接口是抽象类的更进一步. 抽象类中还可以包含非抽象方法, 和字段. 而接口中包含的方法都是抽象方法, 字段只能包含静态常量。
一个简单的接口代码示例
java
interface IShape {
void draw();
}
class Cycle implements IShape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("○");
}
}
public class Data {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IShape shape = new Rect();
shape.draw();
}
}定义接口的注意事项:
- 使用 interface 定义一个接口
- 接口中的方法一定是抽象方法, 因此可以省略 abstract
- 接口中的方法一定是 public, 因此可以省略 public
- Cycle 使用 implements 继承接口. 此时表达的含义不再是 "扩展", 而是 "实现"
- 在调用的时候同样可以创建一个接口的引用, 对应到一个子类的实例.
- 接口不能单独被实例化
定义一个完整的接口是这样的:
interface Ishape{
public static final int num = 10;
public abstruct void draw();
}
但是严格来说我们在定义一个接口的时候通常会省略 public static final 和 public abstruct ,在我们定义接口的时候里面的变量和方法会自动加上。
省略之后的写法:
interface Ishape{
int num = 10;
void draw();
}
实现多个接口
有的时候我们需要让一个类同时继承自多个父类. 这件事情在有些编程语言通过 多继承 的方式来实现的.然而 Java 中只支持单继承, 一个类只能 extends 一个父类. 但是可以同时实现多个接口, 也能达到多继承类似的效果。
代码示例:
java
interface Ifly{
void fly();
}
interface Irunning{
void running();
}
interface Iswimming{
void swimming();
}
abstract class Animal{
public String name;
public int age;
public Animal(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
abstract public void eat();
}
class Dog extends Animal implements Iswimming , Irunning{
public Dog(String name,int age){
super(name,age);
}
@Override
public void running() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在跑");
}
@Override
public void swimming() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在游泳");
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃狗粮");
}
}
public class Data{
public static void test1(Animal animal){
animal.eat();
}
public static void test2(Ifly ifly){
ifly.fly();
}
public static void test3(Iswimming iswimming){
iswimming.swimming();
}
public static void test4(Irunning irunning){
irunning.running();
}
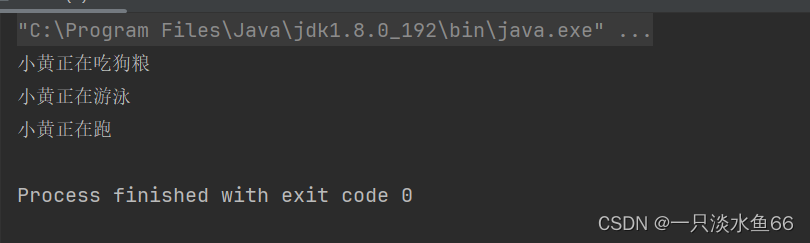
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1(new Dog("小黄" ,20));
test3(new Dog("小黄" ,20));
test4(new Dog("小黄" ,20));
}
}上面的代码展示了 Java 面向对象编程中最常见的用法: 一个类继承一个父类, 同时实现多种接口。
在这个代码中我们定义了三个接口:Ifly 、Irunning 、Iswimming 。一个抽象类:Animal 。然后定义了一个类来继承这个抽象类并且实现了两个接口。
上述代码运行结果:
接口的常见使用案例
Comparable接口
给对象数组排序
代码示例:
java
