1. 系统概述
The Elastic Stack,包括Elasticsearch、Kibana、Beats和Logstash(也成为ELK Stack)
Elasticsearch:简称ES,是一个开源的高扩展的分布式全文搜索引擎,是整个Elastic Stack技术栈的核心。它可以近乎实时地存储、检索数据;本身扩展性很好,可以扩展到上百台服务器,处理PB级的数据。
Kibana:是一个免费且开放的用户界面,能够让你对Elasticsearch数据进行可视化,并让您在Elastic Stack中进行导航。您可以进行各种操作,从跟踪查询负载,到理解请求如何流经您的整个应用,都能轻松完成。
Beats:是一款采集系统监控数据的代理agent,是在被监控服务器上以客户端形式运行的数据收集器的统称,可以直接把数据发送给Elasticsearch或者通过Logstash发送给Elasticsearch,然后进行后续的数据分析活动。
Logstash:服务器端数据处理管道,能够从多个来源采集数据,转换数据,然后将数据发送到合适的存储库中
1.1 索引和分片
分片是 Elasticsearch 在集群中分发数据的关键。
把分片想象成数据的容器。文档存储在分片中,然后分片分配到集群中的节点上。当集群扩容或缩小,Elasticsearch 将会自动在节点间迁移分片,以使集群保持平衡。
一个分片(shard)是一个最小级别"工作单元(worker unit)",它只是保存了索引中所有数据的一部分。
这类似于 MySql 的分库分表,只不过 Mysql 分库分表需要借助第三方组件而 ES 内部自身实现了此功能。
分片可以是主分片(primary shard)或者是复制分片(replica shard)。
在集群中唯一一个空节点上创建一个叫做 blogs 的索引。默认情况下,一个索引被分配 5 个主分片,下面只分配 3 个主分片和一个复制分片(每个主分片都有一个复制分片):
1.1.1 主分片
在一个多分片的索引中写入数据时,通过路由来确定具体写入哪一个分片中,大致路由过程如下:
shard = hash(routing) % number_of_primary_shardsrouting 是一个可变值,默认是文档的 _id ,也可以设置成一个自定义的值。routing 通过 hash 函数生成一个数字,然后这个数字再除以 number_of_primary_shards (主分片的数量)后得到余数 。这个在 0 到 number_of_primary_shards 之间的余数,就是所寻求的文档所在分片的位置。
这解释了为什么要在创建索引的时候就确定好主分片的数量并且永远不会改变这个数量:因为如果数量变化了,那么所有之前路由的值都会无效,文档也再也找不到了。
索引中的每个文档属于一个单独的主分片,所以主分片的数量决定了索引最多能存储多少数据(实际的数量取决于数据、硬件和应用场景)。
1.1.2 复制分片
复制分片只是主分片的一个副本,它可以防止硬件故障导致的数据丢失,同时可以提供读请求,比如搜索或者从别的 shard 取回文档。
每个主分片都有一个或多个副本分片,当主分片异常时,副本可以提供数据的查询等操作。主分片和对应的副本分片是不会在同一个节点上的,所以副本分片数的最大值是 n -1(其中 n 为节点数)。
当索引创建完成的时候,主分片的数量就固定了,但是复制分片的数量可以随时调整,根据需求扩大或者缩小规模。如把复制分片的数量从原来的 1 增加到 2 :
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPUT localhost:9200/blogs/_settings -d '
{
"number_of_replicas": 2
}'分片本身就是一个完整的搜索引擎,它可以使用单一节点的所有资源。主分片或者复制分片都可以处理读请求------搜索或文档检索,所以数据的冗余越多,能处理的搜索吞吐量就越大。
对文档的新建、索引和删除请求都是写操作,必须在主分片上面完成之后才能被复制到相关的副本分片,ES为了提高写入的能力这个过程是并发写的,同时为了解决并发写的过程中数据冲突的问题,ES 通过乐观锁的方式控制,每个文档都有一个_version(版本)号,当文档被修改时版本号递增。一旦所有的副本分片都报告写成功才会向协调节点报告成功,协调节点向客户端报告成功。
1.2 分片的存储
ES集群中每个节点通过路由都知道集群中的文档的存放位置,所以每个节点都有处理读写请求的能力。
在一个写请求被发送到某个节点后,该节点即为协调节点,协调节点会根据路由公式计算出需要写到哪个分片上,再将请求转发到该分片的主分片节点上。假设shard=hash(routing)%4=0,则过程大致如下:
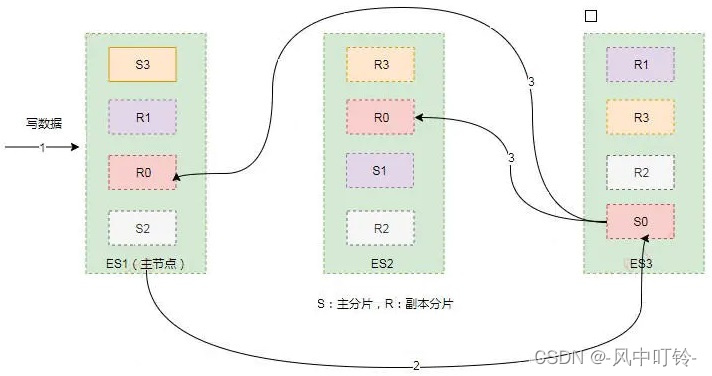
- 客户端向ES1节点(协调节点)发送写请求,通过路由计算公式得到值为0,则当前数据应被写到主分片S0上。
- ES1节点将请求转发到S0主分片所在的节点ES3,ES3接受请求并写入到磁盘。
- 并发将数据复制到两个副本分片R0上,其中通过乐观并发控制数据的冲突。一旦所有的副本分片都报告成功,则节点ES3将向协调节点报告成功,协调节点向客户端报告成功。
2. 环境搭建
2.1 环境初始化
- 准备三台服务器,配置及角色如下:
| IP地址 | 主机名 | CPU | 内存 | 磁盘 | 角色 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.19.101 | host1.test.com | 2 core | 4G | 20G+ | ES node |
| 192.168.19.102 | host2.test.com | 2 core | 4G | 20G+ | ES node |
| 192.168.19.103 | host3.test.com | 2 core | 4G | 20G+ | ES node |
- 基础设置
配置IP地址、主机名、hosts等,并设置免密登陆
-
关闭Selinux,防火墙(也可以不用关,后面添加规则)
[root@host1 ~]# sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@host1 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@host2 ~]# sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@host2 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@host3 ~]# sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
[root@host3 ~]# setenforce 0 -
安装同步工具,并编写同步脚本
[root@host1 ~]# yum install rsync -y
[root@host2 ~]# yum install rsync -y
[root@host3 ~]# yum install rsync -y
bash
[root@host1 ~]# vim /usr/local/sbin/data_rsync.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ $# -ne 1 ];then
echo "Usage: $0 /path/file"
exit
fi
if [ ! -e $1 ];then
echo "[ $1 ] dir or file not find!"
exit
fi
# 获取父路径
fullpath=`dirname $1`
# 获取子路径
basename=`basename $1`
# 进入父路径
cd $fullpath
for ((host_id=2;host_id<=3;host_id++))
do
# 使终端输出变为绿色
tput setaf 2
echo ===== rsyncing host${host_id}.test.com: $basename =====
# 使终端恢复原来的颜色
tput setaf 7
# 将数据同步到其他两个节点
rsync -az $basename `whoami`@host${host_id}:$fullpath
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo "命令执行成功!"
fi
done
[root@host1 ~]# chmod +x /usr/local/sbin/data_rsync.sh 测试脚本
[root@host1 ~]# echo "111" >> /tmp/1.txt
[root@host1 ~]# data_rsync.sh /tmp/1.txt
===== rsyncing host2.test.com: 1.txt =====
命令执行成功!
