apply
DataFrame.apply(func, axis=0, broadcast=False, raw=False, reduce=None, args=(), **kwds)
第一个参数是函数
可以在Series或DataFrame上执行一个函数
支持对行、列或单个值进行处理
python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
f = lambda x: x.max()-x.min()
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(4,3),columns=list('bde'),index=['utah', 'ohio', 'texas', 'oregon'])
print(df)
'''
b d e
utah -0.631142 0.081229 -0.791898
ohio 1.571634 0.801737 1.478349
texas -0.408345 -1.920296 1.001519
oregon 0.013308 2.496898 -0.580166
'''
t1 = df.apply(f)
print(t1)
'''
b 2.202776
d 4.417194
e 2.270247
dtype: float64
'''
t2 = df.apply(f, axis=1)
print(t2)
'''
utah 0.873127
ohio 0.769897
texas 2.921815
oregon 3.077063
dtype: float64
'''
df = pd.read_csv('C:/data/temp.csv')
df.apply(['max', 'min'])
'''
name team Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
max Zachary E 98 99 99 99
min Aaron A 1 1 1 2
'''
df.apply({'Q1':'max', 'Q2': 'min'})
'''
Q1 98
Q2 1
dtype: int64
'''
df.apply({'Q1':'mean', 'Q2': ['max', 'min']})
'''
Q1 Q2
mean 49.2 NaN
max NaN 99.0
min NaN 1.0
'''
df = pd.DataFrame([[4, 9]] * 3, columns=['A', 'B'])
df
''' A B
0 4 9
1 4 9
2 4 9
'''
# 使用numpy通用函数 (如 np.sqrt(df)):
df.apply(np.sqrt)
'''
A B
0 2.0 3.0
1 2.0 3.0
2 2.0 3.0
'''
# 使用聚合功能
df.apply(np.sum, axis=0)
'''
A 12
B 27
dtype: int64agg/aggregate
DataFrame.agg(func, axis=0, *args, **kwargs)
func : function, str, list 或者 dict。用于聚合数据的函数。如果是函数,则必须在传递给 DataFrame 或传递给 DataFrame.apply。可接受的组合为:
函数 function
字符串函数名 string function name
函数和/或函数名列表,如 [np.sum, 'mean']
轴标签->函数、函数名称或此类列表的字典
axis : {0 or 'index', 1 or 'columns'}, 默认 0如果 0 或者 'index':将函数应用于每列
如果 1 或者 'columns': 将函数应用于每一行
Series.agg
python
s = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4])
s
'''
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
dtype: int64
'''
s.agg('min')
# 1
s.agg(['min', 'max'])
'''
min 1
max 4
dtype: int64
'''
# 指定索引名
s.agg(A=max)
'''
A 4
dtype: int64
'''
s.agg(Big=max, Small=min)
'''
Big 4
Small 1
dtype: int64
'''DataFrame.agg
python
df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9],
[np.nan, np.nan, np.nan]],
columns=['A', 'B', 'C'])
# 在行上聚合这些函数
df.agg(['sum', 'min'])
'''
A B C
sum 12.0 15.0 18.0
min 1.0 2.0 3.0
'''
# 每列有不同的聚合
df.agg({'A' : ['sum', 'min'], 'B' : ['min', 'max']})
'''
A B
sum 12.0 NaN
min 1.0 2.0
max NaN 8.0
'''
# 在列上聚合
df.agg("mean", axis="columns")
'''
0 2.0
1 5.0
2 8.0
3 NaN
dtype: float64
'''DataFrameGroupBy.agg
agg 可以为分组对象调用方法,与 DataFrame 的一点不同是,DataFrameGroupBy 对象在使用 agg 时可以指定计算引擎(engine 参数)和 引擎的参数(engine_kwargs)。
