Flutter for OpenHarmony 进阶:表达式解析算法与计算器核心实现
文章目录
- [Flutter for OpenHarmony 进阶:表达式解析算法与计算器核心实现](#Flutter for OpenHarmony 进阶:表达式解析算法与计算器核心实现)
-
- 摘要
- 一、表达式解析概述
-
- [1.1 表达式类型](#1.1 表达式类型)
- [1.2 运算符优先级](#1.2 运算符优先级)
- [1.3 解析流程](#1.3 解析流程)
- 二、中缀表达式转后缀表达式
-
- [2.1 转换算法(调度场算法)](#2.1 转换算法(调度场算法))
- [2.2 词法分析](#2.2 词法分析)
- [2.3 完整转换示例](#2.3 完整转换示例)
- 三、后缀表达式求值
-
- [3.1 求值算法](#3.1 求值算法)
- [3.2 求值过程示例](#3.2 求值过程示例)
- 四、双栈算法实现
-
- [4.1 一次遍历算法](#4.1 一次遍历算法)
- [4.2 支持括号的算法](#4.2 支持括号的算法)
- 五、浮点数精度处理
-
- [5.1 浮点数精度问题](#5.1 浮点数精度问题)
- [5.2 精度处理方案](#5.2 精度处理方案)
- 六、高级运算符支持
-
- [6.1 幂运算](#6.1 幂运算)
- [6.2 科学计算函数](#6.2 科学计算函数)
- [6.3 扩展词法分析器](#6.3 扩展词法分析器)
- 七、错误处理机制
-
- [7.1 错误类型定义](#7.1 错误类型定义)
- [7.2 错误检测](#7.2 错误检测)
- [7.3 友好的错误提示](#7.3 友好的错误提示)
- 八、性能优化策略
-
- [8.1 缓存机制](#8.1 缓存机制)
- [8.2 懒惰求值](#8.2 懒惰求值)
- [8.3 增量计算](#8.3 增量计算)
- 九、总结
摘要
表达式解析是计算器应用的核心技术,涉及字符串分析、语法解析、数值计算等多个领域。本文深入讲解表达式解析算法的实现原理,详细介绍中缀表达式转后缀表达式、双栈求值算法、浮点数精度处理等高级技术点。通过本文学习,读者将掌握计算器核心算法的完整实现方案,了解如何构建高效、准确的表达式解析系统。
一、表达式解析概述
1.1 表达式类型
中缀表达式
- 运算符位于操作数中间
- 符合人类书写习惯
- 需要处理运算符优先级
- 示例:3 + 4 × 5
后缀表达式(逆波兰表示法)
- 运算符位于操作数后面
- 不需要括号和优先级
- 易于计算机处理
- 示例:3 4 5 × +
前缀表达式
- 运算符位于操作数前面
- Lisp语言采用此表示法
- 示例:+ 3 × 4 5
1.2 运算符优先级
| 优先级 | 运算符 | 结合性 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | () | 从左到右 |
| 2 | × ÷ % | 从左到右 |
| 3 | + - | 从左到右 |
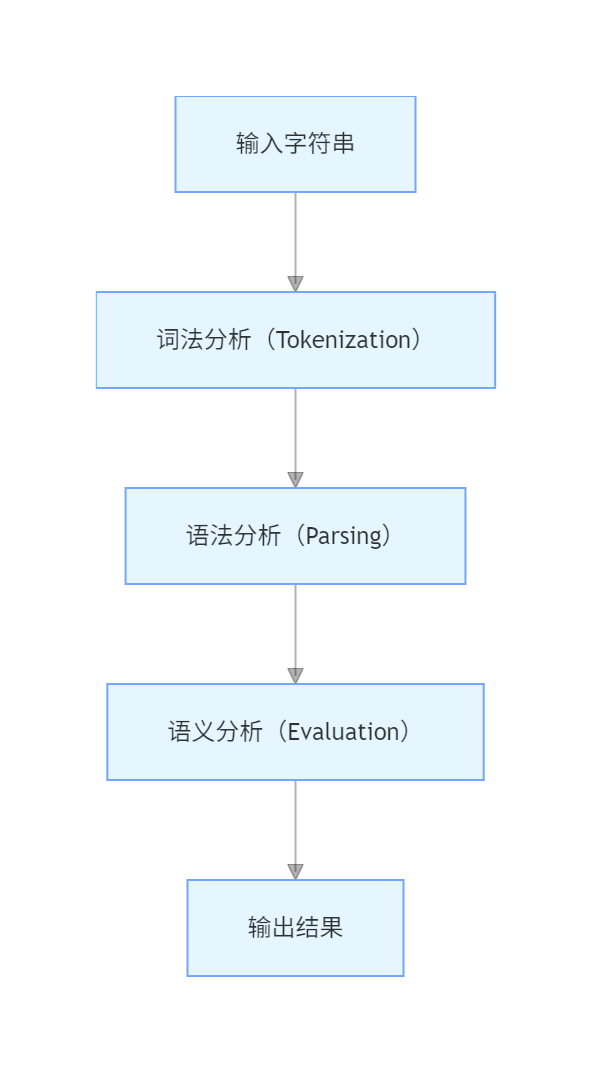
1.3 解析流程
二、中缀表达式转后缀表达式
2.1 转换算法(调度场算法)
dart
class ShuntingYardAlgorithm {
// 运算符优先级
int getPrecedence(String operator) {
switch (operator) {
case '+':
case '-':
return 1;
case '×':
case '÷':
case '%':
return 2;
default:
return 0;
}
}
// 判断是否为运算符
bool isOperator(String token) {
return ['+', '-', '×', '÷', '%'].contains(token);
}
// 中缀转后缀
List<String> infixToPostfix(List<String> infixTokens) {
List<String> output = [];
List<String> operatorStack = [];
for (var token in infixTokens) {
if (isOperator(token)) {
// 处理运算符
while (operatorStack.isNotEmpty &&
isOperator(operatorStack.last) &&
getPrecedence(operatorStack.last) >= getPrecedence(token)) {
output.add(operatorStack.removeLast());
}
operatorStack.add(token);
} else if (token == '(') {
// 左括号直接入栈
operatorStack.add(token);
} else if (token == ')') {
// 右括号:弹出直到左括号
while (operatorStack.isNotEmpty && operatorStack.last != '(') {
output.add(operatorStack.removeLast());
}
if (operatorStack.isNotEmpty) {
operatorStack.removeLast(); // 移除左括号
}
} else {
// 操作数直接输出
output.add(token);
}
}
// 弹出栈中剩余运算符
while (operatorStack.isNotEmpty) {
output.add(operatorStack.removeLast());
}
return output;
}
}2.2 词法分析
dart
class Lexer {
// 将表达式字符串转换为Token列表
static List<String> tokenize(String expression) {
List<String> tokens = [];
