平滑升级与回滚
在进行之前先了解这三组信号的用途
| 信号 | 核心用途 | 作用对象 | 执行后关键结果 | 核心特性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| kill -USR2 | 启动新版本升级 | 旧 Nginx 主进程 | 新旧进程共存,新进程接管新请求 | 升级启动,不中断服务 |
| kill -WINCH | 平滑切流到新版本 | 旧 Nginx 主进程 | 旧 worker 优雅退出,新进程独占请求 | 切流核心,保留回滚兜底 |
| kill -HUP | 紧急回滚到旧版本 | 旧 Nginx 主进程 | 旧主进程重启旧 worker,接管所有请求 | 回滚核心,秒级切回,无中断 |
先下载高版本的nginx
bash
[root@nginx ~]# wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.29.4.tar.gz隐藏版本并自定义名称
bash
#编译nginx隐藏版本
[root@nginx ~]# tar zxf nginx-1.29.4.tar.gz
[root@nginx ~]# cd nginx-1.29.4/src/core/
[root@nginx core]# vim nginx.h
#define nginx_version 1029004
#define NGINX_VERSION ""
#define NGINX_VER "牛逼哈拉少/" NGINX_VERSION
#文件编辑完成后进行源码编译即可
[root@nginx core]# cd ../../
[root@nginx nginx-1.29.4]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module
[root@nginx nginx-1.29.4]# make
[root@nginx nginx-1.29.4]# cd objs/
[root@nginx objs]# ls
autoconf.err nginx ngx_auto_config.h ngx_modules.c src
Makefile nginx.8 ngx_auto_headers.h ngx_modules.o
[root@Nginx objs]# cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
[root@Nginx sbin]# ls
nginx
#对旧版本进行备份
[root@nginx sbin]# cp nginx nginx.old
[root@Nginx sbin]# \cp -f /root/nginx-1.29.4/objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx升级
bash
[root@nginx sbin]# ls /usr/local/nginx/logs/
access.log error.log nginx.pid
[root@nginx sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 5577 0.0 0.0 11148 2072 ? Ss 10:19 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 5578 0.0 0.1 15424 5016 ? S 10:19 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 5649 0.0 0.0 6636 2176 pts/0 S+ 10:38 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
#开启新版本的进程,生成就进程pid的oldbin
[root@nginx sbin]# kill -USR2 5577
[root@nginx sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 5577 0.0 0.0 11148 2456 ? Ss 10:19 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 5578 0.0 0.1 15424 5016 ? S 10:19 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 5650 0.0 0.1 11188 6656 ? S 10:38 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 5651 0.0 0.1 15464 5280 ? S 10:38 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 5653 0.0 0.0 6636 2176 pts/0 S+ 10:38 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@nginx sbin]# ls /usr/local/nginx/logs/
access.log error.log nginx.pid nginx.pid.oldbin
[root@nginx sbin]# nginx -V
nginx version: 牛逼哈拉少/
......
#回收旧版本的进程
[root@nginx sbin]# kill -WINCH 5577
[root@nginx sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 5577 0.0 0.0 11148 2456 ? Ss 10:19 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
root 5650 0.0 0.1 11188 6656 ? S 10:38 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 5651 0.0 0.1 15464 5280 ? S 10:38 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 5660 0.0 0.0 6636 2176 pts/0 S+ 10:40 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx回滚
bash
[root@nginx sbin]# cp nginx nginx.new -p
[root@nginx sbin]# \cp nginx.old nginx -pf
[root@nginx sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 5577 0.0 0.0 11148 2456 ? Ss 10:19 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
root 5650 0.0 0.1 11188 6656 ? S 10:38 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 5651 0.0 0.1 15464 5280 ? S 10:38 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 5679 0.0 0.0 6636 2176 pts/0 S+ 10:41 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
#唤醒旧版本的进程
[root@nginx sbin]# kill -HUP 5577
[root@nginx sbin]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.28.1
......
#回收新版本存在的进程
[root@nginx sbin]# kill -WINCH 5650
[root@nginx sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 5577 0.0 0.0 11148 2456 ? Ss 10:19 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
root 5650 0.0 0.1 11188 6656 ? S 10:38 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 5680 0.0 0.1 15424 5016 ? S 10:41 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 5683 0.0 0.0 6636 2176 pts/0 S+ 10:42 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
