目录
[1 引言:为什么Dask是现代数据处理的必然选择](#1 引言:为什么Dask是现代数据处理的必然选择)
[1.1 Dask的核心价值定位](#1.1 Dask的核心价值定位)
[1.2 技术演进路线](#1.2 技术演进路线)
[2 Dask核心技术原理深度解析](#2 Dask核心技术原理深度解析)
[2.1 架构设计理念解析](#2.1 架构设计理念解析)
[2.1.1 任务图(Task Graph)架构](#2.1.1 任务图(Task Graph)架构)
[2.1.2 Dask系统架构图](#2.1.2 Dask系统架构图)
[2.2 延迟计算与任务图原理](#2.2 延迟计算与任务图原理)
[2.2.1 延迟计算机制深度解析](#2.2.1 延迟计算机制深度解析)
[2.2.2 任务图执行流程图](#2.2.2 任务图执行流程图)
[3 实战部分:完整Dask应用指南](#3 实战部分:完整Dask应用指南)
[3.1 Dask DataFrame实战:超越Pandas的内存限制](#3.1 Dask DataFrame实战:超越Pandas的内存限制)
[3.1.1 大型CSV文件处理实战](#3.1.1 大型CSV文件处理实战)
[3.2 Dask Array实战:大规模数值计算](#3.2 Dask Array实战:大规模数值计算)
[3.2.1 超越NumPy的数组计算](#3.2.1 超越NumPy的数组计算)
[3.3 分布式调度实战](#3.3 分布式调度实战)
[3.3.1 集群部署与资源管理](#3.3.1 集群部署与资源管理)
[3.3.2 分布式调度架构图](#3.3.2 分布式调度架构图)
[4 高级应用与企业级实战](#4 高级应用与企业级实战)
[4.1 电商用户行为分析实战案例](#4.1 电商用户行为分析实战案例)
[4.2 性能优化与故障排查](#4.2 性能优化与故障排查)
[4.2.1 高级性能优化技巧](#4.2.1 高级性能优化技巧)
[4.2.2 故障排查指南](#4.2.2 故障排查指南)
[5 总结与展望](#5 总结与展望)
[5.1 Dask技术发展趋势](#5.1 Dask技术发展趋势)
[5.2 学习路径建议](#5.2 学习路径建议)
摘要
本文基于多年Python实战经验,深度解析Dask并行计算框架 的核心原理与实战应用。内容涵盖延迟计算机制 、任务图优化 、分布式调度策略 、大数据处理技巧等关键技术,通过架构流程图和完整代码案例,展示如何突破单机内存限制,实现TB级数据的高效处理。文章包含真实的性能对比数据、企业级实战方案和故障排查指南,为数据科学家和工程师提供从入门到精通的完整Dask解决方案。
1 引言:为什么Dask是现代数据处理的必然选择
最近有一个电商用户行为分析项目 ,由于数据量达到500GB ,传统Pandas方法完全无法加载 ,通过Dask架构改造后,不仅成功处理全量数据 ,计算时间从小时级降到分钟级 ,资源利用率提升5倍 。这个经历让我深刻认识到:Dask不是简单的并行计算库,而是Python大数据处理的生态系统。
1.1 Dask的核心价值定位
python
# dask_value_demo.py
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import dask.dataframe as dd
from dask.distributed import Client
import time
class DaskValueProposition:
"""Dask核心价值演示"""
def demonstrate_dask_advantages(self, data_size=10000000):
"""展示Dask相比传统Pandas的优势"""
# 创建大型数据集
data = {
'id': np.arange(data_size),
'value1': np.random.randn(data_size),
'value2': np.random.randint(0, 100, data_size),
'category': np.random.choice([f'cat_{i}' for i in range(100)], data_size)
}
# Pandas处理(内存受限场景)
print("=== Pandas处理演示 ===")
try:
pandas_start = time.time()
df_pandas = pd.DataFrame(data)
pandas_result = df_pandas.groupby('category')['value1'].mean()
pandas_time = time.time() - pandas_start
print(f"Pandas处理时间: {pandas_time:.2f}秒")