StringBuffer numberBuffer = StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < expression.length; i++) {
String char = expression[i];
if (isDigit(char) || char == '.') {
// 数字字符,添加到数字缓冲区
numberBuffer.write(char);
} else {
// 非数字字符
if (numberBuffer.isNotEmpty) {
tokens.add(numberBuffer.toString());
numberBuffer.clear();
}
if (char.trim().isNotEmpty) {
tokens.add(char);
}
}
}
// 添加最后一个数字
if (numberBuffer.isNotEmpty) {
tokens.add(numberBuffer.toString());
}
return tokens;
}
static bool isDigit(String char) {
return char.codeUnitAt(0) >= '0'.codeUnitAt(0) &&
char.codeUnitAt(0) <= '9'.codeUnitAt(0);
}
}2.3 完整转换示例
dart
void main() {
final algorithm = ShuntingYardAlgorithm();
// 示例:3 + 4 × 5
final infix = ['3', '+', '4', '×', '5'];
final postfix = algorithm.infixToPostfix(infix);
print('中缀: $infix');
print('后缀: $postfix');
// 输出: 中缀: [3, +, 4, ×, 5]
// 后缀: [3, 4, 5, ×, +]
}三、后缀表达式求值
3.1 求值算法
dart
class PostfixEvaluator {
// 后缀表达式求值
double evaluate(List<String> postfixTokens) {
List<double> stack = [];
for (var token in postfixTokens) {
if (_isNumber(token)) {
// 操作数入栈
stack.add(double.parse(token));
} else if (_isOperator(token)) {
// 运算符:弹出两个操作数进行计算
if (stack.length < 2) {
throw ArgumentError('表达式无效');
}
double b = stack.removeLast();
double a = stack.removeLast();
double result = _applyOperator(a, b, token);
stack.add(result);
}
}
if (stack.length != 1) {
throw ArgumentError('表达式无效');
}
return stack.last;
}
bool _isNumber(String token) {
return double.tryParse(token) != null;
}
bool _isOperator(String token) {
return ['+', '-', '×', '÷', '%'].contains(token);
}
double _applyOperator(double a, double b, String operator) {
switch (operator) {
case '+':
return a + b;
case '-':
return a - b;
case '×':
return a * b;
case '÷':
if (b == 0) {
throw ArgumentError('除数不能为零');
}
return a / b;
case '%':
return a % b;
default:
throw ArgumentError('未知运算符: $operator');
}
}
}3.2 求值过程示例
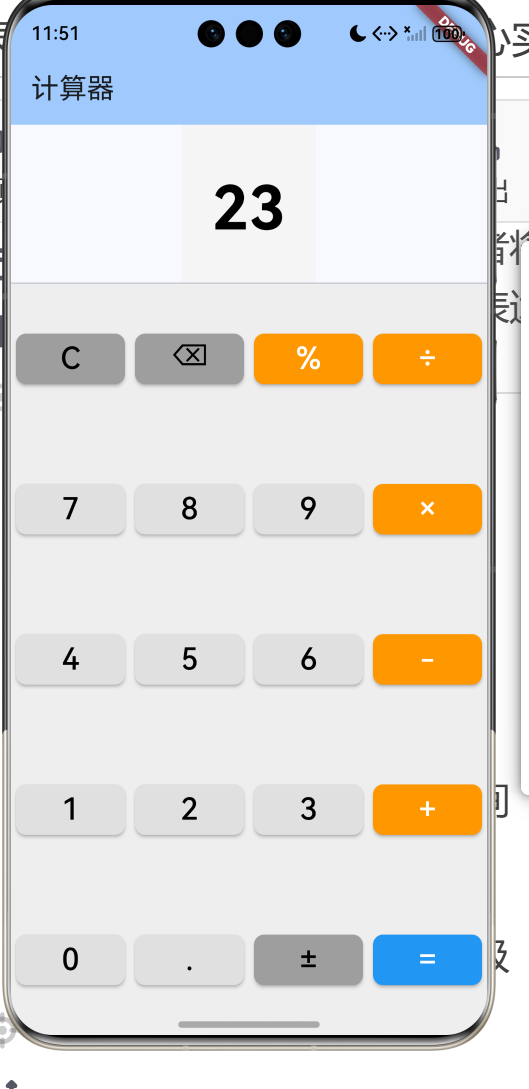
表达式:3 4 5 × +
步骤:
1. 3 → 栈: [3]
2. 4 → 栈: [3, 4]
3. 5 → 栈: [3, 4, 5]
4. × → 弹出5, 4,计算 4×5=20 → 栈: [3, 20]
5. + → 弹出20, 3,计算 3+20=23 → 栈: [23]
结果: 23
四、双栈算法实现
4.1 一次遍历算法
dart
class ExpressionParser {
// 运算符栈和操作数栈
List<double> _operandStack = [];
List<String> _operatorStack = [];
// 运算符优先级
int _getPrecedence(String op) {
switch (op) {
case '+':
case '-':
return 1;
case '×':
case '÷':
case '%':
return 2;
default:
return 0;
}
}
// 判断是否需要计算
bool _shouldCalculate(String newOperator) {
if (_operatorStack.isEmpty) return false;
String topOperator = _operatorStack.last;
return _getPrecedence(topOperator) >= _getPrecedence(newOperator);
}
// 执行一次计算
void _calculate() {
if (_operandStack.length < 2 || _operatorStack.isEmpty) {
return;
}
double b = _operandStack.removeLast();