#如果旧版本的进程没用的话就可以kill -9删除了
[root@nginx sbin]# kill -9 5650编写Nginx启动文件systemd
bash
#百度搜索模板
systemd site:nginx.org #搜索内容 site:搜索网址
[root@nginx ~]# cd /lib/systemd/system
[root@nginx system]# vim nginx.service
[Unit]
Description=The NGINX HTTP and reverse proxy server
After=syslog.target network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid #指定nginx启动的pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t #指定nginx -t检查配置文件命令
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #指定nginx启动命令
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
#使编写的配置生效
[root@nginx system]# systemctl daemon-reload
#在启动时要确保nginx已经关闭不然会冲突导致报错
[root@nginx system]# systemctl enable --now nginxNginx配置文件参数详解
1.nginx主配置文件说明
主配置文件结构:四部分
main block:主配置段,即全局配置段
#事件驱动相关的配置
event {
...
}
#http/https 作为web服务器相关配置段
http {
...
}
#默认配置文件不包括下面两个部分
#mail 作为邮件服务器相关配置段
mail {
...
}
#stream 反向代理相关配置段
stream {
...
}2.全局配置块参数
默认打开全局配置参数
user nginx nginx; #启动Nginx工作进程的用户和组
worker_processes [number | auto]; #启动Nginx工作进程的数量,一般设为和CPU核心数相同,可以设置为auto同步cpu核心数
worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010 00000100 00001000 | auto ; #将worker进程与cpu核数绑定,避免进程在不同核心上来回切换造成消耗
#示例
CPU MASK: 00000001:0号CPU
00000010:1号CPU
10000000:7号CPU
worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000;第0号---第3号CPU
worker_cpu_affinity 0101 1010;
worker_rlimit_nofile 100000; # 所有worker最多打开100000个文件描述符
# 最好与ulimit -n 或者limits.conf的值保持一致
#错误日志记录配置,语法:error_log file [debug | info | notice | warn | error | crit
| alert | emerg]
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid文件保存路径
#pid logs/nginx.pid;示例:cpu与核心绑定示例
bash
worker_processes auto;
worker_cpu_affinity 01 10;
[root@nginx ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo
cpu cores : 6
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes auto;
worker_cpu_affinity 000001 000010 000100 001000 010000 100000;
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -t
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -s reload
[root@nginx ~]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 881 0.0 0.0 11148 3352 ? Ss 15:18 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 1450 0.0 0.1 15456 5132 ? S 15:20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 1451 0.0 0.1 15456 5004 ? S 15:20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 1452 0.0 0.1 15456 5132 ? S 15:20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 1453 0.0 0.1 15456 5004 ? S 15:20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 1454 0.0 0.1 15456 5004 ? S 15:20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 1455 0.0 0.1 15456 5004 ? S 15:20 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 1457 0.0 0.0 6636 2304 pts/0 S+ 15:20 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@nginx ~]# ps axo pid,cmd,psr | grep nginx
881 nginx: master process /usr/ 4
1450 nginx: worker process 0
1451 nginx: worker process 1
1452 nginx: worker process 2
1453 nginx: worker process 3
1454 nginx: worker process 4
1455 nginx: worker process 5
1459 grep --color=auto nginx 33.events块配置参数
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
events {
worker_connections 10000; #单个woker工作进程最大并发数
use epoll; #使用epoll机制来实现高并发
#Nginx支持众多的事件驱动,
#比如:select、poll、epoll,只能设置在events模块中设置
accept_mutex on; #同一时刻一个请求访问只激活一个work进程赖处理
#不开启则一个请求到来唤醒所有worker,称为"惊群"
#默认为off,on为开启
multi_accept on; #把数据缓存多个到一定程度,同时发送给worker处理
#不开启则实时发送,打开后worker进程可以同时接受多个网络请求
#默认为off,on为开启
}
示例:实现nginx高并发配置
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_rlimit_nofile 100000;
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 10000;
}
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -s reload
#测试并发
[root@nginx ~]# dnf install httpd-tools -y
[root@Nginx ~]# ab -n 100000 -c10000 http://172.25.254.100/index.html
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1913912 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking 172.25.254.100 (be patient)
