Haproxy七层代理
一,负载均衡
1.1 什么是负载均衡
负载均衡(Load Balance)简称LB,是一种服务或基于硬件设备等实现的高可用反向代理技术,负载均衡将特定的业务(Web服务,网络流量等)分担的指定的一个或多个后端特定的服务器或设备,从而提高了公司业务的并发处理能力,提高了业务的高可用性,方便了业务后期的水平动态扩展
1.2 负载均衡类型
1.2.1 四层负载均衡
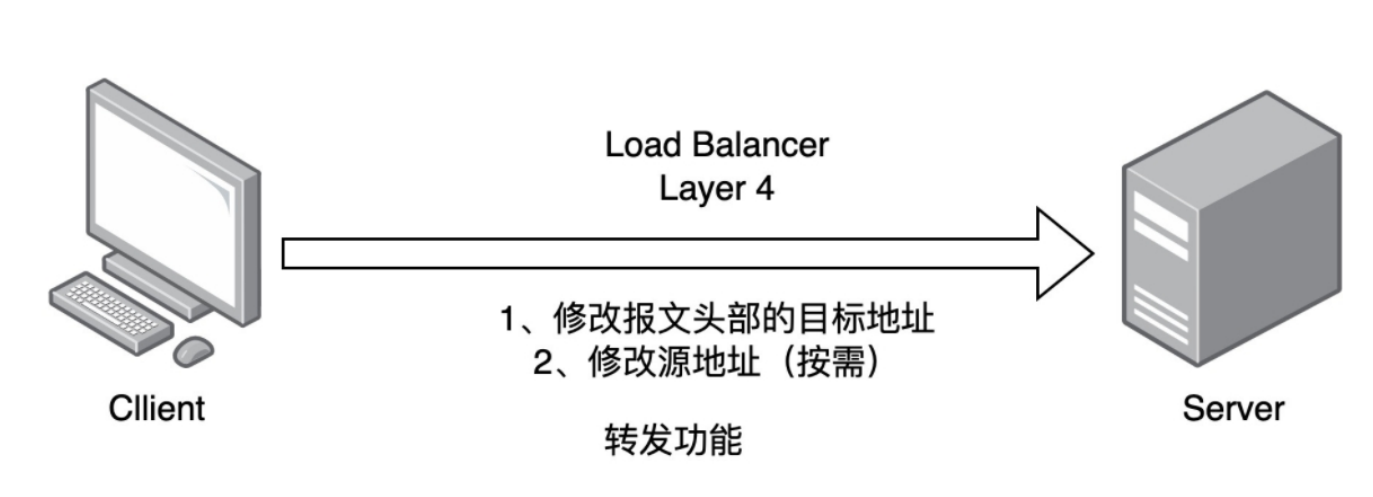
1,通过ip+port决定负载均衡的去向
2,对流量请求进行NAT处理,转发至后台服务器
3,记录TCP,UDP流量分别是由哪台服务器处理,后续该请求连接的流量都通过该服务器处理
4,支持四层的软件
- LVS:重量级四层负载均衡器
- Nginx:轻量级四层负载均衡器,可缓存(Nginx四层是通过upstream模块)
- Haproxy:模拟四层转发
1.2.2 七层负载均衡
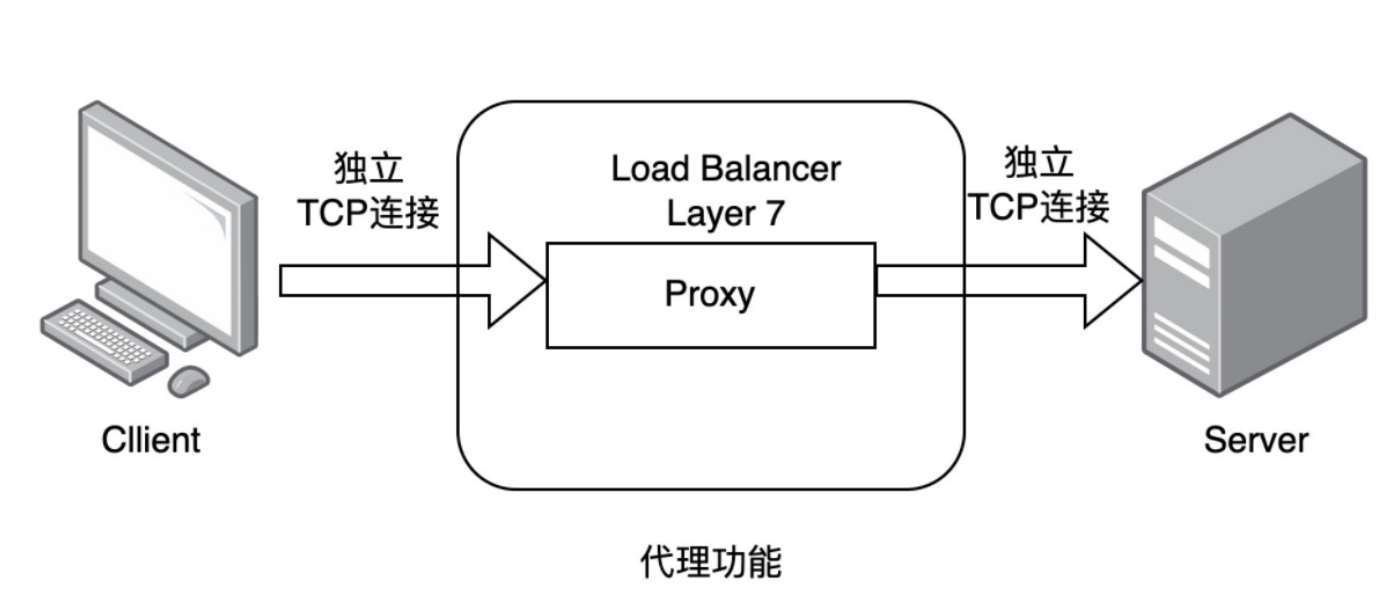
1,通过虚拟url或主机IP进行流量识别,根据应用层信息进行解析,决定是否需要进行负载均衡
2,代理后台服务器与客户端建立联系
3,支持7层代理的软件:
- Nginx:基于http协议(Nginx七层是通过proxy_pass)
- Haproxy:七层代理,会话保持、标记、路径转移等
1.2.3 四层和七层的区别
就是在对后台的服务器进行负载均衡的时候,依据四层的信息或七层的信息来决定怎么样转发流量
四层负载均衡,通过发布三层的IP地址,加上四层的端口号,来决定哪些流量需要做负载均衡,对需要的流量进行NAT处理,转发至后台服务器,并记录下这个TCP或UDP的流量是由哪台服务器处理的,后续这个连接的所有流量都打到这台服务器
七层负载均衡,就是在四层的基础上,考虑应用层的特征,比如一个Web网页服务器的负载均衡,除根据VIP加80端口辨别是否需要处理的流量,还可根据七层URL,浏览器类型,等判断是否进行负载均衡
1,分层位置:四层负载均衡是在传输层以下,七层负载均衡是在应用层以下
2,性能:四层负载均衡结构无需解析报文内容,在网络吞吐量与处理能力上较高;七层可支持解析应用层报文信息,识别URL,Cookie等信息
3,原理:四层是基于IP+PORT;七层是基于URL或者主机IP等
4,功能类别:四层负载均衡类似于路由器;七层类似于代理服务器
5,安全性:四层无法识别DDOS攻击;七层可防御SYN Cookie等攻击
二,Haproxy简介
Haproxy是法国开发者 威力塔罗在2000年用C开发的一个开源软件
是一款具备高并发(万级以上),高性能的TCP和HTTP负载均衡器
支持基于cookie的持久性,自动故障切换,支持正则表达式及Web状态统计
三,Haproxy的安装和服务信息
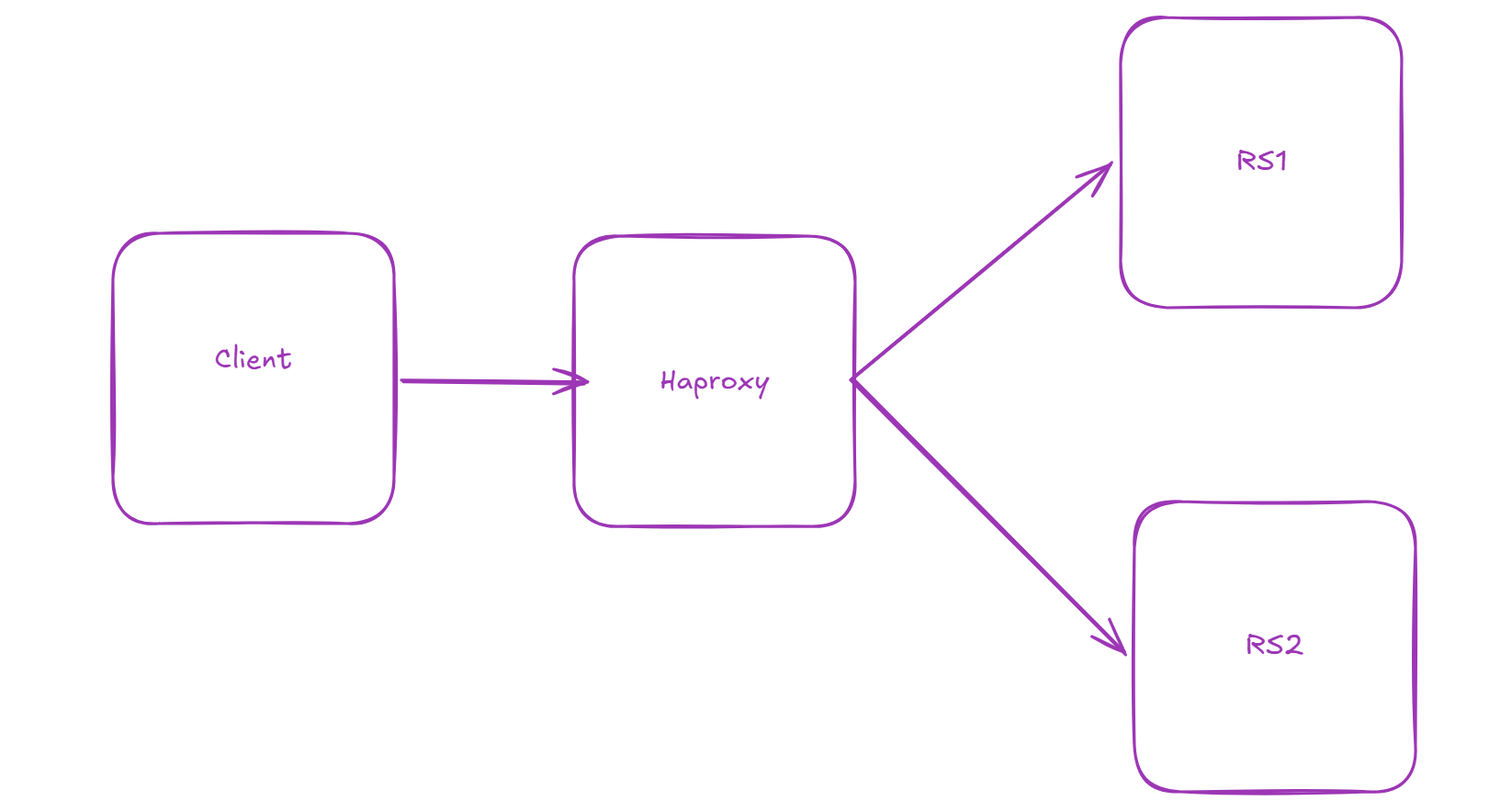
3.1 实验环境
| 主机 | IP |
|---|---|
| 客户端 | windows |
| Haproxy | 对外:192.168.136.100 对内:192.168.146.100 |
| RS1 | 192.168.146.10 |
| RS2 | 192.168.146.20 |
3.2 软件安装
软件包下载地址
bash
# 阿里 GitHub安装软件包
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# dnf install haproxy查看版本
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# haproxy -v
HAProxy version 2.4.22-f8e3218 2023/02/14 - https://haproxy.org/
Status: long-term supported branch - will stop receiving fixes around Q2 2026.
Known bugs: http://www.haproxy.org/bugs/bugs-2.4.22.html
Running on: Linux 5.14.0-570.12.1.el9_6.x86_64 #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Fri Apr 4 10:41:31 EDT 2025 x86_643.3 Haproxy的基本配置信息
官方文档
bash
http://cbonte.github.io/haproxy-dconv/配置文件大致分为两部分,分别是:
global:全局参数配置
- 进程以及安全配置相关的参数
- 性能调整相关参数
- Debug参数
proxies:代理配置段
- defaults:为frontend,backend,listen提供默认配置
- frontend:前端,相当于nginx的server{}
- backend:后端,相当于nginx的upstream{}
- listen:同时拥有前后端,配置简单,推荐生产使用
3.3.1 global配置
3.3.1.1 global配置参数说明
bash
global
log 127.0.0.1 local2 # 定义全局的syslog服务器;日志服务器需要开启UDP,最多可定义两个
chroot /var/lib/haproxy # 锁定运行目录
pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid # 指定pid文件
maxconn 4000 # 指定最大连接数
user haproxy # 指定haproxy的运行用户
group haproxy # 指定haproxy的运行组
daemon # 指定haproxy以守护进程方式进行
# turn on stats unix socket
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats # 指定haproxy的套接字文件
nbproc 2 # 指定haproxy的work进程数量,默认是1个
cpu-map 1 0 # 指定第一个work绑定第一个cpu核心
cpu-map 2 1 # 指定第二个work绑定第二个cpu核心
nbthread 2 # 指定haproxy的线程数量,默认每个进程一个线程,此参数与nbproc互斥
maxsslconn 100000 # 每个haproxy进程ssl最大连接数,用于haproxy配置证书的场景下
maxconnrate 100 # 指定每个客户端每秒建立连接的最大数量3.3.1.2 多进程和线程
多进程和socket文件配置如下:
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
global
nbproc 2 # 启用多进程