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(String name, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[" + this.name + ":" + this.score + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.score - o.score;
}
}
public class Data{
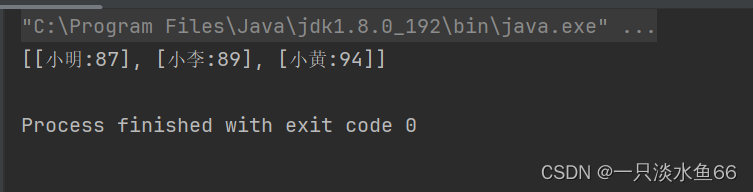
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student[] student = {
new Student("小明",87),
new Student("小黄",94),
new Student("小李",89)};
Arrays.sort(student);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(student));
}
}在这个代码中我们定义了一个 Student 类:
class Student {
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(String name, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[" + this.name + ":" + this.score + "]";
}
}
然后用这个类创建了一个数组:
Student[] student = { new Student("小明",87), new Student("小黄",94), new Student("小李",89)};
接着我们给 Student 类实现接口 Comparable<Student> ,这样我们就可以给该类实例化的成员进行比较大小。
上述代码的运行结果:
**注意事项:**对于 sort 方法来说, 需要传入的数组的每个对象都是 "可比较" 的, 需要具备 compareTo 这样的能力. 通过重写 compareTo 方法的方式, 就可以定义比较规则。
Comparator接口
另外一种比较一个类的两个实例的方法:
代码示例:
java
class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
public String name;
public int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return this.age - o.age;
}
}
class AgeComparator implements Comparator<Person>{
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return o1.age - o2.age;
}
}
class NameComparator implements Comparator<Person>{
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return o1.name.compareTo(o2.name);
}
}
public class Data{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("小明",20);
Person p2 = new Person("小黄",30);
System.out.println(p1.compareTo(p2));
AgeComparator agecomparator = new AgeComparator();
System.out.println(agecomparator.compare(p1,p2));
NameComparator namecomparator = new NameComparator();
namecomparator.compare(p1,p2);
}
}在这个代码中我们为了进行比较,额外创建了一个类来实现 Comparator 接口并且在该类里面重写 compare 方法。
Clonable 接口
浅拷贝 VS 深拷贝
浅拷贝示例
代码示例:
java
class Person implements Cloneable{
public int age;
public Person(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public class Data{
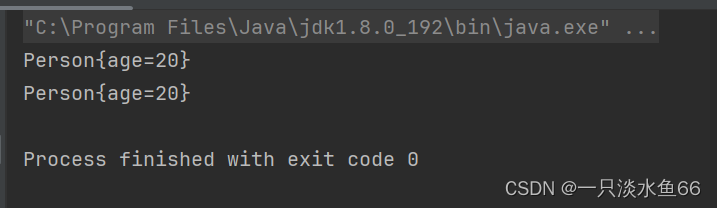
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person p1 = new Person(20);
