背景
在 浅解 Junit 4 第二篇: Runner 和 ParentRunner 一文中,我们初步探讨了 JUnit 4 是如何找到并运行带有 @Test 注解的方法的。在此基础上,我们继续探索 JUnit 4 里的其他核心类。本文会 初步探讨 Suite (测试套件) 是如何把测试类组合起来的。本文的主角是 ⬇️
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> org.junit.runners.Suite \text{org.junit.runners.Suite} </math>org.junit.runners.Suite
要点
Suite继承了ParentRunner<Runner>- 调用
Suite的构造函数时,子节点会保存在org.junit.runners.Suite#runners字段中(每个子节点都是Runner的实例) Suite作为亲节点,会负责查找和运行子节点
正文
一个具体的场景: 用 Nand 来实现 Not/And/Or
在 浅解 Junit 4 第二篇: Runner 和 ParentRunner 一文中有关于 "用 Nand 来实现 Not/And/Or" 这个场景的更多描述,在那篇文章里,也提供了完整的代码。考虑到 Not/And/Or 都是基本的逻辑运算,我们可以用一个 Suite (测试套件) 来对它们打包进行测试。于是我们需要添加一个 BasicGateSuite.java 文件 ⬇️
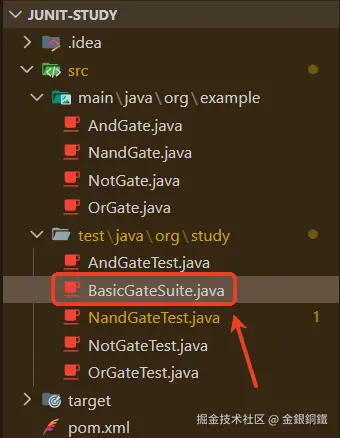
其内容如下
java
package org.study;
import org.junit.runner.JUnitCore;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Suite;
@RunWith(Suite.class)
@Suite.SuiteClasses({NotGateTest.class, AndGateTest.class, OrGateTest.class})
public class BasicGateSuite {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JUnitCore.runClasses(BasicGateSuite.class);