返回:DataFrame
aggregate(self, func=None,engine=None, engine_kwargs=None,*args, **kwargs)
engine:str, 默认 None,有:
- 'cython' : 通过cython的C扩展执行函数
- 'numba' : 通过numba中的JIT编译代码运行函数
- None : 默认为 "cython" 或全局设置 compute.use_numba
python
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
"A": [1, 1, 2, 2],
"B": [1, 2, 3, 4],
"C": [0.362838, 0.227877, 1.267767, -0.562860],
}
)
df
'''
A B C
0 1 1 0.362838
1 1 2 0.227877
2 2 3 1.267767
3 2 4 -0.562860
'''
# 聚合是针对每个列的
df.groupby('A').agg('min')
'''
B C
A
1 1 0.227877
2 3 -0.562860
'''
# 多重聚合
df.groupby('A').agg(['min', 'max'])
'''
B C
min max min max
A
1 1 2 0.227877 0.362838
2 3 4 -0.562860 1.267767
'''
# 选择要聚合的列
df.groupby('A').B.agg(['min', 'max'])
'''
min max
A
1 1 2
2 3 4
'''
# 每列的聚合不同
df.groupby('A').agg({'B': ['min', 'max'], 'C': 'sum'})
'''
B C
min max sum
A
1 1 2 0.590715
2 3 4 0.704907
'''
grouped = df.groupby("A")# 分组对象
grouped["C"].agg([np.sum, np.mean, np.std])# 指定列,多个聚合
'''
sum mean std
A
1 0.590715 0.295357 0.095432
2 0.704907 0.352454 1.294449
'''
grouped.agg([np.sum, np.mean, np.std])# 所有列分别多个聚合
'''
B C
sum mean std sum mean std
A
1 3 1.5 0.707107 0.590715 0.295357 0.095432
2 7 3.5 0.707107 0.704907 0.352454 1.294449
'''聚合滚动窗口 Rolling.agg
python
df = pd.DataFrame({"A": [1, 2, 3], "B": [4, 5, 6], "C": [7, 8, 9]})
df
'''
A B C
0 1 4 7
1 2 5 8
2 3 6 9
'''
df.rolling(2).sum()
'''
A B C
0 NaN NaN NaN
1 3.0 9.0 15.0
2 5.0 11.0 17.0
'''
df.rolling(2).agg({"A": "sum", "B": "min"})
'''
A B
0 NaN NaN
1 3.0 4.0
2 5.0 5.0
'''stack() 和 unstack()
stack() 函数会将数据从"表格结构"变成"花括号结构",即将其行索引变成列索引,反之,
unstack() 函数将数据从"花括号结构"变成"表格结构",即要将其中一层的列索引变成行索引。
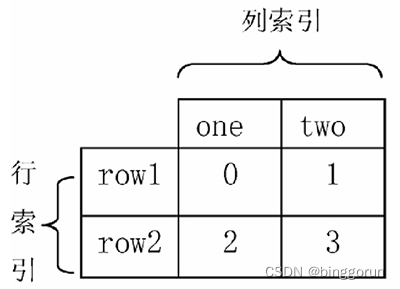 表格结构
表格结构 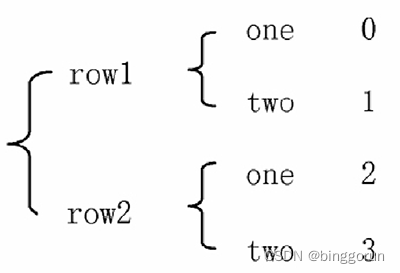 花括号结构
花括号结构
stack() 函数
DataFrame.stack(level=-1,dropna=True)
- level:接收 int、str、list,默认为 -1,表示从列轴到索引轴堆叠的级别,定义为一个索引或标签,或者索引或标签列表;
- dropna:接收布尔值,默认为 True,表示是否在缺失值的结果框架/系列中删除行。将列级别堆叠到索引轴上可以创建原始数据帧中缺失的索引值和列值的组合。
函数返回值为 DataFrame 或 Series。
unstack() 函数
DataFrame.unstack(level=-1, fill_value=None)
Series.unstack(level=-1, fill_value=None)
- level:接收 int、string 或其中的列表,默认为 -1(最后一级),表示 unstack 索引的级别或级别名称。
- fill_value:如果取消堆栈,则用此值替换 NaN 缺失值,默认为 None。
函数返回值为 DataFrame 或 Series。
python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
#创建DataFrame
data = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(4).reshape((2, 2)),
index=pd.Index(['row1', 'row2'], name='rows'),
columns=pd.Index(['one', 'two'], name='cols'))