socket: Too many open files (24) #并发数量过多导致访问失败
#处理本地文件系统的并发文件数量
[root@nginx ~]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf #永久生效但要重启
* - nofile 100000 #打开文件最大个数
* - noproc 100000 #打开程序最大个数
[root@nginx ~]# ulimit -n 100000 #临时生效
[root@nginx ~]# ulimit -n
100000
[root@bginx ~]# ab -n 100000 -c10000 http://172.25.254.100/index.html
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1913912 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking 172.25.254.100 (be patient)
Completed 10000 requests
Completed 20000 requests
Completed 30000 requests
Completed 40000 requests
Completed 50000 requests4.http块配置参数
http块是Nginx服务器配置中的重要部分,缓存、代理和日志格式定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块都可以在这设置,http块可以包含多个server块,而一个server块中又可以包含多个location块。
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
#在响应报文中将指定的文件扩展名映射至MIME对应的类型
include mime.types; #可以识别文本,图像,音频,视频等其他的数据
default_type application/octet-stream; #没有识别的默认类型,例如php,ngxin不识别需要安装php才能渲染呈现
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log logs/access.log main; #使用定义为main的日志格式,存放在根目录的logs/access.log中
sendfile on; #零拷贝功能,sendfile系统调用在两个文件描述符之间直接传递数据(完全在内核中操作)
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65; #长连接超时时间,单位是s
#gzip on; #开启压缩功能
server {
#web服务配置
}
include "/usr/local/nginx/conf.d/*.conf"; #导入其他路径的配置文件,子配置文件
#要放在默认发布文件目录下,不然会覆盖默认
}示例:识别php文件为text/html类型
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/html/index.php
<?php
phpinfo()
?>
[root@nginx ~]# curl -I 172.25.254.100/index.php
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.26.1
Date: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 12:31:48 GMT
Content-Type: application/octet-stream #php不属于mime类型中,所以使用默认
Content-Length: 23
Last-Modified: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 11:17:36 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "688f4550-17"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
default_type text/html;
[root@nginx ~]# curl -I 172.25.254.100/index.php
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.26.1
Date: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 12:35:22 GMT
Content-Type: text/html #将识别类型改为text/html
Content-Length: 23
Last-Modified: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 11:17:36 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "688f4550-17"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
default_type test/php;
[root@nginx ~]# curl -I 172.25.254.100/index.php
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.26.1
Date: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 12:35:22 GMT
Content-Type: test/php #可以自定义将识别不出来的设为想要的类型
Content-Length: 23
Last-Modified: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 11:17:36 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "688f4550-17"
Accept-Ranges: bytes基于域名的web站点发布
bash
#创建基于域名的发布根目录
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir /webdata/nginx/fjwyyy.org/fjw/html -p
#生成发布文件
[root@nginx ~]# echo fjw.fjwyyy.org > /webdata/nginx/fjwyyy.org/fjw/html/index.html
#创建子配置目录
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir /usr/local/nginx/conf.d
#创建子配置文件
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fjwyyy.org;
root /webdata/nginx/fjwyyy.org/fjw/html/;
}
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
......
include "/usr/local/nginx/conf.d/*.conf"; #放在server{}下面防止识别有误
}
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -t
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -s reload
#添加本地解析
[root@nginx ~]# vim /etc/hosts
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fjwyyy.org
fjw.fjwyyy.orglocation中的root与alias
- root:指定web的家目录,在定义location的时候,文件的绝对路径等于 root+location
- alias:定义路径别名,会把访问的路径重新定义到其指定的路径,文档映射的另一种机制;
- 访问路径为文件指定路径也要为文件则相当于软连接
- 访问路径为指定路径也要为目录然后查看目录下的index.html
root示例
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fjw.org;
location / {
root /webdata/nginx/fjwyyy.org/fjw/html/;
}
