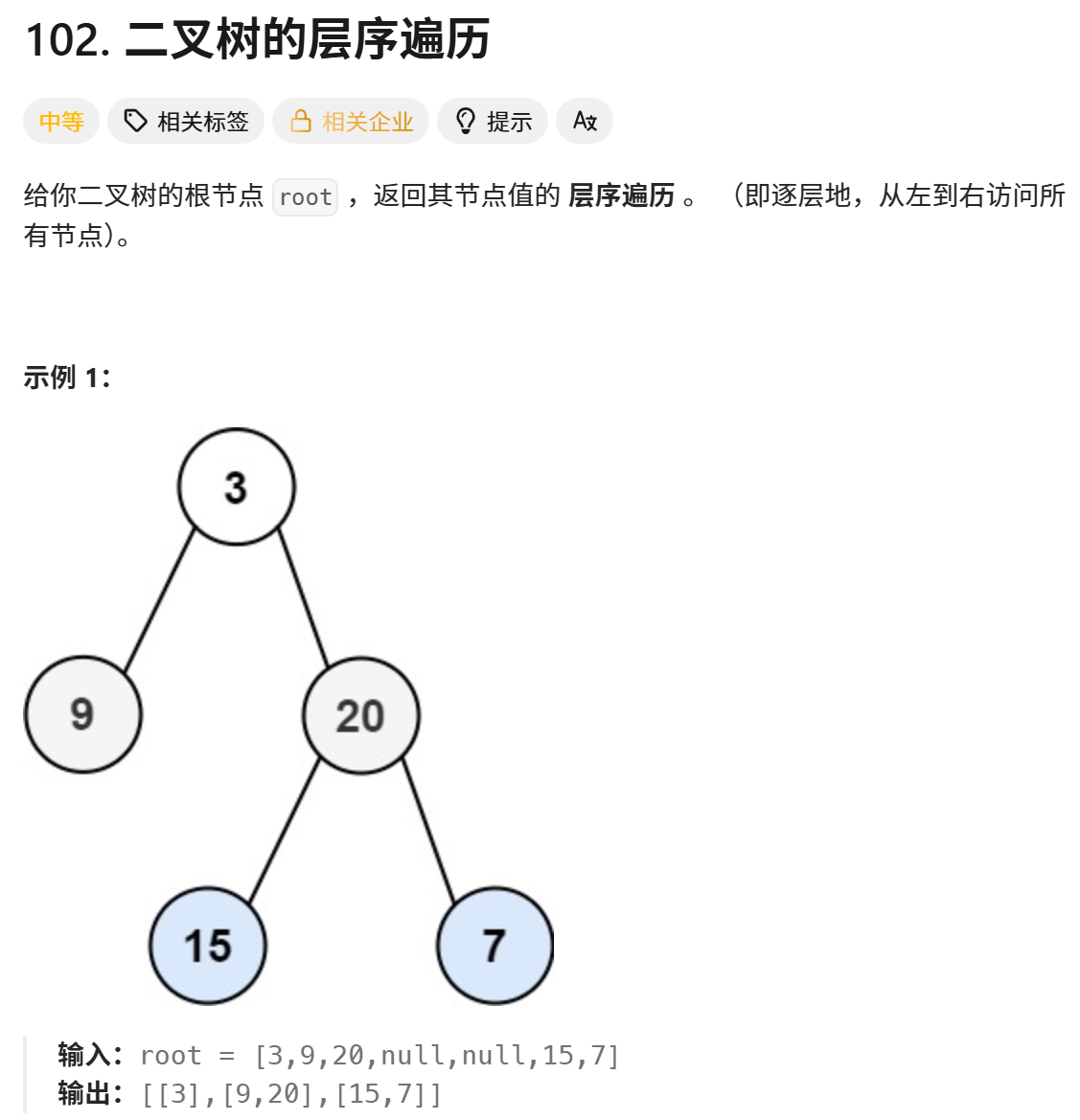
python
from typing import List, Optional
from collections import deque
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
"""
二叉树的层序遍历
使用队列进行广度优先搜索(BFS)
时间复杂度:O(n),每个节点访问一次
空间复杂度:O(n),队列中最多存储一层节点
"""
if not root:
return []
result = []
queue = deque([root]) # 使用队列存储节点
while queue:
level_size = len(queue) # 当前层的节点数
level_values = [] # 存储当前层的节点值
# 遍历当前层的所有节点
for _ in range(level_size):
node = queue.popleft()
level_values.append(node.val)
# 将子节点加入队列(先左后右)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
result.append(level_values)
return result
# 示例用法
solution = Solution()
# 构建一个示例二叉树
# 3
# / \
# 9 20
root = TreeNode(3)
root.left = TreeNode(9)
root.right = TreeNode(20)
root.right.left = TreeNode(15)
root.right.right = TreeNode(7)
print("Level order traversal:", solution.levelOrder(root)) # 输出: Level order traversal:101.对称二叉树
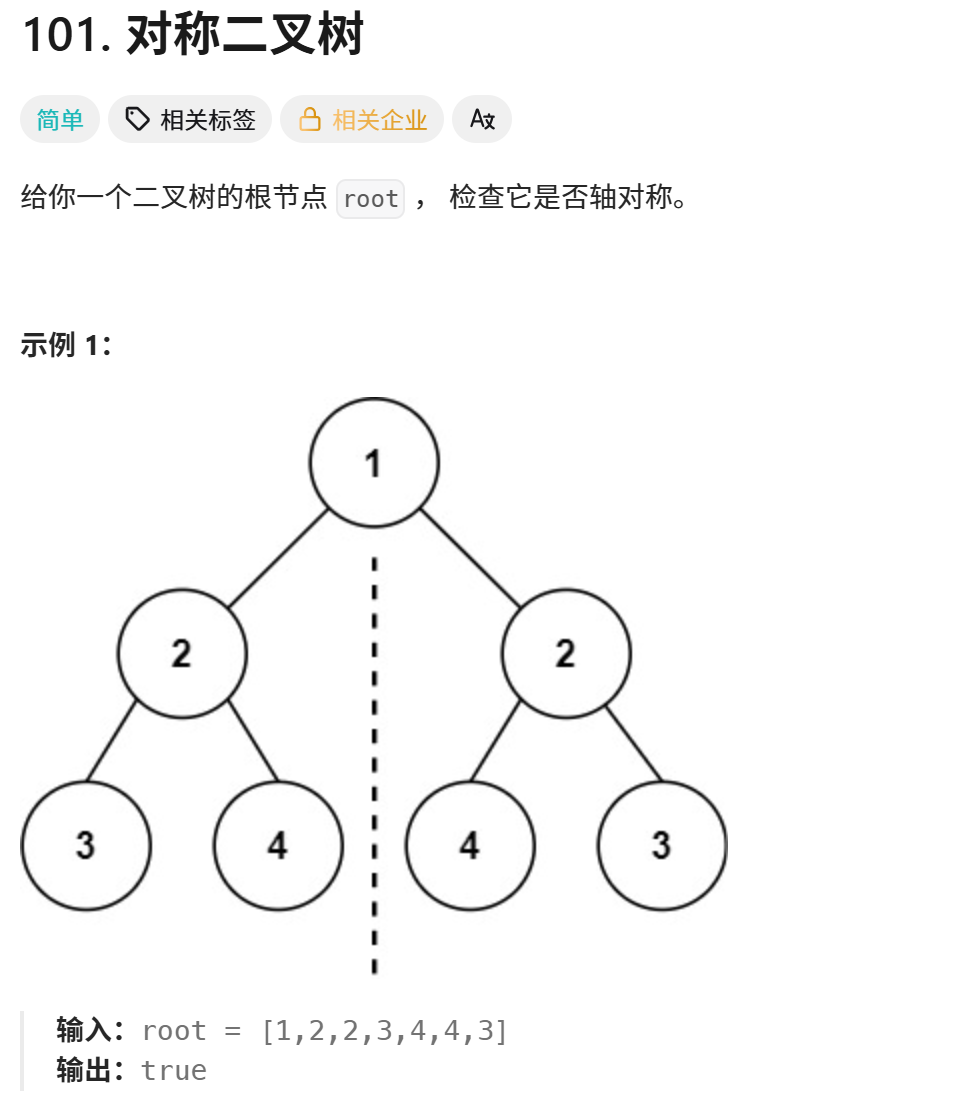
python
from typing import Optional
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
"""
检查二叉树是否轴对称
递归方法:
1. 如果根节点为空,返回True
2. 定义一个辅助函数检查两个树是否镜像对称
3. 检查左右子树是否镜像
时间复杂度:O(n),每个节点访问一次