Person p2 = (Person)p1.clone();
System.out.println(p1);
System.out.println(p2);
}
}这里我们定义了一个类 Person 并且实现了接口 Cloneable 重写了方法 clone 。在测试类中我们将 p1 里面的内容拷贝到了 p2 里面。
代码运行结果:
接着我们再定义一个 Money 类:
class Money{ public double money = 19.9; }
并且在 Person 类中使用这个类:
class Person implements Cloneable{ public int age; public Money m = new Money(); public Person(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "age=" + age + '}'; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
接着我们再进行拷贝,将 p1 里面的内容拷贝到 p2 里面,然后我们改变 p2 里面的内容,并且将其输出:
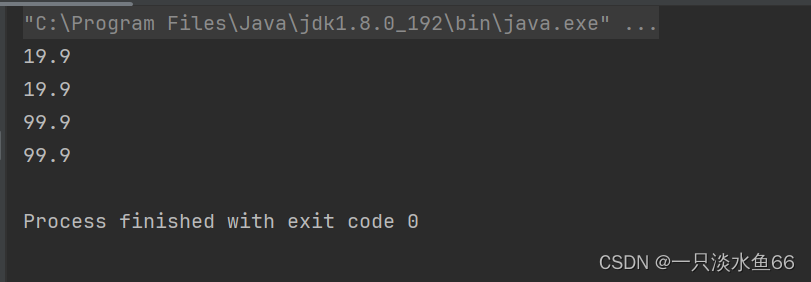
很快我们就能看出一个问题:改变 p2 里面的内容,而 p1 里面的内容也跟着改变了呢?
接着我们引入深拷贝的理念:
深拷贝示例
代码示例:
java
class Money implements Cloneable{
public double money = 19.9;
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
class Person implements Cloneable{
public int age;
public Money m = new Money();
public Person(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person tmp = (Person)super.clone();
tmp.m = (Money)this.m.clone();
return tmp;
}
}
public class Data{
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person p1 = new Person(20);
Person p2 = (Person)p1.clone();
System.out.println(p1.m.money);
System.out.println(p2.m.money);
p2.m.money = 99.9;
System.out.println(p1.m.money);
System.out.println(p2.m.money);
}
}运行结果:
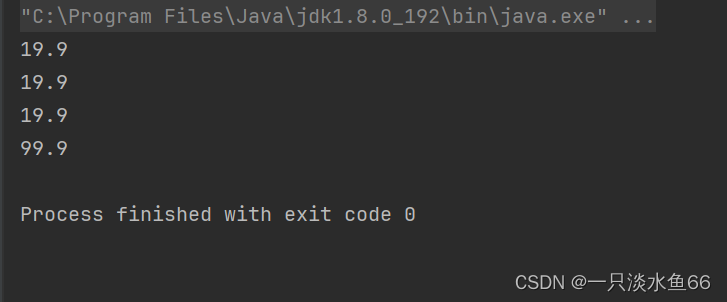
我们发现我们刚刚提出的问题被解决了。
这里我们改变了两个地方:
1、 将 Money 类也实现 Clonable 接口重写 clone 方法,将其具备能被拷贝的能力。
class Money implements Cloneable{ public double money = 19.9; @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
2、重写 Person 类里面的 clone 方法。
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Person tmp = (Person)super.clone(); tmp.m = (Money)this.m.clone(); return tmp; }
接口间的继承
接口可以继承一个接口, 达到复用的效果. 使用 extends 关键字。
java
interface IRunning {
void run();
}
interface ISwimming {
void swim();
}
interface IAmphibious extends IRunning, ISwimming {
void eat();
}接口间的继承相当于把多个接口合并在一起。这里我们定义接口 Iamphibious 来继承了接口 IRunning 和接口 ISwimming 。这样该接口就有了另外两个接口里面的抽象方法,并且该接口也可以定义另外的抽象方法。
总结
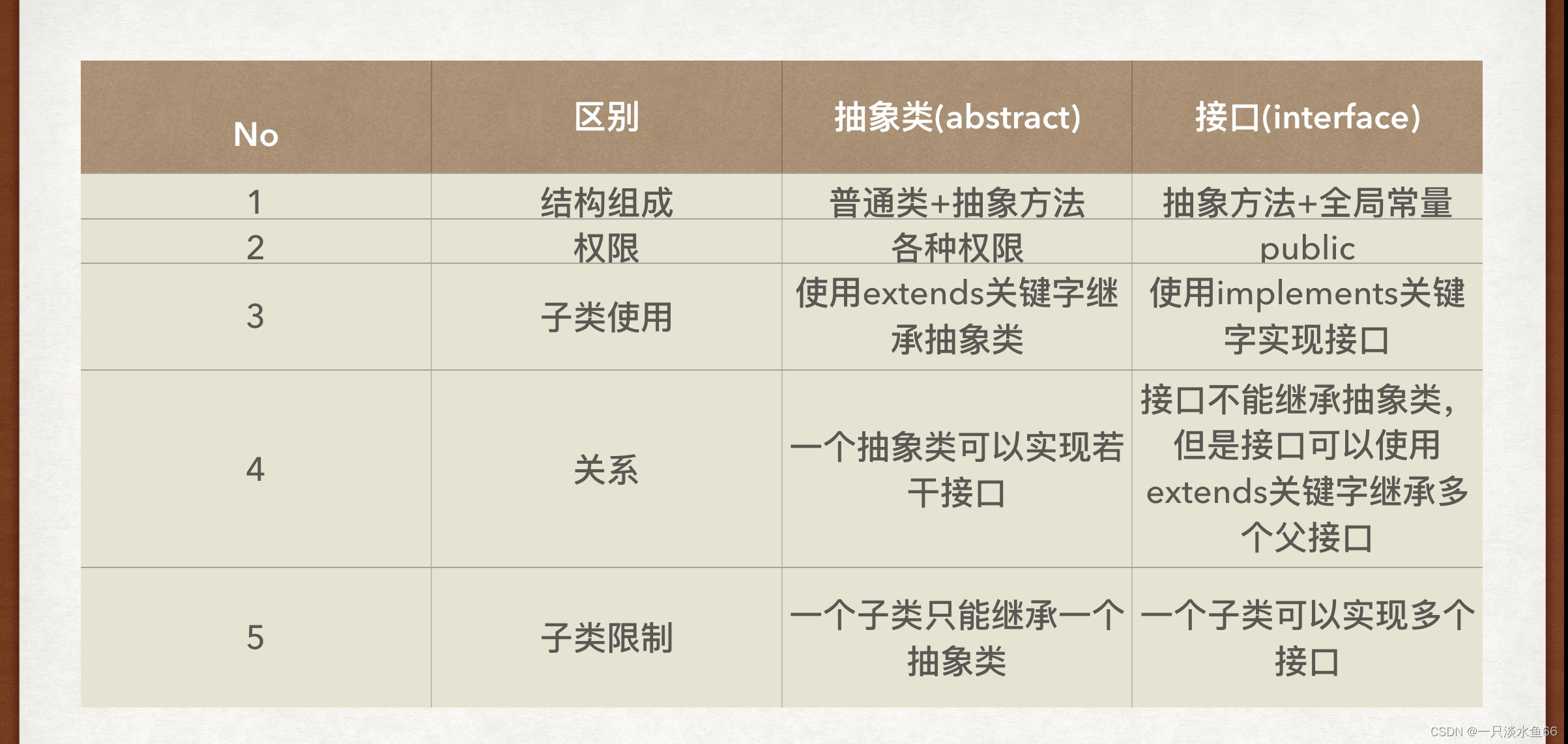
抽象类与接口的区别:
核心区别: 抽象类中可以包含普通方法和普通字段, 这样的普通方法和字段可以被子类直接使用(不必重写), 而接口中不能包含普通方法, 子类必须重写所有的抽象方法。