double a = _operandStack.removeLast();
String operator = _operatorStack.removeLast();
double result;
switch (operator) {
case '+':
result = a + b;
break;
case '-':
result = a - b;
break;
case '×':
result = a * b;
break;
case '÷':
if (b == 0) {
throw ArgumentError('除数不能为零');
}
result = a / b;
break;
case '%':
result = a % b;
break;
default:
throw ArgumentError('未知运算符: $operator');
}
_operandStack.add(result);
}
// 解析并计算表达式
double parse(String expression) {
_operandStack.clear();
_operatorStack.clear();
List<String> tokens = Lexer.tokenize(expression);
for (var token in tokens) {
double? number = double.tryParse(token);
if (number != null) {
// 操作数入栈
_operandStack.add(number);
} else if (['+', '-', '×', '÷', '%'].contains(token)) {
// 运算符:先计算高优先级运算
while (_shouldCalculate(token)) {
_calculate();
}
_operatorStack.add(token);
}
}
// 计算剩余运算
while (_operatorStack.isNotEmpty) {
_calculate();
}
if (_operandStack.length != 1) {
throw ArgumentError('表达式无效');
}
return _operandStack.last;
}
}4.2 支持括号的算法
dart
class AdvancedExpressionParser {
List<double> _operandStack = [];
List<String> _operatorStack = [];
int _getPrecedence(String op) {
if (op == '(') return 0;
switch (op) {
case '+':
case '-':
return 1;
case '×':
case '÷':
case '%':
return 2;
default:
return 0;
}
}
void _calculate() {
if (_operandStack.length < 2 || _operatorStack.isEmpty) return;
double b = _operandStack.removeLast();
double a = _operandStack.removeLast();
String operator = _operatorStack.removeLast();
double result = _applyOperator(a, b, operator);
_operandStack.add(result);
}
double _applyOperator(double a, double b, String operator) {
switch (operator) {
case '+':
return a + b;
case '-':
return a - b;
case '×':
return a * b;
case '÷':
return b == 0 ? double.nan : a / b;
case '%':
return a % b;
default:
throw ArgumentError('未知运算符: $operator');
}
}
double parse(String expression) {
_operandStack.clear();
_operatorStack.clear();
List<String> tokens = Lexer.tokenize(expression);
for (var token in tokens) {
double? number = double.tryParse(token);
if (number != null) {
_operandStack.add(number);
} else if (token == '(') {
_operatorStack.add(token);
} else if (token == ')') {
// 计算直到遇到左括号
while (_operatorStack.isNotEmpty && _operatorStack.last != '(') {
_calculate();
}
_operatorStack.removeLast(); // 移除左括号
} else if (['+', '-', '×', '÷', '%'].contains(token)) {
while (_operatorStack.isNotEmpty &&
_operatorStack.last != '(' &&
_getPrecedence(_operatorStack.last) >= _getPrecedence(token)) {
_calculate();
}
_operatorStack.add(token);
}
}
// 计算剩余运算
while (_operatorStack.isNotEmpty) {
_calculate();
}
return _operandStack.last;
}
}五、浮点数精度处理
5.1 浮点数精度问题
dart
void precisionDemo() {