print(data)
'''
cols one two
rows
row1 0 1
row2 2 3
'''
#使用stack()函数改变data层次化结构
result = data.stack()
print('data改变成"花括号"结构','\n',result)
'''
data改变成"花括号"结构
rows cols
row1 one 0
two 1
row2 one 2
two 3
'''
print('恢复到原来结构','\n',result.unstack())
'''
恢复到原来结构
cols one two
rows
row1 0 1
row2 2 3
'''
print(result.unstack(0))
'''
rows row1 row2
cols
one 0 2
two 1 3
'''
print(result.unstack('rows'))
#创建Series
s1 = pd.Series([0, 1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
s2 = pd.Series([4, 5, 6], index=['c', 'd', 'e'])
data2 = pd.concat([s1, s2], keys=['one', 'two'])
print(data2)
'''
one a 0
b 1
c 2
d 3
two c 4
d 5
e 6
dtype: int64
'''
print('将data2改变成表格结构','\n',data2.unstack())
'''
将data2改变成表格结构
a b c d e
one 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 NaN
two NaN NaN 4.0 5.0 6.0
'''
#使用stack()函数改变成"花括号"结构,并删除缺失值行
print(data2.unstack().stack())
'''
one a 0.0
b 1.0
c 2.0
d 3.0
two c 4.0
d 5.0
e 6.0
dtype: float64
'''
#使用stack()函数改变成"花括号"结构,不删除缺失值行
print(data2.unstack().stack(dropna=False))
'''
one a 0.0
b 1.0
c 2.0
d 3.0
e NaN
two a NaN
b NaN
c 4.0
d 5.0
e 6.0
dtype: float64
'''
#用字典创建DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'left': result, 'right': result + 3},
columns=pd.Index(['left', 'right'], name='side'))
print(df)
'''
side left right
rows cols
row1 one 0 3
two 1 4
row2 one 2 5
two 3 6
'''
#使用unstack()、stack()函数
print(df.unstack('rows'))
'''
side left right
rows row1 row2 row1 row2
cols
one 0 2 3 5
two 1 3 4 6
'''
print(df.unstack('rows').stack('side'))
'''
rows row1 row2
cols side
one left 0 2
right 3 5
two left 1 3
right 4 6
'''concat()和merge()
- 轴向连接(concatenation): pd.concat() 可以沿一个轴将多个DataFrame对象连接在一起, 形成一个新的Dataframe对象
- 融合(merging):pd.merge()方法可以根据一个或多个键将不同DataFrame中的行连接起来。
concat() 轴向连接
concat() 函数可以将数据根据不同的轴作进行合并
pd.concat(objs, axis=0, join='outer')
- objs: series、dataframe或者是panel构成的序列list
- axis: 需要合并链接的轴,0是行,1是列,默认是0
- join:连接的方式 inner:得到的是两表的交集,或者outer:得到的是两表的并集,默认是outer;
join='outer',axis=0
当join='outer',axis参数为0时,列进行并集处理,纵向表拼接,缺失值由NaN填充,并且会保留原有数据的行索引
python
dict1={
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3']}
df1=pd.DataFrame(dict1)
dict2={
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3'],
'D': ['D0', 'D1', 'D2', 'D3']}
df2=pd.DataFrame(dict2)
pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=0, join='outer')
'''
A B C D
0 A0 B0 C0 NaN
1 A1 B1 C1 NaN
2 A2 B2 C2 NaN
3 A3 B3 C3 NaN
0 NaN B0 C0 D0
1 NaN B1 C1 D1
2 NaN B2 C2 D2
3 NaN B3 C3 D3
'''
pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=0,join='outer',ignore_index=True) # 使用ignore_index参数置为 true, 重新生成一个新的index
'''
A B C D
0 A0 B0 C0 NaN
1 A1 B1 C1 NaN
2 A2 B2 C2 NaN
3 A3 B3 C3 NaN
4 NaN B0 C0 D0
5 NaN B1 C1 D1
6 NaN B2 C2 D2
7 NaN B3 C3 D3
'''join='outer',axis=1
当join='outer',axis参数为1时,行进行并集处理,横向表拼接,缺失值由NaN填充
python
pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=1,join='outer')
'''
A B C B C D
0 A0 B0 C0 B0 C0 D0
1 A1 B1 C1 B1 C1 D1
2 A2 B2 C2 B2 C2 D2
3 A3 B3 C3 B3 C3 D3
'''join=inner, axis=0
python
pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=0,join='inner',ignore_index=True)
'''
B C
0 B0 C0
1 B1 C1
2 B2 C2
3 B3 C3
4 B0 C0
5 B1 C1
6 B2 C2
7 B3 C3
'''merge() 融合
merge(left, right, how='inner', on=None)
- left和right, 两个要合并的DataFrame(对应的左连接和右连接)
- how: 连接的方式, 有inner(内连接)、left(左连接)、right(右连接)、outer(外连接), 默认为 inner
- on: 指的是用于连接的列索引名称, 必须存在于左右两个DataFrame中, 如果没有指定且其他参数也没有指定,则两个DataFrame列名交集作为连接键
inner(内连接)
merge()默认做inner连接,并且使用两个DataFrame的列名交集(key)作为连接键,同样,最终连接的数据也是两个DataFramekey列数据的交集
python
dict1={
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3']}
df1=pd.DataFrame(dict1)
df1
'''
A B C
0 A0 B0 C0
1 A1 B1 C1
2 A2 B2 C2
3 A3 B3 C3
'''
dict2={
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B4', 'B5'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3'],
'D': ['D0', 'D1', 'D2', 'D3']}
df2=pd.DataFrame(dict2)
df2
'''
B C D
0 B0 C0 D0
1 B1 C1 D1
2 B4 C2 D2
3 B5 C3 D3
'''
pd.merge(df1,df2)
'''
A B C D
0 A0 B0 C0 D0
1 A1 B1 C1 D1
'''outer (外连接)
当merge()做outer连接时最终连接的数据是两个DataFramekey列数据的并集,缺失的内容由NaN填充
python
pd.merge(df1,df2,on=['B','C'],how='outer')
'''
A B C D
0 A0 B0 C0 D0
1 A1 B1 C1 D1
2 A2 B2 C2 NaN
3 A3 B3 C3 NaN
4 NaN B4 C2 D2
5 NaN B5 C3 D3
'''left(左连接)
当merge()做left连接时,最终连接的数据将以left数据的链接建为准合并两个数据的列数据,缺失的内容由NaN填充
python
pd.merge(df1,df2,on=['B'],how='left')
'''
A B C_x C_y D
0 A0 B0 C0 C0 D0
1 A1 B1 C1 C1 D1
2 A2 B2 C2 NaN NaN
3 A3 B3 C3 NaN NaN
'''right (右连接)
当merge()做right连接时,最终连接的数据将以right数据的链接建为准合并两个数据的列数据,缺失的内容由NaN填充
python
pd.merge(df1,df2,on=['B'],how='right')
'''
A B C_x C_y D
0 A0 B0 C0 C0 D0
1 A1 B1 C1 C1 D1
2 NaN B4 NaN C2 D2
3 NaN B5 NaN C3 D3
'''应用场景
1)两张同类型的表合并成一张表,可使用concat( )将两个表沿着0轴合并;
2)两张相互关联的表(如用户信息、订单信息) 需要关联生成一张完整的表,可使用merge()根据用户ID将两个表合并成一个完整的表;
lambda
语法格式:lambda arguments: expression
- lambda是 Python 的关键字,用于定义 lambda 函数。
- arguments 是参数列表,可以包含零个或多个参数,但必须在冒号(:)前指定。
- expression 是一个表达式,用于计算并返回函数的结果。
python
f = lambda: "Hello, world!"
print(f()) # 输出: Hello, world!