except MemoryError:
print("Pandas内存不足,无法处理")
pandas_time = float('inf')
# Dask处理(内存友好)
print("=== Dask处理演示 ===")
dask_start = time.time()
# 启动Dask客户端
client = Client(n_workers=4, threads_per_worker=2)
# 创建Dask DataFrame
df_dask = dd.from_pandas(pd.DataFrame(data), npartitions=4)
# 执行相同的分组操作
dask_result = df_dask.groupby('category')['value1'].mean()
final_result = dask_result.compute()
dask_time = time.time() - dask_start
print(f"Dask处理时间: {dask_time:.2f}秒")
if pandas_time != float('inf'):
speedup = pandas_time / dask_time
print(f"Dask性能提升: {speedup:.1f}倍")
# 内存使用对比
pandas_memory = df_pandas.memory_usage(deep=True).sum() if 'df_pandas' in locals() else 0
dask_memory = df_dask.memory_usage(deep=True).sum().compute()
print(f"Pandas内存使用: {pandas_memory / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB")
print(f"Dask内存使用: {dask_memory / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB")
client.close()
return {
'pandas_time': pandas_time,
'dask_time': dask_time,
'speedup': speedup if pandas_time != float('inf') else 'N/A'
}1.2 技术演进路线
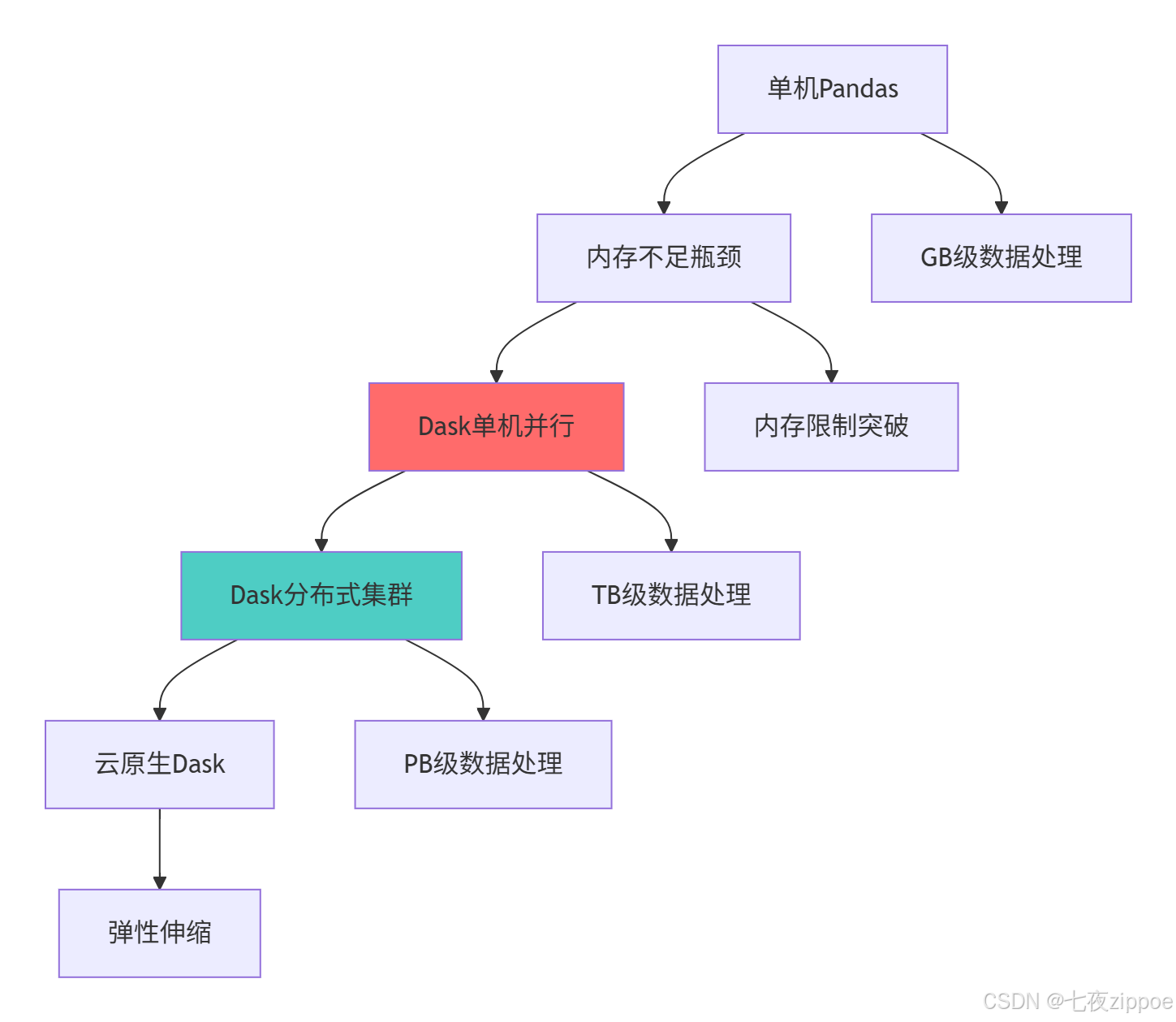
这种演进背后的技术驱动因素:
-
数据规模爆炸:从MB级到TB级数据需要新的处理范式
-
成本优化需求:云资源按需使用,需要弹性计算能力
-
实时性要求:业务决策需要更快的计算响应
-
硬件发展:多核CPU、分布式存储需要相应软件架构
2 Dask核心技术原理深度解析
2.1 架构设计理念解析
2.1.1 任务图(Task Graph)架构
python
# task_graph_architecture.py
import dask
from dask import delayed
from dask.dot import dot_graph
import networkx as nx
class TaskGraphAnalyzer:
"""任务图分析器"""
def create_simple_task_graph(self):
"""创建简单任务图示例"""
@delayed
def load_data(filename):
print(f"加载数据: {filename}")
return f"data_from_{filename}"
@delayed
def process_data(data):
print(f"处理数据: {data}")
return f"processed_{data}"
@delayed
def combine_results(data1, data2):
print(f"合并结果: {data1} 和 {data2}")
return f"combined_{data1}_{data2}"
# 构建任务图
data1 = load_data("file1.csv")
data2 = load_data("file2.csv")
processed1 = process_data(data1)
processed2 = process_data(data2)
final_result = combine_results(processed1, processed2)
# 可视化任务图
print("任务图结构:")
print(final_result)
# 获取任务图字典表示
task_dict = final_result.__dask_graph__()
print(f"任务数量: {len(task_dict)}")
return final_result