===== rsyncing host3.test.com: 1.txt =====
命令执行成功!
[root@host2 ~]# cat /tmp/1.txt
111-
时间同步
[root@host1 ~]# timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
[root@host2 ~]# timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
[root@host2 ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf
#server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server host1.test.com iburst
[root@host2 ~]# systemctl restart chronyd.service[root@host3 ~]# timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
[root@host3 ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf
#server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server host1.test.com iburst
[root@host3 ~]# systemctl restart chronyd.service
2.2 ES单机部署
- 下载指定的ES版本
创建yum源然后进行安装
bash
[root@host1 ~]# cat >> /etc/yum.repos.d/es.repo << 'EOF'
> [es]
> name=Elasticsearch repository for 7.x packages
> baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/yum
> gpgcheck=0
> enabled=0
> autorefresh=1
> EOF
[root@host1 ~]# yum install elasticsearch这里因为要装三台服务器,因此直接下载软件包,然后本地安装
bash
[root@host1 ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.17.6-x86_64.rpm
[root@host1 ~]# yum localinstall elasticsearch-7.17.6-x86_64.rpm -y- 部署JDK环境-可选
默认ES提供了openjdk的环境,这里暂时跳过
bash
[root@host1 ~]# /usr/share/elasticsearch/jdk/bin/java -version
openjdk version "18.0.2" 2022-07-19
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 18.0.2+9-61)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 18.0.2+9-61, mixed mode, sharing)- 修改配置
yml
[root@host1 ~]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: elk # 集群名称,若不指定,则默认是elasticsearch,日志文件的前缀也是集群名称
node.name: host1 # 指定节点的名称,可以自定义,推荐使用当前的主机名,要求集群唯一
network.host: 0.0.0.0 # ES服务监听的IP地址,通常应该写服务器对外提供服务的IP
discovery.seed_hosts: ["host1.test.com"] # 服务发现的主机列表,对于单点部署而言,主机列表和"network.host"字段配置相同即可,也可以写IP地址- 开启防火墙端口
bash
[root@host1 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=9200/tcp --permanent
success
[root@host1 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=9300/tcp --permanent
success
[root@host1 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success-
启动服务器并检查
[root@host1 ~]# systemctl start elasticsearch.service
[root@host1 ~]# netstat -nutlp |grep 9.00
tcp6 0 0 :::9200 :::* LISTEN 58301/java
tcp6 0 0 :::9300 :::* LISTEN 58301/java[root@host1 ~]# curl 127.0.0.1:9200
{
"name" : "host1",
"cluster_name" : "elk",
"cluster_uuid" : "pWmdbW36Rje-hsJ_DFSFwA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.17.6",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "rpm",
"build_hash" : "f65e9d338dc1d07b642e14a27f338990148ee5b6",
"build_date" : "2022-08-23T11:08:48.893373482Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.11.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
2.3 ES集群部署
-
首先下载软件包,然后安装
[root@host1 ~]# for i in {host2,host3};do scp elasticsearch-7.17.6-x86_64.rpm i:/tmp/;done [root@host1 ~]# for i in {host2,host3};do ssh i 'yum localinstall -y /tmp/elasticsearch-7.17.6-x86_64.rpm';done
-
修改配置
[root@host1 ~]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
discovery.seed_hosts: ["host1.test.com","host2.test.com","host3.test.com"]
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["host1.test.com","host2.test.com","host3.test.com"]
[root@host1 ~]# data_rsync.sh /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
===== rsyncing host2.test.com: elasticsearch.yml =====
命令执行成功!
===== rsyncing host3.test.com: elasticsearch.yml =====
命令执行成功![root@host1 ~]# for i in {host2,host3};do ssh i "sed -i 's/node.name: host1/node.name: i/g' /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml";done
-
清空原有配置,并启动服务
删除原有集群信息
[root@host1 ~]# systemctl stop elasticsearch
[root@host1 ~]# rm -rf /var/{lib,log}/elasticsearch/*修改防火墙
[root@host2 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=9200/tcp --permanent
success