cpu-map 1 0 # 进程和cpu核心绑定防止cpu抖动从而减少系统资源的消耗
cpu-map 2 1 # 2 表示第二个进程,1表示第二个CPU核心查看进程信息

启用多线程
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
daemon
# turn on stats unix socket
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats
# utilize system-wide crypto-policies
ssl-default-bind-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
ssl-default-server-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
# nbproc 2
# cpu-map 1 0
# cpu-map 2 1
nbthread 2
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service
3.3.2 proxies配置
3.3.2.1 proxies参数说明
| 参数 | 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| defaults[] | proxies | 默认配置项,针对以下的frontend、backend和listen生效,可以多个name也可以没有name |
| frontend | proxies | 前端servername,类似于Nginx的一个虚拟主机server和LVS服务器集群 |
| backend | proxies | 后端服务器组,等于nginx的upstream和LVS中的RS服务器 |
| listen | proxies | 将frontend和backend合并在一起配置,相当于frontend和backend配置更简洁,生产常用 |
📓
name字段只能使用大小写字母,数字,'-'(dash),'-'(underscore),'-'(dot)和'-'(colon),并且严格区分大小写
3.3.2.2 Proxies配置-defaults
bash
defaults
mode http # Haproxy实例使用的链接协议
log global # 指定日志地址和记录日志条目的syslog/rsyslog日志设备
# 此处的global表示使用global配置段中设定的log值
option httplog # 日志记录选择,httplog表示记录与HTTP会话相关的各种属性值
option dontlognull # dontlognull表示不记录空会话链接日志
option http-server-close # 等待客户端完整HTTP请求的时间,此处等待为10S
option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8 # 透传客户端真实IP至后端web服务器
# 在Apache配置文件中加入:<br>%{X-Forward-For}i
# 在webserver中看日志即可看到地址穿透信息
option redispatch # 当server id对应的服务器挂掉后,强制定向到其他健康的服务器,重新派发
retries 3 # 后端服务器连接的重连次数
timeout http-request 10s # 等待客户端发送完整的HTTP请求时间
timeout queue 1m # 请求在Haproxy在队列中等待的超时时间
timeout connect 10s # Haproxy连接后端服务器的超时时间
timeout client 1m # 客户端与Haproxy连接的超时时间
timeout server 1m # Haproxy连接后端服务器的超时时间
timeout http-keep-alive 10s # Haproxy连接后端服务器的超时时间
timeout check 10s # 后端服务器健康的检查时间
maxconn 3000 # Haproxy允许的最大并发连接数3.3.2.3 Proxies配置-frontend
frontend配置参数:
bash
bind:指定Haproxy的监听地址,可以是IPV4或IPV6,可同时监听多个IP或端口,可同时用于listen字段中
# 格式:
bind [<address>]:<port_range> [,...] [param*]
# 注意:如果需要绑定在非本机的IP,需要开启内核参数:net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind=1
backlog <backlog> # 针对所有server配置,当前端服务器的连接数达到上限后的后援队列长度,不支持backendfrontend 配置示例:
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
frontend webserver
bind 192.168.136.100:80
use_backend webserver-803.3.2.4 Proxies配置-backend
- 定义一组后端服务器,backend服务器将被frontend进行调用
- 注意:backend的名称必须唯一,并且必须在listen或frontend中事先定义好才可以使用,否则服务起不来
bash
mode http|tcp # 指定负载类型协议,和对应得frontend必须一致
option # 配置选项
server # 定义后端服务器,必须指定IP和端口🚩
option后面加httpchk,smtpchk,mysql-check,pgsql-check,ssl-hello-chk方法,可以用于实现更多应用层检测功能
server配置
bash
# 针对一个server配置
check # 对指定real进行健康状态检查,如果不加此配置,默认不开启,只有check后面什么也没有也可以启动检查功能
# 默认对相应的后端服务器IP和端口,利用TCP连接进行周期性健康性的检查,必须指定端口才可以
addr<IP> # 可指定的健康状态检测IP,可以专门的数据段的网段,减少业务网络的流量
port<num> # 指定健康状态的检测端口
inter<num> # 健康检测间隔时间,默认2000sms
fail<num> # 后端服务器从线上转为线下的检查的连续失效次数,默认为3
rise<num> # 后端服务器从线下恢复线上的检查的连接的有效次数,默认为2
weight<weight> # 默认为1,最大值为256,0(状态为蓝色)表示不参与负载均衡,但仍接受持久连接
backup # 将后端服务器标记为备份状态,只在所有非备份主机down时提供服务
