欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:推箱子游戏完整开发指南
文章目录
- [Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:推箱子游戏完整开发指南](#Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:推箱子游戏完整开发指南)
-
- 摘要
- 一、项目背景与功能概述
-
- [1.1 推箱子游戏介绍](#1.1 推箱子游戏介绍)
- [1.2 应用功能规划](#1.2 应用功能规划)
- [1.3 地图元素设计](#1.3 地图元素设计)
- 二、数据模型设计
-
- [2.1 地图表示](#2.1 地图表示)
- [2.2 关卡数据结构](#2.2 关卡数据结构)
- [2.3 游戏状态](#2.3 游戏状态)
- 三、技术选型与架构设计
-
- [3.1 核心技术栈](#3.1 核心技术栈)
- [3.2 应用架构](#3.2 应用架构)
- [3.3 游戏逻辑流程](#3.3 游戏逻辑流程)
- 四、关卡管理系统
-
- [4.1 加载关卡](#4.1 加载关卡)
- [4.2 关卡切换](#4.2 关卡切换)
- [4.3 深拷贝地图](#4.3 深拷贝地图)
- 五、移动逻辑实现
-
- [5.1 移动玩家](#5.1 移动玩家)
- [5.2 推箱子逻辑](#5.2 推箱子逻辑)
- [5.3 碰撞检测流程图](#5.3 碰撞检测流程图)
- 六、胜利判断
-
- [6.1 检查胜利条件](#6.1 检查胜利条件)
- [6.2 胜利对话框](#6.2 胜利对话框)
- 七、UI界面实现
-
- [7.1 地图渲染](#7.1 地图渲染)
- [7.2 元素颜色和图标](#7.2 元素颜色和图标)
- [7.3 控制按钮](#7.3 控制按钮)
- [7.4 控制区域布局](#7.4 控制区域布局)
- 八、关卡设计技巧
-
- [8.1 关卡难度递增](#8.1 关卡难度递增)
- [8.2 关卡设计原则](#8.2 关卡设计原则)
- 九、扩展功能
-
- [9.1 撤销功能](#9.1 撤销功能)
- [9.2 键盘控制](#9.2 键盘控制)
- [9.3 最佳记录](#9.3 最佳记录)
- 十、运行效果与测试
-
- [10.1 项目运行命令](#10.1 项目运行命令)
- [10.2 功能测试清单](#10.2 功能测试清单)
- 十一、总结
摘要
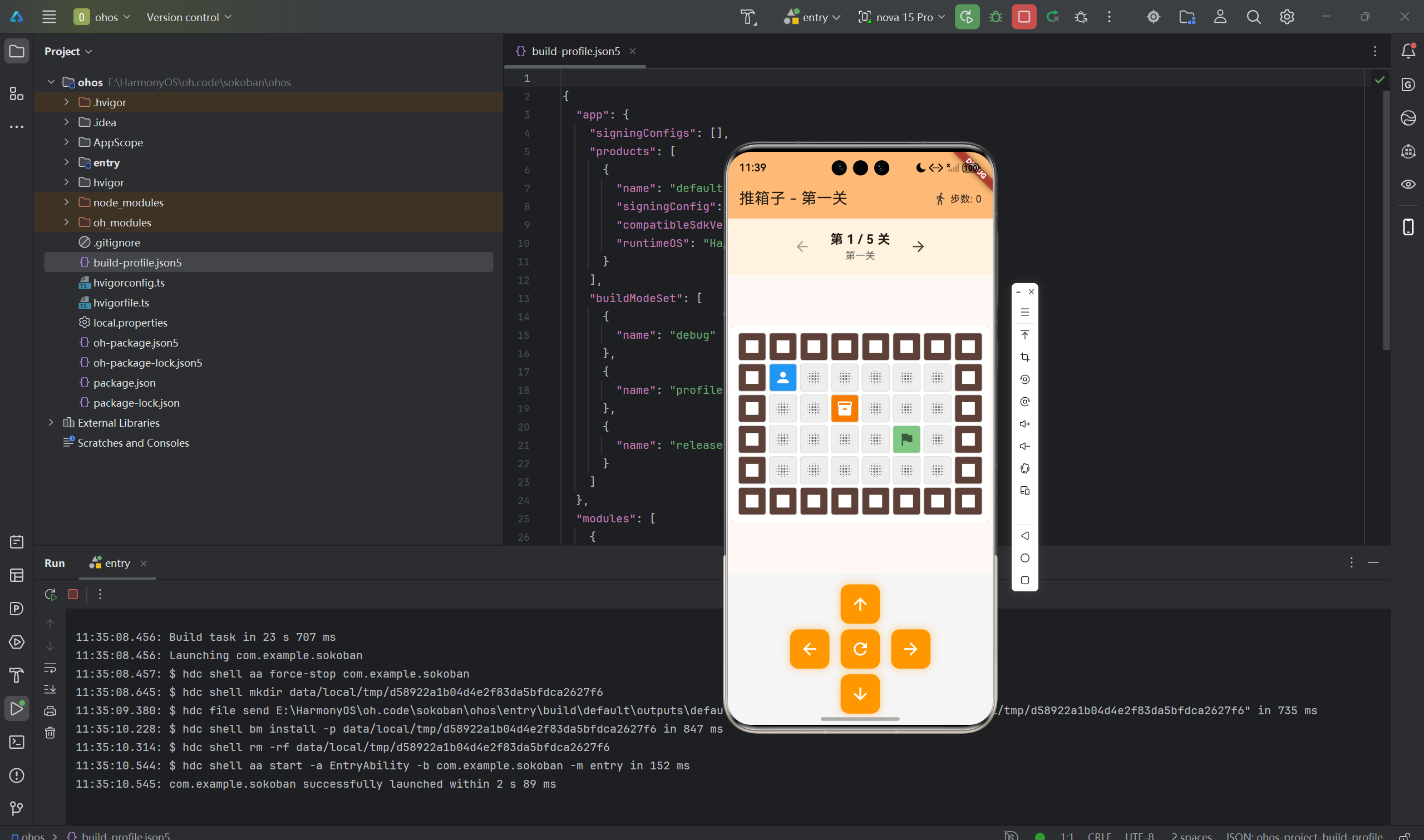