[root@host2 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=9300/tcp --permanent
success
[root@host2 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@host3 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=9200/tcp --permanent
success
[root@host3 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=9300/tcp --permanent
success
[root@host3 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success启动服务
[root@host1 ~]# for i in {host1,host2,host3};do ssh $i 'systemctl start elasticsearch';done-
验证配置
[root@host1 ~]# curl 192.168.19.101:9200
{
"name" : "host1",
"cluster_name" : "elk",
"cluster_uuid" : "2JVerg8ATyuzX23vU50eWA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.17.6",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "rpm",
"build_hash" : "f65e9d338dc1d07b642e14a27f338990148ee5b6",
"build_date" : "2022-08-23T11:08:48.893373482Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.11.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}[root@host1 ~]# curl 192.168.19.101:9200/_cat/nodes
192.168.19.103 13 96 8 0.07 0.16 0.15 cdfhilmrstw - host3
192.168.19.102 31 97 10 0.18 0.27 0.20 cdfhilmrstw * host2
192.168.19.101 23 96 9 0.13 0.24 0.17 cdfhilmrstw - host1
[root@host1 ~]# curl 192.168.19.101:9200/_cat/nodes?v
ip heap.percent ram.percent cpu load_1m load_5m load_15m node.role master name
192.168.19.103 18 96 0 0.01 0.03 0.08 cdfhilmrstw - host3
192.168.19.102 9 97 0 0.00 0.03 0.10 cdfhilmrstw * host2
192.168.19.101 28 96 0 0.01 0.05 0.10 cdfhilmrstw - host1
2.4 Kibana部署
-
下载并安装软件,只需要在一台服务器上安装即可
[root@host1 ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-7.17.6-x86_64.rpm
[root@host1 ~]# yum localinstall -y kibana-7.17.6-x86_64.rpm -
修改配置
[root@host1 ~]# vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
server.host: "192.168.19.101"
server.name: "elk-kibana"
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://host1:9200","http://host3:9200","http://host2:9200"]
i18n.locale: "zh-CN"
[root@host1 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=5601/tcp --permanent
success
[root@host1 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success -
启动服务并验证
[root@host1 ~]# systemctl start kibana.service
浏览器输入http://192.168.19.101:5601可以进行访问,这里查看监控信息
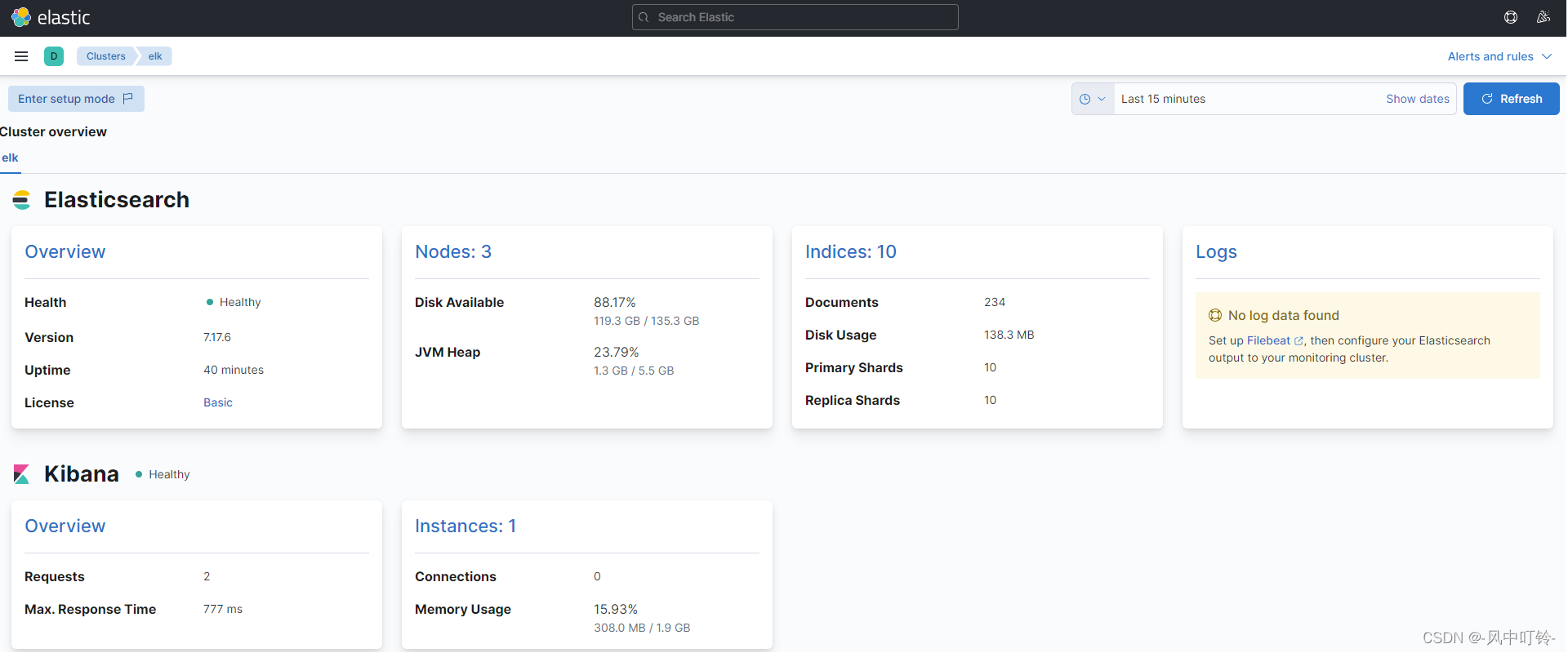
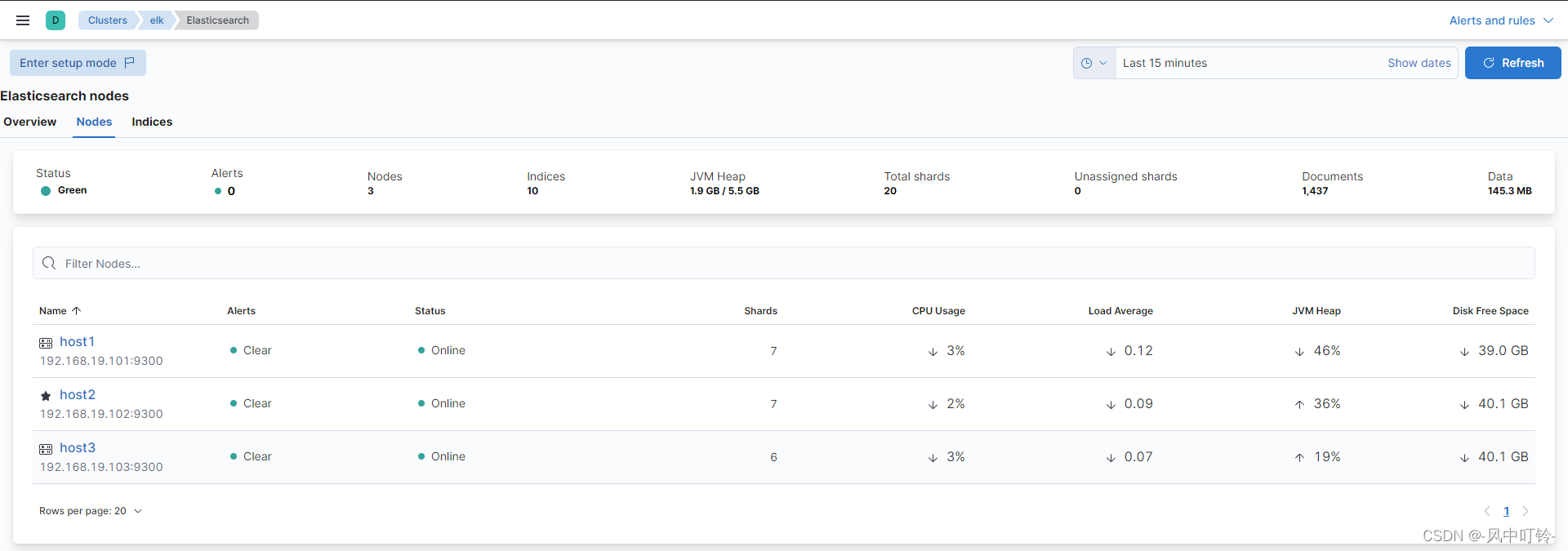
2.5 filebeats部署
-
下载和安装软件
[root@host2 ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-7.17.4-x86_64.rpm
[root@host2 ~]# yum localinstall filebeat-7.17.4-x86_64.rpm -y -
案例1:从标准输入中得到信息
[root@host2 ~]# mkdir /etc/filebeat/config
[root@host2 ~]# cat > /etc/filebeat/config/01-stdin-to-console.yml << 'EOF'指定输入的类型
filebeat.inputs:
指定输入的类型为stdin,表示标准输入
- type: stdin
指定输出的类型
output.console:
pretty: true
EOF
测试
[root@host2 ~]# filebeat -e -c /etc/filebeat/config/01-stdin-to-console.yml
2022-09-08T22:25:51.262+0800 INFO instance/beat.go:685 Home path: [/usr/share/filebeat] Config path: [/etc/filebeat] Data path: [/var/lib/filebeat] Logs path: [/var/log/filebeat] Hostfs Path: [/]
2022-09-08T22:25:51.263+0800 INFO instance/beat.go:693 Beat ID: 76b7876b-051a-4df8-8b13-bd013ac5ec59
2022-09-08T22:25:51.264+0800 INFO [seccomp] seccomp/seccomp.go:124 Syscall filter successfully installed
2022-09-08T22:25:51.264+0800 INFO [beat] instance/beat.go:1039 Beat info {"system_info": {"beat": {"path": {"config": "/etc/filebeat", "data": "/var/lib/filebeat", "home": "/usr/share/filebeat", "logs": "/var/log/filebeat"}, "type": "filebeat", "uuid": "76b7876b-051a-4df8-8b13-bd013ac5ec59"}}}
2022-09-08T22:25:51.264+0800 INFO [beat] instance/beat.go:1048 Build info {"system_info": {"build": {"commit": "ea28c0419dc4ede9318c4b34a732ce11b03482b7", "libbeat": "7.17.4", "time": "2022-05-18T16:46:57.000Z", "version": "7.17.4"}}}
2022-09-08T22:25:51.264+0800 INFO [beat] instance/beat.go:1051 Go runtime info {"system_info": {"go": {"os":"linux","arch":"amd64","max_procs":2,"version":"go1.17.9"}}}