disable # 将后端服务器标记为不可用状态,即维护状态,除了持久模式
redirecct prefix http://www.baidu.com/ # 将请求临时(302)重定向至其他URL,只适用于http模式
maxconn<maxconn> # 当前后端server的最大并发连接数配置示例:
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
# static backend for serving up images, stylesheets and such
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
backend static
balance roundrobin
server static 127.0.0.1:4331 check
backend webserver-80
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service效果:
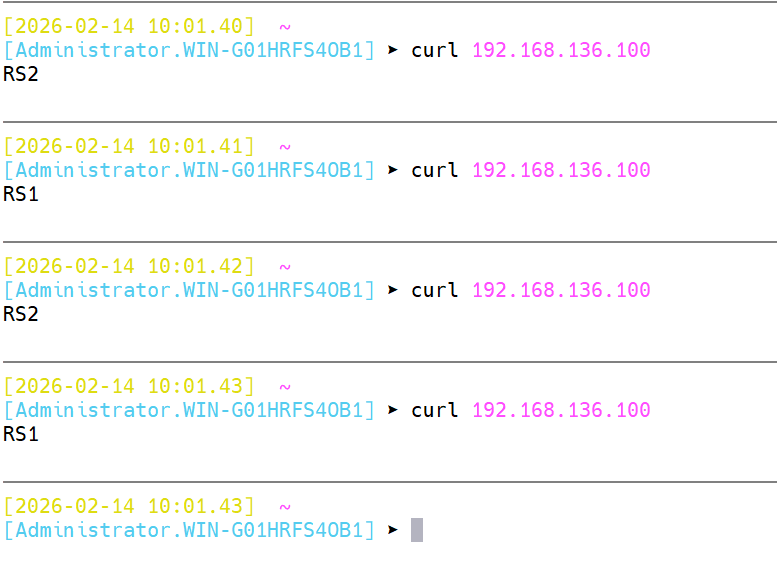
3.3.2.5 Proxies配置-listen 简化配置
使用listen替换frontend和backend的方式,简化设置,通常只适用于TCP协议的应用
配置示例:
bash
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# common defaults that all the 'listen' and 'backend' sections will
# use if not designated in their block
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
defaults
mode http
log global
option httplog
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
option forwardfor
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
# 以注释frontend和backend的配置
use_backend static if url_static
default_backend app
#frontend webserver
# bind 192.168.136.100:80
# use_backend webserver-80
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# static backend for serving up images, stylesheets and such
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
backend static
balance roundrobin
server static 127.0.0.1:4331 check
#backend webserver-80
# server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
# server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5效果
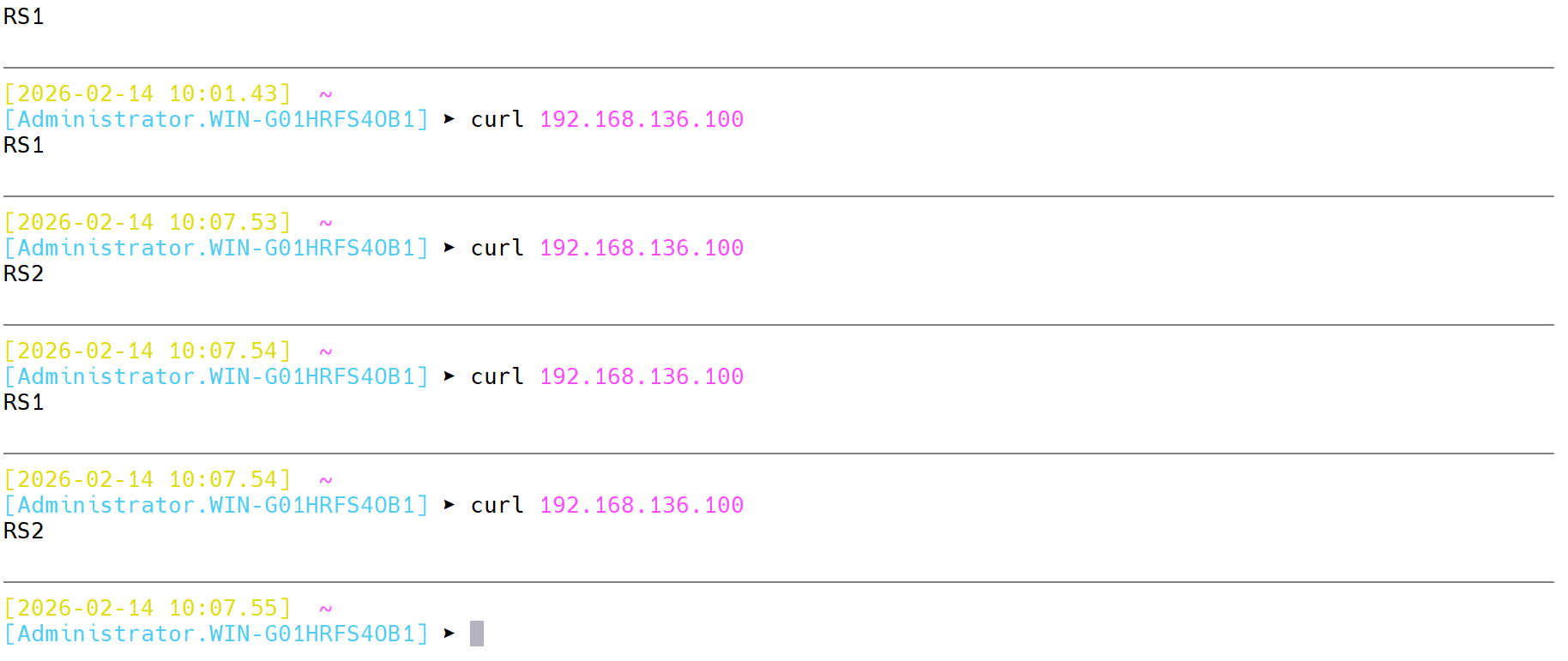
3.4 socat工具
对服务器动态权重和其他状态可以使用socat工具进行调整,Socat是Linux下的一个多功能的网络工具,主要的特点是在两个数据流之间建立双向通道,且支持众多协议和链接方式,如IP,TCP,UDP等
示例:
bash
# 修改配置文件
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
# turn on stats unix socket
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats
# 查看haproxy状态
[root@Haproxy ~]# echo "show info" | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
Name: HAProxy
Version: 2.4.22-f8e3218
Release_date: 2023/02/14
Nbthread: 2
Nbproc: 1
Process_num: 1
Pid: 27435
Uptime: 0d 3h15m51s
Uptime_sec: 11751
Memmax_MB: 0
PoolAlloc_MB: 0
PoolUsed_MB: 0
PoolFailed: 0
Ulimit-n: 8037
Maxsock: 8037
Maxconn: 4000
Hard_maxconn: 4000
CurrConns: 0
CumConns: 31006
CumReq: 6
MaxSslConns: 0
CurrSslConns: 0
CumSslConns: 0
Maxpipes: 0
PipesUsed: 0
PipesFree: 0
ConnRate: 0
ConnRateLimit: 0
MaxConnRate: 2
SessRate: 0
SessRateLimit: 0
MaxSessRate: 2
SslRate: 0
SslRateLimit: 0
MaxSslRate: 0
SslFrontendKeyRate: 0
SslFrontendMaxKeyRate: 0
SslFrontendSessionReuse_pct: 0
SslBackendKeyRate: 0
SslBackendMaxKeyRate: 0
SslCacheLookups: 0
SslCacheMisses: 0
CompressBpsIn: 0
CompressBpsOut: 0
CompressBpsRateLim: 0
Tasks: 20
Run_queue: 0
Idle_pct: 100
node: Haproxy
Stopping: 0
Jobs: 5
Unstoppable Jobs: 1
Listeners: 4
ActivePeers: 0
ConnectedPeers: 0
DroppedLogs: 0
BusyPolling: 0
FailedResolutions: 0
TotalBytesOut: 2720
TotalSplicdedBytesOut: 0
BytesOutRate: 0
DebugCommandsIssued: 0
CumRecvLogs: 0
Build info: 2.4.22-f8e3218
Memmax_bytes: 0
