0 缘起
岁末年初,要写网络安全工作总结,其中涉及到电脑终端设备的检查情况。对于使用Windows系统的电脑,可以使用SysInfo来收集信息,对于基于Linux的国产电脑,目前还没有发现比较好的信息收集程序,当然Linux自身提供了的功能丰富的命令,编写一个shell脚本也可以实现,但用户可以直接看到脚本内容,总觉得差点意思,还是有一个编译成二进制的可执行文件为佳 。
1 确定编程语言、编译器
1.1 编程语言
在Linux系统中,生成二进制可执行文件可以使用C、C++、Go等编程语言。
在学校里学过C 语言,现在可重新拾起来了。
1.2 编译器
选定了C语言,那么编译器可以使用GCC(GNU Compiler Collection)或Clang。
我使用的国产电脑使用的是Kylin | 麒麟,先看看这个系统里是否已经安装了GCC(GNU Compiler Collection)或Clang。
1.2.1 检查和安装GCC
输入命令gcc回车。
purpleendurer @ bash $ g++cc++
gcc: fatal error: no input files
compilation terminated.
看来已经安装有GCC了。
再查看GCC帮助信息,输入命令gcc --help回车:
purpleendurer @ bash $ g++cc --help++
Usage: gcc [options] file...
Options:
-pass-exit-codes Exit with highest error code from a phase
--help Display this information
--target-help Display target specific command line options
--help={common|optimizers|params|target|warnings|[^]{joined|separate|undocumented}}[,...]
Display specific types of command line options
(Use '-v --help' to display command line options of sub-processes)
--version Display compiler version information
-dumpspecs Display all of the built in spec strings
-dumpversion Display the version of the compiler
-dumpmachine Display the compiler's target processor
-print-search-dirs Display the directories in the compiler's search path
-print-libgcc-file-name Display the name of the compiler's companion library
-print-file-name=<lib> Display the full path to library <lib>
-print-prog-name=<prog> Display the full path to compiler component <prog>
-print-multiarch Display the target's normalized GNU triplet, used as
a component in the library path
-print-multi-directory Display the root directory for versions of libgcc
-print-multi-lib Display the mapping between command line options and
multiple library search directories
-print-multi-os-directory Display the relative path to OS libraries
-print-sysroot Display the target libraries directory
-print-sysroot-headers-suffix Display the sysroot suffix used to find headers
-Wa,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the assembler
-Wp,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the preprocessor
-Wl,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the linker
-Xassembler <arg> Pass <arg> on to the assembler
-Xpreprocessor <arg> Pass <arg> on to the preprocessor
-Xlinker <arg> Pass <arg> on to the linker
-save-temps Do not delete intermediate files
-save-temps=<arg> Do not delete intermediate files
-no-canonical-prefixes Do not canonicalize paths when building relative
prefixes to other gcc components
-pipe Use pipes rather than intermediate files
-time Time the execution of each subprocess
-specs=<file> Override built-in specs with the contents of <file>
-std=<standard> Assume that the input sources are for <standard>
--sysroot=<directory> Use <directory> as the root directory for headers
and libraries
-B <directory> Add <directory> to the compiler's search paths
-v Display the programs invoked by the compiler
-### Like -v but options quoted and commands not executed
-E Preprocess only; do not compile, assemble or link
-S Compile only; do not assemble or link
-c Compile and assemble, but do not link
-o <file> Place the output into <file>
-pie Create a position independent executable
-shared Create a shared library
-x <language> Specify the language of the following input files
Permissible languages include: c c++ assembler none
'none' means revert to the default behavior of
guessing the language based on the file's extension
Options starting with -g, -f, -m, -O, -W, or --param are automatically
passed on to the various sub-processes invoked by gcc. In order to pass
other options on to these processes the -W<letter> options must be used.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<file:///usr/share/doc/gcc-5/README.Bugs>.
clang查看GCC版本,输入命令gcc --version回车:
purpleendurer @ bash $ ++gcc --version++
gcc (Ubuntu/Linaro 5.4.0-6kord1~16.04.12) 5.4.0 20160609
Copyright (C) 2015 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
如果系统中没有安装GCC,可以试试以下命令:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install build-essential
build-essential包里包含了gcc、g++、make等基本工具。
或
sudo dnf groupinstall "Development Tools"
或
sudo yum groupinstall "Development Tools"
Development Tools 是一个软件包组,包含了进行软件开发所需的核心工具集,通常包括以下关键组件:
- 编译器:gcc(GNU C编译器)、gcc-c++(GNU C++编译器),用于编译C和C++代码。
- 构建工具:make(自动化构建工具)、cmake(跨平台项目管理工具,在部分版本中可能包含)。
- 调试工具:gdb(GNU调试器),用于调试程序。
- 二进制工具:binutils(包含链接器ld、汇编器as等)。
- 版本控制与辅助工具:git(分布式版本控制系统,在较新版本中常被包含)、autoconf、automake、libtool(用于生成可移植的构建系统)。
- 其他开发工具:bison(语法分析器生成器)、flex(词法分析器生成器)、strace(系统调用跟踪)、pkgconf(用于管理编译和链接标志)。
1.2.2检查和安装Clang
输入命令clan回车。
purpleendurer @ bash $ ++clang++
程序"clang"尚未安装。 您可以使用以下命令安装:
sudo apt install clang
系统中没有安装clan,并提供了安装命令sudo apt install clang。
2 集成开发环境(IDE)
虽然直接使用命令行和文本编辑器是完全可行的,但使用集成开发环境(IDE)或代码编辑器可以提供更丰富的功能,如代码高亮、自动完成、调试工具等。
一些流行的选择包括:
- Visual Studio Code:一个轻量级但功能强大的编辑器,支持C语言开发,可以通过安装C/C++扩展来增强功能。
- CLion:由JetBrains开发的一个强大的商业IDE,支持多种编程语言,包括C和C++。它提供了代码分析、调试和版本控制集成等功能。
- Code::Blocks:一个开源的C、C++和Fortran IDE,提供了项目管理、代码补全、调试等功能。
我先不用IDE。
3 实现Hello world
3.1 创建hello.c
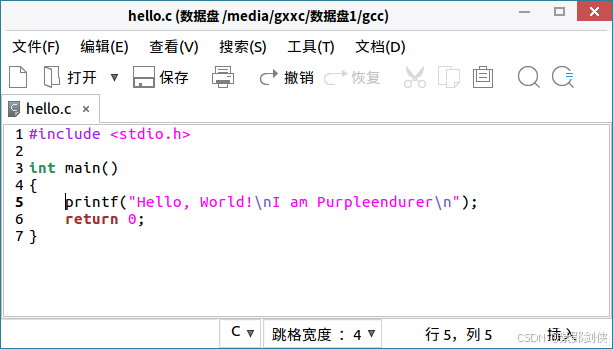
使用Kylin | 麒麟内置的文本编辑器,输入以下代码,保存为hello.c:
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello, World!\nI am Purpleendurer\n");
return 0;
}Kylin | 麒麟内置的文本编辑器居然支持代码高亮。
3.2 编译hello.c
在命令行进入hello.c文件所在目录,输入命令gcc hello.c -o hello回车:
purpleendurer @ bash $++gcc hello.c -o hello++
命令执行完了没有反馈信息。
3.3 运行hello
在命令行输入命令./hello回车:
purpleendurer @ bash $ ++./hello++
Hello, World!
I am Purpleendurer