推箱子(Sokoban)是一款经典的益智游戏,玩家需要将箱子推到指定的目标位置。本文将详细介绍如何使用Flutter for OpenHarmony框架开发一款功能完整的推箱子游戏。文章涵盖了游戏地图设计、碰撞检测算法、关卡管理系统、UI交互控制等核心技术点。通过本文学习,读者将掌握Flutter在鸿蒙平台上开发游戏类应用的完整流程,了解二维网格游戏的实现方法。
一、项目背景与功能概述
1.1 推箱子游戏介绍
推箱子是一款经典的益智游戏:
- 目标:将所有箱子推到目标点
- 规则:只能推不能拉,一次只能推一个箱子
- 难度:需要策略规划,走错可能无法完成
1.2 应用功能规划
| 功能模块 | 具体功能 |
|---|---|
| 关卡系统 | 多个难度递增的关卡 |
| 移动控制 | 上下左右移动 |
| 碰撞检测 | 墙壁、箱子检测 |
| 胜利判断 | 箱子全部归位 |
| 步数统计 | 记录移动步数 |
| 关卡切换 | 上一关/下一关 |
| 重置功能 | 重新开始当前关卡 |
1.3 地图元素设计
| 元素 | 数值 | 颜色 | 图标 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 空地 | 0 | 灰色 | 无 |
| 墙 | 1 | 棕色 | 方块 |
| 箱子 | 2 | 橙色 | 箱子 |
| 目标点 | 3 | 绿色 | 旗帜 |
| 箱子在目标点 | 5 | 深绿 | 勾选 |
二、数据模型设计
2.1 地图表示
使用二维数组表示地图:
dart
final List<List<int>> _map = [
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], // 第一行:墙
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], // 空地
[1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1], // 箱子
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 1], // 目标点
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
];2.2 关卡数据结构
dart
final List<Map<String, dynamic>> _levels = [
{
'name': '第一关',
'map': [...], // 地图数据
'startX': 1, // 玩家初始X位置
'startY': 1, // 玩家初始Y位置
},
// 更多关卡...