空间复杂度:O(h),递归栈深度,h为树的高度
"""
if not root:
return True
def is_mirror(left: Optional[TreeNode], right: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
# 两个都为空,对称
if not left and not right:
return True
# 一个为空一个不为空,不对称
if not left or not right:
return False
# 值不相等,不对称
if left.val != right.val:
return False
# 递归检查:左子树的左节点和右子树的右节点,左子树的右节点和右子树的左节点
return (is_mirror(left.left, right.right) and
is_mirror(left.right, right.left))
return is_mirror(root.left, root.right)
# 示例用法
solution = Solution()
# 构建一个示例二叉树
# 1
# / \
# 2 2
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(2)
print("Is symmetric:", solution.isSymmetric(root)) # 输出: Is symmetric: True752.打开转盘锁

python
from typing import List
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def openLock(self, deadends: List[str], target: str) -> int:
"""
打开转盘锁的最少旋转次数
思路:使用BFS搜索从"0000"到target的最短路径
每个状态有8个邻居(4个拨轮,每个可以向上或向下转一次)
死亡数字deadends相当于障碍,不能访问
时间复杂度:O(10000) = O(1),因为状态空间是有限的
空间复杂度:O(10000)
"""
# 特殊情况处理
if target == "0000":
return 0
# 将deadends转换为集合,方便快速查找
deadends_set = set(deadends)
if "0000" in deadends_set:
return -1
# BFS队列,存储(当前密码, 步数)
queue = deque()