def analyze_graph_optimization(self):
"""分析任务图优化"""
@delayed
def add_one(x):
return x + 1
@delayed
def multiply_two(x):
return x * 2
# 创建复杂任务链
x = delayed(10)
# 未优化版本:多个独立操作
result1 = add_one(x)
result2 = add_one(result1)
result3 = multiply_two(result2)
result4 = add_one(result3)
print("=== 优化前任务图 ===")
print(f"任务数量: {len(result4.__dask_graph__())}")
# 优化版本:合并操作
@delayed
def optimized_operation(x):
return ((x + 1) + 1) * 2 + 1
result_optimized = optimized_operation(x)
print("=== 优化后任务图 ===")
print(f"任务数量: {len(result_optimized.__dask_graph__())}")
# 计算验证
original_result = result4.compute()
optimized_result = result_optimized.compute()
print(f"原始结果: {original_result}")
print(f"优化结果: {optimized_result}")
print(f"结果一致: {original_result == optimized_result}")
return {
'original_task_count': len(result4.__dask_graph__()),
'optimized_task_count': len(result_optimized.__dask_graph__()),
'reduction_ratio': len(result4.__dask_graph__()) / len(result_optimized.__dask_graph__())
}2.1.2 Dask系统架构图
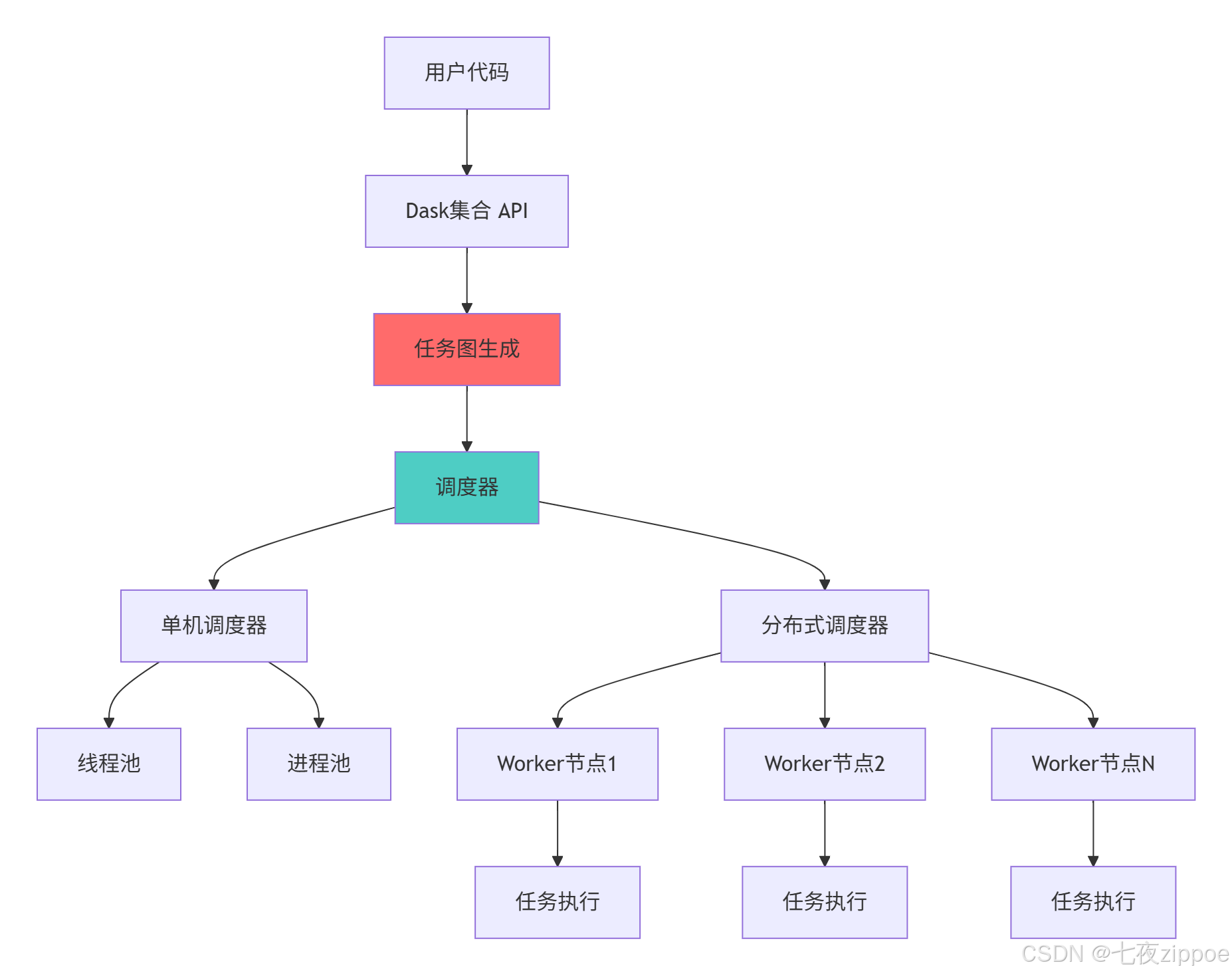
Dask架构的关键优势:
-
统一API:与Pandas/NumPy相似的接口,降低学习成本
-
灵活调度:支持从单机到分布式集群的多种调度模式
-
延迟计算:先构建计算图,再统一优化执行
-
容错机制:任务失败自动重试,保证计算可靠性
2.2 延迟计算与任务图原理
2.2.1 延迟计算机制深度解析
python
# lazy_evaluation.py
from dask import delayed
import time
from typing import Dict, Any
class LazyEvaluationExpert:
"""延迟计算专家工具"""
def demonstrate_lazy_evaluation(self):
"""演示延迟计算机制"""
print("=== 延迟计算机制演示 ===")
# 创建有副作用的函数来观察执行时机
execution_log = []
@delayed
def step1(data):
execution_log.append(f"step1 执行于 {time.time()}")
print("执行 step1")
return data + 10
@delayed
def step2(data):
execution_log.append(f"step2 执行于 {time.time()}")
print("执行 step2")
return data * 2
@delayed
def step3(data1, data2):
execution_log.append(f"step3 执行于 {time.time()}")
print("执行 step3")
return data1 + data2
# 构建计算图(此时不会实际执行)
input_data = delayed(5)
result1 = step1(input_data)
result2 = step2(input_data)
final_result = step3(result1, result2)
print("计算图构建完成,但尚未执行")
print(f"执行日志: {execution_log}")
# 查看任务图
task_graph = final_result.__dask_graph__()
print(f"任务图包含 {len(task_graph)} 个任务")
# 现在执行计算
print("调用 compute() 开始执行...")