print(0.1 + 0.2); // 0.30000000000000004
print(0.3 - 0.1); // 0.19999999999999998
print(1.2 × 3); // 3.5999999999999996
}5.2 精度处理方案
方案一:四舍五入
dart
class PrecisionHandler {
static const int DEFAULT_PRECISION = 10;
// 四舍五入到指定精度
static double round(double value, int precision) {
double factor = pow(10, precision).toDouble();
return (value * factor).roundToDouble() / factor;
}
// 智能格式化
static String format(double value) {
// 检查是否为整数
if (value == value.truncateToDouble()) {
return value.toInt().toString();
}
// 四舍五入
double rounded = round(value, DEFAULT_PRECISION);
// 检查四舍五入后是否为整数
if (rounded == rounded.truncateToDouble()) {
return rounded.toInt().toString();
}
// 转换为字符串并移除尾部零
String result = rounded.toString();
if (result.contains('.')) {
result = result.replaceAll(RegExp(r'0+$'), '');
result = result.replaceAll(RegExp(r'\.$'), '');
}
return result;
}
}方案二:使用BigInt
dart
class BigIntCalculator {
// 位数
final int scale;
BigIntCalculator({this.scale = 10});
// 转换为BigInt
BigInt toBigInt(double value) {
return (value * pow(10, scale)).toInt().toBigInt();
}
// 从BigInt转换回double
double fromBigInt(BigInt value) {
return value.toInt() / pow(10, scale);
}
// 加法
double add(double a, double b) {
BigInt bigA = toBigInt(a);
BigInt bigB = toBigInt(b);
return fromBigInt(bigA + bigB);
}
// 乘法
double multiply(double a, double b) {
BigInt bigA = toBigInt(a);
BigInt bigB = toBigInt(b);
return fromBigInt((bigA * bigB) ~/ BigInt.from(10).pow(scale));
}
}方案三:使用decimal包
dart
// pubspec.yaml
dependencies:
decimal: ^2.3.3
// 代码
import 'package:decimal/decimal.dart';
class DecimalCalculator {
static String calculate(String a, String b, String operator) {
Decimal decA = Decimal.parse(a);
Decimal decB = Decimal.parse(b);
Decimal result;
switch (operator) {
case '+':
result = decA + decB;
break;
case '-':
result = decA - decB;
break;
case '×':
result = decA * decB;
break;
case '÷':
result = decA / decB;
break;
default:
throw ArgumentError('未知运算符');
}
return result.toString();
}
}六、高级运算符支持
6.1 幂运算
dart
double power(double base, double exponent) {
return pow(base, exponent).toDouble();
}
// 添加到运算符判断
String _applyOperator(double a, double b, String operator) {
switch (operator) {
// ... 其他运算符
case '^':
return power(a, b);
default:
throw ArgumentError('未知运算符: $operator');
}
}6.2 科学计算函数
dart
class ScientificCalculator {
// 三角函数
static double sin(double radians) {
return dartMath.sin(radians);
}
static double cos(double radians) {
return dartMath.cos(radians);
}
static double tan(double radians) {
return dartMath.tan(radians);
}
// 对数函数
static double log(double value) {
if (value <= 0) {
throw ArgumentError('对数的真数必须大于零');
}
return dartMath.log(value);
}
static double log10(double value) {
