数据库sql语句讲解
01 数据库语句应用介绍
1)SQL语句概念介绍
- SQL语句:Structured Query Language(结构化查询语言),用于数据库管理的命令
- SQL语句使用规范 :
- SQL 92:命令执行更复杂
- SQL 99:命令执行更简单
2)SQL语句常见分类
-
DDL(Data Definition Language)语句 - 数据定义语句
- 作用:管理数据库和数据表,管理数据表中的索引信息
- 命令:
create、alter、drop、show
-
DCL(Data Control Language)语句 - 数据控制语句
- 作用:管理用户权限信息
- 命令:
grant、revoke
-
DML(Data Manipulation Language)语句 - 数据操控语句 *****
- 作用:管理数据表中的数据内容
- 命令:
insert、delete、update
-
DQL(Data Query Language)语句 - 数据查询语句
- 作用:查询调取表中的数据信息
- 命令:
select(单表查询数据、多表查询数据)
3)数据库数据类型
作用:
- 定义数据表中的数据以什么方式进行存储
- 便于进行数据信息检索
数据类型常见分类:
类型一:数值类型
- 整数类型 :
int(不同整数类型区别:影响存储数据的取值范围) - 小数类型 :
float(不同小数类型区别:影响小数位的精度)
类型二:字符类型
- 字符类型 :
char(定长)/varchar(变长)- 不同字符类型区别:影响数据字符存储数量
类型三:特殊类型
- 满足特殊数据信息存储
- 时间类型 :
date - 枚举类型 :
enum
4)数据表中约束和属性信息
约束信息:对表中录入数据做一定的限制
-
PK约束(主键约束):确保设置主键约束的列,必须录入的数据非空且唯一
- 举例:学生表 - 学号列
-
UK约束(唯一约束):确保设置唯一约束的列,必须录入的数据唯一
- 举例:学生表 - 手机号
-
NN约束(非空约束):确保设置非空约束的列,必须录入的数据非空
- 举例:学生表 - 姓名
-
FK约束(外键约束):多业务操作多张数据表进行数据录入或删除时,确保操作的顺序性
属性信息:对数据类型和约束信息的补充,保证录入数据的完善性
default:可以填入默认数据信息,配合PK约束和NN约束使用auto_increment:可以指定列实现数据自增功能,配合PK约束使用comment:给指定列设置注释信息unsigned:保证数值列字段信息必须非负
02 数据库语句应用练习
1)DDL语句类型练习
针对数据库操作练习:
创建数据库:
sql
create database 库名;
create schema 库名;PS:创建数据库时,数据库的名称最好有意义,不要和数据库服务中一些语句名称一致
查看数据库:
sql
show databases;
show databases like 'w%';
show create database www; -- 查看数据库详细创建语句,还可以利用此命令完成数据的备份切换数据库:
sql
use 库名;
use blog;
select database(); -- 查看当前使用的数据库删除数据库:
sql
drop database `table`;
drop database blog;针对数据表操作练习:
创建数据表:
sql
-- 语法结构:
create table 表名 (
字段01名称 数据类型 属性信息/约束信息,
字段02名称 数据类型 属性信息/约束信息,
字段03名称 数据类型 属性信息/约束信息,
约束信息/索引信息
)存储引擎(文件系统) 字符集;
-- 示例:
CREATE TABLE student (
id int NOT NULL COMMENT '学号信息',
name varchar(45) NOT NULL COMMENT '学生名',
age tinyint unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT '学生年龄',
gender enum('M','F','N') NOT NULL DEFAULT 'N' COMMENT '学生性别',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci COMMENT='学生表'查看数据表:
sql
show tables; -- 查看所有表
desc student; -- 查看表结构
show create table student; -- 查看表创建方法,可以实现独立表空间迁移修改数据表:
方式一:修改表名
sql
rename table 原有表名 to 新表名;
rename table blog to kodbox;
alter table 原表名 rename 新表名;方式二:修改数据表字段信息
sql
-- 添加新字段:
alter table student add column telno char(11) not null unique key comment '手机号';
alter table student add column telno02 char(11) not null unique key comment '手机号' after name;
alter table student add column telno03 char(11) not null unique key comment '手机号' before id;
-- 字段信息说明:
-- 字段名:telno(电话号码)
-- 数据类型:CHAR(11)(固定长度为11的字符串)
-- 约束:NOT NULL(该字段不允许为空,必须填写值)
-- 约束:UNIQUE KEY(该字段的值在整个表中必须是唯一的,不能重复)
-- 注释:'手机号'(对该字段的说明注释)
-- 删除无用字段:
alter table student drop column telno03;方式三:修改数据表字段数据类型、约束、属性信息
sql
alter table student modify name char(64) unique key null comment '学生名';删除数据表:
sql
-- 删除数据表本身:
drop table 表名;
drop table blog;
-- 清空数据表数据:
delete from 表名; -- 少量数据表(10万以内)
truncate table 表名; -- 大量数据表(10万以内)2)DML语句类型练习
插入数据信息:
sql
-- 标准方式:
insert into 表名 (字段01名称,字段02名称,...) values (值01,值02,...);
-- 简化方式:
insert into student (name,age) values ('xiaoB',20);
insert into student values (3,'xiaoC',18,'M');
insert into student values (4,'xiaoD',18,'M'),(5,'xiaoE',20,'F');修改数据信息:
sql
update 表名 set 字段01名称=修改的值,字段02名称=修改的值 where 修改数据条件;
update student set age=20,gender='F' where id=3;删除数据信息:
sql
delete from 表名 where 删除条件列;
delete from student where id=3;3)DQL语句类型练习