];2.3 游戏状态
dart
class _GamePageState extends State<GamePage> {
int _currentLevelIndex = 0; // 当前关卡索引
int _playerX = 0; // 玩家X坐标
int _playerY = 0; // 玩家Y坐标
late List<List<int>> _currentMap; // 当前地图
int _steps = 0; // 步数
}三、技术选型与架构设计
3.1 核心技术栈
状态管理
- StatefulWidget管理游戏状态
- setState更新UI
UI组件
- Container:地图格子
- Icon:游戏元素图标
- IconButton:控制按钮
- InteractiveViewer:缩放支持
交互设计
- 按钮控制移动
- 触摸滑动支持
- 键盘方向键
3.2 应用架构
GamePage (游戏页面)
├── AppBar
│ └── 步数显示
├── 关卡信息区域
│ ├── 上一关按钮
│ ├── 关卡名称
│ └── 下一关按钮
├── 游戏地图区域
│ └── 地图网格 (多个格子)
│ ├── 墙壁/箱子/目标点
│ └── 玩家
└── 控制区域
├── 方向按钮
└── 重置按钮3.3 游戏逻辑流程
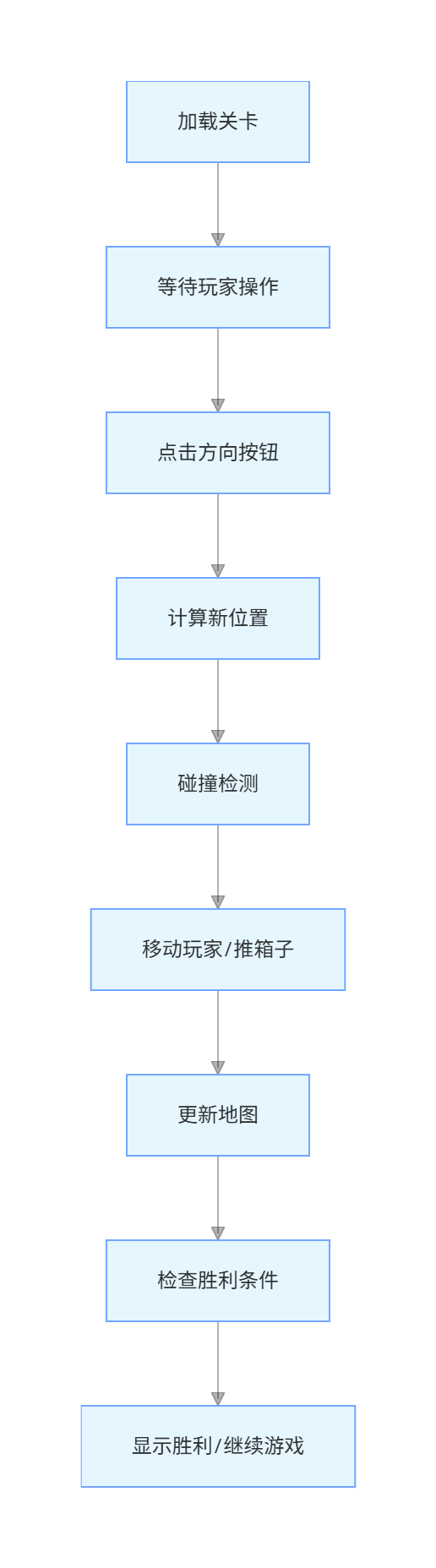
四、关卡管理系统
4.1 加载关卡
dart
void _loadLevel(int index) {
final level = _levels[index];
// 深拷贝地图,避免修改原始数据
_currentMap = (level['map'] as List<List<int>>)
.map((row) => List<int>.from(row))
.toList();
_playerX = level['startX'] as int;
_playerY = level['startY'] as int;
_steps = 0;
setState(() {});
}4.2 关卡切换
dart
// 上一关
void _previousLevel() {
if (_currentLevelIndex > 0) {
_currentLevelIndex--;
_loadLevel(_currentLevelIndex);
}
}
// 下一关
void _nextLevel() {
if (_currentLevelIndex < _levels.length - 1) {
_currentLevelIndex++;
_loadLevel(_currentLevelIndex);
}
}
// 重置当前关卡
void _resetLevel() {
_loadLevel(_currentLevelIndex);
}4.3 深拷贝地图
为什么需要深拷贝:
- 原始地图数据需要保留
- 每次重玩都要从初始状态开始
- 避免关卡间数据污染
dart
// 错误的方式:浅拷贝
_currentMap = level['map']; // 会修改原始数据
// 正确的方式:深拷贝
_currentMap = (level['map'] as List<List<int>>)
.map((row) => List<int>.from(row))
.toList();五、移动逻辑实现
5.1 移动玩家
dart
void _movePlayer(int dx, int dy) {
final newX = _playerX + dx;
final newY = _playerY + dy;
// 检查边界
if (newX < 0 || newX >= _currentMap[0].length ||
newY < 0 || newY >= _currentMap.length) {
return;
}
final targetElement = _currentMap[newY][newX];
// 碰到墙,不能移动
if (targetElement == 1) {
return;
}
// 碰到箱子
if (targetElement == 2 || targetElement == 5) {
_tryPushBox(newX, newY, dx, dy);
return;
}
// 移动到空地或目标点
_playerX = newX;
_playerY = newY;
_steps++;
setState(() {});
}5.2 推箱子逻辑
dart
void _tryPushBox(int boxX, int boxY, int dx, int dy) {
final boxNewX = boxX + dx;