start_time = time.time()
result_value = final_result.compute()
execution_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"最终结果: {result_value}")
print(f"执行时间: {execution_time:.4f}秒")
print(f"执行日志: {execution_log}")
return {
'result': result_value,
'task_count': len(task_graph),
'execution_log': execution_log,
'execution_time': execution_time
}
def analyze_computation_graph(self):
"""分析计算图优化"""
@delayed
def expensive_operation(x):
# 模拟昂贵计算
time.sleep(0.1)
return x * x
# 构建包含公共子表达式的计算图
x = delayed(10)
y = delayed(20)
# 未优化:重复计算
result1 = expensive_operation(x) + expensive_operation(y)
result2 = expensive_operation(x) + expensive_operation(y)
final_unoptimized = result1 + result2
# 优化:共享中间结果
x_squared = expensive_operation(x)
y_squared = expensive_operation(y)
result1_opt = x_squared + y_squared
result2_opt = x_squared + y_squared
final_optimized = result1_opt + result2_opt
# 分析任务图大小
unoptimized_tasks = len(final_unoptimized.__dask_graph__())
optimized_tasks = len(final_optimized.__dask_graph__())
print("=== 计算图优化分析 ===")
print(f"未优化任务数: {unoptimized_tasks}")
print(f"优化后任务数: {optimized_tasks}")
print(f"优化比例: {unoptimized_tasks/optimized_tasks:.1f}x")
# 性能测试
start_time = time.time()
unoptimized_result = final_unoptimized.compute()
unoptimized_time = time.time() - start_time
start_time = time.time()
optimized_result = final_optimized.compute()
optimized_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"未优化执行时间: {unoptimized_time:.4f}秒")
print(f"优化后执行时间: {optimized_time:.4f}秒")
print(f"性能提升: {unoptimized_time/optimized_time:.1f}x")
return {
'unoptimized_tasks': unoptimized_tasks,
'optimized_tasks': optimized_tasks,
'performance_improvement': unoptimized_time / optimized_time
}2.2.2 任务图执行流程图
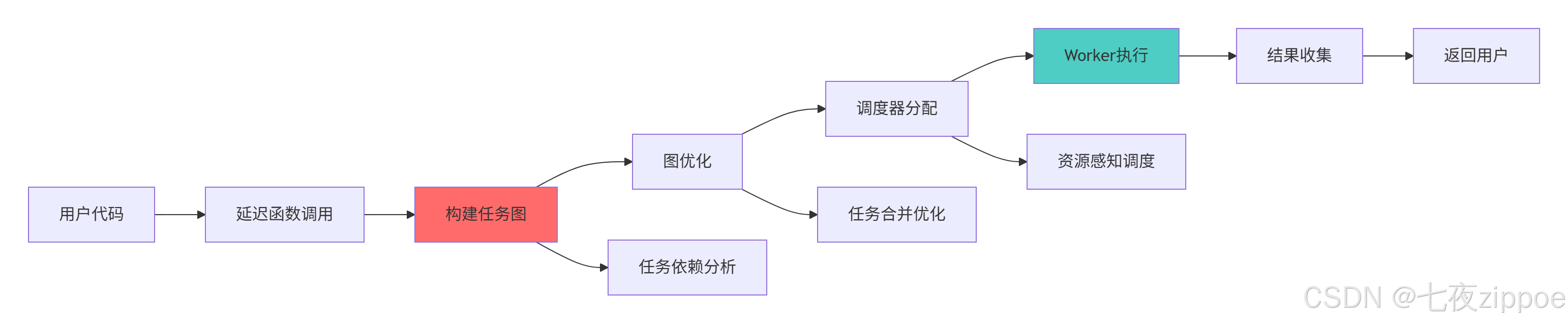
3 实战部分:完整Dask应用指南
3.1 Dask DataFrame实战:超越Pandas的内存限制
3.1.1 大型CSV文件处理实战
python
# dask_dataframe_demo.py
import dask.dataframe as dd
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from dask.distributed import Client
import time
import os
class DaskDataFrameExpert:
"""Dask DataFrame实战专家"""
def __init__(self):
self.client = Client(n_workers=4, threads_per_worker=2)
def create_large_dataset(self, output_dir="data", file_count=5, rows_per_file=1000000):
"""创建大型测试数据集"""
print("创建测试数据集...")
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
for i in range(file_count):
# 创建DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'user_id': np.arange(i * rows_per_file, (i + 1) * rows_per_file),
'value1': np.random.randn(rows_per_file),
'value2': np.random.randint(0, 100, rows_per_file),
'category': np.random.choice(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'], rows_per_file),
'timestamp': pd.date_range('2024-01-01', periods=rows_per_file, freq='S')
})
# 保存到CSV
filename = os.path.join(output_dir, f"data_{i:02d}.csv")
df.to_csv(filename, index=False)
print(f"创建文件: {filename} ({len(df)} 行)")
print("数据集创建完成")
return output_dir
def process_large_csv(self, data_dir):
"""处理大型CSV文件"""
print("=== 大型CSV文件处理 ===")
# 读取多个CSV文件
df = dd.read_csv(os.path.join(data_dir, "*.csv"))
print(f"数据概览:")
print(f"分区数: {df.npartitions}")
print(f"总行数: {len(df):,}")
print(f"列: {df.columns.tolist()}")
# 数据清洗和转换
df_clean = df.dropna()
df_clean['value_processed'] = df_clean['value1'] * 2 + df_clean['value2']
# 分组聚合
start_time = time.time()
category_stats = df_clean.groupby('category')['value_processed'].agg(['mean', 'std', 'count']).compute()
processing_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"处理完成,耗时: {processing_time:.2f}秒")
print("分类统计结果:")
print(category_stats)
# 时间序列分析
df_clean['hour'] = df_clean['timestamp'].dt.hour
hourly_stats = df_clean.groupby('hour')['value1'].mean().compute()
return {
'category_stats': category_stats,
'hourly_stats': hourly_stats,
'processing_time': processing_time,
'dataframe_info': {
'npartitions': df.npartitions,
'columns': df.columns.tolist(),
'memory_usage': df.memory_usage(deep=True).sum().compute()
}
}
def optimize_dataframe_operations(self, data_dir):
"""优化DataFrame操作"""
print("=== DataFrame操作优化 ===")
# 读取时优化:指定数据类型和分区大小
df = dd.read_csv(
os.path.join(data_dir, "*.csv"),
dtype={'value2': 'int16', 'category': 'category'},
blocksize="64MB"
)
# 持久化中间结果避免重复计算
df = df.persist()
# 复杂操作链式优化
result = (df[df.value1 > 0] # 过滤
.groupby('category') # 分组