location /login {
root /webdata/nginx/fjwyyy.org/fjw/html/;
}
}
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -t
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -s reload
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fjw.org
www.fjwyyy.org
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fjw.org/login/
loginalias示例
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fjw.org;
location /passwd { #指定为文件下面路径也要为文件,相当于软连接
alias /etc/passwd;
}
location /passwd/ { #指定为目录下面也要为目录,/mnt/下的index.html,重定向到目录查找底下的默认发布文件
alias /mnt;
}
}
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -t
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -s reload
#测试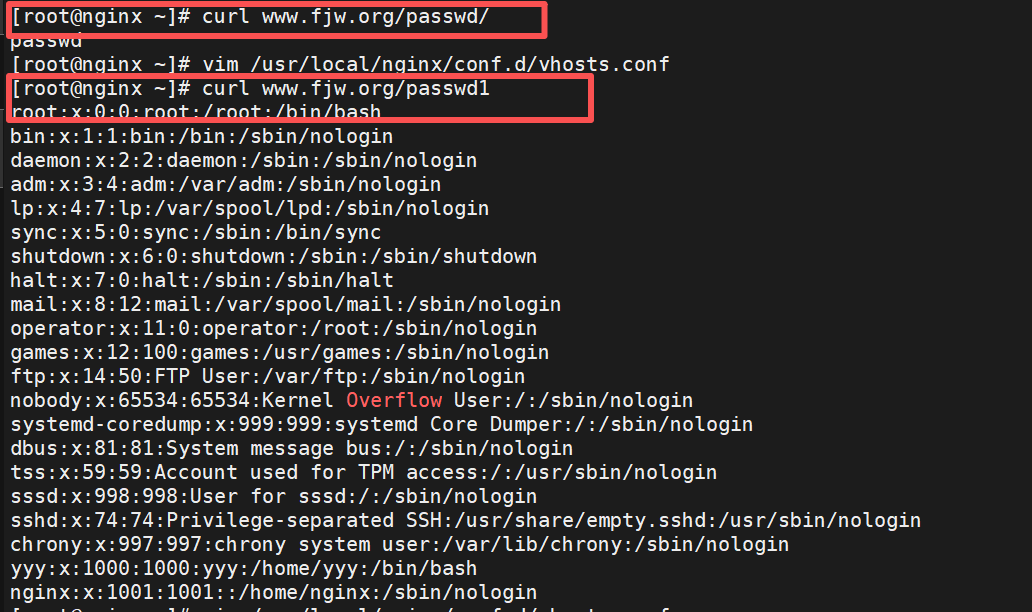
location字符匹配
location是用于匹配请求 URI(统一资源标识符)的核心配置指令,它可以根据不同的 URI 路径设置不同的处理规则(如反向代理、静态文件访问、重定向等)。
修饰符与匹配规则
Nginx 的location匹配遵循 "优先匹配特定规则,再匹配通用规则" 的原则,不同修饰符对应不同的优先级(从高到低排序):
| 修饰符 | 名称 | 匹配规则 | 优先级 |
|---|---|---|---|
= |
精确匹配 | 仅匹配与匹配路径完全一致的 URI。 |
最高 |
^~ |
前缀匹配(优先) | 匹配以匹配路径为前缀的 URI,且一旦匹配成功,不再检查其他正则匹配,区分大小写,也包含正则。 |
次高 |
| 无 | 一般匹配(普通) | 匹配以匹配路径为前缀的 URI,但优先级低于正则匹配,不识别正则表达式。 |
较低 |
~ |
正则匹配(区分大小写) | 按正则表达式匹配 URI,区分大小写。 | 较高 |
~* |
正则匹配(不区分大小写) | 按正则表达式匹配 URI,不区分大小写(如匹配.html和.HTML)。 |
较高 |
#匹配优先级从高到低:
"=" > "^~" > "/*",不带符号
1.示例-精准匹配
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
location = /test {
return 200 "punct = \n"; #returun 200.只要访问/test无论是否存在都会返回200存在成功,并输出"punct = \n"
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
punct =
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test1
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/1test
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>2.示例-正则前缀匹配
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
# location = /test {
# return 200 "punct = \n";
# }
location ^~ /test {
return 200 "punct = ^~\n";
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
punct = ^~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test/a/b
punct = ^~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/testc
punct = ^~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/aatestc
\<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.26.1</center>
</body>
</html>
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/TEST #区分大小写
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.26.1</center>
</body>
</html>3.示例-正则匹配(区分大小写)
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
# location = /test {
# return 200 "punct = \n";
# }
# location ^~ /test {
# return 200 "punct = ^~\n";
# }
location ~ /test {
return 200 "punct = ~\n";
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
punct = ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/testa
punct = ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test/a/
punct = ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/atest
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.26.1</center>
</body>
</html>
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/test #匹配的是url要加/
punct = ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/TEST #也区分大小写
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>4.示例-正则匹配(不区分大小写)
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
# location = /test {
# return 200 "punct = \n";
# }
# location ^~ /test {
# return 200 "punct = ^~\n";
# }
# location ~ /test {
# return 200 "punct = ~\n";
# }
location ~* /test {
return 200 "punct = ~*\n";
}
}
#测试
#效果基本与正则匹配一致,只是不区分大小写
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
punct = ~*
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/TEST
punct = ~*
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/TEST
punct = ~*
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/aTEST
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>5.示例-一般匹配
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
# location = /test {
# return 200 "punct = \n";
# }
# location ^~ /test {
# return 200 "punct ^~\n";
# }
# location ~ /test {
# return 200 "punct ~\n";
# }
# location ~* /test {
# return 200 "punct ~*\n";
# }
location /test {