queue.append(("0000", 0))
# 记录已访问的状态
visited = set()
visited.add("0000")
# BFS搜索
while queue:
current, steps = queue.popleft()
# 生成所有可能的下一步状态
for i in range(4): # 4个拨轮
# 向上转
next_up = self.rotate_up(current, i)
if next_up == target:
return steps + 1
if next_up not in visited and next_up not in deadends_set:
visited.add(next_up)
queue.append((next_up, steps + 1))
# 向下转
next_down = self.rotate_down(current, i)
if next_down == target:
return steps + 1
if next_down not in visited and next_down not in deadends_set:
visited.add(next_down)
queue.append((next_down, steps + 1))
# 无法解锁
return -1
def rotate_up(self, s: str, i: int) -> str:
"""
将第i位数字向上旋转(加1),0->1, 1->2, ..., 9->0
"""
num = int(s[i])
num = (num + 1) % 10
return s[:i] + str(num) + s[i+1:]
def rotate_down(self, s: str, i: int) -> str:
"""
将第i位数字向下旋转(减1),0->9, 1->0, ..., 9->8
"""
num = int(s[i])
num = (num - 1) % 10
return s[:i] + str(num) + s[i+1:]
# 示例用法
solution = Solution()
deadends = ["0201","0101","0102","1212","2002"]
target = "0202"
print("Minimum moves to unlock:", solution.openLock(deadends, target)) # 输出: Minimum moves to unlock: 6