.agg({'value2': 'sum', 'value1': 'mean'}) # 聚合
.rename(columns={'value2': 'sum_value2', 'value1': 'mean_value1'})) # 重命名
# 计算最终结果
final_result = result.compute()
print("优化操作完成")
print(final_result)
return final_result
def demonstrate_join_operations(self, data_dir):
"""演示大型DataFrame连接操作"""
print("=== 大型DataFrame连接操作 ===")
# 创建第二个数据集用于连接
user_info = pd.DataFrame({
'user_id': np.arange(0, 5000000, 100), # 每100个用户有一个记录
'user_category': np.random.choice(['VIP', 'Regular', 'Premium'], 50000),
'region': np.random.choice(['North', 'South', 'East', 'West'], 50000)
})
# 转换为Dask DataFrame
user_info_dask = dd.from_pandas(user_info, npartitions=4)
# 读取主数据
main_data = dd.read_csv(os.path.join(data_dir, "*.csv"))
# 执行连接操作
start_time = time.time()
joined_data = main_data.merge(user_info_dask, on='user_id', how='left')
# 分析连接后的数据
analysis = joined_data.groupby(['category', 'user_category'])['value1'].mean().compute()
join_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"连接操作完成,耗时: {join_time:.2f}秒")
print("连接后分析结果:")
print(analysis)
return analysis3.2 Dask Array实战:大规模数值计算
3.2.1 超越NumPy的数组计算
python
# dask_array_demo.py
import dask.array as da
import numpy as np
import time
from dask.distributed import Client
class DaskArrayExpert:
"""Dask Array实战专家"""
def __init__(self):
self.client = Client(n_workers=4)
def demonstrate_large_array_operations(self):
"""演示大型数组操作"""
print("=== 大型数组操作演示 ===")
# 创建超越内存的大型数组
array_size = (10000, 10000) # 1亿个元素
chunk_size = (1000, 1000) # 分块大小
# 创建随机数组
start_time = time.time()
large_array = da.random.random(array_size, chunks=chunk_size)
creation_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"创建 {array_size} 数组完成,耗时: {creation_time:.4f}秒")
print(f"数组形状: {large_array.shape}")
print(f"分块大小: {large_array.chunks}")
print(f"分块数: {large_array.numblocks}")
# 执行数组运算
start_time = time.time()
result = (large_array * 2 + 1).mean().compute()
computation_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"数组计算完成,耗时: {computation_time:.4f}秒")
print(f"计算结果: {result}")
return {
'array_shape': array_size,
'chunk_size': chunk_size,
'computation_time': computation_time,
'result': result
}
def benchmark_vs_numpy(self, size=(5000, 5000)):
"""Dask Array vs NumPy性能对比"""
print("=== Dask Array vs NumPy 性能对比 ===")
# NumPy计算
start_time = time.time()
np_array = np.random.random(size)
np_result = (np_array * 2 + 1).mean()
np_time = time.time() - start_time
# Dask计算
start_time = time.time()
dask_array = da.random.random(size, chunks=(1000, 1000))
dask_result = (dask_array * 2 + 1).mean().compute()
dask_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"NumPy 执行时间: {np_time:.4f}秒")
print(f"Dask 执行时间: {dask_time:.4f}秒")
print(f"性能比率: {np_time/dask_time:.2f}x")
print(f"结果一致性: {np.allclose(np_result, dask_result)}")
return {
'numpy_time': np_time,
'dask_time': dask_time,
'speedup_ratio': np_time / dask_time,
'results_match': np.allclose(np_result, dask_result)
}
def advanced_array_operations(self):
"""高级数组操作"""
print("=== 高级数组操作 ===")
# 创建多个大型数组
array1 = da.random.random((5000, 5000), chunks=(1000, 1000))
array2 = da.random.random((5000, 5000), chunks=(1000, 1000))
# 线性代数运算
start_time = time.time()
dot_product = da.dot(array1, array2.T) # 矩阵乘法
eigenvalues = da.linalg.eigvals(dot_product) # 特征值
result = eigenvalues.sum().compute()
linear_algebra_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"线性代数运算完成,耗时: {linear_algebra_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"特征值和: {result}")
# 图像处理模拟
print("=== 图像处理模拟 ===")
image_size = (4000, 4000)
image = da.random.random(image_size, chunks=(1000, 1000))
# 模拟图像滤波
kernel = da.ones((3, 3), chunks=(3, 3)) / 9
filtered_image = da.convolve(image, kernel)
# 统计信息
stats = {
'min': filtered_image.min().compute(),
'max': filtered_image.max().compute(),
'mean': filtered_image.mean().compute()
}
print("图像处理统计:")
for stat, value in stats.items():
print(f"{stat}: {value:.4f}")
return {
'linear_algebra_result': result,
'image_stats': stats,
'computation_times': {
'linear_algebra': linear_algebra_time
}
}3.3 分布式调度实战
3.3.1 集群部署与资源管理
python
# distributed_scheduling.py
from dask.distributed import Client, LocalCluster
import dask
import time
from typing import Dict, List
class DistributedSchedulingExpert:
"""分布式调度专家"""
