cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
int m;
};
class B{
public:
int m;
virtual void foo(void){
}
};
int main(void){
A a;
B b;
cout << "a size : " << sizeof(a) << endl;
cout << "b size : " << sizeof(b) << endl;
return 0;
}- 每一个含有虚函数(无论是其本身的,还是继承而来的)的类都至少有一个与之对应的虚函数表,其中存放着该类所有的虚函数对应的函数指针
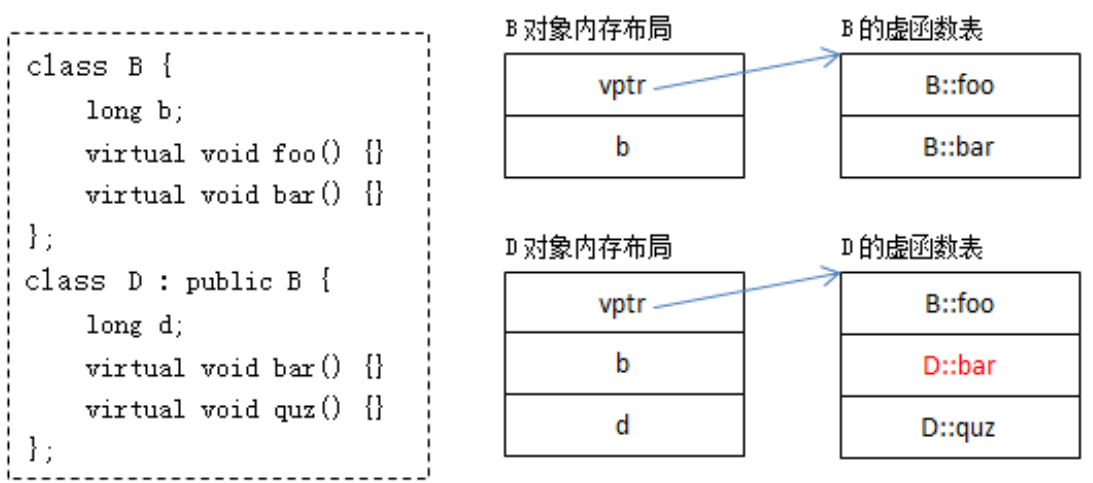
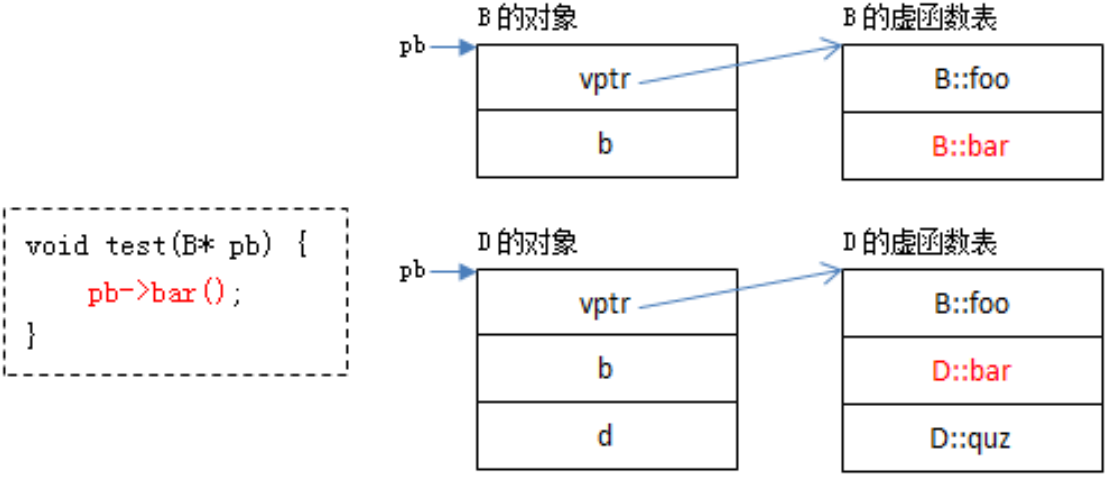
- 当编译器编译以下test函数时只知道pb是B*类型的指针,并不知道它指向的具体对象类型 :pb可能指向的是B的对象,也可能指向的是D的对象。
- 只有当程序执行过程中给test函数传递了具体参数才能确定pb指向了哪个对象,从而确定访问哪个虚表,从而实现了多态