}
}Suite (测试套件) 如何把测试类组合起来
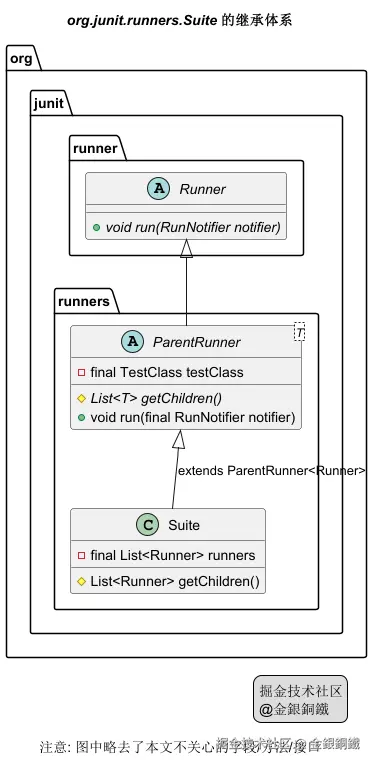
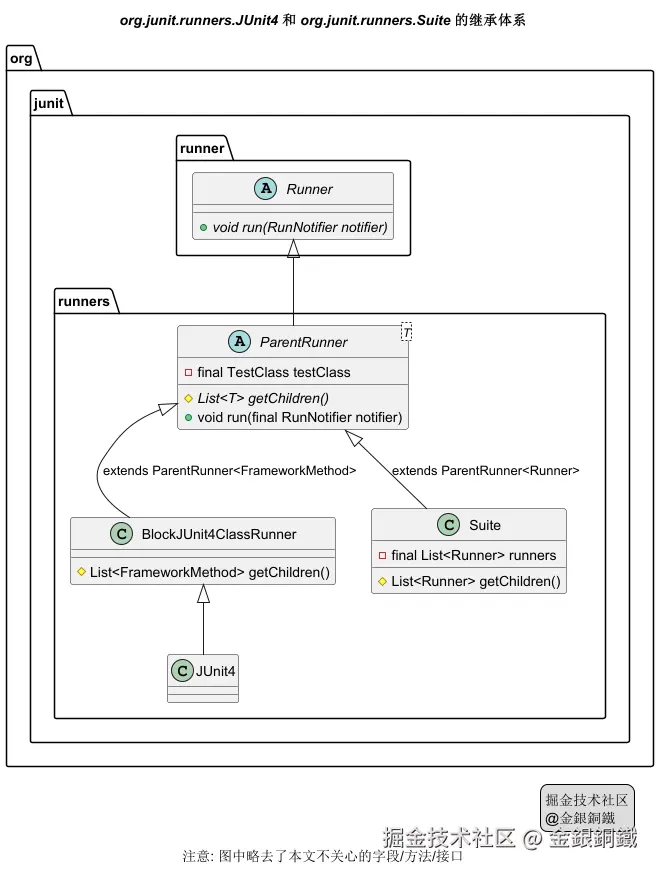
ParentRunner 继承了 Runner,而 Suite 继承了 ParentRunner<Runner>,简要的类图如下 ⬇️
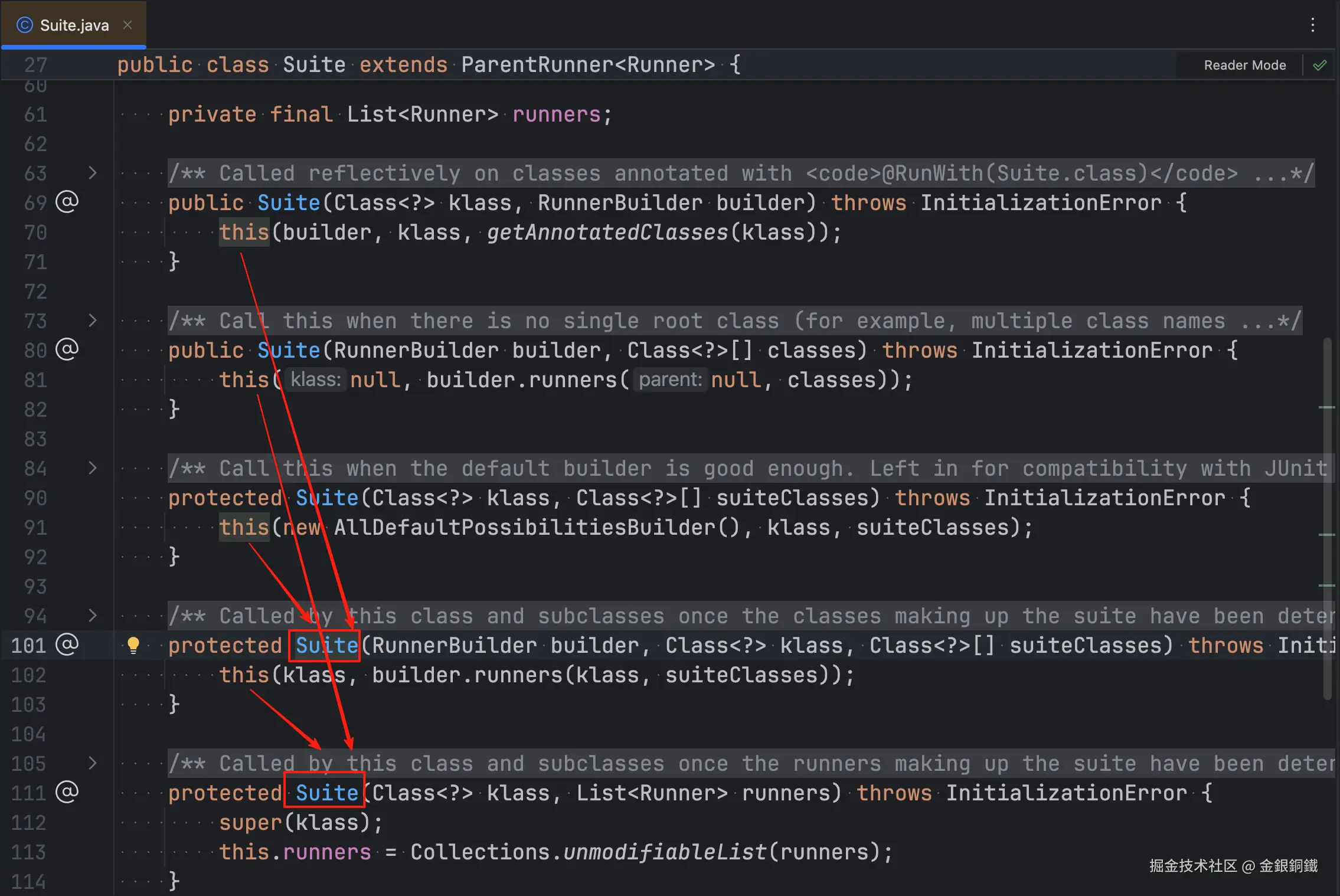
Suite 类中有 5 个构造函数,前 4 个构造函数会直接或间接地调用最后一个构造函数,它们的调用关系如下图所示 ⬇️
我们在第 5 个构造函数里打一个断点(比如可以在第 113 行打一个断点),然后 debug BasicGateSuite 里的 main 方法,可以看到 runners 参数里包含了 3 个元素
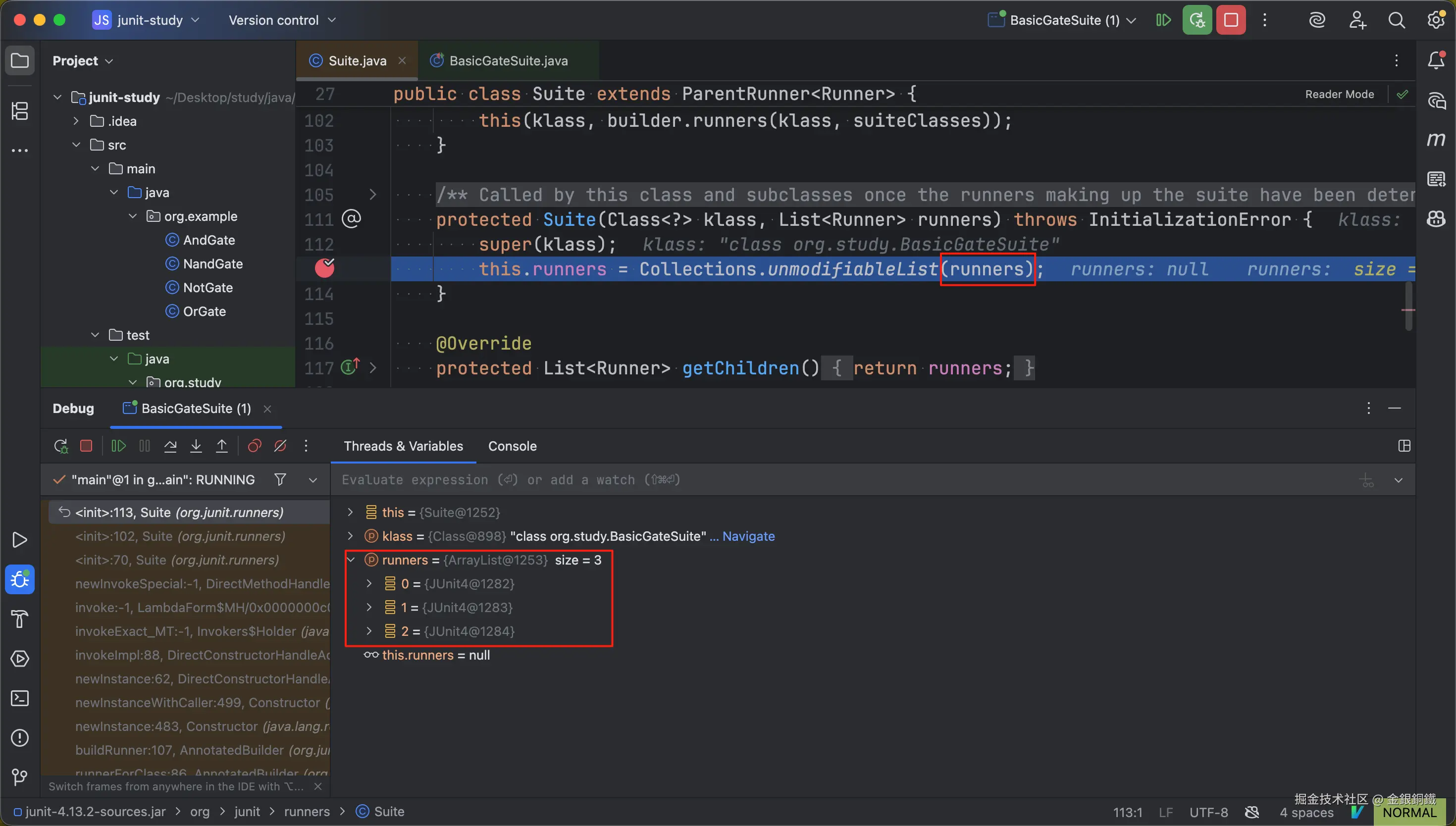 以下标为 0 的元素为例,我们看一下它的详细内容
以下标为 0 的元素为例,我们看一下它的详细内容
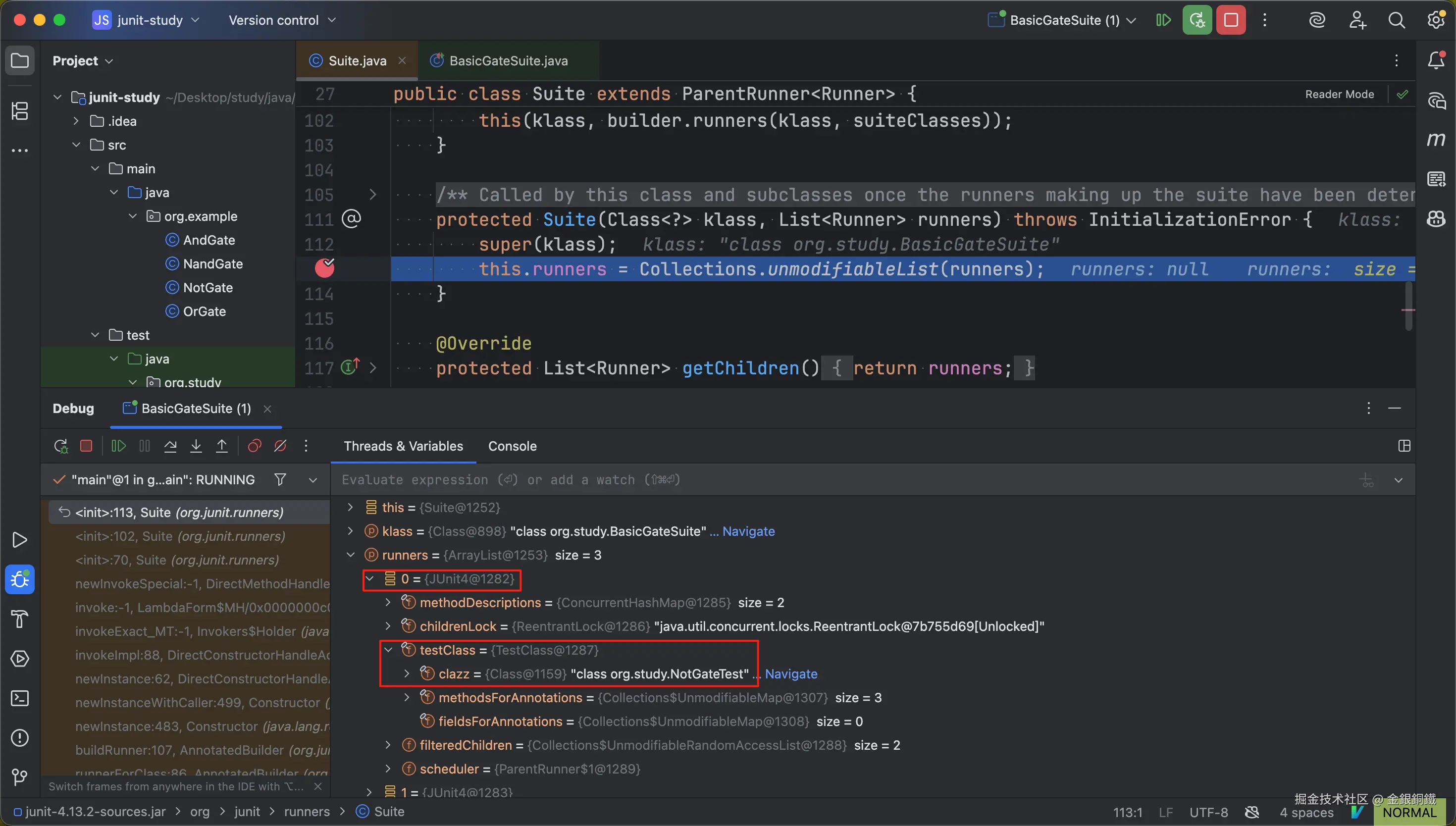
可以看到 runners 中下标为 0 的元素是一个 JUnit4 的实例(这个类的全称是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> org.junit.runners.JUnit4 \text{org.junit.runners.JUnit4} </math>org.junit.runners.JUnit4)
JUnit4 类继承了 BlockJUnit4ClassRunner 类,而 BlockJUnit4ClassRunner 类继承了 ParentRunner<FrameworkMethod>,简要的类图如下 ⬇️
我们可以把 Suite 看成一个"亲子结构"
- 亲(
Parent):Suite自身(它是子节点的容器) - 子(
Child): 作为子节点的其他Runner
以 BasicGateSuite 为例
| 测试类的名称 | 对应的 Runner 是什么类型 |
|---|---|
BasicGateSuite |