2022-09-08T22:25:51.266+0800 INFO [beat] instance/beat.go:1055 Host info {"system_info": {"host": {"architecture":"x86_64","boot_time":"2022-09-08T21:35:02+08:00","containerized":false,"name":"host2.test.com","ip":["127.0.0.1/8","::1/128","fe80::6a25:8732:c295:7eb6/64","fe80::211e:2860:c317:c529/64","fe80::300a:1fca:6473:7d6e/64","192.168.19.102/24","fe80::20c:29ff:fe8a:bc8b/64","192.168.122.1/24"],"kernel_version":"3.10.0-1062.el7.x86_64","mac":["00:0c:29:8a:bc:81","00:0c:29:8a:bc:8b","52:54:00:c5:da:6d","52:54:00:c5:da:6d"],"os":{"type":"linux","family":"redhat","platform":"centos","name":"CentOS Linux","version":"7 (Core)","major":7,"minor":7,"patch":1908,"codename":"Core"},"timezone":"CST","timezone_offset_sec":28800,"id":"431657410e98435590ed19d25f8e19ba"}}}
2022-09-08T22:25:51.266+0800 INFO [beat] instance/beat.go:1084 Process info {"system_info": {"process": {"capabilities": {"inheritable":null,"permitted":["chown","dac_override","dac_read_search","fowner","fsetid","kill","setgid","setuid","setpcap","linux_immutable","net_bind_service","net_broadcast","net_admin","net_raw","ipc_lock","ipc_owner","sys_module","sys_rawio","sys_chroot","sys_ptrace","sys_pacct","sys_admin","sys_boot","sys_nice","sys_resource","sys_time","sys_tty_config","mknod","lease","audit_write","audit_control","setfcap","mac_override","mac_admin","syslog","wake_alarm","block_suspend"],"effective":["chown","dac_override","dac_read_search","fowner","fsetid","kill","setgid","setuid","setpcap","linux_immutable","net_bind_service","net_broadcast","net_admin","net_raw","ipc_lock","ipc_owner","sys_module","sys_rawio","sys_chroot","sys_ptrace","sys_pacct","sys_admin","sys_boot","sys_nice","sys_resource","sys_time","sys_tty_config","mknod","lease","audit_write","audit_control","setfcap","mac_override","mac_admin","syslog","wake_alarm","block_suspend"],"bounding":["chown","dac_override","dac_read_search","fowner","fsetid","kill","setgid","setuid","setpcap","linux_immutable","net_bind_service","net_broadcast","net_admin","net_raw","ipc_lock","ipc_owner","sys_module","sys_rawio","sys_chroot","sys_ptrace","sys_pacct","sys_admin","sys_boot","sys_nice","sys_resource","sys_time","sys_tty_config","mknod","lease","audit_write","audit_control","setfcap","mac_override","mac_admin","syslog","wake_alarm","block_suspend"],"ambient":null}, "cwd": "/root", "exe": "/usr/share/filebeat/bin/filebeat", "name": "filebeat", "pid": 3435, "ppid": 3085, "seccomp": {"mode":"filter","no_new_privs":true}, "start_time": "2022-09-08T22:25:50.680+0800"}}}
2022-09-08T22:25:51.266+0800 INFO instance/beat.go:328 Setup Beat: filebeat; Version: 7.17.4
2022-09-08T22:25:51.267+0800 INFO [publisher] pipeline/module.go:113 Beat name: host2.test.com
2022-09-08T22:25:51.267+0800 WARN beater/filebeat.go:202 Filebeat is unable to load the ingest pipelines for the configured modules because the Elasticsearch output is not configured/enabled. If you have already loaded the ingest pipelines or are using Logstash pipelines, you can ignore this warning.
2022-09-08T22:25:51.268+0800 INFO [monitoring] log/log.go:142 Starting metrics logging every 30s
2022-09-08T22:25:51.268+0800 INFO instance/beat.go:492 filebeat start running.
2022-09-08T22:25:51.269+0800 INFO memlog/store.go:119 Loading data file of '/var/lib/filebeat/registry/filebeat' succeeded. Active transaction id=0
2022-09-08T22:25:51.269+0800 INFO memlog/store.go:124 Finished loading transaction log file for '/var/lib/filebeat/registry/filebeat'. Active transaction id=0
2022-09-08T22:25:51.269+0800 WARN beater/filebeat.go:411 Filebeat is unable to load the ingest pipelines for the configured modules because the Elasticsearch output is not configured/enabled. If you have already loaded the ingest pipelines or are using Logstash pipelines, you can ignore this warning.