return 200 "punct \'\' \n";
}
}
#测试
#类似前缀匹配^~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
punct ''
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test/a
punct ''
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/testa
punct ''
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/atest
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/test/a
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>6.示例-"\"的作用
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
# location = /test {
# return 200 "punct = \n";
# }
# location ^~ /test {
# return 200 "punct ^~\n";
# }
# location ~ /test {
# return 200 "punct ~\n";
# }
# location ~* /test {
# return 200 "punct ~*\n";
# }
# location /test {
# return 200 "punct \'\' \n";
# }
location ~* \.(png|JPG|CSS)$ { #命中结尾的文件,且不区分大小写
return 200 "punct ~\n";
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/fjw.css
punct ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/fjw.png
punct ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/fjw.PNG
punct ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/fjw
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>7.示例-检测优先级
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
location = /test {
return 200 "=\n";
}
location ^~ /test {
return 200 "^~\n";
}
location ~* /test { #~*与~优先级一致,谁在上面谁优先级就高,区别就是~*区分大小写
return 200 "~*\n";
}
location ~ /test {
return 200 "~\n";
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
=
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/testa
^~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/test
~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/TEST
~*
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/TEST
~*补充
bash
#^~ 与 无符号 不能同时存在不然会报错只能存在其一
#由于无符号的前缀匹配优先级最低
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
location /test {
return 200 "haha\n"; #优先级最低
}
location = /test {
return 200 "=\n";
}
location ~ /test {
return 200 "~\n";
}
location ~* /test {
return 200 "~*\n";
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
=
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/testa
~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/Testa
~*
#当把其他location注释后剩下无符号的前缀匹配才能生效
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
haha长链接优化
长连接配置一般在主配置文件设置,在http块中设置,设置后子配置文件的全部站点都生效;
参数配置
#默认配置
http {
#keepalive_timeout 0; #长连接超时次数,在长连接期间发送三次请求就超时断开
keepalive_timeout 65; #长连接超时时间
}
#示例
keepalive_timeout 3;
keepalive_timeout 65 60;
#开启长连接后,显示给客户端的会话保持时间为60s,单次长连接累计请求达到指定次数请求或65秒就会被断开,第二个数字60为发送给客户端应答报文头部中显示的超时时间设置为60s:如不设置客户端将不显示超时时间。设定长连接时间
bash
#安装测试软件
[root@nginx ~]# dnf install telnet -y
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
keepalive_timeout 5;
[root@Nginx ~]# nginx -s reload
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# telnet www.fjw.org 80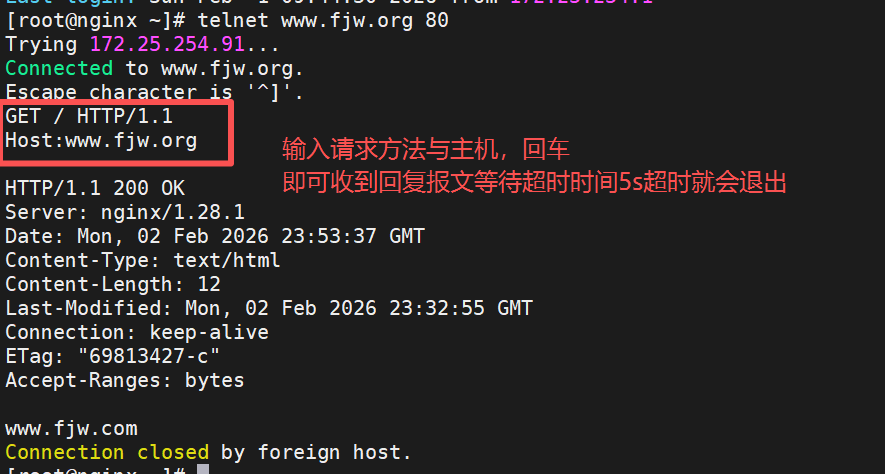
设定超时次数
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
keepalive_requests 3;
keepalive_timeout 65 60;
[root@Nginx ~]# nginx -s reload
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# telnet www.fjw.org 80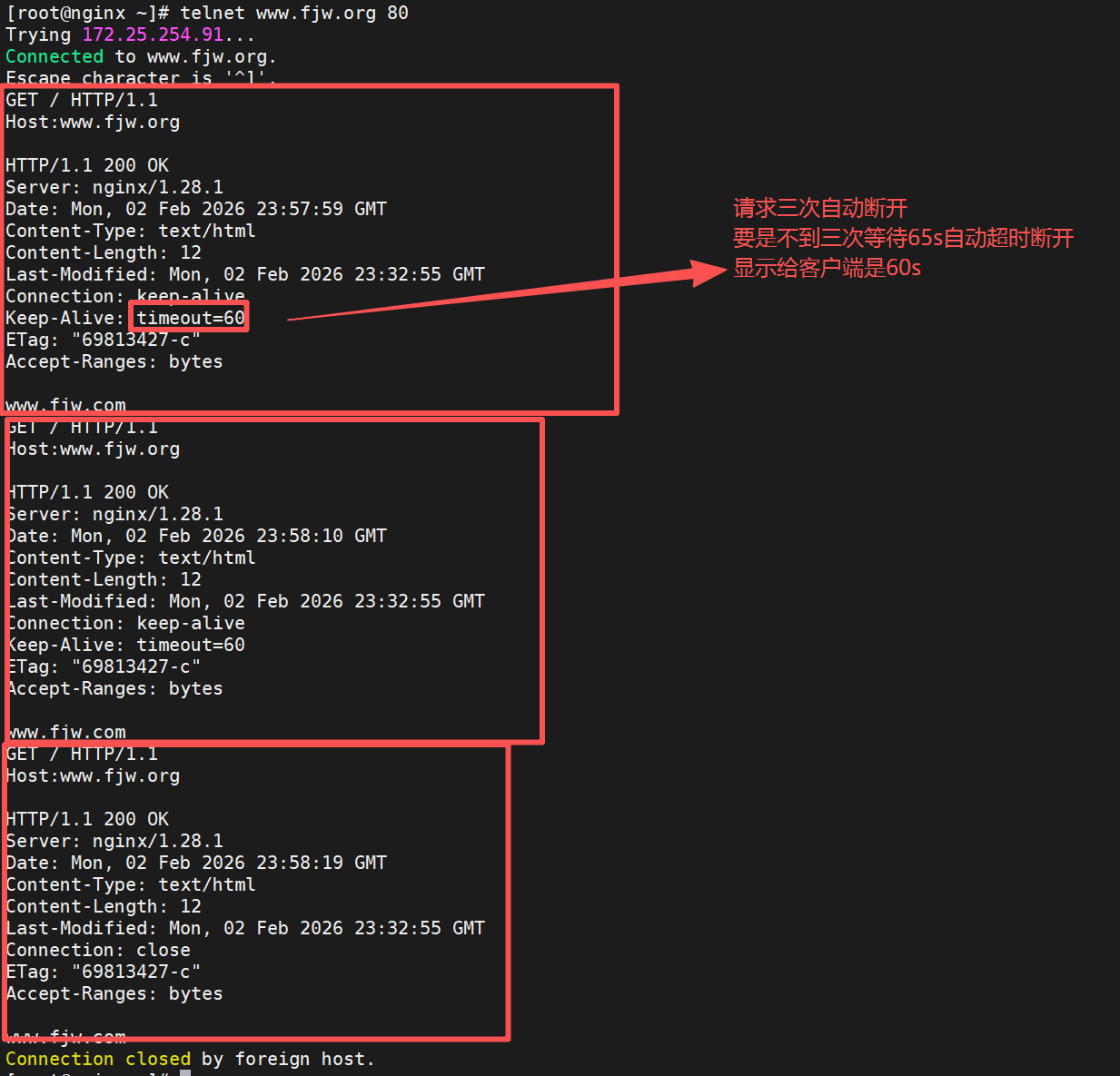
NginxWeb页面账户认证
由 ngx_http_auth_basic_module 模块提供此功能
创建加密信息
bash
#使用不了htpasswd时要下载httpd-tools包
#创建加密信息,-c创建,-m使用md5加密,-b非交互生成
[root@nginx ~]# htpasswd -cmb /usr/local/nginx/.htpasswd fjw fjw
#进行创建后,想要添加用户认证信息不用加-c,-c参数会覆盖
[root@nginx ~]# htpasswd -mb /usr/local/nginx/.htpasswd yyy yyy
[root@nginx ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/.htpasswd
fjw:$apr1$rYDpBBuw$x701q1axSqvBDgXFV81QM/
yyy:$apr1$OZHKwo15$YKoStu20qFtVls5la9fz50编辑配置文件
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fjwyyy.org;
root /webdata/nginx/fjwyyy.org/fjw/html;
location /admin {
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
auth_basic "login passwd";
auth_basic_user_file "/usr/local/nginx/.htpasswd";
}
}
[root@nginx ~]# systemctl restart nginx.service
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir /usr/local/nginx/html/admin/