if (value <= 0) {
throw ArgumentError('对数的真数必须大于零');
}
return dartMath.log(value) / dartMath.ln10;
}
// 平方根
static double sqrt(double value) {
if (value < 0) {
throw ArgumentError('不能对负数开平方');
}
return dartMath.sqrt(value);
}
// 阶乘
static int factorial(int n) {
if (n < 0) {
throw ArgumentError('阶乘的参数必须是非负整数');
}
if (n <= 1) return 1;
int result = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
result *= i;
}
return result;
}
}6.3 扩展词法分析器
dart
class AdvancedLexer {
static List<String> tokenize(String expression) {
List<String> tokens = [];
StringBuffer buffer = StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < expression.length; i++) {
String char = expression[i];
// 处理函数名
if (isLetter(char)) {
buffer.write(char);
// 读取完整的函数名
while (i + 1 < expression.length && isLetter(expression[i + 1])) {
i++;
buffer.write(expression[i]);
}
tokens.add(buffer.toString());
buffer.clear();
}
// 处理数字
else if (isDigit(char) || char == '.') {
buffer.write(char);
while (i + 1 < expression.length &&
(isDigit(expression[i + 1]) || expression[i + 1] == '.')) {
i++;
buffer.write(expression[i]);
}
tokens.add(buffer.toString());
buffer.clear();
}
// 处理运算符和括号
else if (char.trim().isNotEmpty) {
tokens.add(char);
}
}
return tokens;
}
static bool isLetter(String char) {
return (char.codeUnitAt(0) >= 'A'.codeUnitAt(0) &&
char.codeUnitAt(0) <= 'Z'.codeUnitAt(0)) ||
(char.codeUnitAt(0) >= 'a'.codeUnitAt(0) &&
char.codeUnitAt(0) <= 'z'.codeUnitAt(0));
}
static bool isDigit(String char) {
return char.codeUnitAt(0) >= '0'.codeUnitAt(0) &&
char.codeUnitAt(0) <= '9'.codeUnitAt(0);
}
}七、错误处理机制
7.1 错误类型定义
dart
enum CalculatorErrorType {
syntaxError, // 语法错误
divisionByZero, // 除以零
invalidOperator, // 无效运算符
mismatchedParentheses, // 括号不匹配
emptyExpression, // 空表达式
overflow, // 数值溢出
}
class CalculatorError implements Exception {
final CalculatorErrorType type;
final String message;
CalculatorError(this.type, this.message);
@override
String toString() => 'CalculatorError: $message';
}7.2 错误检测
dart
class ErrorDetector {
// 检查括号是否匹配
static void checkParentheses(String expression) {
int count = 0;
for (var char in expression.split('')) {
if (char == '(') {
count++;
} else if (char == ')') {
count--;
if (count < 0) {
throw CalculatorError(
CalculatorErrorType.mismatchedParentheses,
'括号不匹配:右括号过多',
);
}
}
}
if (count > 0) {
throw CalculatorError(
CalculatorErrorType.mismatchedParentheses,
'括号不匹配:左括号过多',
);
}
}
// 检查表达式有效性
static void validateExpression(String expression) {
if (expression.trim().isEmpty) {
throw CalculatorError(
CalculatorErrorType.emptyExpression,
'表达式为空',
);
}
// 检查连续运算符
if (RegExp(r'[+\-×÷%^]{2,}').hasMatch(expression)) {
throw CalculatorError(
CalculatorErrorType.syntaxError,