2022-09-08T22:25:51.269+0800 INFO [registrar] registrar/registrar.go:109 States Loaded from registrar: 0
2022-09-08T22:25:51.269+0800 INFO [crawler] beater/crawler.go:71 Loading Inputs: 1
2022-09-08T22:25:51.269+0800 INFO [crawler] beater/crawler.go:117 starting input, keys present on the config: [filebeat.inputs.0.type]
2022-09-08T22:25:51.270+0800 INFO [crawler] beater/crawler.go:148 Starting input (ID: 16876905907669988323)
2022-09-08T22:25:51.270+0800 INFO [crawler] beater/crawler.go:106 Loading and starting Inputs completed. Enabled inputs: 1
2022-09-08T22:25:51.270+0800 INFO [stdin.harvester] log/harvester.go:309 Harvester started for paths: [] {"harvester_id": "0679ecff-06e2-49ac-bff0-5573f6c23685"}
hello world
{
"@timestamp": "2022-09-08T14:28:48.892Z",
"@metadata": {
"beat": "filebeat",
"type": "_doc",
"version": "7.17.4"
},
"input": {
"type": "stdin"
},
"host": {
"name": "host2.test.com"
},
"agent": {
"ephemeral_id": "f670a976-0db6-4175-977d-2c25533247eb",
"id": "76b7876b-051a-4df8-8b13-bd013ac5ec59",
"name": "host2.test.com",
"type": "filebeat",
"version": "7.17.4",
"hostname": "host2.test.com"
},
"ecs": {
"version": "1.12.0"
},
"log": {
"file": {
"path": ""
},
"offset": 0
},
"message": "hello world"
}-
案例2:从日志文件中得到信息
[root@host2 ~]# vim /etc/filebeat/config/02-log-to-console.yml
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