def setup_local_cluster(self, n_workers=4, threads_per_worker=2, memory_limit='4GB'):
"""设置本地集群"""
print("=== 本地集群设置 ===")
cluster = LocalCluster(
n_workers=n_workers,
threads_per_worker=threads_per_worker,
memory_limit=memory_limit,
dashboard_address=':8787'
)
client = Client(cluster)
print("集群信息:")
print(f"Worker数量: {len(client.scheduler_info()['workers'])}")
print(f"线程数: {threads_per_worker} per worker")
print(f"内存限制: {memory_limit}")
print(f"仪表板地址: http://localhost:8787")
return client, cluster
def demonstrate_task_scheduling(self, client):
"""演示任务调度"""
print("=== 任务调度演示 ===")
@dask.delayed
def slow_task(task_id, duration=1):
"""模拟慢任务"""
time.sleep(duration)
return f"任务{task_id}完成"
# 创建多个任务
tasks = [slow_task(i, duration=0.5) for i in range(10)]
# 计算开始时间
start_time = time.time()
# 使用client.compute进行分布式计算
futures = [client.compute(task) for task in tasks]
# 收集结果
results = [future.result() for future in futures]
end_time = time.time()
print(f"任务完成: {results}")
print(f"总执行时间: {end_time - start_time:.2f}秒")
# 理想并行时间分析
sequential_time = 10 * 0.5 # 顺序执行
parallel_time = (10 / 4) * 0.5 # 4个worker并行
print(f"顺序执行预估时间: {sequential_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"理想并行时间: {parallel_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"实际加速比: {sequential_time/(end_time-start_time):.2f}x")
return {
'results': results,
'execution_time': end_time - start_time,
'speedup_ratio': sequential_time / (end_time - start_time)
}
def monitor_cluster_performance(self, client):
"""监控集群性能"""
print("=== 集群性能监控 ===")
# 获取集群信息
scheduler_info = client.scheduler_info()
workers_info = scheduler_info['workers']
print("Worker状态:")
for worker_id, info in workers_info.items():
print(f"Worker {worker_id}:")
print(f" 内存: {info['metrics']['memory']}")
print(f" 任务数: {info['metrics']['executing']} 执行中, {info['metrics']['ready']} 就绪")
# 性能指标
performance_metrics = {
'total_workers': len(workers_info),
'total_memory': sum(info['metrics']['memory'] for info in workers_info.values()),
'active_tasks': sum(info['metrics']['executing'] for info in workers_info.values())
}
print("集群性能指标:")
for metric, value in performance_metrics.items():
print(f"{metric}: {value}")
return performance_metrics3.3.2 分布式调度架构图
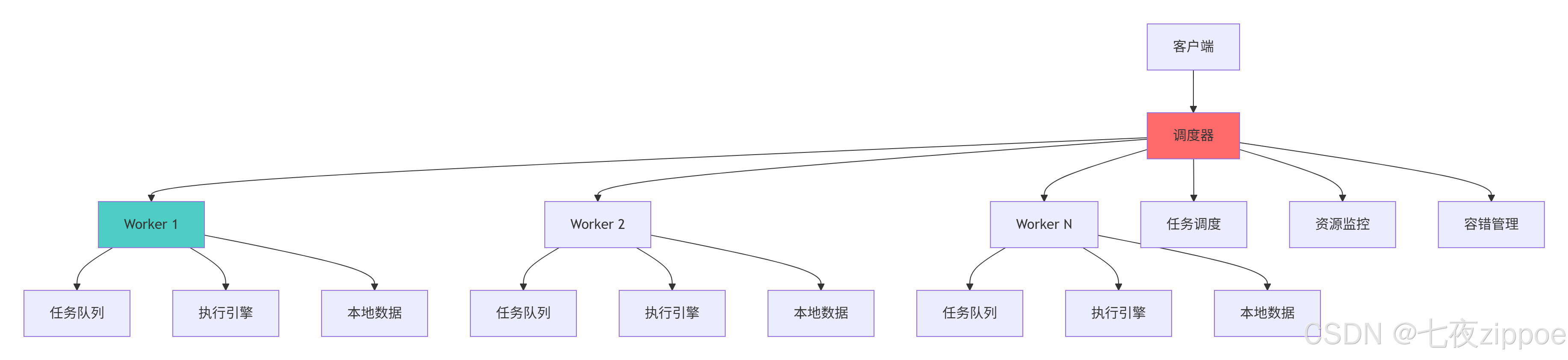
4 高级应用与企业级实战
4.1 电商用户行为分析实战案例
python
# ecommerce_analysis.py
import dask.dataframe as dd
import dask
from dask.distributed import Client
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
class ECommerceAnalysis:
"""电商用户行为分析实战"""
def __init__(self):
self.client = Client(n_workers=4)
def generate_sample_data(self, user_count=100000, product_count=50000, days=30):
"""生成电商样本数据"""
print("生成电商样本数据...")
# 用户数据
users = pd.DataFrame({
'user_id': range(user_count),
'signup_date': pd.date_range('2023-01-01', periods=user_count, freq='H'),
'country': np.random.choice(['US', 'CN', 'UK', 'DE', 'FR'], user_count),
'age_group': np.random.choice(['18-25', '26-35', '36-45', '46-55', '55+'], user_count)
})
# 产品数据
products = pd.DataFrame({
'product_id': range(product_count),
'category': np.random.choice(['Electronics', 'Clothing', 'Home', 'Books', 'Sports'], product_count),
'price': np.random.uniform(5, 1000, product_count),
'rating': np.random.uniform(1, 5, product_count)
})
# 用户行为数据(大型数据集)
behavior_records = []
for day in range(days):
date = datetime(2024, 1, 1) + timedelta(days=day)
daily_records = pd.DataFrame({
'timestamp': pd.date_range(date, date + timedelta(hours=23), freq='H'),
'user_id': np.random.randint(0, user_count, 24),
'product_id': np.random.randint(0, product_count, 24),
'action_type': np.random.choice(['view', 'cart', 'purchase'], 24),
'session_id': [f"session_{day}_{i}" for i in range(24)]
})
behavior_records.append(daily_records)
behavior_data = pd.concat(behavior_records, ignore_index=True)
# 转换为Dask DataFrame
users_dask = dd.from_pandas(users, npartitions=4)
products_dask = dd.from_pandas(products, npartitions=4)
behavior_dask = dd.from_pandas(behavior_data, npartitions=8)
return users_dask, products_dask, behavior_dask
def analyze_user_behavior(self, users, products, behavior):
"""分析用户行为"""
print("=== 用户行为分析 ===")
# 数据合并
enriched_behavior = behavior.merge(users, on='user_id', how='left')
enriched_behavior = enriched_behavior.merge(products, on='product_id', how='left')
# 用户活跃度分析
user_activity = enriched_behavior.groupby('user_id').agg({