final boxNewY = boxY + dy;
// 检查箱子新位置边界
if (boxNewX < 0 || boxNewX >= _currentMap[0].length ||
boxNewY < 0 || boxNewY >= _currentMap.length) {
return;
}
final boxTargetElement = _currentMap[boxNewY][boxNewX];
// 箱子后面是墙或另一个箱子,不能推
if (boxTargetElement == 1 || boxTargetElement == 2 || boxTargetElement == 5) {
return;
}
// 移动箱子
final currentElement = _currentMap[boxY][boxX];
// 恢复箱子原来位置的状态
if (currentElement == 5) {
_currentMap[boxY][boxX] = 3; // 箱子从目标点上移开
} else {
_currentMap[boxY][boxX] = 0; // 箱子从普通地移开
}
// 设置箱子新位置的状态
if (boxTargetElement == 3) {
_currentMap[boxNewY][boxNewX] = 5; // 箱子推到目标点
} else {
_currentMap[boxNewY][boxNewX] = 2; // 箱子推到普通地
}
// 移动玩家
_playerX = boxX;
_playerY = boxY;
_steps++;
setState(() {});
// 检查胜利
_checkWin();
}5.3 碰撞检测流程图
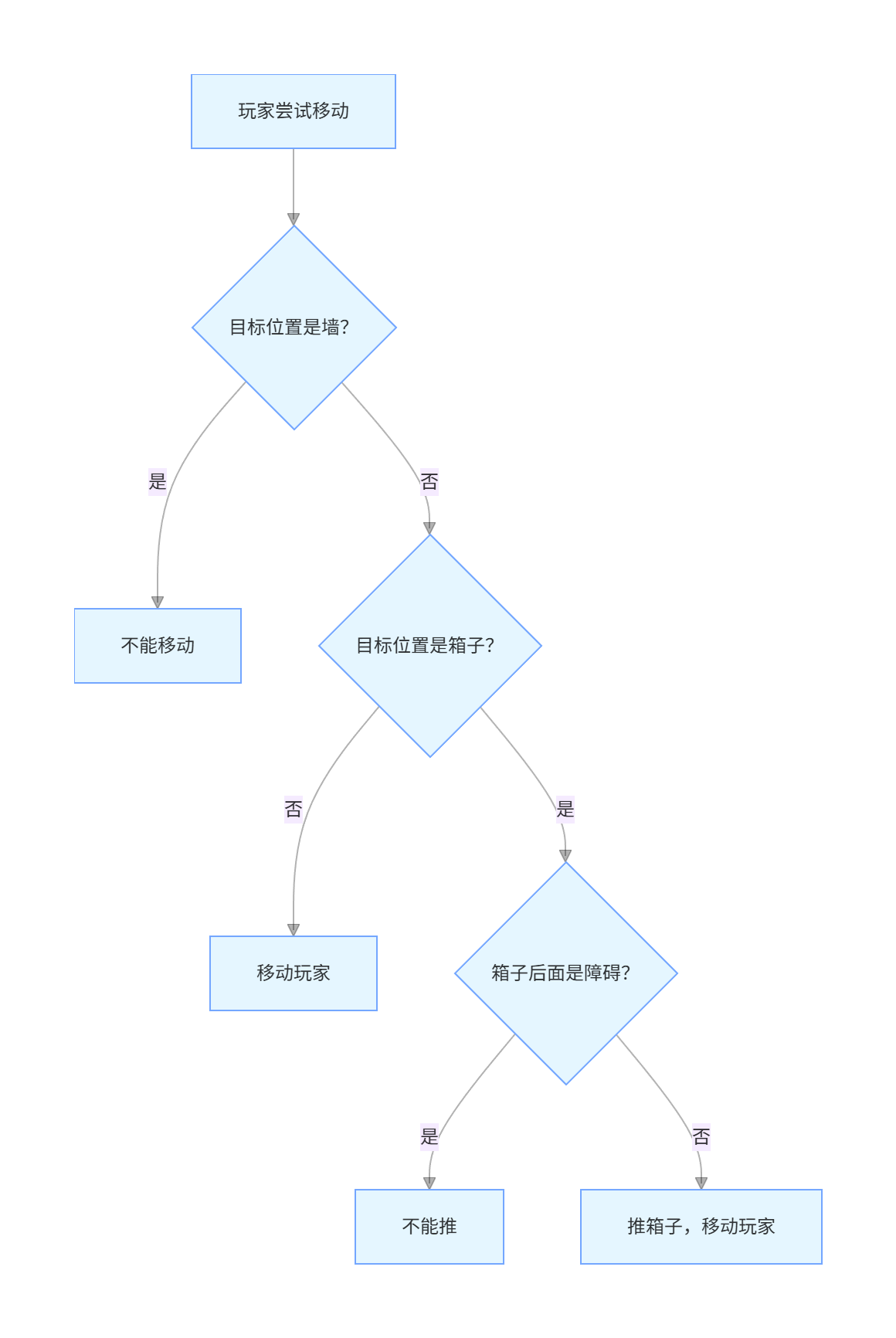
六、胜利判断
6.1 检查胜利条件
dart
void _checkWin() {
bool allBoxesOnTarget = true;
for (final row in _currentMap) {
for (final cell in row) {
if (cell == 2) {
// 还有箱子不在目标点上
allBoxesOnTarget = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (allBoxesOnTarget) {
Future.delayed(const Duration(milliseconds: 300), () {
if (!mounted) return;
_showWinDialog();
});
}
}6.2 胜利对话框
dart
void _showWinDialog() {
showDialog(
context: context,
barrierDismissible: false,
builder: (context) => AlertDialog(
title: const Text('恭喜过关!'),
content: Column(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: [
const Icon(Icons.celebration, size: 64, color: Colors.orange),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
Text('关卡: ${_levels[_currentLevelIndex]['name']}'),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
Text('步数: $_steps'),
],
),
actions: [
TextButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.pop(context);
_loadLevel(_currentLevelIndex);
},
child: const Text('重玩'),
),
if (_currentLevelIndex < _levels.length - 1)
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.pop(context);
_currentLevelIndex++;
_loadLevel(_currentLevelIndex);
},
child: const Text('下一关'),
),
],
),
);
}七、UI界面实现
7.1 地图渲染
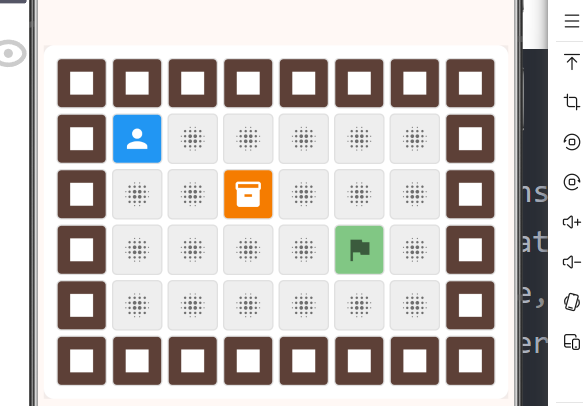
dart