PoolAlloc_bytes: 116608
PoolUsed_bytes: 116608
Start_time_sec: 1771034870
Tainted: 0
# 查看集群权重
[root@Haproxy ~]# echo get weight webserver-80/web2 | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
1 (initial 1)
[root@Haproxy ~]# echo get weight webserver-80/web1 | socat stdio /var/lib/haproxy/stats
1 (initial 1)四,haproxy的算法
Haproxy通过固定参数balance指明对后端服务器的调度算法
balance参数可以配置在listen或backend中
Haproxy调度算法分为静态和动态调度算法
4.1 静态算法
按照事先定义好的规则轮询公平调度,不关心后端服务器的当前负载等状态,且无法实时修改权重,只能重启haproxy生效
4.1.1 static-rr:基于权重的轮询制度
- 不支持运行时利用socat进行权重的调整
- 不支持服务慢启动
- 其后端主机个数没有限制,相当于LVS中的wrr
📔
慢启动就是在服务器刚启动时不会把访问流量一下子给它,而是先给一部分,没问题后,再给另外一部分
示例:
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
option forwardfor
balance static-rr
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service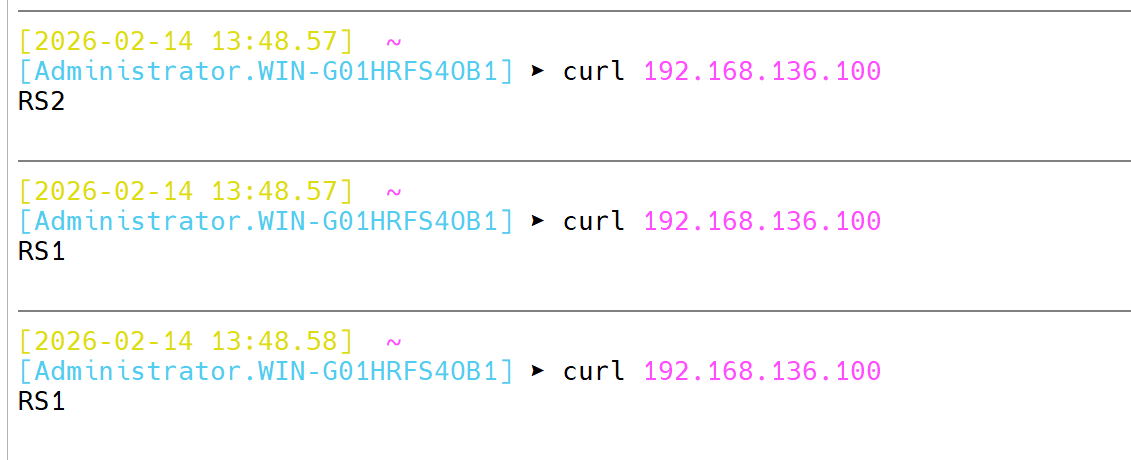
4.1.2 first
- 根据服务器在列表中的位置,自上而下进行调度
- 其只会当第一台服务器连接数上限,新请求才会分配给下一台服务器
- 其会忽略权重设置
- 不支持使用socat动态调整权重,可设置0和1,设置其他值无效
示例:
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
option forwardfor
balance first # 调度算法
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2 maxconn 1 # 为实验效果,把最大并发连接数设置1
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service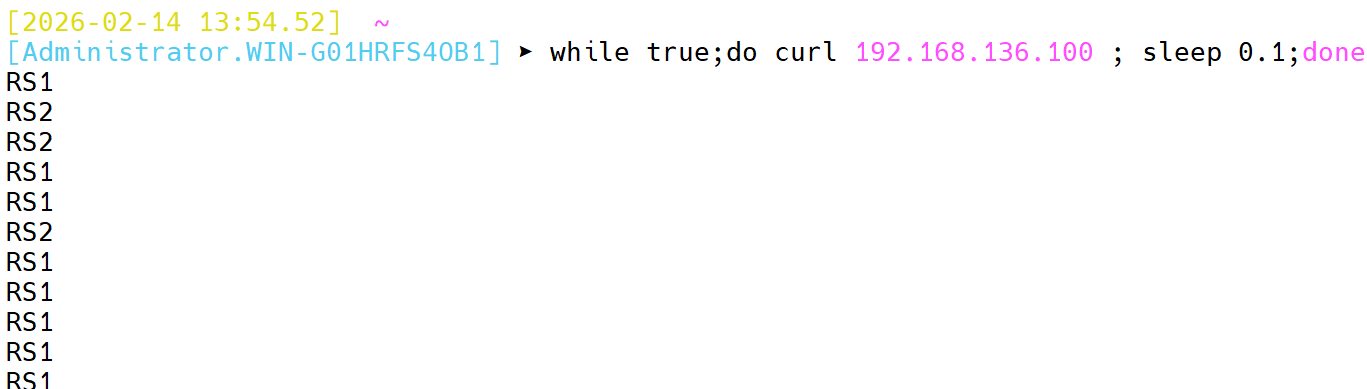
4.2 动态算法
动态算法
- 基于后端服务器状态进行调度适当调整
- 新请求有限调度到负载较低的服务器
- 权重可以在haproxy运行时动态调整无需重启
4.2.1 roundrobin
1,基于权重的轮询动态调度算法
2,支持权重运行时调整,不同于LVS中的rr轮询模式
3,Haproxy的roundrobin支持慢启动
4,其每个后端backend最多支持4095个real server
5,支持对real server权重的动态调整
6,roundrobin为默认调度算法,应用广泛
示例:
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
maxconn 3000
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
balance roundrobin
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service4.2.2 leastconn
- leastconn加权的最少连接的动态
- 支持权重的运行时调整和慢启动
- 比较适合长连接的场景使用,比如Mysql场景
示例
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
maxconn 3000
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
balance leastconn
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service4.3 其他算法
其他算法即可作为静态算法,还可以为动态算法
4.3.1 source
源地址hash,基于用户源地址hash并将请求转发到后端服务器,后续同一个源地址请求会被转发到同一台后端服务器上。此方式后端服务器数据量发生发生变化后时,会导致很多用户转到新的服务器上,默认为静态方式,可以通过hash-type支持的选项更改这个算法一般是在不插入Cookie的TCP模式下使用,也可给拒绝会话cookie的客户提供最好的会话粘性,适用于session会话保持但不支持cookie和缓存的场景源地址有两种转发客户端请求到后端服务器的服务器选取计算方式,分别是取模法和一致性hash
示例
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
maxconn 3000
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
balance source
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service
🗒
如果客户端为一个家庭,那么这个家庭的所有流量都会打到这个服务器上,这是source的缺陷
4.3.1.1 map-based 取模法
map-based:取模法,对source地址进行hash计算,再基于服务器总权重的取模,最终结果决定将此请求转发至对应的后端服务器
此方法是静态的,即不支持在线调整权重,不支持慢启动,可实现对后端服务器均衡调度
缺点是当服务器的总权重发生变化时,即使服务器上下线,都会导致总权重的变化导致调度结果整体的变化
hash-type默认的算法为此算法
⛵️
取模运算就是将两个数相除之后的余数,10%7=3
map-based算法:基于权重取模,hash(source_ip)%所有后端服务器相加的总权重
📡比如当源hash值为1111,1112,1113,三台服务器a b c的权重均为1,即abc的调度标签分别会被设定为0 1 2 (1111%3=1 1112%3=2 1113%3=0)
1111 ---> nodeb
1112 ---> nodec
1113 ---> nodea
如果a下线后,权重数量发生变化
1111%2=1 1112%2=0 1113%2=1
1112和1113被调度到的主机发送变化,这样会导致会话丢失
4.3.1.2 一致性hash
一致性哈希,当服务器的总权重发生变化时,对调度结果影响是局部的,不会引起太大的波动