单表查询数据
创建测试数据:
bash
mysql -uroot -pxiaoQ123 < world.sql1)利用 select+from 查看表中所有数据
sql
-- 查看city表中所有字段数据信息
select * from city;
select name,population from city;PS:不要在企业环境中,对大表数据进行全表查看(磁盘-内存-展示 消耗磁盘性能-IO性能)
2)利用 select+from+where 过滤指定数据信息
等值查询数据信息:
sql
-- 查询中国的所有城市信息
select * from city where countrycode='CHN';范围查询数据信息:
sql
-- 查询人口数量大于100w城市信息
select * from city where population >1000000;
-- 可用操作符:> < <= >= 多个条件进行数据查询:
sql
-- 查询中国城市人口数量,并且将人口数量大于100w城市进行显示
select * from city where countrycode='CHN' and population>1000000;
-- 查询中国城市人口数量,将人口数量大于200w,和小于1w城市信息都进行显示
select * from city where countrycode='CHN' and population >2000000 or countrycode='CHN' and population <10000;
select * from city where countrycode="CHN" and (population<=10000 or Population>=2000000);
-- and:将关联的多个条件进行逐一数据过滤
-- or:将关联的多个条件分别进行过滤,将过滤后结果进行整合模糊条件进行数据查询:
sql
-- 查询中国城市信息,将城市名称是a开头城市显示
select * from city where countrycode='CHN' and name like 'a%';特殊组合信息查询(配合in,not in,between and):
sql
-- 查询中国和美国的所有城市
select * from city where countrycode='CHN' or countrycode='USA';
select * from city where countrycode in ('CHN','USA');
-- 查询中国人口数量在 50000w~100000w之间城市信息
select * from city where countrycode='CHN' and population>50000 and population<100000;
select * from city where countrycode='CHN' and population between 50000 and 100000;去重查询数据信息:
sql
-- 统计中国有多少个省份
select distinct District from city where countrycode='CHN';3)select+from+group by 分组查询数据信息
分组查询作用:可以将不同类型的条件信息进行分类,将不同类型中的数据进行统计分析
聚合函数应用:
sum():求和函数count():计数函数max():最大值函数min():最小值函数avg():平均值函数
sql
-- 根据city数据表,求出每个国家的人口总数 group by countrycode
select countrycode,sum(population) from city group by countrycode;
-- 根据city数据表,查询中国各个省份的城市数量 group by District
-- 查询需求中只要有:每个/各个 -- 应用分组查询,每个/各个关键字后面条件作为分组条件列
select District,count(name) from city where countrycode='chn' group by District;
-- 根据city数据表,查询中国各个省份的城市数量,以及显示每个省份城市信息
select District,count(name),group_concat(name) from city where countrycode='chn' group by District\Ggroup by语句执行逻辑:
- 根据group by语句后面指定条件列进行排序
group by countrycode - 根据group by语句后面指定条件列进行合并
group by countrycode chn - 根据group by语句中应用聚合函数,将不同分组区域数据进行聚合统计
sum(population)
分组查询数据经典报错:
ERROR 1055 (42000):
Expression #3 of SELECT list is not in GROUP BY clause and contains nonaggregated column 'world.city.Name' which is not functionally dependent on columns in GROUP BY clause; this is incompatible with sql_mode=only_full_group_by此时输出数据信息,不符合关系型数据库结构(一行对应一行)
4)select+from+having
having:表示根据条件进行过滤查询(可以将聚合后临时产生的列作为条件列查询)where:表示根据条件进行过滤查询(只能根据表中已有的条件列进行过滤)
sql
-- 根据city数据表,求出每个国家的人口总数,将人口总数大于1000w国家信息,和人口信息进行输出
select countrycode,sum(population) from city group by countrycode having sum(population)>50000000;5)select+from+order by 做排序
sql
-- 根据city数据表,求出每个国家的人口总数,将人口总数大于1000w国家信息,并进行国家人口信息排序
mysql> select countrycode,sum(population) from city group by countrycode having sum(population)>50000000 order by sum(population) desc;
+-------------+-----------------+
| countrycode | sum(population) |
+-------------+-----------------+
| CHN | 175953614 |
| IND | 123298526 |
| BRA | 85876862 |
| USA | 78625774 |
| JPN | 77965107 |
| RUS | 69150700 |
| MEX | 59752521 |
+-------------+-----------------+
7 rows in set (0.03 sec)6)select+from+limit 截取部分信息输出(head)
sql
-- 根据city数据表,求出每个国家的人口总数,将人口总数大于1000w国家信息,并显示国家人口数量最多的三个国家