和 BasicGateSuite 对应的 Runner 是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> org.junit.runners.Suite \text{org.junit.runners.Suite} </math>org.junit.runners.Suite 的实例 |
NotGateTest |
和 NotGateTest 对应的 Runner 是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> org.junit.runners.JUnit4 \text{org.junit.runners.JUnit4} </math>org.junit.runners.JUnit4 的实例 |
AndGateTest |
和 AndGateTest 对应的 Runner 是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> org.junit.runners.JUnit4 \text{org.junit.runners.JUnit4} </math>org.junit.runners.JUnit4 的实例 |
OrGateTest |
和 OrGateTest 对应的 Runner 是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> org.junit.runners.JUnit4 \text{org.junit.runners.JUnit4} </math>org.junit.runners.JUnit4 的实例 |
我们记
- 和
BasicGateSuite对应的Runner为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Runner BasicGateSuite \text{Runner}_\text{BasicGateSuite} </math>RunnerBasicGateSuite - 和
NotGateTest对应的Runner为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Runner NotGateTest \text{Runner}_\text{NotGateTest} </math>RunnerNotGateTest - 和
AndGateTest对应的Runner为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Runner AndGateTest \text{Runner}_\text{AndGateTest} </math>RunnerAndGateTest - 和
OrGateTest对应的Runner为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Runner OrGateTest \text{Runner}_\text{OrGateTest} </math>RunnerOrGateTest
那么 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Runner BasicGateSuite \text{Runner}_\text{BasicGateSuite} </math>RunnerBasicGateSuite 是亲节点,它的三个子节点是
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Runner NotGateTest \text{Runner}_\text{NotGateTest} </math>RunnerNotGateTest
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Runner AndGateTest \text{Runner}_\text{AndGateTest} </math>RunnerAndGateTest
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Runner OrGateTest \text{Runner}_\text{OrGateTest} </math>RunnerOrGateTest
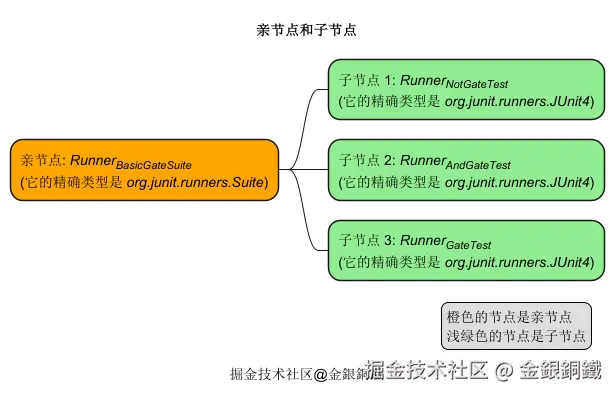