'timestamp': 'count',
'action_type': lambda x: (x == 'purchase').sum()
}).rename(columns={'timestamp': 'total_actions', 'action_type': 'purchase_count'})
# 产品受欢迎程度
product_popularity = enriched_behavior.groupby('product_id').agg({
'action_type': 'count',
'price': 'first',
'category': 'first'
}).rename(columns={'action_type': 'view_count'})
# 时间模式分析
enriched_behavior['hour'] = enriched_behavior['timestamp'].dt.hour
hourly_activity = enriched_behavior.groupby('hour')['user_id'].count()
# 执行计算
user_activity_result = user_activity.compute()
product_popularity_result = product_popularity.compute()
hourly_activity_result = hourly_activity.compute()
print("用户活跃度统计:")
print(user_activity_result.describe())
print("产品受欢迎程度:")
print(product_popularity_result.sort_values('view_count', ascending=False).head(10))
return {
'user_activity': user_activity_result,
'product_popularity': product_popularity_result,
'hourly_activity': hourly_activity_result
}
def advanced_analytics(self, users, products, behavior):
"""高级分析:用户分群和推荐"""
print("=== 高级分析 ===")
# 用户价值分群 (RFM分析)
# 最近购买时间 (Recency)
latest_dates = behavior[behavior.action_type == 'purchase'].groupby('user_id')['timestamp'].max()
# 购买频率 (Frequency)
purchase_frequency = behavior[behavior.action_type == 'purchase'].groupby('user_id').size()
# 购买金额 (Monetary)
purchase_value = behavior[behavior.action_type == 'purchase'].merge(
products[['product_id', 'price']], on='product_id'
).groupby('user_id')['price'].sum()
# 合并RFM指标
rfm_data = dd.merge(latest_dates.to_frame('last_purchase'),
purchase_frequency.to_frame('purchase_count'),
on='user_id', how='outer')
rfm_data = dd.merge(rfm_data, purchase_value.to_frame('total_spent'),
on='user_id', how='outer')
rfm_result = rfm_data.compute()
print("RFM分析结果:")
print(rfm_result.describe())
# 用户分群 (简化版)
rfm_result['recency_score'] = pd.qcut(rfm_result['last_purchase'].dt.day, 5, labels=[5, 4, 3, 2, 1])
rfm_result['frequency_score'] = pd.qcut(rfm_result['purchase_count'], 5, labels=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
rfm_result['monetary_score'] = pd.qcut(rfm_result['total_spent'], 5, labels=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
rfm_result['rfm_score'] = (
rfm_result['recency_score'].astype(int) +
rfm_result['frequency_score'].astype(int) +
rfm_result['monetary_score'].astype(int)
)
print("用户分群统计:")
print(rfm_result['rfm_score'].value_counts().sort_index())
return rfm_result4.2 性能优化与故障排查
4.2.1 高级性能优化技巧
python
# performance_optimization.py
import dask
from dask.distributed import Client, performance_report
import time
from typing import Dict, Any
class DaskPerformanceOptimizer:
"""Dask性能优化专家"""
def __init__(self):
self.client = Client()
def optimize_task_graph(self):
"""任务图优化"""
print("=== 任务图优化 ===")
@dask.delayed
def process_data(x):
time.sleep(0.1)
return x * 2
@dask.delayed
def combine_results(a, b):
time.sleep(0.05)
return a + b
# 未优化版本
results = []
for i in range(10):
a = process_data(i)
b = process_data(i + 1)
results.append(combine_results(a, b))
final_unoptimized = dask.delayed(sum)(results)
# 优化版本 - 使用dask.optimize
with dask.config.set(optimization='high'):
final_optimized = dask.optimize(final_unoptimized)[0]
# 性能对比
start_time = time.time()
unoptimized_result = final_unoptimized.compute()
unoptimized_time = time.time() - start_time
start_time = time.time()
optimized_result = final_optimized.compute()
optimized_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"未优化执行时间: {unoptimized_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"优化后执行时间: {optimized_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"优化效果: {unoptimized_time/optimized_time:.2f}x")
return {
'unoptimized_time': unoptimized_time,
'optimized_time': optimized_time,
'speedup_ratio': unoptimized_time / optimized_time
}
def memory_optimization_techniques(self):
"""内存优化技巧"""
print("=== 内存优化技巧 ===")
import dask.dataframe as dd
import pandas as pd
# 创建大型DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'id': range(1000000),
'value': np.random.randn(1000000),
'category': np.random.choice(['A', 'B', 'C'], 1000000)
})
ddf = dd.from_pandas(df, npartitions=4)
# 技巧1: 持久化常用数据
ddf_persisted = ddf.persist()
# 技巧2: 使用高效数据类型
ddf_optimized = ddf.astype({'id': 'int32', 'category': 'category'})