Widget _buildMap() {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.white,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(8),
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: Colors.black.withValues(alpha: 0.1),
blurRadius: 10,
spreadRadius: 2,
),
],
),
child: Column(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: List.generate(_currentMap.length, (y) {
return Row(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: List.generate(_currentMap[y].length, (x) {
final element = _currentMap[y][x];
final isPlayer = x == _playerX && y == _playerY;
return Container(
width: 40,
height: 40,
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(2),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: isPlayer ? Colors.blue : _getElementColor(element),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(4),
border: Border.all(color: Colors.grey.shade300),
),
child: Icon(
isPlayer ? Icons.person : _getElementIcon(element),
color: _getElementIconColor(element, isPlayer),
size: 24,
),
);
}),
);
}),
),
);
}7.2 元素颜色和图标
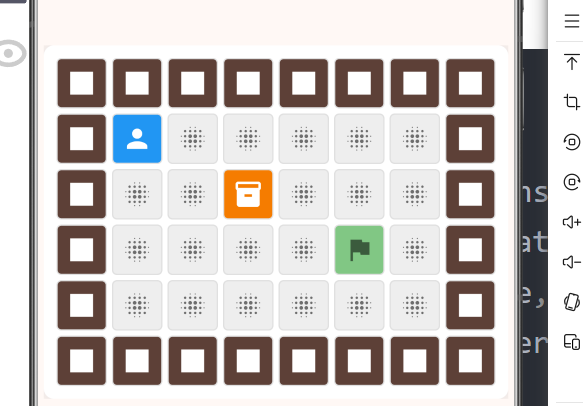
dart
Color _getElementColor(int element) {
switch (element) {
case 1: return Colors.brown.shade700; // 墙
case 2: return Colors.orange.shade700; // 箱子
case 3: return Colors.green.shade300; // 目标点
case 5: return Colors.green.shade600; // 箱子在目标点
default: return Colors.grey.shade200; // 空地
}
}
IconData _getElementIcon(int element) {
switch (element) {
case 1: return Icons.square;
case 2: return Icons.inventory_2;
case 3: return Icons.flag;
case 5: return Icons.check_circle;
default: return Icons.blur_on;
}
}7.3 控制按钮

dart
Widget _buildControlButton(IconData icon, VoidCallback? onPressed) {
return Container(
width: 56,
height: 56,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.orange,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: Colors.orange.withValues(alpha: 0.3),
blurRadius: 8,
spreadRadius: 2,
),
],
),
child: IconButton(
onPressed: onPressed,
icon: Icon(icon, color: Colors.white, size: 28),
style: IconButton.styleFrom(
backgroundColor: Colors.orange,