亲节点 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Runner BasicGateSuite \text{Runner}_\text{BasicGateSuite} </math>RunnerBasicGateSuite 负责查找和运行子节点
小结
目前已经出现了四个重要的类 👇
| 类 | 主要作用 | javadoc 截图 |
|---|---|---|
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> TestClass \text{TestClass} </math>TestClass | 对测试类进行封装,通过 TestClass 可以找到带有指定注解的字段/方法 |  |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Runner \text{Runner} </math>Runner | 负责运行测试 | 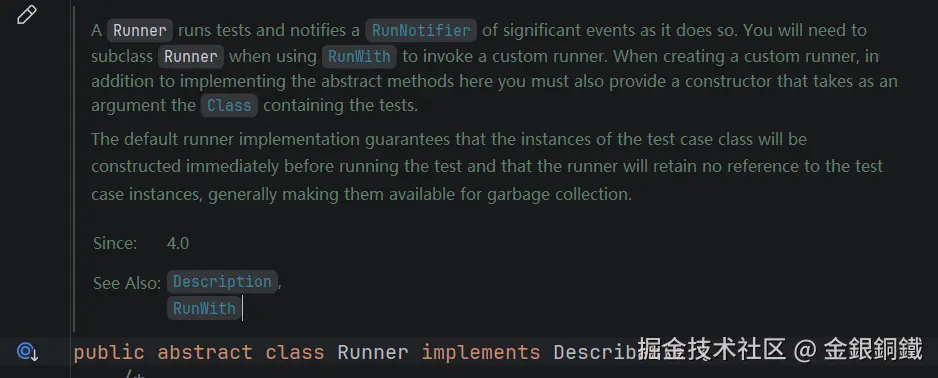 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ParentRunner \text{ParentRunner} </math>ParentRunner | 如果我们将一个 Runner 视为亲子结构,则可以让这个 Runner 继承 ParentRunner. 典型的子类有 BlockJUnit4ClassRunner Suite |
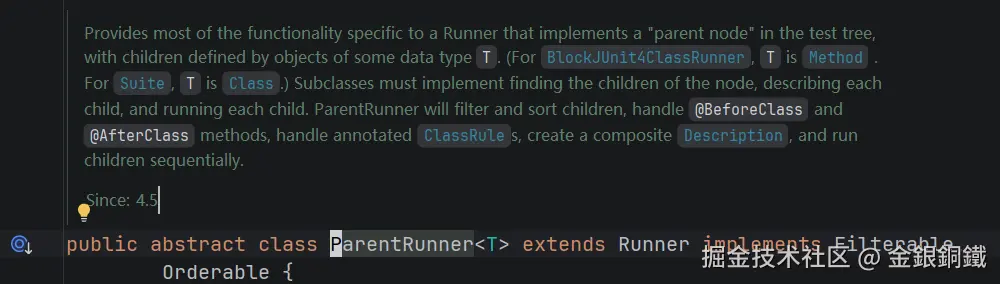 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Suite \text{Suite} </math>Suite | Suite 继承了 ParentRunner,它可以驱动子节点(子节点也是 Runner) |
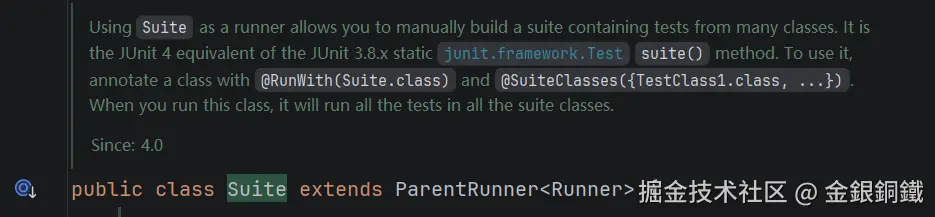 |
这四个类的 Fully Qualified Class Name 列举如下 👇
| 类 | Fully Qualified Class Name |
|---|---|
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> TestClass \text{TestClass} </math>TestClass | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> org.junit.runners.model.TestClass \text{org.junit.runners.model.TestClass} </math>org.junit.runners.model.TestClass |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Runner \text{Runner} </math>Runner | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> org.junit.runner.Runner \text{org.junit.runner.Runner} </math>org.junit.runner.Runner |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ParentRunner \text{ParentRunner} </math>ParentRunner | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> org.junit.runners.ParentRunner \text{org.junit.runners.ParentRunner} </math>org.junit.runners.ParentRunner |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> Suite \text{Suite} </math>Suite | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> org.junit.runners.Suite \text{org.junit.runners.Suite} </math>org.junit.runners.Suite |
其他
文中"org.junit.runners.Suite 的继承体系"那张图是如何画出来的?