paths:- /tmp/test.log
output.console:
pretty: true[root@host2 ~]# touch /tmp/test.log
[root@host2 ~]# filebeat -e -c /etc/filebeat/config/02-log-to-console.yml # 然后追加信息到test.log中
{
"@timestamp": "2022-09-08T15:11:30.972Z",
"@metadata": {
"beat": "filebeat",
"type": "_doc",
"version": "7.17.4"
},
"agent": {
"name": "host2.test.com",
"type": "filebeat",
"version": "7.17.4",
"hostname": "host2.test.com",
"ephemeral_id": "4168d1e8-0dae-4178-9077-c31804bf0a1b",
"id": "76b7876b-051a-4df8-8b13-bd013ac5ec59"
},
"ecs": {
"version": "1.12.0"
},
"message": "222",
"log": {
"offset": 8,
"file": {
"path": "/tmp/test.log"
}
},
"input": {
"type": "log"
},
"host": {
"name": "host2.test.com"
}
} - type: log
filebeat默认是按行来进行读取,如果写入新的消息后没有换行,默认filebeat是不会产生消息的以
log.json会记录上次一读取的位置,以offset字段来记录,下一次读取时会获取offset值,然后继续读取日志文件
[root@host2 ~]# tail -n1 /var/lib/filebeat/registry/filebeat/log.json
{"k":"filebeat::logs::native::35680998-64768","v":{"timestamp":[2062558890204,1662649891],"ttl":-1,"type":"log","identifier_name":"native","id":"native::35680998-64768","prev_id":"","source":"/tmp/test.log","offset":12,"FileStateOS":{"inode":35680998,"device":64768}}}
# offset是12,意味着下一次从12开始读,注意,换行符也是一个字符如果有特殊需求,这个offset是可以调整的
- 配置文件调整
添加多个数据源:
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
paths:
- /tmp/test.log
- /tmp/*.txt
- type: log
paths:
- /tmp/*/*.log给输入数据添加tag