该hash算法是动态的,支持使用socat等工具进行在线权重调整,支持慢启动
算法
bash
1,后端服务器哈希环点keyA=hash(后端服务器虚拟IP)%(2^32)
2,客户机哈希环点key1=hash(client_ip)%(2^32)
3,将keyA和Key1都放在hash环上,将用户请求调度到离key1最近的keyA对应的后端服务器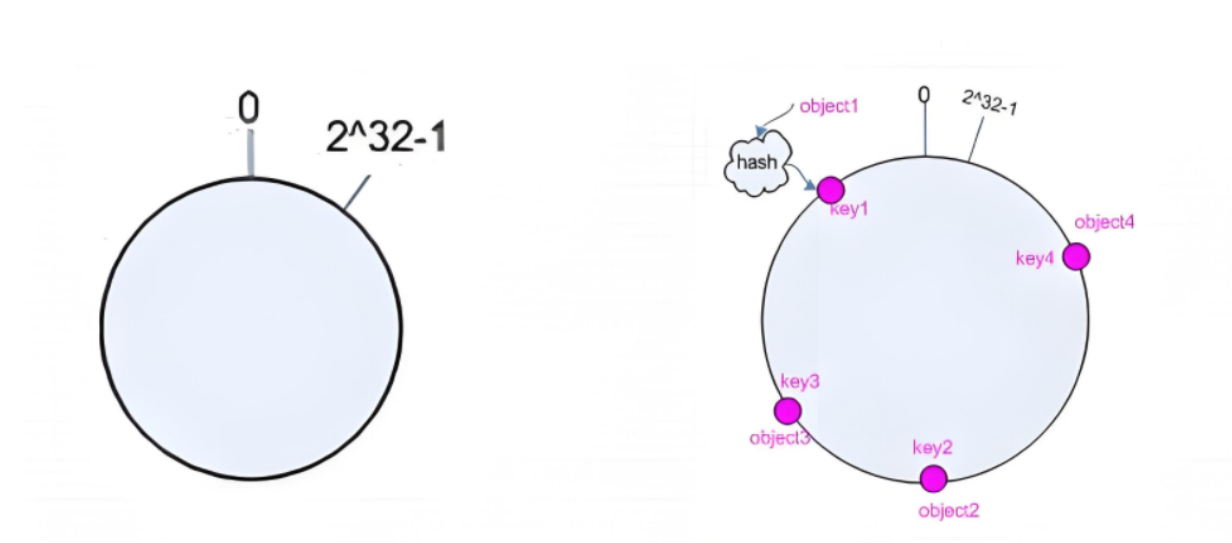
hash环偏斜问题
bash
增加虚拟服务器IP数量,比如:一个后端服务器根据权重为1生成1000个虚拟IP,再hash。而后端服务器权重为2则生成2000的虚拟IP,再hash,最终在hash环上生成3000个节点,从而解决hash环偏斜问题hash对象
Hash对象到后端服务器的映射关系
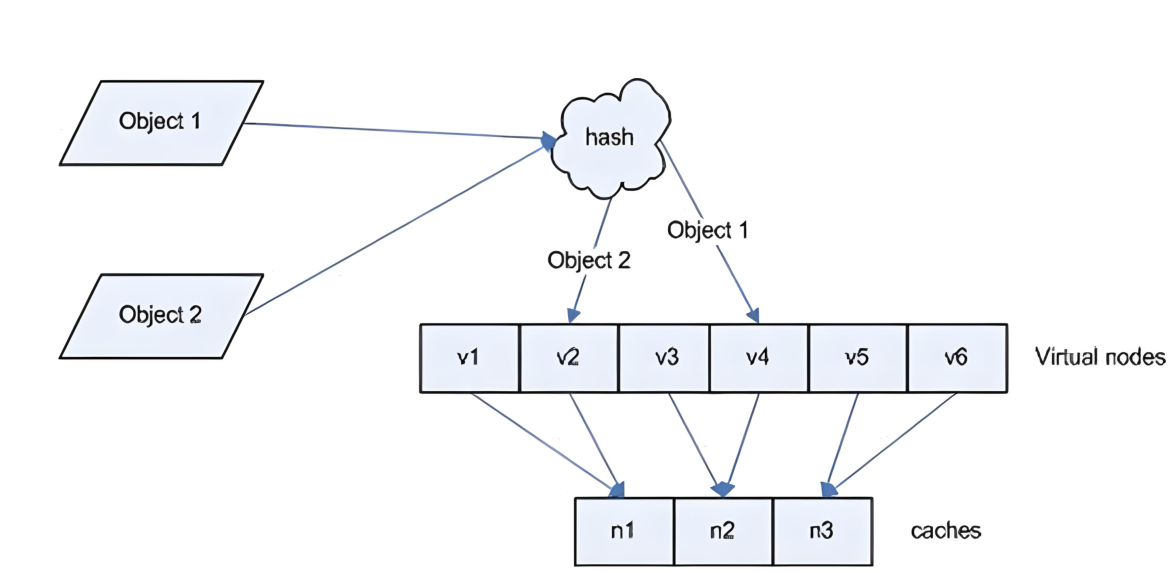
一致性hash示意图
后端服务器在线与离线的调度方式
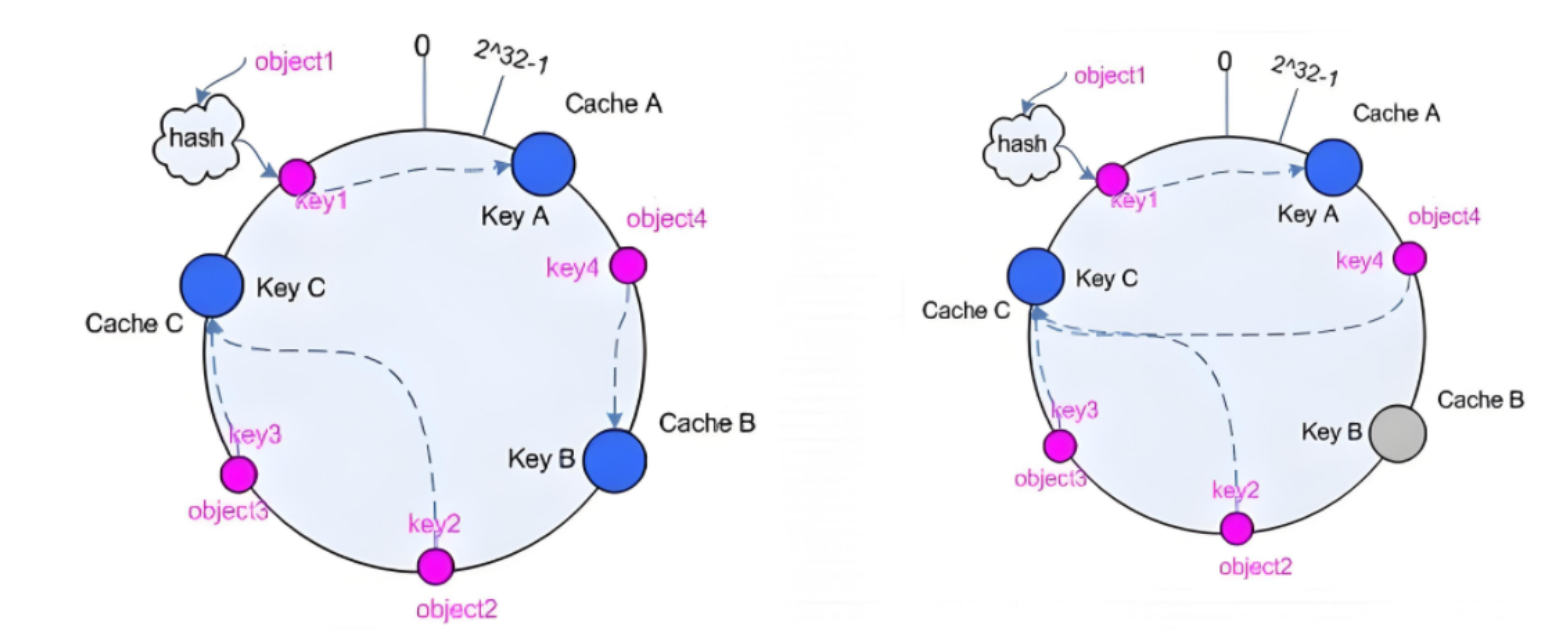
一致性hash配置示例
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
balance source
hash-type consistent
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service4.3.2 uri
基于对用户请求的URL的左半部分或整个URi做hash,再将hash结果对总权重进行取模后
根据最终结果将请求转发到后端指定服务器
适用于后端是缓存服务器场景
默认为静态算法,也可以通过hash-type指定map-based和consistent,来定义使用取模法还是一致性hash
🏭
注意:此算法基于应用层,所以只支持mode http,不支持mode tcp
<scheme>://<user>:<password>@<host>:<port>/<path>;<params>?<query>#<frag>
左半部分:/<path>;<params>
整个uri:/<path>;<params>?<query>#<frag>
uri取模法配置示例
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
maxconn 3000
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
balance uri
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.serviceuri一致性hash配置示例
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
maxconn 3000
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
balance uri
hash-type consistent
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service访问测试
访问不同的uri,确认可以将用户同样的请求转发至相同的服务器
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl 192.168.136.100/index.html
RS1
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl 192.168.136.100/index1.html
RS1 INDEX1
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl 192.168.136.100/index2.html
RS2 INDEX2
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl 192.168.136.100/index3.html
RS1 INDEX3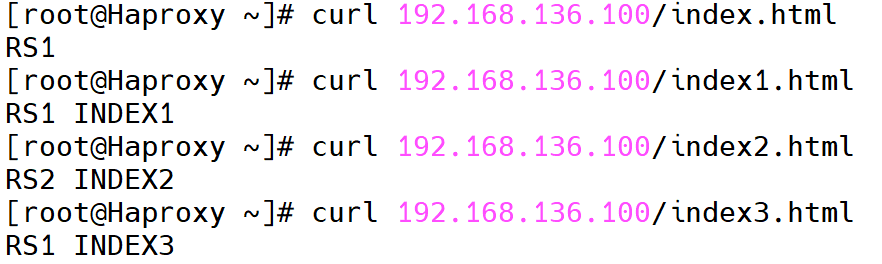
4.3.3 url_param
url_param对用户请求的url中的params部分中的一个参数key对应的value值作hash计算,并由服务器总权重相除以后派发至某挑出的服务器,后端搜索同一个数据会被调度到同一台服务器,多用与电商
通常用于追踪用户,以确保来自同一个用户的请求始终发往同一个real server
如果没key,将按照roundrobin算法
bash
# 假设
url = http://www.onepiece.com/lee/bar/index.html?key=value
# 则
host = "www.onepiece.com"
url_param = "key=value"4.3.3.1 url_param取模法配置示例
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
balance url_param name,userid
hash-type consistent
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service访问测试
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl 192.168.136.100/index.html?name=lee
RS1
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl 192.168.136.100/index.html?name=sdadfdsfds
RS2
4.3.4 hdr
针对用户每个http头部(header)请求中的指定信息做hash
此处由name指定的http首部会被取出并做hash计算
然后由服务器总权重取模以后派发至某挑出的服务器,如果无有效值,则会使用默认的轮询
配置示例
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
maxconn 3000
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
balance hdr(User-Agent)
hash-type consistent
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service测试
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl -vA "sougou" 192.168.136.100
* Trying 192.168.136.100:80...