foregroundColor: Colors.white,
),
),
);
}7.4 控制区域布局
dart
Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
color: Colors.grey.shade100,
child: Column(
children: [
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
_buildControlButton(Icons.arrow_upward, () => _movePlayer(0, -1)),
],
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
_buildControlButton(Icons.arrow_back, () => _movePlayer(-1, 0)),
const SizedBox(width: 16),
_buildControlButton(Icons.refresh, _resetLevel),
const SizedBox(width: 16),
_buildControlButton(Icons.arrow_forward, () => _movePlayer(1, 0)),
],
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
_buildControlButton(Icons.arrow_downward, () => _movePlayer(0, 1)),
],
),
],
),
)八、关卡设计技巧
8.1 关卡难度递增
dart
// 第一关:1个箱子,简单布局
Level 1:
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
[1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1] // 1个箱子
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 1] // 1个目标
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
// 第二关:2个箱子
Level 2:
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
[1, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, 0, 1] // 2个箱子
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
[1, 0, 3, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1] // 2个目标
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
// 第五关:3个箱子,复杂布局
Level 5:
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]
[1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1, 1]
[1, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, 1] // 3个箱子
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1]
[0, 1, 0, 3, 0, 1, 0]
[0, 1, 3, 0, 3, 1, 0] // 3个目标
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]8.2 关卡设计原则
- 可解性:确保关卡有解
- 循序渐进:难度逐步增加
- 空间利用:合理利用有限空间
- 陷阱设计:设置一些容易走错的路径
- 测试验证:每个关卡都要测试可解
九、扩展功能
9.1 撤销功能
dart
final List<Map<String, dynamic>> _history = [];
void _movePlayer(int dx, int dy) {
// 保存当前状态
_history.add({
'playerX': _playerX,
'playerY': _playerY,
'map': List<List<int>>.from(
_currentMap.map((row) => List<int>.from(row))
),
'steps': _steps,
});
// 执行移动...