mysql> select countrycode,sum(population) from city group by countrycode having sum(population)>50000000 order by sum(population) desc limit 3;
+-------------+-----------------+
| countrycode | sum(population) |
+-------------+-----------------+
| CHN | 175953614 |
| IND | 123298526 |
| BRA | 85876862 |
+-------------+-----------------+
3 rows in set (0.03 sec)完整查询语句顺序 :select+from+where+group by+having+order by+limit
多表查询数据
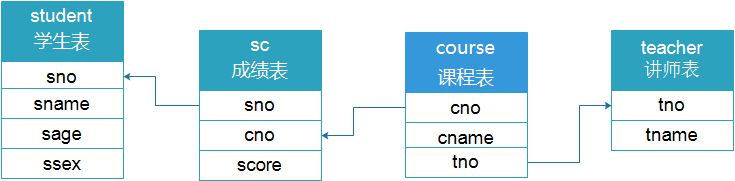
创建多表查询的测试数据:
sql
# 创建多表查询所需模拟数据库和数据表信息
CREATE DATABASE school CHARSET utf8;
USE school;
CREATE TABLE student (
sno INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '学号',
sname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
sage TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
ssex ENUM('f','m') NOT NULL DEFAULT 'm' COMMENT '性别'
) ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE course (
cno INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY COMMENT '课程编号',
cname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '课程名字',
tno INT NOT NULL COMMENT '教师编号'
) ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE sc (
sno INT NOT NULL COMMENT '学号',
cno INT NOT NULL COMMENT '课程编号',
score INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '成绩'
) ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE teacher (
tno INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY COMMENT '教师编号',
tname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '教师名字'
) ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8;
# 在数据库与数据表中插入模拟数据
INSERT INTO student(sno,sname,sage,ssex)
VALUES
(1,'zhang3',18,'m'),
(2,'zhang4',18,'m'),
(3,'li4',18,'m'),
(4,'wang5',19,'f'),
(5,'zh4',18,'m'),
(6,'zhao4',18,'m'),
(7,'ma6',19,'f'),
(8,'oldboy',20,'m'),
(9,'oldgirl',20,'f'),
(10,'oldp',25,'m');
INSERT INTO teacher(tno,tname)
VALUES
(101,'oldboy'),
(102,'xiaoQ'),
(103,'xiaoA'),
(104,'xiaoB');
INSERT INTO course(cno,cname,tno)
VALUES
(1001,'linux',101),
(1002,'python',102),
(1003,'mysql',103),
(1004,'go',105);
INSERT INTO sc(sno,cno,score)
VALUES
(1,1001,80),
(1,1002,59),
(2,1002,90),
(2,1003,100),
(3,1001,99),
(3,1003,40),
(4,1001,79),
(4,1002,61),
(4,1003,99),
(5,1003,40),
(6,1001,89),
(6,1003,77),
(7,1001,67),
(7,1003,82),
(8,1001,70),
(9,1003,80),
(10,1003,96);
SELECT * FROM student;
SELECT * FROM teacher;
SELECT * FROM course;
SELECT * FROM sc;表说明:
course:课程表sc:成绩表student:学生表teacher:讲师表
如何将多张表进行连接查询:
1)内连接查询数据(将多张表的交集数据进行整合)
SQL 92语法:
sql
select * from A,B where A.id=B.id;
mysql> select * from teacher,course where teacher.tno=course.tno;
+-----+--------+------+--------+-----+
| tno | tname | cno | cname | tno |
+-----+--------+------+--------+-----+
| 101 | oldboy | 1001 | linux | 101 |
| 102 | xiaoQ | 1002 | python | 102 |
| 103 | xiaoA | 1003 | mysql | 103 |
+-----+--------+------+--------+-----+SQL 99语法:
sql
select * from A join B on A.id=B.id;
mysql> select * from teacher join course on teacher.tno=course.tno;
+-----+--------+------+--------+-----+
| tno | tname | cno | cname | tno |
+-----+--------+------+--------+-----+
| 101 | oldboy | 1001 | linux | 101 |
| 102 | xiaoQ | 1002 | python | 102 |
| 103 | xiaoA | 1003 | mysql | 103 |
+-----+--------+------+--------+-----+2)外连接查询数据
SQL 99语法:
左外连接(显示左边表中的所有内容):
sql
select * from A left join B on A.id=B.id;