- type: log
paths:
- /tmp/test.log
tags: "test log"
# 添加后在日志中会有显示:
"@timestamp": "2022-09-09T08:15:45.706Z",
"@metadata": {
"beat": "filebeat",
"type": "_doc",
"version": "7.17.4"
},
"message": "test log",
"tags": [
"test log"
],
...给输入数据添加field,作用和tag类似,但是是以键-值的方式出现
- type: log
paths:
- /tmp/test.log
tags: "test log"
fields:
name: bruce
usage: test- 将数据输出到elasticsearch
修改配置文件,并运行filebeat
[root@host2 ~]# vim /etc/filebeat/config/03-log-to-es.yml
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
paths:
- /tmp/test.log
tags: "test log"
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["http://192.168.19.101:9200","http://192.168.19.102:9200","http://192.168.19.103:9200"]
[root@host2 ~]# filebeat -e -c /etc/filebeat/config/03-log-to-es.yml 创建一个索引
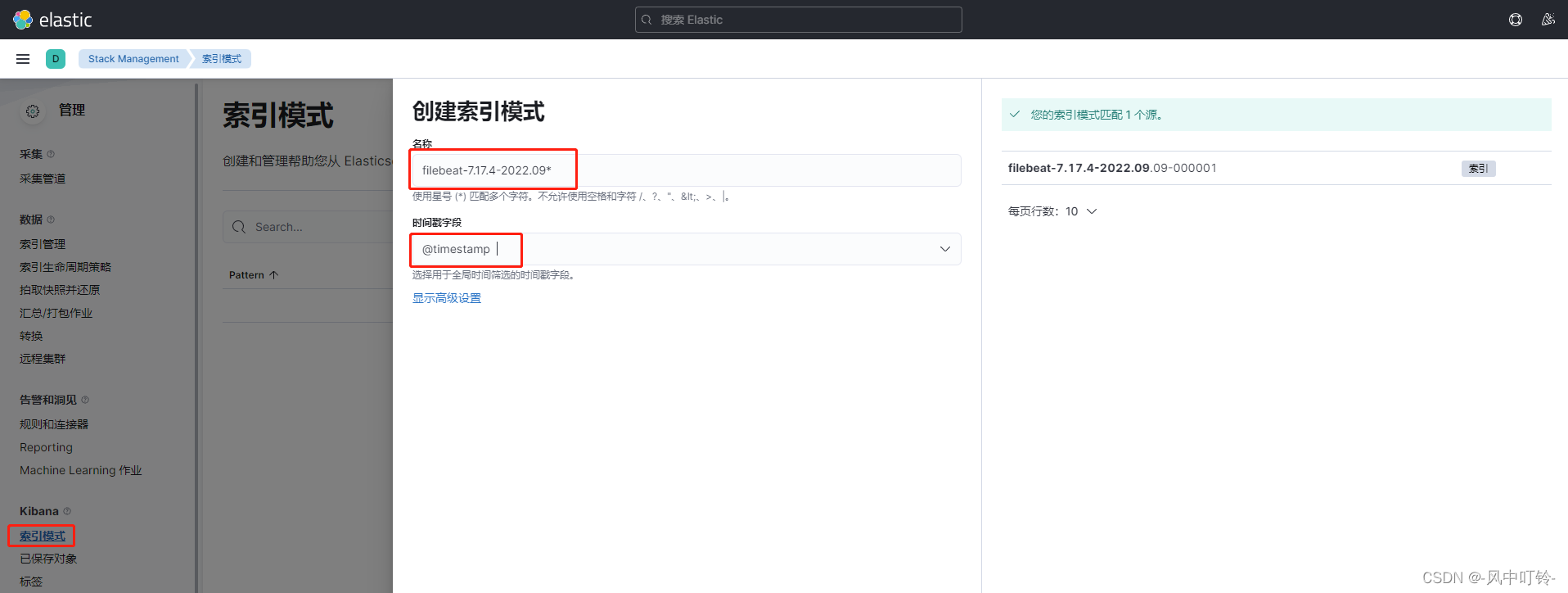
去查找日志信息
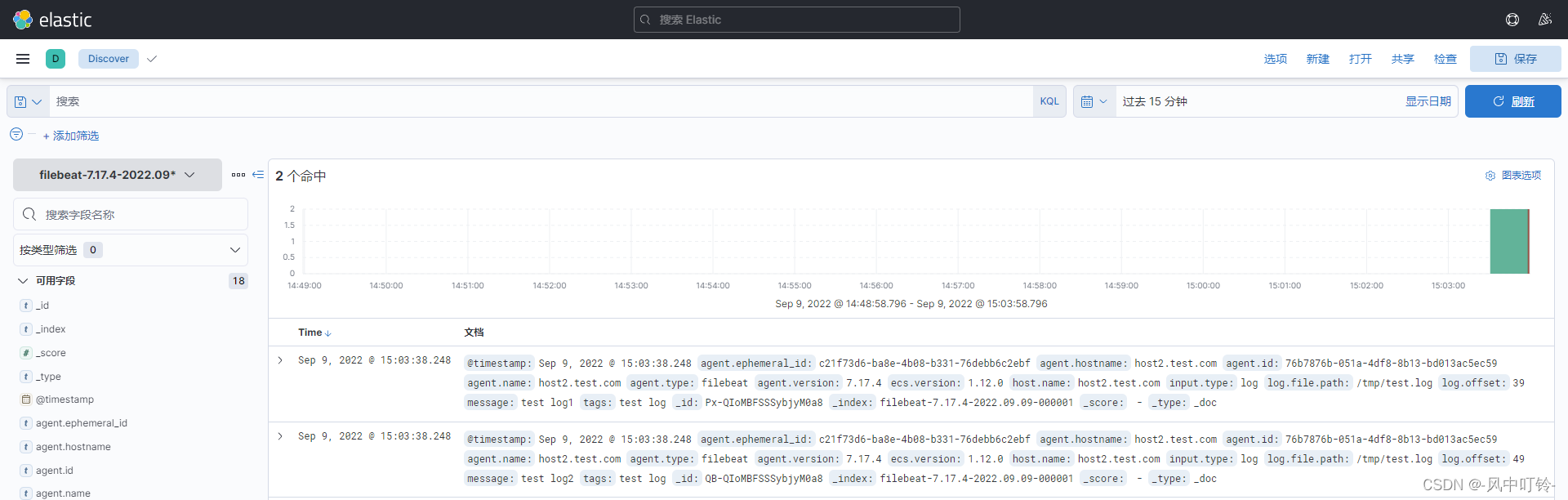
得到的日志信息,可以查看详细的内容
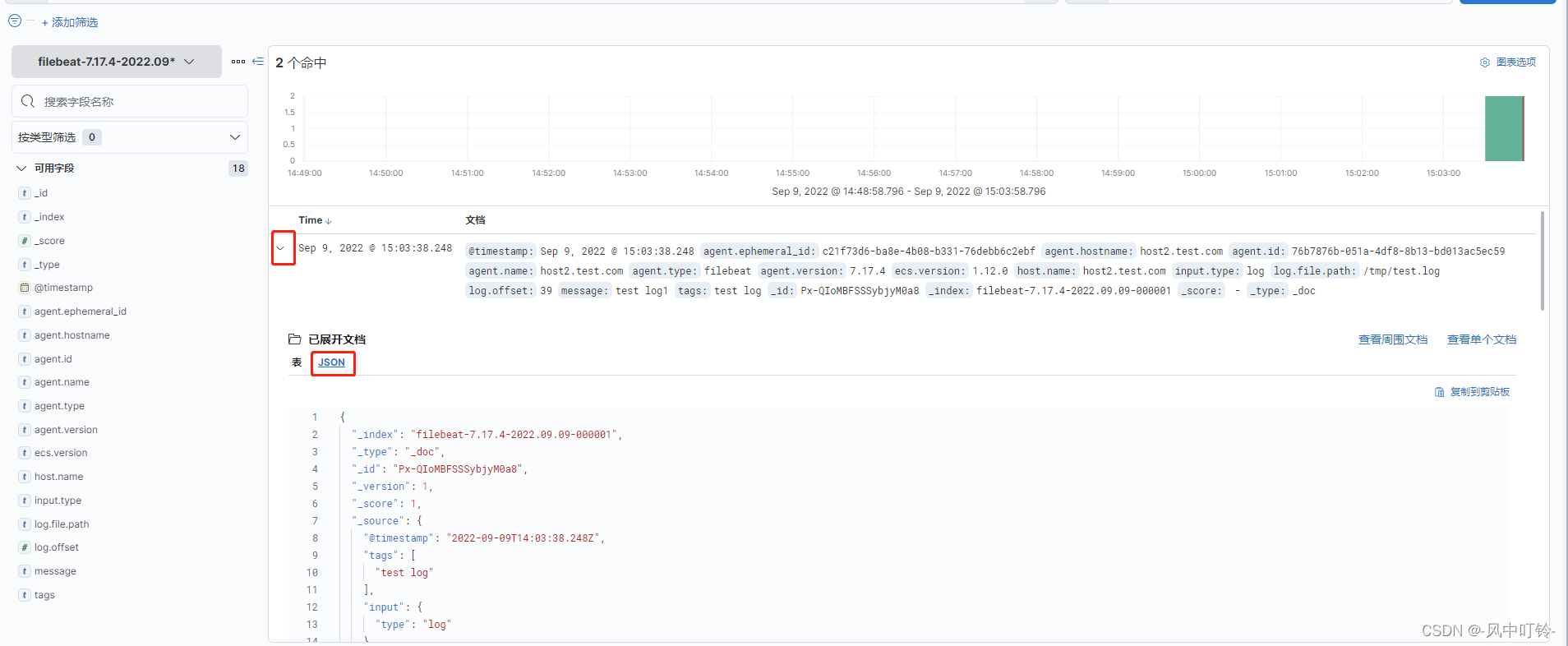
如果想要查看tag字段
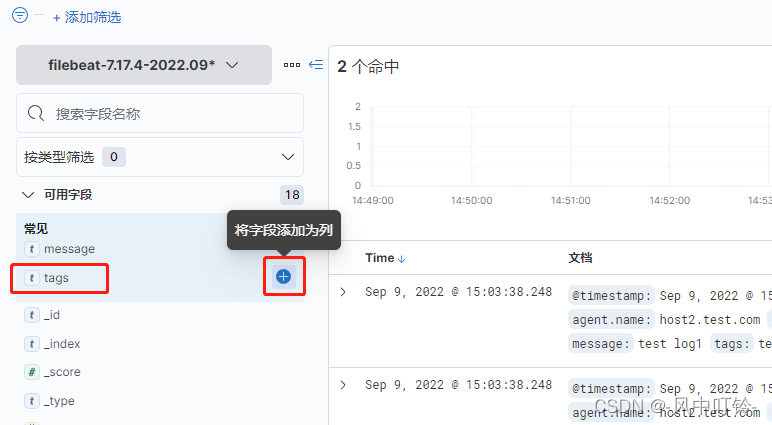
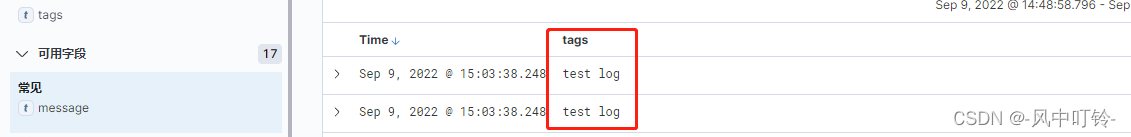
多个字段可以同时看

- 在filebeat中添加索引,标示某个日志
yml
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["http://192.168.19.101:9200","http://192.168.19.102:9200","http://192.168.19.103:9200"]
index: "bruce-test-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}"
# 关闭索引的生命周期,若开启则上面的index配置会被忽略
setup.ilm.enabled: false
# 设置索引模板的名称
setup.template.name: "bruce-test"