* Connected to 192.168.136.100 (192.168.136.100) port 80 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: 192.168.136.100
> User-Agent: sougou
> Accept: */*
>
* Mark bundle as not supporting multiuse
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< date: Sun, 15 Feb 2026 05:04:48 GMT
< server: Apache/2.4.62 (Red Hat Enterprise Linux)
< last-modified: Sat, 14 Feb 2026 00:38:34 GMT
< etag: "4-64abdf11bd153"
< accept-ranges: bytes
< content-length: 4
< content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
<
RS2
* Connection #0 to host 192.168.136.100 left intact
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl -vA "edge" 192.168.136.100
* Trying 192.168.136.100:80...
* Connected to 192.168.136.100 (192.168.136.100) port 80 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: 192.168.136.100
> User-Agent: edge
> Accept: */*
>
* Mark bundle as not supporting multiuse
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< date: Sun, 15 Feb 2026 05:04:53 GMT
< server: Apache/2.4.62 (Red Hat Enterprise Linux)
< last-modified: Sat, 14 Feb 2026 00:37:55 GMT
< etag: "4-64abdeec84068"
< accept-ranges: bytes
< content-length: 4
< content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
<
RS1
* Connection #0 to host 192.168.136.100 left intact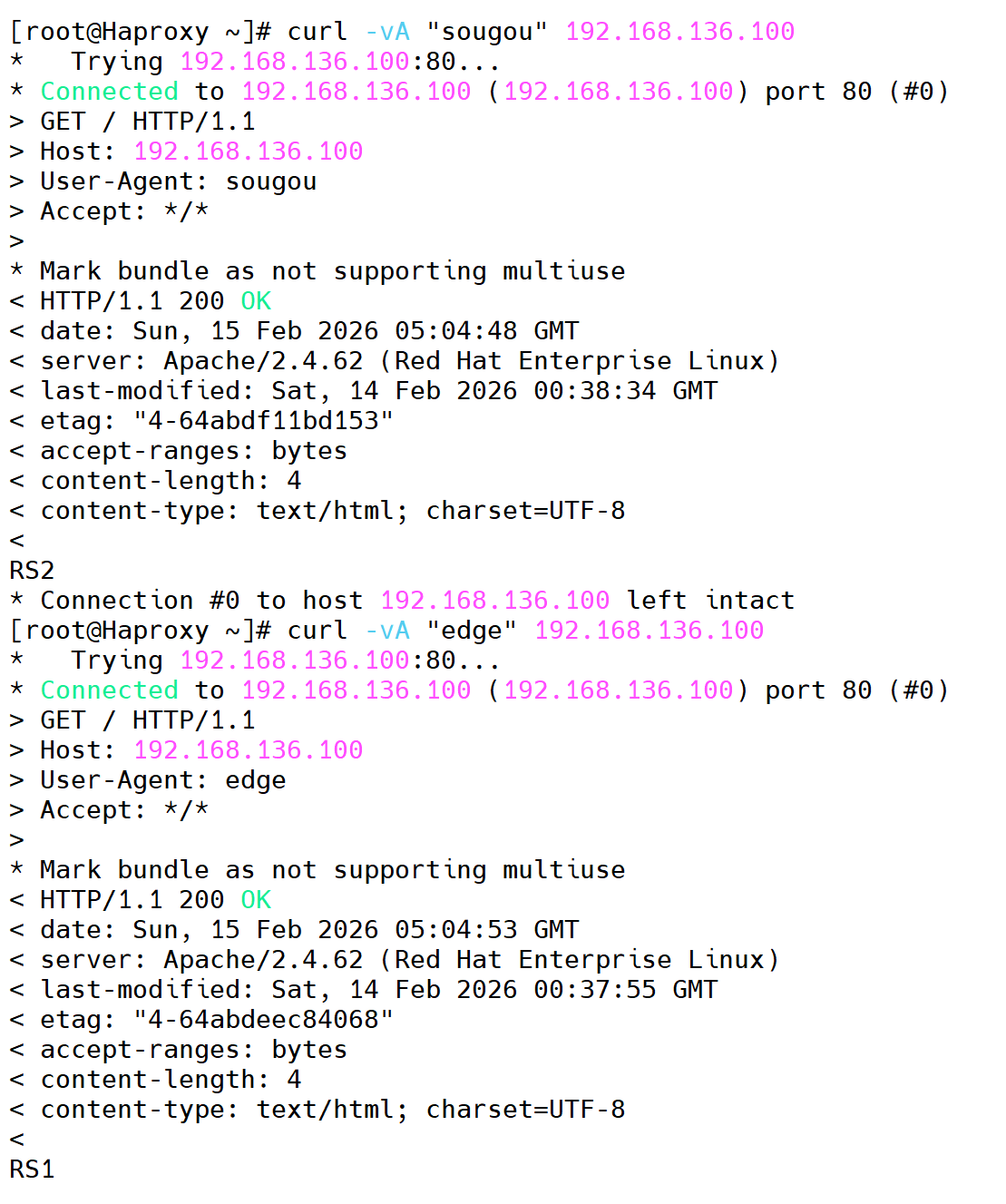
4.3.5 算法总结
bash
# 静态
static-rr --------- tcp/http
first --------- tcp/http
# 动态
roundrobin -------- tcp/http
leastconn -------- tcp/http
random -------- tcp/http
# 以下动静态取决于hash_type是否consistent
source ------- tcp/http
uri ---------- http
url_param ---- http
hdr ---------- http4.3.6 各算法使用场景
bash
first # 使用较少
static-rr # 做了session共享的web集群
roundrobin
random
leastconn # 数据库
source
# 基于客户端公网IP的会话保持
uri --------- http # 缓存服务器,CDN服务器,百度,腾讯,阿里云
url_param --- http # 可以实现session保持
hdr # 基于客户端请求报文做下一步处理五,高级功能及配置
5.1 基于cookie的会话保持
cookie value:为当前server指定cookie值,实现基于cookie的会话粘性,相对于基于source地址hash调度算法对客户端更准确,同时也加大了haproxy负载,目前此模式应用较少,已经被session共享服务器代替
🥖
不支持tcp mode,使用http mode
5.1.1 配置选项
bash
cookie name [rewirte | insert | prefix][indirect][nocache][postonly][preserve][httponly][secure].....