[root@nginx ~]# echo admin > /usr/local/nginx/html/admin/index.html测试
bash
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fjwyyy.org/admin/
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fjwyyy.org/admin/ -ufjw:fjw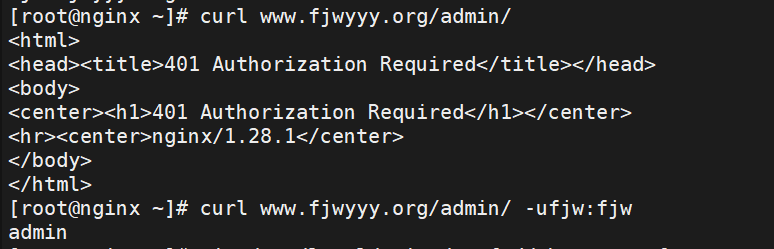
自定义错误页面
生成测试错误页面
bash
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir /usr/local/nginx/errorpage
[root@nginx ~]# echo "太不巧了,你要访问的页面辞职了!!" > /usr/local/nginx/errorpage/errormessage编辑配置
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fjw.org;
error_page 404 405 503 502 /error; #指定location的位置
location /fjw/ { #不存在页面
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
}
location /error {
alias /usr/local/nginx/errorpage/errormessage;
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fjw.org/fjw/
太不巧了,你要访问的页面辞职了!!使用root的写法
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fjw.org;
error_page 404 405 503 502 /errorpage/errormessage;
location /fjw/ {
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
}
location /errorpage/ {
root /usr/local/nginx/;
}
}
#效果一致要注意对root与alias的理解自定义错误日志
编辑配置参数
bash
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/nginx/logs/fjw.org/
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fjw.org;
error_page 404 405 503 502 /errorpage/errormessage;
access_log logs/fjw.org/fjw.access; #这里的默认发布目录是主配置文件指定的默认发布目录,相对路径指定日志路径,可加main参数指定日志格式要在主配置文件开启日志格式参数
error_log logs/fjw.org/fjw.error error; #error为日志错误日志级别
location /fjw/ {
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
}
location /errorpage/ {
root /usr/local/nginx/;
}
}
#测试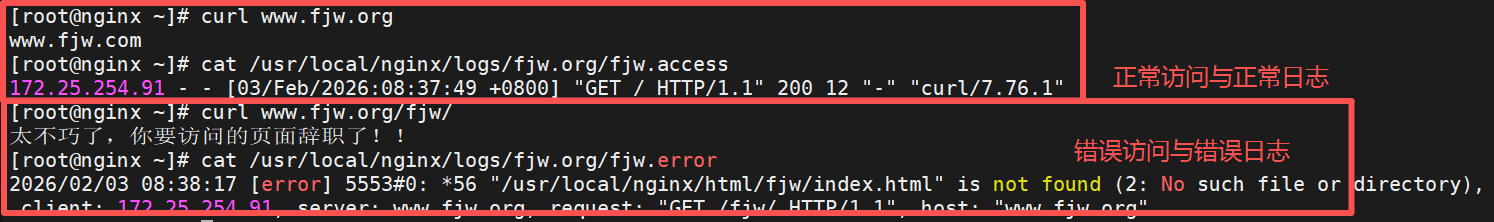
Nginx的文件检测
- try_files会按顺序检查文件是否存在,返回第一个找到的文件或文件夹(结尾加斜线表示为文件夹),如 果所有文件或文件夹都找不到,会进行一个内部重定向到最后一个参数。
- 只有最后一个参数可以引起一 个内部重定向,之前的参数只设置内部URI的指向。
- 最后一个参数是回退URI且必须存在,否则会出现内 部500错误。
- 一般为最后一个参数创建一个默认页面
创建测试页面
bash
[root@nginx ~]# echo default > /usr/local/nginx/errorpage/default.html编辑参数
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fjw.org;
root /webdata/nginx/fjw.org/fjw/html/;
error_page 404 405 503 502 /errorpage/errormessage;
access_log logs/fjw.org/fjw.access;
error_log logs/fjw.org/fjw.error error;
try_files $uri $uri.html $uri/index.html /errorpage/default.html; #如果都不存在就看default.html,而不是跳转到错误页面
location /errorpage/ {
root /usr/local/nginx/;
}
}
#测试
#随便访问不存在的路径不是跳转错误页面了
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fjw.org/fjw
default
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fjw.org/abcadad
defaultNginx中建立下载服务器
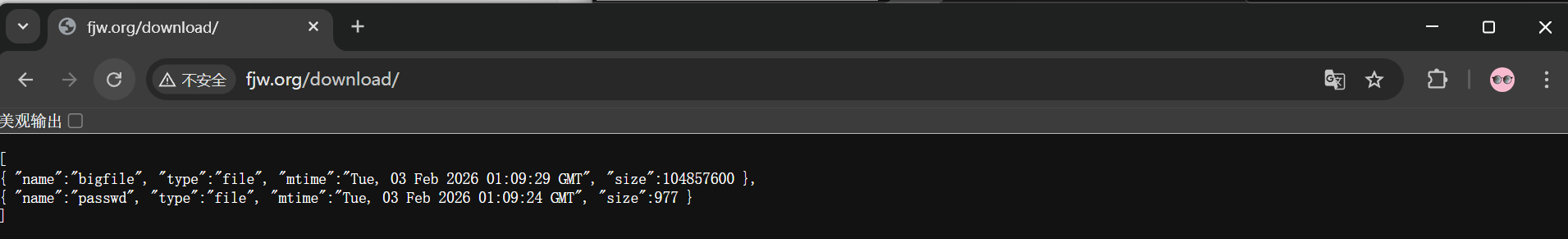
生成测试文件
bash
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/nginx/download
[root@nginx ~]# cp /etc/passwd /usr/local/nginx/download/
[root@nginx ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/usr/local/nginx/download/bigfile bs=1M count=100编辑配置参数
bash
[root@nginx ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fjw.org;
root /webdata/nginx/fjw.org/fjw/html/;
error_page 404 405 503 502 /errorpage/errormessage;
access_log logs/fjw.org/fjw.access;
error_log logs/fjw.org/fjw.error error;
try_files $uri $uri.html $uri/index.html /errorpage/default.html;
location /errorpage/ {
root /usr/local/nginx/;
}
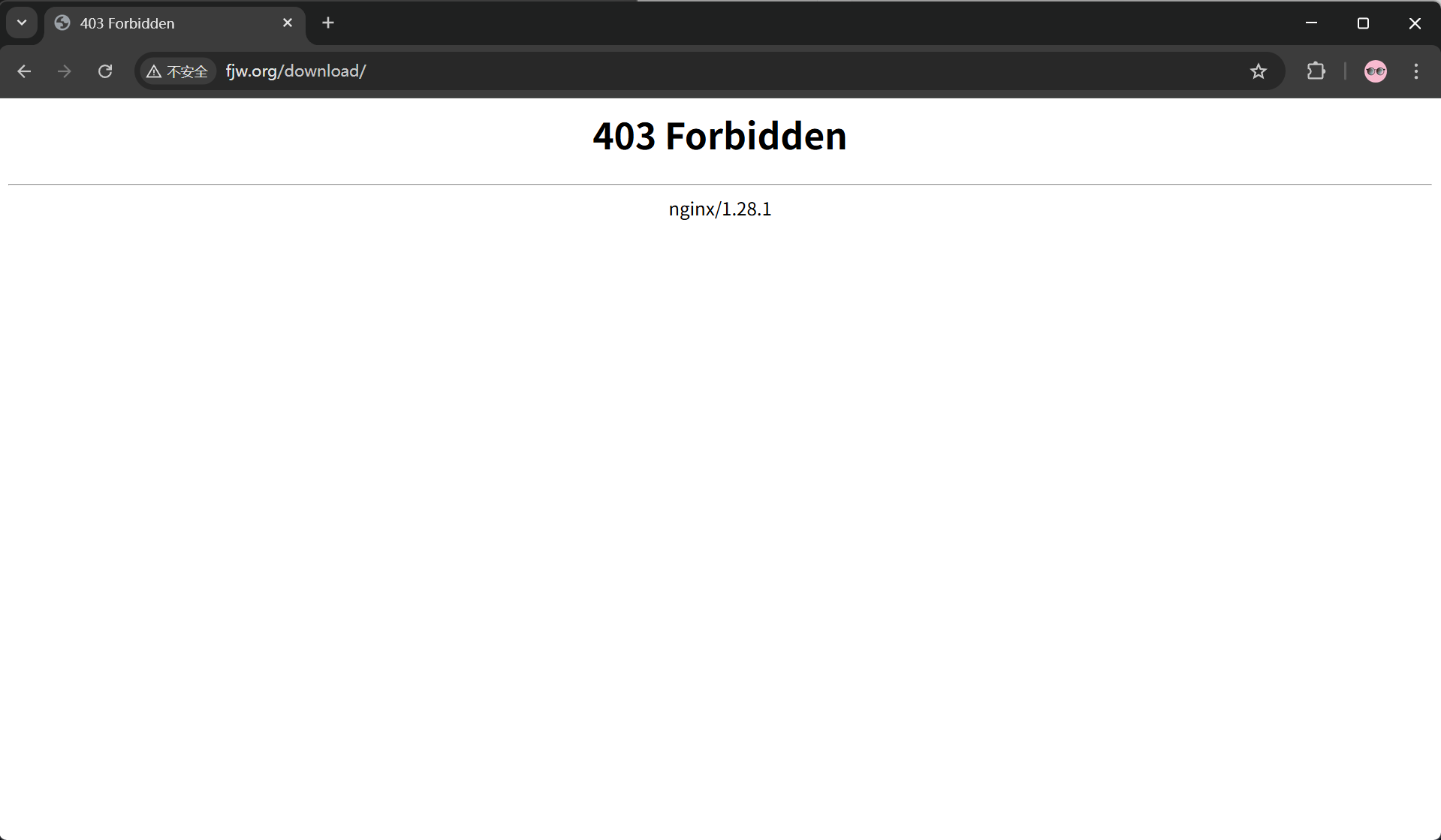
location /download {
root /usr/local/nginx;
}
}访问
开启列表功能
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
......
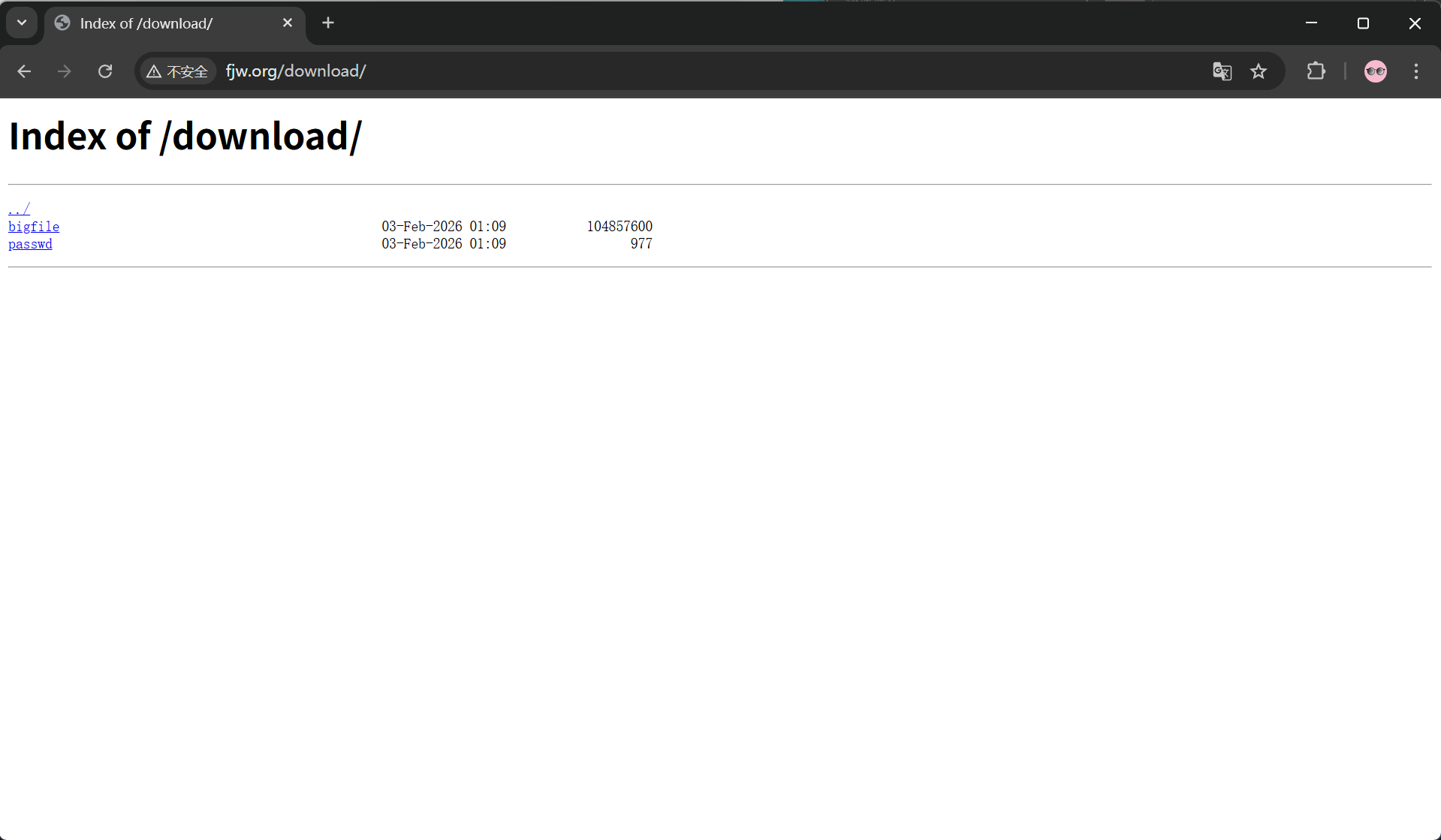
location /download {
root /usr/local/nginx;
autoindex on;
#开启自动索引功能,由于没默认发布文件,要想作为下载服务器就要自动索引存在的文件便于显示
}
......再次访问
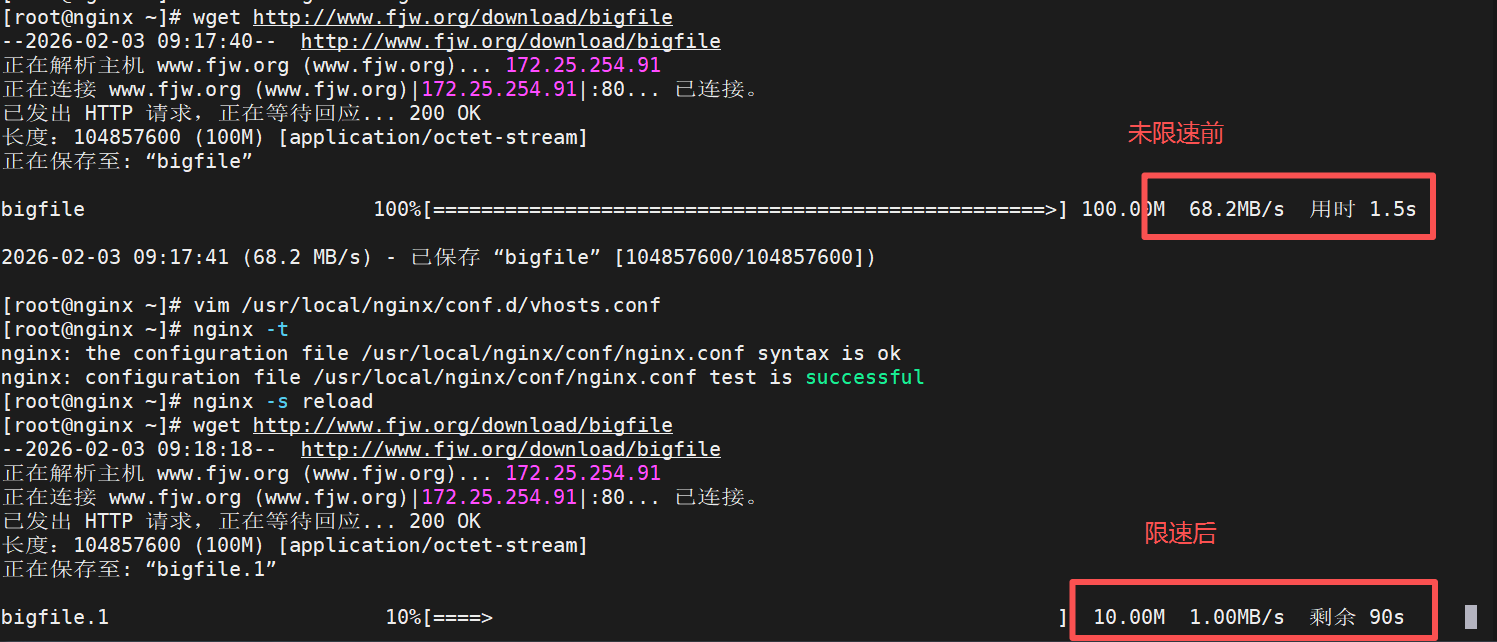
下载控速配置
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
......
location /download {
root /usr/local/nginx;
autoindex on;
limit_rate 1024k; #限制下载速度/s,默认不限速
}
......
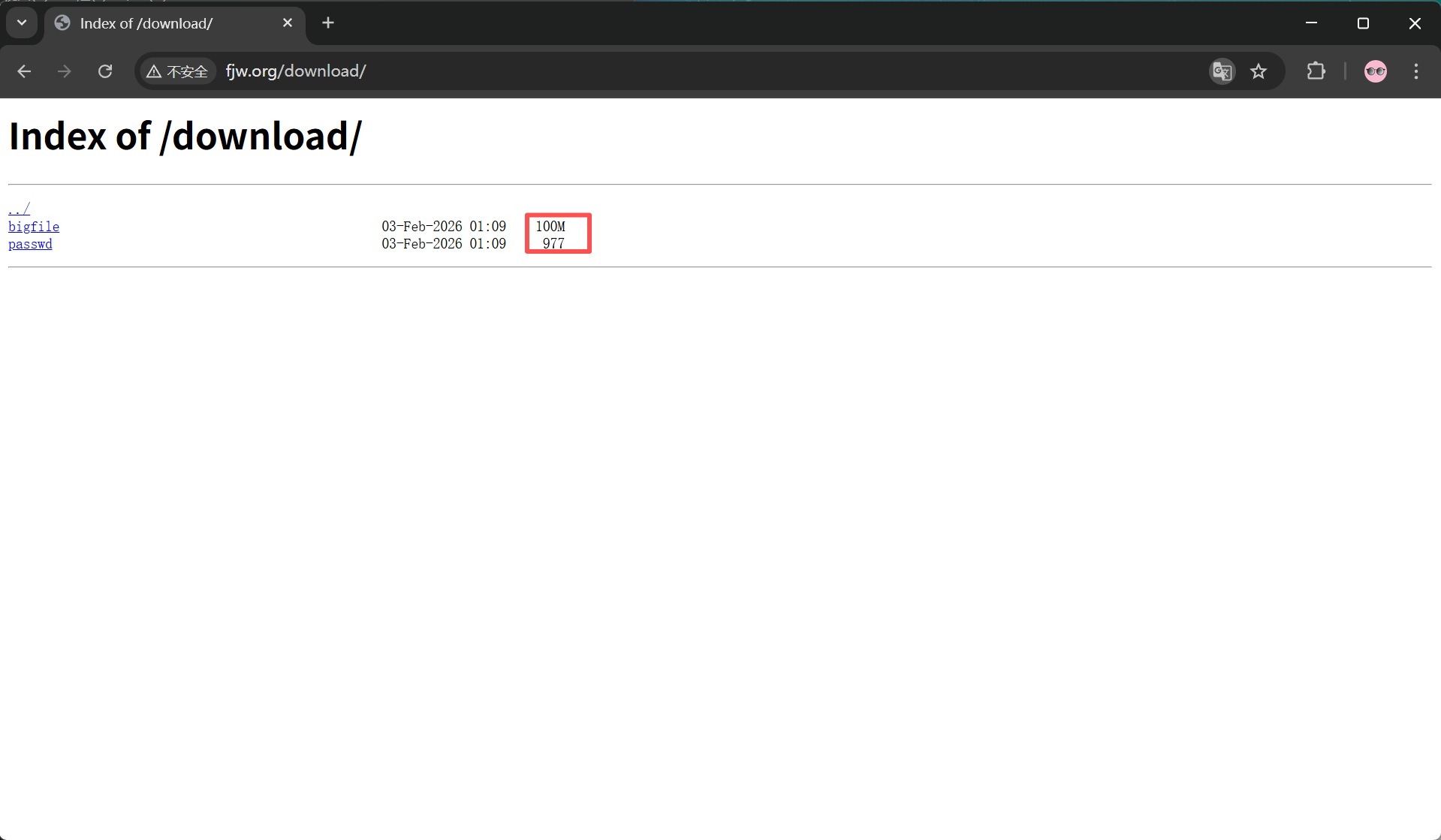
显示文件大小优化
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
......
location /download {
root /usr/local/nginx;
autoindex on;
limit_rate 1024k;
autoindex_exact_size off; #计算文件确切大小,off为显示大概大小(kb,mb,gb)
}
......