// 限制历史记录数量
if (_history.length > 100) {
_history.removeAt(0);
}
}
void _undo() {
if (_history.isEmpty) return;
final lastState = _history.removeLast();
_playerX = lastState['playerX'] as int;
_playerY = lastState['playerY'] as int;
_currentMap = (lastState['map'] as List<List<int>>)
.map((row) => List<int>.from(row))
.toList();
_steps = lastState['steps'] as int;
setState(() {});
}9.2 键盘控制
dart
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return KeyboardListener(
focusNode: FocusNode(),
onKeyEvent: (KeyEvent event) {
if (event is KeyDownEvent) {
switch (event.logicalKey) {
case LogicalKeyboardKey.arrowUp:
_movePlayer(0, -1);
break;
case LogicalKeyboardKey.arrowDown:
_movePlayer(0, 1);
break;
case LogicalKeyboardKey.arrowLeft:
_movePlayer(-1, 0);
break;
case LogicalKeyboardKey.arrowRight:
_movePlayer(1, 0);
break;
}
}
},
child: Scaffold(...),
);
}9.3 最佳记录
dart
final Map<int, int> _bestScores = {};
void _checkWin() {
if (allBoxesOnTarget) {
// 更新最佳记录
if (!_bestScores.containsKey(_currentLevelIndex) ||
_steps < _bestScores[_currentLevelIndex]!) {
_bestScores[_currentLevelIndex] = _steps;
}
_showWinDialog();
}
}
// 显示最佳记录
Text('最佳: ${_bestScores[_currentLevelIndex] ?? '-'} 步')十、运行效果与测试
10.1 项目运行命令
bash
cd E:\HarmonyOS\oh.code\sokoban
flutter run -d ohos10.2 功能测试清单
移动测试
- 方向按钮控制移动
- 碰到墙壁不能移动
- 可以推动单个箱子
- 不能同时推多个箱子
关卡测试
- 上一关/下一关切换
- 关卡正确加载
- 重置功能正常
胜利测试
- 箱子全部归位触发胜利
- 显示步数统计
- 重玩按钮功能正常
- 最后一关无下一关按钮
UI测试
- 地图正确渲染
- 玩家位置正确
- 元素颜色正确
- 缩放功能正常
十一、总结
本文详细介绍了使用Flutter for OpenHarmony开发推箱子游戏的完整过程,涵盖了以下核心技术点:
- 地图设计:二维数组表示、元素编码
- 移动逻辑:玩家移动、箱子推动、碰撞检测
- 关卡管理:关卡加载、切换、重置
- 胜利判断:状态检测、对话框显示
- UI实现:地图渲染、控制按钮
- 状态管理:游戏状态、步数统计
- 数据结构:深拷贝、历史记录
这个项目展示了Flutter在游戏开发中的完整流程。读者可以基于此项目添加更多功能:
- 撤销/重做功能
- 键盘控制支持
- 更多关卡
- 关卡编辑器
- 最佳记录排行
- 游戏音效
- 动画效果
通过本文的学习,读者应该能够独立开发类似的网格类游戏,掌握Flutter在鸿蒙平台上的游戏开发技巧。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区 : 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区