mysql> select * from teacher left join course on teacher.tno=course.tno;
+-----+--------+------+--------+------+
| tno | tname | cno | cname | tno |
+-----+--------+------+--------+------+
| 101 | oldboy | 1001 | linux | 101 |
| 102 | xiaoQ | 1002 | python | 102 |
| 103 | xiaoA | 1003 | mysql | 103 |
| 104 | xiaoB | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+-----+--------+------+--------+------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)右外连接(显示右边表中的所有内容):
sql
select * from A right join B on A.id=B.id;
mysql> select * from teacher right join course on teacher.tno=course.tno;
+------+--------+------+--------+-----+
| tno | tname | cno | cname | tno |
+------+--------+------+--------+-----+
| 101 | oldboy | 1001 | linux | 101 |
| 102 | xiaoQ | 1002 | python | 102 |
| 103 | xiaoA | 1003 | mysql | 103 |
| NULL | NULL | 1004 | go | 105 |
+------+--------+------+--------+-----+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)连表查询数据方法:
步骤一:需要先获取表与表之间的关联(构建ER模型)
步骤二:根据查询需求,获取需要的表信息
步骤三:将多张关联的表进行拼接
步骤四:根据需求查询数据内容
示例练习:
01 统计zhang3,学习了几门课?
sql
-- 涉及表:student sc course
select * from student
join sc on student.sno=sc.sno
join course on sc.cno=course.cno;
-- 完整查询:
select student.sname,count(course.cname) from student
join sc on student.sno=sc.sno
join course on sc.cno=course.cno
where student.sname='zhang3';02 查询所有老师所教学生不及格的信息?
sql
-- 涉及表:student sc course
select student.sname,sc.score,course.cname from student
join sc on student.sno=sc.sno
join course on sc.cno=course.cno
where sc.score<60;课后作业:
-
根据之前可道云业务平台,找到保存用户和密码信息的表,并试着直接在数据库中修改用户密码
-
完成连接查询练习题
技巧:统计谁就是group by谁,以谁为分组
练习题答案:
1. 查询平均成绩大于60分的同学的学号和平均成绩
sql
select sno,avg(score) from sc group by sno having avg(score)>60;2. 查询所有同学的学号,姓名,选课数,总成绩
sql
select student.sno,sname,count(cno),sum(score) from student
join sc on student.sno=sc.sno
group by student.sno,sname;3. 查询各科成绩最高和最低的分,以如下形式显示:课程ID,最高分,最低分
sql
select sc.cno,max(score),min(score) from sc
join course on sc.cno=course.cno
group by sc.cno;4. 统计各位老师,所教课程的及格率
sql
-- 注意where必须在group by之前(更正)
select teacher.tname,course.cname,concat(floor(count(case when sc.score>=60 then 1 end)/count(*)*100),"%") from teacher
join course on teacher.tno=course.tno
join sc on course.cno=sc.cno
group by teacher.tno,course.cno;5. 查询每门课程被选修的学生数
sql
select sc.cno,count(sno),cname from sc
join course on sc.cno=course.cno
group by sc.cno;6. 查询出只选修了一门课程的全部学生的学号和姓名
sql
select student.sno,sname from student
join sc on student.sno=sc.sno
group by student.sno having count(cno)=1;7. 查询选修课程门数超过1门的学生信息
sql
select student.sno,sname,sage,ssex from student
join sc on student.sno=sc.sno
group by student.sno having count(cno)>1;8. 统计每门课程:优秀(85分以上),良好(70-85),一般(60-70),不及格(小于60)
sql
select course.cname as 课程名,
group_concat(case when sc.score>85 then student.sname end) as 优秀,
group_concat(case when sc.score>=70 and sc.score<85 then student.sname end) as 良好,
group_concat(case when sc.score>=60 and sc.score<70 then student.sname end) as 一般,
group_concat(case when sc.score<60 then student.sname end) as 不及格
from student
join sc on student.sno=sc.sno
join course on sc.cno=course.cno
group by course.cno;9. 查询平均成绩大于85的所有学生的学号、姓名和平均成绩
sql
select student.sno,sname,avg(score) from student
join sc on student.sno=sc.sno
group by student.sno having avg(score)>85;