9.2 Join Methods
A join method is the mechanism for joining two row sources.
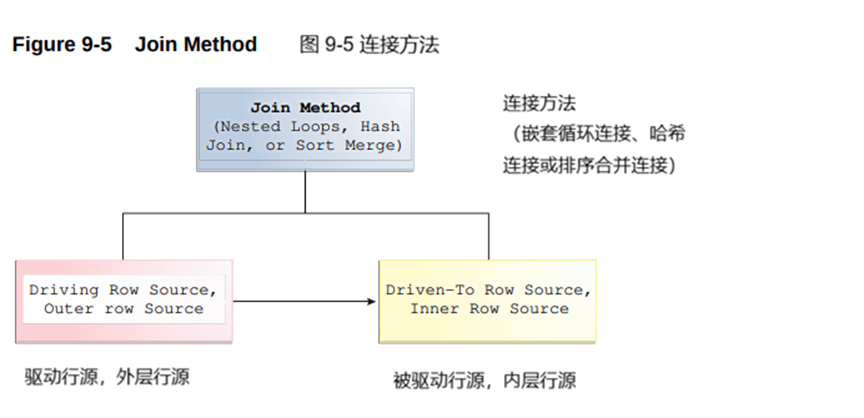
Depending on the statistics, the optimizer chooses the method with the lowest estimated cost. As shown in Figure 9-5, each join method has two children: the driving (also called outer) row source and the driven-to (also called inner) row source.
9.2 连接方法
连接方法是用于连接两个行源的机制。
优化器会根据统计信息,选择预估成本最低的方法。如图 9-5 所示,每种连接方法都包含两个子项:驱动行源(也称为外部行源)和被驱动行源(也称为内部行源)。
9.2.1 Nested Loops Joins
Nested loops join an outer data set to an inner data set.
For each row in the outer data set that matches the single-table predicates, the
database retrieves all rows in the inner data set that satisfy the join predicate. If an
index is available, then the database can use it to access the inner data set by rowid.
9.2.1 嵌套循环连接
嵌套循环连接将外部数据集与内部数据集进行连接。
对于外部数据集中符合单表谓词条件的每一行数据,数据库会检索内部数据集中所有满足连接谓词条件的行。若存在可用索引,数据库则可借助该索引通过行标识符访问内部数据集。
9.2.1.1 When the Optimizer Considers Nested Loops Joins
Nested loops joins are useful when the database joins small subsets of data, the database joins large sets of data with the optimizer mode set to FIRST_ROWS, or the join condition is an efficient method of accessing the inner table.
9.2.1.1 优化器选用嵌套循环连接的场景
当数据库对数据的小子集进行连接、数据库在优化器模式设置为FIRST_ROWS时对大型数据集进行连接,或者连接条件是访问内部表的高效方式时,嵌套循环连接是适用的。
Note:
The number of rows expected from the join is what drives the optimizer decision, not the size of the underlying tables. For example, a query might join two tables of a billion rows each, but because of the filters the optimizer expects data sets of 5 rows each.
注意:
驱动优化器决策的关键因素是连接操作预期返回的行数,而非底层表的物理规模。例如,某个查询可能需要连接两个各含十亿行的表,但由于筛选条件的存在,优化器可能预估每个数据集仅包含5行数据。
In general, nested loops joins work best on small tables with indexes on the join conditions. If a row source has only one row, as with an equality lookup on a primary key value (for example, WHERE employee_id=101), then the join is a simple lookup. The optimizer always tries to put the smallest row source first, making it the driving table.
通常来说,嵌套循环连接最适合在连接条件上建有索引的小表场景。如果某个行源仅包含单行数据,例如基于主键值的等值查找(如WHERE employee_id=101),那么此时的连接操作就简化为直接查找。优化器始终尝试将最小的行源置于首位,使其成为驱动表。
Various factors enter into the optimizer decision to use nested loops. For example, the database may read several rows from the outer row source in a batch. Based on the number of rows retrieved, the optimizer may choose either a nested loop or a hash join to the inner row source. For example, if a query joins departments to driving table employees, and if the predicate specifies a value in employees.last_name, then the database might read enough entries in the index on last_name to determine whether an internal threshold is passed. If the threshold is not passed, then the optimizer picks a nested loop join to departments, and if the threshold is passed, then the database performs a hash join, which means reading the rest of employees, hashing it into memory, and then joining to departments.
优化器选择嵌套循环连接时会综合考虑多种因素。例如,数据库可能以批处理方式从外层行源读取多行数据。根据检索到的数据行数量,优化器可能选择对内层行源采用嵌套循环连接或哈希连接。举例说明:若查询需要连接departments表与驱动表employees,且谓词条件指定了employees.last_name字段的值,则数据库可能会读取last_name索引中的足够条目以判断是否超过内部阈值。若未超过阈值,优化器将选择对departments表采用嵌套循环连接;若超过阈值,则数据库会执行哈希连接------即读取employees表的剩余数据、将其哈希化存入内存,再与departments表进行连接。
If the access path for the inner loop is not dependent on the outer loop, then the result can be a Cartesian product: for every iteration of the outer loop, the inner loop produces the same set of rows. To avoid this problem, use other join methods to join two independent row sources.
如果内层循环的访问路径不依赖于外层循环,那么连接结果可能形成笛卡尔积:外层循环的每次迭代都会使内层循环产生完全相同的行集合。为避免此问题,应采用其他连接方法来连接两个相互独立的数据行源。
See Also:
另请参阅:
• "Table 19-2"
• "Adaptive Query Plans"
9.2.1.2 How Nested Loops Joins Work
9.2.1.2 嵌套循环连接的工作原理
Conceptually, nested loops are equivalent to two nested for loops.
For example, if a query joins employees and departments, then a nested loop in pseudocode might be:
从概念上讲,嵌套循环连接等价于两个嵌套的for循环结构。
例如,若某查询需要连接employees和departments表,则其伪代码形式的嵌套循环可能如下所示:
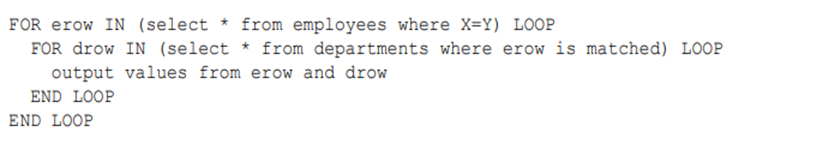
The inner loop is executed for every row of the outer loop. The employees table is the "outer" data set because it is in the exterior for loop. The outer table is sometimes called a driving table. The departments table is the "inner" data set because it is in the interior for loop.
内层循环会针对外层循环的每一行数据执行。employees表作为"外层"数据集,因为它处于外部for循环中(外标有时也称为驱动表)。departments表则作为"内层"数据集,因为它处于内部for循环中。
A nested loops join involves the following basic steps:
- The optimizer determines the driving row source and designates it as the outer loop. The outer loop produces a set of rows for driving the join condition. The row source can be a table accessed using an index scan, a full table scan, or any other operation that generates rows.
嵌套循环连接包含以下基本步骤:
1.优化器确定驱动行源并将其指定为外层循环。外层循环生成用于驱动连接条件的行集合。该行源可以是使用索引扫描访问的表、全表扫描或任何其他能够产生数据行的操作。
The number of iterations of the inner loop depends on the number of rows retrieved in the outer loop. For example, if 10 rows are retrieved from the outer table, then the database must perform 10 lookups in the inner table. If 10,000,000 rows are retrieved from the outer table, then the database must perform 10,000,000 lookups in the inner table.
内层循环的迭代次数完全取决于外层循环检索到的数据行数量。例如,若从外层表检索到10行数据,则数据库需在内层表执行10次查找操作;若从外层表检索到10,000,000行数据,则数据库必须在内层表执行10,000,000次查找操作。
-
The optimizer designates the other row source as the inner loop. The outer loop appears before the inner loop in the execution plan, as follows:
-
优化器将另一个行源指定为内层循环。
在执行计划中,外层循环显示于内层循环之前,如下所示:

- For every fetch request from the client, the basic process is as follows:
a. Fetch a row from the outer row source
b. Probe the inner row source to find rows that match the predicate criteria
c. Repeat the preceding steps until all rows are obtained by the fetch request Sometimes the database sorts rowids to obtain a more efficient buffer access pattern.
- 针对客户端的每次提取请求,基本处理流程如下:
a. 从外层行源获取一行数据
b. 探测内层行源以查找满足谓词条件的匹配行
c. 重复上述步骤直至提取请求获取全部所需行
有时数据库会对行ID进行排序,以获得更高效的缓冲区访问模式。
9.2.1.3 Nested Nested Loops
The outer loop of a nested loop can itself be a row source generated by a different nested loop.
9.2.1.3 嵌套的嵌套循环
嵌套循环的外层循环本身也可以是另一个嵌套循环生成的行源。
The database can nest two or more outer loops to join as many tables as needed. Each loop is a data access method. The following template shows how the database iterates through three nested loops:
数据库可以嵌套两个或更多外层循环,以连接任意数量的表。每个循环对应一种数据访问方法。以下模板展示了数据库如何遍历三层嵌套循环:

The database orders the loops as follows:
-
- The database iterates through NESTED LOOPS 1:
数据库按以下顺序组织各层循环:
- 数据库遍历嵌套循环1:

The output of NESTED LOOP 1 is a row source.
嵌套循环1的输出是一个行源。
- The database iterates through NESTED LOOPS 2, using the row source generated by NESTED LOOPS 1 as its outer loop:
- 数据库遍历嵌套循环2,将嵌套循环1生成的行源作为其外层循环:

The output of NESTED LOOPS 2 is another row source.
嵌套循环2的输出是另一个行源。
-
- The database iterates through NESTED LOOPS 3, using the row source generated by NESTED LOOPS 2 as its outer loop:
- 数据库遍历嵌套循环3,将嵌套循环2生成的行源作为其外层循环:

Example 9-2 Nested Nested Loops Join
Suppose you join the employees and departments tables as follows:
示例9-2 嵌套的嵌套循环连接
假设你需要连接employees表和departments表,具体如下:

The plan reveals that the optimizer chose two nested loops (Step 1 and Step 2) to access the data:
执行计划显示,优化器选择了两层嵌套循环(步骤1和步骤2)来访问数据:
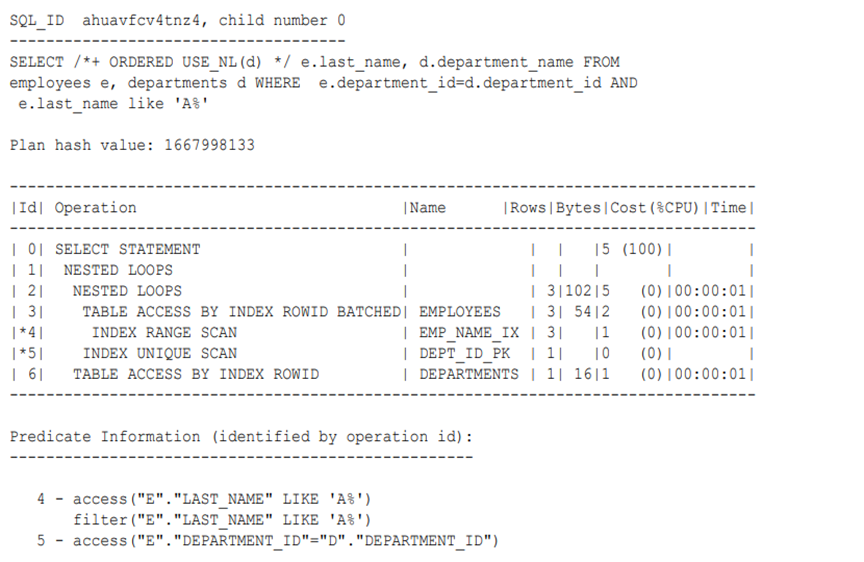
In this example, the basic process is as follows:
- The database begins iterating through the inner nested loop (Step 2) as follows:
a. The database searches the emp_name_ix for the rowids for all last names that begins with A (Step 4).
For example:
在此示例中,基本处理流程如下:
1.数据库开始遍历内层嵌套循环(步骤2),具体过程为:
a. 数据库扫描emp_name_ix索引,查找所有以A开头的姓氏对应的行ID(步骤4)。
例如:

b. Using the rowids from the previous step, the database retrieves a batch of rows from the employees table (Step 3). For example:
b. 使用上一步骤获取的行ID,数据库从employees表中批量检索数据行(步骤3)。例如:

come back from the row source. If too many rows are returned, then the optimizer switches to a different join method.
c. For each row in the outer row source, the database scans the dept_id_pk index to obtain the rowid in departments of the matching department ID (Step 5), and joins it to the employees rows. For example:
从行源中返回数据。如果返回的行数过多,优化器会切换为不同的连接方法。
c. 针对外层行源中的每一行,数据库扫描dept_id_pk索引以获取departments表中匹配部门ID的行ID(步骤5),并将其与employees表中的行进行连接。例如:

These rows become the outer row source for the outer nested loop (Step 1).
- The database iterates through the outer nested loop as follows:
a. The database reads the first row in outer row source.
For example:
这些行成为外层嵌套循环(步骤1)的外层行源。
- 数据库按如下方式遍历外层嵌套循环:
a. 数据库读取外层行源中的第一行。
例如:

b. The database uses the departments rowid to retrieve the corresponding row from departments (Step 6), and then joins the result to obtain the requested values (Step 1).
For example:
b. 数据库使用departments表的行ID从departments表中检索对应的数据行(步骤6),然后将结果连接以获取请求的字段值(步骤1)。
例如:

c. The database reads the next row in the outer row source, uses the departments rowid to retrieve the corresponding row from departments (Step 6), and iterates through the loop until all rows are retrieved.
The result set has the following form:
c. 数据库读取外层行源中的下一行,使用departments表的行ID从departments表中检索对应的数据行(步骤6),并循环执行此过程直至获取所有行。
结果集呈现形式如下:
示,每种连接方法都包含两个子项:驱动行源(也称为外部行源)和被驱动行源(也称为内部行源)。