# 设置索引模板的匹配模式
setup.template.pattern: "bruce-test-*"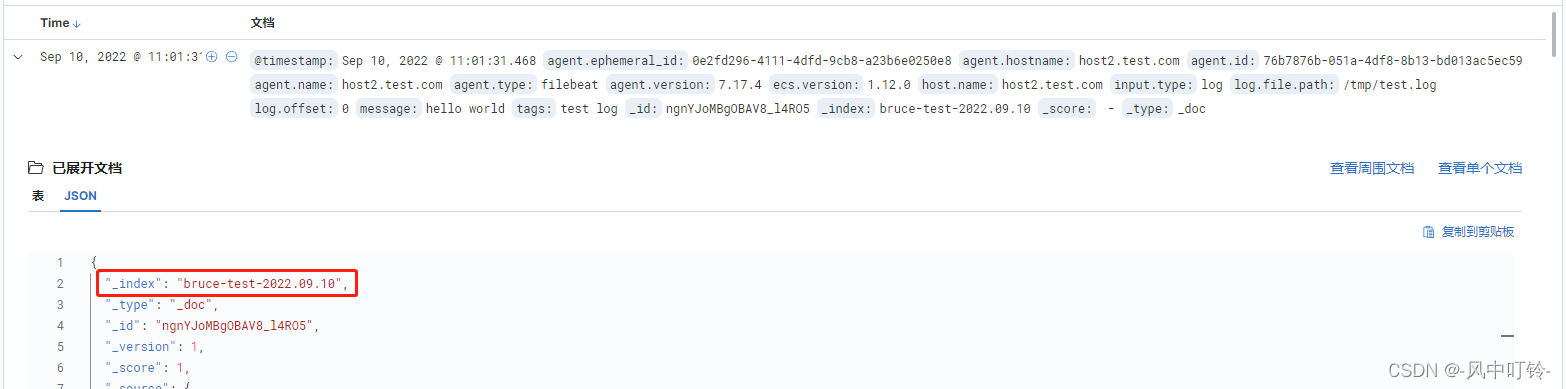
更复杂的写法
yml
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["http://192.168.19.101:9200","http://192.168.19.102:9200","http://192.168.19.103:9200"]
# index: "bruce-test-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}"
indices:
- index: "bruce-test-warn-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}"
when.contains:
message: "WARN" # 根据消息内容的不同给消息分配不同的标签,这里还可以使用tags
- index: "bruce-test-err-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}"
when.contains:
message: "ERR"
setup.ilm.enabled: false
setup.template.name: "bruce-test"
setup.template.pattern: "bruce-test-*"目前的测试结果是要产生数据,索引才会出现:
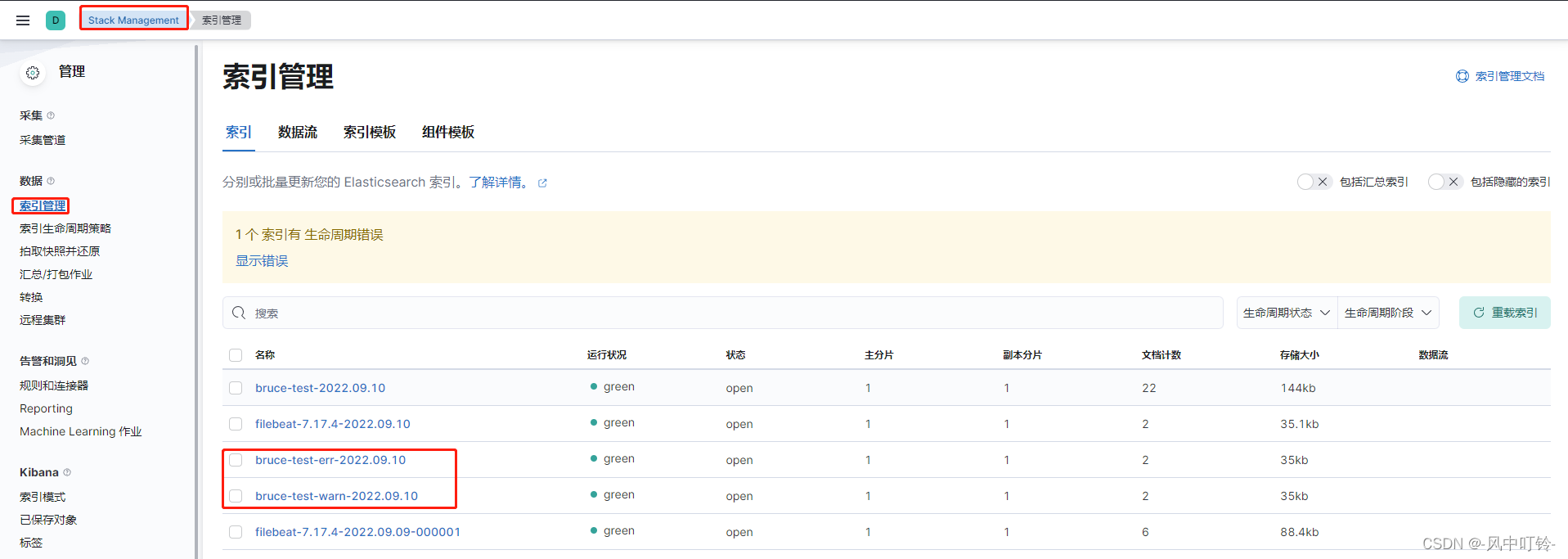
查看两个索引模式,并查看数据
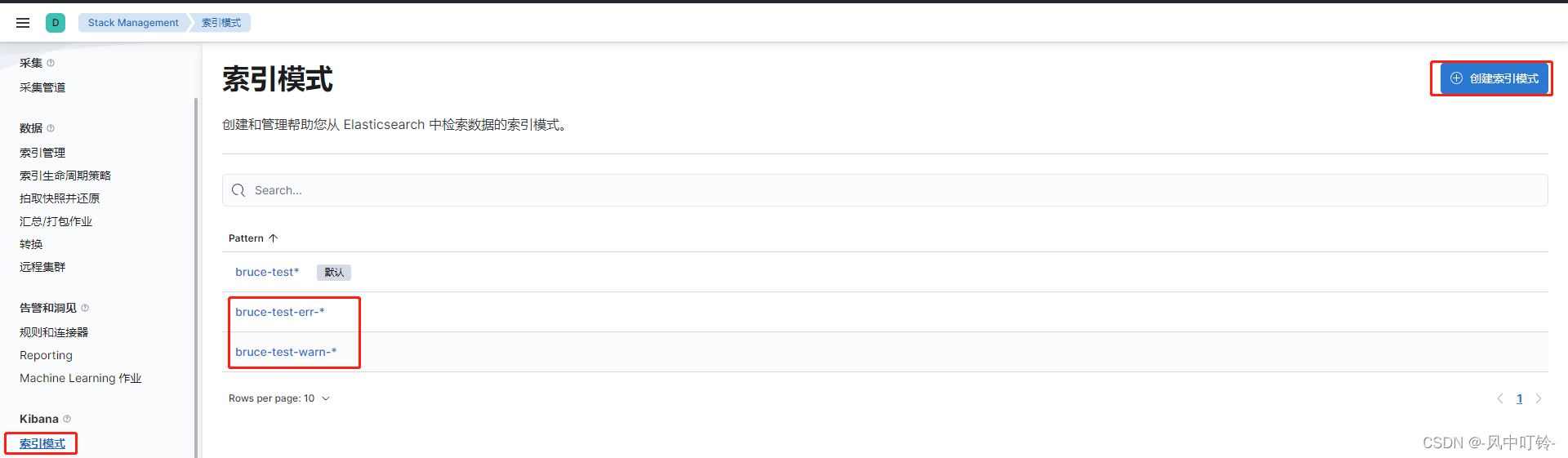
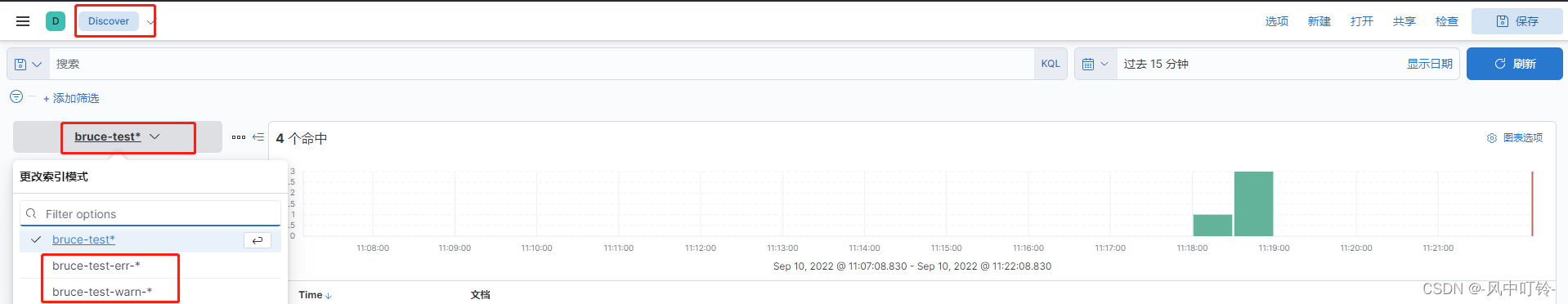
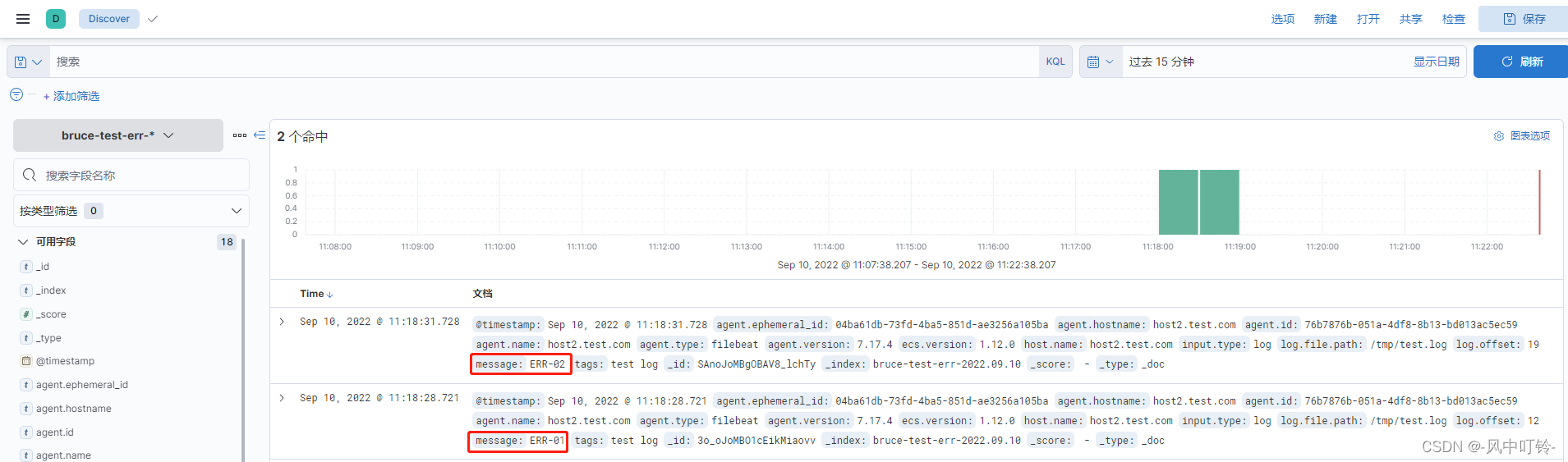
-
修改索引的分片和副本数量
覆盖已有的索引模板
setup.template.overwrite: false
setup.template.settings:设置分片数量,一般和集群数量一致
index.number_of_shards: 3
设置副本数量,要求小于集群数量,超过过后集群会变成黄色
index.number_of_replicas: 1
集群的三种颜色
红色:集群的部分主分片无法访问
黄色:集群的部分副本无法访问
绿色:集群的朱分片和副本分片可以访问
- 匹配部分日志(黑白名单)
yml
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
paths:
- /tmp/test.log
tags: "test log"
include_lines: ["^ERR","^WARN"] # 只有以ERR和WARN开头的日志条目才会被采集,区分大小写,支持通配符
exclude_lines: ["info"] # 包含info的行不会被采集通常不建议黑白名单一起使用,可以根据需要选择一种