name # cookie的key名称,用于实现持久连接
insert # 插入新的cookie,默认不插入cookie
indirect # 如果客户端已有cookie,则不会再发生cookie信息
nocache # 当client和haproxy之间有缓存服务器时,不允许中间服务器缓存cookie
这会导致很多经过同一个CDN的请求都发送到同一台后端服务器5.1.2 配置示例
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
maxconn 3000
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
cookie WEB insert nocache indirect
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service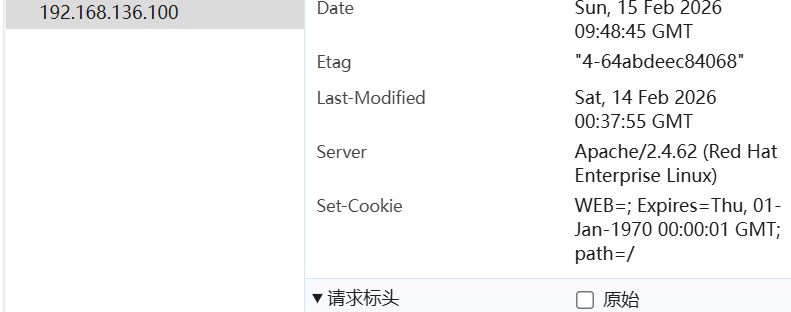
5.2 Haproxy状态页
通过web界面,显示当前的Haproxy的运行状态
5.2.1 状态页配置项
bash
stats enable # 基于默认的参数启用stats page
stats hide-version # 将状态页中haproxy版本隐藏
stats retresh<delay># 设定自动刷新时间间隔,默认不自动刷新
stats uri<prefix> # 自定义stats page uri,默认不自动刷新
stats auth <user>:<passwd> #认证时的账号和密码,可自定义多个用户,每行定义一个用户
no authentication
stats admin {if | unless}<cond> # 启用stats page的管理功能5.2.2 启动状态页
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
maxconn 3000
listen webserver-80
bind 192.168.136.100:80
cookie WEB insert nocache indirect
stats enable
stats uri /status # 自定义stats page uri
stats auth lee:lee # 认证
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5 weight 2
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service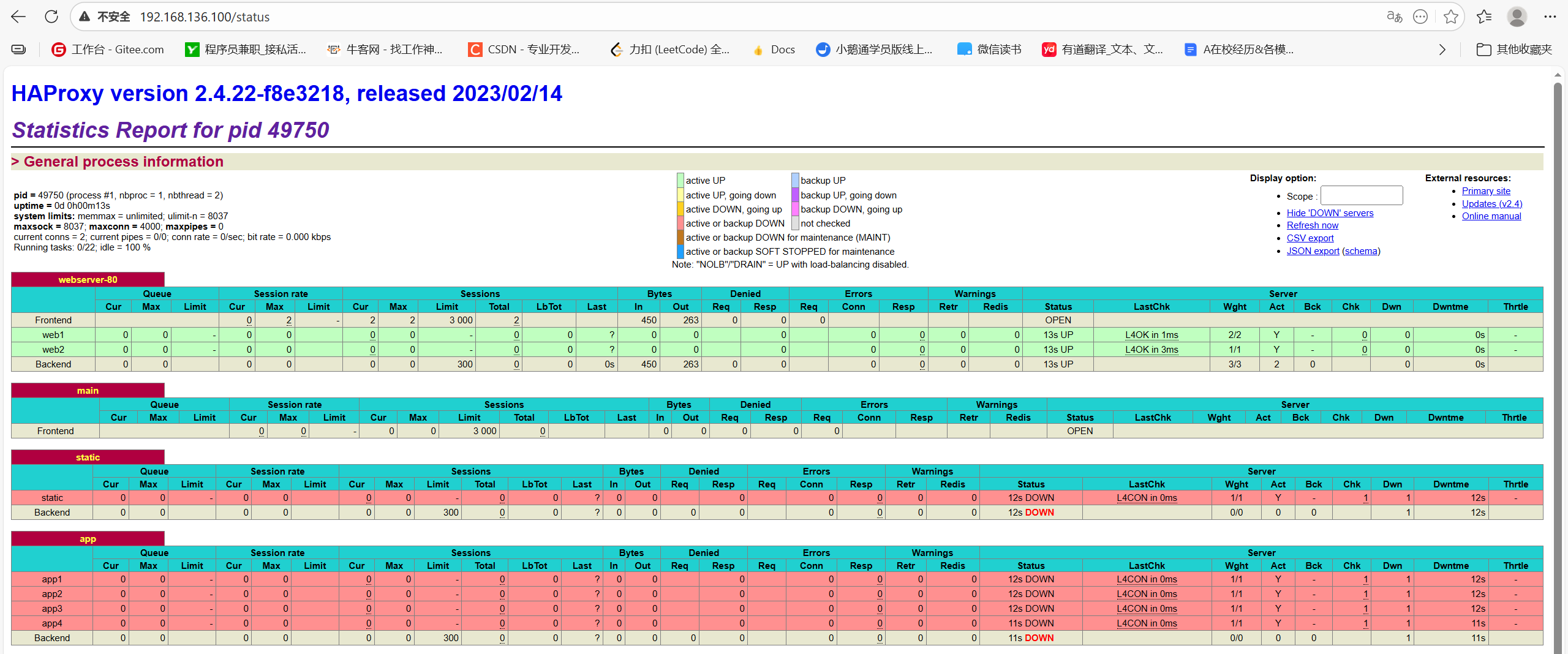
5.2.3 登陆状态页
bash
#pid为当前pid号,process为当前进程号,nbproc和nbthread为一共多少进程和每个进程多少个线程
pid = 27134 (process #1, nbproc = 1, nbthread = 1)
#启动了多长时间
uptime = 0d 0h00m04s
#系统资源限制:内存/最大打开文件数/
system limits: memmax = unlimited; ulimit-n = 200029
#最大socket连接数/单进程最大连接数/最大管道数maxpipes
maxsock = 200029; maxconn = 100000; maxpipes = 0
#当前连接数/当前管道数/当前连接速率
current conns = 2; current pipes = 0/0; conn rate = 2/sec; bit rate = 0.000 kbps
#运行的任务/当前空闲率
Running tasks: 1/14; idle = 100 %
active UP: #在线服务器
backup UP: #标记为backup的服务器
active UP, going down: #监测未通过正在进入down过程
backup UP, going down: #备份服务器正在进入down过程
active DOWN, going up: #down的服务器正在进入up过程
backup DOWN, going up: #备份服务器正在进入up过程
active or backup DOWN: #在线的服务器或者是backup的服务器已经转换成了down状态
not checked: #标记为不监测的服务器
#active或者backup服务器人为下线的
active or backup DOWN for maintenance (MAINT)
#active或者backup被人为软下线(人为将weight改成0)
active or backup SOFT STOPPED for maintenance5.3 IP透传
web服务器中需要记录客户端的真实IP地址,用于做访问统计,安全防护,行为分析等场景
5.3.1 七层IP透传
在haproxy工作在七层的时候,可以透传客户端真实IP至服务器
配置
bash
option forwardfor [except <network>][header <name>][if-none]