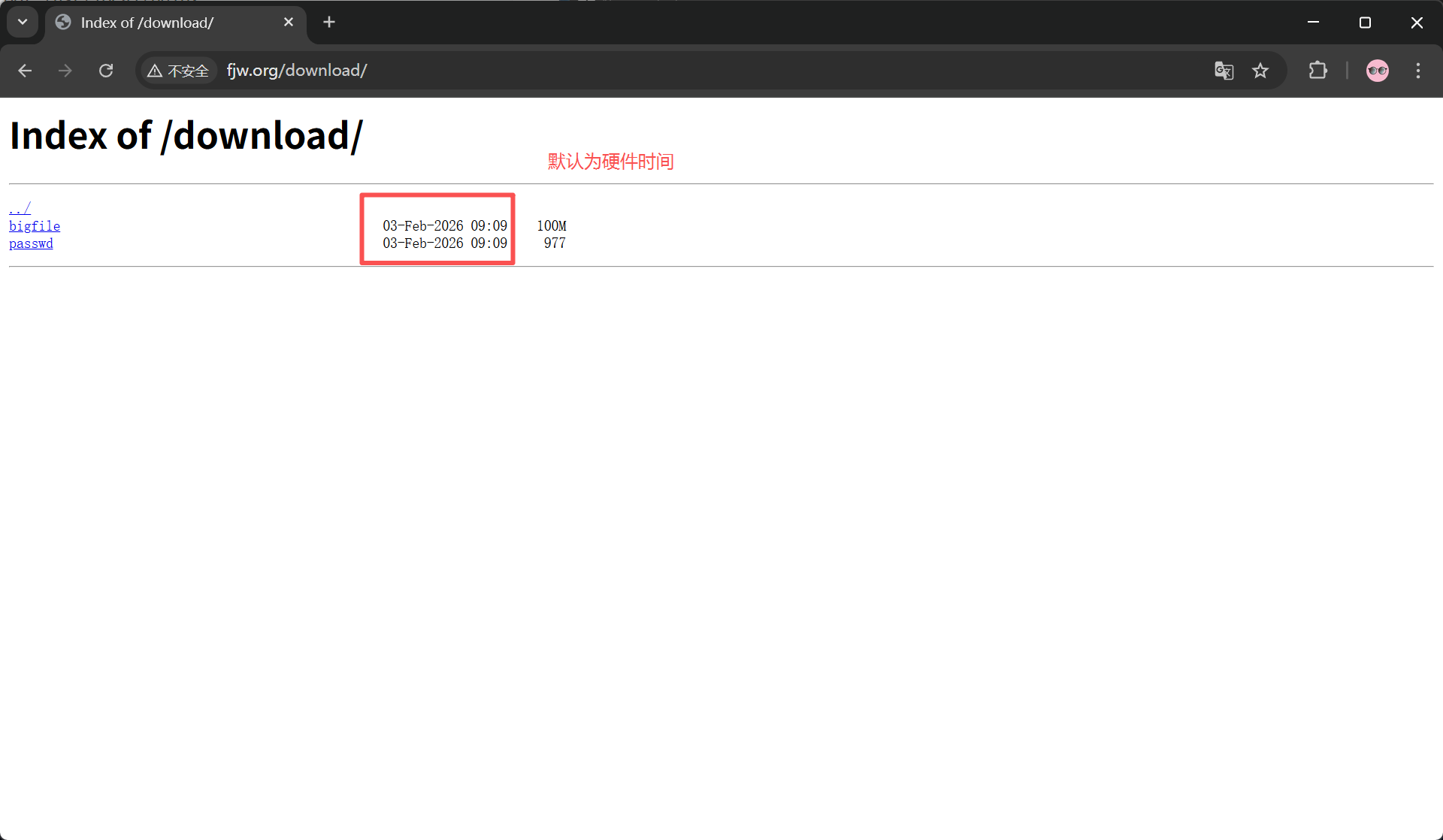
时间显示调整
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
......
location /download {
root /usr/local/nginx;
autoindex on;
limit_rate 1024k;
autoindex_exact_size off;
autoindex_localtime on; #on显示本机时间而不是格林威治时间
}
......
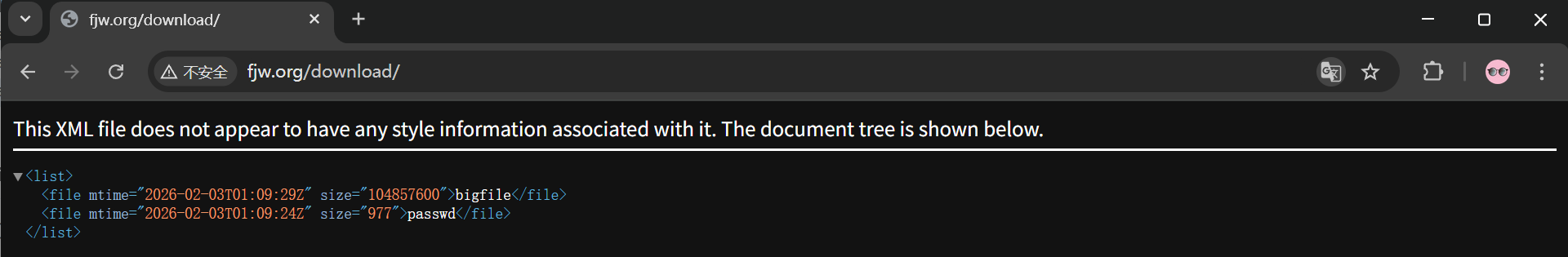
设定页面风格
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
......
location /download {
root /usr/local/nginx;
autoindex on;
limit_rate 1024k;
autoindex_exact_size off;
autoindex_localtime on;
autoindex_format html | xml | json | jsonp; #设置网页显示风格,指定一种显示风格
}
......xml风格
json风格
Nginx的状态页
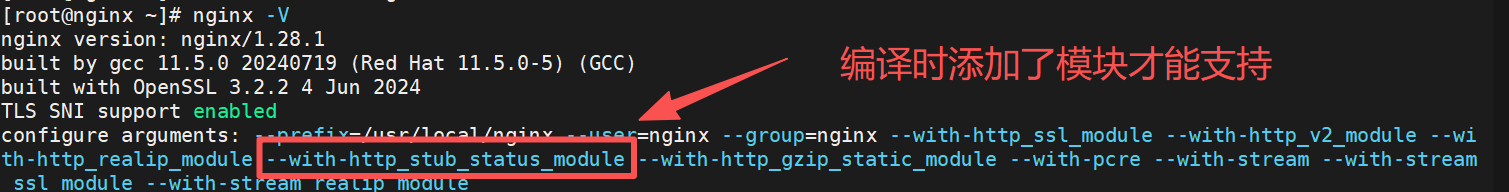
bash
#建议创建认证用户来访问,一般状态页要认证才能查看不是所有人都能看
[root@nginx ~]# htpasswd -cmb /usr/local/nginx/.htpasswd fjw fjw
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fjw.org;
location /status {
stub_status; #开启状态页功能
auth_basic "status page";
auth_basic_user_file "/usr/local/nginx/.htpasswd";
allow 172.25.254.0/24;
deny all;
}
}
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -t
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -s reload在访问浏览器测试
状态页面
bash
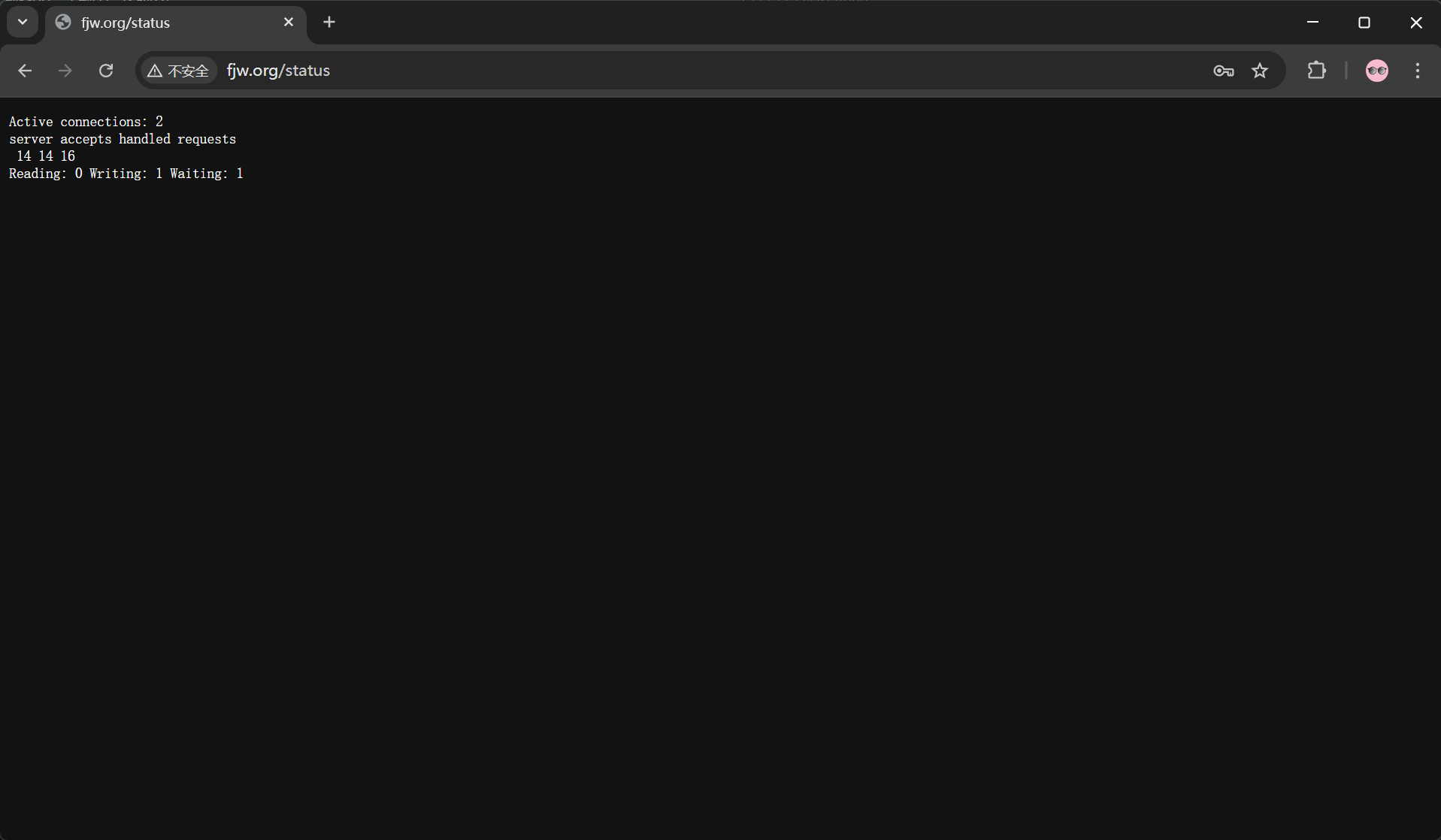
#状态页信息参数
Active connections: #当前处于活动状态的客户端连接数
#包括连接等待空闲连接数=reading+writing+waiting
accepts: #统计总值,Nginx自启动后已经接受的客户端请求连接的总数。
handled: #统计总值,Nginx自启动后已经处理完成的客户端请求连接总数
#通常等于accepts,除非有因worker_connections限制等被拒绝的连接
requests: #统计总值,Nginx自启动后客户端发来的总的请求数
Reading: #当前状态,正在读取客户端请求报文首部的连接的连接数
#数值越大,说明排队现象严重,性能不足
Writing: #当前状态,正在向客户端发送响应报文过程中的连接数,数值越大,说明访问量很大
Waiting: #当前状态,正在等待客户端发出请求的空闲连接数开启 keep-alive的情况下,这个值等于active -- (reading+writing)Nginx的压缩功能
Nginx支持对指定类型的文件进行压缩然后再传输给客户端,而且压缩还可以设置压缩比例,压缩后的文 件大小将比源文件显著变小,样有助于降低出口带宽的利用率,降低企业的IT支出,不过会占用相 应的CPU资源。