我用了 PlantUML 来画这张图,代码如下
puml
@startuml
'https://plantuml.com/class-diagram
title <i>org.junit.runners.Suite</i> 的继承体系
org.junit.runner.Runner <|-- org.junit.runners.ParentRunner
org.junit.runners.ParentRunner <|-- org.junit.runners.Suite: extends ParentRunner<Runner>
abstract class org.junit.runner.Runner {
+{abstract} void run(RunNotifier notifier)
}
abstract class org.junit.runners.ParentRunner<T> {
-final TestClass testClass
#{abstract} List<T> getChildren()
+void run(final RunNotifier notifier)
}
class org.junit.runners.Suite {
-final List<Runner> runners
#List<Runner> getChildren()
}
caption 注意: 图中略去了本文不关心的字段/方法/接口
legend right
掘金技术社区
@金銀銅鐵
endlegend
@enduml文中"org.junit.runners.JUnit4 的继承体系"那张图是如何画出来的?
我用了 PlantUML 来画这张图,代码如下
puml
@startuml
'https://plantuml.com/class-diagram
title <i>org.junit.runners.JUnit4</i> 和 <i>org.junit.runners.Suite</i> 的继承体系
org.junit.runner.Runner <|-- org.junit.runners.ParentRunner
org.junit.runners.ParentRunner <|-- org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner: extends ParentRunner<FrameworkMethod>
org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner <|-- org.junit.runners.JUnit4
org.junit.runners.ParentRunner <|-- org.junit.runners.Suite: extends ParentRunner<Runner>
abstract class org.junit.runner.Runner {
+{abstract} void run(RunNotifier notifier)
}
abstract class org.junit.runners.ParentRunner<T> {
-final TestClass testClass
#{abstract} List<T> getChildren()
+void run(final RunNotifier notifier)
}
class org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner {
#List<FrameworkMethod> getChildren()
}
class org.junit.runners.Suite {
-final List<Runner> runners
#List<Runner> getChildren()
}
caption 注意: 图中略去了本文不关心的字段/方法/接口
legend right
掘金技术社区
@金銀銅鐵
endlegend
@enduml文中"亲节点和子节点"那张图是如何画出来的?
我用了 PlantUML 来画这张图,代码如下
puml
@startmindmap
'https://plantuml.com/mindmap-diagram
caption 掘金技术社区@金銀銅鐵
title 亲节点和子节点
*[#Orange]:亲节点: <i>Runner<sub>BasicGateSuite</sub></i>
(它的精确类型是 <i>org.junit.runners.Suite</i>);
**[#lightgreen]:子节点 1: <i>Runner<sub>NotGateTest</sub></i>
(它的精确类型是 <i>org.junit.runners.JUnit4</i>);
**[#lightgreen]:子节点 2: <i>Runner<sub>AndGateTest</sub></i>
(它的精确类型是 <i>org.junit.runners.JUnit4</i>);
**[#lightgreen]:子节点 3: <i>Runner<sub>GateTest</sub></i>
(它的精确类型是 <i>org.junit.runners.JUnit4</i>);
legend right
橙色的节点是亲节点
浅绿色的节点是子节点
endlegend
@endmindmap