[except <network>] # 请求报文来自此处指定的网络时不予添加此首部
[header <name>] # 使用自定义的首部名称,而非"X-Forward-For",示例:X-client
[if-none] # 如果没有首部才添加首部,如果有使用默认值
bash
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
<IfModule log_config_module>
#
# The following directives define some format nicknames for use with
# a CustomLog directive (see below).
#
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b %{X-Forwarded-For}i \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" common
<IfModule logio_module>
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl restart httpd.service
# 测试
─
[2026-02-15 20:32.53] ~
[Administrator.WIN-G01HRFS4OB1] ⮞ curl 192.168.136.100
RS1
✓
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[2026-02-15 20:32.54] ~
[Administrator.WIN-G01HRFS4OB1] ⮞ curl 192.168.136.100
RS2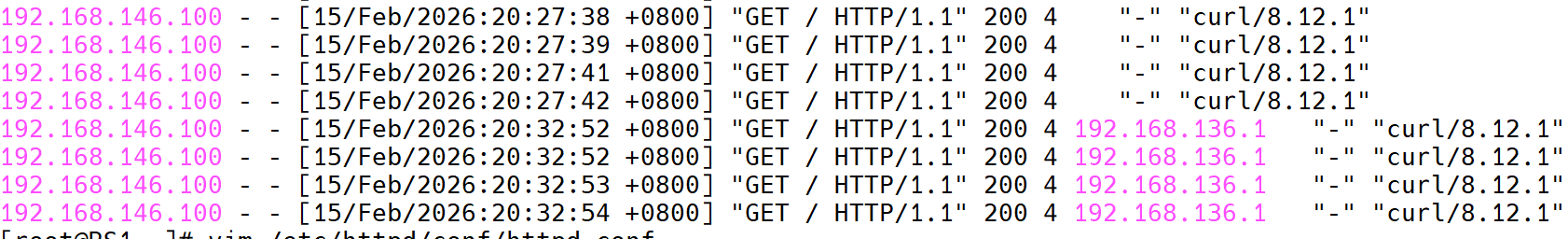
5.4 ACL
访问控制列表(Access Control Lists),是基于包过滤的访问控制技术,针对设定的条件对经过服务器传输的数据包进行过滤,基于请求报文头部中的源地址,源端口,目标地址,目标端口进行操作,比如允许其通过或丢弃
5.4.1 ACL配置选项
bash
# 用ACL来定义一个acl
acl <aclname> <criterion> [flags] [operator] [<value>]
acl 名称 匹配规则 匹配模式 具体操作符 操作对象类型5.4.1.1 ACL-Name 名称
bash
acl test path_end -m sub /a
# ACL名称,可以使用大写字母A-Z,小写字母a-z,数字0-9,冒号,点,中横线,下划线,严格区分大小写5.4.1.2 ACL-Criterion 匹配规范
定义ACL匹配规范,即:判断条件
bash
hdr string # 提取一个HTTP请求报文的首部
hdr ([<name> [<occ>]]) # 完全匹配字符串,<occ>表示在多值中使用得到值的出现次数
hdr_beg([<name> [<occ>]]) # 前缀匹配,header中指定匹配内容的begin
hdr_end([<name> [<occ>]]) # 后缀匹配,header中指定匹配内容的end
hdr_dom([<name> [<occ>]]) # 域匹配,header中的dom(host)
hdr_dir([<name> [,<occ>]]):路径匹配,header的uri路径
hdr_len([<name> [,<occ>]]):长度匹配,header的长度匹配
hdr_reg([<name> [,<occ>]]):正则表达式匹配,自定义表达式(regex)模糊匹配
hdr_sub([<name> [,<occ>]]):子串匹配,header中的uri模糊匹配 模糊匹配c 报文中a/b/c也会匹配5.4.1.3 ACL-flags 匹配模式
ACL匹配模式
-i 不区分大小写
-m 使用指定的正则表达式匹配方法
-n 不做DNS解析
-u 禁止acl重名,否则多个同名ACL匹配或关系5.4.1.4 ACL-operator具体操作符
ACL操作符
bash
整数比较:eq、ge、gt、le、lt
字符比较:
- exact match (-m str) :字符串必须完全匹配模式
- substring match (-m sub) :在提取的字符串中查找模式,如果其中任何一个被发现,ACL将匹配
- prefix match (-m beg) :在提取的字符串首部中查找模式,如果其中任何一个被发现,ACL将匹配
- suffix match (-m end) :将模式与提取字符串的尾部进行比较,如果其中任何一个匹配,则ACL进行匹配
- subdir match (-m dir) :查看提取出来的用斜线分隔("/")的字符串,如其中任一个匹配,则ACL进行匹配
- domain match (-m dom) :查找提取的用点(".")分隔字符串,如果其中任何一个匹配,则ACL进行匹配5.4.1.5 ACL-value操作对象
bash
The ACL engine can match these types against patterns of the following types :
- Boolean #布尔值
- integer or integer range #整数或整数范围,比如用于匹配端口范围
- IP address / network #IP地址或IP范围, 192.168.0.1 ,192.168.0.1/24
- string--> www.timinglee.org
exact #精确比较
substring #子串
suffix #后缀比较
prefix #前缀比较
subdir #路径, /wp-includes/js/jquery/jquery.js
domain #域名,www.timinglee.org
- regular expression #正则表达式
- hex block #16进制5.4.2 多个ACL的组合调用方式
多个ACL的逻辑处理
bash
与:隐式默认使用
或:使用"or" 或 "||"表示
否定:使用"!"表示5.4.3 ACL示例-域名匹配
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
frontend testacl
bind :80
acl web_host hdr_dom(host) www.onepiece.com
use_backend onepiece_host if web_host
default_backend default_webserver
backend onepiece_host
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check
backend default_webserver
server web1 192.168.136.100:8808 check
# 测试
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl 192.168.136.100
DEFAULT
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl www.onepiece.com
RS1
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl www.onepiece.com
RS2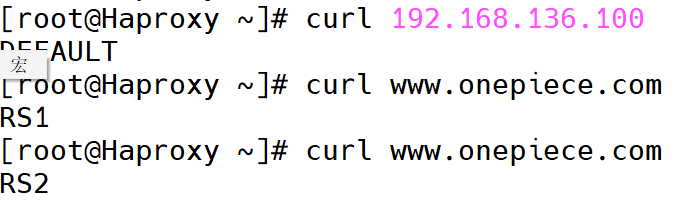
5.4.4 ACL示例-基于源IP或子网调度访问
将指定的源地址调度到指定的web服务器
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
frontend testacl
bind :80
acl ip_test src 192.168.136.1 192.168.146.0/24
use_backend ip_test-host if ip_test
default_backend default_webserver
backend ip_test-host
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check
backend default_webserver
server web1 192.168.136.100:8808 check
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl 192.168.136.100
DEFAULT
─
[2026-02-16 12:06.34] ~
[Administrator.WIN-G01HRFS4OB1] ⮞ curl 192.168.136.100
RS2
✓
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[2026-02-16 12:06.35] ~
[Administrator.WIN-G01HRFS4OB1] ⮞ curl 192.168.136.100
RS1
✓
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[2026-02-16 12:06.35] ~
[Administrator.WIN-G01HRFS4OB1] ⮞ curl 192.168.136.100
RS2
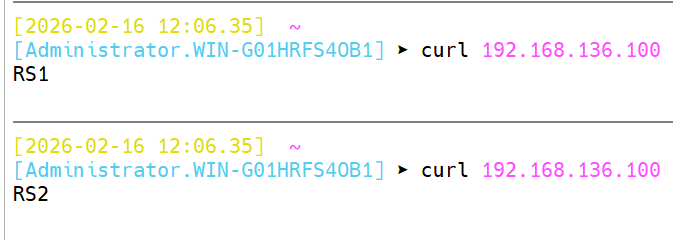
5.4.5 ACL示例-基于源地址的访问控制
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
frontend testacl
bind :80
acl web_host hdr_dom(host) www.onepiece.com
acl ip_test src 192.168.136.1 192.168.146.0/24
http-request deny if web_host
default_backend default_webserver
backend ip_test-host
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check
backend default_webserver
server web1 192.168.136.100:8808 check
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl www.onepiece.com
<html><body><h1>403 Forbidden</h1>
Request forbidden by administrative rules.
</body></html>
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl 192.168.136.100
DEFAULT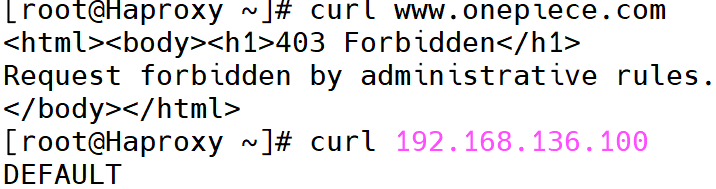
5.5 自定义Haproxy错误页面
对指定的报错进行重定向,进行显示错误页面
使用errorfile和errorloc指令的两种方法,可以实现自定义错误页面
bash
# 自定义错误页
errorfile <code> <file>
<code> # HTTP status code 支持200 400 403 405 408 425 429
<file> # 包含完整HTTP响应头的错误页文件的绝对路径,建议后缀".http"示例
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /haproxy/errorpage/503.http
HTTP/1.0 503 Service Unavailable^M
Cache-Control: no-cache^M
Connection: close^M
Content-Type: text/html^M
^M
<html><body><h1>503 Service Unavailable</h1>
onepiece`
</body></html>
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
errorfile 503 /haproxy/errorpage/503.http
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl 192.168.136.100
<html><body><h1>503 Service Unavailable</h1>
onepiece`
</body></html>测试
bash
关闭RS的服务,访问
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl 192.168.136.100
<html><body><h1>503 Service Unavailable</h1>
onepiece`
</body></html>
5.6 基于http重定向的错误页面
bash
# 错误页面重定向
errorloc <code> <url>示例
bash
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
errorloc 503 https://www.baidu.com
[root@Haproxy ~]# systemctl restart haproxy.service
# 测试
浏览器访问192.168.136.1005.7 Haproxy http 实现
haproxy可以实现https的证书安全,从用户到haproxy为https,从haproxy到后端服务器用http通信
但基于性能考虑,生产中证书都是在后端服务器比如nginx上实现
bash
# 证书制作
[root@Haproxy ~]# mkdir /etc/haproxy/certs
[root@Haproxy ~]# openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -sha256 -keyout /etc/haproxy/certs/onepiece.org.key -x509 -days 365 -out /etc/haproxy/certs/onepiece.org.crt
# 配置
[root@Haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
frontend webserver
bind *:80
redirect scheme https if !{ ssl_fc }
use_backend webcluster
frontend webserver-https
bind *:443 ssl crt /etc/haproxy/certs/onepiece.org.pem
use_backend webcluster
backend webcluster
balance roundrobin
server web1 192.168.146.10:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
server web2 192.168.146.20:80 check inter 3s fall 3 rise 5
[root@Haproxy ~]# cat /etc/haproxy/certs/onepiece.org.crt /etc/haproxy/certs/onepiece.org.key > /etc/haproxy/certs/onepiece.org.pem
[root@Haproxy ~]# curl -Ik https://www.onepiece.com
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
date: Mon, 16 Feb 2026 06:02:00 GMT
server: Apache/2.4.62 (Red Hat Enterprise Linux)
last-modified: Sat, 14 Feb 2026 00:37:55 GMT
etag: "4-64abdeec84068"
accept-ranges: bytes
content-length: 4
content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8