Nginx对文件的压缩功能是依赖于模块 ngx_http_gzip_module,默认是内置模块。
配置参数如下
#启用或禁用gzip压缩,默认关闭
gzip on | off;
#压缩比由低到高从1到9,默认为1,值越高压缩后文件越小,但是消耗cpu比较高。基本设定未4或者5
gzip_comp_level 4;
#禁用IE6 gzip功能,早期的IE6之前的版本不支持压缩
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.";
#gzip压缩的最小文件,小于设置值的文件将不会压缩
gzip_min_length 1k;
#启用压缩功能时,协议的最小版本,默认HTTP/1.1
gzip_http_version 1.0 | 1.1;
#指定Nginx服务需要向服务器申请的缓存空间的个数和大小,平台不同,默认:32 4k或者16 8k;
gzip_buffers number size;
#指明仅对哪些类型的资源执行压缩操作;默认为gzip_types text/html,不用显示指定,否则出错
gzip_types mime-type ...;
#如果启用压缩,是否在响应报文首部插入"Vary: Accept-Encoding",一般建议打开
gzip_vary on | off;
#预压缩,即直接从磁盘找到对应文件的gz后缀的式的压缩文件返回给用户,无需消耗服务器CPU
#注意: 来自于ngx_http_gzip_static_module模块
gzip_static on | off;生成测试文件
bash
[root@nginx ~]# echo smallfile > /usr/local/nginx/html/small.html
[root@nginx ~]# cp /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log /usr/local/nginx/html/bigfile.txt #大文件后缀为txt才能被识别 开启压缩功能
bash
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
gzip on;
gzip_comp_level 4;
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.";
gzip_min_length 1024k;
gzip_buffers 32 1024k;
gzip_types text/plain application/javascript application/x-javascript text/css application/xml text/javascript application/x-httpd-php image/gif image/png;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_static on;
......
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -t
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -s reload
#做好主机的解析
[root@nginx ~]# vim /etc/hosts测试
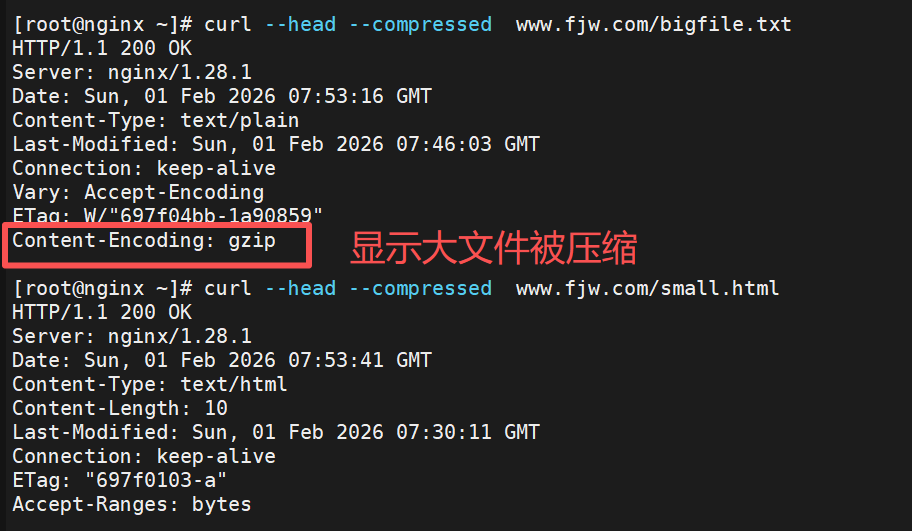
bash
#--head 仅获取响应头,不下载正文 --compressed告知服务器可接受压缩格式的响应
[root@nginx ~]# curl --head --compressed www.fjw.com/bigfile.txt
[root@nginx ~]# curl --head --compressed www.fjw.com/small.html