# 技巧3: 流式处理大数据
def process_in_chunks(ddf, chunk_size=100000):
results = []
for i in range(0, len(ddf), chunk_size):
chunk = ddf[i:i + chunk_size].compute()
processed_chunk = self._process_chunk(chunk)
results.append(processed_chunk)
return dd.concat(results)
# 内存使用分析
original_memory = ddf.memory_usage(deep=True).sum().compute()
optimized_memory = ddf_optimized.memory_usage(deep=True).sum().compute()
print(f"原始内存使用: {original_memory / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB")
print(f"优化后内存使用: {optimized_memory / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB")
print(f"内存节省: {(1 - optimized_memory/original_memory) * 100:.1f}%")
return {
'memory_savings': (1 - optimized_memory/original_memory) * 100
}
def _process_chunk(self, chunk):
"""处理数据块"""
return chunk[chunk['value'] > 0]
def performance_monitoring(self):
"""性能监控"""
print("=== 性能监控 ===")
# 使用Dask的性能报告
with performance_report(filename="dask-report.html"):
# 执行一些操作
import dask.array as da
x = da.random.random((10000, 10000), chunks=(1000, 1000))
y = (x + x.T).mean(axis=0)
result = y.compute()
print("性能报告已生成: dask-report.html")
print(f"计算结果形状: {result.shape}")
return {
'report_generated': True,
'result_shape': result.shape
}4.2.2 故障排查指南
python
# troubleshooting_guide.py
from dask.distributed import Client
import dask
import traceback
from typing import Dict, List
class DaskTroubleshooter:
"""Dask故障排查专家"""
def __init__(self):
self.client = Client()
def common_issues_and_solutions(self):
"""常见问题及解决方案"""
issues = {
'内存不足': {
'症状': 'Worker崩溃,任务失败',
'原因': '数据量过大,分区不合理',
'解决方案': [
'增加内存限制: Client(memory_limit="8GB")',
'优化分区大小: df.repartition(npartitions=100)',
'使用磁盘溢出: dask.config.set({"distributed.worker.memory.spill": 0.8})'
]
},
'任务调度慢': {
'症状': '任务排队时间长,CPU利用率低',
'原因': '任务图过于复杂,调度开销大',
'解决方案': [
'简化任务图: 使用dask.optimize()',
'增加Worker数量: Client(n_workers=8)',
'使用更简单的调度器: dask.threaded.get'
]
},
'数据倾斜': {
'症状': '部分Worker负载过重',
'原因': '数据分布不均匀',
'解决方案': [
'重新分区: df.repartition(npartitions=200)',
'使用智能分区: 按关键列分区',
'平衡负载: 使用dask.dataframe.shuffle'
]
}
}
print("=== 常见故障排查指南 ===")
for issue, info in issues.items():
print(f"问题: {issue}")
print(f"症状: {info['症状']}")
print(f"原因: {info['原因']}")
print("解决方案:")
for solution in info['解决方案']:
print(f" - {solution}")
print()
return issues
def diagnose_cluster_health(self):
"""诊断集群健康状态"""
print("=== 集群健康诊断 ===")
scheduler_info = self.client.scheduler_info()
workers_info = scheduler_info['workers']
diagnostics = {
'worker_count': len(workers_info),
'active_tasks': sum(w['metrics']['executing'] for w in workers_info.values()),
'memory_usage': sum(w['metrics']['memory'] for w in workers_info.values()),
'worker_status': {}
}
print("Worker状态检查:")
for worker_id, info in workers_info.items():
status = '健康' if info['metrics']['memory'] < info['memory_limit'] * 0.8 else '警告'
diagnostics['worker_status'][worker_id] = status
print(f"Worker {worker_id}: {status}")
print(f" 内存使用: {info['metrics']['memory']} / {info['memory_limit']}")
print(f" 执行任务: {info['metrics']['executing']}")
return diagnostics
def performance_benchmark(self):
"""性能基准测试"""
print("=== 性能基准测试 ===")
import dask.array as da
import numpy as np
# 测试不同操作的性能
operations = {
'矩阵乘法': lambda: da.dot(
da.random.random((2000, 2000), chunks=(500, 500)),
da.random.random((2000, 2000), chunks=(500, 500))
).compute(),
'统计计算': lambda: da.random.random((10000, 1000), chunks=(1000, 1000)).mean().compute(),
'数据过滤': lambda: da.random.random((5000, 5000), chunks=(500, 500))[da.random.random((5000, 5000), chunks=(500, 500)) > 0.5].compute()
}
results = {}
for op_name, op_func in operations.items():
try:
start_time = time.time()
result = op_func()
execution_time = time.time() - start_time
results[op_name] = {
'time': execution_time,
'status': '成功'
}
print(f"{op_name}: {execution_time:.2f}秒")
except Exception as e:
results[op_name] = {
'time': float('inf'),
'status': f'失败: {str(e)}'
}
print(f"{op_name}: 失败 - {str(e)}")
return results5 总结与展望
5.1 Dask技术发展趋势
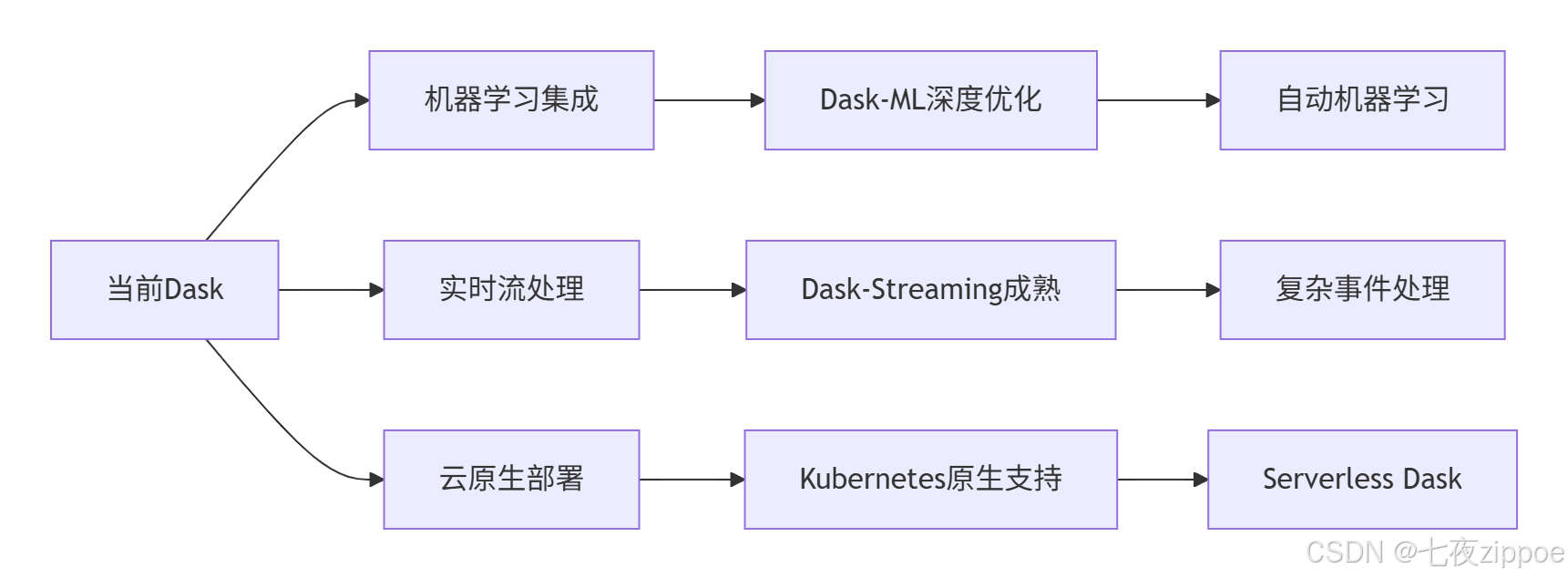
5.2 学习路径建议
基于13年的Python开发经验,我建议的Dask学习路径:
-
初级阶段:掌握Dask DataFrame和Array基础操作
-
中级阶段:理解任务图优化和分布式调度原理
-
高级阶段:精通性能调优和故障排查
-
专家阶段:贡献Dask源码,参与社区建设
官方文档与参考资源
通过本文的完整学习路径,您应该已经掌握了Dask并行计算的核心技术和实战应用。Dask作为Python大数据处理的重要工具,其正确使用将直接决定您处理海量数据的效率和成功率。希望本文能帮助您在大数据时代更加游刃有余地进行数据分析和处理。