x = lambda a : a + 10
print(x(5))#输出:15
x = lambda a, b, c : a + b + c
print(x(5, 6, 2))## 输出: 13lambda 函数通常与内置函数如 map()、filter() 和 reduce() 一起使用,以便在集合上执行操作
map()函数逐一处理
python
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared = list(map(lambda x: x**2, numbers))
print(squared) # 输出: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]filter()筛选
python
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
even_numbers = list(filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, numbers))
print(even_numbers) # 输出:[2, 4, 6, 8]reduce() 累计计算
python
from functools import reduce
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# 使用 reduce() 和 lambda 函数计算乘积
product = reduce(lambda x, y: x * y, numbers)
print(product) # 输出:120query数据筛选
query()方法允许你使用字符串表达式来筛选DataFrame的行。这个表达式类似于你在Python中使用的常规表达式,但是它专门针对DataFrame的列名和值。
python
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个示例DataFrame
data = {
'A': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'B': [5, 6, 7, 8],
'C': ['p', 'q', 'r', 's']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# 使用query()方法筛选A列大于2的行
filtered_df = df.query('A > 2')
print(filtered_df)
'''
A B C
2 3 7 r
3 4 8 s
'''
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个示例DataFrame
data = {
'A': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'B': [5, 6, 7, 8],
'C': ['p', 'q', 'r', 's']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
#两者都需要满足的并列条件使用符号 &,或 单词 and
#只需要满足其中之一的条件使用符号 |,或 单词 or
# 筛选A列大于2且B列小于等于7的行
filtered_df = df.query('A > 2 and B <= 7')
print(filtered_df)
'''
A B C
2 3 7 r
'''
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个示例DataFrame
data = {
'A': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'B': [5, 6, 7, 8],
'C': ['p', 'qu', 'r', 's']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# 筛选C列以'q'开头的行
filtered_df = df.query('C.str.startswith("q")')
print(filtered_df)
'''
A B C
1 2 6 qu
'''
# 通过变量来筛选数据,在变量前使用 @ 符号即可
name = 'Python数据之道'
df.query('brand == @name')
# 当需要在某列中筛选多个符合要求的值的时候,可以通过列表(list)来实现;需要注意下 双引号 和 单引号的分开使用
df.query('brand in ["Python数据之道","价值前瞻"]')
# df.query("brand in ['Python数据之道','价值前瞻']")query()方法还可以与其他pandas功能(如groupby()、sort_values()等)结合使用,以执行更复杂的数据操作。
python
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个示例DataFrame
data = {
'A': [1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4],
'B': [5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9],
'C': ['p', 'q', 'r', 's', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# 按A列分组,并在每个组内筛选B列的最大值
grouped_df = df.groupby('A').apply(lambda x: x.query('B == B.max()'))
print(grouped_df)
'''
A B C
A
1 1 1 6 q
2 3 2 7 s
3 5 3 8 q
4 7 4 9 s
'''Sample
random.sample()
random.sample(population, k)
- 参数population表示要从中进行抽样的序列,可以是一个列表、元组或集合等可迭代对象。
- 参数k表示要抽取的样本数量,必须是一个非负整数且不大于population的长度。
- 无重复抽样
python
import random
colors = ['red', 'blue', 'green', 'yellow', 'orange']
sample_colors = random.sample(colors, 2)
print(sample_colors) # 输出类似 ['yellow', 'blue']choices()重复抽样
需要指定抽样次数k(k命名参数),并通过参数weights来为每个元素指定权重(默认情况下,每个元素的权重相等)
python
import random
x = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
print(random.choices(x, weights = [10, 1, 1], k = 3))
# 输出可能为:['apple', 'banana', 'apple'], ['apple', 'apple', 'cherry']等DataFrame 对象的方法
DataFrame.sample(n=None, frac=None, replace=False, weights=None, random_state=None, axis=None)
- n(int或None):指定要抽取的样本数量。如果指定了 n,则 frac 应设置为 None。
- frac(float或None):指定要抽取的样本占原数据框的比例。可以是小数,表示抽取的比例,例如 frac=0.25 表示抽取 25% 的样本。如果同时指定了 n 和 frac,将使用 frac 参数。
- replace(bool,默认为False):控制是否允许重复抽样。 True:则允许同一样本被抽取多次; False:不允许重复抽样。
- weights(str或数组型,默认为None):指定每个样本的权重。可以是列名,指示样本权重的列,也可以是权重数组。
- random_state(int或RandomState实例或None,默认为None):控制随机抽样的随机化过程。指定一个整数可实现可重复的随机抽样。
- axis({0或'index',1或'columns'},默认为0):指定抽样的轴。如果为 0 或 'index',则在行上进行抽样;如果为 1 或 'columns',则在列上进行抽样。
python
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('C:/Users/Admin/Desktop/data.txt', sep='\t')
# 从数据框中抽取10个样本
sampled_data = df.sample(n=10)
# 从数据框中抽取总样本的30%
sampled_data_frac = df.sample(frac=0.3)
# 从数据框中进行有放回抽样(允许重复)
sampled_with_replacement = df.sample(n=10, replace=True)
# 指定每个样本的权重进行抽样
sampled_with_weights = df.sample(n=10, weights='column_with_weights')
# 指定随机种子以实现可重复抽样
sampled_with_seed = df.sample(n=10, random_state=42)