'连续的运算符',
);
}
// 检查运算符位置
if (RegExp(r'^[+\-×÷%^]|[+\-×÷%^]$').hasMatch(expression)) {
throw CalculatorError(
CalculatorErrorType.syntaxError,
'运算符位置错误',
);
}
}
// 检查数值溢出
static void checkOverflow(double value) {
if (!value.isFinite) {
throw CalculatorError(
CalculatorErrorType.overflow,
'数值溢出',
);
}
}
}7.3 友好的错误提示
dart
class ErrorHandler {
static String getErrorMessage(CalculatorError error) {
switch (error.type) {
case CalculatorErrorType.syntaxError:
return '表达式语法错误';
case CalculatorErrorType.divisionByZero:
return '不能除以零';
case CalculatorErrorType.invalidOperator:
return '无效的运算符';
case CalculatorErrorType.mismatchedParentheses:
return '括号不匹配';
case CalculatorErrorType.emptyExpression:
return '请输入表达式';
case CalculatorErrorType.overflow:
return '数值过大或过小';
}
}
static String getUserFriendlyMessage(dynamic error) {
if (error is CalculatorError) {
return getErrorMessage(error);
} else if (error is ArgumentError) {
return error.message;
} else if (error is FormatException) {
return '数字格式错误';
} else {
return '未知错误';
}
}
}八、性能优化策略
8.1 缓存机制
dart
class CachedCalculator {
final Map<String, double> _cache = {};
double calculate(String expression) {
// 检查缓存
if (_cache.containsKey(expression)) {
return _cache[expression]!;
}
// 计算结果
double result = _parse(expression);
// 存入缓存
_cache[expression] = result;
return result;
}
void clearCache() {
_cache.clear();
}
}8.2 懒惰求值
dart
class LazyEvaluator {
String? _lastExpression;
double? _lastResult;
double evaluate(String expression) {
// 如果表达式没变,返回上次结果
if (expression == _lastExpression && _lastResult != null) {
return _lastResult!;
}
// 计算新结果
double result = _parse(expression);
// 更新缓存
_lastExpression = expression;
_lastResult = result;
return result;
}
}8.3 增量计算
dart
class IncrementalCalculator {
double? _lastResult;
String? _lastOperator;
double calculate(double operand, String? operator) {
if (_lastResult == null || operator == null) {
_lastResult = operand;
return operand;
}
double result;
switch (operator) {
case '+':
result = _lastResult! + operand;
break;
case '-':
result = _lastResult! - operand;
break;
case '×':
result = _lastResult! * operand;
break;
case '÷':
result = _lastResult! / operand;
break;
default:
result = operand;
}
_lastResult = result;
return result;
}
void reset() {
_lastResult = null;
_lastOperator = null;
}
}九、总结
本文深入讲解了计算器应用中表达式解析算法的实现技术,主要内容包括:
- 表达式类型:中缀、后缀、前缀表达式及其转换
- 调度场算法:中缀转后缀的标准算法
- 双栈求值:一次遍历完成解析和计算
- 浮点数精度:多种精度处理方案
- 高级运算符:幂运算、科学计算函数
- 错误处理:完善的错误检测和提示机制
- 性能优化:缓存、懒惰求值、增量计算
掌握这些技术可以让你开发出功能强大、计算准确的科学计算器。在实际项目中,还需要考虑用户体验、边界条件、性能优化等方面,确保应用的稳定性和可靠性。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区 : 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区